Composition of Mars on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The composition of Mars covers the branch of the
 Mars is differentiated, which—for a
Mars is differentiated, which—for a  Based on these data sources, scientists think that the most abundant chemical elements in the Martian crust are
Based on these data sources, scientists think that the most abundant chemical elements in the Martian crust are
 Mars is fundamentally an
Mars is fundamentally an
 The mineral olivine occurs all over the planet, but some of the largest concentrations are in Nili Fossae, an area containing
The mineral olivine occurs all over the planet, but some of the largest concentrations are in Nili Fossae, an area containing  The lavas of ST2 have been interpreted as
The lavas of ST2 have been interpreted as  True intermediate and
True intermediate and 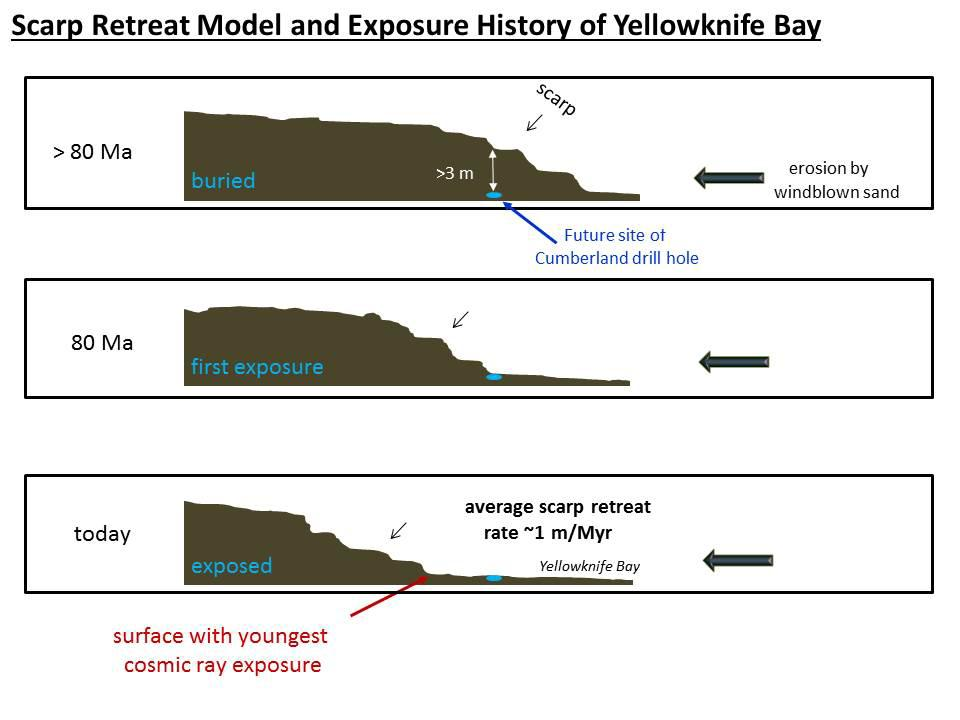 In the journal Science from September 2013, researchers described a different type of rock called "'' Jake M''" or "'' Jake Matijevic (rock)'',” It was the first rock analyzed by the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer instrument on the Curiosity rover, and it was different from other known martian igneous rocks as it is alkaline (>15% normative nepheline) and relatively fractionated. ''Jake M'' is similar to terrestrial mugearites, a rock type typically found at ocean islands and continental rifts. ''Jake M'' discovery may mean that alkaline magmas may be more common on Mars than on Earth and that Curiosity could encounter even more fractionated alkaline rocks (for example, phonolites and
In the journal Science from September 2013, researchers described a different type of rock called "'' Jake M''" or "'' Jake Matijevic (rock)'',” It was the first rock analyzed by the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer instrument on the Curiosity rover, and it was different from other known martian igneous rocks as it is alkaline (>15% normative nepheline) and relatively fractionated. ''Jake M'' is similar to terrestrial mugearites, a rock type typically found at ocean islands and continental rifts. ''Jake M'' discovery may mean that alkaline magmas may be more common on Mars than on Earth and that Curiosity could encounter even more fractionated alkaline rocks (for example, phonolites and
 Much of the Martian surface is deeply covered by dust as fine as talcum powder. The global predominance of dust obscures the underlying bedrock, making spectroscopic identification of primary minerals impossible from orbit over many areas of the planet. The red/orange appearance of the dust is caused by
Much of the Martian surface is deeply covered by dust as fine as talcum powder. The global predominance of dust obscures the underlying bedrock, making spectroscopic identification of primary minerals impossible from orbit over many areas of the planet. The red/orange appearance of the dust is caused by

 Layered sedimentary deposits are widespread on Mars. These deposits probably consist of both
Layered sedimentary deposits are widespread on Mars. These deposits probably consist of both


 Examination in 2004 of Meridiani rocks, showed the first strong ''in situ'' evidence for past water by detecting the mineral
Examination in 2004 of Meridiani rocks, showed the first strong ''in situ'' evidence for past water by detecting the mineral
Image:MSL landing sites topograph.png, Map of actual (and proposed) Rover landing sites including Gale Crater.
Image:Mars Science Laboratory landing ellipse reduced.jpg, Gale Crater - Landing site is within
Traverse Map
of the ''Curiosity'' rover on Mars (August 1, 2013)
3-D
.
Mars - Geologic Map
(
original
/
video (00:56)
.
Video (04:32) - Evidence: Water "Vigorously" Flowed On Mars - September, 2012
{{Portal bar, Solar System Geology of Mars Geochemistry
geology of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial g ...
that describes the make-up of the planet Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
.
Elemental composition
terrestrial planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, ...
—implies that it has a central core
Core or cores may refer to:
Science and technology
* Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages
* Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding
* Core (optical fiber), the signal-carrying portion of an optical fiber
* Core, the centra ...
made up of metallic iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
and nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
surrounded by a less dense, silicate mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
and crust. Like Earth, Mars appears to have a molten iron core, or at least a molten outer core. However, there does not appear to be convection in the mantle. Presently Mars shows little geological activity.
The elemental composition of Mars is different from Earth's in several significant ways. First, Martian meteorite analysis suggests that the planet's mantle is about twice as rich in iron as the Earth's mantle. The planet's distinctive red color is due to iron oxide
Iron oxides are chemical compounds composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. All are black magnetic solids. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of wh ...
s on its surface. Second, its core is richer in sulphur. Third, the Martian mantle is richer in potassium and phosphorus than Earth's and fourth, the Martian crust contains a higher percentage of volatile elements such as sulphur and chlorine than the Earth's crust does. Many of these conclusions are supported by ''in situ'' analyses of rocks and soils on the Martian surface.
Much of what we know about the elemental composition of Mars comes from orbiting spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, ...
and landers. (See Exploration of Mars
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding its geology and habi ...
for list.) Most of these spacecraft carry spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the ...
s and other instruments to measure the surface composition of Mars by either remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Ear ...
from orbit or ''in situ
''In situ'' (; often not italicized in English) is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position." It can mean "locally", "on site", "on the premises", or "in place" to describe where an event takes place and is used in ...
'' analyses on the surface. We also have many actual samples of Mars in the form of meteorites
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object ...
that have made their way to Earth. Martian meteorites
A Martian meteorite is a rock that formed on Mars, was ejected from the planet by an impact event, and traversed interplanetary space before landing on Earth as a meteorite. , 277 meteorites had been classified as Martian, less than half a p ...
