Chief Joseph on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Hin-mah-too-yah-lat-kekt'' (or ''Hinmatóowyalahtq̓it'' in Americanist orthography), popularly known as Chief Joseph, Young Joseph, or Joseph the Younger (March 3, 1840 – September 21, 1904), was a leader of the Wal-lam-wat-kain (Wallowa) band of
''Hin-mah-too-yah-lat-kekt'' (or ''Hinmatóowyalahtq̓it'' in Americanist orthography), popularly known as Chief Joseph, Young Joseph, or Joseph the Younger (March 3, 1840 – September 21, 1904), was a leader of the Wal-lam-wat-kain (Wallowa) band of
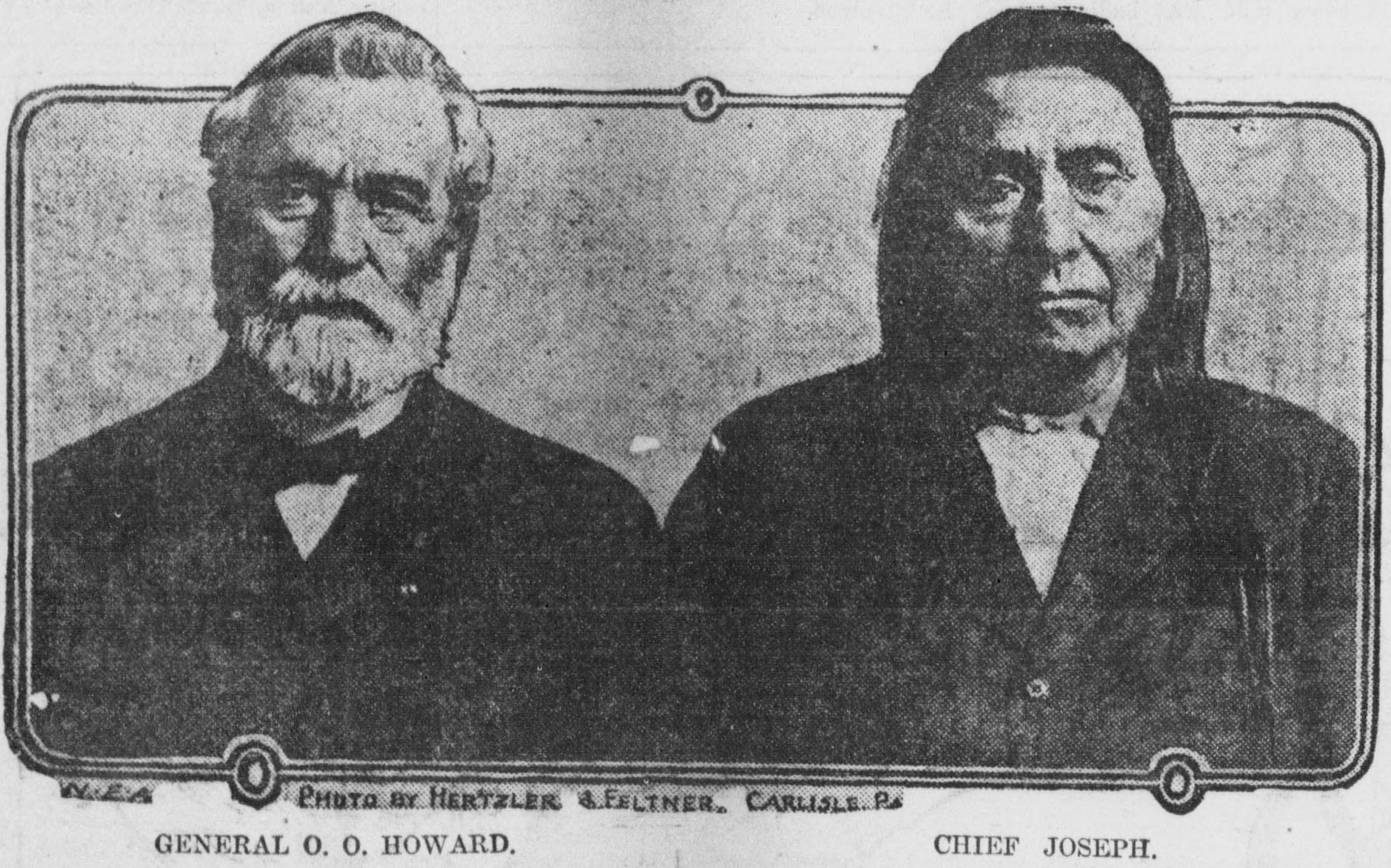
 In 1873, Joseph negotiated with the federal government to ensure his people could stay on their land in the Wallowa Valley. But in 1877, the government reversed its policy, and Army General Oliver O. Howard threatened to attack if the Wallowa band did not relocate to the Idaho reservation with the other Nez Perce. Joseph reluctantly agreed. Before the outbreak of hostilities, General Howard held a council at Fort Lapwai to try to convince Joseph and his people to relocate. Joseph finished his address to the general, which focused on human equality, by expressing his " isbelief thatthe Great Spirit Chief gave one kind of men the right to tell another kind of men what they must do." Howard reacted angrily, interpreting the statement as a challenge to his authority. When Toohoolhoolzote protested, he was jailed for five days.
The day following the council, Joseph, White Bird, and Looking Glass all accompanied Howard to examine different areas within the reservation. Howard offered them a plot of land that was inhabited by whites and Native Americans, promising to clear out the current residents. Joseph and his chieftains refused, adhering to their tribal tradition of not taking what did not belong to them. Unable to find any suitable uninhabited land on the reservation, Howard informed Joseph that his people had 30 days to collect their livestock and move to the reservation. Joseph pleaded for more time, but Howard told him he would consider their presence in the Wallowa Valley beyond the 30-day mark an act of war.
