Church of the Nativity, Bethlehem on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Church of the Nativity, or Basilica of the Nativity,; ar, كَنِيسَةُ ٱلْمَهْد; el, Βασιλική της Γεννήσεως; hy, Սուրբ Ծննդեան տաճար; la, Basilica Nativitatis is a
''Crusader bell towers''
Over the centuries, the surrounding compound has been expanded, and today it covers approximately 12,000 square meters, comprising three different monasteries: one
''The Basilica of Nativity: Restoration works continue to reveal hidden jewels''
, posted 2016-06-21, accessed 8 April 2018 As detailed in the bilingual Greek and Latin inscription in the altar space, the mosaic decoration was made by a teamwork headed by a painter named Ephraim. Another bilingual, Latin and Syriac, inscription located in the lower half of a mosaic panel displaying an angel in the northern wall of the nave bears witness to the work of a painter named Basil, who was probably a local Syrian Melkite. The two artists collaborated within the same workshop.
 The religiously significant silver star marking the exact birthplace of Jesus was removed in October 1847 from the Grotto of the Nativity by the Greek Orthodox. The church was under the control of the Ottoman Empire, but around Christmas 1852,
The religiously significant silver star marking the exact birthplace of Jesus was removed in October 1847 from the Grotto of the Nativity by the Greek Orthodox. The church was under the control of the Ottoman Empire, but around Christmas 1852,
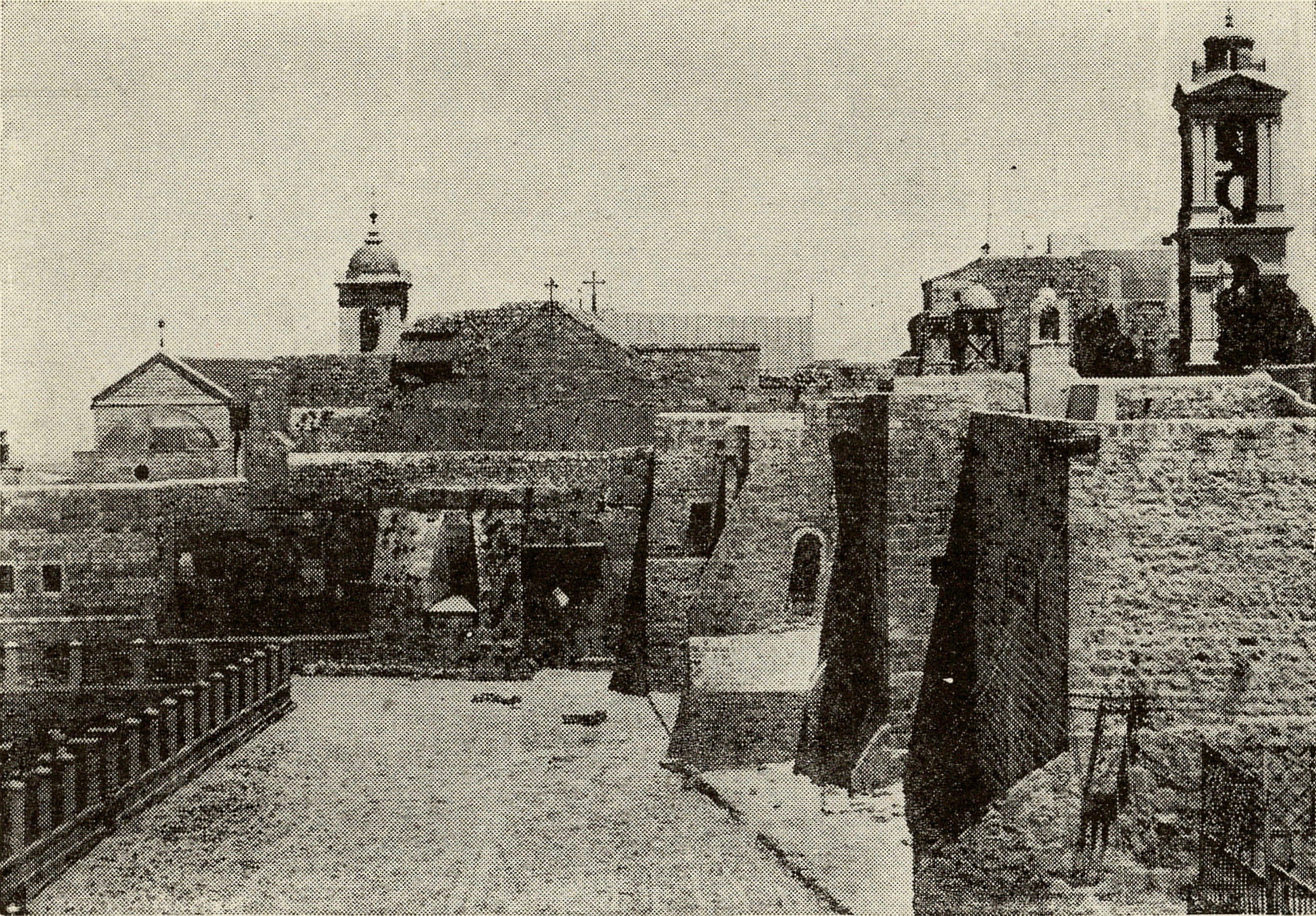
 In 1918 British governor, Colonel
In 1918 British governor, Colonel
 The centrepiece of the Nativity complex is the Grotto of the Nativity, a cave which enshrines the site where Jesus is said to have been born.
The core of the complex connected to the Grotto consists of the Church of the Nativity itself, and the adjoining Roman Catholic Church of St. Catherine north of it.
The centrepiece of the Nativity complex is the Grotto of the Nativity, a cave which enshrines the site where Jesus is said to have been born.
The core of the complex connected to the Grotto consists of the Church of the Nativity itself, and the adjoining Roman Catholic Church of St. Catherine north of it.

