Colmar Pocket on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Colmar Pocket (french: Poche de Colmar; de , Brückenkopf Elsass) was the area held in central
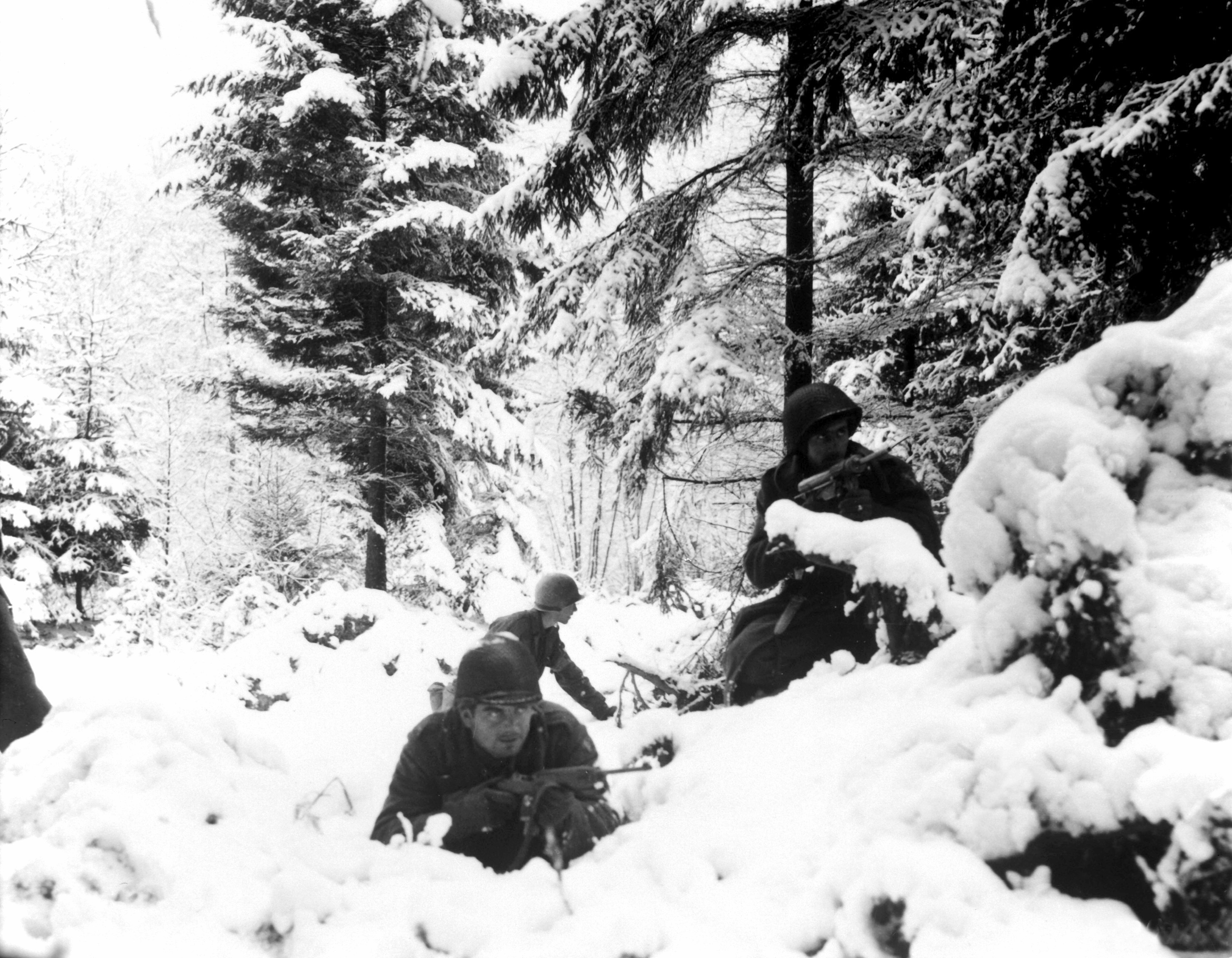 The winter of 1944-45 was uncommonly cold for northwestern Europe. In his ''History of the French First Army'', General de Lattre described the weather in Alsace as "Siberian" with temperatures of -20 °C (-4 °F), strong winds, and over three feet (1 m) of snow.De Lattre, p. 338
The Alsatian Plain is flat and offers an attacker practically no cover other than occasional woods. The plain is also a drainage basin for the Rhine and is consequently cut by many streams and drainage canals with
The winter of 1944-45 was uncommonly cold for northwestern Europe. In his ''History of the French First Army'', General de Lattre described the weather in Alsace as "Siberian" with temperatures of -20 °C (-4 °F), strong winds, and over three feet (1 m) of snow.De Lattre, p. 338
The Alsatian Plain is flat and offers an attacker practically no cover other than occasional woods. The plain is also a drainage basin for the Rhine and is consequently cut by many streams and drainage canals with
 General Émile Béthouart's
General Émile Béthouart's
 The division's 7th Infantry Regiment pushed to the south, clearing the region between the Fecht and Ill Rivers. During the clearing operations of the 7th Infantry, Private First Class
The division's 7th Infantry Regiment pushed to the south, clearing the region between the Fecht and Ill Rivers. During the clearing operations of the 7th Infantry, Private First Class
 Noting the difficult progress of all Allied units against German resistance in the Colmar Pocket, General de Lattre requested reinforcements from the U.S. 6th Army Group. Concurring, General Devers subordinated the Headquarters of the U.S. XXI Corps to the French First Army. General Milburn's XXI Corps took up position between the two French corps on 28 January and assumed command of the U.S. 3rd and 28th Infantry Divisions. Two additional U.S. divisions were also assigned to the XXI Corps - the U.S. 75th Infantry Division and the U.S. 12th Armored Division. Finally, the French 5th Armored Division, 1st Parachute Regiment, and 1st ''Choc'' (commando) Battalion were placed under XXI Corps' command. The XXI Corps was given the mission of capturing the city of Colmar and driving on the bridge at Breisach.
