Chichimec War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Chichimeca War (1550–90) was a military conflict between the
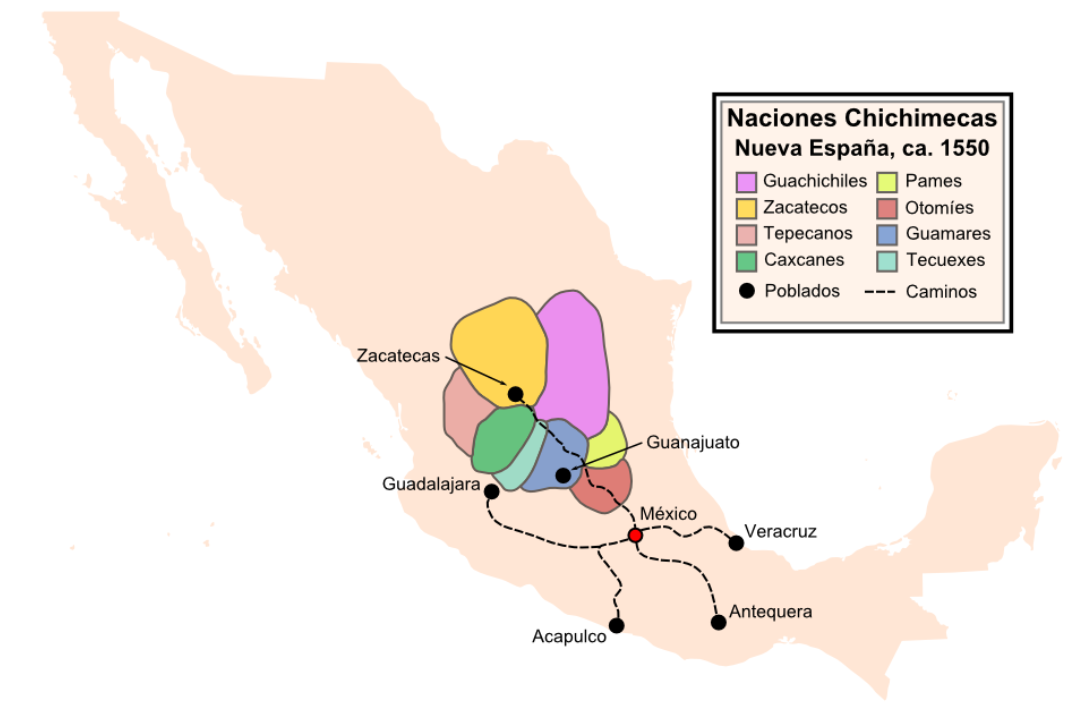
 On September 8, 1546, natives near the
On September 8, 1546, natives near the
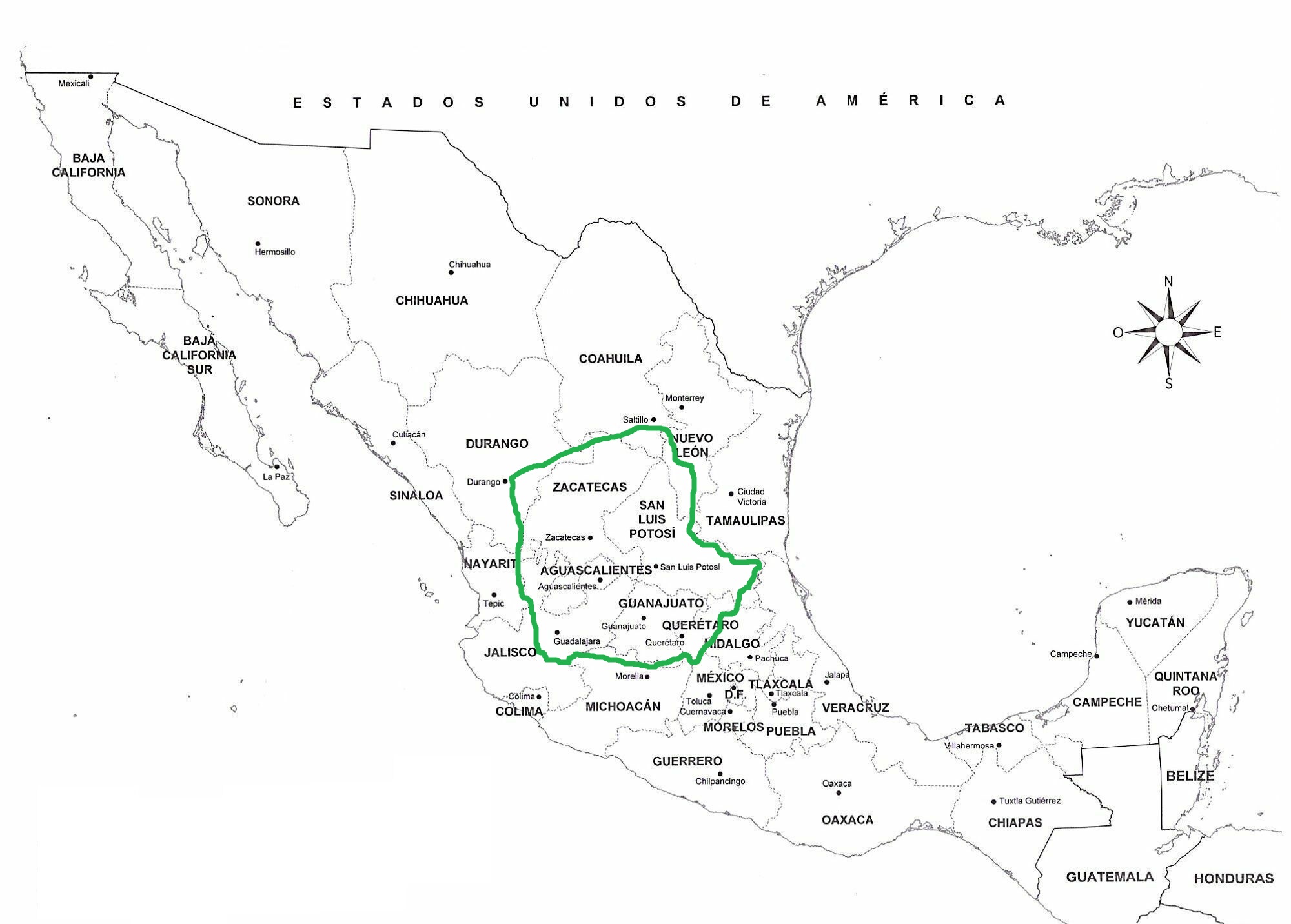 The Chichimecas were nomadic and semi-nomadic people who occupied the large desert basin stretching from present day
The Chichimecas were nomadic and semi-nomadic people who occupied the large desert basin stretching from present day
 The conflict proved much more difficult and enduring than the Spanish anticipated. The first outbreak of hostilities was in late 1550 when Zacatecos attacked supply routes of Purépecha. A few days later they were attacking Spanish colonies less than south of modern-day Zacatecas. In 1551 the Guachichile and Guamares joined in, killing 14 Spanish soldiers at an outpost of
The conflict proved much more difficult and enduring than the Spanish anticipated. The first outbreak of hostilities was in late 1550 when Zacatecos attacked supply routes of Purépecha. A few days later they were attacking Spanish colonies less than south of modern-day Zacatecas. In 1551 the Guachichile and Guamares joined in, killing 14 Spanish soldiers at an outpost of
