Coleopter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
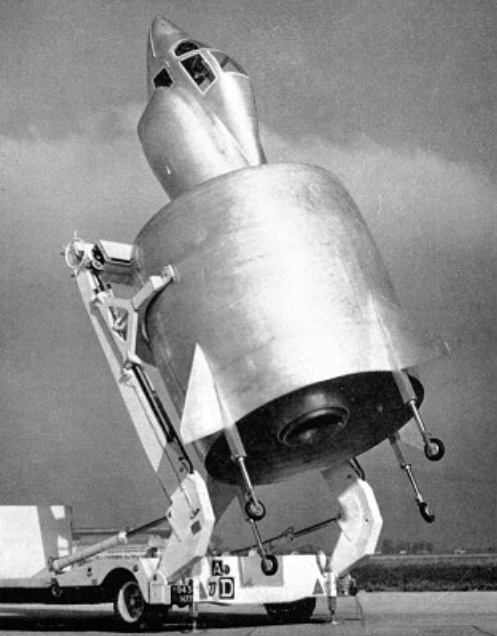
 A coleopter is a type of
A coleopter is a type of
A Coleopter patent
{{Aircraft types (by method of thrust and lift) Aircraft configurations Rotorcraft Tailsitter aircraft

 A coleopter is a type of
A coleopter is a type of VTOL
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft is one that can take off and land vertically without relying on a runway. This classification can include a variety of types of aircraft including helicopters as well as thrust-vectoring fixed-wi ...
aircraft design that uses a ducted fan
In aeronautics, a ducted fan is a thrust-generating mechanical fan or propeller mounted within a cylindrical duct or shroud. Other terms include ducted propeller or shrouded propeller. When used in vertical takeoff and landing
(VTOL) applicati ...
as the primary fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft t ...
of the entire aircraft. Generally they appear to be a large barrel-like extension at the rear, with a small cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, usually near the front of an aircraft or spacecraft, from which a pilot controls the aircraft.
The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the controls that e ...
area suspended above it. Coleopters are generally designed as tail-sitter
A tail-sitter, or tailsitter, is a type of VTOL aircraft that takes off and lands on its tail, then tilts horizontally for forward flight.
Originating in the 1920s with the inventor Nikola Tesla, the first aircraft to adopt a tail-sitter configur ...
s. The term is an anglicisation
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influe ...
of the French '' coléoptère'' "beetle" after the first actual implementation of this design, the SNECMA Coléoptère
The SNECMA C.450 Coléoptère (meaning "beetle" in French, descended from Greek for "sheathed wing") was a vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft that was designed by the French company SNECMA and manufactured by Nord Aviation. While w ...
of the mid-1950s.
The first design of an aircraft clearly using the coleopter concept was developed during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. From 1944 on, the Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
was suffering from almost continual daytime attacks on its airfields and was finding it almost impossible to conduct large-scale operations. Their preferred solution was to introduce some sort of VTOL interceptor that could be launched from any open location, and there were many proposals for such a system. Heinkel
Heinkel Flugzeugwerke () was a German aircraft manufacturing company founded by and named after Ernst Heinkel. It is noted for producing bomber aircraft for the Luftwaffe in World War II and for important contributions to high-speed flight, with ...
conducted a series of design studies as part of their Heinkel Wespe
The Heinkel Wespe ( en, Wasp) was a project study by the German company Heinkel for a tail-sitting, vertical take off and landing-interceptor aircraft. The aircraft did not have conventional wings, but instead featured a large rotor. Completed in ...
and Heinkel Lerche
The Heinkel Lerche ( en, Lark) was the name of a set of project studies made by German aircraft designer Heinkel in 1944 and 1945 for a revolutionary VTOL fighter and ground-attack aircraft.
The ''Lerche'' was an early coleopter design. It would ...
programs. The Wespe intended to use a Benz 2,000 hp turboprop engine, but these were not forthcoming and the Lerche used two Daimler-Benz DB 605
The Daimler-Benz DB 605 is a German aircraft engine built during World War II. Developed from the DB 601, the DB 605 was used from 1942 to 1945 in the Messerschmitt Bf 109 fighter, and the Bf 110 and Me 210C heavy fighters.
The DB 610, a pa ...
piston engines instead. Nothing ever came of either design.
In the immediate post-war era, most VTOL research involved helicopters. However, as the limitations of the simple rotary wing became clear, teams started looking for other solutions and many turned to using jet engines directly for vertical thrust. SNECMA (now Safran Aircraft Engines
Safran Aircraft Engines, previously Snecma (''Société nationale d'études et de construction de moteurs d'aviation'') or Snecma Moteurs, is a French aerospace engine manufacturer headquartered in Courcouronnes and a subsidiary of Safran. It ...
