
Charleston is the largest city in the
U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of
South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, the
county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US ...
of
Charleston County
Charleston County is located in the U.S. state of South Carolina along the Atlantic coast. As of the 2020 census, its population was 408,235, making it the third most populous county in South Carolina (behind Greenville and Richland counties). ...
,
and the principal city in the
Charleston–North Charleston metropolitan area. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint of South Carolina's coastline on
Charleston Harbor
The Charleston Harbor is an inlet (8 sq mi/20.7 km²) of the Atlantic Ocean at Charleston, South Carolina. The inlet is formed by the junction of Ashley and Cooper rivers at . Morris and Sullivan's Islands shelter the entrance. Charleston ...
, an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean formed by the confluence of the
Ashley Ashley is a place name derived from the Old English words '' æsc'' (“ash”) and '' lēah'' (“meadow”). It may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Ashley (given name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name ...
,
Cooper
Cooper, Cooper's, Coopers and similar may refer to:
* Cooper (profession), a maker of wooden casks and other staved vessels
Arts and entertainment
* Cooper (producers), alias of Dutch producers Klubbheads
* Cooper (video game character), in ...
, and
Wando rivers. Charleston had a population of 150,277 at the
2020 census.
The 2020 population of the Charleston metropolitan area, comprising
Berkeley,
Charleston, and
Dorchester counties, was 799,636 residents,
the third-largest in the state and the 74th-largest metropolitan statistical area in the United States.
Charleston was founded in 1670 as Charles Town, honoring
King CharlesII, at Albemarle Point on the west bank of the
Ashley River
The Ashley River is a blackwater and tidal river in South Carolina, rising from the Wassamassaw and Great Cypress Swamps in western Berkeley County. It consolidates its main channel about five miles west of Summerville, widening into a ti ...
(now
Charles Towne Landing) but relocated in 1680 to its present site, which became the fifth-largest city in
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
within ten years. It remained
unincorporated Unincorporated may refer to:
* Unincorporated area, land not governed by a local municipality
* Unincorporated entity, a type of organization
* Unincorporated territories of the United States, territories under U.S. jurisdiction, to which Congress ...
throughout the colonial period; its government was handled directly by a colonial legislature and a governor sent by
Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
. Election districts were organized according to
Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of t ...
parishes, and some social services were managed by Anglican
wardens and
vestries
A vestry was a committee for the local secular and ecclesiastical government for a parish in England, Wales and some English colonies which originally met in the vestry or sacristy of the parish church, and consequently became known colloquially ...
. Charleston adopted its present spelling with its incorporation as a
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
in 1783. Population growth in the interior of South Carolina influenced the removal of the state government to
Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region i ...
in 1788, but Charleston remained among the ten largest cities in the United States through the
1840 census
The United States census of 1840 was the sixth census of the United States. Conducted by the Census Office on June 1, 1840, it determined the resident population of the United States to be 17,069,453 – an increase of 32.7 percent over the 12, ...
.
Charleston's significance in American history is tied to its role as a major slave trading port. Charleston slave traders like
Joseph Wragg
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
were the first to break through the monopoly of the
Royal African Company
The Royal African Company (RAC) was an English mercantile ( trading) company set up in 1660 by the royal Stuart family and City of London merchants to trade along the west coast of Africa. It was led by the Duke of York, who was the brother ...
and pioneered the large-scale slave trade of the 18th century; almost one half of slaves imported to the United States arrived in Charleston. In 2018, the city formally apologized for its role in the American slave trade after CNN noted that slavery "riddles the history" of Charleston.
Geography
The city proper consists of six distinct districts.
*Downtown, or sometimes referred to as "The Peninsula", is Charleston's center city separated by the Ashley River to the west and the Cooper River to the east.
*
West Ashley
West Ashley, or more formally, west of the Ashley, is one of the six distinct areas of the city proper of Charleston, South Carolina. As of July 2022, its estimated population was 83,996. Its name is derived from the fact that the land is west of ...
, residential area to the west of Downtown bordered by the Ashley River to the east and the Stono River to the west
*
Johns Island, far western limits of Charleston, bordered by the Stono River to the east, Kiawah River to the south and
Wadmalaw Island
Wadmalaw Island is an island located in Charleston County, South Carolina, United States. It is one of the Sea Islands, a chain of tidal and barrier islands on the Atlantic Ocean.