 The main Basilica of the Nativity is maintained by the
The main Basilica of the Nativity is maintained by the
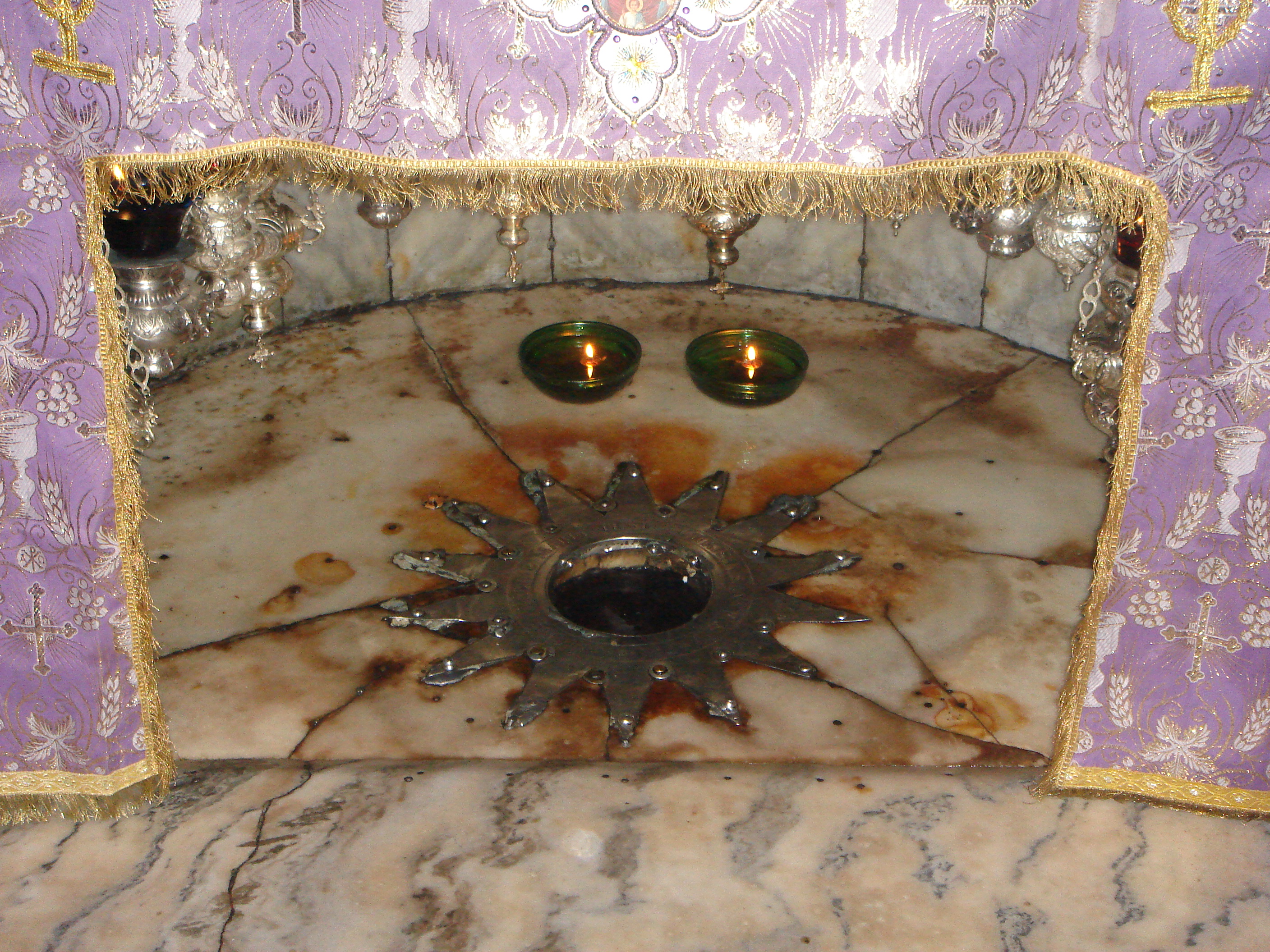 The Grotto of the Nativity, the place where Jesus is said to have been born, is an underground space which forms the crypt of the Church of the Nativity. It is situated underneath its main altar, and it is normally accessed by two staircases on either side of the chancel. The grotto is part of a network of caves, which are accessed from the adjacent Church St Catherine's. The tunnel-like corridor connecting the Grotto to the other caves is normally locked.
The cave has an eastern niche said to be the place where Jesus was born, which contains the Altar of Nativity. The exact spot where Jesus was born is marked beneath this altar by a 14-pointed silver star with the Latin inscription ''Hic De Virgine Maria Jesus Christus Natus Est-1717'' ("Here Jesus Christ was born to the Virgin Mary"-1717). It was installed by the Catholics in 1717, removed – allegedly by the Greeks – in 1847, and replaced by the Turkish government in 1853. The star is set into the marble floor and surrounded by 15 silver lamps representing the three Christian communities: six belong to the Greek Orthodox, four to the Catholics, and five to the Armenian Apostolic. The Altar of the Nativity is maintained by the
The Grotto of the Nativity, the place where Jesus is said to have been born, is an underground space which forms the crypt of the Church of the Nativity. It is situated underneath its main altar, and it is normally accessed by two staircases on either side of the chancel. The grotto is part of a network of caves, which are accessed from the adjacent Church St Catherine's. The tunnel-like corridor connecting the Grotto to the other caves is normally locked.
The cave has an eastern niche said to be the place where Jesus was born, which contains the Altar of Nativity. The exact spot where Jesus was born is marked beneath this altar by a 14-pointed silver star with the Latin inscription ''Hic De Virgine Maria Jesus Christus Natus Est-1717'' ("Here Jesus Christ was born to the Virgin Mary"-1717). It was installed by the Catholics in 1717, removed – allegedly by the Greeks – in 1847, and replaced by the Turkish government in 1853. The star is set into the marble floor and surrounded by 15 silver lamps representing the three Christian communities: six belong to the Greek Orthodox, four to the Catholics, and five to the Armenian Apostolic. The Altar of the Nativity is maintained by the
File:Christmas in Manger Square 2004.JPG, Christmas Eve 2006 in
''The Mystic Cave. A History of the Nativity Church in Bethlehem''
Rome-Brno, Viella, 2017. *Bianca e Gustav Kühnel, ''The Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem. The Crusader Lining of an Early Christian Basilica'', Regensburg, 2019. *Alessandri, Claudio (ed.), ''The Restoration of the Nativity Church in Bethlehem'', Boca Raton, 2020.
Winfried Weber, abstract of ''Reflections on the reconstruction of the Constantine Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem''. It presents a reconsideration of the Constantinian eastern ending of the church: a polygonal baptistery included in the basilica, rather than a tall octagonal tower rising high above it.