 In 1584, the Bishop of Guadalajara made a proposal for a "Christian remedy" to the war: the establishment of new towns with priests, soldiers, and friendly Indians to gradually Christianize the Chichimecas. The Viceroy, Alvaro Manrique de Zuniga, followed this idea in 1586 with a policy of removing many Spanish soldiers from the frontier as they were considered more a provocation than a remedy. The Viceroy opened negotiations with Chichimeca leaders and negotiated tools, food, clothing, and land to encourage them through "gentle persuasion". He forbade further failing military operations. One of the key people behind these negotiations was
In 1584, the Bishop of Guadalajara made a proposal for a "Christian remedy" to the war: the establishment of new towns with priests, soldiers, and friendly Indians to gradually Christianize the Chichimecas. The Viceroy, Alvaro Manrique de Zuniga, followed this idea in 1586 with a policy of removing many Spanish soldiers from the frontier as they were considered more a provocation than a remedy. The Viceroy opened negotiations with Chichimeca leaders and negotiated tools, food, clothing, and land to encourage them through "gentle persuasion". He forbade further failing military operations. One of the key people behind these negotiations was
About 20,000 of them live in an isolated area on the borders of Jalisco and
A Look into Guanajuato's Past
."
The History of Zacatecas
'. Houston Institute for Culture. 2004. *Schmal, John P.