Geography
Wadmalaw Island is located generally to the southwest o ...
to the west
*
James Island, popular residential area between Downtown and the town of
Folly Beach with portions of the independent town of James Island intermixed
*Cainhoy Peninsula, far eastern limits of Charleston bordered by the Wando River to the west and Nowell Creek to the east
*
Daniel Island, residential area to the north of downtown, east of the Cooper River and west of the Wando River
Topography

The incorporated city fitted into as late as the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, but has since greatly expanded, crossing the
Ashley River
The Ashley River is a blackwater and tidal river in South Carolina, rising from the Wassamassaw and Great Cypress Swamps in western Berkeley County. It consolidates its main channel about five miles west of Summerville, widening into a ti ...
and encompassing
James Island and some of
Johns Island. The city limits also have expanded across the Cooper River, encompassing
Daniel Island and the
Cainhoy area. The present city has a total area of , of which is land and is covered by water.
North Charleston
North Charleston is the third-largest city in the state of South Carolina.City Planning Department (2008-07)City of North Charleston boundary map. City of North Charleston. Retrieved January 21, 2011. On June 12, 1972, the city of North Charlest ...
blocks any expansion up the peninsula, and
Mount Pleasant occupies the land directly east of the Cooper River.
Charleston Harbor
The Charleston Harbor is an inlet (8 sq mi/20.7 km²) of the Atlantic Ocean at Charleston, South Carolina. The inlet is formed by the junction of Ashley and Cooper rivers at . Morris and Sullivan's Islands shelter the entrance. Charleston ...
runs about southeast to the Atlantic with an average width of about , surrounded on all sides except its entrance.
Sullivan's Island lies to the north of the entrance and
Morris Island
Morris Island is an 840-acre (3.4 km²) uninhabited island in Charleston Harbor in South Carolina, accessible only by boat. The island lies in the outer reaches of the harbor and was thus a strategic location in the American Civil War. The ...
to the south. The entrance itself is about wide; it was originally only deep but began to be enlarged in the 1870s. The tidal rivers (
Wando, Cooper,
Stono
Stono, also known as Jordan's Point (pronounced "Jer-don"), is a historic home located at Lexington, Virginia. It was built about 1818, and is a cruciform shaped brick dwelling consisting of a two-story, three-bay, central section with one-stor ...
, and Ashley) are evidence of a
submergent or drowned coastline. There is a submerged river delta off the mouth of the harbor, and the Cooper River is deep.
Climate

Charleston has a
humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
''Cfa''), with mild winters, hot humid summers, and significant rainfall all year long. Summer is the wettest season; almost half of the annual rainfall occurs from June to September in the form of
thundershower
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are someti ...
s. Fall remains relatively warm through the middle of November. Winter is short and mild, and is characterized by occasional rain. Measurable snow (≥) has a median occurrence of only once per decade at the airport, but freezing rain is more common; a snowfall/freezing rain event on January 3, 2018, was the first such event in Charleston since December 26, 2010.
However, fell at the airport on December 23, 1989, during the
December 1989 United States cold wave
The December 1989 United States cold wave was a series of cold waves into the central and eastern United States from mid-December 1989 through Christmas. On December 21-23, a massive high pressure area pushed many areas into record lows. On the mor ...
, the largest single-day fall on record, contributing to a single-storm and seasonal record of snowfall.
Downtown Charleston's climate is considerably milder than the airport's due to stronger maritime influence. This is especially true in the winter, with the average January low in downtown being to the airport's for example.
The highest temperature recorded within city limits was on June 2, 1985, and June 24, 1944; the lowest was on
February 14, 1899. At the airport, where official records are kept, the historical range is on August 1, 1999, down to on
January 21, 1985.
Hurricanes are a major threat to the area during the summer and early fall, with several severe hurricanes hitting the area—most notably
Hurricane Hugo
Hurricane Hugo was a powerful Cape Verde tropical cyclone that inflicted widespread damage across the northeastern Caribbean and the Southeastern United States in September 1989. Across its track, Hugo affected approximately 2 million peopl ...
on September 21, 1989 (a
category 4 storm). The dewpoint from June to August ranges from .
