Climate of Turkey on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The coastal areas of
The coastal areas of
 The coastal areas of
The coastal areas of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
bordering the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
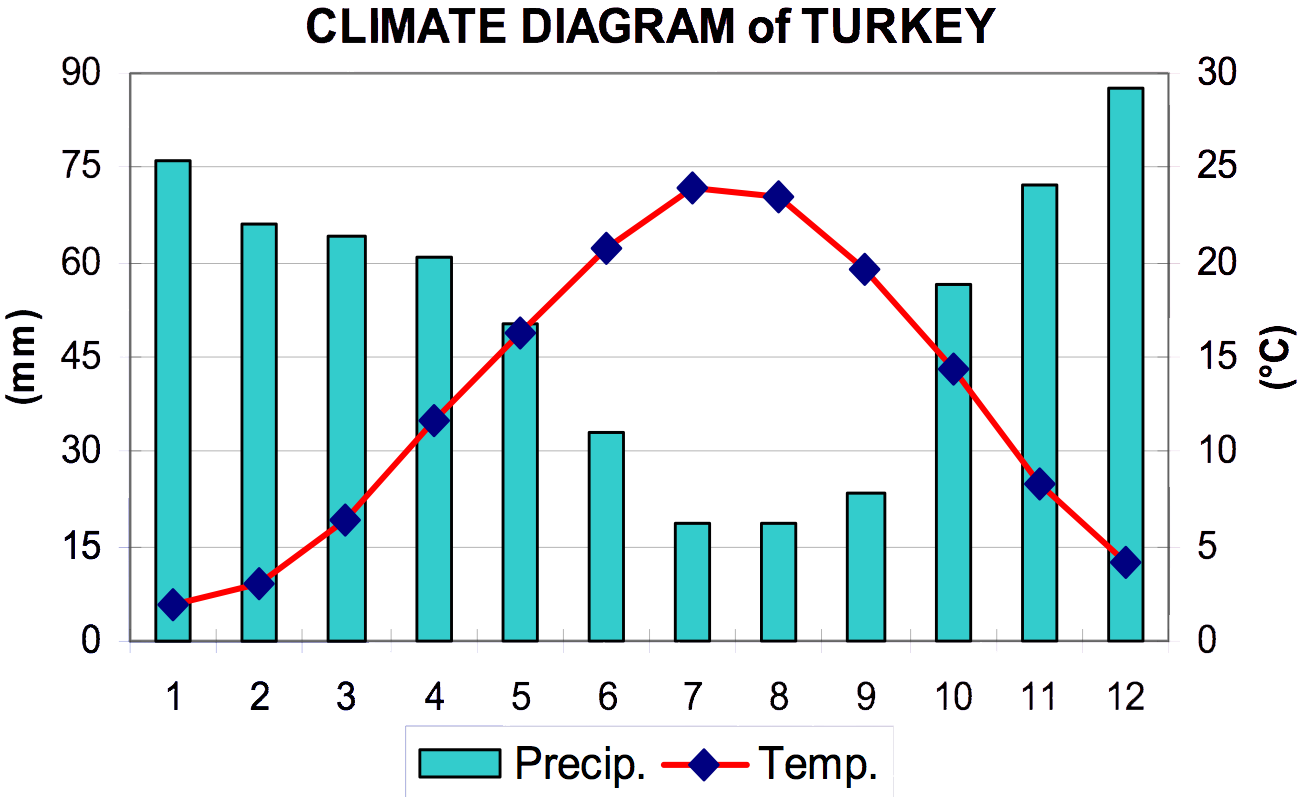
have a hot-summer Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
, with hot, dry summers and mild to cool, wet winters. The coastal areas of Turkey bordering the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
have a temperate Oceanic climate with warm, wet summers and cool to cold, wet winters. The Turkish Black Sea coast receives the most precipitation and is the only region of Turkey that receives high precipitation throughout the year. The eastern part of that coast averages 2,500 millimeters annually which is the highest precipitation in the country.
The coastal areas of Turkey
bordering the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via t ...
(including Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
), which connects the Aegean Sea and the Black Sea, have a transitional climate between a temperate Mediterranean climate and a temperate Oceanic climate with warm to hot, moderately dry summers and cool to cold, wet winters. Snow does occur on the coastal areas of the Sea of Marmara and the Black Sea almost every winter, but it usually lies no more than a few days. On the other hand, it is rare in the coastal areas of the Aegean Sea and very rare in the coastal areas of the Mediterranean Sea.
Conditions can be much harsher in the more arid interior. Mountains close to the coast prevent maritime influences from extending inland, giving the central Anatolian plateau of the interior of Turkey a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
with sharply contrasting season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and ...
s.
Winters on the plateau are especially severe. Temperatures of −30 °C to −40 °C (−22 °F to −40 °F) do occur in northeastern Anatolia, and snow may lie on the ground at least 120 days of the year and in the mountains almost the entire year. In central Anatolia the temperatures can drop below -20 °C (-4 °F), with higher elevated parts dropping below -30 °C (- 22 °F) at times. Summers are hot and dry, with temperatures generally around or above 30 °C (86 °F) in the day. Nights are cool. Annual precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
averages about 400 millimetres (15 in), with actual amounts determined by elevation. The driest regions are the Konya Plain and the Malatya Plain The Malatya Plain is a plain in Eastern Turkey between the Euphrates valley to the east and the
Taurus Mountains to the south and southeast. Its altitude varies between 700 and 1100 meters above the sea level.
The climate in the area is semi-arid, ...
, where annual rainfall frequently is less than 300 millimetres (12 in). May is generally the wettest month, whereas July and August are the driest.
Below are the climates from the seven census regions of Turkey, showing how varied they can be in different places around the country:
See also
*Climate change in Turkey
Climate change in Turkey includes changes in the climate of Turkey, their effects and how the country is adapting to those changes. Turkey's annual and maximum temperatures are rising, and 2020 was the third hottest year on record. Turkey wil ...
* Geography of Turkey
The Anatolian side of Turkey is a large, roughly rectangular peninsula that bridges southeastern Europe and Asia. Thrace, the European portion of Turkey comprises 3%The Dorling Kindersley World Reference Atlas. New York: Dorling Kindersley, 2014 ...
* Environmental issues in Turkey
References and notes
{{Europe topic, Climate ofTurkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...