For their part, the German high command misread the Allied objectives, believing the Allied assault to be a general pressure along the front designed to induce collapse at any given point. Hitler had agreed to a partial withdrawal in the north (the Erstein salient) during the night of 28 January but forbade a general withdrawal over the Rhine.Clarke and Smith, p. 548 German outposts in the Vosges Mountains were pulled back, but the confusion of the withdrawal and the pressures of the battlefield resulted in many units becoming mixed with one another. While this did not affect the numbers available for combat, it did lower the defensive cohesion of the German units. On 29 January, ''Heeresgruppe Oberrhein'' was dissolved as a headquarters, and the units in the Colmar Pocket were again subordinated to ''Heeresgruppe G'' (Army Group G), under the command of '' SS- Obergruppenführer'' Paul Hausser.
Noting the difficult progress of all Allied units against German resistance in the Colmar Pocket, General de Lattre requested reinforcements from the U.S. 6th Army Group. Concurring, General Devers subordinated the Headquarters of the U.S. XXI Corps to the French First Army. General Milburn's XXI Corps took up position between the two French corps on 28 January and assumed command of the U.S. 3rd and 28th Infantry Divisions. Two additional U.S. divisions were also assigned to the XXI Corps - the U.S. 75th Infantry Division and the U.S. 12th Armored Division. Finally, the French 5th Armored Division, 1st Parachute Regiment, and 1st ''Choc'' (commando) Battalion were placed under XXI Corps' command. The XXI Corps was given the mission of capturing the city of Colmar and driving on the bridge at Breisach.
For their part, the German high command misread the Allied objectives, believing the Allied assault to be a general pressure along the front designed to induce collapse at any given point. Hitler had agreed to a partial withdrawal in the north (the Erstein salient) during the night of 28 January but forbade a general withdrawal over the Rhine.Clarke and Smith, p. 548 German outposts in the Vosges Mountains were pulled back, but the confusion of the withdrawal and the pressures of the battlefield resulted in many units becoming mixed with one another. While this did not affect the numbers available for combat, it did lower the defensive cohesion of the German units. On 29 January, ''Heeresgruppe Oberrhein'' was dissolved as a headquarters, and the units in the Colmar Pocket were again subordinated to ''Heeresgruppe G'' (Army Group G), under the command of '' SS- Obergruppenführer'' Paul Hausser.
 Having been on the defense to this point in the battle, General Norman Cota's 28th Division was teamed with the French armored combat command CC4 and told to take the city of Colmar. Leading with the U.S. 109th Infantry Regiment on 2 February, the infantry crossed an anti-tank ditch north of the city, while the French armor located a crossing point over the obstacle. This accomplished, the French armor plunged into Colmar reaching the ''Place Rapp'' (Rapp Square) at 11:30. On 2–3 February, the 109th Infantry, the French CC4, 1st Parachute Regiment and commandos cleared the city of Germans. In a symbolic act, the French 152nd Infantry Regiment re-entered Colmar, its pre-war garrison. Pushing south on 3 February the 112th Infantry entered Turckheim () and cleared Ingersheim () to the west of Colmar.Gaujac, p. 126 Other units of the 28th Division joined the French in blocking German exit routes from the Vosges Mountains. On 6 February, the 28th Division moved eastwards to the Rhône-Rhine Canal on the south flank of the U.S. XXI Corps ending 28th Division participation in the battle.
Having been on the defense to this point in the battle, General Norman Cota's 28th Division was teamed with the French armored combat command CC4 and told to take the city of Colmar. Leading with the U.S. 109th Infantry Regiment on 2 February, the infantry crossed an anti-tank ditch north of the city, while the French armor located a crossing point over the obstacle. This accomplished, the French armor plunged into Colmar reaching the ''Place Rapp'' (Rapp Square) at 11:30. On 2–3 February, the 109th Infantry, the French CC4, 1st Parachute Regiment and commandos cleared the city of Germans. In a symbolic act, the French 152nd Infantry Regiment re-entered Colmar, its pre-war garrison. Pushing south on 3 February the 112th Infantry entered Turckheim () and cleared Ingersheim () to the west of Colmar.Gaujac, p. 126 Other units of the 28th Division joined the French in blocking German exit routes from the Vosges Mountains. On 6 February, the 28th Division moved eastwards to the Rhône-Rhine Canal on the south flank of the U.S. XXI Corps ending 28th Division participation in the battle.
 On 3 February, the 12th Armored Division moved south through 28th Division lines with the objective of linking up with the French I Corps and splitting the Colmar Pocket. Combat Command B (CCB) seized a bridgehead near Sundhoffen () and CCR advanced on the road between Colmar and Rouffach (). The following day, CCA captured Hattstatt () on the Colmar-Rouffach Road, but CCR found its way blocked by German defenses. On 5 February, CCA entered Rouffach and made contact with the 4th Moroccan Mountain Division of the French I Corps, some 17 days after French I Corps launched its assault. The same day, CCR entered the village of Herrlisheim-près-Colmar (), and so the 12th Armored Division attacked, for a second time, a town named Herrlisheim in Alsace (the battles of the 12th Armored Division in mid-January 1945, at Herrlisheim north of Strasbourg saw several battalions of the division manhandled by German troops in the Gambsheim bridgehead.) Thereafter, during the battle, the 12th Armored Division screened German exit routes from the Vosges Mountains and supported the 28th Division by fire.
On 3 February, the 12th Armored Division moved south through 28th Division lines with the objective of linking up with the French I Corps and splitting the Colmar Pocket. Combat Command B (CCB) seized a bridgehead near Sundhoffen () and CCR advanced on the road between Colmar and Rouffach (). The following day, CCA captured Hattstatt () on the Colmar-Rouffach Road, but CCR found its way blocked by German defenses. On 5 February, CCA entered Rouffach and made contact with the 4th Moroccan Mountain Division of the French I Corps, some 17 days after French I Corps launched its assault. The same day, CCR entered the village of Herrlisheim-près-Colmar (), and so the 12th Armored Division attacked, for a second time, a town named Herrlisheim in Alsace (the battles of the 12th Armored Division in mid-January 1945, at Herrlisheim north of Strasbourg saw several battalions of the division manhandled by German troops in the Gambsheim bridgehead.) Thereafter, during the battle, the 12th Armored Division screened German exit routes from the Vosges Mountains and supported the 28th Division by fire.