(often called SNC's, for Shergottites, Nakhlites, and Chassignites—the groups of meteorites first shown to have a martian origin) provide data on the chemical composition of Mars' crust and interior that would not otherwise be available except through a sample return mission
A sample-return mission is a spacecraft mission to collect and return samples from an extraterrestrial location to Earth for analysis. Sample-return missions may bring back merely atoms and molecules or a deposit of complex compounds such as lo ...
.
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
, iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
, aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
, and potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmos ...
. These elements are major components of the minerals comprising igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
rocks. The elements titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion i ...
, chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hard ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of ...
, sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
, phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable ...
, and chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
are less abundant but are still important components of many accessory minerals in rocks and of secondary minerals (weathering products) in the dust and soils (the regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestr ...
). On September 5, 2017, scientists reported that the ''Curiosity'' rover detected boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the '' boron group'' it has t ...
, an essential ingredient for life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy ...
on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
, on the planet Mars. Such a finding, along with previous discoveries that water may have been present on ancient Mars, further supports the possible early habitability of Gale Crater on Mars.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
is present as water (H2O) ice and in hydrated minerals. Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
occurs as carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
(CO2) in the atmosphere and sometimes as dry ice
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is commonly used for temporary refrigeration as CO2 does not have a liquid state at normal atmospheric pressure and sublimates directly from the solid state to the gas state. It is used primarily ...
at the poles. An unknown amount of carbon is also stored in carbonates
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ...
. Molecular nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
(N2) makes up 2.7 percent of the atmosphere. As far as we know, organic compounds
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The s ...
are absent except for a trace of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
detected in the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A ...
. On 16 December 2014, NASA reported the ''Curiosity'' rover detected a "tenfold spike", likely localized, in the amount of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
in the Martian atmosphere. Sample measurements taken "a dozen times over 20 months" showed increases in late 2013 and early 2014, averaging "7 parts of methane per billion in the atmosphere." Before and after that, readings averaged around one-tenth that level.
Mineralogy and petrology
 Mars is fundamentally an
Mars is fundamentally an igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
planet. Rocks on the surface and in the crust consist predominantly of minerals that crystallize from magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natura ...
. Most of our current knowledge about the mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
composition of Mars comes from spectroscopic data from orbiting spacecraft, ''in situ'' analyses of rocks and soils from six landing sites, and study of the Martian meteorites. Spectrometers currently in orbit include THEMIS
In Greek mythology and religion, Themis (; grc, Θέμις, Themis, justice, law, custom) is one of the twelve Titan children of Gaia and Uranus, and the second wife of Zeus. She is the goddess and personification of justice, divine order, fai ...
(Mars Odyssey
''2001 Mars Odyssey'' is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use spectro ...
), OMEGA (Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA). The ''Mars Express'' mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally ref ...
), and CRISM
The Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) is a visible-infrared spectrometer aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter searching for mineralogic indications of past and present water on Mars. The CRISM instrument team compris ...
(Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, an ...
). The two Mars exploration rovers each carry an Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS
:''APXS is also an abbreviation for APache eXtenSion tool, an extension for Apache web servers.''
An alpha particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS) is a spectrometer that analyses the chemical element composition of a sample from scattered alpha part ...
), a thermal emission spectrometer ( Mini-TES), and Mössbauer spectrometer to identify minerals on the surface.
On October 17, 2012, the Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
on the planet Mars at " Rocknest" performed the first X-ray diffraction analysis of Martian soil. The results from the rover's CheMin analyzer revealed the presence of several minerals, including feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) felds ...
, pyroxenes
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (F ...
and olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers qui ...
, and suggested that the Martian soil in the sample was similar to the "weathered basaltic soils" of Hawaiian volcanoes.
Primary rocks and minerals
The dark areas of Mars are characterised by themafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks in ...
rock-forming minerals olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers qui ...
, pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe I ...
, and plagioclase
Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more p ...
feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) felds ...
. These minerals are the primary constituents of basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
, a dark volcanic rock that also makes up the Earth's oceanic crust and the lunar maria
The lunar maria (; singular: mare ) are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient asteroid impacts on the far side on the Moon that triggered volcanic activity on the opposite (near) side. They were dubbed , Latin for 'seas' ...
.
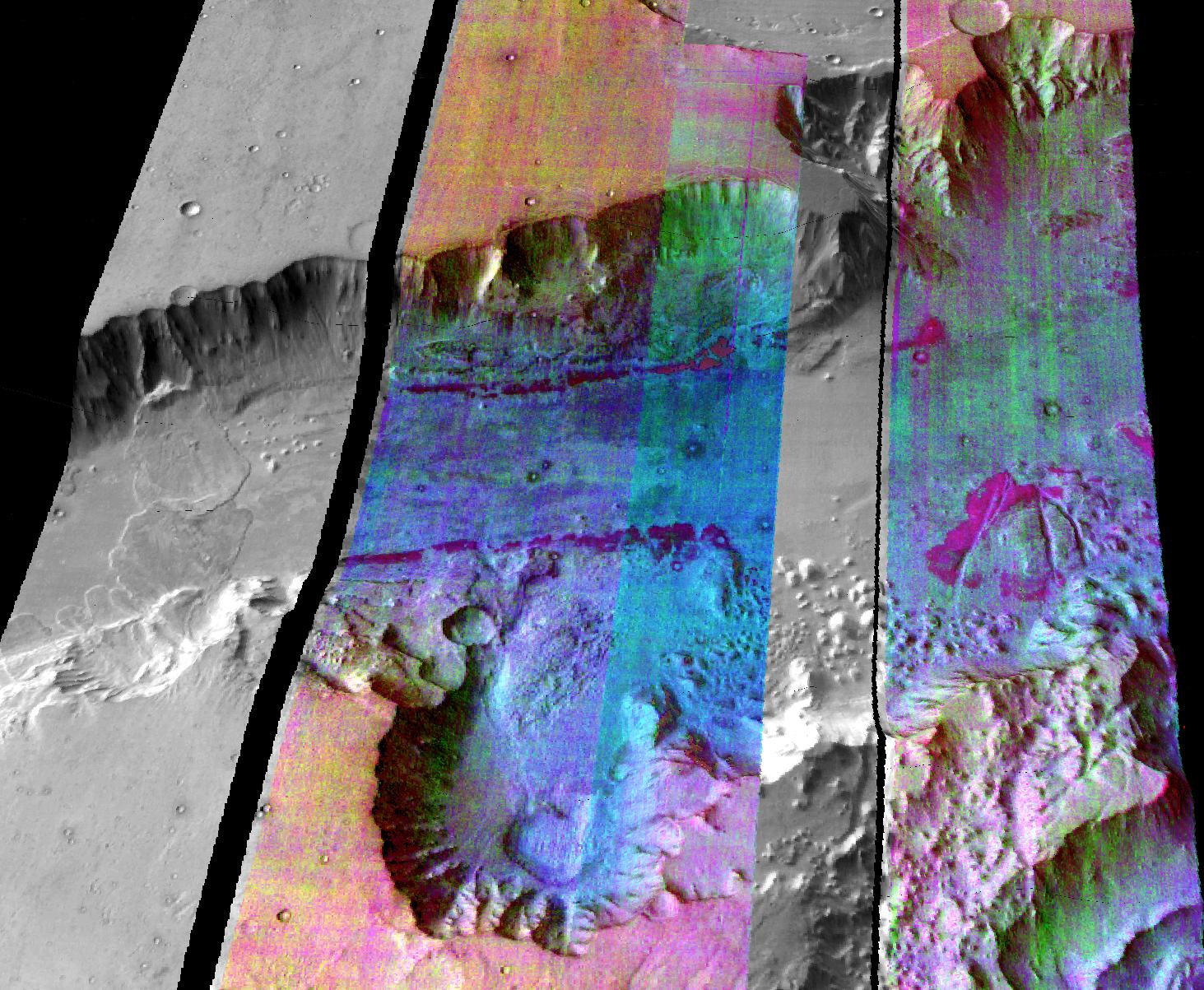
 The mineral olivine occurs all over the planet, but some of the largest concentrations are in Nili Fossae, an area containing
The mineral olivine occurs all over the planet, but some of the largest concentrations are in Nili Fossae, an area containing Noachian
The Noachian is a geologic system and early time period on the planet Mars characterized by high rates of meteorite and asteroid impacts and the possible presence of abundant surface water. The absolute age of the Noachian period is uncertain ...
