Cities of the ancient Near East on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The earliest cities in history were in the
 (ordered from north to south)
(ordered from north to south)

 (ordered from north to south)
(ordered from north to south)

Geospatial: Mapping Iraq's Ancient Cities
Ancient cities grew pretty much like modern ones, say scientists
(February 2015), ''
ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, ...
, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC or with that by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in the 4th century BC.
The largest cities of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
Near East housed several tens of thousands of people. Memphis
Memphis most commonly refers to:
* Memphis, Egypt, a former capital of ancient Egypt
* Memphis, Tennessee, a major American city
Memphis may also refer to:
Places United States
* Memphis, Alabama
* Memphis, Florida
* Memphis, Indiana
* Memp ...
in the Early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
, with some 30,000 inhabitants, was the largest city of the time by far. Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center t ...
is estimated to have had a population of 40,000 inhabitants in the Intermediate Bronze age. Ur in the Middle Bronze Age is estimated to have had some 65,000 inhabitants; Babylon in the Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
similarly had a population of some 50,000–60,000. Niniveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ban ...
had some 20,000–30,000, reaching 100,000 only in the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
(around 700 BC).
In Akkadian and Hittite orthography, URU became a determinative sign denoting a city, or combined with KUR "land" the kingdom or territory controlled by a city, e.g. "the king of the country of (the city of) Hatti". The KI determinative is used following place names (toponyms) in both Sumerian and Akkadian.
Mesopotamia
Lower Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia
(ordered from north to south) *Urfa
Urfa, officially known as Şanlıurfa () and in ancient times as Edessa, is a city in southeastern Turkey and the capital of Şanlıurfa Province. Urfa is situated on a plain about 80 km east of the Euphrates River. Its climate features ex ...
* Shanidar cave
Shanidar Cave ( ku, Zewî Çemî Şaneder ,ئەشکەوتی شانەدەر, ) is an archaeological site located on Bradost Mountain, within the Zagros Mountains, in the Erbil Governorate of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq.
It is known for the ...
* Urkesh
Urkesh or Urkish ( Akkadian: 𒌨𒆧𒆠 UR.KIŠKI, 𒌨𒋙𒀭𒄲𒆠 UR.KEŠ3KI; modern Tell Mozan; ar, تل موزان) is a tell, or settlement mound, located in the foothills of the Taurus Mountains in Al-Hasakah Governorate, northeaster ...
(Urkish) (''Tell Mozan'')
* Tell Leilan
Tell Leilan is an archaeological site situated near the Wadi Jarrah in the Khabur River basin in Al-Hasakah Governorate, northeastern Syria. The site has been occupied since the 5th millennium BC. During the late third millennium, the site wa ...
(''Shekhna'', ''Shubat-Enlil'')
* Tell Arbid
Tell Arbid is an ancient Near East archaeological site in the Khabur River Basin region of Al-Hasakah Governorate, Syria. It is located 45 km south of Tell Mozan, the site of ancient Urkesh.
History
The history and identity of Tell Arbi ...
* Harran
Harran (), historically known as Carrhae ( el, Kάρραι, Kárrhai), is a rural town and district of the Şanlıurfa Province in southeastern Turkey, approximately 40 kilometres (25 miles) southeast of Urfa and 20 kilometers from the border cr ...
* Chagar Bazar
Chagar Bazar (Šagir Bazar, Arabic: تل شاغربازار) is a tell, or settlement mound, in northern Al-Hasakah Governorate, Syria. It is a short distance from the major ancient city of Nagar (Tell Brak). The site was occupied from the Halaf ...
* Mardaman
Mardaman (modern Bassetki) was a northern Mesopotamian city that existed between ca.2200 and 1200 BC. It was uncovered in 2018 after translation of 92 cuneiform tablets. The tablets were discovered in summer 2017, near the Kurdish village of Bas ...
(''Bassetki
, image_skyline =
, imagesize =
, image_caption =
, pushpin_map = Iraqi Kurdistan
, pushpin_mapsize=
, map_caption = Location in Iraqi Kurdistan
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name =
, subdivision_type1 = Governo ...