Returning home, Joseph called a council among his people. At the council, he spoke on behalf of peace, preferring to abandon his father's grave over war. Toohoolhoolzote, insulted by his incarceration, advocated war. In June 1877, the Wallowa band began making preparations for the long journey to the reservation, meeting first with other bands at Rocky Canyon. At this council, too, many leaders urged war, while Joseph continued to argue in favor of peace. While the council was underway, a young man whose father had been killed rode up and announced that he and several other young men had retaliated by killing four white settlers. Still hoping to avoid further bloodshed, Joseph and other non-treaty Nez Perce leaders began moving people away from Idaho.
In 1873, Joseph negotiated with the federal government to ensure his people could stay on their land in the Wallowa Valley. But in 1877, the government reversed its policy, and Army General Oliver O. Howard threatened to attack if the Wallowa band did not relocate to the Idaho reservation with the other Nez Perce. Joseph reluctantly agreed. Before the outbreak of hostilities, General Howard held a council at Fort Lapwai to try to convince Joseph and his people to relocate. Joseph finished his address to the general, which focused on human equality, by expressing his " isbelief thatthe Great Spirit Chief gave one kind of men the right to tell another kind of men what they must do." Howard reacted angrily, interpreting the statement as a challenge to his authority. When Toohoolhoolzote protested, he was jailed for five days.
The day following the council, Joseph, White Bird, and Looking Glass all accompanied Howard to examine different areas within the reservation. Howard offered them a plot of land that was inhabited by whites and Native Americans, promising to clear out the current residents. Joseph and his chieftains refused, adhering to their tribal tradition of not taking what did not belong to them. Unable to find any suitable uninhabited land on the reservation, Howard informed Joseph that his people had 30 days to collect their livestock and move to the reservation. Joseph pleaded for more time, but Howard told him he would consider their presence in the Wallowa Valley beyond the 30-day mark an act of war.
Returning home, Joseph called a council among his people. At the council, he spoke on behalf of peace, preferring to abandon his father's grave over war. Toohoolhoolzote, insulted by his incarceration, advocated war. In June 1877, the Wallowa band began making preparations for the long journey to the reservation, meeting first with other bands at Rocky Canyon. At this council, too, many leaders urged war, while Joseph continued to argue in favor of peace. While the council was underway, a young man whose father had been killed rode up and announced that he and several other young men had retaliated by killing four white settlers. Still hoping to avoid further bloodshed, Joseph and other non-treaty Nez Perce leaders began moving people away from Idaho.
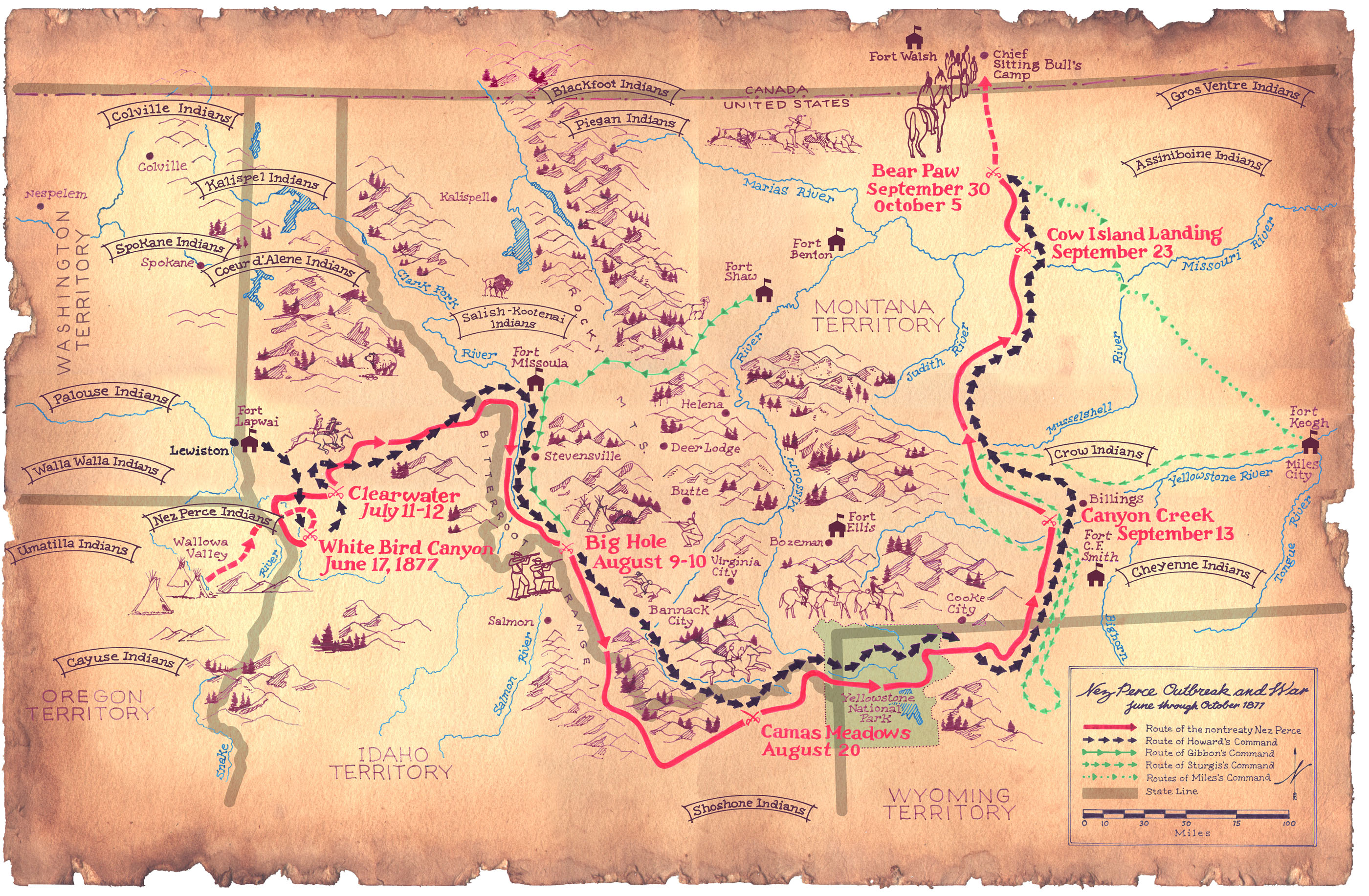 The U.S. Army's pursuit of about 750 Nez Perce and a small allied band of the
The U.S. Army's pursuit of about 750 Nez Perce and a small allied band of the
 By the time Joseph had surrendered, 150 of his followers had been killed or wounded. Their plight, however, did not end. Although Joseph had negotiated with Miles and Howard for a safe return home for his people, General Sherman overruled this decision and forced Joseph and 400 followers to be taken on unheated rail cars to
By the time Joseph had surrendered, 150 of his followers had been killed or wounded. Their plight, however, did not end. Although Joseph had negotiated with Miles and Howard for a safe return home for his people, General Sherman overruled this decision and forced Joseph and 400 followers to be taken on unheated rail cars to
 An indomitable voice of conscience for the West, still in exile from his homeland, Chief Joseph died on September 21, 1904, according to his doctor, "of a broken heart". Meany and Curtis helped Joseph's family bury their chief near the village of
An indomitable voice of conscience for the West, still in exile from his homeland, Chief Joseph died on September 21, 1904, according to his doctor, "of a broken heart". Meany and Curtis helped Joseph's family bury their chief near the village of