) developed a series of such systems as part of the SNECMA Atar Volant
The SNECMA Atar Volant or C.400 P1 was a French turbojet engine produced by SNECMA as part of their "Atar" series.
Encased in a basic fairing which could hold fuel and remote-control equipment, the unit weighed 5,600 pounds (2550 kg ...
series during the 1950s. To further improve the design, SNECMA had Nord Aviation
Nord-Aviation ( en, Northern Aviation) was a state-owned French aircraft manufacturer. The bulk of its facilities were based on the site of Bourges airport, in the département of Cher, in central France.
On 1 October 1954, Nord Aviation was cr ...
build an annular wing and adapted it to the last of the Volant series to produce the SNECMA Coléoptère
The SNECMA C.450 Coléoptère (meaning "beetle" in French, descended from Greek for "sheathed wing") was a vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft that was designed by the French company SNECMA and manufactured by Nord Aviation. While w ...
. The Coléoptère first flew on 6 May 1959, but crashed on 25 July and no replacement was built. Even in this limited testing period, the design showed several serious problems related to the high angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed syst ...
of the engine, which made control tricky.
In the US, Hiller Aircraft
Hiller Aircraft Company was founded in 1942 as Hiller Industries by Stanley Hiller to develop helicopters.
History
Stanley Hiller, then seventeen, established the first helicopter factory on the West Coast of the United States, located in Berkele ...
had been working on a number of ducted fan flying platforms originally designed by Charles Zimmerman. After some early successes, the Army demanded a series of changes that continued to increase the size and weight of the platform, which introduced new stability problems. These generally required more size and power to correct, and no satisfactory design came from these efforts. Instead, Hiller approached the Navy with the idea of building a full coleopter design. This emerged as the Hiller VXT-8 which was significantly similar to the SNECMA design, although it used a propeller instead of a jet engine. However, the introduction of turbine-powered helicopters like the Bell UH-1 Iroquois
The Bell UH-1 Iroquois (nicknamed "Huey") is a utility military helicopter designed and produced by the American aerospace company Bell Helicopter. It is the first member of the prolific Huey family, as well as the first turbine-powered helico ...
so significantly improved their performance over piston-powered designs that the Navy lost interest in the VXT-8 in spite of even better estimated performance. Only a mock-up was completed.
Convair
Convair, previously Consolidated Vultee, was an American aircraft manufacturing company that later expanded into rockets and spacecraft. The company was formed in 1943 by the merger of Consolidated Aircraft and Vultee Aircraft. In 1953, i ...
selected the coleopter layout for their Model 49 proposal, entered into the Advanced Aerial Fire Support System
The Lockheed AH-56 Cheyenne was an attack helicopter developed by Lockheed for the United States Army. It rose from the Army's Advanced Aerial Fire Support System (AAFSS) program to field the service's first dedicated attack helicopter. Lock ...
(AAFSS). AAFSS asked for a new high-speed helicopter design for the attack and escort roles, and gathered an impressive array of gyrodyne
A gyrodyne is a type of VTOL aircraft with a helicopter rotor-like system that is driven by its engine for takeoff and landing only, and includes one or more conventional propeller or jet engines to provide forward thrust during cruising fli ...
s, dual-rotor designs and similar advances on conventional designs, but nothing was as unconventional as the Model 49. The Army "went conventional" however, and selected the Lockheed AH-56 Cheyenne
The Lockheed AH-56 Cheyenne was an attack helicopter developed by Lockheed for the United States Army. It rose from the Army's Advanced Aerial Fire Support System (AAFSS) program to field the service's first dedicated attack helicopter. Lock ...
and Sikorsky S-66
The Sikorsky S-67 Blackhawk was a private-venture, prototype attack helicopter built in 1970 with Sikorsky Aircraft research and development (R&D) funds. A tandem, two-seat aircraft designed around the dynamic drive and rotor systems of the Siko ...
for further development.
See also
* Focke-Wulf TriebflügelReferences
* Jay Spenser, ''Vertical Challenge: The Hiller Aircraft Story'', University of Washington Press, 1998 * Tony Landis and Dennis Jenkins, ''Lockheed AH-56A Cheyenne'', Specialty Press Publishers and Wholesalers, 2000External links
A Coleopter patent
{{Aircraft types (by method of thrust and lift) Aircraft configurations Rotorcraft Tailsitter aircraft