Cloud chamber on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A cloud chamber, also known as a Wilson cloud chamber, is a particle detector used for visualizing the passage of  A cloud chamber consists of a sealed environment containing a
A cloud chamber consists of a sealed environment containing a
 Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (1869–1959), a Scottish
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (1869–1959), a Scottish
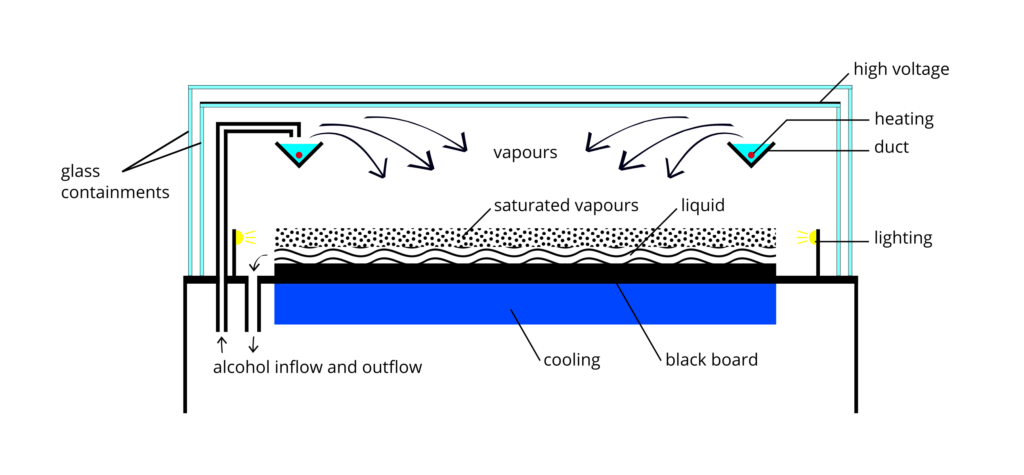 Diffusion-type cloud chambers will be discussed here. A simple cloud chamber consists of the sealed environment, a warm top plate and a cold bottom plate (See Fig. 3). It requires a source of liquid alcohol at the warm side of the chamber where the liquid evaporates, forming a vapor that cools as it falls through the gas and condenses on the cold bottom plate. Some sort of ionizing radiation is needed.
Diffusion-type cloud chambers will be discussed here. A simple cloud chamber consists of the sealed environment, a warm top plate and a cold bottom plate (See Fig. 3). It requires a source of liquid alcohol at the warm side of the chamber where the liquid evaporates, forming a vapor that cools as it falls through the gas and condenses on the cold bottom plate. Some sort of ionizing radiation is needed.
"Wilson Cloud Chamber"
Updated 05/13/2016. Fig. 5 shows an example of an alpha particle from a Pb-210 pin-type source undergoing
File:Particle Tracks in AWAN Expansion Cloud Chamber.jpg, Particle tracks from radioisotopes in an expansion cloud chamber. (Left) Alpha tracks from Am-241 source, with one beta track possibly from its daughter radionuclide, Pa-233. (Right) Beta tracks from Sr-90/Y-90 source.
File:Home Made Cloud Chamber.webm, A Home Made Cloud Chamber.
File:Nuclear particle in a diffusion cloud chamber.png, Image taken in the Pic du Midi at 2877 m in a Phywe PJ45 cloud chamber (size of surface is 45 x 45 cm). This rare picture shows in a single shot the 4 particles that are detectable in a cloud chamber : proton, electron, muon (probably) and alpha
File:Cloud chamber bionerd.jpg, Cloud chamber with visible tracks from
ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
.
 A cloud chamber consists of a sealed environment containing a
A cloud chamber consists of a sealed environment containing a supersaturated
In physical chemistry, supersaturation occurs with a solution when the concentration of a solute exceeds the concentration specified by the value of solubility at equilibrium. Most commonly the term is applied to a solution of a solid in a li ...
vapour of water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
or alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
. An energetic charged particle (for example, an alpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , whi ...
or beta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, � ...
) interacts with the gaseous mixture by knocking electrons
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
off gas molecules via electrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest ( static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for ...
forces during collisions, resulting in a trail of ionized gas particles. The resulting ions act as condensation centers around which a mist-like trail of small droplets form if the gas mixture is at the point of condensation. These droplets are visible as a "cloud" track that persists for several seconds while the droplets fall through the vapor. These tracks have characteristic shapes. For example, an alpha particle track is thick and straight, while a beta particle track is wispy and shows more evidence of deflections by collisions.