 *In the children's fiction book, '' Thunder Rolling in the Mountains'', by Newbery medalist Scott O'Dell and Elizabeth Hall, the story of Chief Joseph is told by Joseph's daughter, Sound of Running Feet.
*The saga of Chief Joseph is depicted in
*In the children's fiction book, '' Thunder Rolling in the Mountains'', by Newbery medalist Scott O'Dell and Elizabeth Hall, the story of Chief Joseph is told by Joseph's daughter, Sound of Running Feet.
*The saga of Chief Joseph is depicted in
 Multiple manmade and natural geographic features have been named for Joseph, such as:
*
Multiple manmade and natural geographic features have been named for Joseph, such as:
*
''Chief Joseph's Own Story''
Originally published in the ''
''Today in History: October 5''
U.S. Library of Congress
Friends of the Bear Paw, Big Hole & Canyon Creek Battlefields
- University of Washington Library
A Personal Web Tribute
– Idaho Indian Tribes Project – Nez Perce
– Political elements of Nez Perce history during the mid-1800s * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Joseph, Chief 1840 births 1904 deaths 19th-century Native Americans 20th-century Native Americans American humanitarians Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest Native American history of Oregon Native American leaders Native American people of the Indian Wars Nez Perce people Nez Perce War People from Lewiston, Idaho Native American people from Oregon
 ''Hin-mah-too-yah-lat-kekt'' (or ''Hinmatóowyalahtq̓it'' in Americanist orthography), popularly known as Chief Joseph, Young Joseph, or Joseph the Younger (March 3, 1840 – September 21, 1904), was a leader of the Wal-lam-wat-kain (Wallowa) band of
''Hin-mah-too-yah-lat-kekt'' (or ''Hinmatóowyalahtq̓it'' in Americanist orthography), popularly known as Chief Joseph, Young Joseph, or Joseph the Younger (March 3, 1840 – September 21, 1904), was a leader of the Wal-lam-wat-kain (Wallowa) band of Nez Perce
The Nez Percé (; autonym in Nez Perce language: , meaning "we, the people") are an Indigenous people of the Plateau who are presumed to have lived on the Columbia River Plateau in the Pacific Northwest region for at least 11,500 years.Ames, K ...
, a Native American tribe of the interior Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Tho ...
region of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, in the latter half of the 19th century. He succeeded his father Tuekakas (Chief Joseph the Elder) in the early 1870s.
Chief Joseph led his band of Nez Perce during the most tumultuous period in their history, when they were forcibly removed by the United States federal government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a fe ...
from their ancestral lands in the Wallowa Valley of northeastern Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
onto a significantly reduced reservation in the Idaho Territory. A series of violent encounters with white settlers in the spring of 1877 culminated in those Nez Perce who resisted removal, including Joseph's band and an allied band of the Palouse
The Palouse ( ) is a distinct geographic region of the northwestern United States, encompassing parts of north central Idaho, southeastern Washington, and, by some definitions, parts of northeast Oregon. It is a major agricultural area, prima ...
tribe, to flee the United States in an attempt to reach political asylum
The right of asylum (sometimes called right of political asylum; ) is an ancient juridical concept, under which people persecuted by their own rulers might be protected by another sovereign authority, like a second country or another ent ...
alongside the Lakota people, who had sought refuge in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
under the leadership of Sitting Bull.
At least 700 men, women, and children led by Joseph and other Nez Perce chiefs were pursued by the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
under General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
Oliver O. Howard in a fighting retreat known as the Nez Perce War
The Nez Perce War was an armed conflict in 1877 in the Western United States that pitted several bands of the Nez Perce tribe of Native Americans and their allies, a small band of the ''Palouse'' tribe led by Red Echo (''Hahtalekin'') and ...