'. 2004. *Hernandez, Manuel G. "Cartas de Indias: Publicalas Por Primera Vez" Ministerio De Formento 1877. 326–340. Madrid. Print. *Santa Maria, Guillermo de. "Guerra de los Chichimecas : Mexico 1575 – Zirosto 1580" Paleography by Carrillo Cazares, Alberto. 2nd Ed. University of Guadalajara, Michoacan College, University of Norte, University Los Lagos, 220. San Luis College 2003. Print. (1) Translated from: "Despues estros mismos Zacatecas, dende a pocos dias, hicieron otro salto en unas recuas de Cristobal de Onate y de Diego de Ybarra, una legua antes Zenagulla del Monte y tres de Zacatecas, en que hicieron muncho dano." (2) Translated from: "Es que se haga alguna cantidad de soldados, a los quales se les pague sueldo, en virtue de una Real cedula de V.M. en que V.M. manda se pague, la tercia parte, de la Real hazienda, y las otras does, por los mineros y personas interesads" (3) Translated from: "ninguno puede sustentar la Guerra con dos ni tres cauallos, y la costa es muy grande, asi de las armas como de los cauallo y nunguno puede sustentar la Guerra con dos nit res cauallos, y la costa es muy grande, asi de las armas como de los cauallos y comida, que cada dia se les mueren y se los matan, y es el trabajo grandisimo . . . sienten tanto todos la paga de lo que les toca, que, si yo lo puediese remidar con uender quanto tengo, lo haria, por euitar el descontento de la gente, que a todos les parece que se a de pagar de la Real caja" (4) Translated from: "Ya he dado quenta particular a V.M. de lo que toca a la Guerra de los chichimecas, y del incombiniente que se sigue a todas las minas de aquel districto, en que aquellos indos anden tan lebantados y con tanto numero y desberguanca; y demas, desto, soy informado que en Zacatecas ay munchas minas ceradas" {{Authority control 1546 in New Spain Colonial Mexico History of Mesoamerica Mesoamerican warfare Rebellions against the Spanish Empire Wars involving the indigenous peoples of North America Conflicts in 1546 History of Aguascalientes History of Guanajuato History of Jalisco History of San Luis Potosí History of Zacatecas Battles won by indigenous peoples of the Americas
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
and the Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajio region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that d ...
Confederation established in the territories today known as the Central Mexican Plateau
The Central Mexican Plateau, also known as the Mexican Altiplano ( es, Altiplanicie Mexicana), is a large arid-to-semiarid plateau that occupies much of northern and central Mexico. Averaging above sea level, it extends from the United States b ...
, called by the Conquistadores La Gran Chichimeca La Gran Chichimeca was a term used by the Spanish ''conquistadores'' of the 16th century to refer to an area of the northern central Mexican ''altiplano'' (plateau), a territory which today is encompassed by the modern Mexican states of Jalisco, A ...
. The epicenter of the hostilities was the region now called the Bajío. The Chichimeca War is recorded as the longest and most expensive military campaign confronting the Spanish Empire and indigenous people in Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica ...
. The forty-year conflict was settled through several peace treaties driven by the Spaniards which led to the pacification and, ultimately, the streamlined integration of the native populations into the New Spain society.
The Chichimeca War (1550-1590) began eight years after the two-year Mixtón War
The Mixtón War (1540-1542) was a rebellion by the Caxcan people of northwestern Mexico against the Spanish conquerors. The war was named after Mixtón, a hill in Zacatecas which served as an Indigenous stronghold.
The Caxcanes
Although othe ...
. It can be considered a continuation of the rebellion as the fighting did not come to a halt in the intervening years. Unlike in the Mixtón rebellion, the Caxcan
The Caxcan were a partly nomadic indigenous people of Mexico. Under their leader, Tenamaztle, the Caxcan were allied with the Zacatecos against the Spaniards during the Mixtón Rebellion in 1540-42. During the rebellion, they were described as ...
es were now allied with the Spanish. The war was fought in what are the present-day Mexican states of Zacatecas
, image_map = Zacatecas in Mexico (location map scheme).svg
, map_caption = State of Zacatecas within Mexico
, coordinates =
, coor_pinpoint =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type ...
, Guanajuato, Aguascalientes, Jalisco, Queretaro, and San Luis Potosí.
Prelude

 On September 8, 1546, natives near the
On September 8, 1546, natives near the Cerro de la Bufa
Bufa Hill or El Cerro de la Bufa is a hill found east of historic downtown Zacatecas City, Zacatecas, Mexico, of historic and cultural significance in the Zacatecas state.