{{Authority control Nativity of Jesus Christmas events and celebrations Basilica churches in Asia Ancient churches in the Holy Land 4th-century churches 6th-century establishments in the Byzantine Empire Buildings of Justinian I Church buildings in the Kingdom of Jerusalem Status quo holy places Christianity in Bethlehem Churches in the West Bank Eastern Orthodox church buildings in the State of Palestine Roman Catholic churches in Bethlehem Roman Catholic churches in the State of Palestine World Heritage Sites in the State of Palestine 2014 fires in Asia
basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's Forum (Roman), forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building ...
located in Bethlehem
Bethlehem (; ar, بيت لحم ; he, בֵּית לֶחֶם '' '') is a city in the central West Bank, Palestine, about south of Jerusalem. Its population is approximately 25,000,Amara, 1999p. 18.Brynen, 2000p. 202. and it is the capital o ...
in the Occupied
' (Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October ...
West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
in the State of Palestine. The grotto it contains holds a prominent religious significance to Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
of various denominations as the birthplace
The place of birth (POB) or birthplace is the place where a person was born. This place is often used in legal documents, together with name and date of birth, to uniquely identify a person. Practice regarding whether this place should be a cou ...
of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
. The grotto is the oldest site continuously used as a place of worship in Christianity, and the basilica is the oldest major church in the Holy Land.
The church was originally commissioned by Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
a short time after his mother Helena's visit to Jerusalem and Bethlehem in 325–326, on the site that was traditionally considered to be the birthplace of Jesus. That original basilica was likely built between 330 and 333, being already mentioned in 333, and was dedicated on 31 May 339. It was probably destroyed by fire during the Samaritan revolts
The Samaritan revolts (c. 484–573) were a series of insurrections in Palaestina Prima province, launched by the Samaritans against the Eastern Roman Empire. The revolts were marked by great violence on both sides, and their brutal suppression ...
of the sixth century, possibly in 529, and a new basilica was built a number of years later by Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire, to Fall of Constantinople, its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. On ...
Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
(r. 527–565), who added a porch
A porch (from Old French ''porche'', from Latin ''porticus'' "colonnade", from ''porta'' "passage") is a room or gallery located in front of an entrance of a building. A porch is placed in front of the facade of a building it commands, and form ...
or narthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of early Christian and Byzantine basilicas and churches consisting of the entrance or lobby area, located at the west end of the nave, opposite the church's main altar. Traditionally the narthex ...
, and replaced the octagonal sanctuary with a cruciform
Cruciform is a term for physical manifestations resembling a common cross or Christian cross. The label can be extended to architectural shapes, biology, art, and design.
Cruciform architectural plan
Christian churches are commonly describe ...
transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building wi ...
complete with three apses, but largely preserved the original character of the building, with an atrium and a basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's Forum (Roman), forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building ...
consisting of a nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
with four side aisle
An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, certain types of buildings, such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, par ...
s.
*
The Church of the Nativity, while remaining basically unchanged since the Justinianic reconstruction, has seen numerous repairs and additions, especially from the Crusader period, such as two bell towers (now gone), wall mosaics and paintings (partially preserved).Custodia terrae sanctae, Bethlehem Sanctuary''Crusader bell towers''
Over the centuries, the surrounding compound has been expanded, and today it covers approximately 12,000 square meters, comprising three different monasteries: one
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
, one Armenian Apostolic, and one Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
, of which the first two contain bell towers built during the modern era.
The silver star marking the spot where Christ was born, inscribed in Latin, was stolen in October 1847 by Greek monks who wished to remove this Catholic item. Some assert that this was a contributing factor in the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
against the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
. Others assert that the war grew out of the wider European situation.
Since 2012, the Church of the Nativity is a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
and was the first to be listed by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
under 'Palestine'.
Since 1852 the rights of the three religious communities are ruled by Status Quo.
Base in scripture
Of the four canonical gospels, Matthew and Luke mention the birth of Jesus, both placing it in Bethlehem. Luke mentions the manger: "and she gave birth to her firstborn, a son. She wrapped him in cloths and placed him in a manger, because there was no guest room available for them."History
Holy site before Constantine (ca. 4 BC–AD 326)
The holy site known as the Nativity Grotto is thought to be the cave in whichJesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
was born. In 135, Emperor Hadrian had the site above the grotto converted into a worship place for Adonis
In Greek mythology, Adonis, ; derived from the Canaanite word ''ʼadōn'', meaning "lord". R. S. P. Beekes, ''Etymological Dictionary of Greek'', Brill, 2009, p. 23. was the mortal lover of the goddess Aphrodite.
One day, Adonis was gored by ...
, the mortal lover of Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols inclu ...
, the Greek goddess of beauty and desire. Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
claimed in 420 that the grotto had been consecrated to the worship of Adonis, and that a sacred grove was planted there in order to completely wipe out the memory of Jesus from the world.
Around AD 248, Greek philosopher Origen
Origen of Alexandria, ''Ōrigénēs''; Origen's Greek name ''Ōrigénēs'' () probably means "child of Horus" (from , "Horus", and , "born"). ( 185 – 253), also known as Origen Adamantius, was an early Christian scholar, ascetic, and theo ...
of Alexandria wrote the following about the grotto:
In Bethlehem the cave is pointed out where He was born, and the manger in the cave where He was wrapped in swaddling clothes. And the rumor is in those places, and among foreigners of the Faith, that indeed Jesus was born in this cave who is worshiped and reverenced by the Christians.
Constantinian basilica (326–529 or 556)
The firstbasilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's Forum (Roman), forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building ...
on this site was built by Emperor Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
, on the site identified by his mother, Empress Helena
Flavia Julia Helena ''Augusta'' (also known as Saint Helena and Helena of Constantinople, ; grc-gre, Ἑλένη, ''Helénē''; AD 246/248– c. 330) was an '' Augusta'' and Empress of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine th ...
and Bishop Makarios of Jerusalem. The construction started in 326 under the supervision of Makarios, who followed Constantine's orders, and was dedicated on 31 May 339—however, it had already been visited in 333 by the Bordeaux Pilgrim
The ''Itinerarium Burdigalense'' ("Bordeaux Itinerary"), also known as the ''Itinerarium Hierosolymitanum'' ("Jerusalem Itinerary"), is the oldest known Christian ''itinerarium''. It was written by the "Pilgrim of Bordeaux", an anonymous pilgrim ...
, at which time it was already in use.
Construction of this early church was carried out as part of a larger project following the First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea (; grc, Νίκαια ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I in AD 325.
This ecumenical council was the first effort ...
during Constantine's reign, aimed to build churches on the sites assumed at the time to have witnessed the crucial events in the life of Jesus. The design of the basilica centered around three major architectural sections:
#At the eastern end, an apse in a polygonal shape (broken pentagon, rather than the once proposed, but improbable full octagon), encircling a raised platform with an opening in its floor of ca. 4 metres diameter that allowed direct view of the Nativity site underneath. An ambulatory with side rooms surrounded the apse.