-aged rocks. Another large olivine-rich outcrop is in Ganges Chasma
Ganges Chasma is a deep canyon at the eastern end of the vast Valles Marineris system on Mars, an offshoot of Capri Chasma, and is in the Coprates quadrangle. It is named after the River Ganges in South Asia. Ganges Chasma is thought to have form ...
, an eastern side chasm of Valles Marineris
Valles Marineris (; Latin for '' Mariner Valleys'', named after the ''Mariner 9'' Mars orbiter of 1971–72 which discovered it) is a system of canyons that runs along the Martian surface east of the Tharsis region. At more than long, wide and ...
(pictured). Olivine weathers rapidly into clay minerals in the presence of liquid water. Therefore, areas with large outcroppings of olivine-bearing rock indicate that liquid water has not been abundant since the rocks formed.
Pyroxene minerals are also widespread across the surface. Both low-calcium (ortho-) and high-calcium (clino-) pyroxenes are present, with the high-calcium varieties associated with younger volcanic shields and the low-calcium forms (enstatite
Enstatite is a mineral; the magnesium endmember of the pyroxene silicate mineral series enstatite (MgSiO3) – ferrosilite (FeSiO3). The magnesium rich members of the solid solution series are common rock-forming minerals found in igneous and ...
) more common in the old highland terrain. Because enstatite melts at a higher temperature than its high-calcium cousin, some researchers have argued that its presence in the highlands indicates that older magmas on Mars had higher temperatures than younger ones.
Between 1997 and 2006, the Thermal Emission Spectrometer
The Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) is an instrument on board Mars Global Surveyor. TES collects two types of data, hyperspectral thermal infrared data from 6 to 50 micrometres (μm) and bolometric visible-NIR (0.3 to 2.9 μm) measurements. T ...
(TES) on the Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through t ...
(MGS) spacecraft mapped the global mineral composition of the planet. TES identified two global-scale volcanic units on Mars. Surface Type 1 (ST1) characterises the Noachian-aged highlands and consists of unaltered plagioclase- and clinopyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe I ...
-rich basalts. Surface Type 2 (ST2) is common in the younger plains north of the dichotomy boundary and is more silica rich than ST1. The lavas of ST2 have been interpreted as
The lavas of ST2 have been interpreted as andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predo ...
s or basaltic andesite
Basaltic andesite is a volcanic rock that is intermediate in composition between basalt and andesite. It is composed predominantly of augite and plagioclase. Basaltic andesite can be found in volcanoes around the world, including in Central Am ...
s, indicating the lavas in the northern plains originated from more chemically evolved, volatile-rich magmas. (See Igneous differentiation
In geology, igneous differentiation, or magmatic differentiation, is an umbrella term for the various processes by which magmas undergo bulk chemical change during the partial melting process, cooling, emplacement, or eruption. The sequence of ...
and Fractional crystallization.) However, other researchers have suggested that ST2 represents weathered basalts with thin coatings of silica glass or other secondary minerals that formed through interaction with water- or ice-bearing materials.
 True intermediate and
True intermediate and felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, wh ...
rocks are present on Mars, but exposures are uncommon. Both TES and the Thermal Emission Imaging System
The Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) is a camera on board the 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter. It images Mars in the visible and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum in order to determine the thermal properties of the surface and ...
(THEMIS) on the Mars Odyssey spacecraft have identified high-silica rocks in Syrtis Major and near the southwestern rim of the crater Antoniadi
Eugène Michel Antoniadi (Greek: Ευγένιος Αντωνιάδης; 1 March 1870 – 10 February 1944) was a Greek- French astronomer.
Biography
Antoniadi was born in Istanbul (Constantinople) but spent most of his adult life in Fran ...
. The rocks have spectra resembling quartz-rich dacite
Dacite () is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained ( aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhyo ...
s and granitoids, suggesting that at least some parts of the Martian crust may have a diversity of igneous rocks similar to Earth's. Some geophysical evidence suggests that the bulk of the Martian crust may actually consist of basaltic andesite
Basaltic andesite is a volcanic rock that is intermediate in composition between basalt and andesite. It is composed predominantly of augite and plagioclase. Basaltic andesite can be found in volcanoes around the world, including in Central Am ...
or andesite. The andesitic crust is hidden by overlying basaltic lavas that dominate the surface composition but are volumetrically minor.
Rocks studied by Spirit Rover
Spirit or spirits may refer to:
Liquor and other volatile liquids
* Spirits, a.k.a. liquor, distilled alcoholic drinks
* Spirit or tincture, an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol
* Volatile (especially flammable) liquids, ...
in Gusev crater can be classified in different ways. The amounts and types of minerals make the rocks primitive basalts—also called picritic basalts. The rocks are similar to ancient terrestrial rocks called basaltic komatiites
Komatiite () is a type of ultramafic mantle-derived volcanic rock defined as having crystallised from a lava of at least 18 wt% MgO. Komatiites have low silicon, potassium and aluminium, and high to extremely high magnesium content. Komatiite wa ...
. Rocks of the plains also resemble the basaltic shergottites, meteorites which came from Mars. One classification system compares the amount of alkali elements to the amount of silica on a graph; in this system, Gusev plains rocks lie near the junction of basalt, picrobasalt, and tephrite. The Irvine-Barager classification calls them basalts.McSween, etal. 2004. Basaltic Rocks Analyzed by the Spirit Rover in Gusev Crater. Science : 305. 842–845
On March 18, 2013, NASA reported evidence from instruments on the Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
of mineral hydration
In chemistry, mineral hydration is an inorganic chemical reaction which adds water to the crystal structure of a mineral, usually creating a new mineral, usually called a '' hydrate''.
In geological terms, the process of mineral hydration is ...
, likely hydrated calcium sulfate
Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Paris ...
, in several rock samples including the broken fragments of "Tintina" rock and "Sutton Inlier" rock as well as in veins
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated ...
and nodules in other rocks like "Knorr" rock and "Wernicke" rock. Analysis using the rover's DAN instrument provided evidence of subsurface water, amounting to as much as 4% water content, down to a depth of , in the rover's traverse from the ''Bradbury Landing
Bradbury Landing is the August 6, 2012, landing site within Gale crater on planet Mars of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) ''Curiosity'' rover. On August 22, 2012, on what would have been his 92nd birthday, NASA named the site for author Ra ...
'' site to the ''Yellowknife Bay'' area in the ''Glenelg'' terrain.
