Clipping (audio) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Clipping is a form of
Clipping is a form of
 In
In
 Clipping is a form of
Clipping is a form of waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its graph as a function of time, independent of its time and magnitude scales and of any displacement in time.David Crecraft, David Gorham, ''Electro ...
distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signa ...
that occurs when an amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost t ...
is overdriven and attempts to deliver an output voltage or current beyond its maximum capability. Driving an amplifier into clipping may cause it to output power in excess of its power rating.
In the frequency domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a s ...
, clipping produces strong harmonics in the high-frequency range (as the clipped waveform comes closer to a squarewave
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same duration at minimum and maximum. In an ideal square wave, the transitions b ...
). The extra high-frequency weighting of the signal could make tweeter
A tweeter or treble speaker is a special type of loudspeaker (usually dome, inverse dome or horn-type) that is designed to produce high audio frequencies, typically deliver high frequencies up to 100 kHz. The name is derived from the high ...
damage more likely than if the signal was not clipped.
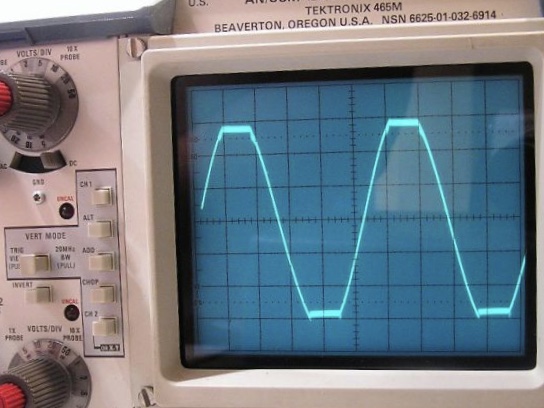
In some cases, the distortion associated with clipping is unwanted, and is visible on an oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (informally a scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying electrical voltages as a two-dimensional plot of one or more signals as a function of time. The main purposes are to display repetiti ...
even if it is inaudible. However, clipping is often used in music for artistic effect, especially in heavier genres.
Overview
When an amplifier is pushed to create a signal with more power than its power supply can produce, it will amplify the signal only up to its maximum capacity, at which point the signal can be amplified no further. As the signal simply "cuts" or "clips" at the maximum capacity of the amplifier, the signal is said to be "clipping". The extra signal which is beyond the capability of the amplifier is simply cut off, resulting in asine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in ...
becoming a distorted square-wave-type waveform.
Amplifiers have voltage, current and thermal limits. Clipping may occur due to limitations in the power supply or the output stage. Some amplifiers are able to deliver peak power without clipping for short durations before energy stored in the power supply is depleted or the amplifier begins to overheat.
Sound
Manyelectric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar (however combinations of the two - a semi-acoustic guitar and an electric acoustic gu ...
players
Players may refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''Players'' (1979 film), a film starring Ali MacGraw
* ''Players'' (2012 film), a Bollywood film
* ''Players'' (Dicks novel), a novel by Terrance Dicks, based on the television series ''Doc ...
intentionally overdrive their amplifiers (or insert a "fuzz box") to cause clipping in order to get a desired sound (see guitar distortion).
Some audiophiles believe that the clipping behavior of vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s with little or no negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by othe ...
is superior to that of transistors
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
, in that vacuum tubes clip more gradually than transistors (i.e. ''soft'' clipping, and mostly even harmonics), resulting in harmonic distortion that is generally less objectionable.
Effects
In a transistorized amplifier with hard clipping, the gain of the transistor will be reducing (leading to nonlinear distortion) as the output current increases and the voltage across the transistor reduces close to the saturation voltage (for bipolar transistors), and so "full power" for the purposes of measuring distortion in amplifiers is usually taken as a few percent ''below'' clipping. Because the clipped waveform has more area underneath it than the smaller unclipped waveform, the amplifier produces more power than its rated (sine wave
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in ...
) output when it is clipping. This extra power can damage the loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A ''speaker system'', also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or ...
. It may cause damage to the amplifier's power supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As ...
or simply blow a fuse
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to protect ...
.
The additional high frequency energy in the harmonics generated by an amplifier operating in clipping can damage the tweeter
A tweeter or treble speaker is a special type of loudspeaker (usually dome, inverse dome or horn-type) that is designed to produce high audio frequencies, typically deliver high frequencies up to 100 kHz. The name is derived from the high ...
in a connected loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A ''speaker system'', also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or ...
via overheating.