#A five-aisled basilica in continuation of the eastern apse, one bay shorter than the still standing Justinianic reconstruction.
#A porticoed atrium.
The structure was burned and destroyed in one of the Samaritan Revolts
The Samaritan revolts (c. 484–573) were a series of insurrections in Palaestina Prima province, launched by the Samaritans against the Eastern Roman Empire. The revolts were marked by great violence on both sides, and their brutal suppression ...
of 529 or 556, in the second of which Jews seem to have joined the Samaritans.
Justinian's basilica (6th century)
The basilica was rebuilt in its present form in the 6th century on the initiative of Byzantine EmperorJustinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renova ...
(527–565), after the destruction of either 529 or 556. It was probably accomplished after the Emperor's death, as is indicated by the dating of the wooden elements embedded in the church walls between 545 and 665, which was provided by the dendrochronological analyses made during the recent restoration works.
The Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
under Khosrau II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩, Husrō), also known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian king (shah) of Iran, ruling fr ...
invaded Palestine and conquered nearby Jerusalem in 614, but they did not destroy the structure. According to legend, their commander Shahrbaraz
Shahrbaraz (also spelled Shahrvaraz or Shahrwaraz; New Persian: ), was shah (king) of the Sasanian Empire from 27 April 630 to 9 June 630. He usurped the throne from Ardashir III, and was killed by Iranian nobles after forty days. Before usurp ...
was moved by the depiction above the church entrance of the Three Magi
The biblical Magi from Middle Persian ''moɣ''(''mard'') from Old Persian ''magu-'' 'Zoroastrian clergyman' ( or ; singular: ), also referred to as the (Three) Wise Men or (Three) Kings, also the Three Magi were distinguished foreigners in the G ...
wearing the garb of Persian Zoroastrian
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ...
priests, so he ordered that the building be spared.
Crusader period (1099-1187)
The Church of the Nativity was used as the primary coronation church for Crusader kings, from the second ruler of theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establish ...
in 1100 and until 1131. In an earlier phase starting from ca. 1130, the Crusaders promoted the redecoration of the building in the medium of wall painting: images of saints were displayed in the central and southern colonnades of the nave, largely on the initiative of private donors, as is shown by the frequent use of dedicatory inscriptions and portraits. Remnants of a cycle of narrative scenes are preserved in the north-western pillar of the choir and the south transepts, as well as in the chapel located below the bell tower.
The Crusaders undertook extensive decoration and restoration on the basilica and grounds, a process that continued until 1169, from 1165 to 1169 even through a sort of "joint venture" between the Latin Bishop of Bethlehem, Raoul, the Latin King Amalric I of Jerusalem
Amalric or Amaury I ( la, Amalricus; french: Amaury; 113611 July 1174) was King of Jerusalem from 1163, and Count of Jaffa and Ascalon before his accession. He was the second son of Melisende and Fulk of Jerusalem, and succeeded his older brot ...
and the Byzantine emperor Manuel I Komnenos.Latin Patriarchate of Jerusalem''The Basilica of Nativity: Restoration works continue to reveal hidden jewels''
, posted 2016-06-21, accessed 8 April 2018 As detailed in the bilingual Greek and Latin inscription in the altar space, the mosaic decoration was made by a teamwork headed by a painter named Ephraim. Another bilingual, Latin and Syriac, inscription located in the lower half of a mosaic panel displaying an angel in the northern wall of the nave bears witness to the work of a painter named Basil, who was probably a local Syrian Melkite. The two artists collaborated within the same workshop.

Ayyubid and Mamluk periods (1187-1516)
The Ayyubid conquest of Jerusalem and its area in 1187 was without consequences for the Nativity church. The Greek-Melkite clergy was granted the right to serve in the church, and similar concessions were given almost immediately also to other Christian denominations. In the year 1227 the church was embellished with an elegantly carved wooden door, the remnants of which can still be seen in the narthex. As detailed in its double, Armenian and Arabic inscription, it was made by two Armenian monks, Father Abraham and Father Arakel, in the times of King Hethum I of Cilicia (1224-1269) and the Emir of Damascus, and Saladin's nephew, al-Mu'azzam Isa. In 1229Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II
Frederick II (German: ''Friedrich''; Italian: ''Federico''; Latin: ''Federicus''; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusal ...
signed an agreement with Sultan al-Kamil
Al-Kamil ( ar, الكامل) (full name: al-Malik al-Kamil Naser ad-Din Abu al-Ma'ali Muhammad) (c. 1177 – 6 March 1238) was a Muslim ruler and the fourth Ayyubid sultan of Egypt. During his tenure as sultan, the Ayyubids defeated the Fifth Cr ...
which led to the restitution of the Holy Places to the Crusaders. The property of the Nativity Church came back into the possession of the Latin clergy on the condition that Muslim pilgrims may be allowed to visit the holy cave.
Latin hegemony probably lasted until the incursion of Khwarezmian Turks in April 1244. On that occasion, the church treasures, now preserved in the Terra Sancta Museum in Jerusalem, were concealed underground and rediscovered only in 1863. The church was devastated, but not destroyed, the major damage being the dilapidation of its roof.
Under Mamluk rule, the church was used by different Christian denominations, including Greeks, Armenians, Copts, Ethiopians, and Syrians. In 1347 the Franciscans of the newly established Custody of the Holy Land
, native_name_lang = Latin
, named_after=
, image = Coat_of_arms_of_the_Custodian_of_the_Holy_Land.jpg
, image_size = 200px
, alt=
, caption = Coat of arms of the Custody of the Holy Land
, map ...
were bestowed with the ownership of the former monastery of the regular canons to the north of the basilica. The Friars managed to gain a hegemonic role in Bethlehem until the Ottoman period.
Starting from the late 13th century, pilgrims lament the dilapidation of the church interior by order of Mamluk authorities: in particular, the marble revetments of the walls and floor were gradually removed, until they thoroughly disappeared.
The Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
committed resources to restore the roof in August 1448, and multiple regions contributed supplies to have the church roof repaired in 1480: England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
supplied the lead, the Second Kingdom of Burgundy
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various states located in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. The historical Burgundy correlates with the border area of France, Italy and Switzerland and includes the major modern cities of Geneva and ...
supplied the wood, and the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
provided the labor.