 In compliance with General Eisenhower's direction, the Colmar Pocket was eliminated, and the U.S. 6th Army Group stood on the Rhine, from the Swiss border to a region well north of Strasbourg. The German 19th Army, although not completely destroyed, lost the bulk of its experienced combat troops (only the 708th Volksgrenadier Division escaped somewhat intact)Weigley, p. 599 and was forced to reform in
In compliance with General Eisenhower's direction, the Colmar Pocket was eliminated, and the U.S. 6th Army Group stood on the Rhine, from the Swiss border to a region well north of Strasbourg. The German 19th Army, although not completely destroyed, lost the bulk of its experienced combat troops (only the 708th Volksgrenadier Division escaped somewhat intact)Weigley, p. 599 and was forced to reform in
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
, France, by the German Nineteenth Army from November 1944 to February 1945, against the U.S. 6th Army Group (6th AG) during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. It was formed when 6th AG liberated southern and northern Alsace and adjacent eastern Lorraine, but could not clear central Alsace. During Operation Nordwind in December 1944, the 19th Army attacked north out of the Pocket in support of other German forces attacking south from the Saar
Saar or SAAR has several meanings:
People Given name
* Saar Boubacar (born 1951), Senegalese professional football player
* Saar Ganor, Israeli archaeologist
* Saar Klein (born 1967), American film editor
Surname
* Ain Saar (born 1968), E ...
into northern Alsace. In late January and early February 1945, the French First Army (reinforced by the U.S. XXI Corps) cleared the Pocket of German forces.
Background
Formation of the Pocket
A German bridgehead on the west bank of theRhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
long and deep was formed in November 1944 when the German defenses in the Vosges Mountains
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
collapsed under the pressure of an offensive by the U.S. 6th Army Group. General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny
Jean Joseph Marie Gabriel de Lattre de Tassigny (2 February 1889 – 11 January 1952) was a French général d'armée during World War II and the First Indochina War. He was posthumously elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France in 1952.
As ...
's French First Army forced the Belfort Gap and destroyed the German IV Luftwaffe Field Corps
IV may refer to:
Businesses and organizations
*Immigration Voice, an activist organization
*Industrievereinigung, Federation of Austrian Industry
* Intellectual Ventures, a privately held intellectual property company
*InterVarsity Christian Fell ...
near the town of Burnhaupt in the southern Vosges Mountains. Soon afterwards, French forces reached the Rhine in the region north of the Swiss border between Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning '' mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin department, in the Grand Est region, eastern France, close to the Swiss and German borders. It is the largest city in Haut-Rhin and second largest in Alsace a ...
and Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (B ...
. Likewise, in the northern Vosges Mountains, the French 2nd Armored Division spearheaded a U.S. Seventh Army
The Seventh Army was a United States army created during World War II that evolved into the United States Army Europe (USAREUR) during the 1950s and 1960s. It served in North Africa and Italy in the Mediterranean Theater of Operations and Fra ...
advance, forced the Saverne Gap, and drove to the Rhine, liberating Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
on 23 November 1944. The effect of these two advances was to collapse the German presence in southern Alsace west of the Rhine to a semi-circular bridgehead centered on the town of Colmar
Colmar (, ; Alsatian: ' ; German during 1871–1918 and 1940–1945: ') is a city and commune in the Haut-Rhin department and Grand Est region of north-eastern France. The third-largest commune in Alsace (after Strasbourg and Mulhouse), it i ...
that came to be known as the ''Colmar Pocket''.
German view
Apart from Normandy, the areas of France most bitterly defended by the Germans were Alsace and Lorraine. This occurred in part because the Allied surge across France in 1944 was slowed down by logistical difficulties as the Allies reached the easternmost extent of France, but the primary reason for the stout German defenses of these regions is that Alsace and Lorraine were claimed as part of Germany and would be defended as strongly as any other German soil. This perception informed Hitler's decisions of 24 November and 27 November 1944, that committed GeneralSiegfried Rasp
__NOTOC__
Siegfried Rasp (10 January 1898 – 2 February 1968) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II.
Awards and decorations
* Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 15 April 1944 as Generalmajor
is the Germani ...
's 19th Army to a do-or-die defense of the region around Colmar. On 26 November, the Germans formed Army Group Oberrhein under the command of Heinrich Himmler and tasked his command with the defense of the front between the Bienwald
The Bienwald is a large forested area in the southern Pfalz region of Germany near the towns of Kandel and Wörth am Rhein. The western edge defines the eastern extent of the Wissembourg Gap, a corridor of open terrain between the Bienwald ...
and the Swiss border. Of prime importance to the German defense around Colmar were the bridges over the Rhine at Breisach
Breisach (formerly Altbreisach; Low Alemannic: ''Alt-Brisach'') is a town with approximately 16,500 inhabitants, situated along the Rhine in the Rhine Valley, in the district Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, about halfway ...
and Chalampé, since it was over these bridges that supplies were delivered.