Clipping can occur within a system as processing (e.g. an all-pass filter
An all-pass filter is a signal processing filter that passes all frequencies equally in gain, but changes the phase relationship among various frequencies. Most types of filter reduce the amplitude (i.e. the magnitude) of the signal applied to i ...
) can change the phase relationship between spectral components of a signal in such a way as to create excessive peak outputs. The excessive peaks may become clipped even though the system can play any simple sine wave signals of the same level without clipping.
Electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar (however combinations of the two - a semi-acoustic guitar and an electric acoustic gu ...
ists frequently and intentionally overdrive their guitar amplifier
A guitar amplifier (or amp) is an electronic device or system that strengthens the electrical signal from a pickup on an electric guitar, bass guitar, or acoustic guitar so that it can produce sound through one or more loudspeakers, which ar ...
s to cause clipping and other distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signa ...
in order to get a desired sound.
Digital clipping
digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are ...
, clipping occurs when the signal is restricted by the range of a chosen representation. For example, in a system using 16-bit signed integers, 32767 is the largest positive value that can be represented. If, during processing, the amplitude of the signal is doubled, sample
Sample or samples may refer to:
Base meaning
* Sample (statistics), a subset of a population – complete data set
* Sample (signal), a digital discrete sample of a continuous analog signal
* Sample (material), a specimen or small quantity of ...
values of, for instance, 32000 should become 64000, but instead cause an integer overflow
In computer programming, an integer overflow occurs when an arithmetic operation attempts to create a numeric value that is outside of the range that can be represented with a given number of digits – either higher than the maximum or lower ...
and saturate to the maximum, 32767. Clipping is preferable to the alternative in digital systems—wrapping—which occurs if the digital processor is allowed to overflow, ignoring the most significant bit
In computing, bit numbering is the convention used to identify the bit positions in a binary number.
Bit significance and indexing
In computing, the least significant bit (LSB) is the bit position in a binary integer representing the binar ...
s of the magnitude, and sometimes even the sign of the sample value, resulting in gross distortion of the signal.
Avoiding clipping
The simplest way to avoid clipping is to reduce the signal level. Alternatively the system can be improved to support higher signal level without clipping. Some audiophiles will use amplifiers that are rated for power outputs over twice the speaker's ratings. Alimiter
In electronics, a limiter is a circuit that allows signals below a specified input power or level to pass unaffected while attenuating (lowering) the peaks of stronger signals that exceed this threshold. Limiting is a type of dynamic range comp ...
can be used to dynamically bring the levels of the loud parts of a signal down (for example, bass
Bass or Basses may refer to:
Fish
* Bass (fish), various saltwater and freshwater species
Music
* Bass (sound), describing low-frequency sound or one of several instruments in the bass range:
** Bass (instrument), including:
** Acoustic bass gui ...
and snare drum
The snare (or side drum) is a percussion instrument that produces a sharp staccato sound when the head is struck with a drum stick, due to the use of a series of stiff wires held under tension against the lower skin. Snare drums are often used ...
s).
Many amplifier designers have incorporated circuits to prevent clipping. The simplest circuits act like a fast limiter, which engages about one decibel before the clipping point. A more complex circuit, called "soft-clip", has been used from the 1980s onward to limit the signal at the input stage. The soft-clip feature begins to engage prior to clipping, for instance starting at 10 dB below maximum output power. The output waveform retains a rounded characteristic even in the presence of an overload input signal as much as 10 dB higher than maximum specified.
Repairing a clipped signal
It is preferable to avoid clipping, but if a recording has clipped, and cannot be re-recorded, repair is an option. The goal of repair is to make up a plausible replacement for the clipped part of the signal. Complex hard-clipped signals cannot be restored to their original state because the information contained in the peaks that are clipped is completely lost. Soft-clipped signals can be restored to their original state to within a case-dependent tolerance because no part of the original signal is completely lost. In this case, the degree of information loss is proportional to the degree of compression caused by the clipping. Lightly clipped bandwidth-limited signals that are highly oversampled have the potential for perfect repair. Several methods can partially restore a clipped signal. Once the clipped portion is known, one can attempt partial recovery. One such method isinterpolation
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one often has ...
