Computer-aided engineering on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Computer-aided engineering (CAE) is the broad usage of
Computer-aided engineering (CAE) is the broad usage of
Why do we need a CAE Software or Numerical Simulations?
Computer Aided Engineering Journal WP:LINKROT
(FEA, CAD, ...)
Integrated Computer Aided Engineering Journal
Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering
Predictive engineering analytics
{{Authority control Computer-aided engineering software Product lifecycle management Engineering disciplines
 Computer-aided engineering (CAE) is the broad usage of
Computer-aided engineering (CAE) is the broad usage of computer software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consist ...
to aid in engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
analysis tasks. It includes , , , durability
Durability is the ability of a physical product to remain functional, without requiring excessive maintenance or repair, when faced with the challenges of normal operation over its design lifetime. There are several measures of durability in us ...
and optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfi ...
. It is included with computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve co ...
(CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) also known as computer-aided modeling or computer-aided machining is the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing of work pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most ...
(CAM) in the collective abbreviation " CAx".
Overview
Computer-aided engineering primarily uses computer-aided design (CAD) software, which are sometimes called CAE tools. CAE tools are used, to analyze the robustness and performance of components and assemblies. CAE tools encompass simulation, validation, and optimization of products and manufacturing tools. CAE systems aim to be major providers of information to help support design teams in decision-making. Computer-aided engineering is used in various fields, like automotive, aviation, space, and shipbuilding industries. CAE systems can provide support to businesses. This is achieved by the use of reference architectures and their ability to place information views on the business process. Reference architecture is the basis from which information is modeled, especially product and manufacturing models. The term CAE has been used to describe the use of computer technology within engineering in a broader sense than just engineering analysis. It was in this context that the term was coined by Jason Lemon, founder of SDRC in the late 1970s. This definition is however better known today by the terms CAx and PLM. CAE systems are individually considered a singlenode
In general, a node is a localized swelling (a " knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex).
Node may refer to:
In mathematics
* Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph
* Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, line ...
on a total information network and each node may interact with other nodes on the network.
CAE fields and phases
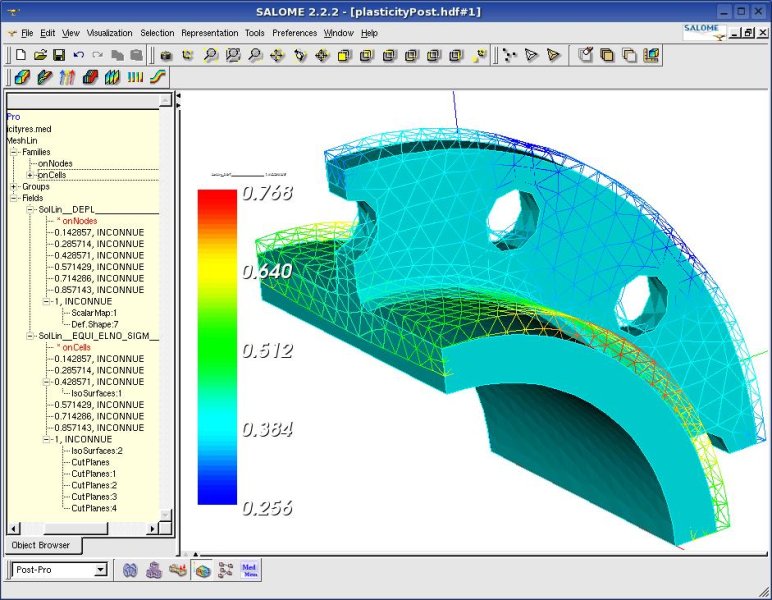
CAE areas covered include: * Stress analysis on components and assemblies usingfinite element analysis
The finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat ...
(FEA);
*Thermal and fluid flow analysis computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate ...
(CFD);
* Multibody dynamics (MBD) and kinematics
Kinematics is a subfield of physics, developed in classical mechanics, that describes the motion of points, bodies (objects), and systems of bodies (groups of objects) without considering the forces that cause them to move. Kinematics, as a fiel ...
;
*Analysis tools for process simulation for operations such as casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a ''casting'', which is ejecte ...
, molding, and die press forming;
*Optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criterion, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfi ...
of the product or process.
In general, there are three phases in any computer-aided engineering task:
*Pre-processing – defining the model and environmental factors to be applied to it (typically a finite element model, but facet, voxel
In 3D computer graphics, a voxel represents a value on a regular grid in three-dimensional space. As with pixels in a 2D bitmap, voxels themselves do not typically have their position (i.e. coordinates) explicitly encoded with their values. I ...
, and thin sheet methods are also used);
*Analysis solver (usually performed on high powered computers);
*Post-processing of results (using visualization tools).
This cycle is iterated, often many times, either manually or with the use of commercial optimization software.
CAE in the automotive industry
CAE tools are widely used in theautomotive industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of companies and organizations involved in the design, development, manufacturing, marketing, and selling of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industries by revenue (from 16 % ...
. Their use has enabled automakers to reduce product development costs and time while improving the safety, comfort, and durability of the vehicles they produce. The predictive capability of CAE tools has progressed to the point where much of the design verification is done using computer simulations (diagnosis) rather than physical prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and software programming. A prototype is generally used to ...
testing. CAE dependability is based upon all proper assumptions as inputs and must identify critical inputs (BJ). Even though there have been many advances in CAE, and it is widely used in the engineering field, physical testing is still a must. It is used for verification and model updating, to accurately define loads and boundary conditions, and for final prototype sign-off.
The future of CAE in the product development process
Even though CAE has built a strong reputation as a verification, troubleshooting and analysis tool, there is still a perception that sufficiently accurate results come rather late in the design cycle to really drive the design. This can be expected to become a problem as modern products become ever more complex. They include smart systems, which leads to an increased need for multi-physics analysis including controls, and contain new lightweight materials, with which engineers are often less familiar. CAE software companies and manufacturers are constantly looking for tools and process improvements to change this situation. On the software side, they are constantly looking to develop more powerful solvers, to better utilize computer resources, and to include engineering knowledge in pre and post-processing. On the process side, they try to achieve a better alignment between 3D CAE, 1D system simulation, and physical testing. This should increase modeling realism and calculation speed. CAE software companies and manufacturers try to better integrate CAE in the overall product lifecycle management. In this way they can connect product design with product use, which is needed for smart products. This enhanced engineering process is also referred to as predictive engineering analytics.See also
References
Further reading
* B. Raphael and I.F.C. Smith (2003).'' Fundamentals of computer aided engineering.'' John Wiley. .External links
Why do we need a CAE Software or Numerical Simulations?
Computer Aided Engineering Journal WP:LINKROT
(FEA, CAD, ...)
Integrated Computer Aided Engineering Journal
Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering
Predictive engineering analytics
{{Authority control Computer-aided engineering software Product lifecycle management Engineering disciplines