Allied limitations
The logistical crisis and heavy combat of autumn 1944 had dulled the fighting edge of Allied forces throughout northwestern Europe, and the U.S. 6th Army Group was no exception. Restricted logistical support imposed limits on the usage of artillery ammunition and the number of divisions the Allies could effectively employ in the front lines. Faulty forecasts for the numbers of infantry replacements needed prevented U.S. rifle companies from maintaining full strength. On the part of the French, their replacement system was limited by the amount of training infrastructure they had been able to re-establish since reentering France in August 1944 and was further strained by a controversial French decision to "whiten" the French forces in Alsace by sending experienced Senegalese and other colonial troops—exhausted from fighting in Italy—to the south and replacing them with French Forces of the Interior (FFI) troops of varying quality and experience. While the FFI troops were capable of defensive operations, they had to undergo a steep learning curve in order to become effective at offensive operations, particularly where complex activities such as combined-arms operations were concerned. Thus, at the close of November 1944, the French First Army deployed two kinds of units—highly experienced colonial units and "green" units that had recently received a large influx of FFI troops. Coupled with a supporting arms structure (artillery, engineers, etc.) that was weaker than that of other Allied field armies, the sag in French First Army troop proficiency allowed the Germans to hold the Colmar Pocket against an unsuccessful French offensive from 15–22 December 1944.Allied force redeployments
On New Year's Day 1945, the Germans launched ''Unternehmen Nordwind'' (Operation "North Wind"), one objective of which was the recapture ofStrasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
. German troops of the 198th Infantry Division and the 106th Panzer Brigade attacked north out of the Colmar Pocket from 7–13 January. Although the defending French II Corps suffered some minor losses during this attack, the French held the front south of Strasbourg and frustrated German attempts to recapture the city. Following the failure of ''Nordwind'', the 6th Army Group was ordered to collapse the Colmar Pocket as part of General Dwight D. Eisenhower's plan for all Allied forces to close on the Rhine prior to invading Germany. Since the bulk of Allied troops surrounding the Colmar Pocket were French, this mission was assigned to the French First Army.
The U.S. 3rd Infantry Division
The 3rd Infantry Division (3ID) (nicknamed Rock of the Marne) is a combined arms division of the United States Army based at Fort Stewart, Georgia. It is a direct subordinate unit of the XVIII Airborne Corps and U.S. Army Forces Command. Its cu ...
had moved into the Vosges Mountains
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
during mid-December to replace the worn-out U.S. 36th Infantry Division
The 36th Infantry Division ("Arrowhead"), also known as the "Panther Division", "Lone Star Division",Jacob Devers
Jacob Loucks Devers (; 8 September 1887 – 15 October 1979) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the 6th Army Group in the European Theater during World War II. He was involved in the development and adoption of numerous ...
, commander of the 6th Army Group, arranged for the transfer of a U.S. division from another part of the front. The U.S. 28th Infantry Division duly arrived from the Ardennes
The Ardennes (french: Ardenne ; nl, Ardennen ; german: Ardennen; wa, Årdene ; lb, Ardennen ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Be ...
front and took up position along the right flank of the U.S. 3rd Infantry Division. With the 28th Division in the Kaysersberg Valley, the 3rd Division would be able to concentrate for an attack against two German divisions, the 708th '' Volksgrenadier'' and the 189th Infantry. Additionally, a U.S. armored division, the 10th, was scheduled to support the offensive, but as events developed, it was the U.S. 12th Armored Division that was eventually committed to the battle.
Weather and terrain
 The winter of 1944-45 was uncommonly cold for northwestern Europe. In his ''History of the French First Army'', General de Lattre described the weather in Alsace as "Siberian" with temperatures of -20 °C (-4 °F), strong winds, and over three feet (1 m) of snow.De Lattre, p. 338
The Alsatian Plain is flat and offers an attacker practically no cover other than occasional woods. The plain is also a drainage basin for the Rhine and is consequently cut by many streams and drainage canals with
The winter of 1944-45 was uncommonly cold for northwestern Europe. In his ''History of the French First Army'', General de Lattre described the weather in Alsace as "Siberian" with temperatures of -20 °C (-4 °F), strong winds, and over three feet (1 m) of snow.De Lattre, p. 338
The Alsatian Plain is flat and offers an attacker practically no cover other than occasional woods. The plain is also a drainage basin for the Rhine and is consequently cut by many streams and drainage canals with alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. ...
-coated bottoms, making them treacherous for vehicles to ford. Dotting the plain are small villages made up of sturdy masonry houses whose multi-storey construction offered defending troops a commanding view of the surrounding fields.
Battle
Initial French attack against the south flank of the Colmar Pocket
 General Émile Béthouart's
General Émile Béthouart's French I Corps
The 1st Army Corps (french: 1er Corps d'Armée) was first formed before World War I. During World War II it fought in the Campaign for France in 1940, on the Mediterranean islands of Corsica and Elba in 1943 - 1944, and in the campaigns to li ...
(French: ''Ier Corps d'Armée'') attacked on 20 January 1945. The 2nd and 4th Moroccan Divisions had as their initial objective Ensisheim (). The 9th Colonial Division conducted secondary attacks on the right flank of the corps, north of Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning '' mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin department, in the Grand Est region, eastern France, close to the Swiss and German borders. It is the largest city in Haut-Rhin and second largest in Alsace a ...
.Clarke and Smith, p. 539 In support were tanks of the French 1st Armored Division. Attacking in a snowstorm, the French I Corps initially achieved tactical surprise against its opponent, General Erich Abraham
Erich Abraham (27 March 1895 – 7 March 1971) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany who command the 76th Infantry Division then the LXIII Corps on the Western Front during World War II. He was also a recipient of the Knight's Cross ...
's ''LXIII. Armeekorps''. The attack of the French I Corps slowed through the night as German counterattacks began. The difficult weather and terrain coupled with a German defense in depth stymied the French I Corps advance and severely limited its success.Clarke and Smith, p. 541 The French attack, however, succeeded in drawing German mobile reserves (the 106th ''Panzer'' Brigade and the 654th Heavy Antitank Battalion) and the German 2nd Mountain Division
The 2nd Mountain Division (german: 2. Gebirgs Division) was a ''Gebirgsjäger'' division of the German Army which served in World War II, mainly in the northernmost sector of the Eastern Front, near the Arctic. Formed in 1938, the division was di ...
south. However, even this limited success was not without significant cost: one brigade of the French 1st Armored Division, Combat Command 1 (CC1), lost 36 of some 50 medium tanks to land mine
A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automati ...
s. Losses in other tank units were similar.
