Climate of Bahrain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



 The
The



 The
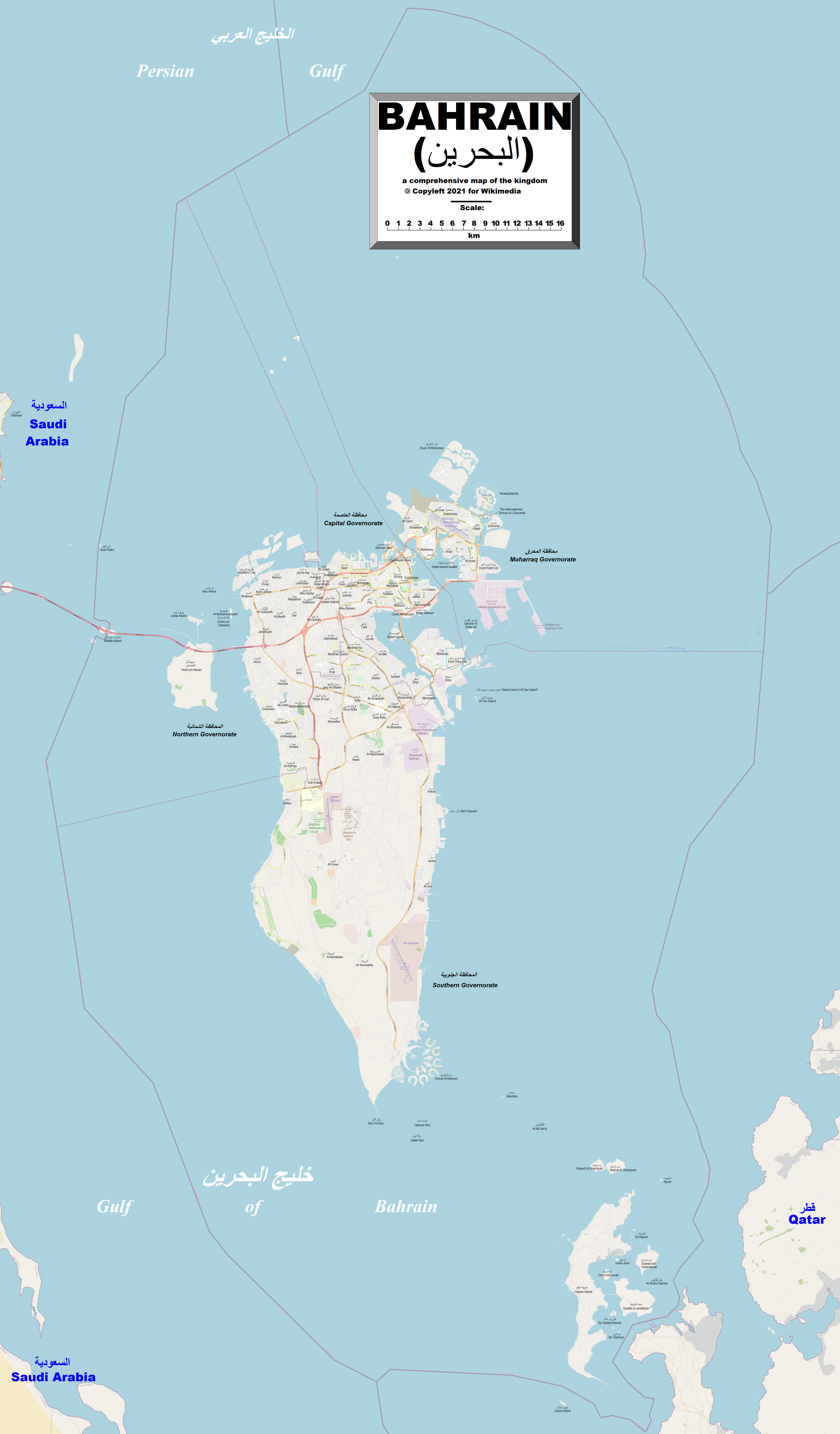
The Kingdom of Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ad ...
consists of Bahrain Island
Bahrain Island ( ar, جزيرة البحرين ''Jazīrah al-Baḥrayn''), also known as al-Awal Island and formerly as Bahrein, is the largest island within the archipelago of Bahrain, and forms the bulk of the country's land mass while hosting ...
and 33 of the p37 Bahrain Islands, lying in the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Persis, Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a Mediterranean sea (oceanography), me ...