. The skill with which the Nez Perce fought and the manner in which they conducted themselves in the face of incredible adversity earned them widespread admiration from their military opponents and the American public, and coverage of the war in U.S. newspapers led to popular recognition of Chief Joseph and the Nez Perce.
In October 1877, after months of fugitive resistance, most of the surviving remnants of Joseph's band were cornered in northern Montana Territory
The Territory of Montana was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 26, 1864, until November 8, 1889, when it was admitted as the 41st state in the Union as the state of Montana.
Original boundaries
...
, just from the Canadian border. Unable to fight any longer, Chief Joseph surrendered to the Army with the understanding that he and his people would be allowed to return to the reservation in western Idaho. He was instead transported between various forts and reservations on the southern Great Plains before being moved to the Colville Indian Reservation
The Colville Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in the northwest United States, in north central Washington, inhabited and managed by the Confederated Tribes of the Colville Reservation, which is federally recognized.
Established ...
in the state of Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, where he died in 1904.
Chief Joseph's life remains an iconic event in the history of the American Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
. For his passionate, principled resistance to his tribe's forced removal, Joseph became renowned as both a humanitarian and a peacemaker.
Background
Chief Joseph was born ''Hinmuuttu-yalatlat'' (alternatively ''Hinmaton-Yalaktit'' or ''Hin-mah-too-yah-lat-kekt''Nez Perce
The Nez Percé (; autonym in Nez Perce language: , meaning "we, the people") are an Indigenous people of the Plateau who are presumed to have lived on the Columbia River Plateau in the Pacific Northwest region for at least 11,500 years.Ames, K ...
: "Thunder Rolling Down the Mountain"], or ''Hinmatóoyalahtq'it'' Thunder traveling to higher areas" in the Wallowa Valley of northeastern Oregon. He was known as Young Joseph during his youth because his father, Tuekakas, was baptized with the same Christian name and later become known as "Old Joseph" or "Joseph the Elder".
While initially hospitable to the region's white settlers, Joseph the Elder grew wary when they demanded more Indian lands. Tensions grew as the settlers appropriated traditional Indian lands for farming and livestock. Isaac Stevens
Isaac Ingalls Stevens (March 25, 1818 – September 1, 1862) was an American military officer and politician who served as governor of the Territory of Washington from 1853 to 1857, and later as its delegate to the United States House of Represe ...
, governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
of the Washington Territory
The Territory of Washington was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from the ...
, organized a council to designate separate areas for natives and settlers in 1855. Joseph the Elder and the other Nez Perce chiefs signed the Treaty of Walla Walla
The Walla Walla Council (1855) was a meeting in the Pacific Northwest between the United States and sovereign tribal nations of the Cayuse, Nez Perce, Umatilla, Walla Walla, and Yakama. The council occurred on May 29 – June 11; ...
, with the United States establishing a Nez Perce reservation encompassing in present-day Idaho, Oregon, and Washington. The 1855 reservation maintained much of the traditional Nez Perce lands, including Joseph's Wallowa Valley. It is recorded that the elder Joseph requested that Young Joseph protect their 7.7-million-acre homeland, and guard his father's burial place.
In 1863, however, an influx of new settlers, attracted by a gold rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New ...
, led the government to call a second council. Government commissioners asked the Nez Perce to accept a new, much smaller reservation of situated around the village of Lapwai in western Idaho Territory, and excluding the Wallowa Valley. In exchange, they were promised financial rewards, schools, and a hospital for the reservation. Chief Lawyer
Hallalhotsoot, also Hal-hal-tlos-tsot or "Lawyer" (c. 1797–1876) was a leader of the Niimíipu (Nez Perce) and among its most famous, after Chief Joseph. He was the son of Twisted Hair, who welcomed and befriended the exhausted Lewis and ...
and one of his allied chiefs signed the treaty on behalf of the Nez Perce Nation, but Joseph the Elder and several other chiefs were opposed to selling their lands and did not sign.
Their refusal to sign caused a rift between the "non-treaty" and "treaty" bands of Nez Perce. The "treaty" Nez Perce moved within the new reservation's boundaries, while the "non-treaty" Nez Perce remained on their ancestral lands. Joseph the Elder demarcated Wallowa land with a series of poles, proclaiming, "Inside this boundary all our people were born. It circles the graves of our fathers, and we will never give up these graves to any man."
Leadership of the Nez Perce
Joseph the Younger succeeded his father as leader of the Wallowa band in 1871. Before his death, the latter counseled his son: Joseph commented: "I clasped my father's hand and promised to do as he asked. A man who would not defend his father's grave is worse than a wild beast." The non-treaty Nez Perce suffered many injustices at the hands of settlers and prospectors, but out of fear of reprisal from the militarily superior Americans, Joseph never allowed any violence against them, instead making many concessions to them in the hope of securing peace. A handwritten document mentioned in the Oral History of the Grande Ronde recounts an 1872 experience by Oregon pioneer Henry Young and two friends in search of acreage at Prairie Creek, east of Wallowa Lake. Young's party was surrounded by 40–50 Nez Perce led by Chief Joseph. The Chief told Young that white men were not welcome near Prairie Creek, and Young's party was forced to leave without violence. In 1873, Joseph negotiated with the federal government to ensure his people could stay on their land in the Wallowa Valley. But in 1877, the government reversed its policy, and Army General Oliver O. Howard threatened to attack if the Wallowa band did not relocate to the Idaho reservation with the other Nez Perce. Joseph reluctantly agreed. Before the outbreak of hostilities, General Howard held a council at Fort Lapwai to try to convince Joseph and his people to relocate. Joseph finished his address to the general, which focused on human equality, by expressing his " isbelief thatthe Great Spirit Chief gave one kind of men the right to tell another kind of men what they must do." Howard reacted angrily, interpreting the statement as a challenge to his authority. When Toohoolhoolzote protested, he was jailed for five days.