 In the journal Science from September 2013, researchers described a different type of rock called "'' Jake M''" or "'' Jake Matijevic (rock)'',” It was the first rock analyzed by the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer instrument on the Curiosity rover, and it was different from other known martian igneous rocks as it is alkaline (>15% normative nepheline) and relatively fractionated. ''Jake M'' is similar to terrestrial mugearites, a rock type typically found at ocean islands and continental rifts. ''Jake M'' discovery may mean that alkaline magmas may be more common on Mars than on Earth and that Curiosity could encounter even more fractionated alkaline rocks (for example, phonolites and
In the journal Science from September 2013, researchers described a different type of rock called "'' Jake M''" or "'' Jake Matijevic (rock)'',” It was the first rock analyzed by the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer instrument on the Curiosity rover, and it was different from other known martian igneous rocks as it is alkaline (>15% normative nepheline) and relatively fractionated. ''Jake M'' is similar to terrestrial mugearites, a rock type typically found at ocean islands and continental rifts. ''Jake M'' discovery may mean that alkaline magmas may be more common on Mars than on Earth and that Curiosity could encounter even more fractionated alkaline rocks (for example, phonolites and trachytes
Trachyte () is an extrusive igneous rock composed mostly of alkali feldspar. It is usually light-colored and aphanitic (fine-grained), with minor amounts of mafic minerals, and is formed by the rapid cooling of lava enriched with silica and alk ...
).
On December 9, 2013, NASA researchers described, in a series of six articles in the journal Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
, many new discoveries from the Curiosity rover. Possible organics were found that could not be explained by contamination. Although the organic carbon was probably from Mars, it can all be explained by dust and meteorites that have landed on the planet. Because much of the carbon was released at a relatively low temperature in Curiosity's Sample Analysis at Mars
Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) is a suite of instruments on the Mars Science Laboratory ''Curiosity'' rover. The SAM instrument suite will analyze organics and gases from both atmospheric and solid samples.
It was developed by the NASA Goddard S ...
(SAM) instrument package, it probably did not come from carbonates in the sample. The carbon could be from organisms, but this has not been proven. This organic-bearing material was obtained by drilling 5 centimeters deep in a site called ''Yellowknife Bay'' into a rock called “'' Sheepbed mudstone''”. The samples were named '' John Klein'' and ''Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic counties of England, historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th c ...
''. Microbes could be living on Mars by obtaining energy from chemical imbalances between minerals in a process called chemolithotrophy which means “eating rock.” However, in this process only a very tiny amount of carbon is involved — much less than was found at ''Yellowknife Bay''.
Using SAM's mass spectrometer
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is us ...
, scientists measured isotopes
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass numbers ...
of helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic ta ...
, neon
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypt ...
, and argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice a ...
that cosmic rays
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our ...
produce as they go through rock. The fewer of these isotopes they find, the more recently the rock has been exposed near the surface. The 4-billion-year-old lakebed rock drilled by Curiosity was uncovered between 30 million and 110 million years ago by winds which sandblasted away 2 meters of overlying rock. Next, they hope to find a site tens of millions of years younger by drilling close to an overhanging outcrop.
The absorbed dose and dose equivalent from galactic cosmic rays and solar energetic particles on the Martian surface for ~300 days of observations during the current solar maximum was measured. These measurements are necessary for human missions to the surface of Mars, to provide microbial survival times of any possible extant or past life, and to determine how long potential organic biosignature
A biosignature (sometimes called chemical fossil or molecular fossil) is any substance – such as an element, isotope, or molecule – or phenomenon that provides scientific evidence of past or present life. Measurable attribute ...
s can be preserved. This study estimates that a few meters drill is necessary to access possible biomolecule
A biomolecule or biological molecule is a loosely used term for molecules present in organisms that are essential to one or more typically biological processes, such as cell division, morphogenesis, or developmental biology, development. Biom ...
s. The actual absorbed dose measured by the Radiation Assessment Detector
The Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD) is an instrument mounted on the Mars Science Laboratory ''Curiosity'' rover. It was the first of ten instruments to be turned on during the mission.
Purpose
The first role of RAD was to characterize the b ...
(RAD) is 76 mGy/yr at the surface. Based on these measurements, for a round trip Mars surface mission with 180 days (each way) cruise, and 500 days on the Martian surface for this current solar cycle, an astronaut would be exposed to a total mission dose equivalent of ~1.01 sievert
The sievert (symbol: SvNot be confused with the sverdrup or the svedberg, two non-SI units that sometimes use the same symbol.) is a unit in the International System of Units (SI) intended to represent the stochastic health risk of ionizing rad ...
. Exposure to 1 sievert is associated with a 5 percent increase in risk for developing fatal cancer. NASA's current lifetime limit for increased risk for its astronauts operating in low-Earth orbit is 3 percent. Maximum shielding from galactic cosmic rays can be obtained with about 3 meters of Martian soil.
The samples examined were probably once mud that for millions to tens of millions of years could have hosted living organisms. This wet environment had neutral pH, low salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
, and variable redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or ...
states of both iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
and sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
species. These types of iron and sulfur could have been used by living organisms. C, H, O, S, N, and P were measured directly as key biogenic elements, and by inference, P is assumed to have been there as well. The two samples, '' John Klein'' and ''Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic counties of England, historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th c ...
'', contain basaltic minerals, Ca-sulfates, Fe oxide/hydroxides, Fe-sulfides, amorphous material, and trioctahedral smectite
A smectite (from ancient Greek ''σμηκτός'' smektos 'lubricated'; ''σμηκτρίς'' smektris 'walker's earth', 'fuller's earth'; rubbing earth; earth that has the property of cleaning) is a mineral mixtures of various swelling sheet sil ...
s (a type of clay). Basaltic minerals in the mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from '' shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.' ...
are similar to those in nearby aeoliandeposits. However, the mudstone has far less Fe- forsterite plus magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With ...
, so Fe-forsterite (type of olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers qui ...
) was probably altered to form smectite (a type of clay) and magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With ...
. A Late Noachian
The Noachian is a geologic system and early time period on the planet Mars characterized by high rates of meteorite and asteroid impacts and the possible presence of abundant surface water. The absolute age of the Noachian period is uncertain ...
/EarlyHesperian
The Hesperian is a system (stratigraphy), geologic system and geologic timescale, time period on the planet Mars characterized by widespread Volcanology of Mars, volcanic activity and catastrophic flooding that carved immense outflow channels acr ...
or younger age indicates that clay mineral formation on Mars extended beyond Noachian time; therefore, in this location neutral pH lasted longer than previously thought.
Dust and soils
 Much of the Martian surface is deeply covered by dust as fine as talcum powder. The global predominance of dust obscures the underlying bedrock, making spectroscopic identification of primary minerals impossible from orbit over many areas of the planet. The red/orange appearance of the dust is caused by
Much of the Martian surface is deeply covered by dust as fine as talcum powder. The global predominance of dust obscures the underlying bedrock, making spectroscopic identification of primary minerals impossible from orbit over many areas of the planet. The red/orange appearance of the dust is caused by iron(III) oxide
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe2O3. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4), which also occurs naturally a ...
( nanophase Fe2O3) and the iron(III) oxide-hydroxide
Iron(III) oxide-hydroxide or ferric oxyhydroxideA. L. Mackay (1960): "β-Ferric Oxyhydroxide". ''Mineralogical Magazine'' (''Journal of the Mineralogical Society''), volume 32, issue 250, pages 545-557. is the chemical compound of iron, oxygen ...
mineral goethite
Goethite (, ) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the "α" polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient t ...
.
The Mars Exploration Rovers identified magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With ...
as the mineral responsible for making the dust magnetic. It probably also contains some titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion i ...
.
The global dust cover and the presence of other wind-blown sediments has made soil compositions remarkably uniform across the Martian surface. Analysis of soil samples from the Viking landers in 1976 shows that the soils consist of finely broken up basaltic rock fragments and are highly enriched in sulphur and chlorine, probably derived from volcanic gas emissions.
