Charpy impact test on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In materials science, the Charpy impact test, also known as the Charpy V-notch test, is a
In materials science, the Charpy impact test, also known as the Charpy V-notch test, is a
 In materials science, the Charpy impact test, also known as the Charpy V-notch test, is a
In materials science, the Charpy impact test, also known as the Charpy V-notch test, is a standardized
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization ...
high strain rate
In materials science, strain rate is the change in strain ( deformation) of a material with respect to time.
The strain rate at some point within the material measures the rate at which the distances of adjacent parcels of the material change ...
test which determines the amount of energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
absorbed by a material during fracture. Absorbed energy is a measure of the material's notch toughness
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing.
The test was pivotal in understanding the fracture problems of ships during World War II.
The test was developed around 1900 by S. B. Russell (1898, American) and Georges Charpy (1901, French). The test became known as the Charpy test in the early 1900s due to the technical contributions and standardization efforts by Charpy.
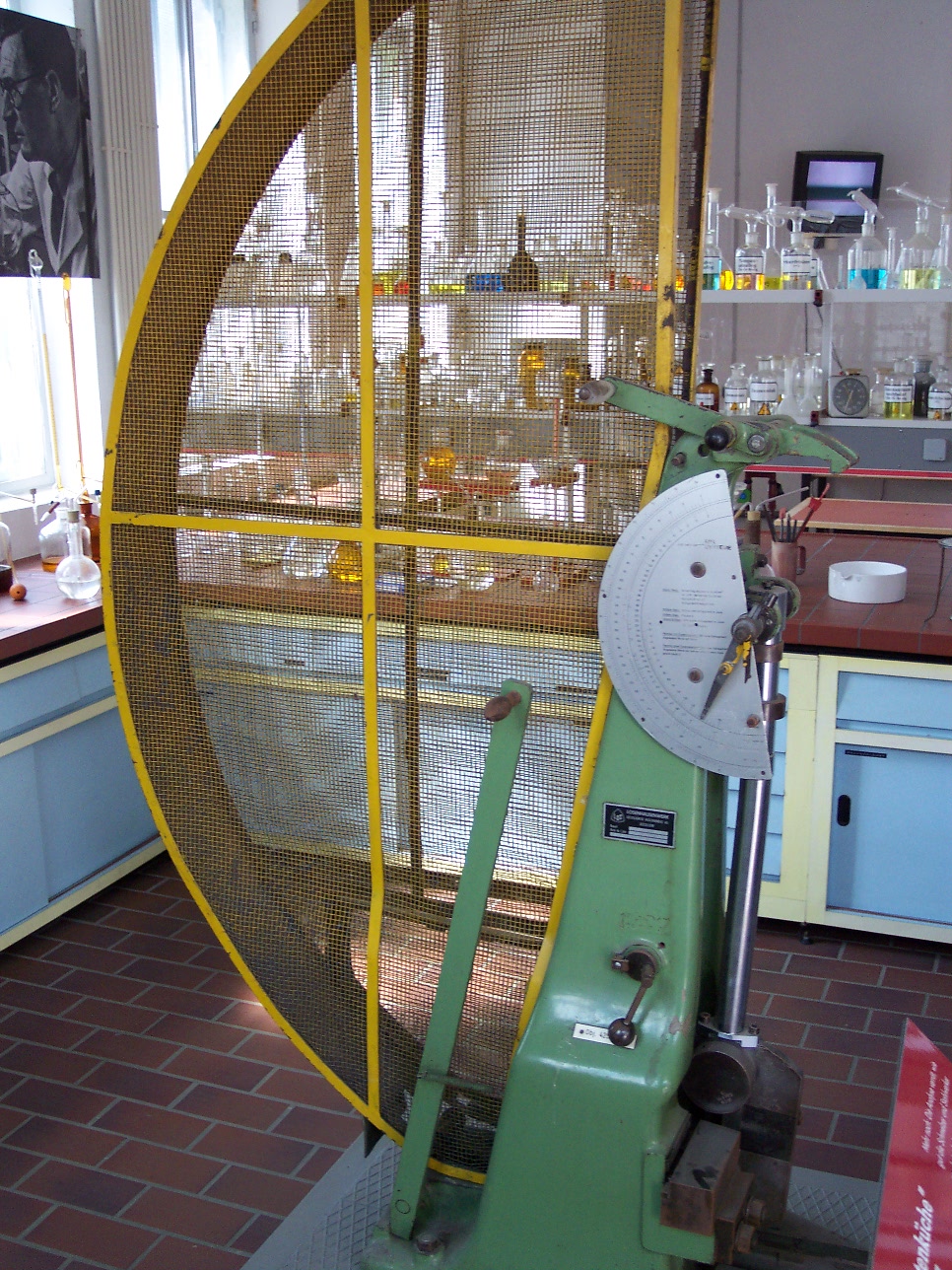 The apparatus consists of a
The apparatus consists of a
CalculatorVideo on the Charpy impact test
Fracture mechanics Materials testing
History
In 1896, S. B. Russell introduced the idea of ''residual fracture energy'' and devised a pendulum fracture test. Russell's initial tests measured un-notched samples. In 1897, Frémont introduced a test to measure the same phenomenon using a spring-loaded machine. In 1901, Georges Charpy proposed a standardized method improving Russell's by introducing a redesigned pendulum and notched sample, giving precise specifications.Definition
 The apparatus consists of a
The apparatus consists of a pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward th ...
of known mass and length that is dropped from a known height to impact a notched specimen of material. The energy transferred to the material can be inferred by comparing the difference in the height of the hammer before and after the fracture (energy absorbed by the fracture event).