'')
* Kahat (''Tell Barri'')
* Tell Fekheriye (''Washukanni?'')
* Hadatu (''Arslan Tash'')
* Carchemish
Carchemish ( Turkish: ''Karkamış''; or ), also spelled Karkemish ( hit, ; Hieroglyphic Luwian: , /; Akkadian: ; Egyptian: ; Hebrew: ) was an important ancient capital in the northern part of the region of Syria. At times during it ...
(''Djerabis'')
* Til Barsip
Til Barsip or Til Barsib ( Hittite Masuwari, modern Tell Ahmar; ar, تل أحمر) is an ancient site situated in Aleppo Governorate, Syria by the Euphrates river about 20 kilometers south of ancient Carchemish.
History
The site was inhabited a ...
(''Tell Ahmar'')
* Tell Chuera
Tell Chuera is an ancient Near Eastern tell site in Raqqa Governorate, northern Syria. It lies between the Balikh and Khabur rivers.
Archaeological research
The site was first described by Max von Oppenheim in 1913. Excavations were begun in 1 ...
* Mumbaqat (''Tall Munbāqa, Ekalte'')
* Al-Rawda
* Nabada (''Tell Beydar'')
* Nagar (''Tell Brak'')
* Telul eth-Thalathat
Telul eth-Thalathat is an archaeological site located west of Mosul and just east of Tal Afar in Nineveh Province (Iraq).
History of archaeological research
The site consists of at least five separate tells or settlement mounds. Telul eth-Tha ...
* Tepe Gawra
Tepe Gawra (Kurdish for "Great Mound") is an ancient Mesopotamian settlement 15 miles NNE of Mosul in northwest Iraq that was occupied between 5000 and 1500 BC. It is roughly a mile from the site of Nineveh and 2 miles E of the site of Khors ...
* Tell Arpachiyah (''Tepe Reshwa'')
* Shibaniba (''Tell Billa'')
* Tarbisu Tarbiṣu (modern Sherif Khan, Ninawa Governorate, Iraq) was an ancient city about 3 miles north of Nineveh.
History
Tarbiṣu was a minor town until the control of the Assyrian Empire was moved to
nearby Nineveh by Sennacherib. Two palaces were ...
(''Sherif Khan'')
* Nineveh (''Ninua'')
* Qatara or Karana (''Tell al-Rimah'')
* Tell Hamoukar
* Dur Sharrukin
Dur-Sharrukin ("Fortress of Sargon"; ar, دور شروكين, Syriac: ܕܘܪ ܫܪܘ ܘܟܢ), present day Khorsabad, was the Assyrian capital in the time of Sargon II of Assyria. Khorsabad is a village in northern Iraq, 15 km northeast of Mo ...
(''Khorsabad'')
* Tell Shemshara
Tell may refer to:
*Tell (archaeology), a type of archaeological site
*Tell (name), a name used as a given name and a surname
* Tell (poker), a subconscious behavior that can betray information to an observant opponent
Arts, entertainment, and ...
(''Shusharra'')
* Erbil (''Urbilim'', ''Arba-Ilu'')
* Kurd Qaburstan (''Qabra?'')
* Tell Taya
Tell Taya is an archaeological site at a '' tell'' (hill city) in Nineveh Province (Iraq). It was occupied from the third to the first millennia BCE.
History of archaeological research
The site was first recorded by Seton Lloyd in 1938 during hi ...
* Tell Hassuna
Tell Hassuna is a tell, or settlement mound, in the Nineveh Province (Iraq), about 35km south-west of Nineveh. It is the type site for the Hassuna culture (early sixth millennium BCE).
History of archaeological research
Tell Hassuna was found ...
* Balawat (Imgur-Enlil)
* Tell es-Sweyhat
* Tell Hadidi (''Azu'')
* Nimrud
Nimrud (; syr, ܢܢܡܪܕ ar, النمرود) is an ancient Assyrian city located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah ( ar, السلامية), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a m ...
* Emar
)
, image = View_from_the_Byzantine_Tower_at_Meskene,_ancient_Barbalissos.jpg
, alt =
, caption = View from the Byzantine Tower at Meskene, ancient Barbalissos
, map_type = Syria
, map_alt =
, map_size = 200
...