Ottoman period, first three centuries (16th–18th)
After the Ottoman conquest of Palestine in 1516, the Nativity church suffered from a long decay. The nave was largely abandoned and used for profane purposes. In the aim to prevent people from entering the church with horses and cattle, the main entrance was walled up and transformed into a diminutive door, known until our days as the "Door of Humility", since visitors are forced to bend down to go through it. An elevated chancel, provided with three doors, thoroughly separated the nave from the east end of the building, which was reserved for liturgical activities. The Ottoman period was characterized by increasing tensions between the different Christian denominations. In 1637, Greeks were granted hegemony by theSublime Porte
The Sublime Porte, also known as the Ottoman Porte or High Porte ( ota, باب عالی, Bāb-ı Ālī or ''Babıali'', from ar, باب, bāb, gate and , , ), was a synecdoche for the central government of the Ottoman Empire.
History
The name ...
and the Franciscans were expelled from the holy cave. In 1621 the Armenian Patriarch Grigor Paronter bought the partly ruined buildings to the south of the courtyard and established there a monastery and a hospice for pilgrims. In 1639, the Cretan painter Jeremias Palladas was commissioned by the Greek Patriarch to paint new icons to embellish the church. Further works were made in 1671 on the initiative of Patriarch Dositheos II. In 1675, Dositheos managed to gain control also of the nave, and promoted restorations of the floor and the roof, as well as the making of a new iconostasis. The Franciscans were restored in their rights in 1690, but they lose their hegemony once again in 1757, when the Greek Orthodox were granted full ownership of the upper church and the authorization to keep the keys to the grotto. Afterwards, a redecoration of the church was promoted: the nave was newly paved, the bema was provided with a solemn iconostasis and a wooden baldachin was erected over the main altar.
Because of uninterrupted water infiltrations from the roof, the Crusader mosaics started falling down, as is documented in many pilgrims' accounts from the 16th century onwards.
Nineteenth century
Earthquakes inflicted significant damage to the Church of the Nativity between 1834 and 1837. The 1834 Jerusalem earthquake damaged the church's bell tower, the furnishings in the cave on which the church is built, and other parts of its structure. Minor damages were further inflicted by a series of strong aftershocks in 1836 and theGalilee earthquake of 1837
The Galilee earthquake of 1837, often called the Safed earthquake, shook the Galilee on January 1 and is one of a number of moderate to large events that have occurred along the Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system that marks the boundary of t ...
. As part of the repairs executed by the Greek Orthodox after receiving a firman in 1842, a wall was built between the nave and aisles, used at the time as a market, and the eastern part of the church containing the choir, which allowed for worship to be continued there.
 The religiously significant silver star marking the exact birthplace of Jesus was removed in October 1847 from the Grotto of the Nativity by the Greek Orthodox. The church was under the control of the Ottoman Empire, but around Christmas 1852,
The religiously significant silver star marking the exact birthplace of Jesus was removed in October 1847 from the Grotto of the Nativity by the Greek Orthodox. The church was under the control of the Ottoman Empire, but around Christmas 1852, Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew ...
forced the Ottomans to recognise Catholic France as the "sovereign authority" over Christian holy sites in the Holy Land. The Sultan of Turkey replaced the silver star at the grotto, complete with a Latin inscription, but the Christian Orthodox Russian Empire disputed the change in authority. They cited the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca ( tr, Küçük Kaynarca Antlaşması; russian: Кючук-Кайнарджийский мир), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on 21 July 1774, in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kayn ...
and then deployed armies to the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
area. As a result, the Ottomans issued firmans essentially reversing their earlier decision, renouncing the French treaty, and restoring to the Orthodox Christians the sovereign authority over the churches of the Holy Land for the time being, thus increasing local tensions—and all this fuelled the conflict between the Russian and the Ottoman empires over the control of holy sites around the region.
Twentieth century to the present

 In 1918 British governor, Colonel
In 1918 British governor, Colonel Ronald Storrs
Sir Ronald Henry Amherst Storrs (19 November 1881 – 1 November 1955) was an official in the British Foreign and Colonial Office. He served as Oriental Secretary in Cairo, Military Governor of Jerusalem, Governor of Cyprus, and Governor of No ...
, demolished the wall erected in 1842 by the Greek Orthodox between nave and choir.
The passageway which connects St. Jerome's Cave and the Cave of the Nativity was expanded in February 1964, allowing easier access for visitors. American businessman Stanley Slotkin was visiting at the time and purchased a quantity of the limestone rubble, more than a million irregular fragments about across. He sold them to the public encased in plastic crosses, and they were advertised in infomercials in 1995.
During the Second Intifada in April 2002, the church was the site of a month-long siege in which approximately 50 armed Palestinians wanted by the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) took refuge inside the church. Christians in the church gave refuge to the fighters, giving them food, water, and protection from Israeli military forces stationed outside. Israeli media claimed that the Christians inside were being held hostage, however, parishioners inside the church say they and the church were treated with respect.
Curtains caught fire in the grotto beneath the church on 27 May 2014, which resulted in some slight damage.
The church's joint owners undertook a major renovation starting in September 2013, probably to be completed in 2021 (see also under Restoration (2013–2019)).
World Heritage Site
In 2012, the church complex became the first Palestinian site to be listed as aWorld Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
by the World Heritage Committee
The World Heritage Committee selects the sites to be listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the World Heritage List and the List of World Heritage in Danger, defines the use of the World Heritage Fund and allocates financial assistance ...
at its 36th session on 29 June. It was approved by a secret vote of 13–6 in the 21-member committee, according to UNESCO spokeswoman Sue Williams, and following an emergency candidacy procedure that by-passed the 18-month process for most sites, despite the opposition of the United States and Israel. The site was approved under criteria four and six. The decision was a controversial one on both technical and political terms. It was placed on the List of World Heritage in Danger
The List of World Heritage in Danger is compiled by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) through the World Heritage Committee according to Article 11.4 of the World Heritage Convention,Full title: ''Conv ...
from 2012 to 2019, as it was suffering from damages due to water leaks.
Restoration (2013–2019)
=Endangered status
= The basilica was placed on the 2008 Watch List of the 100 Most Endangered Sites by theWorld Monuments Fund
World Monuments Fund (WMF) is a private, international, non-profit organization dedicated to the preservation of historic architecture and cultural heritage sites around the world through fieldwork, advocacy, grantmaking, education, and trainin ...