The day following the council, Joseph, White Bird, and Looking Glass all accompanied Howard to examine different areas within the reservation. Howard offered them a plot of land that was inhabited by whites and Native Americans, promising to clear out the current residents. Joseph and his chieftains refused, adhering to their tribal tradition of not taking what did not belong to them. Unable to find any suitable uninhabited land on the reservation, Howard informed Joseph that his people had 30 days to collect their livestock and move to the reservation. Joseph pleaded for more time, but Howard told him he would consider their presence in the Wallowa Valley beyond the 30-day mark an act of war.
Returning home, Joseph called a council among his people. At the council, he spoke on behalf of peace, preferring to abandon his father's grave over war. Toohoolhoolzote, insulted by his incarceration, advocated war. In June 1877, the Wallowa band began making preparations for the long journey to the reservation, meeting first with other bands at Rocky Canyon. At this council, too, many leaders urged war, while Joseph continued to argue in favor of peace. While the council was underway, a young man whose father had been killed rode up and announced that he and several other young men had retaliated by killing four white settlers. Still hoping to avoid further bloodshed, Joseph and other non-treaty Nez Perce leaders began moving people away from Idaho.
In 1873, Joseph negotiated with the federal government to ensure his people could stay on their land in the Wallowa Valley. But in 1877, the government reversed its policy, and Army General Oliver O. Howard threatened to attack if the Wallowa band did not relocate to the Idaho reservation with the other Nez Perce. Joseph reluctantly agreed. Before the outbreak of hostilities, General Howard held a council at Fort Lapwai to try to convince Joseph and his people to relocate. Joseph finished his address to the general, which focused on human equality, by expressing his " isbelief thatthe Great Spirit Chief gave one kind of men the right to tell another kind of men what they must do." Howard reacted angrily, interpreting the statement as a challenge to his authority. When Toohoolhoolzote protested, he was jailed for five days.
The day following the council, Joseph, White Bird, and Looking Glass all accompanied Howard to examine different areas within the reservation. Howard offered them a plot of land that was inhabited by whites and Native Americans, promising to clear out the current residents. Joseph and his chieftains refused, adhering to their tribal tradition of not taking what did not belong to them. Unable to find any suitable uninhabited land on the reservation, Howard informed Joseph that his people had 30 days to collect their livestock and move to the reservation. Joseph pleaded for more time, but Howard told him he would consider their presence in the Wallowa Valley beyond the 30-day mark an act of war.
Returning home, Joseph called a council among his people. At the council, he spoke on behalf of peace, preferring to abandon his father's grave over war. Toohoolhoolzote, insulted by his incarceration, advocated war. In June 1877, the Wallowa band began making preparations for the long journey to the reservation, meeting first with other bands at Rocky Canyon. At this council, too, many leaders urged war, while Joseph continued to argue in favor of peace. While the council was underway, a young man whose father had been killed rode up and announced that he and several other young men had retaliated by killing four white settlers. Still hoping to avoid further bloodshed, Joseph and other non-treaty Nez Perce leaders began moving people away from Idaho.
Nez Perce War
 The U.S. Army's pursuit of about 750 Nez Perce and a small allied band of the
The U.S. Army's pursuit of about 750 Nez Perce and a small allied band of the Palouse
The Palouse ( ) is a distinct geographic region of the northwestern United States, encompassing parts of north central Idaho, southeastern Washington, and, by some definitions, parts of northeast Oregon. It is a major agricultural area, prima ...
tribe, led by Chief Joseph and others, as they attempted to escape from Idaho became known as the Nez Perce War
The Nez Perce War was an armed conflict in 1877 in the Western United States that pitted several bands of the Nez Perce tribe of Native Americans and their allies, a small band of the ''Palouse'' tribe led by Red Echo (''Hahtalekin'') and ...
. Initially they had hoped to take refuge with the Crow Nation
The Crow, whose autonym is Apsáalooke (), also spelled Absaroka, are Native Americans living primarily in southern Montana. Today, the Crow people have a federally recognized tribe, the Crow Tribe of Montana, with an Indian reservation loca ...
in the Montana Territory
The Territory of Montana was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 26, 1864, until November 8, 1889, when it was admitted as the 41st state in the Union as the state of Montana.
Original boundaries
...
, but when the Crow refused to grant them aid, the Nez Perce went north in an attempt to obtain asylum with the Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
band led by Sitting Bull, who had fled to Canada following the Great Sioux War
The Great Sioux War of 1876, also known as the Black Hills War, was a series of battles and negotiations that occurred in 1876 and 1877 in an alliance of Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne against the United States. The cause of the war was the ...
in 1876. In ''Hear Me, My Chiefs!: Nez Perce Legend and History'', Lucullus V. McWhorter argues that the Nez Perce were a peaceful people that were forced into war by the United States when their land was stolen from them. McWhorter interviewed and befriended Nez Perce warriors such as Yellow Wolf, who stated, "Our hearts have always been in the valley of the Wallowa".
Robert Forczyk states in his book ''Nez Perce 1877: The Last Fight'' that the tipping point of the war was that "Joseph responded that his clan's traditions would not allow him to cede the Wallowa Valley". The band led by Chief Joseph never signed the treaty moving them to the Idaho reservation. General Howard, who was dispatched to deal with Chief Joseph and the Nez Perce, tended to believe the Nez Perce were right about the treaty: "the new treaty finally agreed upon excluded the Wallowa, and vast regions besides".
For over three months, the Nez Perce deftly outmaneuvered and battled their pursuers, traveling more than across present-day Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
, Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyomi ...
, Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the s ...