The notch in the sample affects the results of the impact test,
thus it is necessary for the notch to be of regular dimensions and geometry. The size of the sample can also affect results, since the dimensions determine whether or not the material is in plane strain
In continuum mechanics, the infinitesimal strain theory is a mathematical approach to the description of the deformation of a solid body in which the displacements of the material particles are assumed to be much smaller (indeed, infinitesimal ...
. This difference can greatly affect the conclusions made.
The ''Standard methods for Notched Bar Impact Testing of Metallic Materials'' can be found in ASTM E23,ASTM E23 Standard Test Methods for Notched Bar Impact Testing of Metallic Materials ISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
148-1ISO 148-1 Metallic materials - Charpy pendulum impact test - Part 1: Test method or EN 10045-1 (retired and replaced with ISO 148-1),EN 10045-1 Charpy impact test on metallic materials. Test method (V- and U-notches) where all the aspects of the test and equipment used are described in detail.
Quantitative results
The quantitative result of the impact tests the energy needed to fracture a material and can be used to measure the toughness of the material. There is a connection to theyield strength
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and ...
but it cannot be expressed by a standard formula. Also, the strain rate may be studied and analyzed for its effect on fracture.
The ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) may be derived from the temperature where the energy needed to fracture the material drastically changes. However, in practice there is no sharp transition and it is difficult to obtain a precise transition temperature (it is really a transition region). An exact DBTT may be empirically derived in many ways: a specific absorbed energy, change in aspect of fracture (such as 50% of the area is cleavage), etc.
Qualitative results
The qualitative results of the impact test can be used to determine theductility
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile str ...
of a material.
If the material breaks on a flat plane, the fracture was brittle, and if the material breaks with jagged edges or shear lips, then the fracture was ductile. Usually, a material does not break in just one way or the other and thus comparing the jagged to flat surface areas of the fracture will give an estimate of the percentage of ductile and brittle fracture.
Sample sizes
According to ASTM A370, the standard specimen size for Charpy impact testing is 10 mm × 10 mm × 55 mm. Subsize specimen sizes are: 10 mm × 7.5 mm × 55 mm, 10 mm × 6.7 mm × 55 mm, 10 mm × 5 mm × 55 mm, 10 mm × 3.3 mm × 55 mm, 10 mm × 2.5 mm × 55 mm. Details of specimens as per ASTM A370 (Standard Test Method and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products). According to EN 10045-1 (retired and replaced with ISO 148), standard specimen sizes are 10 mm × 10 mm × 55 mm. Subsize specimens are: 10 mm × 7.5 mm × 55 mm and 10 mm × 5 mm × 55 mm. According to ISO 148, standard specimen sizes are 10 mm × 10 mm × 55 mm. Subsize specimens are: 10 mm × 7.5 mm × 55 mm, 10 mm × 5 mm × 55 mm and 10 mm × 2.5 mm × 55 mm. According to MPIF Standard 40, the standard unnotched specimen size is 10 mm (±0.125 mm) x 10 mm (±0.125 mm) x 55 mm (±2.5 mm).Impact test results on low- and high-strength materials
The impact energy of low-strength metals that do not show a change of fracture mode with temperature, is usually high and insensitive to temperature. For these reasons, impact tests are not widely used for assessing the fracture-resistance of low-strength materials whose fracture modes remain unchanged with temperature. Impact tests typically show a ductile-brittle transition for low-strength materials that do exhibit change in fracture mode with temperature such asbody-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties of ...
(BCC) transition metals.
Generally, high-strength materials have low impact energies which attest to the fact that fractures easily initiate and propagate in high-strength materials. The impact energies of high-strength materials other than steels or BCC transition metals are usually insensitive to temperature. High-strength BCC steels display a wider variation of impact energy than high-strength metal that do not have a BCC structure because steels undergo microscopic ductile-brittle transition. Regardless, the maximum impact energy of high-strength steels is still low due to their brittleness.
See also
* Izod impact strength test *Brittle
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. Br ...
* Impact force
In mechanics, an impact is a high force or shock applied over a short time period when two or more bodies collide. Such a force or acceleration usually has a greater effect than a lower force applied over a proportionally longer period. Th ...
Notes
{{reflistExternal links
Calculator
Fracture mechanics Materials testing