Climate of Liechtenstein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The principality of
The principality of


 The principality of
The principality of Liechtenstein
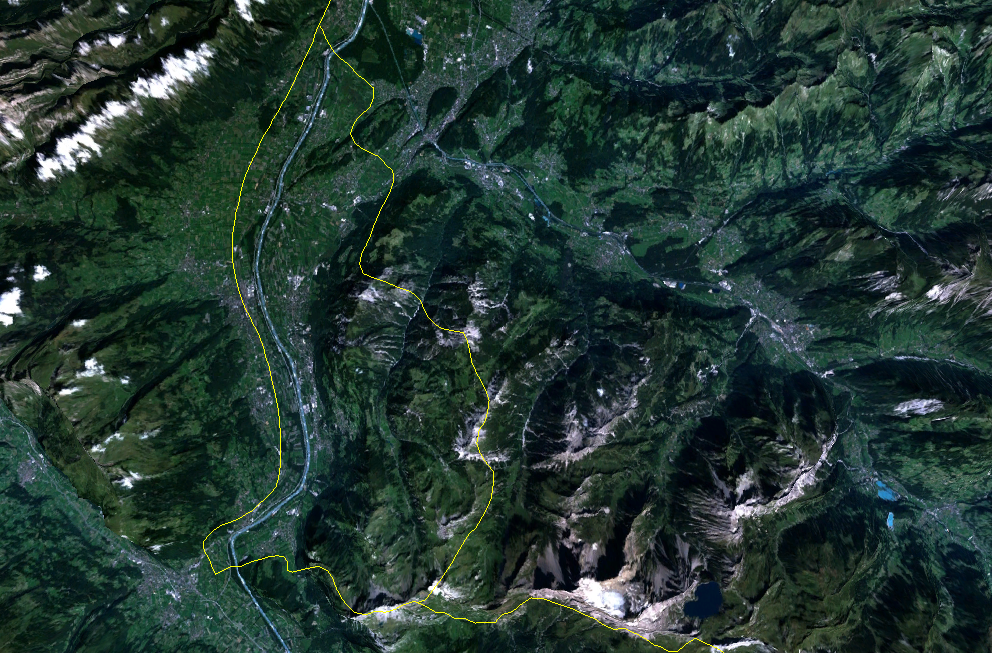
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarch ...
encompasses most of the eastern half of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
Valley, wedged between Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and Switzerland. The majority of the country's population is found in the western half along the Rhine River. Along with Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, Liechtenstein is one of only two doubly landlocked countries in the world.
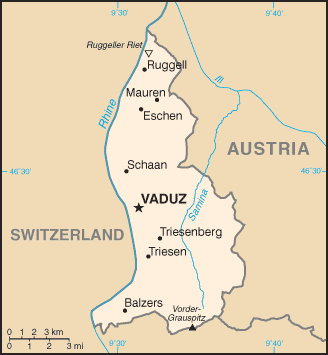
Statistics
Geographic coordinates: Area: 160 km2 (land, 0 km2 water) Land boundaries :''total:'' 76 km :''border countries:'' Austria 35 km, Switzerland 41 km Lake :The only lake in Liechtenstein is theGampriner Seele
Gampriner Seele is the only lake in Liechtenstein. It was created by a flood of the Rhine River with enormous erosion in 1927. The lake lies at 435 metres above Sea Level in the village of Bendern–Gamprin.
Gampriner Seele is surrounded by a de ...
.
Land use
:''arable land:'' 21.88%
:''permanent crops:'' 0%
:''other:'' 78.12% (2011)
Terrain
:Mostly mountainous (Alps) with Rhine Valley in western third
Natural resources:
: Hydroelectric potential, arable land
Extreme points:
* North - river Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, Ruggell
Ruggell is a municipality of Liechtenstein. It is the northernmost and lowest elevated municipality. As of 2019, it has a population of 2,322.
History
The name is said to be from the Latin for "clearing the land" (roncale - ad roncalem). Most know ...
* South - summit of Mazorakopf/Falknishorn (2,452 m), Triesen
Triesen () is the third largest of Liechtenstein's municipalities. It contains several historic churches dating from the fifteenth century. It also has a weaving mill from 1863 that is considered a historical monument. The population is around 5, ...
* East - border post 28, above Nenzinger Himmel
* West - river Rhine, Balzers
Balzers is a village located in southern Liechtenstein. As of 2019, the village had a total population of 4,642. The main part of the village is situated along the east bank of the Rhine.
History and culture
Historically, the present-day form o ...
* highest - Vorder Grauspitz (2,599 m), Triesen
Triesen () is the third largest of Liechtenstein's municipalities. It contains several historic churches dating from the fifteenth century. It also has a weaving mill from 1863 that is considered a historical monument. The population is around 5, ...
* lowest - Bangserfeld (429 m), Ruggell
Ruggell is a municipality of Liechtenstein. It is the northernmost and lowest elevated municipality. As of 2019, it has a population of 2,322.
History
The name is said to be from the Latin for "clearing the land" (roncale - ad roncalem). Most know ...
Climate
Continental; cold, cloudy winters with frequent snow or rain; cool to moderately warm, cloudy, humid summers, great variety ofmicroclimates
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. The term may refer to areas as small as a few squa ...
based on elevation.
Environment - international agreements
''Party to:''Air Pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different typ ...
,
Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants,
Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides,
Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94,
Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds,
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
,
Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
,
Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol,
Desertification,
Endangered Species,
Hazardous Wastes
Hazardous waste is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment. Hazardous waste is a type of dangerous goods. They usually have one or more of the following hazardous traits: ignitability, reactivity, cor ...
,
Ozone Layer Protection
The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force o ...
,
Wetlands,
''Signed, but not ratified:''
Law of the Sea
References
Lists of coordinates