Metropolitan Statistical Area
As defined by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget, for use by the U.S. Census Bureau and other U.S. Government agencies for statistical purposes only, Charleston is included within the Charleston–North Charleston, SC Metropolitan Statistical Area and the smaller Charleston-North Charleston urban area. The
Charleston–North Charleston metropolitan area consists of three counties:
Charleston,
Berkeley, and
Dorchester. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, the metropolitan statistical area had a total population of 799,636 people.
North Charleston
North Charleston is the third-largest city in the state of South Carolina.City Planning Department (2008-07)City of North Charleston boundary map. City of North Charleston. Retrieved January 21, 2011. On June 12, 1972, the city of North Charlest ...
is the second-largest city in the metro area and ranks as the third-largest city in the state;
Mount Pleasant and
Summerville are the next-largest cities. These cities combined with other incorporated and unincorporated areas along with the city of Charleston form the
Charleston-North Charleston urban area with a population of 548,404 . The metropolitan statistical area also includes a separate and much smaller urban area within Berkeley County,
Moncks Corner
Moncks Corner is a town in and the county seat of Berkeley County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 7,885 at the 2010 census. As defined by the U.S. Census Bureau, Moncks Corner is included within the Charleston-North Charleston-S ...
(with a 2000 population of 9,123).
The traditional parish system persisted until the
Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction era was a period in American history following the American Civil War (1861–1865) and lasting until approximately the Compromise of 1877. During Reconstruction, attempts were made to rebuild the country after the bloo ...
, when counties were imposed. Nevertheless, traditional parishes still exist in various capacities, mainly as public service districts. When the city of Charleston was formed, it was defined by the limits of the Parish of St. Philip and St. Michael, now also includes parts of St. James' Parish, St. George's Parish, St. Andrew's Parish, and St. John's Parish, although the last two are mostly still incorporated rural parishes.
History

Colonial era (1670–1786)
 King Charles II
King Charles II granted the
chartered Province of Carolina
Province of Carolina was a province of England (1663–1707) and Great Britain (1707–1712) that existed in North America and the Caribbean from 1663 until partitioned into North and South on January 24, 1712. It is part of present-day Alabam ...
to eight of his loyal friends, known as the
Lords Proprietors
A lord proprietor is a person granted a royal charter for the establishment and government of an English colony in the 17th century. The plural of the term is "lords proprietors" or "lords proprietary".
Origin
In the beginning of the European ...
, on March 24, 1663. In 1670,
Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
William Sayle
Captain William Sayle (c. 1590–1671) was a prominent British landholder who was Governor of Bermuda in 1643 and again in 1658. As an Independent in religion and politics, and an adherent of Oliver Cromwell, he was dissatisfied with life in Ber ...
arranged for several shiploads of settlers from
Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
and
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estima ...
. These settlers established what was then called Charles Town at Albemarle Point, on the west bank of the Ashley River, a few miles northwest of the present-day city center. Charles Town became the first comprehensively planned town in the
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centu ...
. Its governance, settlement, and development was to follow a visionary plan known as the
Grand Model prepared for the Lords Proprietors by
John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 – 28 October 1704) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers and commonly known as the "father of liberalism". Considered one of ...
. Because the
Carolina's Fundamental Constitutions was never ratified, however, Charles Town was never incorporated during the colonial period. Instead,
local ordinance
A local ordinance is a law issued by a local government. such as a municipality, county, parish, prefecture, or the like.
China
In Hong Kong, all laws enacted by the territory's Legislative Council remain to be known as ''Ordinances'' () a ...
s were passed by the provincial government, with day-to-day administration handled by the
wardens and
vestries
A vestry was a committee for the local secular and ecclesiastical government for a parish in England, Wales and some English colonies which originally met in the vestry or sacristy of the parish church, and consequently became known colloquially ...
of
StPhilip's and
StMichael's Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of t ...
parishes
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or ...
.
At the time of
European colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense be ...