Unlike most of the terrain on the Alsatian Plain, the terrain the French I Corps fought in was hemmed in by woodlands and urban areas, and so ground was won only slowly in January after the first day of the attack. The 4th Moroccan Mountain Division was able to push only some two miles (3 km) to the northeast in the direction of Cernay (). On the 4th Division's right flank and to the southeast, the 2nd Moroccan Infantry Division enjoyed greater success, pushing almost four miles (6 km) to the northeast in the direction of WittelsheimGaujac, p. 94 (). On the right flank and starting from the city of Mulhouse, the 9th Colonial Division also pushed through the suburbs of Mulhouse and the woods north of the city, with CC1 taking Richwiller () and the 6th Colonial Infantry Regiment liberating Wittenheim (). On 24 January, a German armored counterattack near Richwiller was repulsed by the French colonial troops, with the Germans losing 15 tanks and tank destroyers. Overall, the gains of the French I Corps were greater in the western part (right flank) of its sector of the front, but the Germans in large part succeeded in stalemating the corps' advance.
Allied attack in the north
General Joseph de Goislard de Monsabert's ''II e Corps d'Armée'' launched its attack on 22–23 January. The attacking units were the U.S. 3rd Infantry Division and the French 1st March Infantry Division. South of the 3rd Division, the U.S. 28th Infantry Division defended its sector of the front. In reserve was the French 2nd Armored Division.Push to the Colmar Canal and the battle for Jebsheim
General John W. O'Daniel's 3rd U.S. Infantry Division attacked to the southeast on 22 January, aiming to cross the Ill River, bypass the city of Colmar to the north, and open a path for the tanks of the French 5th Armored Division to drive on the railway bridge supplying the Germans in the Colmar Pocket at Neuf-Brisach. The division's 7th Infantry Regiment pushed to the south, clearing the region between the Fecht and Ill Rivers. During the clearing operations of the 7th Infantry, Private First Class
The division's 7th Infantry Regiment pushed to the south, clearing the region between the Fecht and Ill Rivers. During the clearing operations of the 7th Infantry, Private First Class Jose F. Valdez
Private First Class Jose F. Valdez (January 3, 1925 – February 17, 1945) was a United States Army soldier who posthumously received the Medal of Honor — the United States' highest military decoration — for his actions near Rosenkranz, Franc ...
sacrificed himself at a small railway station near Rosenkranz () to cover the withdrawal of other members of his squad and was posthumously
Posthumous may refer to:
* Posthumous award - an award, prize or medal granted after the recipient's death
* Posthumous publication
Posthumous publication refers to material that is published after the author's death. This can be because the auth ...
awarded the Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of val ...
. The 30th Infantry Regiment moved southeast, crossed the Ill River north of the timber bridge at the Maison Rouge farm, and moved south early on 23 January, capturing the Maison Rouge bridge (). The 30th Infantry then moved south into the Riedwihr Woods (French: ''Bois de Riedwihr''), toward the towns of Riedwihr () and Holtzwihr ().
The bridge at Maison Rouge proved unable to support U.S. tanks (the bridge collapsed under the weight of a tank), and so the 30th Infantry had only minimal antitank capability ( bazookas and three 57 mm anti-tank guns) when they were counter-attacked late in the afternoon by German infantry and heavy tank destroyers of the 708th ''Volksgrenadier'' Division and 280th Assault Gun Battalion. Without cover and unable to dig foxholes because of the frozen terrain, the 30th Infantry was forced to withdraw, taking heavy casualties when the withdrawal assumed the character of a rout. The 30th Infantry reformed on the west bank of the Ill but was out of action for three days while it reorganized.
On 25 January, the U.S. 15th Infantry Regiment followed the course of the 30th Infantry and recaptured the bridge at Maison Rouge. A German counterattack, again supported by heavy tank destroyers, overran an exposed rifle company of the 15th Infantry around 08:00 but was unable to drive on the bridge because of U.S. defensive fire. Later in the day, U.S. engineers
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the li ...
erected a bridge over the Ill north of Maison Rouge, and a battalion of the 15th Infantry supported by tanks attacked to the south, finally securing the bridgehead. Over the next two days, the 15th Infantry pushed south toward the towns of Riedwihr and Holtzwihr, entering the Riedwihr Woods. German counterattacks were common, but the U.S. troops were able to parry them with support from tanks and tank destroyers.
On 26 January, on the south edge of the Riedwihr Woods, a German force of infantry and tanks emerged from Holtzwihr to counterattack Company B of the 15th Infantry. Believing the odds hopeless, Lieutenant Audie Murphy ordered his men to withdraw into the woods. Murphy climbed onto a burning M10 tank destroyer and engaged the Germans with the vehicle's heavy machine gun while calling for artillery fire on his own position. Unable to determine where Murphy was firing from, the German force first became confused and then was bombed by U.S. fighter-bombers
A fighter-bomber is a fighter aircraft that has been modified, or used primarily, as a light bomber or attack aircraft. It differs from bomber and attack aircraft primarily in its origins, as a fighter that has been adapted into other roles, wh ...
that had found a hole in the clouds over the battlefield. Dismayed, the German force retreated back to Holtzwihr, pursued by Lieutenant Murphy. He was subsequently awarded the Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of val ...
. Riedwihr fell to the 15th Infantry on 26 January, and Holtzwihr was taken by the 30th Infantry on 27 January. The 30th Infantry continued south, reaching the Colmar Canal on 29 January.Clarke and Smith, p. 547
The capture of Jebsheim () was necessary to protect the north flank of the 3rd Division's advance. With the 3rd Division advancing ahead of the French 1 March Infantry Division on the 3rd Division's north flank, General O'Daniel committed the U.S. 254th Infantry Regiment (part of the U.S. 63rd Infantry Division but attached to the U.S. 3rd Infantry Division for the duration of operations in the Colmar Pocket) to capture Jebsheim. On 26–27 January, troops of the German 136th Mountain Infantry Regiment defended Jebsheim against the advance of the 254th Infantry.Gaujac, p. 103 On 28–29 January, Jebsheim was taken by the 254th Infantry, French tanks of Combat Command 6 (French 5th Armored Division), and a battalion of the French 1st Parachute Regiment. Subsequently, the 254th Infantry continued to push east in the direction of the Rhône-Rhine Canal. Meanwhile, the 7th Infantry had moved forward, and along with the 15th Infantry Regiment and French 5th Armored Division tanks, were positioned to drive on the fortified town of Neuf-Brisach, about five miles (8 km) distant from the 3rd Division spearheads.
