Circular triangle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 Long arcs can produce concave figures regardless of whether individual edges are curved inwards or outwards. Inward curved arcs can create self-intersecting forms, such as the a
Long arcs can produce concave figures regardless of whether individual edges are curved inwards or outwards. Inward curved arcs can create self-intersecting forms, such as the a 
 Circular triangles can be seen in
Circular triangles can be seen in
geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is ...
, a circular triangle is a triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non- colline ...
with circular arc edges.
Construction
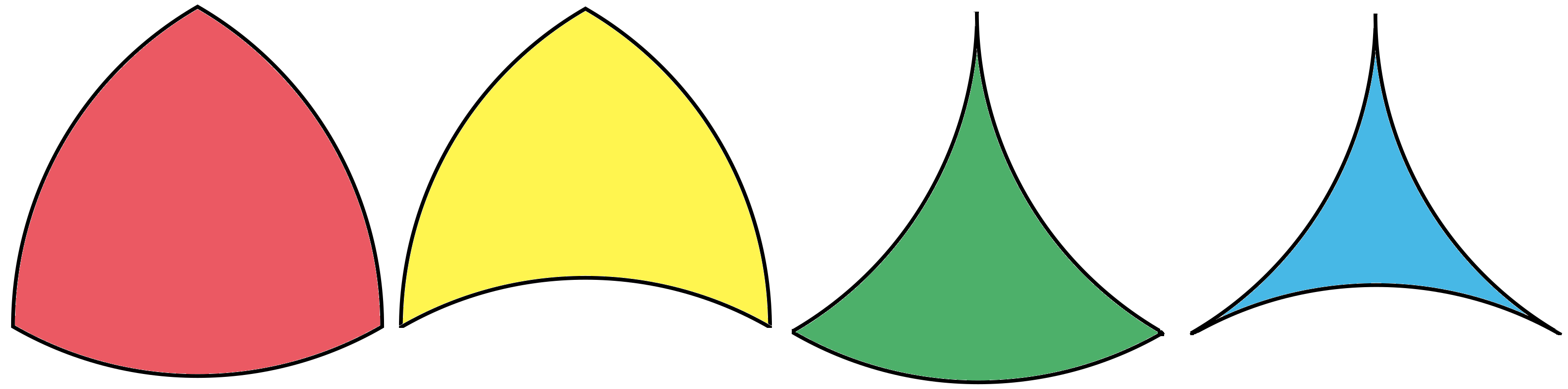
A convex circular triangle may be constructed by threecircle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is con ...
s intersecting each other and represents the area of intersection. Its edges are all curved outwards. The sum of the internal angle
In geometry, an angle of a polygon is formed by two sides of the polygon that share an endpoint. For a simple (non-self-intersecting) polygon, regardless of whether it is convex or non-convex, this angle is called an interior angle (or ) if ...
s of a circular triangle is greater than 180°. A Reuleaux triangle is a special case based on an equilateral triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each oth ...
where the center of each arc is on the opposite vertex.
A circular horn triangle is a similar concept, but represents the area interior to 3 mutually tangent circles so all of the internal angle
In geometry, an angle of a polygon is formed by two sides of the polygon that share an endpoint. For a simple (non-self-intersecting) polygon, regardless of whether it is convex or non-convex, this angle is called an interior angle (or ) if ...
s are zero. The arbelos
In geometry, an arbelos is a plane region bounded by three semicircles with three apexes such that each corner of each semicircle is shared with one of the others (connected), all on the same side of a straight line (the ''baseline'') that conta ...
is a special case with three collinear
In geometry, collinearity of a set of points is the property of their lying on a single line. A set of points with this property is said to be collinear (sometimes spelled as colinear). In greater generality, the term has been used for aligned o ...
vertices and three semicircular
In mathematics (and more specifically geometry), a semicircle is a one-dimensional locus of points that forms half of a circle. The full arc of a semicircle always measures 180° (equivalently, radians, or a half-turn). It has only one line o ...
edges..
Other circular triangles can have a mixture of convex and concave circular arc edges.
: Long arcs can produce concave figures regardless of whether individual edges are curved inwards or outwards. Inward curved arcs can create self-intersecting forms, such as the a
Long arcs can produce concave figures regardless of whether individual edges are curved inwards or outwards. Inward curved arcs can create self-intersecting forms, such as the a triquetra
The triquetra ( ; from the Latin adjective ''triquetrus'' "three-cornered") is a triangular figure composed of three interlaced arcs, or (equivalently) three overlapping '' vesicae piscis'' lens shapes. It is used as an ornamental design in ar ...
figure:
:
Tessellations
 Circular triangles can be seen in
Circular triangles can be seen in tessellation
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety o ...
.
See also
*Hyperbolic triangle
In hyperbolic geometry, a hyperbolic triangle is a triangle in the hyperbolic plane. It consists of three line segments called ''sides'' or ''edges'' and three points called ''angles'' or ''vertices''.
Just as in the Euclidean case, three poi ...
– a triangle that has straight sides in hyperbolic geometry, but is drawn as circular in some models of hyperbolic geometry
* Lune
Lune may refer to:
Rivers
*River Lune, in Lancashire and Cumbria, England
*River Lune, Durham, in County Durham, England
*Lune (Weser), a 43 km-long tributary of the Weser in Germany
* Lune River (Tasmania), in south-eastern Tasmania, Australia
P ...
and Lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
– circular digon
In geometry, a digon is a polygon with two sides (edges) and two vertices. Its construction is degenerate in a Euclidean plane because either the two sides would coincide or one or both would have to be curved; however, it can be easily visu ...
s
References
* Richard Courant, Herbert Robbins, ''What Is Mathematics?: An Elementary Approach to Ideas and Methods'', pp. 378–37External links
* * * {{elementary-geometry-stub Piecewise-circular curves Types of triangles