Secondary (alteration) minerals
Minerals produced throughhydrothermal alteration
Metasomatism (from the Greek μετά ''metá'' "change" and σῶμα ''sôma'' "body") is the chemical alteration of a rock by hydrothermal and other fluids. It is the replacement of one rock by another of different mineralogical and chemical co ...
and weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs '' in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement ...
of primary basaltic minerals are also present on Mars. Secondary minerals include hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
, phyllosilicates
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, silica (silicon dioxide, ) is usually consid ...
(clay minerals), goethite
Goethite (, ) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the "α" polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient t ...
, jarosite
Jarosite is a basic hydrous sulfate of potassium and ferric iron (Fe-III) with a chemical formula of KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6. This sulfate mineral is formed in ore deposits by the oxidation of iron sulfides. Jarosite is often produced as a byproduct d ...
, iron sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
minerals, opaline silica, and gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywa ...
. Many of these secondary minerals require liquid water to form (aqueous minerals).
Opaline silica and iron sulphate minerals form in acidic (low pH) solutions. Sulphates have been found in a variety of locations, including near Juventae Chasma, Ius Chasma, Melas Chasma
Melas Chasma is a canyon on Mars, the widest segment of the Valles Marineris canyon system, located east of Ius Chasma at 9.8°S, 283.6°E in Coprates quadrangle. It cuts through layered deposits that are thought to be sediments from an old la ...
, Candor Chasma, and Ganges Chasma
Ganges Chasma is a deep canyon at the eastern end of the vast Valles Marineris system on Mars, an offshoot of Capri Chasma, and is in the Coprates quadrangle. It is named after the River Ganges in South Asia. Ganges Chasma is thought to have form ...
. These sites all contain fluvial
In geography and geology, fluvial processes are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by them. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluviog ...
landforms indicating that abundant water was once present. Spirit rover discovered sulfates and goethite in the Columbia Hills.Christensen, P.R. (2005) Mineral Composition and Abundance of the Rocks and Soils at Gusev and Meridiani from the Mars Exploration Rover Mini-TES Instruments AGU Joint Assembly, 23–27 May 2005 http://www.agu.org/meetings/sm05/waissm05.html Klingelhofer, G., et al. (2005) Lunar Planet. Sci. XXXVI abstr. 2349
Some of the mineral classes detected may have formed in environments suitable (i.e., enough water and the proper pH) for life. The mineral smectite (a phyllosilicate) forms in near-neutral waters. Phyllosilicates and carbonates are good for preserving organic matter, so they may contain evidence of past life. Sulfate deposits preserve chemical and morphological fossils, and fossils of microorganisms form in iron oxides like hematite. The presence of opaline silica points toward a hydrothermal environment that could support life. Silica is also excellent for preserving evidence of microbes.
Sedimentary rocks

 Layered sedimentary deposits are widespread on Mars. These deposits probably consist of both
Layered sedimentary deposits are widespread on Mars. These deposits probably consist of both sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
and poorly indurated
Friability ( ), the condition of being friable, describes the tendency of a solid substance to break into smaller pieces under duress or contact, especially by rubbing. The opposite of friable is indurate.
Substances that are designated hazardous, ...
or unconsolidated sediments. Thick sedimentary deposits occur in the interior of several canyons in Valles Marineris, within large craters in Arabia and Meridiani Planum
The Meridiani Planum (alternately Meridiani plain, Meridiani plains, Terra Meridiani, or Terra Meridiani plains) is either a large plain straddling the equator of Mars and covered with a vast number of spherules containing a lot of iron oxide or ...
(see Henry Crater
Henry is a large crater in the Arabia quadrangle of Mars. It is in diameter and was named after the brothers Paul Henry and Prosper Henry, both of whom were French telescope makers and astronomers.
Arago crater is to the east of Henry, Barth ...
for example), and probably comprise much of the deposits in the northern lowlands (e.g., Vastitas Borealis
(Latin 'northern waste') is the largest lowland region of Mars. It is in the northerly latitudes of the planet and encircles the northern polar region. Vastitas Borealis is often simply referred to as the northern plains, northern lowlands or ...
Formation). The Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity landed in an area containing cross-bedded (mainly eolian) sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
s (Burns formation). Fluvial-deltaic deposits are present in Eberswalde Crater and elsewhere, and photogeologic evidence suggests that many craters and low lying intercrater areas in the southern highlands contain Noachian-aged lake sediments.
While the possibility of carbonates on Mars has been of great interest to astrobiologists and geochemists alike, there was little evidence for significant quantities of carbonate deposits on the surface. In the summer of 2008, the TEGA and WCL experiments on the 2007 ''Phoenix'' Mars lander found between 3–5wt% (percent by weight) calcite (CaCO3) and an alkaline soil. In 2010, analyses by the Mars Exploration Rover ''Spirit'' identified outcrops rich in magnesium-iron carbonate (16–34 wt%) in the Columbia Hills of Gusev crater. The magnesium-iron carbonate most likely precipitated from carbonate-bearing solutions under hydrothermal conditions at near-neutral pH in association with volcanic activity during the Noachian Period.
Carbonates
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ...
(calcium or iron carbonates) were discovered in a crater on the rim of Huygens Crater, located in the Iapygia quadrangle. The impact on the rim exposed material that had been dug up from the impact that created Huygens. These minerals represent evidence that Mars once had a thicker carbon dioxide atmosphere with abundant moisture, since these kind of carbonates only form when there is a lot of water. They were found with the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars
The Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) is a visible-infrared spectrometer aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter searching for mineralogic indications of past and present water on Mars. The CRISM instrument team compri ...
(CRISM) instrument on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, an ...
. Earlier, the instrument had detected clay minerals. The carbonates were found near the clay minerals. Both of these minerals form in wet environments. It is supposed that billions of years ago Mars was much warmer and wetter. At that time, carbonates would have formed from water and the carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere. Later the deposits of carbonate would have been buried. The double impact has now exposed the minerals. Earth has vast carbonate deposits in the form of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
.
Spirit Rover discoveries in the Aeolis quadrangle
The rocks on the plains of Gusev are a type ofbasalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
. They contain the mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers qui ...
, pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe I ...
, plagioclase
Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more p ...
, and magnetite, and they look like volcanic basalt as they are fine-grained with irregular holes (geologists would say they have vesicles and vugs
A vug, vugh, or vugg (
) is a small- to medium-sized cavity inside rock. It may be formed through a variety of processes. Most commonly, cracks and fissures opened by tectonic activity ( folding and faulting) are partially filled by quartz, c ...
).Arvidson, R. E., et al. (2004) Science, 305, 821–824
Much of the soil on the plains came from the breakdown of the local rocks. Fairly high levels of nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
were found in some soils; probably from meteorites
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object ...
.
Analysis shows that the rocks have been slightly altered by tiny amounts of water. Outside coatings and cracks inside the rocks suggest water deposited minerals, maybe bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
compounds. All the rocks contain a fine coating of dust and one or more harder rinds of material. One type can be brushed off, while another needed to be ground off by the Rock Abrasion Tool
The Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) is a grinding and brushing installation on NASA’s twin Mars Exploration Rovers, ''Spirit'' (MER-A) and '' Opportunity'' (MER-B), which landed on Mars in January 2004. It was designed, developed and continues to be ...
(RAT).
There are a variety of rocks in the Columbia Hills (Mars)
The Columbia Hills are a range of low hills inside Gusev crater on Mars. They were observed by the Mars Exploration Rover '' Spirit'' when it landed within the crater in 2004. They were promptly given an unofficial name by NASA since they were th ...
, some of which have been altered by water, but not by very much water.