, and Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
. One of those battles was led by Captain Perry and two cavalry companies of the U.S. Army led by Captain Trimble and Lieutenant Theller, who engaged Chief Joseph and his people at White Bird Canyon on June 17, 1877. The Nez Perce repelled the attack, killing 34 soldiers, while suffering only three Nez Perce wounded. The Nez Perce continued to repel the Army's advances, eventually reaching the Clearwater River, where they united with another Nez Perce chief, Looking Glass, and his group, bringing the size of their party to 740, though only 200 of these were warriors. The final battle of the Nez Perce War occurred approximately south of the Canadian border where the Nez Perce were camped on Snake Creek near the Bears Paw Mountains, close to present-day Chinook in Blaine County, Montana
Blaine County is a county in the U.S. state of Montana. As of the 2020 census, the population was 7,044. Its county seat is Chinook. The county was named for James G. Blaine, former United States Secretary of State. It is on the north line of ...
. A U.S. Army detachment commanded by General Nelson A. Miles
Nelson Appleton Miles (August 8, 1839 – May 15, 1925) was an American military general who served in the American Civil War, the American Indian Wars, and the Spanish–American War.
From 1895 to 1903, Miles served as the last Commanding Gen ...
and accompanied by Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enr ...
scouts intercepted the Nez Perce on September 30 at the Battle of Bear Paw. After his initial attacks were repelled, Miles violated a truce and captured Chief Joseph; however, he would later be forced to exchange Chief Joseph for one of his captured officers.
General Howard arrived on October 3, leading the opposing cavalry, and was impressed with the skill with which the Nez Perce fought, using advance and rear guards, skirmish lines, and field fortifications. Following a devastating five-day siege during freezing weather, with no food or blankets and the major war leaders dead, Chief Joseph formally surrendered to General Miles on the afternoon of October 5, 1877. The battle is remembered in popular history by the words attributed to Joseph at the formal surrender:
The popular legend deflated, however, when the original pencil draft of the report was revealed to show the handwriting of the later poet and lawyer Lieutenant Charles Erskine Scott Wood
Charles Erskine Scott Wood or C.E.S. Wood (February 20, 1852January 22, 1944) was an American author, civil liberties advocate, artist, soldier, attorney, and Georgist. He is best known as the author of the 1927 satirical bestseller, '' Heavenly ...
, who claimed to have taken down the great chief's words on the spot. In the margin it read, "Here insert Joseph's reply to the demand for surrender".
Although Joseph was not technically a war chief and probably did not command the retreat, many of the chiefs who did had died. His speech brought attention, and therefore credit, his way. He earned the praise of General William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his com ...
and became known in the press as "The Red Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
". However, as Francis Haines argues in ''Chief Joseph and the Nez Perce Warrior'', the battlefield successes of the Nez Perce during the war were due to the individual successes of the Nez Perce men and not that of the fabled military genius of Chief Joseph. Haines supports his argument by citing L. V. McWhorter, who concluded "that Chief Joseph was not a military man at all, that on the battlefield he was without either skill or experience". Furthermore, Merle Wells argues in ''The Nez Perce and Their War'' that the interpretation of the Nez Perce War of 1877 in military terms as used in the United States Army's account distorts the actions of the Nez Perce. Wells supports his argument: "The use of military concepts and terms is appropriate when explaining what the whites were doing, but these same military terms should be avoided when referring to Indian actions; the United States use of military terms such as 'retreat' and 'surrender' has created a distorted perception of the Nez Perce War, to understand this may lend clarity to the political and military victories of the Nez Perce."
Aftermath
 By the time Joseph had surrendered, 150 of his followers had been killed or wounded. Their plight, however, did not end. Although Joseph had negotiated with Miles and Howard for a safe return home for his people, General Sherman overruled this decision and forced Joseph and 400 followers to be taken on unheated rail cars to
By the time Joseph had surrendered, 150 of his followers had been killed or wounded. Their plight, however, did not end. Although Joseph had negotiated with Miles and Howard for a safe return home for his people, General Sherman overruled this decision and forced Joseph and 400 followers to be taken on unheated rail cars to Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth () is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., and the oldest perma ...
, in eastern Kansas, where they were held in a prisoner of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of w ...
campsite for eight months. Toward the end of the following summer, the surviving Nez Perce were taken by rail to a reservation in the Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land as a sovereign ...
(now Oklahoma); they lived there for seven years. Many of them died of epidemic diseases while there.
In 1879, Chief Joseph went to Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
to meet with President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Rutherford B. Hayes
Rutherford Birchard Hayes (; October 4, 1822 – January 17, 1893) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 19th president of the United States from 1877 to 1881, after serving in the U.S. House of Representatives and as governo ...
and plead his people's case. Although Joseph was respected as a spokesman, opposition in Idaho prevented the U.S. government from granting his petition to return to the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Tho ...
. Finally, in 1885, Chief Joseph and his followers were granted permission to return to the Pacific Northwest to settle on the reservation around Kooskia, Idaho
Kooskia ( ) is a city in Idaho County, Idaho, United States. It is at the confluence of the South and Middle forks of the Clearwater River, combining to become the main river. The population was 607 at the 2010 census, down from 675 in 2000.
H ...
. Instead, Joseph and others were taken to the Colville Indian Reservation
The Colville Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in the northwest United States, in north central Washington, inhabited and managed by the Confederated Tribes of the Colville Reservation, which is federally recognized.
Established ...
in Nespelem, Washington
Nespelem is a town in Okanogan County, Washington, United States. The population was 236 at the 2010 census. The town is located on the Colville Indian Reservation. The name Nespelem is derived from a local Native American term meaning "large fl ...
, far from both their homeland in the Wallowa Valley and the rest of their people in Idaho.