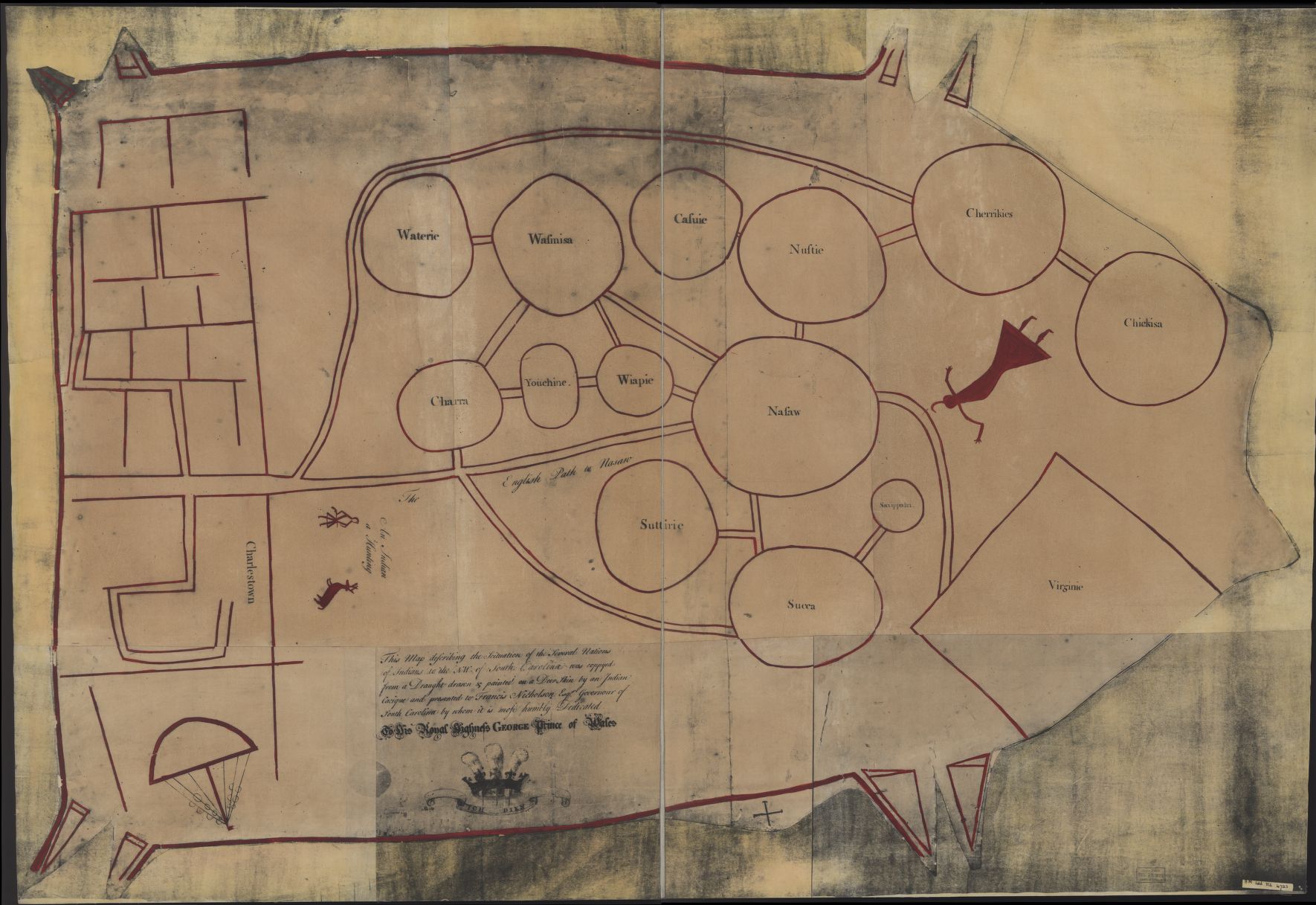
, the area was inhabited by the
indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
Cusabo
The Cusabo or Cosabo were a group of American Indian tribes who lived along the coast of the Atlantic Ocean in what is now South Carolina, approximately between present-day Charleston and south to the Savannah River, at the time of European colon ...