Name
The origin of Bufa Hill's name is disputed. What is, perhaps, the b ...
in what would become the city of Zacatecas showed the Spaniard Juan de Tolosa several pieces of silver-rich ore. News of the silver strike soon spread across New Spain. The dream of quick wealth caused a large number of Spaniards to migrate from southern Mexico to the present-day city of Zacatecas in the heartland of La Gran Chichimeca. Soon the mines of San Martín, Chalchihuites, Avino, Sombrerete, Fresnillo, Mazapil, and Nieves were established. The Chichimeca nations resented the intrusions by the Spanish on their sovereign ancestral lands. Spanish soldiers soon began raiding native territory trying to acquire slaves for the mines. To supply and communicate with the mines in and near Zacatecas, new roads were built from Querétaro and Jalisco across Chichimeca lands. The caravans full of goods along the roads were economic targets for Chichimecan warriors.
Chichimecas
 The Chichimecas were nomadic and semi-nomadic people who occupied the large desert basin stretching from present day
The Chichimecas were nomadic and semi-nomadic people who occupied the large desert basin stretching from present day Saltillo
Saltillo () is the capital and largest city of the northeastern Mexican state of Coahuila and is also the municipal seat of the municipality of the same name. Mexico City, Monterrey, and Saltillo are all connected by a major railroad and highwa ...
and Durango in the north to Querétaro and Guadalajara in the south. Within this area of about , the Chichimecas lived primarily by hunting and gathering, especially mesquite beans, the edible parts of the agave plants, and the fruit (tunas) and leaves of cactus. In favored areas some of the Chichimeca grew corn and other crops. Chichimeca population is hard to estimate, although based on the average density of nomadic cultures they probably numbered 30,000 to 60,000. The Chichimecas lived in rancherias of crude shelters or natural shelters such as caves, frequently moving from one area to another to take advantage of seasonal foods and hunting. The Chichimeca referred to themselves as "Children of the Wind", living religiously from the natural land. The characteristics most noted about them by the Spanish was that both women and men wore little clothing, grew their hair long, and painted and tattooed their bodies. They were often accused of cannibalism, although this accusation has been disputed, due to the Spanish attempt to smear natives as savages in order to justify forced conversion to Catholicism by Spain during the Mexican Inquisition
The Mexican Inquisition was an extension of the Spanish Inquisition into New Spain. The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was not only a political event for the Spanish, but a religious event as well. In the early 16th century, the Reformat ...
.
The Chichimecas Confederation consisted of four main nations: Guachichiles, Pames, Guamares, and Zacatecos. These nations had decentralized governments, and were more of independent states. Due to decentralized political unity, their territories overlapped and other Chichimecs joined one or another in raids.
The Guachichil
The Guachichil, Cuauchichil, or Quauhchichitl, are an Indigenous people of Mexico. Pre-contact, they occupied the most extensive territory of all the indigenous Chichimeca Nations tribes in pre-Columbian Central Mexico.
The Guachichiles roamed t ...
es' territory centered on the area around what would become the city of San Luis Potosí. They seem to have been the most numerous of the four ethnic groups and the de facto leaders of the Chichimecas. Their name meant "Red Colored Hair" from a pigment that they also applied to their skin and clothing. Living in close proximity to the silver road between Querétaro and Zacatecas, they were the most feared of the native raiders.
The Pames lived north of present-day Mexican state of Querétaro and south and east of the Guachichiles. They were the least warlike and militant of the Chichimecas. They had absorbed some of the religious and cultural practices of the more urbanized native nations.
The Guamare
The Guamare people were an indigenous people of Mexico, who were established mostly in Guanajuato and at the border of Jalisco. They were part of the Chichimecas, a group of a nomadic hunter-gatherer culture and called themselves Children of the ...
s lived mostly in present-day Mexican state of Guanajuato. They possibly had more political unity than other Chichimecas and were considered by one writer as the most "treacherous and destructive of all the Chichimecas and the most astute." The Guamares and the mestizo population of Dolores Hidalgo
Dolores Hidalgo (; in full, Dolores Hidalgo Cuna de la Independencia Nacional, en, Dolores Hidalgo Birthplace of exicanNational Independence) is the name of a city and the surrounding municipality in the north-central part of the Mexican state o ...
, on the silver road to San Miguel de Allende
San Miguel de Allende () is the principal city in the municipality of San Miguel de Allende, located in the far eastern part of Guanajuato, Mexico. A part of the Bajío region, the city lies from Mexico City, 86 km (53 mi) from Queré ...
, also initiated the Mexican War for Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
, then shortly after sent a battalion of reinforcements to the Battle of Puebla
The Battle of Puebla ( es, Batalla de Puebla; french: Bataille de Puebla) took place on 5 May, Cinco de Mayo, 1862, near Puebla de Zaragoza during the Second French intervention in Mexico. French troops under the command of Charles de Lorencez ...
during the French intervention in Mexico.