Cloud chambers were invented in the early 1900s by the Scottish physicist Charles Thomson Rees Wilson. They played a prominent role in experimental particle physics from the 1920s to the 1950s, until the advent of the bubble chamber. In particular, the discoveries of the positron
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. It has an electric charge of +1 '' e'', a spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same mass as an electron. When a positron collide ...
in 1932 (see Fig. 1) and the muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of , but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As w ...
in 1936, both by Carl Anderson (awarded a Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
in 1936), used cloud chambers. Discovery of the kaon by George Rochester and Clifford Charles Butler in 1947, also was made using a cloud chamber as the detector. In each of these cases, cosmic rays
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our ...
were the source of ionizing radiation. Yet they were also used with artificial sources of particles, for example in radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeu ...
applications as part of the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
.
Invention
 Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (1869–1959), a Scottish
Charles Thomson Rees Wilson (1869–1959), a Scottish physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
, is credited with inventing the cloud chamber. Inspired by sightings of the Brocken spectre
A Brocken spectre (British English; American spelling Brocken specter; german: Brockengespenst), also called Brocken bow, mountain spectre, or spectre of the Brocken is the magnified (and apparently enormous) shadow of an observer cast in mid ai ...
while working on the summit of Ben Nevis in 1894, he began to develop expansion chambers for studying cloud formation and optical phenomena in moist air. Very rapidly he discovered that ions could act as centers for water droplet formation in such chambers. He pursued the application of this discovery and perfected the first cloud chamber in 1911. In Wilson's original chamber (See Fig. 2) the air inside the sealed device was saturated with water vapor, then a diaphragm was used to expand the air inside the chamber ( adiabatic expansion), cooling the air and starting to condense water vapor. Hence the name expansion cloud chamber is used. When an ionizing particle passes through the chamber, water vapor condenses on the resulting ions and the trail of the particle is visible in the vapor cloud. Wilson received half the Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
in 1927 for his work on the cloud chamber (the same year as Arthur Compton received half the prize for the Compton Effect
Compton scattering, discovered by Arthur Holly Compton, is the scattering of a high frequency photon after an interaction with a charged particle, usually an electron. If it results in a decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) of the photon ...
). This kind of chamber is also called a pulsed chamber because the conditions for operation are not continuously maintained. Further developments were made by Patrick Blackett
Patrick Maynard Stuart Blackett, Baron Blackett (18 November 1897 – 13 July 1974) was a British experimental physicist known for his work on cloud chambers, cosmic rays, and paleomagnetism, winning the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1948. ...
who utilised a stiff spring to expand and compress the chamber very rapidly, making the chamber sensitive to particles several times a second. A cine film was used to record the images.
The diffusion cloud chamber was developed in 1936 by Alexander Langsdorf. This chamber differs from the expansion cloud chamber in that it is continuously sensitized to radiation, and in that the bottom must be cooled to a rather low temperature, generally colder than . Instead of water vapor, alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
is used because of its lower freezing point. Cloud chambers cooled by dry ice or Peltier effect thermoelectric cooling are common demonstration and hobbyist devices; the alcohol used in them is commonly isopropyl alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group ( chemical formula ) it is the s ...
or methylated spirit.
Structure and operation
 Diffusion-type cloud chambers will be discussed here. A simple cloud chamber consists of the sealed environment, a warm top plate and a cold bottom plate (See Fig. 3). It requires a source of liquid alcohol at the warm side of the chamber where the liquid evaporates, forming a vapor that cools as it falls through the gas and condenses on the cold bottom plate. Some sort of ionizing radiation is needed.
Diffusion-type cloud chambers will be discussed here. A simple cloud chamber consists of the sealed environment, a warm top plate and a cold bottom plate (See Fig. 3). It requires a source of liquid alcohol at the warm side of the chamber where the liquid evaporates, forming a vapor that cools as it falls through the gas and condenses on the cold bottom plate. Some sort of ionizing radiation is needed.
Isopropanol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group (chemical formula ) it is the sim ...
, methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is ...
, or other alcohol vapor saturates the chamber. The alcohol falls as it cools down and the cold condenser provides a steep temperature gradient. The result is a supersaturated environment. As energetic charged particles pass through the gas they leave ionization trails. The alcohol vapor condenses around gaseous ion trails left behind by the ionizing particles. This occurs because alcohol and water molecules are polar, resulting in a net attractive force toward a nearby free charge (See Fig. 4). The result is a misty cloud-like formation, seen by the presence of droplets falling down to the condenser. When the tracks are emitted from a source, their point of origin can easily be determined.Zani, G. Dept. of Physics, Brown University, RI USA"Wilson Cloud Chamber"
Updated 05/13/2016. Fig. 5 shows an example of an alpha particle from a Pb-210 pin-type source undergoing
Rutherford scattering
In particle physics, Rutherford scattering is the elastic scattering of charged particles by the Coulomb interaction. It is a physical phenomenon explained by Ernest Rutherford in 1911 that led to the development of the planetary Rutherford model ...
.