, whom the settlers declared war on in October 1671. The settlers initially allied with the
Westo, a northern indigenous tribe that traded in enslaved Indians. The settlers abandoned their alliance with the Westo in 1679 and allied with the Cusabo instead.
The initial settlement quickly dwindled away and disappeared while another village—established by the settlers on Oyster Point at the confluence of the Ashley and Cooper rivers around 1672—thrived. This second settlement formally replaced the original Charles Town in 1680. (The original site is now commemorated as
Charles Towne Landing.) The second location was more defensible and had access to a fine natural harbor. The new town had become the fifth largest in North America by 1690.
A
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
outbreak erupted in 1698, followed by an earthquake in February 1699. The latter caused a fire that destroyed about a third of the town. During rebuilding, a
yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
outbreak killed about 15% of the remaining inhabitants. Charles Town suffered between five and eight major
yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
outbreaks over the first half of the 18th century.
It developed a reputation as one of the least healthy locations in the
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centu ...
for ethnic Europeans.
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
was endemic. Although malaria did not have such high mortality as yellow fever, it caused much illness. It was a major health problem through most of the city's history before dying out in the 1950s after use of pesticides cut down on the mosquitoes that transmitted it.
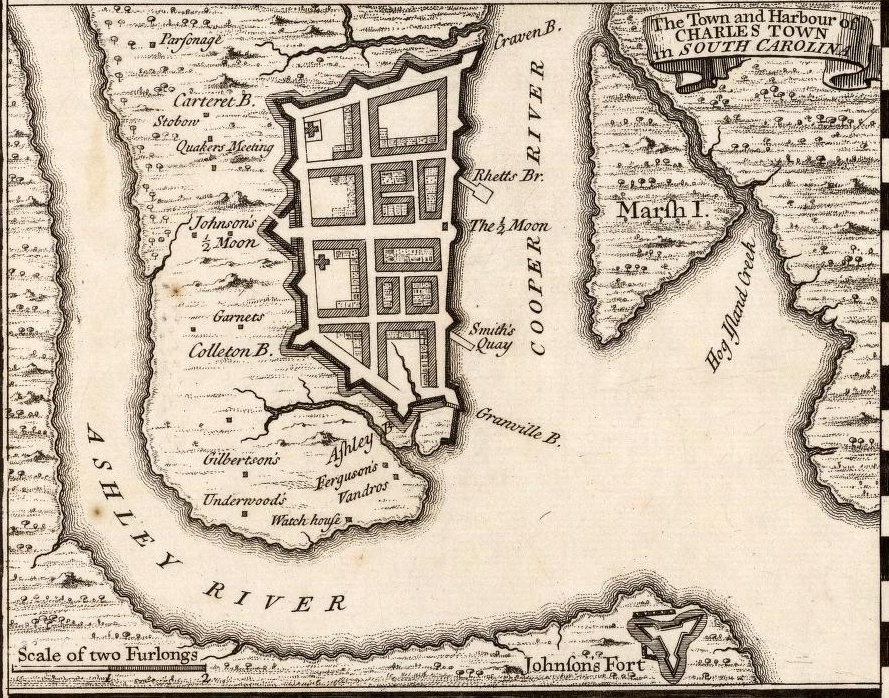
Charles Town was fortified according to a plan developed in 1704 under
Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Nathaniel Johnson. Both
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
contested Britain's claims to the region. Various bands of
Native Americans and independent
pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
also raided it.
On September 5–6, 1713 (O.S.) a violent
hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
passed over Charles Town. The
Circular Congregational Church manse was damaged during the storm, in which church records were lost. Much of Charles Town was flooded as "the Ashley and Cooper rivers became one." At least seventy people died in the disaster.
From the 1670s Charleston attracted pirates. The combination of a weak government and corruption made the city popular with pirates, who frequently visited and raided the city. Charles Town was besieged by the pirate
Blackbeard
Edward Teach (alternatively spelled Edward Thatch, – 22 November 1718), better known as Blackbeard, was an English pirate who operated around the West Indies and the eastern coast of Britain's North American colonies. Little is known abou ...
for several days in May 1718. Blackbeard released his hostages and left in exchange for a chest of medicine from
Governor Robert Johnson.