Push to the Rhine in the north
On the left flank and north of the U.S. 3rd Division, General Garbay's French 1 March Infantry Division (French: ''1re Division de Marche d'Infanterie'', formerly known as the 1st Free French Division) attacked to the east on 23 January with the Rhine River as their objective. Facing four battalions of the 708th Volksgrenadier Division (part of General Max Grimmeiss' LXIV Army Corps) supported by heavy tank destroyers and artillery, the 1st Division's 1st Brigade fought in conditions similar to that experienced by the Americans to the south. The Germans mounted a defense in depth, using positions in the villages and forests to command the open ground to their front and liberally planting land mines to slow and channelize the French advance. Two battalions of the 708th Volksgrenadier Division counterattacked the French bridgeheads over the Ill River around 17:00 on 23 January but were repulsed. Wishing to avoid dug-in German infantry and armor in the Elsenheim Woods (), General Garbay directed the 1st Brigade to concentrate their advance along the road from Illhaeusern () to Elsenheim. On 26–27 January, the 1st Brigade concentrated on opening this route and skirting the obstacle posed by the Elsenheim Woods, with a key attack into the woods made by the 3rd Battalion of the March Regiment of theFrench Foreign Legion
The French Foreign Legion (french: Légion étrangère) is a corps of the French Army which comprises several specialties: infantry, cavalry, engineers, airborne troops. It was created in 1831 to allow foreign nationals into the French Army ...
(''R.M.L.E.'') on 27 January. At heavy cost, the village of Grussenheim () was taken on 28 January by supporting tanks of the French 2nd Armored Division. Against crumbling German resistance, the French surged forward, taking Elsenheim and Marckolsheim () on 31 January and reaching the Rhine River the following day.Boussard, p. 175 In the course of its operations in the Colmar Pocket, the French 1st Division suffered casualties of 220 killed, 1,240 wounded, 96 missing, and 550 trench-foot cases.
Allied reinforcements
 Noting the difficult progress of all Allied units against German resistance in the Colmar Pocket, General de Lattre requested reinforcements from the U.S. 6th Army Group. Concurring, General Devers subordinated the Headquarters of the U.S. XXI Corps to the French First Army. General Milburn's XXI Corps took up position between the two French corps on 28 January and assumed command of the U.S. 3rd and 28th Infantry Divisions. Two additional U.S. divisions were also assigned to the XXI Corps - the U.S. 75th Infantry Division and the U.S. 12th Armored Division. Finally, the French 5th Armored Division, 1st Parachute Regiment, and 1st ''Choc'' (commando) Battalion were placed under XXI Corps' command. The XXI Corps was given the mission of capturing the city of Colmar and driving on the bridge at Breisach.
For their part, the German high command misread the Allied objectives, believing the Allied assault to be a general pressure along the front designed to induce collapse at any given point. Hitler had agreed to a partial withdrawal in the north (the Erstein salient) during the night of 28 January but forbade a general withdrawal over the Rhine.Clarke and Smith, p. 548 German outposts in the Vosges Mountains were pulled back, but the confusion of the withdrawal and the pressures of the battlefield resulted in many units becoming mixed with one another. While this did not affect the numbers available for combat, it did lower the defensive cohesion of the German units. On 29 January, ''Heeresgruppe Oberrhein'' was dissolved as a headquarters, and the units in the Colmar Pocket were again subordinated to ''Heeresgruppe G'' (Army Group G), under the command of '' SS- Obergruppenführer'' Paul Hausser.
Noting the difficult progress of all Allied units against German resistance in the Colmar Pocket, General de Lattre requested reinforcements from the U.S. 6th Army Group. Concurring, General Devers subordinated the Headquarters of the U.S. XXI Corps to the French First Army. General Milburn's XXI Corps took up position between the two French corps on 28 January and assumed command of the U.S. 3rd and 28th Infantry Divisions. Two additional U.S. divisions were also assigned to the XXI Corps - the U.S. 75th Infantry Division and the U.S. 12th Armored Division. Finally, the French 5th Armored Division, 1st Parachute Regiment, and 1st ''Choc'' (commando) Battalion were placed under XXI Corps' command. The XXI Corps was given the mission of capturing the city of Colmar and driving on the bridge at Breisach.
For their part, the German high command misread the Allied objectives, believing the Allied assault to be a general pressure along the front designed to induce collapse at any given point. Hitler had agreed to a partial withdrawal in the north (the Erstein salient) during the night of 28 January but forbade a general withdrawal over the Rhine.Clarke and Smith, p. 548 German outposts in the Vosges Mountains were pulled back, but the confusion of the withdrawal and the pressures of the battlefield resulted in many units becoming mixed with one another. While this did not affect the numbers available for combat, it did lower the defensive cohesion of the German units. On 29 January, ''Heeresgruppe Oberrhein'' was dissolved as a headquarters, and the units in the Colmar Pocket were again subordinated to ''Heeresgruppe G'' (Army Group G), under the command of '' SS- Obergruppenführer'' Paul Hausser.
Push to the Rhine in the center
The 3rd Division continued its south and east sidestepping maneuver. On the evening of 29 January, divisional artillery fired 16,000 105 mm and 155 mm rounds during a three-hour preparation for the assault of the 7th and 15th Infantry Regiments south across the Colmar Canal.Gaujac, p. 114 The infantry crossed between 21:00 and midnight. After the crossings were secured, engineers began the construction of threeBailey bridge
A Bailey bridge is a type of portable, pre-fabricated, truss bridge. It was developed in 1940–1941 by the British for military use during the Second World War and saw extensive use by British, Canadian and American military engineering units ...
s over the canal to enable armored vehicles to cross. The following day, the French armored combat commands CC4 and CC5 (both of the 5th Armored Division) crossed the canal, with CC4 supporting the U.S. 7th Infantry and CC5 supporting the U.S. 15th Infantry. Soon thereafter, the 15th Infantry and CC5 took Urschenheim in a brisk action, while the 7th Infantry was held up in front of Horbourg. The same day, the 254th Infantry attacked east toward Artzenheim
Artzenheim (; ; gsw-FR, Aarze) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
See also
* Communes of the Haut-Rhin department
The following is a list of the 366 communes of the French department of Haut-Rhin. ...
with support of the French armored combat command CC6, but the Germans employed artillery support and dug-in Jagdpanther tank destroyers to parry the thrust, destroying six French tanks and four halftracks. Artzenheim was taken by the French II Corps on 1 February.