(''Tell Meskene'')
* Tall Bazi
Tall Bazi, is an ancient Near East archaeological site in Raqqa Governorate of Syria in the same general area as Mari and Ebla. It is located on the Euphrates river in upper Syria, about 60 kilometers south of Turkey near the abandoned town of T ...
('' Armanum?'')
* Qal'at Jarmo
* Arrapha
Arrapha or Arrapkha ( Akkadian: ''Arrapḫa''; ar, أررابخا ,عرفة) was an ancient city in what today is northeastern Iraq, thought to be on the site of the modern city of Kirkuk.
In 1948, ''Arrapha'' became the name of the residential ...
* Kar-Tukulti-Ninurta
* Assur
Aššur (; Sumerian: AN.ŠAR2KI, Assyrian cuneiform: ''Aš-šurKI'', "City of God Aššur"; syr, ܐܫܘܪ ''Āšūr''; Old Persian ''Aθur'', fa, آشور: ''Āšūr''; he, אַשּׁוּר, ', ar, اشور), also known as Ashur and Qal ...
* Ekallatum Ekallatum ( Akkadian: 𒌷𒂍𒃲𒈨𒌍, URUE2.GAL.MEŠ, Ekallātum, "the Palaces") was an ancient Amorite city-state and kingdom in upper Mesopotamia. The exact location of it has not yet been identified, but it is thought to be located somewher ...
* Nuzi
Nuzi (or Nuzu; Akkadian Gasur; modern Yorghan Tepe, Iraq) was an ancient Mesopotamian city southwest of the city of Arrapha (modern Kirkuk), located near the Tigris river. The site consists of one medium-sized multiperiod tell and two small s ...
(''Yorghan Tepe'', ''Gasur'')
* Tell al-Fakhar
Tell al-Fakhar ( ar, تل الفخار "Pottery Mound") is a '' tell'', or archaeological settlement mound, in Kirkuk Governorate, northeastern Iraq. Excavations were carried out at the site between 1967 and 1969 by the Directorate-General of Ant ...
(''Kurruhanni?'')
* Tell Taban
Tell Taban is an archaeological site in north-eastern Syria in the Al-Hasakah Governorate. It is the site of the ancient city of Ṭābetu.
Archaeology
The site was first excavated from 1997 until 1999 as a salvage operation in response to the ...
(''Ṭābetu'', ''Ṭābatum'')
* Terqa
Terqa is the name of an ancient city discovered at the site of Tell Ashara on the banks of the middle Euphrates in Deir ez-Zor Governorate, Syria, approximately from the modern border with Iraq and north of the ancient site of Mari, Syria. ...
(''Tell Ashara'')
* Doura Europos
* Mari (''Tell Hariri'')
* Haradum
Haradum (modern Khirbit ed-Diniye (also Khirbet ed-Diniyé), Iraq) was an ancient Near East city on the middle Euphrates about 90 kilometers southeast of Mari. It was part of the ancient region of Suhum. The name of the town meant "the place w ...
(''Khirbet ed-Diniyeh'')
* Tell es Sawwan
* Nerebtum or Kiti (''Tell Ishchali'')
* Tell Agrab
Tell Agrab (or Aqrab) is a tell or settlement mound southeast of Eshnunna in the Diyala region of Iraq.
History
Tell Agrab was occupied during the Jemdet Nasr and Early Dynastic periods through the Akkadian and Larsa periods. It was during ...
* Dur-Kurigalzu
Dur-Kurigalzu (modern ' in Baghdad Governorate, Iraq) was a city in southern Mesopotamia, near the confluence of the Tigris and Diyala rivers, about west of the center of Baghdad. It was founded by a Kassite king of Babylon, Kurigalzu I (died ...
(''Aqar Quf'')
* Shaduppum
Shaduppum (modern Tell Harmal) is an archaeological site in Baghdad Governorate (Iraq). Nowadays, it lies within the borders of modern Baghdad.
History of archaeological research
The site, 150 meters in diameter and 5 meters high, was excavated ...