The Zacateco
The Zacatecos (or Zacatecas) is the name of an indigenous group, one of the peoples called Chichimecas by the Aztecs. They lived in most of what is now the state of Zacatecas and the northeastern part of Durango. They have many direct descendan ...
s lived in the present-day Mexican states of Zacatecas
, image_map = Zacatecas in Mexico (location map scheme).svg
, map_caption = State of Zacatecas within Mexico
, coordinates =
, coor_pinpoint =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type ...
and Durango. They had participated in the earlier Mixtón War
The Mixtón War (1540-1542) was a rebellion by the Caxcan people of northwestern Mexico against the Spanish conquerors. The war was named after Mixtón, a hill in Zacatecas which served as an Indigenous stronghold.
The Caxcanes
Although othe ...
and thus were experienced fighters against the Spanish. Some of the Zacatecos grew maize; others were nomadic.
The nomadic culture of the Chichimecas made it difficult for the Spanish to defeat them. The bow was their principal weapon and one experienced observer said the Zacatecos were "the best archers in the world." Their bows were short, usually less than four feet long, their arrows were long and thin and made of reed and tipped with obsidian, volcanic rock sharper than a modern-day razor. Despite the fragility of the obsidian arrows they had excellent penetrating qualities, even against Spanish armor which was ''de rigueur'' for soldiers fighting the Chichimeca. Many-layered buckskin armor was preferred to chain mail
Chain mail (properly called mail or maille but usually called chain mail or chainmail) is a type of armour consisting of small metal rings linked together in a pattern to form a mesh. It was in common military use between the 3rd century BC and ...
as obsidian arrows penetrated the links of the mail.
The Chichimeca bow and arrow was expertly crafted allowing for penetration of Spanish armor. There are two Spanish accounts of the Chichimeca's archery skill that Powell writes in his book:
On one occasion I saw them throw an orange into the air, and they shot into it so many arrows that, having held it in the air for much time, it finally fell in minute pieces" (Powell 48). "One of don Alonso de Castilla's soldiers had an arrow pass through the head of his horse, including a crownpiece of double buckskin and metal, and into his chest, so he fell with the horse dead on the ground 'this was seen by many who are still living' (Powell 48).
The Chichimeca were a nomadic culture making them very mobile and experts of rough terrain with vegetation filled (mostly cactus) land in which they always looked for hiding spots. "His long use of the food native to the Gran Chichimeca gave him far greater mobility than the sedentary invader, who was tied to domesticated livestock, agriculture, and imported supplies. The Chichimeca could and did cut off these supplies, destroy the livestock, and thus paralyze the economic and military vitality of the invaders; this was seldom possible in reverse" (Powell 44). They attacked in small groups ranging from five to two hundred warriors. In one account, with only fifty Zacateco warriors, the Chichimeca killed two hundred Spaniard soldiers in one battle. They had no shortage of raiding parties because of the highly valued supplies attracting warriors from far off allowing for the highest quality of trade goods.
As the war escalated, both the Spanish and Chichimeca adapted and bettered their defensive and offensive tactics. "He he Chichimecasent spies into Spanish towns for appraisal of the enemy's plans and strength; he developed a far-flung system of lookouts and scouts (atalays); and, in major attacks, settlements were softened by preliminary and apparently systematic killing and stealing of horses and other livestock, this being an attempt, sometimes successful, to change his intended victim from horseman to foot soldier" (Powell 46). When they attacked they used a very good tactic that terrified the animals and scared the Spanish. The Guachichil especially would disguise themselves as grotesque animals using animal heads and paint then yelled like crazed beasts making the Spanish lose control of horses and livestock. The Spanish started to set up many forts, bought mercenaries, and tried to use as many slaves as they could.
Chichimeca battle tactics were mostly ambushes and raids on the Spanish. Some of their raids were conducted by up to 200 men, groups of 40 to 50 warriors were more common, about the size of a modern infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
company or platoon with attachments, respectively. During the war, the Chichimecas learned to ride horses and use them in war. This was perhaps the first time that the Spanish in North America faced mounted Native warriors. The undeniable advantage for the Spanish was their use of horses and other animals of burden that they had introduced to the Americas. Horses were unknown to the Americas before the Spanish imported them in 1519.