Joseph continued to lead his Wallowa band on the Colville Reservation, at times coming into conflict with the leaders of the 11 other unrelated tribes also living on the reservation. Chief Moses
Chief Moses (born ''Kwiltalahun'', later called ''Sulk-stalk-scosum'' - "The Sun Chief") (c. 1829 – March 25, 1899) was a Native American chief of the Sinkiuse-Columbia, in what is now Washington state. The territory of his tribe extended ...
of the Sinkiuse-Columbia, in particular, resented having to cede a portion of his people's lands to Joseph's people, who had "made war on the Great Father".
In his last years, Joseph spoke eloquently against the injustice of United States policy toward his people and held out the hope that America's promise of freedom and equality might one day be fulfilled for Native Americans as well. In 1897, he visited Washington, D.C. again to plead his case. He rode with Buffalo Bill in a parade honoring former President Ulysses Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ...
in New York City, but he was a topic of conversation for his traditional headdress more than his mission.
In 1903, Chief Joseph visited Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest regio ...
, a booming young town, where he stayed in the Lincoln Hotel as guest to Edmond Meany, a history professor at the University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW, simply Washington, or informally U-Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington.
Founded in 1861, Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast; it was established in Seattl ...
. It was there that he also befriended Edward Curtis
Edward Sherriff Curtis (February 19, 1868 – October 19, 1952) was an American photographer and ethnologist whose work focused on the American West and on Native American people. Sometimes referred to as the "Shadow Catcher", Curtis traveled ...
, the photographer, who took one of his most memorable and well-known photographs. Joseph also visited President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
in Washington, D.C. the same year. Everywhere he went, it was to make a plea for what remained of his people to be returned to their home in the Wallowa Valley, but it never happened.
Death
 An indomitable voice of conscience for the West, still in exile from his homeland, Chief Joseph died on September 21, 1904, according to his doctor, "of a broken heart". Meany and Curtis helped Joseph's family bury their chief near the village of
An indomitable voice of conscience for the West, still in exile from his homeland, Chief Joseph died on September 21, 1904, according to his doctor, "of a broken heart". Meany and Curtis helped Joseph's family bury their chief near the village of Nespelem, Washington
Nespelem is a town in Okanogan County, Washington, United States. The population was 236 at the 2010 census. The town is located on the Colville Indian Reservation. The name Nespelem is derived from a local Native American term meaning "large fl ...
, where many of his tribe's members still live.
Legacy
The Chief Joseph band of Nez Perce who still live on the Colville Reservation bear his name in tribute.Notable dramatic works
*'' I Will Fight No More Forever'' (1975), an historical drama film starring Ned Romero. *'' Buffalo Bill and the Indians, or Sitting Bull's History Lesson'' (1976), Robert Altman's revisionist Western film based on theBroadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
play '' Indians''.
*From 1969 to 1970, actor George Mitchell played Chief Joseph on Broadway
Broadway may refer to:
Theatre
* Broadway Theatre (disambiguation)
* Broadway theatre, theatrical productions in professional theatres near Broadway, Manhattan, New York City, U.S.
** Broadway (Manhattan), the street
**Broadway Theatre (53rd Stree ...
in the play '' Indians''.
Literary works
*Merrill Beal's ''I Will Fight No More Forever: Chief Joseph and the Nez Perce War'' (2000) was positively received both regionally and nationally. *Chief Joseph is sympathetically portrayed in Will Henry's novel of the Nez Perce War, ''From Where the Sun Now Stands'' (1959). The book won the 1960Western Writers of America
Western Writers of America (WWA), founded 1953, promotes literature, both fictional and nonfictional, pertaining to the American West. Although its founders wrote traditional Western fiction, the more than 600 current members also include histori ...
Spur Award for Best Novel of the West.
*Helen Hunt Jackson
Helen Hunt Jackson (pen name, H.H.; born Helen Maria Fiske; October 15, 1830 – August 12, 1885) was an American poet and writer who became an activist on behalf of improved treatment of Native Americans by the United States government. She de ...
recorded one early Oregon settler's tale of her encounter with Joseph in her ''Glimpses of California and the Missions'' (1902):
 *In the children's fiction book, '' Thunder Rolling in the Mountains'', by Newbery medalist Scott O'Dell and Elizabeth Hall, the story of Chief Joseph is told by Joseph's daughter, Sound of Running Feet.
*The saga of Chief Joseph is depicted in
*In the children's fiction book, '' Thunder Rolling in the Mountains'', by Newbery medalist Scott O'Dell and Elizabeth Hall, the story of Chief Joseph is told by Joseph's daughter, Sound of Running Feet.
*The saga of Chief Joseph is depicted in Robert Penn Warren
Robert Penn Warren (April 24, 1905 – September 15, 1989) was an American poet, novelist, and literary critic and was one of the founders of New Criticism. He was also a charter member of the Fellowship of Southern Writers. He founded the liter ...
's poem "Chief Joseph of the Nez Perce" (1982).
*Chief Joseph appears in '' The Secret History of Twin Peaks'' by Mark Frost
Mark Frost (born November 25, 1953) is an American novelist, screenwriter, film-and-television producer and director. He is the co-creator of the mystery television series ''Twin Peaks'' (1990–1991; 2017) and was a writer and executive story ...
. In his speech, Chief Joseph says that he visited "the place known to our is tribe'sancestors, seldom visited, the place of smoke by the great falls and twin mountains, to seek the aid of the Great Spirit Chief in this time of need" in a speech he gives to his people before the retreat, in 1877. Thus he's important to the novel because he is the leader of the Nez Perce
The Nez Percé (; autonym in Nez Perce language: , meaning "we, the people") are an Indigenous people of the Plateau who are presumed to have lived on the Columbia River Plateau in the Pacific Northwest region for at least 11,500 years.Ames, K ...