(''Tell Harmal'')
* Tell al-Dhiba'i
* Seleucia
* Ctesiphon (''Taq Kisra'')
* Zenobia
Septimia Zenobia ( Palmyrene Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; AD 240 – c. 274) was a third-century queen of the Palmyrene Empire in Syria. Many legends surround her ancestry; she was probably not a commoner and she married the ruler of the city ...
(''Halabiye'')
* Hatra
Hatra ( ar, الحضر; syr, ܚܛܪܐ) was an ancient city in Upper Mesopotamia located in present-day eastern Nineveh Governorate in northern Iraq. The city lies northwest of Baghdad and southwest of Mosul.
Hatra was a strongly fortified ...
* Idu
* Rabana-Merquly (''Natounia?'')
Iran

Asia Minor (Modern-day Turkey)
The Levant

Arabian Peninsula

Nubia
*Jebel Barkal
Jebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal ( ar, جبل بركل) is a mesa or large rock outcrop located 400 km north of Khartoum, next to Karima in Northern State in Sudan, on the Nile River, in the region that is sometimes called Nubia. The jebel is 1 ...
* Kerma
Kerma was the capital city of the Kerma culture, which was located in present-day Sudan at least 5,500 years ago. Kerma is one of the largest archaeological sites in ancient Nubia. It has produced decades of extensive excavations and research, i ...
* Meroë
Meroë (; also spelled ''Meroe''; Meroitic: or ; ar, مرواه, translit=Meruwah and ar, مروي, translit=Meruwi, label=none; grc, Μερόη, translit=Meróē) was an ancient city on the east bank of the Nile about 6 km north-east ...
* Napata
Napata (Old Egyptian ''Npt'', ''Npy''; Meroitic ''Napa''; grc, Νάπατα and Ναπάται) was a city of ancient Kush at the fourth cataract of the Nile. It is located approximately 1.5 kilometers from the right side of the river at the ...
Horn of Africa
*Adulis
Adulis (Sabaean: ሰበኣ
𐩱 𐩵 𐩡 𐩪, gez, ኣዱሊስ, grc, Ἄδουλις) was an ancient city along the Red Sea in the Gulf of Zula, about south of Massawa. Its ruins lie within the modern Eritrean city of Zula. It was the e ...
* Aksum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole regio ...
(Axum)
* Keskese
Keskese ge'ez ግእዝ (ከስከሰ) sebea ሰበአ (𐩫𐩪𐩫𐩪) is an archaeological site in Eritrea. It is the seat of an ancient D'mt kingdom ruin, and is situated north of Matara. Dating from around 500 BCE, it is renowned for its ...
* Matara
* Qohaito
Qohaito ( Tigrinya: ቆሓይቶ)was a major ancient city in what is now the Debub region of Eritrea. It was a pre-Aksumite settlement that thrived during the Aksumite period. The city was located over 2,500 meters above sea level, on a high plat ...
* Sembel
Sembel, located in the capital of Asmara, Maekel Region of Eritrea, is East Africa's oldest archaeological site, dated back to as early as 800 BCE.BBC News, Oldest African settlement found in Eritrea, BBC News 22 May 2002
Overview
Sembel was t ...
* Yeha
Yeha ( gez, ይሐ ''yiḥa'', older ESA 𐩥𐩢 ''ḤW''; Old South Arabian: 𐩺𐩢𐩱 ''Yḥʾ'') is a town in the Maekelay Zone of the northern Tigray Region in Ethiopia. It likely served as the capital of the pre-Aksumite kingdom of D'm ...