or extrapolation
In mathematics, extrapolation is a type of estimation, beyond the original observation range, of the value of a variable on the basis of its relationship with another variable. It is similar to interpolation, which produces estimates between know ...
of known samples. Advanced implementations may use cubic splines to attempt to restore a continuously differentiable
In mathematics, a differentiable function of one real variable is a function whose derivative exists at each point in its domain. In other words, the graph of a differentiable function has a non- vertical tangent line at each interior point in ...
signal. While these reconstructions are only an approximation of the original, the subjective quality may be improved. Other methods include copying the signal directly from one stereo channel to another, as it may be the case that only one channel is clipped.
Several software solutions of varying results and methods exist to repair clipping: CrumplePop ClipRemover, MAGIX Sound Forge, iZotope RX De-Clip, Acon Digital Acon or ACON may refer to:
*Acon, Eure, a commune in the Eure department in northern France
*'' Aconitum'', a plant used in homeopathy
* Åcon, science fiction convention held in Mariehamn, Åland, Finland
* Africa Cup of Nations, a football tourna ...
Restoration Suite, Adobe Audition
Adobe Audition is a digital audio workstation developed by Adobe Inc. featuring both a multitrack, non-destructive mix/edit environment and a destructive-approach waveform editing view.
Origins
Syntrillium Software was founded in the early 19 ...
, Thimeo Stereo Tool, declipping solutions from CEDAR Audio, and Audacity plugins such as Clip Fix.
Causes
In analog audio equipment, there are several causes of clipping: # The peak-to-peak output of a solid-state transformerless amplifier is limited by thepower supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As ...
voltage.
# An amplifier may have an asymmetrical output swing and clipping may begin earlier on one half of the output waveform.
# In audio amplifiers using unregulated linear power supplies, if the filter capacitor is not large enough, it is possible for ripple voltage to cause clipping that also contains some AC line frequency harmonics. In a switched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, switched power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently.
Like ...
the switching fequency is more dominant in the ripple voltage and outside the audio band while in a regulated power supply the ripple voltage is rejected.
# A vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
can only move a limited number of electrons
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
in a given amount of time, dependent on its size, temperature, and metals. The resulting fall-off in amplification with increasing output current results in ''soft clipping''.
# Amplifying devices may also have limits on their inputs, for example excessive base current to a bipolar transistor or excessive grid current to a vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
. Operating outside these limits can distort the input signal, if it comes from a high enough impedance source, or damage the amplifying device requiring a limiting circuit for protection; see below.
# An amplifier may limit its current output, or the input voltage, for a variety of reasons both intentional or not. Intentional limiting circuits would not be expected to come into effect in normal operation, but only when the output load resistance is too low or the input signal level is exceptionally high, for example. The result of this form of clipping might not create a flat top to the voltage waveform, but rather a flat top to the current waveform.
# A transformer (most commonly used between stages and at the output in tube equipment) will clip when its ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) which results in a large observed magnetic permeability, and in many cases a large magnetic coercivity allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic materials ...
core becomes electromagnetically saturated.
Detection
Clipping in a circuit can be detected by comparing the original input signal with an output signal with adjustment for applied gain. For instance, if a circuit has 10 dB of applied gain, it can be tested for clipping by attenuating the output signal by 10 dB and comparing it to the input signal. The difference between the two signals can be used to illuminate clipping detection indicators and can be used to decrease the gain of a preceding circuit to manage clipping. Clipped signals will often be squarized, where third harmonics are contextual outliers in a Fourier Transform. In the case of an expected sine wave, the presence of odd harmonics will often suggest the signal has been hard clipped. A “soft clip” will have a knee on both sides of the plateau, which will show the presence of several even overtones in the lower frequency spectrum.See also
*Clipper (electronics)
In electronics, a clipper is a circuit designed to prevent a signal from exceeding a predetermined reference voltage level. A clipper does not distort the remaining part of the applied waveform. Clipping circuits are used to select, for purpos ...
* Dynamic range compression
Dynamic range compression (DRC) or simply compression is an audio signal processing operation that reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds, thus reducing or ''compressing'' an audio signal's dynamic range. Compression is ...
* Tube sound
Notes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Clipping (Audio) Audio engineering Sound production technology