:
The present state of the church is worrying. Many roof timbers are rotting, and have not been replaced since the 19th century. The rainwater that seeps into the building not only accelerates the rotting of the wood and damages the structural integrity of the building, but also damages the 12th-century wall mosaics and paintings. The influx of water also means that there is an ever-present chance of an electrical fire. If another earthquake were to occur on the scale of the one of 1834, the result would most likely be catastrophic. ... It is hoped that the listing will encourage its preservation, including getting the three custodians of the church—the Greek Orthodox Church, the Armenian Orthodox Church, and the Franciscan order—to work together, which has not happened for hundreds of years. The Israeli government and the Palestinian Authority would also have to work together to protect it.A Presidential committee for the restoration of the Nativity Church was appointed in 2008. In the following year, an international consortium team of experts from different Universities, under the supervision of Prof. Claudio Alessandri (University of Ferrara, Italy), was given the task of planning and coordinating the restoration works.
=Logistics and organisation
= In 2010, the Palestinian Authority announced that a multimillion-dollar restoration programme was imminent. Although a majority Muslim nation, albeit with a significant Christian minority, Palestinians consider the church a national treasure and one of their most visited tourist sites. President Mahmoud Abbas has been actively involved in the project, which is led by Ziad al-Bandak. The project is partially funded by Palestinians and conducted by a team of Palestinian and international experts.=Restoration process
= The initial phase of the restoration work was completed in early 2016. New windows have been installed, structural repairs on the roof have been completed and art works and mosaics have been cleaned and restored. The works went further with the consolidation of the narthex, the cleaning and consolidation of all wooden elements, the cleaning of wall mosaics, mural paintings, and floor mosaics. The works came to an end in 2020.=Discoveries
= Italian restoration workers uncovered a seventh surviving mosaic angel in July 2016, which was previously hidden under plaster. According to the Italian restorer Marcello Piacenti, the mosaics "are made of gold leaf placed between two glass plates" and solely "faces and limbs are drawn with small pieces of stone."Property and administration
The property rights, liturgical use and maintenance of the church are regulated by a set of documents and understandings known as the Status Quo. The church is owned by three church authorities, theGreek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
(most of the building and furnishings), the Armenian Apostolic and the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
(each of them with lesser properties). The Coptic Orthodox
The Coptic Orthodox Church ( cop, Ϯⲉⲕ̀ⲕⲗⲏⲥⲓⲁ ⲛ̀ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ ⲛ̀ⲟⲣⲑⲟⲇⲟⲝⲟⲥ, translit=Ti.eklyseya en.remenkimi en.orthodoxos, lit=the Egyptian Orthodox Church; ar, الكنيسة القبطي� ...
and Syriac Orthodox are holding minor rights of worship at the Armenian church in the northern transept, and at the Altar of Nativity.
There have been repeated brawls among monk trainees over quiet respect for others' prayers, hymns and even the division of floor space for cleaning duties. The Palestinian police are often called to restore peace and order.
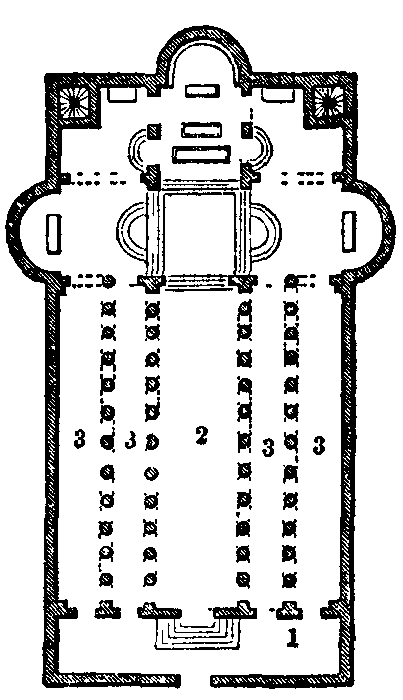
Site architecture and layout
 The centrepiece of the Nativity complex is the Grotto of the Nativity, a cave which enshrines the site where Jesus is said to have been born.
The core of the complex connected to the Grotto consists of the Church of the Nativity itself, and the adjoining Roman Catholic Church of St. Catherine north of it.
The centrepiece of the Nativity complex is the Grotto of the Nativity, a cave which enshrines the site where Jesus is said to have been born.
The core of the complex connected to the Grotto consists of the Church of the Nativity itself, and the adjoining Roman Catholic Church of St. Catherine north of it.
Outer courtyard
Bethlehem's main city square,Manger Square
Manger Square ( ar, ميدان المهد; he, כיכר האבוס) is a city square in the center of Bethlehem in Palestine. It takes its name from the manger where Jesus is said to have been born which, according to Christian tradition, took ...
, is an extension of the large paved courtyard in front of the Church of the Nativity and St Catherine's. Here crowds gather on Christmas Eve to sing Christmas carols
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year, ...
in anticipation of the midnight services.
Basilica of the Nativity

 The main Basilica of the Nativity is maintained by the
The main Basilica of the Nativity is maintained by the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem
The Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem, el, Πατριαρχεῖον Ἱεροσολύμων, ''Patriarcheîon Hierosolýmōn;'' he, הפטריארכיה היוונית-אורתודוקסית של ירושלים; ar, كنيسة الرو� ...
. It is designed like a typical Roman basilica, with five aisles formed by Corinthian columns
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order ...
, and an apse
In architecture, an apse (plural apses; from Latin 'arch, vault' from Ancient Greek 'arch'; sometimes written apsis, plural apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome, also known as an '' exedra''. ...
in the eastern end containing the sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred place, such as a shrine. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This secondary use can be categorized into human sanctuary, a sa ...
.
The basilica is entered through a very low door called the "Door of Humility."
The church's interior walls feature medieval golden mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
s once covering the side walls, which are now in large parts lost.
The original Roman-style floor of the basilica has been covered over with flagstones, but there is a trap door in the floor which opens up to reveal a portion of the original mosaic pavement from the Constantinian basilica.
There are 44 columns separating the aisles from each other and from the nave, some of which are painted with images of saints, such as the Irish monk Catald
Catald of Taranto (also Cataldus, Cathaluds, Cathaldus, Cat(t)aldo, Cathal; fl. 7th century) was an Irish monk.
Biography
Cataldus was born in Munster and became the disciple and successor of Carthage in the famous School of Lismore, County Wa ...
(fl. 7th century), the patron
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
of the Sicilian Normans, Canute IV
Canute IV ( – 10 July 1086), later known as Canute the Holy ( da, Knud IV den Hellige) or Saint Canute (''Sankt Knud''), was King of Denmark from 1080 until 1086. Canute was an ambitious king who sought to strengthen the Danish monarchy ...
(c. 1042–1086), king of Denmark, and Olaf II (995–1030), king of Norway.
The east end of the church consists of a raised chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse.