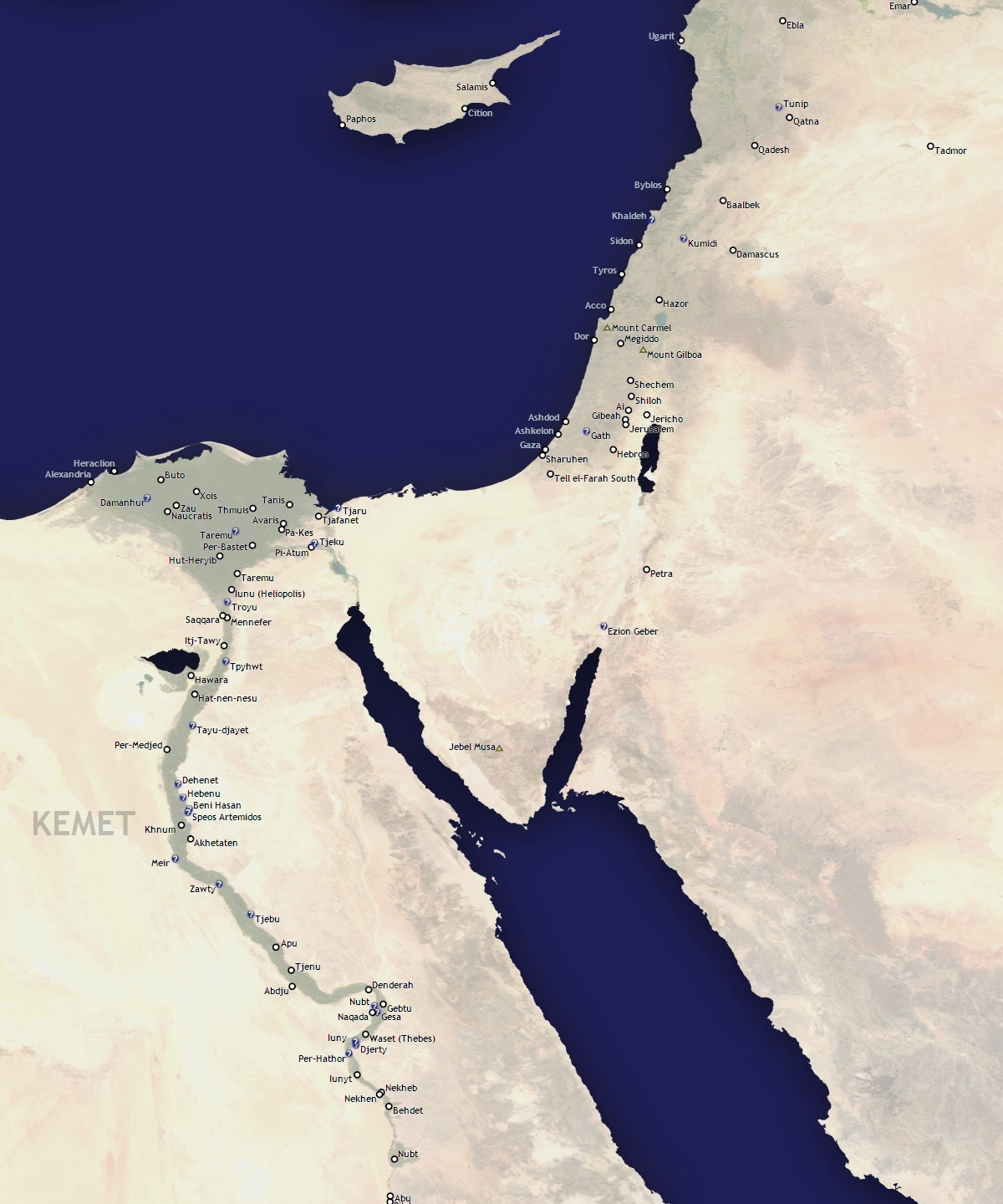
Egypt
See also
*City-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
* Sumerian King List
* Historical urban community sizes
* Short chronology timeline
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Com ...
* List of oldest continuously inhabited cities
* Ancient towns in Saudi Arabia
* List of Ancient Settlements in the UAE
*List of largest metropolitan areas of the Middle East
This is a list of metropolitan areas in Middle East, with their population according to different sources. The list includes metropolitan areas that have a population of over 1.5 million.
List
See also
*List of cities of the ancient Ne ...
References
External links
Geospatial: Mapping Iraq's Ancient Cities
Ancient cities grew pretty much like modern ones, say scientists
(February 2015), ''
Christian Science Monitor
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρισ ...
''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cities Of The ancient Near East
Near East
Ancient Near East
Lists of cities
Ancient history-related lists