Fighting in the zone of the 3rd Division, the French 1st Parachute Regiment attacked and seized Widensolen early on 31 January. By 17:00, patrols of the U.S. 3rd Division had reached the Rhône-Rhine Canal,Gaujac, p. 119 some five miles (8 km) southeast from the division's crossing points over the Colmar Canal. On the same day, French CC6 was relieved from attachment to the U.S. 3rd Division, having taken severe losses with only 13 operational tanks in its tank battalion and 30 effectives in its French Foreign Legion rifle company. In its stead arrived a combat command of the French 2nd Armored Division. On 1 February, the 15th and 30th Infantry Regiments moved south along the Rhône-Rhine Canal reaching the area just north of Neuf-Brisach. On 2–3 February, the 7th Infantry drove south along the same canal passing through Artzenheim and taking Biesheim
Biesheim (; gsw-FR, Biese) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
Archaeology
Remains of a Mithraeum have been unearthed in Biesheim in 1977.
See also
* Communes of the Haut-Rhin department
The fol ...
after a bitter day-long battle. Near Biesheim, Technician 5 Forrest E. Peden of 3rd Division artillery dashed through intense German fire on 3 February to summon help for an ambushed infantry unit. Returning on a light tank, Peden was killed when the tank was hit and destroyed. For his heroism, Peden was posthumously awarded the Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of val ...
.
After a day spent consolidating its positions, the 3rd Division moved south again on 5 February, taking Vogelgrun the following day. The fortified town of Neuf-Brisach was swiftly entered and taken on 6 February, by the 30th Infantry, with the help of two French children and another civilian, who showed the Americans undefended passages into the town.Williams, p. 395 The Germans, having evacuated what remained of their men and equipment, had destroyed the bridge over the Rhine at Breisach
Breisach (formerly Altbreisach; Low Alemannic: ''Alt-Brisach'') is a town with approximately 16,500 inhabitants, situated along the Rhine in the Rhine Valley, in the district Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, about halfway ...
. The taking of Neuf-Brisach marked the end of operations in the Colmar Pocket for the U.S. 3rd Infantry Division.
Clearing the pocket between Colmar and the Rhine
The 75th Division entered the front lines on 31 January, between the U.S. 3rd and 28th Infantry Divisions. Attacking on 1 February, the 289th Infantry Regiment cleared Horbourg and the 290th Infantry Regiment advanced on Andolsheim () occupying the town at 14:00 on 2 February. The same day, the 75th Division made diversionary attacks to cover the Allied drive on the city of Colmar, adjacent to the division's western sector. On 3 February, the 75th Division cleared the Forêt Domaniale () and consolidated its gains the following day. Moving again on 5 February, the division overran Appenwihr (), Hettenschlag (), and WolfgantzenWilliams, p. 393 (). On 6 February, the 75th Division reached the Rhône-Rhine Canal south of Neuf-Brisach.Gaujac, p. 127 This action brought a close to U.S. 75th Infantry Division operations in the Colmar Pocket.Liberation of Colmar
 Having been on the defense to this point in the battle, General Norman Cota's 28th Division was teamed with the French armored combat command CC4 and told to take the city of Colmar. Leading with the U.S. 109th Infantry Regiment on 2 February, the infantry crossed an anti-tank ditch north of the city, while the French armor located a crossing point over the obstacle. This accomplished, the French armor plunged into Colmar reaching the ''Place Rapp'' (Rapp Square) at 11:30. On 2–3 February, the 109th Infantry, the French CC4, 1st Parachute Regiment and commandos cleared the city of Germans. In a symbolic act, the French 152nd Infantry Regiment re-entered Colmar, its pre-war garrison. Pushing south on 3 February the 112th Infantry entered Turckheim () and cleared Ingersheim () to the west of Colmar.Gaujac, p. 126 Other units of the 28th Division joined the French in blocking German exit routes from the Vosges Mountains. On 6 February, the 28th Division moved eastwards to the Rhône-Rhine Canal on the south flank of the U.S. XXI Corps ending 28th Division participation in the battle.
Having been on the defense to this point in the battle, General Norman Cota's 28th Division was teamed with the French armored combat command CC4 and told to take the city of Colmar. Leading with the U.S. 109th Infantry Regiment on 2 February, the infantry crossed an anti-tank ditch north of the city, while the French armor located a crossing point over the obstacle. This accomplished, the French armor plunged into Colmar reaching the ''Place Rapp'' (Rapp Square) at 11:30. On 2–3 February, the 109th Infantry, the French CC4, 1st Parachute Regiment and commandos cleared the city of Germans. In a symbolic act, the French 152nd Infantry Regiment re-entered Colmar, its pre-war garrison. Pushing south on 3 February the 112th Infantry entered Turckheim () and cleared Ingersheim () to the west of Colmar.Gaujac, p. 126 Other units of the 28th Division joined the French in blocking German exit routes from the Vosges Mountains. On 6 February, the 28th Division moved eastwards to the Rhône-Rhine Canal on the south flank of the U.S. XXI Corps ending 28th Division participation in the battle.
Colmar Pocket split
 On 3 February, the 12th Armored Division moved south through 28th Division lines with the objective of linking up with the French I Corps and splitting the Colmar Pocket. Combat Command B (CCB) seized a bridgehead near Sundhoffen () and CCR advanced on the road between Colmar and Rouffach (). The following day, CCA captured Hattstatt () on the Colmar-Rouffach Road, but CCR found its way blocked by German defenses. On 5 February, CCA entered Rouffach and made contact with the 4th Moroccan Mountain Division of the French I Corps, some 17 days after French I Corps launched its assault. The same day, CCR entered the village of Herrlisheim-près-Colmar (), and so the 12th Armored Division attacked, for a second time, a town named Herrlisheim in Alsace (the battles of the 12th Armored Division in mid-January 1945, at Herrlisheim north of Strasbourg saw several battalions of the division manhandled by German troops in the Gambsheim bridgehead.) Thereafter, during the battle, the 12th Armored Division screened German exit routes from the Vosges Mountains and supported the 28th Division by fire.