Course of the war
 The conflict proved much more difficult and enduring than the Spanish anticipated. The first outbreak of hostilities was in late 1550 when Zacatecos attacked supply routes of Purépecha. A few days later they were attacking Spanish colonies less than south of modern-day Zacatecas. In 1551 the Guachichile and Guamares joined in, killing 14 Spanish soldiers at an outpost of
The conflict proved much more difficult and enduring than the Spanish anticipated. The first outbreak of hostilities was in late 1550 when Zacatecos attacked supply routes of Purépecha. A few days later they were attacking Spanish colonies less than south of modern-day Zacatecas. In 1551 the Guachichile and Guamares joined in, killing 14 Spanish soldiers at an outpost of San Miguel de Allende
San Miguel de Allende () is the principal city in the municipality of San Miguel de Allende, located in the far eastern part of Guanajuato, Mexico. A part of the Bajío region, the city lies from Mexico City, 86 km (53 mi) from Queré ...
and forcing abandonment. Other raids near Tlaltenango were reported to have killed 120 Spanish within a few months. Some crucial raids of the early years of the war took place in 1553 and 1554 when many wagon trains on the road to Zacatecas were attacked, all the Spanish en route were killed, and the very substantial sums of 32,000 and 40,000 pesos in goods taken or destroyed. (By comparison, the annual salary of a Spanish soldier was only 300 pesos.) By the end of 1561 it was estimated that more than 4,000 Spaniards and their native allies had been killed by the Chichimecas. Prices for imported food and other commodities in Zacetacas had doubled or tripled due to the dangers of transporting the goods to the city. In the 1570s the rebellion spread as Pames began raiding near Querétaro.
The Spanish government first attempted measures of both carrot and stick to attempt to tamp down the war, but, those failing, in 1567 it adopted the policy of a "war of fire and blood" (''guerra a fuego y a sangre'') – promising death, enslavement, or mutilation to the Chichimeca. One of the priorities of the Spaniards throughout the war was to keep the roads open to Zacatecas and the silver mines – especially the Camino Real from San Miguel de Allende. Without these crucial economic roads open, the Spanish would not be able to fund the war or continue supporting settlements. To do so they created a dozen new presidios (forts), staffed by Spanish soldiers and native ally soldiers, and encouraged more Spanish people to settle in new areas, including what would be the nucleus of the future cities of Celaya
Celaya (; ) is a city and its surrounding municipality in the state of Guanajuato, Mexico, located in the southeast quadrant of the state. It is the third most populous city in the state, with a 2005 census population of 310,413. The municipality ...
, León, Aguascalientes, and San Luis Potosí.
The first main forts were in San Miguel, San Felipe in 1562 and Nombre de Dios in 1563. Yet even then the Chichimeca managed to achieve successes. By 1571, most of the Chichimeca nations were raiding towns and crucial economic routes. In a letter from fry Guillermo de Santa Maria to fry Alonso de Alvarado, it was stated that: "Later those same Zacatecos, made another assault against Onate and Ybara, one legue from Zenaguilla del Monte and three from the mining town of Zacatecas, of which they did a lot of damage" (Santa 220 (1)). After 1560, and especially in the decade of the 1570s, the Chichimecas turned to the raiding of several towns. In a letter written October 31, 1576 by the viceroy of New Spain from the city of Mexico to King Felipe II of Spain he stated:
"We need for some quantity of soldiers to be sent, and to be paid a royal salary as agreed upon by the V.M. and of which the V.M. will send to be paid, a third of the Royal Hacienda (in Mexico city), and by the miners and those interested" (Hernandez 326 (2)).
Also reported in the same letter:
"No one can sustain the war, the cost is too big, neither in arms nor in squadrons can we sustain war. The situation is very crucial, we don't have weapons, squadrons, food because every day our livestock gets stolen or killed of which sustaining the cattle has been very difficult. We don't have enough funds to keep the people happy. Everyone agrees that we need support from the royal box" (Hernandez 326 (3)).
Even after offensives were fully financed by the royal treasury; from 1575 to 1585 the Chichimeca started attacking with even greater military force. In a letter from the viceroy of New Spain, Conde de Coruna, to Felipe II on April 1, 1581: "I have let the V.M. understand about the happenings with the Chichimeca War and about how dire the situation is that all the mines in those districts where the Natives are engaging in battle, and with such a great number and that many mines in Zacatecas are closed" (Hernandez 340 (4)). The Spanish did not attain more success even when they tried other tactics of trickery and deceit. The royal road was destroyed and there was no Spanish fort that was not also destroyed within the Guachihile territory.