's Gulf of Bahrain
The Gulf of Bahrain is an inlet of the Persian Gulf on the east coast of Saudi Arabia, separated from the main body of water by the peninsula of Qatar. It surrounds the islands of Bahrain. The King Fahd Causeway crosses the western section of the ...
off the north shore of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
's Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
. Bahrain's capital city is Manama
Manama ( ar, المنامة ', Bahrani Arabic, Bahrani pronunciation: ) is the capital and largest city of Bahrain, with an approximate population of 200,000 people as of 2020. Long an important trading center in the Persian Gulf, Manama is h ...
. The islands are about off the east coast of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
and from Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
. The total area of the country is about , about four times the size of the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
.
Bahrain Island accounts for about 78% of the kingdom's land area, comprising . It is long from north to south and at its widest point stretches from east to west. The island is surrounded by several of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
's large petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
fields and commands a strategic position amid the Persian Gulf's shipping lanes.
Geographical setting and islands
Following the return of Janan toQatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
in March 2001, that state of Bahrain consists of 33 natural islands in the archipelago.
Around most of Bahrain is a relatively shallow inlet of the Persian Gulf known as the Gulf of Bahrain
The Gulf of Bahrain is an inlet of the Persian Gulf on the east coast of Saudi Arabia, separated from the main body of water by the peninsula of Qatar. It surrounds the islands of Bahrain. The King Fahd Causeway crosses the western section of the ...
. The seabed adjacent to Bahrain is rocky and, mainly off the northern part of the island, covered by extensive coral reefs. Most of the island is low-lying and barren desert. Outcroppings of limestone form low rolling hills, stubby cliffs, and shallow ravine
A ravine is a landform that is narrower than a canyon and is often the product of streambank erosion. The limestone is covered by various densities of saline sand, capable of supporting only the hardiest desert vegetation – chiefly thorn trees and scrub. There is a fertile strip five kilometers wide along the northern coast on which
total:780 km2
''country comparison to the world:'' 188 *land:780 km2 *water: 0 km2 Area comparative *
periodic droughts; dust storms Environment - current issues:
party to:
date
Date or dates may refer to:
*Date (fruit), the fruit of the date palm (''Phoenix dactylifera'')
Social activity
*Dating, a form of courtship involving social activity, with the aim of assessing a potential partner
**Group dating
*Play date, an ...
, almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree native to Iran and surrounding countries, including the Levant. The almond is also the name of the edible and widely cultivated seed of this tree. Within the genus ...
, fig
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of small tree in the flowering plant family Moraceae. Native to the Mediterranean and western Asia, it has been cultivated since ancient times and is now widely grown throughout the world ...
, and pomegranate
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between tall.
The pomegranate was originally described throughout the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean re ...
trees grow. The interior contains an escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escar ...
that rises to 134 meters, the highest point on the island, to form Jabal al Dukhan
The Mountain of Smoke ( ar, جبل الدخان, ) is a hill in the Southern Governorate of Bahrain. At above mean sea level, it is the country's highest point. The Mountain of Smoke is named as such because of the haze which often surrounds it o ...
(Mountain of Smoke), named for the mists that often wreathe the summit. Most of the country's oil well
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may ...
s are situated in the vicinity of Jabal al Dukhan.