Ov ...
, closed by an apse containing the main altar and separated from the chancel by a large gilded iconostasis.
A complex array of sanctuary lamp
Malta - Mosta - Rotunda in 57 ies.
A sanctuary lamp, chancel lamp, altar lamp, everlasting light, or eternal flame is a light that shines before the altar of sanctuaries in many Jewish and Christian places of worship. Prescribed in Exodus 27:20-21 ...
s is placed throughout the entire building.
The open ceiling exposes the wooden rafters, recently restored. The previous 15th-century restoration used beams donated by King Edward IV of England, who also donated lead to cover the roof; however, this lead was taken by the Ottoman Turks, who melted it down for ammunition to use in war against Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
.
Stairways on either side of the chancel lead down to the Grotto.
Grotto of the Nativity
 The Grotto of the Nativity, the place where Jesus is said to have been born, is an underground space which forms the crypt of the Church of the Nativity. It is situated underneath its main altar, and it is normally accessed by two staircases on either side of the chancel. The grotto is part of a network of caves, which are accessed from the adjacent Church St Catherine's. The tunnel-like corridor connecting the Grotto to the other caves is normally locked.
The cave has an eastern niche said to be the place where Jesus was born, which contains the Altar of Nativity. The exact spot where Jesus was born is marked beneath this altar by a 14-pointed silver star with the Latin inscription ''Hic De Virgine Maria Jesus Christus Natus Est-1717'' ("Here Jesus Christ was born to the Virgin Mary"-1717). It was installed by the Catholics in 1717, removed – allegedly by the Greeks – in 1847, and replaced by the Turkish government in 1853. The star is set into the marble floor and surrounded by 15 silver lamps representing the three Christian communities: six belong to the Greek Orthodox, four to the Catholics, and five to the Armenian Apostolic. The Altar of the Nativity is maintained by the
The Grotto of the Nativity, the place where Jesus is said to have been born, is an underground space which forms the crypt of the Church of the Nativity. It is situated underneath its main altar, and it is normally accessed by two staircases on either side of the chancel. The grotto is part of a network of caves, which are accessed from the adjacent Church St Catherine's. The tunnel-like corridor connecting the Grotto to the other caves is normally locked.
The cave has an eastern niche said to be the place where Jesus was born, which contains the Altar of Nativity. The exact spot where Jesus was born is marked beneath this altar by a 14-pointed silver star with the Latin inscription ''Hic De Virgine Maria Jesus Christus Natus Est-1717'' ("Here Jesus Christ was born to the Virgin Mary"-1717). It was installed by the Catholics in 1717, removed – allegedly by the Greeks – in 1847, and replaced by the Turkish government in 1853. The star is set into the marble floor and surrounded by 15 silver lamps representing the three Christian communities: six belong to the Greek Orthodox, four to the Catholics, and five to the Armenian Apostolic. The Altar of the Nativity is maintained by the Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
and Armenian Apostolic churches. The significance of the 14 points on the star is to represent the three sets of 14 generations in the genealogy of Jesus Christ. First 14 from Abraham to David, then 14 from David to the Babylonian captivity, then 14 more to Jesus Christ. In the middle of the 14 pointed star is a circular hole, through which one can reach in to touch the stone that is said to be the original stone that Mary laid on when she gave birth to Jesus.
Roman Catholics are in charge of a section of the grotto known as the "Grotto of the Manger", marking the traditional site where Mary laid the newborn baby in the manger. The Altar of the Magi is located directly opposite from the manger site.
Church of St. Catherine
The adjoining Church of St. Catherine is aRoman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
church dedicated to Catherine of Alexandria
Catherine of Alexandria (also spelled Katherine); grc-gre, ἡ Ἁγία Αἰκατερίνη ἡ Μεγαλομάρτυς ; ar, سانت كاترين; la, Catharina Alexandrina). is, according to tradition, a Christian saint and virgin, ...
, built in a more modern Gothic Revival style. It has been further modernized according to the liturgical trends which followed Vatican II
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the , or , was the 21st ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church. The council met in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome for four periods (or sessions), each lasting between 8 and ...
.
This is the church where the Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem celebrates Midnight Mass on Christmas Eve. Certain customs in this Midnight Mass predate Vatican II, but must be maintained because the '' Status Quo'' was legally fixed by a firman (decree)
A firman ( fa, , translit=farmân; ), at the constitutional level, was a royal mandate or decree issued by a sovereign in an Islamic state. During various periods they were collected and applied as traditional bodies of law. The word firman com ...
in 1852 under the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, which is still in force today.
The bas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
of the Tree of Jesse
The Tree of Jesse is a depiction in art of the ancestors of Jesus Christ, shown in a branching tree which rises from Jesse of Bethlehem, the father of King David. It is the original use of the family tree as a schematic representation of a g ...
is a sculpture by Czesław Dźwigaj which was recently incorporated into the Church of St. Catherine as a gift of Pope Benedict XVI
Pope Benedict XVI ( la, Benedictus XVI; it, Benedetto XVI; german: link=no, Benedikt XVI.; born Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger, , on 16 April 1927) is a retired prelate of the Catholic church who served as the head of the Church and the soverei ...
during his trip to the Holy Land in 2009. It represents an olive tree
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
as the Tree of Jesse
The Tree of Jesse is a depiction in art of the ancestors of Jesus Christ, shown in a branching tree which rises from Jesse of Bethlehem, the father of King David. It is the original use of the family tree as a schematic representation of a g ...
, displaying the genealogy of Jesus
The New Testament provides two accounts of the genealogy of Jesus, one in the Gospel of Matthew and another in the Gospel of Luke. Matthew starts with Abraham, while Luke begins with Adam. The lists are identical between Abraham and David, but ...
from Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
through Joseph, as well as symbolism from the Old Testament. The upper portion is dominated by a crowned figure of Christ the King
Christ the King is a title of Jesus in Christianity referring to the idea of the Kingdom of God where the Christ is described as seated at the right hand of God.
Many Christian denominations consider the kingly office of Christ to be one of ...
in an open-armed pose blessing the Earth. It is situated along the passage used by pilgrims making their way to the Grotto of the Nativity.
Caves accessed from St. Catherine's
Several chapels are found in the caves accessed from St. Catherine's, including the Chapel of Saint Joseph commemorating the angel's appearance to Joseph, commanding him to flee to Egypt; the Chapel of the Innocents, commemorating the children killed by Herod; and the Chapel of SaintJerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
, in the underground cell where tradition holds he lived while translating the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts ...
into Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
(the Vulgate
The Vulgate (; also called (Bible in common tongue), ) is a late-4th-century Latin translation of the Bible.