The increase in number of Spanish soldiers in the Gran Chichimeca was not entirely favorable to the war effort as the soldiers often supplemented their income by slave-raiding, thus reinforcing the animosity of the Chichimeca. Despite the influx of Spanish settlers and soldiers from Southern Mexico to the Gran Chichimeca, the Spanish were always short of soldiers compared to the Chichimeca ever growing recruitment of raiders, often staffing their presidios with only three Spaniards. The Spaniards, even with the assistance from other native soldiers and auxiliaries, especially the Caxcan
The Caxcan were a partly nomadic indigenous people of Mexico. Under their leader, Tenamaztle, the Caxcan were allied with the Zacatecos against the Spaniards during the Mixtón Rebellion in 1540-42. During the rebellion, they were described as ...
s, the Purépecha, and the Otomi
The Otomi (; es, Otomí ) are an indigenous people of Mexico inhabiting the central Mexican Plateau (Altiplano) region.
The Otomi are an indigenous people of Mexico who inhabit a discontinuous territory in central Mexico. They are linguisticall ...
, could not rival the Chichimeca Confederation. The native allies were rewarded with Spanish colonized land, and native soldiers were allowed to ride Spanish horses and carry Spanish swords, formerly banned for use by native allies.
Purchase for Peace
As the war continued unabated, it became clear that the Spanish policy of a war of fire and blood had failed. The royal treasury was being emptied by the demands of the war. Churchmen and others who had initially supported the war of fire and blood now questioned the policy. Mistreatment and enslavement of Chichimeca women, children, and men by Spaniards increasingly came to be seen as the cause of the war. In 1574, the Dominicans, contrary to the Augustinians andFranciscans
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
, declared that the Chichimeca War was unjust and caused by Spanish aggression. Thus, to end the conflict, the Spanish began to change public policy to purchase peace from the Chichimeca and assimilate with them.
 In 1584, the Bishop of Guadalajara made a proposal for a "Christian remedy" to the war: the establishment of new towns with priests, soldiers, and friendly Indians to gradually Christianize the Chichimecas. The Viceroy, Alvaro Manrique de Zuniga, followed this idea in 1586 with a policy of removing many Spanish soldiers from the frontier as they were considered more a provocation than a remedy. The Viceroy opened negotiations with Chichimeca leaders and negotiated tools, food, clothing, and land to encourage them through "gentle persuasion". He forbade further failing military operations. One of the key people behind these negotiations was
In 1584, the Bishop of Guadalajara made a proposal for a "Christian remedy" to the war: the establishment of new towns with priests, soldiers, and friendly Indians to gradually Christianize the Chichimecas. The Viceroy, Alvaro Manrique de Zuniga, followed this idea in 1586 with a policy of removing many Spanish soldiers from the frontier as they were considered more a provocation than a remedy. The Viceroy opened negotiations with Chichimeca leaders and negotiated tools, food, clothing, and land to encourage them through "gentle persuasion". He forbade further failing military operations. One of the key people behind these negotiations was Miguel Caldera
Miguel Caldera (1548–1597) was an important figure in the colonization of Mexico's northern frontier immediately following the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire.
Early life
Caldera was the illegitimate son of a Castilian soldier named Pedro C ...
, a captain who was of both Spanish and Guachichile descent. Beginning in 1590 and continuing for several decades the Spanish implemented the "Purchase for Peace" program by sending large quantities of goods northward to be distributed to the Chichimecas. In 1590 the Viceroy declared the program a success and the roads to Zacatecas safe for the first time in 40 years.
The next step, in 1591, was for a new Viceroy, Luis de Velasco, with help from others such as Caldera, to persuade 400 families of Tlaxcala
Tlaxcala (; , ; from nah, Tlaxcallān ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tlaxcala ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tlaxcala), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 60 municipaliti ...
n Indians, old allies of the Spanish, to establish eight settlements in Chichimeca areas. They served as Christian examples to the Chichimecas and taught animal husbandry and farming to them. In return for moving to the frontier, the Tlaxcalans extracted concessions from the Spanish, including land grants, freedom from taxes, the right to carry arms, and provisions for two years. The Spanish also took steps to curb slavery on Mexico's northern frontier by ordering the arrest of members of the Carabajal family and Gaspar Castaño de Sosa. An essential part of their strategy was conversion of the Chichimeca to Catholicism. The Franciscans sent priests to the frontier to aid in the pacification effort.
The Purchase for Peace program worked to lower the rate of hostilities and the majority of the Chichimecas gradually became sedentary, Catholic, or nominally Catholic.