One author writes about the geology of the nation: "Bahrein lies on a portion of the ancient Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean ( el, Τηθύς ''Tēthús''), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean that covered most of the Earth during much of the Mesozoic Era and early Cenozoic Era, located between the ancient continents ...
geosynclinal belt represented today by the Persian Gulf. The formation of the principal island is the result of pressure from the mountain masses of Persia against the crystalline platform of central Asia, the thrust being absorbed by gentle folding in the geosynclines. The structure of Bahrein is that of a large, single, closed dome covering the entire faulting".
Rocks exposed at the surface consist of:
* Recent sands and coquina
Coquina () is a sedimentary rock that is composed either wholly or almost entirely of the transported, abraded, and mechanically sorted fragments of the shells of mollusks, trilobites, brachiopods, or other invertebrates. The term ''coquina'' ...
s forming flat, raised beaches surrounding the island from which the surface rises gradually to an elevation 150 to 200 feet above sea level. At this point it breaks away into inward-facing cliffs eighty to one hundred feet high completely surrounding an oval central depression about twelve miles long and four wide.
* Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
sands, cross bedded and probably wind deposited, lying in the canyon.
* Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
silicious clay covering a very limited area.
* Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
limestone covering most of the island, the central region of which, known as “Jabal Dukhān “Mountain of Smoke”, rises to a point 439 feet above sea level. The limestone is very porous and is the source of most of the water in the northern half of the island.Faroughy, Abbas. 1951. The Bahrein Islands (750-1951): A Contribution to the Study of Power Politics in the Persian Gulf. New York: Verry, Fisher & Co. Pages 14-15.
In addition to Bahrain Island
Bahrain Island ( ar, جزيرة البحرين ''Jazīrah al-Baḥrayn''), also known as al-Awal Island and formerly as Bahrein, is the largest island within the archipelago of Bahrain, and forms the bulk of the country's land mass while hosting ...
, other islands of significance include Nabih Saleh
Nabih Saleh ( ar, النبيه صالح) is an island of Bahrain in the Arabian Gulf. It lies in the Tubli Bay, east of Bahrain Island, and is south of the capital, Manama, on Bahrain Island.
History
The island is named for the formerly separat ...
, which is northwest of Sitrah
Sitra ( ar, سترة or , ''As-Sitra''), also known as Sitrah ( ar, Jazīrat Sitrah, script=Latn) or Sitra Island ( ar, Jazīrat as-Sitra, script=Latn), is an island in Bahrain.
It lies south of the capital, Manama, on Bahrain Island.
History
; ...
; Jidda Island
Jidda Islands ( ar, جزيرة جدة) are a group of three small uninhabited islets in Bahrain, lying to the west of Bahrain Island and just north of Umm an Nasan in the Persian Gulf. They are west of the capital, Manama, on Bahrain Island.
His ...
and Umm as Sabaan
Umm as Sabaan ( ar, ام الصبان) is an islet in Bahrain. It lies off the north western corner of Bahrain Island, near Budaiya village, and east of Jidda Island, located in the Persian Gulf. It lies west of the capital, Manama, on Bahrain I ...
, to the north of Umm an Nasan
Umm an Nasan island ( ar, ام النعسان) is the fifth largest island in Bahrain.
It is west of the capital, Manama, on Bahrain Island.
Description
Umm an Nasan is privately owned by Prime Minister Khalifa bin Salman Al Khalifa, and is off ...
; and a group of islands
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the List of islands ...
, the largest of which is Hawar, near the coast of Qatar. Nabih Saleh contains several freshwater springs that are used to irrigate the island's extensive date palm groves. The rocky islet of Jiddah
Jeddah ( ), also spelled Jedda, Jiddah or Jidda ( ; ar, , Jidda, ), is a city in the Hejaz region of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) and the country's commercial center. Established in the 6th century BC as a fishing village, Jeddah's pro ...
formerly housed the state prison but has now been converted to a holiday resort. Hawar and the fifteen small islands near it are the subject of a territorial dispute between Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
and Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
. Hawar is nineteen kilometers long and about one and one half kilometers wide. The other islands (such as the Al Garum Islands
Al Garum Islands are the northernmost group of islands of Bahrain. They lie north of the capital, Manama, on Bahrain Island.