[D. Moore. (1997) "A General History of Blackbeard the Pirate, the Queen Anne's Revenge and the Adventure". In ;;Tributaries,;; Volume VII, 1997. pp. 31–35. (North Carolina Maritime History Council)]
Around 1719, the town's name began to be generally written as Charlestown and, excepting those fronting the Cooper River, the old walls were largely removed over the next decade. Charlestown was a center for the inland colonization of
South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
. It remained the southernmost point of the
Southern Colonies until the
Province of Georgia
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
was established in 1732. As noted, the first settlers primarily came from
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
,
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estima ...
and
Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
. The Barbadian and Bermudan immigrants were planters who brought enslaved Africans with them, having purchased them in the
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
.
Early immigrant groups to the city included the
Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
s,
Scottish,
Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, and
Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, as well as
hundreds of Jews, predominately
Sephardi
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
from
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
and major cities of the
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
, where they had been given refuge.
As late as 1830, Charleston's Jewish community was the largest and wealthiest
in North America.
[
By 1708, the majority of the colony's population were ]Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
Africans. They had been brought to Charlestown via the Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and ...
, first as indentured servants
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an "indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensation or debt repayment, ...
and then as slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. In the early 1700s, Charleston's largest slave trader, Joseph Wragg
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
, pioneered the settlement's involvement in the slave trade. Of the estimated 400,000 captive Africans transported to North America to be sold into slavery, 40% are thought to have landed at Sullivan's Island off Charlestown. Free people of color
In the context of the history of slavery in the Americas, free people of color (French: ''gens de couleur libres''; Spanish: ''gente de color libre'') were primarily people of mixed African, European, and Native American descent who were not ...
also migrated from the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
, being descendants of white planters and their Black consorts, and unions among the working classes.[History: Gadsden's Wharf](_blank)
, International African American Museum; accessed March 29, 2018 Devoted to plantation agriculture that depended on enslaved labor, South Carolina became a slave society: it had a majority-Black population from the colonial period until after the Great Migration of the early 20th century, when many rural Blacks moved to northern and midwestern industrial cities to escape Jim Crow laws
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the S ...
.
 At the foundation of the town, the principal items of commerce were
At the foundation of the town, the principal items of commerce were pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, w ...
and pitch for ships
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished ...
and tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
. The early economy developed around the deerskin
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs ...
trade, in which colonists used alliances with the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, th ...
and Creek peoples to secure the raw material.
At the same time, Indians took each other as captives and slaves in warfare. From 1680 to 1720, approximately 40,000 native men, women, and children were sold through the port, principally to the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
such as (Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
and the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the a ...
), but also to other Southern colonies.plantations
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
.Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida ( es, La Florida) was the first major European land claim and attempted settlement in North America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba, the Viceroyalty of New Spain, ...
and French Louisiana
The term French Louisiana refers to two distinct regions:
* first, to colonial French Louisiana, comprising the massive, middle section of North America claimed by France during the 17th and 18th centuries; and,
* second, to modern French Louisi ...
in the 1700s during the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
.[ But it also provoked the ]Yamasee War
The Yamasee War (also spelled Yamassee or Yemassee) was a conflict fought in South Carolina from 1715 to 1717 between British settlers from the Province of Carolina and the Yamasee and a number of other allied Native American peoples, incl ...
of the 1710s that nearly destroyed the colony. After that, South Carolina largely abandoned the Indian slave trade.[
The area's unsuitability for growing ]tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
prompted the Lowcountry
The Lowcountry (sometimes Low Country or just low country) is a geographic and cultural region along South Carolina's coast, including the Sea Islands. The region includes significant salt marshes and other coastal waterways, making it an impor ...
planters
Planters Nut & Chocolate Company is an American snack food company now owned by Hormel Foods. Planters is best known for its processed nuts and for the Mr. Peanut icon that symbolizes them. Mr. Peanut was created by grade schooler Antonio Gentil ...
to experiment with other cash crop
A cash crop or profit crop is an agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate marketed crops from staple crop (or "subsistence crop") in subsist ...