, the people who keep the peace in the woods of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Tho ...
(Twin Peaks
''Twin Peaks'' is an American mystery serial drama television series created by Mark Frost and David Lynch. It premiered on ABC on April 8, 1990, and originally ran for two seasons until its cancellation in 1991. The show returned in 2017 for ...
) before the settlers flood in and industrialize
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econom ...
the area.
Memorials
 Multiple manmade and natural geographic features have been named for Joseph, such as:
*
Multiple manmade and natural geographic features have been named for Joseph, such as:
* Chief Joseph Mountain
Chief Joseph Mountain is a mountain summit located in Wallowa County, Oregon, Wallowa County, Oregon, US.
Description
Chief Joseph Mountain is located five miles south of Joseph, Oregon, in the Wallowa Mountains. It is set within the Eagle Ca ...
, near Joseph, Oregon
*Chief Joseph middle school in Richland, WA
* Chief Joseph Elementary School in Portland, OR
*A statue of Young Chief Joseph in Enterprise, Oregon
Enterprise is a city in and the county seat of Wallowa County, Oregon, United States. The population was 1,940 in the 2010 census.
*A wall-mounted quote by Joseph in The American Adventure in the World Showcase pavilion of Walt Disney World
The Walt Disney World Resort, also called Walt Disney World or Disney World, is an entertainment resort complex in Bay Lake and Lake Buena Vista, Florida, United States, near the cities of Orlando and Kissimmee. Opened on October 1, 1971, ...
's Epcot
Epcot, stylized in all uppercase as EPCOT, is a theme park at the Walt Disney World Resort in Bay Lake, Florida. It is owned and operated by The Walt Disney Company through its Parks, Experiences and Products division. Inspired by an unreal ...
* Chief Joseph Pass in Montana
*Chief Joseph Elementary School in Great Falls, Montana.
*The city of Joseph, Oregon, home of Chief Joseph Days festival.
* Joseph Canyon, in northern Wallowa County, Oregon
Wallowa County () is the northeastern most county in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2020 census, the population was 7,391, making it Oregon's fifth-least populous county. Its county seat is Enterprise. According to ''Oregon Geographic Nam ...
, and southern Asotin County, Washington
Asotin County () is a county in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, the population was 22,285. The county seat is at Asotin, and its largest city is Clarkston. The county was created out of Garfield County in 1883 and deriv ...
*Joseph Creek, on the Oregon–Washington border
* Chief Joseph Scenic Byway in Wyoming
*Chief Joseph Dam
The Chief Joseph Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River, upriver from Bridgeport, Washington. The dam is upriver from the mouth of the Columbia at Astoria, Oregon. It is operated by the USACE Chief Joseph Dam Project Office and the ...
on the Columbia River in Washington, the second-largest hydroelectric power producer in the U.S. and the only dam in the Northwest named after an American Indian
*Chief Joseph is depicted on previously issued $200 Series I U.S. savings bonds
*Chief Joseph Ranch south of Darby, Montana is depicted as the Dutton Ranch on the hit series Yellowstone, starring Kevin Coster.
Tributes in music
In 2014, Micky and the Motorcars released the album "Hearts from Above", which included the song "From Where the Sun Now Stands". The song contains several references to his famous speech. Swedish country pop group Rednex sampled a part of his famous speech in their 2000 single '' The Spirit of the Hawk,'' which became a worldwide hit. In his 2000 release "Something Old, Something New, Something Borrowed...And Some Blues,"Dan Fogelberg
Daniel Grayling Fogelberg (August 13, 1951 – December 16, 2007) was an American musician, songwriter, composer, and multi-instrumentalist. He is known for his 1970s and 1980s songs, including " Longer" (1979), " Same Old Lang Syne" (1980), and ...
mentioned Chief Joseph in the song "Don't Let That Sun Go Down," which was recorded live in 1994 in Knoxville, TN.
In 1983, Fred Small released "The Heart of the Appaloosa".
War shirt
In June 2012, Chief Joseph's 1870s war shirt was sold to a private collection for the sum of $877,500.Halls of fame
In 1973, he was inducted into theHall of Great Westerners
The Hall of Great Westerners was established by the National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum in 1958. Located in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, U.S., the Hall was created to celebrate the contributions of more than 200 men and women of the American ...
of the National Cowboy & Western Heritage Museum.
See also
References
Further reading
* Aoki, Haruo (1994). ''Nez Perce Dictionary''. University of California Publications in Linguistics, Volume 122. Berkeley and Los Angeles:University of California Press
The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by facult ...
.
* Chief Joseph''Chief Joseph's Own Story''
Originally published in the ''
North American Review
The ''North American Review'' (NAR) was the first literary magazine in the United States. It was founded in Boston in 1815 by journalist Nathan Hale and others. It was published continuously until 1940, after which it was inactive until revived at ...
'', April 1879.
* Henry, Will (1976). ''From Where the Sun Now Stands''. New York: Bantam Books. .
* Nerburn, Kent (2005). ''Chief Joseph & the Flight of the Nez Perce: The Untold Story of an American Tragedy''. HarperOne. .
External links
''Today in History: October 5''
U.S. Library of Congress
Friends of the Bear Paw, Big Hole & Canyon Creek Battlefields
- University of Washington Library
A Personal Web Tribute
– Idaho Indian Tribes Project – Nez Perce
– Political elements of Nez Perce history during the mid-1800s * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Joseph, Chief 1840 births 1904 deaths 19th-century Native Americans 20th-century Native Americans American humanitarians Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest Native American history of Oregon Native American leaders Native American people of the Indian Wars Nez Perce people Nez Perce War People from Lewiston, Idaho Native American people from Oregon