The dust in Gusev Crater is the same as dust all around the planet. All the dust was found to be magnetic. Moreover, Spirit found the magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles ...
was caused by the mineral magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With ...
, especially magnetite that contained the element titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion i ...
. One magnet was able to completely divert all dust hence all Martian dust is thought to be magnetic. The spectra of the dust was similar to spectra of bright, low thermal inertia regions like Tharsis
Tharsis () is a vast volcanic plateau centered near the equator in the western hemisphere of Mars. The region is home to the largest volcanoes in the Solar System, including the three enormous shield volcanoes Arsia Mons, Pavonis Mons, and As ...
and Arabia that have been detected by orbiting satellites. A thin layer of dust, maybe less than one millimeter thick covers all surfaces. Something in it contains a small amount of chemically bound water.Bell, J (ed.) The Martian Surface. 2008. Cambridge University Press.
Plains
Observations of rocks on the plains show they contain the minerals pyroxene, olivine, plagioclase, and magnetite. These rocks can be classified in different ways. The amounts and types of minerals make the rocks primitive basalts—also called picritic basalts. The rocks are similar to ancient terrestrial rocks called basaltickomatiites
Komatiite () is a type of ultramafic mantle-derived volcanic rock defined as having crystallised from a lava of at least 18 wt% MgO. Komatiites have low silicon, potassium and aluminium, and high to extremely high magnesium content. Komatiite wa ...
. Rocks of the plains also resemble the basaltic shergottites, meteorites which came from Mars. One classification system compares the amount of alkali elements to the amount of silica on a graph; in this system, Gusev plains rocks lie near the junction of basalt, picrobasalt, and tephrite. The Irvine-Barager classification calls them basalts.
Plain's rocks have been very slightly altered, probably by thin films of water because they are softer and contain veins of light colored material that may be bromine compounds, as well as coatings or rinds. It is thought that small amounts of water may have gotten into cracks inducing mineralization processes).
Coatings on the rocks may have occurred when rocks were buried and interacted with thin films of water and dust.
One sign that they were altered was that it was easier to grind these rocks compared to the same types of rocks found on Earth.
The first rock that Spirit studied was Adirondack. It turned out to be typical of the other rocks on the plains.
Columbia Hills
Scientists found a variety of rock types in the Columbia Hills, and they placed them into six different categories. The six are: Adirondack, Clovis, Wishstone, Peace, Watchtower, Backstay, and Independence. They are named after a prominent rock in each group. Their chemical compositions, as measured by APXS, are significantly different from each other. Most importantly, all of the rocks in Columbia Hills show various degrees of alteration due to aqueous fluids. They are enriched in the elements phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and bromine—all of which can be carried around in water solutions. The Columbia Hills' rocks contain basaltic glass, along with varying amounts of olivine andsulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
s.
The olivine abundance varies inversely with the amount of sulfates. This is exactly what is expected because water destroys olivine but helps to produce sulfates.
The Clovis group is especially interesting because the Mossbauer spectrometer (MB) detected goethite
Goethite (, ) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the "α" polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient t ...
in it. Goethite forms only in the presence of water, so its discovery is the first direct evidence of past water in the Columbia Hills's rocks. In addition, the MB spectra of rocks and outcrops displayed a strong decline in olivine presence,
although the rocks probably once contained much olivine. Olivine is a marker for the lack of water because it easily decomposes in the presence of water. Sulfate was found, and it needs water to form.
Wishstone contained a great deal of plagioclase, some olivine, and anhydrate (a sulfate). Peace rocks showed sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
and strong evidence for bound water, so hydrated sulfates are suspected. Watchtower class rocks lack olivine consequently they may have been altered by water. The Independence class showed some signs of clay (perhaps montmorillonite a member of the smectite group). Clays require fairly long term exposure to water to form.
One type of soil, called Paso Robles, from the Columbia Hills, may be an evaporate deposit because it contains large amounts of sulfur, phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
, and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
.
Also, MB found that much of the iron in Paso Robles soil was of the oxidized, Fe+++ form, which would happen if water had been present.
Towards the middle of the six-year mission (a mission that was supposed to last only 90 days), large amounts of pure silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
were found in the soil. The silica could have come from the interaction of soil with acid vapors produced by volcanic activity in the presence of water or from water in a hot spring environment.
After Spirit stopped working scientists studied old data from the Miniature Thermal Emission Spectrometer, or Mini-TES and confirmed the presence of large amounts of carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate ...
-rich rocks, which means that regions of the planet may have once harbored water. The carbonates were discovered in an outcrop of rocks called "Comanche."
In summary, Spirit found evidence of slight weathering on the plains of Gusev, but no evidence that a lake was there. However, in the Columbia Hills there was clear evidence for a moderate amount of aqueous weathering. The evidence included sulfates and the minerals goethite and carbonates which only form in the presence of water. It is believed that Gusev crater may have held a lake long ago, but it has since been covered by igneous materials. All the dust contains a magnetic component which was identified as magnetite with some titanium. Furthermore, the thin coating of dust that covers everything on Mars is the same in all parts of the planet.
Opportunity rover discoveries in the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle

Opportunity Rover
''Opportunity'', also known as MER-B (Mars Exploration Rover – B) or MER-1, is a robotic rover that was active on Mars from 2004 until 2018. ''Opportunity'' was operational on Mars for sols (). Launched on July 7, 2003, as part of NASA's ...
found that the soil at Meridiani Planum
The Meridiani Planum (alternately Meridiani plain, Meridiani plains, Terra Meridiani, or Terra Meridiani plains) is either a large plain straddling the equator of Mars and covered with a vast number of spherules containing a lot of iron oxide or ...
was very similar to the soil at Gusev crater and Ares Vallis; however in many places at Meridiani the soil was covered with round, hard, gray spherules that were named "blueberries."Yen, A., et al. 2005. An integrated view of the chemistry and mineralogy of martian soils. Nature. 435.: 49–54. These blueberries were found to be composed almost entirely of the mineral hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
. It was decided that the spectra signal spotted from orbit by Mars Odyssey was produced by these spherules. After further study it was decided that the blueberries were concretions formed in the ground by water. Over time, these concretions weathered from what was overlying rock, and then became concentrated on the surface as a lag deposit. The concentration of spherules in bedrock could have produced the observed blueberry covering from the weathering of as little as one meter of rock.Squyres, S. et al. 2004. The Opportunity Rover's Athena Science Investigation at Meridiani Planum, Mars. Science: 1698–1703. Most of the soil consisted of olivine basalt sands that did not come from the local rocks. The sand may have been transported from somewhere else.
Minerals in dust
A Mössbauer spectrograph was made of the dust that gathered on Opportunity's capture magnet. The results suggested that the magnetic component of the dust wastitanomagnetite
Titanomagnetite is a mineral containing oxides of titanium and iron, with the formula Fe2+(Fe3+,Ti)2O4. It is also known as titaniferous magnetite, mogensenite, Ti-magnetite, or titanian magnetite. It is part of the spinel group of minerals. The Cu ...
, rather than just plain magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With ...
, as was once thought. A small amount of olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers qui ...
was also detected which was interpreted as indicating a long arid period on the planet. On the other hand, a small amount of hematite that was present meant that there may have been liquid water for a short time in the early history of the planet.
Because the Rock Abrasion Tool
The Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) is a grinding and brushing installation on NASA’s twin Mars Exploration Rovers, ''Spirit'' (MER-A) and '' Opportunity'' (MER-B), which landed on Mars in January 2004. It was designed, developed and continues to be ...
(RAT) found it easy to grind into the bedrocks, it is thought that the rocks are much softer than the rocks at Gusev crater.