The Vulgate is largely the work of Jerome who, in 382, had been commissioned by Pope Damasus I to revise the Gospels u ...
).
Tombs
According to a tradition not sustained by history, the tombs of four Catholic saints are said to be located beneath the Church of the Nativity, in the caves accessible from the Church of St. Catherine: *Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
, whose remains are said to have been transferred to the basilica of Santa Maria Maggiore in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
* Paula, a disciple and benefactor of Jerome
*Eustochium
Eustochium (c. 368 – September 28, 419 or 420), born ''Eustochium Julia'' at Rome, is also venerated as a saint and was an early Desert Mother. Eustochium was the daughter of Paula of Rome and the third of four daughters of the Roman Senator ...
, the daughter of Paula
*Eusebius of Cremona Eusebius of Cremona was a 5th-century monk, pre-congregational saint, and disciple of Jerome.
Life
He was born in Cremona, Italy. As a young man he travelled to Rome where he became an associate of Jerome, who was a secretary for Pope Damascus. ...
, a disciple of Jerome. A different tradition holds that he is buried in Italy
A number of ancient trough-shaped tombs can be seen in the Catholic-owned caves adjacent to the Nativity Grotto and St Jerome's Cave, some of them inside the Chapel of the Innocents; more tombs can be seen on the southern, Greek-Orthodox side of the Basilica of the Nativity, also presented as being those of the infants murdered by Herod.
According to researcher Haytham Dieck, rock-cut tombs
A rock-cut tomb is a burial chamber that is cut into an existing, naturally occurring rock formation, so a type of rock-cut architecture. They are usually cut into a cliff or sloping rock face, but may go downward in fairly flat ground. It was a ...
and bone fragments in one restricted room of the church date from the 1st century AD. In another clandestine chamber, the Cave of the Holy Innocents, skulls and other bones from as many as 2,000 people (according to Dieck) are collected, but are not clearly infantile.
Christmas in Bethlehem
The Catholic Midnight Mass in Bethlehem on Christmas Eve is broadcast around the world. Festivities begin hours earlier when dignitaries welcome the Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem at the entrance to the city, near Rachel's Tomb. Accompanied by a parade of youth organizations, he then makes his way to Manger Square, where crowds are waiting. Finally, he enters the Catholic Church of Saint Catherine for Mass, after which he leads the way to the adjacent Church of the Nativity. The patriarch carries an icon of Jesus as a child and places it on the hammered star in the cave under the basilica that marks the Nativity site. On the Orthodox Christmas Eve, 13 days later, many visitors and faithful again fill Manger Square, this time to watch processions and receptions for the religious leaders of the different Orthodox communities. Protestants also worship in Bethlehem, either at the Lutheran church or the Church of the Nativity. However, some Protestant congregations go to Beit Sahour, a village near Bethlehem.Gallery
Manger Square
Manger Square ( ar, ميدان المهد; he, כיכר האבוס) is a city square in the center of Bethlehem in Palestine. It takes its name from the manger where Jesus is said to have been born which, according to Christian tradition, took ...
File:Bethlehem-04-Church of the Nativity.jpg, The Door of Humility, main entrance into the Church
File:Bethlehem-08-Church of the Nativity.jpg, Constantine's 4th-century mosaic floor rediscovered in 1934
File:Church of the Nativity, Bethlehem, Palestine.jpg, The interior of the Church of the Nativity circa 1936, photographed by Lewis Larsson
File:Bethlehem-27-Basilica of the Nativity.jpg, Icon of Mary and Jesus ("Mary of Bethleem") near the staircase to the Nativity Grotto
File:Grotto of the Nativity Orthodox Altar.jpg, The upper part of the Altar of the Nativity
File:Birthplace of Jesus.jpg, The Altar of the Nativity, beneath which is the star marking the spot where tradition says Jesus was born
See also
*''Bayt al-Mawlid
Makkah Al Mukarramah Library is a library near the '' Masjid al-Haram'' in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. Since it is believed to stand on the spot where the Islamic prophet Muhammad was born, it is also known as ''Bayt al- Mawlid'' ( ar, بَيْت ٱل� ...
'', the house where Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
is believed to have been born
*Early Christian art and architecture
Early Christian art and architecture or Paleochristian art is the art produced by Christians or under Christian patronage from the earliest period of Christianity to, depending on the definition used, sometime between 260 and 525. In practice, id ...
*List of oldest church buildings
This article lists some but by no means all of the oldest known church buildings in the world. In most instances, buildings listed here were reconstructed numerous times and only fragments of the original buildings have survived. These surviving ...
* Mosque of Omar (Bethlehem), located nearby
*Nativity of Jesus
The nativity of Jesus, nativity of Christ, birth of Jesus or birth of Christ is described in the biblical gospels of Luke and Matthew. The two accounts agree that Jesus was born in Bethlehem in Judaea, his mother Mary was engaged to a man ...
* Palestinian Christians
References
Footnotes
Citations
Further reading
*Hugues Vincent and Félix-Marie Abel, ''Bethléem. Le sanctuaire de la Nativité'', Parigi, 1914. *Bellarmino Bagatti, ''Gli antichi edifici sacri di Betlemme in seguito agli scavi e restauri praticati dalla Custodia di Terra Santa'', Jerusalem, 1952. *Michele Bacci''The Mystic Cave. A History of the Nativity Church in Bethlehem''
Rome-Brno, Viella, 2017. *Bianca e Gustav Kühnel, ''The Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem. The Crusader Lining of an Early Christian Basilica'', Regensburg, 2019. *Alessandri, Claudio (ed.), ''The Restoration of the Nativity Church in Bethlehem'', Boca Raton, 2020.
External links
Winfried Weber, abstract of ''Reflections on the reconstruction of the Constantine Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem''. It presents a reconsideration of the Constantinian eastern ending of the church: a polygonal baptistery included in the basilica, rather than a tall octagonal tower rising high above it.
{{Authority control Nativity of Jesus Christmas events and celebrations Basilica churches in Asia Ancient churches in the Holy Land 4th-century churches 6th-century establishments in the Byzantine Empire Buildings of Justinian I Church buildings in the Kingdom of Jerusalem Status quo holy places Christianity in Bethlehem Churches in the West Bank Eastern Orthodox church buildings in the State of Palestine Roman Catholic churches in Bethlehem Roman Catholic churches in the State of Palestine World Heritage Sites in the State of Palestine 2014 fires in Asia