s. The profitability of growing rice led the planters to pay premiums for slaves from the "Rice Coast" who knew its cultivation; their descendants make up the ethnic Gullah
The Gullah () are an African American ethnic group who predominantly live in the Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, and North Carolina, within the coastal plain and the Sea Islands. Their language and cultu ...
who created their own culture and language in this area. Slaves imported from the Caribbean showed the planter George Lucas's daughter Eliza how to raise and use
Use may refer to:
* Use (law), an obligation on a person to whom property has been conveyed
* Use (liturgy), a special form of Roman Catholic ritual adopted for use in a particular diocese
* Use–mention distinction, the distinction between using ...
indigo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', ...
for dyeing
Dyeing is the application of dyes or pigments on textile materials such as fibers, yarns, and fabrics with the goal of achieving color with desired color fastness. Dyeing is normally done in a special solution containing dyes and particular c ...
in 1747.
Throughout this period, the slaves were sold aboard the arriving ships or at ad hoc gatherings in town's taverns.[ Runaways and minor ]slave rebellion
A slave rebellion is an armed uprising by enslaved people, as a way of fighting for their freedom. Rebellions of enslaved people have occurred in nearly all societies that practice slavery or have practiced slavery in the past. A desire for freed ...
s prompted the 1739 Security Act, which required all white men to carry weapons at all times (even to church on Sundays). Before it had fully taken effect, the Cato or Stono Rebellion
The Stono Rebellion (also known as Cato's Conspiracy or Cato's Rebellion) was a slave revolt that began on 9 September 1739, in the colony of South Carolina. It was the largest slave rebellion in the Southern Colonies, with 25 colonists and 35 t ...
broke out. The white community had recently been decimated by a malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
outbreak, and the rebels killed about 25 white people before being stopped by the colonial militia. As a result of their fears of rebellion, whites killed a total of 35 to 50 Black people.
The planters attributed the violence to recently imported Africans and agreed to a 10-year moratorium on slave importation through Charlestown. They relied for labor upon the slave communities they already held. The 1740 Negro Act also tightened controls, requiring a ratio of one white for every ten Blacks on any plantation (which was often not achieved), and banning slaves from assembling together, growing their own food, earning money, or learning to read. Drums
A drum kit (also called a drum set, trap set, or simply drums) is a collection of drums, cymbals, and other auxiliary percussion instruments set up to be played by one person. The player (drummer) typically holds a pair of matching drumsticks ...
were banned because Africans used them for signaling; slaves were allowed to use string and other instruments. When the moratorium expired and Charlestown reopened to the slave trade in 1750, the memory of the Stono Rebellion resulted in traders avoiding buying slaves from the Congo and Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordinat ...
, whose populations had a reputation for independence.
By the mid-18th century, Charlestown was the hub of the Atlantic slave trade in the Southern Colonies. Even with the decade-long moratorium, its customs processed around 40% of the enslaved Africans brought to North America between 1700 and 1775,plantations
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
and the economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with th ...
based on them made this the wealthiest city in the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centu ...
and the largest in population south of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
. In 1770, the city had 11,000 inhabitants—half slaves—and was the 4th-largest port in the colonies, after Boston, MA, Boston, New York City, New York, and Philadelphia.
The elite began to use their wealth to encourage cultural and social development. America's first theater building was constructed here in 1736; it was later replaced by today's Dock Street Theater. StMichael's was erected in 1753. Benevolent societies were formed by the Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
s, free people of color, Germans, and Jews. The Charleston Library Society, Library Society was established in 1748 by well-born young men who wanted to share the financial cost to keep up with the scientific and philosophical issues of the day.
American Revolution (1776–1783)
 Delegates for the Continental Congress were elected in 1774, and South Carolina declared its independence from Britain on the steps of the Exchange and Provost, Exchange. Slavery was again an important factor in the city's role during the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War. The British attacked the settlement three times, assuming that the settlement had a large base of Loyalist (American Revolution), Loyalists who would rally to their cause once given some military support. The loyalty of white Southerners towards the Crown had largely been forfeited, however, by British legal cases (such as the 1772 Somerset v Stewart, Somersett case which marked the prohibition of slavery in England and Wales; a significant milestone in the Abolitionism, abolitionist struggle) and military tactics (such as Dunmore's Proclamation in 1775) that promised the emancipation of slaves owned by Patriot planters; these efforts did, however, unsurprisingly win the allegiance of thousands of Black Loyalists.