Just above the cold condenser plate there is a volume of the chamber which is sensitive to ionization tracks. The ion trail left by the radioactive particles provides an optimal trigger for condensation and cloud formation. This sensitive volume is increased in height by employing a steep temperature gradient, and stable conditions. A strong electric field is often used to draw cloud tracks down to the sensitive region of the chamber and increase the sensitivity of the chamber. The electric field can also serve to prevent large amounts of background "rain" from obscuring the sensitive region of the chamber, caused by condensation forming above the sensitive volume of the chamber, thereby obscuring tracks by constant precipitation. A black background makes it easier to observe cloud tracks, and typically a tangential light source is needed to illuminate the white droplets against the black background. Often the tracks are not apparent until a shallow pool of alcohol is formed at the condenser plate.
If a magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
is applied across the cloud chamber, positively and negatively charged particles will curve in opposite directions, according to the Lorentz force law
Lorentz is a name derived from the Roman surname, Laurentius, which means "from Laurentum". It is the German form of Laurence. Notable people with the name include:
Given name
* Lorentz Aspen (born 1978), Norwegian heavy metal pianist and keyboa ...
; strong-enough fields are difficult to achieve, however, with small hobbyist setups.
Other particle detectors
The bubble chamber was invented byDonald A. Glaser
Donald Arthur Glaser (September 21, 1926 – February 28, 2013) was an American physicist, neurobiologist, and the winner of the 1960 Nobel Prize in Physics for his invention of the bubble chamber used in subatomic particle physics.
Educati ...
of the United States in 1952, and for this, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1960. The bubble chamber similarly reveals the tracks of subatomic particles, but as trails of bubbles in a superheated liquid, usually liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully l ...
. Bubble chambers can be made physically larger than cloud chambers, and since they are filled with much-denser liquid material, they reveal the tracks of much more energetic particles. These factors rapidly made the bubble chamber the predominant particle detector for a number of decades, so that cloud chambers were effectively superseded in fundamental research by the start of the 1960s.
A spark chamber {{short description, Charged particle detector
A spark chamber is a particle detector: a device used in particle physics for detecting electrically charged particles. They were most widely used as research tools from the 1930s to the 1960s and hav ...
is an electrical device that uses a grid of uninsulated electric wires in a chamber, with high voltages applied between the wires. Energetic charged particles cause ionization of the gas along the path of the particle in the same way as in the Wilson cloud chamber, but in this case the ambient electric fields are high enough to precipitate full-scale gas breakdown in the form of sparks at the position of the initial ionization. The presence and location of these sparks is then registered electrically, and the information is stored for later analysis, such as by a digital computer.
Similar condensation effects can be observed as Wilson cloud
A transient condensation cloud, also called a Wilson cloud, is observable surrounding large explosions in humid air.
When a nuclear weapon or a large amount of a conventional explosive is detonated in sufficiently humid air, the "negative phas ...
s, also called condensation clouds, at large explosions in humid air and other Prandtl–Glauert singularity effects.
See also
* Nuclear emulsion – also used to record and investigate fast charged particles * Bubble chamber *Spark chamber {{short description, Charged particle detector
A spark chamber is a particle detector: a device used in particle physics for detecting electrically charged particles. They were most widely used as research tools from the 1930s to the 1960s and hav ...
* Gilbert U-238 Atomic Energy Laboratory science kit for children (1950–1951)
* Contrail
Notes
References
*Gallery
ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
(short, thick: α-particles; long, thin: β-particles). See also Animated Version
File:Cloud chamber.ogv, Video of a Cloud chamber in action
File:Cloudylabs cloud chamber.jpg, Example of watercooled thermoelectric cloud chamber
File:Radon decay in a cloud chamber.jpg, Cloud chamber with cloud tracks created by particles of ionising radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can t ...
(Image taken after injection of radon
Radon is a chemical element with the symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colourless, odourless, tasteless noble gas. It occurs naturally in minute quantities as an intermediate step in the normal radioactive decay chains th ...
)
File:Radium hands in a cloud chamber (alpha particles).png, Alpha particles from a Radium source in a cloud chamber
File:Radon220 decay in a cloud chamber.jpg, Radon-220 decay in a cloud chamber
File:Alpha particle and electrons from a thorium rod in a cloud chamber.jpg, Alpha particles and electrons (deflected by a magnetic field) from a thorium rod in a cloud chamber
File:Radioactivity of a Thorite mineral seen in a cloud chamber.jpg, Radioactivity of a Thorite mineral seen in a cloud chamber
File:Cloud Chamber with Ion Scrubber.jpg, Diffusion Cloud Chamber with 4.6kV Ion Scrubber
File:Homebrewed Diffusion Cloud Chamber.jpg, Homebrewed TEC / Water-cooled (5-Stage) Diffusion Cloud Chamber
File:Wilson chamber.webm, Video of a Wilson chamber
External links
* , Peter Wothers,Royal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
, December 2012]
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cloud Chamber
Particle detectors
Radioactivity
Scottish inventions
Ionising radiation detectors
Articles containing video clips