Bedrock minerals
Few rocks were visible on the surface where Opportunity landed, but bedrock that was exposed in craters was examined by the suite of instruments on the Rover. Bedrock rocks were found to be sedimentary rocks with a high concentration ofsulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
in the form of calcium and magnesium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate (in English-speaking countries other than the US) is a chemical compound, a salt with the formula , consisting of magnesium cations (20.19% by mass) and sulfate anions . It is a white crystalline solid, ...
s. Some of the sulfates that may be present in bedrocks are kieserite
Kieserite, or magnesium sulfate monohydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula (MgSO4·H2O).
It has a vitreous luster and it is colorless, grayish-white or yellowish. Its hardness is 3.5 and crystallizes in the monoclinic cry ...
, sulfate anhydrate, bassanite
Bassanite is a calcium sulfate mineral with formula CaSO4· H2O or 2CaSO4·H2O. In other words it has half a water molecule per CaSO4 unit, hence its synonym ''calcium sulfate hemihydrate''.
Bassanite was first described in 1910 for an occurrenc ...
, hexahydrite
Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate (in English-speaking countries other than the US) is a chemical compound, a salt with the formula , consisting of magnesium cations (20.19% by mass) and sulfate anions . It is a white crystalline solid, s ...
, epsomite
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula MgSO4·7H2O.
Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as rarely found acicular or fibrous crystals, the normal form is as massiv ...
, and gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywa ...
. Salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
s, such as halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, p ...
, bischofite, antarcticite, bloedite, vanthoffite, or glauberite
Glauberite is a monoclinic sodium calcium sulfate mineral with the formula Na2 Ca( S O4)2.
It was first described in 1808 for material from the El Castellar Mine, Villarrubia de Santiago, Toledo, Castile-La Mancha, Spain. It was named for the ...
may also be present.Squyres, S. et al. 2004. In Situ Evidence for an Ancient Aqueous Environment at Meridian Planum, Mars. Science: 306. 1709–1714.
The rocks contained the sulfates had a light tone compared to isolated rocks and rocks examined by landers/rovers at other locations on Mars. The spectra of these light toned rocks, containing hydrated sulfates, were similar to spectra taken by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer
The Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) is an instrument on board Mars Global Surveyor. TES collects two types of data, hyperspectral thermal infrared data from 6 to 50 micrometres (μm) and bolometric visible-NIR (0.3 to 2.9 μm) measurements. T ...
on board the Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through t ...
. The same spectrum is found over a large area, so it is believed that water once appeared over a wide region, not just in the area explored by Opportunity Rover.
The Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer
:''APXS is also an abbreviation for APache eXtenSion tool, an extension for Apache web servers.''
An alpha particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS) is a spectrometer that analyses the chemical element composition of a sample from scattered alpha part ...
(APXS) found rather high levels of phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
in the rocks. Similar high levels were found by other rovers at Ares Vallis
Ares Vallis is an outflow channel on Mars, named after the Greek name for Mars: Ares, the god of war; it appears to have been carved by fluids, perhaps water. The valley 'flows' northwest out of the hilly Margaritifer Terra, where the Iani ...
and Gusev Crater
Gusev is a crater on the planet Mars and is located at and is in the Aeolis quadrangle. The crater is about 166 kilometers in diameter and formed approximately three to four billion years ago. It was named after Russian astronomer Matvey Gusev ...
, so it has been hypothesized that the mantle of Mars may be phosphorus-rich. The minerals in the rocks could have originated by acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a se ...
weathering of basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
. Because the solubility of phosphorus is related to the solubility of uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
, thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
, and rare earth elements
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silv ...
, they are all also expected to be enriched in rocks.
When Opportunity rover traveled to the rim of Endeavour crater
Endeavour is an impact crater located in the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. Endeavour is about in diameter. Using ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' data, phy ...
, it soon found a white vein that was later identified as being pure gypsum. It was formed when water carrying gypsum in solution deposited the mineral in a crack in the rock. A picture of this vein, called "Homestake" formation, is shown below.
Evidence of water

 Examination in 2004 of Meridiani rocks, showed the first strong ''in situ'' evidence for past water by detecting the mineral
Examination in 2004 of Meridiani rocks, showed the first strong ''in situ'' evidence for past water by detecting the mineral jarosite
Jarosite is a basic hydrous sulfate of potassium and ferric iron (Fe-III) with a chemical formula of KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6. This sulfate mineral is formed in ore deposits by the oxidation of iron sulfides. Jarosite is often produced as a byproduct d ...
, which only forms in water. This discovery proved that water once existed in Meridiani Planum
The Meridiani Planum (alternately Meridiani plain, Meridiani plains, Terra Meridiani, or Terra Meridiani plains) is either a large plain straddling the equator of Mars and covered with a vast number of spherules containing a lot of iron oxide or ...
. In addition, some rocks showed small laminations (layers) with shapes that are only made by gently flowing water. The first such laminations were found in a rock called "The Dells." Geologists would say that the cross-stratification showed festoon geometry from transport in subaqueous ripples. A picture of cross-stratification, also called cross-bedding, is shown on the left.
Box-shaped holes in some rocks were caused by sulfates forming large crystals, and then when the crystals later dissolved, holes, called vugs, were left behind. The concentration of the element bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
in rocks was highly variable probably because it is very soluble. Water may have concentrated it in places before it evaporated. Another mechanism for concentrating highly soluble bromine compounds is frost deposition at night that would form very thin films of water that would concentrate bromine in certain spots.
Rock from impact
One rock, "Bounce Rock," found sitting on the sandy plains was found to be ejecta from an impact crater. Its chemistry was different from the bedrocks. Containing mostly pyroxene and plagioclase and no olivine, it closely resembled a part, Lithology B, of the shergottite meteorite EETA 79001, a meteorite known to have come from Mars. Bounce rock received its name by being near an airbag bounce mark.Meteorites
Opportunity Rover found meteorites just sitting on the plains. The first one analyzed with Opportunity's instruments was called "Heatshield Rock," as it was found near where Opportunity's heatshield landed. Examination with the Miniature Thermal Emission Spectrometer ( Mini-TES), Mossbauer spectrometer, and APXS lead researchers to, classify it as anIAB meteorite
IAB meteorites are a group of iron meteorites according to their overall composition and a group of primitive achondrites because of silicate inclusions that show a strong affinity to winonaites and chondrites.
Description
The IAB meteorites are c ...
. The APXS determined it was composed of 93% iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
and 7% nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
. The cobble named "Fig Tree Barberton" is thought to be a stony or stony-iron meteorite (mesosiderite silicate), while "Allan Hills," and "Zhong Shan" may be iron meteorites.
Geological history
Observations at the site have led scientists to believe that the area was flooded with water a number of times and was subjected to evaporation and desiccation. In the process sulfates were deposited. After sulfates cemented the sediments, hematite concretions grew by precipitation from groundwater. Some sulfates formed into large crystals which later dissolved to leave vugs. Several lines of evidence point toward an arid climate in the past billion years or so, but a climate supporting water, at least for a time, in the distant past.Curiosity Rover discoveries in the Aeolis quadrangle
TheCuriosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
encountered rocks of special interest on the surface of Aeolis Palus
Aeolis Palus is a plain between the northern wall of Gale crater and the northern foothills of Aeolis Mons (Mount Sharp) on Mars. It is located at .
The NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission landed the ''Curiosity'' rover on Aeolis Palus in Aug ...
near Aeolis Mons ("Mount Sharp") in Gale Crater. In the autumn of 2012, rocks studied, on the way from Bradbury Landing
Bradbury Landing is the August 6, 2012, landing site within Gale crater on planet Mars of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) ''Curiosity'' rover. On August 22, 2012, on what would have been his 92nd birthday, NASA named the site for author Ra ...
to Glenelg Intrigue, included "Coronation" rock (August 19, 2012), "Jake Matijevic" rock (September 19, 2012), "Bathurst Inlet" rock (September 30, 2012).
Evidence for ancient water
On September 27, 2012, NASA scientists announced that the ''Curiosity rover'' found evidence for an ancientstreambed
A stream bed or streambed is the bottom of a stream or river (bathymetry) or the physical confine of the normal water flow ( channel). The lateral confines or channel margins are known as the stream banks or river banks, during all but flood ...
suggesting a "vigorous flow" of water on Mars.
On December 3, 2012, NASA reported that ''Curiosity
Curiosity (from Latin '' cūriōsitās'', from ''cūriōsus'' "careful, diligent, curious", akin to ''cura'' "care") is a quality related to inquisitive thinking such as exploration, investigation, and learning, evident by observation in human ...
'' performed its first extensive soil analysis
Soil test may refer to one or more of a wide variety of soil analysis conducted for one of several possible reasons. Possibly the most widely conducted soil tests are those done to estimate the plant-available concentrations of plant nutrients, i ...
, revealing the presence of water molecules, sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
and chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
in the Martian soil. On December 9, 2013, NASA reported that, based on evidence from ''Curiosity'' rover studying Aeolis Palus
Aeolis Palus is a plain between the northern wall of Gale crater and the northern foothills of Aeolis Mons (Mount Sharp) on Mars. It is located at .
The NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission landed the ''Curiosity'' rover on Aeolis Palus in Aug ...
, Gale Crater contained an ancient freshwater lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
which could have been a hospitable environment for microbial life.
Evidence for ancient habitability
In March 2013, NASA reported ''Curiosity
Curiosity (from Latin '' cūriōsitās'', from ''cūriōsus'' "careful, diligent, curious", akin to ''cura'' "care") is a quality related to inquisitive thinking such as exploration, investigation, and learning, evident by observation in human ...
'' found evidence that geochemical
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the e ...
conditions in Gale Crater were once suitable for microbial life after analyzing the first drilled sample of Martian rock, "John Klein" rock at ''Yellowknife Bay'' in Gale Crater. The rover detected water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
, sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic a ...
and hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The under ...
. Chloromethane
Chloromethane, also called methyl chloride, Refrigerant-40, R-40 or HCC 40, is an organic compound with the chemical formula . One of the haloalkanes, it is a colorless, odorless, flammable gas. Methyl chloride is a crucial reagent in industrial ...
and dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible wit ...
were also detected. Related tests found results consistent with the presence of smectite clay minerals.
Detection of organics
On 16 December 2014, NASA reported the ''Curiosity'' rover detected a "tenfold spike", likely localized, in the amount ofmethane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
in the Martian atmosphere. Sample measurements taken "a dozen times over 20 months" showed increases in late 2013 and early 2014, averaging "7 parts of methane per billion in the atmosphere." Before and after that, readings averaged around one-tenth that level.
In addition, high levels of organic chemicals
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The s ...
, particularly chlorobenzene
Chlorobenzene is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.
Uses
Historical
The major use of chlorob ...
, were detected in powder drilled from one of the rocks, named "Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic counties of England, historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th c ...
", analyzed by the Curiosity rover.
Images
Aeolis Palus
Aeolis Palus is a plain between the northern wall of Gale crater and the northern foothills of Aeolis Mons (Mount Sharp) on Mars. It is located at .
The NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission landed the ''Curiosity'' rover on Aeolis Palus in Aug ...
near Aeolis Mons ("Mount Sharp") - North is down.
Image:Curiosity landing site (artist's rendition with 2x vertical exaggeration).jpg, Gale Crater - Landing site is noted - also, alluvial fan
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to semiarid climates, but a ...
(blue) and sediment layers in Aeolis Mons
Mount Sharp, officially Aeolis Mons (), is a mountain on Mars. It forms the central peak within Gale (crater), Gale crater and is located around , rising high from the valley floor. Its ID in the United States Geological Survey's Gazetteer of ...
(cutaway).
Image:PIA16064-Mars Curiosity Rover Treasure Map.jpg, Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
landing site (green dot) - Blue dot marks '' Glenelg Intrigue'' - Blue spot marks "Base of Mount Sharp
Mount Sharp, officially Aeolis Mons (), is a mountain on Mars. It forms the central peak within Gale crater and is located around , rising high from the valley floor. Its ID in the United States Geological Survey's Gazetteer of Planetary Nom ...
" - a planned area of study.
Image:Curiosity Rover (Exaggerated Color) - HiRISE - 20120814.jpg, Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
landing site ("Bradbury Landing
Bradbury Landing is the August 6, 2012, landing site within Gale crater on planet Mars of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) ''Curiosity'' rover. On August 22, 2012, on what would have been his 92nd birthday, NASA named the site for author Ra ...
") viewed by HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
( MRO) (August 14, 2012).
Image:673885main PIA15986-full full.jpg, Aeolis Palus
Aeolis Palus is a plain between the northern wall of Gale crater and the northern foothills of Aeolis Mons (Mount Sharp) on Mars. It is located at .
The NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission landed the ''Curiosity'' rover on Aeolis Palus in Aug ...
and "Mount Sharp" in Gale Crater as viewed by the Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
(August 6, 2012).
Image:PIA16105 malin04ano-br2.jpg, Layers at the base of Aeolis Mons
Mount Sharp, officially Aeolis Mons (), is a mountain on Mars. It forms the central peak within Gale (crater), Gale crater and is located around , rising high from the valley floor. Its ID in the United States Geological Survey's Gazetteer of ...
- dark rock in inset is same size as the Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
( white balanced image).
Image:676029main_pia16052-color-full_full.jpg, Gale Crater rim about North of the Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
(August 9, 2012).
Image:Mars Curiosity Rover-Coronation Rock-N165.jpg, "Coronation" rock on Mars - first target of the ChemCam
Chemistry and Camera complex (ChemCam) is a suite of remote sensing instruments on Mars for the ''Curiosity'' rover. As the name implies, ChemCam is actually two different instruments combined as one: a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIB ...
laser analyzer on the Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
(August 19, 2012).
Image:PIA16192-MarsCuriosityRover-Target-JakeRock-20120927.jpg, " Jake Matijevic" rock on Mars - a target of the APSX and ChemCam
Chemistry and Camera complex (ChemCam) is a suite of remote sensing instruments on Mars for the ''Curiosity'' rover. As the name implies, ChemCam is actually two different instruments combined as one: a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIB ...
instruments on the Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
(September 22, 2012).
Image:PIA14762-MarsCuriosityRover-BathurstInletRock.jpg, "Bathurst Inlet" rock on Mars - as viewed by the MAHLI camera on the Curiosity rover
''Curiosity'' is a car-sized Mars rover designed to explore the Gale crater on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. ''Curiosity'' was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and la ...
(September 30, 2012).
Image:PIA17085-MarsCuriosityRover-TraverseMap-Sol351-20130801.jpg, First-Year & First-MilTraverse Map
of the ''Curiosity'' rover on Mars (August 1, 2013)
3-D
.
See also
References
External links
Mars - Geologic Map
(
USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
, 2014)original
/
crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydropon ...
/ full video (00:56)
.
Video (04:32) - Evidence: Water "Vigorously" Flowed On Mars - September, 2012
{{Portal bar, Solar System Geology of Mars Geochemistry