Geography
There are 4 islands in this reef, and a curved channel was dredged to reach the main island.
Administration
T ...
) are uninhabited and are nesting sites for a variety of migratory birds
Bird migration is the regular seasonal movement, often north and south along a flyway, between breeding and wintering grounds. Many species of bird migrate. Migration carries high costs in predation and mortality, including from hunting by ...
.
Climate
Bahrain features anarid climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
. Bahrain has two seasons: an extremely hot summer and a relatively mild winter. During the summer months, from April to October, afternoon temperatures average and can reach during May, June and July. The combination of intense heat and high humidity makes this season uncomfortable. In addition, a hot, dry southwest wind, known locally as the qaws, periodically blows sand clouds across the barren southern end of Bahrain toward Manama in the summer. Temperatures moderate in the winter months, from November to March, when the range is between . However, humidity often rises above 90% in the winter. From December to March, prevailing winds from the northwest, known as the shamal, bring damp air over the islands. Regardless of the season, daily temperatures are fairly uniform throughout the archipelago. Note that the coldest temperature ever recorded in Bahrain was on January 20, 1964, when it dropped to -5 °C (23 °F) in Awali and 2.7 °C (36 °F) at Bahrain International Airport.
That particular freeze was accompanied by a white-out, with icicles forming on trees and fences at Awali.
Bahrain receives little precipitation. The average annual rainfall is , usually confined to the winter months. No permanent rivers or streams exist on any of the islands. The winter rains tend to fall in brief, torrential downpours, flooding the shallow wadi
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemeral) riverbed that contains water onl ...
s that are dry the rest of the year and impeding transportation. Little of the rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
water is saved for irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,00 ...
or drinking. However, there are numerous natural springs in the northern part of Bahrain and on adjacent islands. Underground freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
deposits also extend beneath the Persian Gulf to the Saudi Arabian coast. Since ancient times, these springs have attracted settlers to the archipelago. Despite increasing salinization, the springs remain an important source of drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, a ...
for Bahrain. Since the early 1980s, however, desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in Soil salinity control, soil desalination, which is an issue f ...
plants, which render seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appro ...
suitable for domestic and industrial use, have provided about 60% of daily water consumption needs.
Area and boundaries
Area:total:780 km2
''country comparison to the world:'' 188 *land:780 km2 *water: 0 km2 Area comparative *
USA
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
- 3.5 times the size of Washington D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 161 km
Maritime claims:
*territorial sea:
*contiguous zone:
*continental shelf: extending to boundaries to be determined
Elevation extremes:
*lowest point: Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Persis, Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a Mediterranean sea (oceanography), me ...
0 m
*highest point: Jabal ad Dukhan 122 m
Resources and land use
Natural resources: *oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
, associated and non associated natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carb ...
s
Land use:
*arable land: 2.11%
*permanent crops: 3.95%
*other: 93.95% (2012)
Irrigated land:
40.15 km2 (2003)
Total renewable water resources:
0.12 m³ (2011)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
*total: 0.36 km³/yr (50%/6%/45%)
*per capita: 386 m³/yr (2003)
Environmental concerns
Natural hazards:periodic droughts; dust storms Environment - current issues:
desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
resulting from the degradation of limited arable land, periods of drought, and dust storms; coastal degradation (damage to coastlines, coral reefs, and sea vegetation) resulting from oil spills and other discharges from large tankers, oil refineries, and distribution stations; lack of freshwater resources (groundwater and seawater are the only sources for all water needs)
Environment - international agreements:party to:
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
, Desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
, Hazardous Wastes
Hazardous waste is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment. Hazardous waste is a type of dangerous goods. They usually have one or more of the following hazardous traits: ignitability, reactivity, cor ...
, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in rela ...
Protection, Wetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
See also
*Notes
References
*Further reading
* * {{coord, 26, 00, N, 50, 33, E, region:BH_source:enwiki-plaintext-parser, display=title