On 3 February, the 12th Armored Division moved south through 28th Division lines with the objective of linking up with the French I Corps and splitting the Colmar Pocket. Combat Command B (CCB) seized a bridgehead near Sundhoffen () and CCR advanced on the road between Colmar and Rouffach (). The following day, CCA captured Hattstatt () on the Colmar-Rouffach Road, but CCR found its way blocked by German defenses. On 5 February, CCA entered Rouffach and made contact with the 4th Moroccan Mountain Division of the French I Corps, some 17 days after French I Corps launched its assault. The same day, CCR entered the village of Herrlisheim-près-Colmar (), and so the 12th Armored Division attacked, for a second time, a town named Herrlisheim in Alsace (the battles of the 12th Armored Division in mid-January 1945, at Herrlisheim north of Strasbourg saw several battalions of the division manhandled by German troops in the Gambsheim bridgehead.) Thereafter, during the battle, the 12th Armored Division screened German exit routes from the Vosges Mountains and supported the 28th Division by fire.
Collapse of the Colmar Pocket
At the start of February, the French I Corps was still clearing scattered German resistance south of the Thur River between Cernay and Ensisheim, both of which were still under German control. The clearing of this area was not completed until 3 February. On 4 February, I Corps assaulted north across the Thur River and, encountering only limited German resistance, the 4th Moroccan Mountain Division was able to push to the southern outskirts of Rouffach. Cernay, abandoned by the Germans, was occupied the same day. The following day, the 4th Moroccan Division linked up with the U.S. 12th Armored Division in Rouffach, and the 9th Colonial Infantry Division attacked Ensisheim, the original corps objective. Hirtzfelden was taken by the 2nd Moroccan Infantry Division on 6 February and the 9th Colonial Division completed the capture of Ensisheim and drove east into the Harth Woods. On 7 February, both the 9th Colonial Division and 1st Armored Division reached the Rhône-Rhine Canal east of Ensisheim. The '' Spahis'' cavalry brigade and the 151st Infantry Regiment cleared the Harth Woods on 8 February while the 1st Armored Division advanced south toward the German bridgehead at Chalampé in addition to linking up with elements of the French 2nd Armored Division at Fessenheim the same day. During this period, the shrinking German presence on the west side of the Rhine was subjected to heavy artillery fire and airstrikes by U.S. and French aircraft. Finally, on 9 February I Corps eliminated the German rearguard at Chalampé, and with no major German forces left on the west bank of the Rhine in the region of Colmar, the Germans blew up the bridge over the Rhine at Chalampé. This signaled the end of Allied operations in the Colmar Pocket and the end of any significant German military presence in Alsace.Aftermath


 In compliance with General Eisenhower's direction, the Colmar Pocket was eliminated, and the U.S. 6th Army Group stood on the Rhine, from the Swiss border to a region well north of Strasbourg. The German 19th Army, although not completely destroyed, lost the bulk of its experienced combat troops (only the 708th Volksgrenadier Division escaped somewhat intact)Weigley, p. 599 and was forced to reform in
In compliance with General Eisenhower's direction, the Colmar Pocket was eliminated, and the U.S. 6th Army Group stood on the Rhine, from the Swiss border to a region well north of Strasbourg. The German 19th Army, although not completely destroyed, lost the bulk of its experienced combat troops (only the 708th Volksgrenadier Division escaped somewhat intact)Weigley, p. 599 and was forced to reform in Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
, using large infusions of inexperienced ''Volkssturm
The (; "people's storm") was a levée en masse national militia established by Nazi Germany during the last months of World War II. It was not set up by the German Army, the ground component of the combined German ''Wehrmacht'' armed forces, ...
'' to replace its grievous losses on the plains of Alsace. The Germans left behind 55 armored vehicles and 66 artillery pieces. The elimination of the Colmar Pocket allowed the 6th Army Group to concentrate on Operation Undertone, its assault to penetrate the Siegfried Line
The Siegfried Line, known in German as the ''Westwall'', was a German defensive line built during the 1930s (started 1936) opposite the French Maginot Line. It stretched more than ; from Kleve on the border with the Netherlands, along the we ...
and invade Germany, undertaken in March 1945.
For the fourth time in 75 years, the province of Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
had changed hands between France and Germany.
After the battle, the French granted the U.S. 3rd Infantry Division the right to wear the Croix de Guerre, and the president awarded the division, as an entity, the Distinguished Unit Citation
The Presidential Unit Citation (PUC), originally called the Distinguished Unit Citation, is awarded to units of the uniformed services of the United States, and those of allied countries, for extraordinary heroism in action against an armed enem ...
. The U.S. 109th Infantry Regiment (28th Division) was also granted the right to wear the Croix de Guerre.BCMR, p 4
Today, numerous streets in Alsace are named after Allied commanders and units that fought in the battle, and there are French and U.S. military cemeteries in the area.
See also
*Allied advance from Paris to the Rhine
The Allied advance from Paris to the Rhine, also known as the Siegfried Line campaign, was a phase in the Western European campaign of World War II.
This phase spans from the end of the Battle of Normandy, or Operation Overlord, (25 August 19 ...
* Alsace campaign
* Battle of the Bulge
The Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Offensive, was the last major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II. The battle lasted from 16 December 1944 to 28 January 1945, towards the end of the war in ...
* Liberation of France
* Operation Nordwind
Notes
;Footnotes ;CitationsReferences
* * * * * * * {{Liberation of France History of Alsace Battles involving France Battles involving the United States Military history of France during World War II Western European Campaign (1944–1945) Lists of coordinates Military operations of World War II involving Germany Battles of World War II involving France Battles of World War II involving the United States Encirclements in World War II