Importance
The Spanish policy evolved to make peace with the Chichimecas had four components: negotiation of peace agreements; welcoming, instead of forcing, conversion to Catholicism; encouraging native allies to settle the frontier to serve as examples and role models; and providing food, other commodities, and tools to potentially hostile natives. This established the pattern of Spanish policy for assimilating natives on their northern frontier. The principal components of the policy of purchase for peace would continue for nearly three centuries and would not be as successful, as later threats from hostile natives such as Apaches and Comanches would demonstrate.Chichimecas today
Over time most of the Chichimeca people transformed their ethnic identities and absorbed into the Catholic population and more assimilated in mainstream Mexican society before and during theMexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
. Large portions of the Guachihil population from La Montesa to Milagros migrated to the larger cities of Zacatecas or Aguascalientes and to the United States into territorials of California, Colorado, and Texas.
The Wixárika or Huichol
The Huichol or Wixárika are an indigenous people of Mexico and the United States living in the Sierra Madre Occidental range in the states of Nayarit, Jalisco, Zacatecas, and Durango, as well as in the United States in the states of California ...
es are believed to be the descendants of the Guachichiles.Ethnologue report for language code: hchAbout 20,000 of them live in an isolated area on the borders of Jalisco and
Nayarit
Nayarit (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Nayarit), is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 20 municipalities and its ...
. They are noted for being conservative, successfully preserving (Wixárika) their language, religion, and culture.
There are about 10,000 speakers of the Pame language
The Pame languages are a group of languages in Mexico that is spoken by around 12,000 Pame people in the state of San Luis Potosí. It belongs to the Oto-Pamean branch of the Oto-Manguean language family.
Distribution and languages
Ethnologue ...
s in Mexico, primarily in the municipality of Santa Maria Acapulco in an isolated region in southeastern San Luis Potosí province. They are conservative and nominal Catholics, but mostly still practicing their traditional religion and customs. Another group of about 1,500 Chichimeca Jonaz live in the state of Guanajuato.Schmal, John P.A Look into Guanajuato's Past
."
References
;Sources * Powell, Philip Wayne. ''Soldiers, Indians, & Silver: The Northward Advance of New Spain, 1550-1600''. Berkeley, California: University of California Press, 1952 (republished 1969) *Schmal, John P.The History of Zacatecas
'. Houston Institute for Culture. 2004. *Schmal, John P.
'. 2004. *Hernandez, Manuel G. "Cartas de Indias: Publicalas Por Primera Vez" Ministerio De Formento 1877. 326–340. Madrid. Print. *Santa Maria, Guillermo de. "Guerra de los Chichimecas : Mexico 1575 – Zirosto 1580" Paleography by Carrillo Cazares, Alberto. 2nd Ed. University of Guadalajara, Michoacan College, University of Norte, University Los Lagos, 220. San Luis College 2003. Print. (1) Translated from: "Despues estros mismos Zacatecas, dende a pocos dias, hicieron otro salto en unas recuas de Cristobal de Onate y de Diego de Ybarra, una legua antes Zenagulla del Monte y tres de Zacatecas, en que hicieron muncho dano." (2) Translated from: "Es que se haga alguna cantidad de soldados, a los quales se les pague sueldo, en virtue de una Real cedula de V.M. en que V.M. manda se pague, la tercia parte, de la Real hazienda, y las otras does, por los mineros y personas interesads" (3) Translated from: "ninguno puede sustentar la Guerra con dos ni tres cauallos, y la costa es muy grande, asi de las armas como de los cauallo y nunguno puede sustentar la Guerra con dos nit res cauallos, y la costa es muy grande, asi de las armas como de los cauallos y comida, que cada dia se les mueren y se los matan, y es el trabajo grandisimo . . . sienten tanto todos la paga de lo que les toca, que, si yo lo puediese remidar con uender quanto tengo, lo haria, por euitar el descontento de la gente, que a todos les parece que se a de pagar de la Real caja" (4) Translated from: "Ya he dado quenta particular a V.M. de lo que toca a la Guerra de los chichimecas, y del incombiniente que se sigue a todas las minas de aquel districto, en que aquellos indos anden tan lebantados y con tanto numero y desberguanca; y demas, desto, soy informado que en Zacatecas ay munchas minas ceradas" {{Authority control 1546 in New Spain Colonial Mexico History of Mesoamerica Mesoamerican warfare Rebellions against the Spanish Empire Wars involving the indigenous peoples of North America Conflicts in 1546 History of Aguascalientes History of Guanajuato History of Jalisco History of San Luis Potosí History of Zacatecas Battles won by indigenous peoples of the Americas