The Battle of Sullivan's Island saw the British fail to capture a partially constructed Fort Moultrie, palmetto palisade from William Moultrie, Col. Moultrie's 2nd South Carolina Regiment, militia regiment on June 28, 1776. The Liberty Flag used by Moultrie's men formed the basis of the later South Carolina flag, and the victory's anniversary continues to be commemorated as Carolina Day.
Making the capture of Charlestown their chief priority, the British sent Henry Clinton (American War of Independence), Sir Henry Clinton, who laid Siege of Charleston, siege to Charleston on April 1, 1780, with about 14,000 troops and 90 ships. Bombardment began on March 11, 1780. The Patriots, led by Benjamin Lincoln, had about 5,500 men and inadequate fortifications to repel the forces against them. After the British cut his supply lines and lines of retreat at the battles of Battle of Monck's Corner, Monck's Corner and Battle of Lenud's Ferry, Lenud's Ferry, Lincoln's surrender on May 12, 1780 became the greatest List of American Revolutionary War battles, American defeat of the war.
The British continued to hold Charlestown for over a year following Siege of Yorktown (1781), their defeat at Yorktown in 1781, although they alienated local planters by refusing to restore full civil government. Nathanael Greene had entered the state after Cornwallis's Battle of Guilford Courthouse, pyrrhic victory at Guilford Courthouse and kept the area under a kind of siege. British Army officer Alexander Leslie (British Army officer), Alexander Leslie, commanding Charlestown, requested a truce in March 1782 to purchase food for his garrison and the town's inhabitants. Greene refused and formed a brigade under Mordecai Gist to counter British forays. Charlestown was finally evacuated by the British in December 1782. Greene presented the British leaders of the town with the Moultrie Flag.
Delegates for the Continental Congress were elected in 1774, and South Carolina declared its independence from Britain on the steps of the Exchange and Provost, Exchange. Slavery was again an important factor in the city's role during the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War. The British attacked the settlement three times, assuming that the settlement had a large base of Loyalist (American Revolution), Loyalists who would rally to their cause once given some military support. The loyalty of white Southerners towards the Crown had largely been forfeited, however, by British legal cases (such as the 1772 Somerset v Stewart, Somersett case which marked the prohibition of slavery in England and Wales; a significant milestone in the Abolitionism, abolitionist struggle) and military tactics (such as Dunmore's Proclamation in 1775) that promised the emancipation of slaves owned by Patriot planters; these efforts did, however, unsurprisingly win the allegiance of thousands of Black Loyalists.
The Battle of Sullivan's Island saw the British fail to capture a partially constructed Fort Moultrie, palmetto palisade from William Moultrie, Col. Moultrie's 2nd South Carolina Regiment, militia regiment on June 28, 1776. The Liberty Flag used by Moultrie's men formed the basis of the later South Carolina flag, and the victory's anniversary continues to be commemorated as Carolina Day.
Making the capture of Charlestown their chief priority, the British sent Henry Clinton (American War of Independence), Sir Henry Clinton, who laid Siege of Charleston, siege to Charleston on April 1, 1780, with about 14,000 troops and 90 ships. Bombardment began on March 11, 1780. The Patriots, led by Benjamin Lincoln, had about 5,500 men and inadequate fortifications to repel the forces against them. After the British cut his supply lines and lines of retreat at the battles of Battle of Monck's Corner, Monck's Corner and Battle of Lenud's Ferry, Lenud's Ferry, Lincoln's surrender on May 12, 1780 became the greatest List of American Revolutionary War battles, American defeat of the war.
The British continued to hold Charlestown for over a year following Siege of Yorktown (1781), their defeat at Yorktown in 1781, although they alienated local planters by refusing to restore full civil government. Nathanael Greene had entered the state after Cornwallis's Battle of Guilford Courthouse, pyrrhic victory at Guilford Courthouse and kept the area under a kind of siege. British Army officer Alexander Leslie (British Army officer), Alexander Leslie, commanding Charlestown, requested a truce in March 1782 to purchase food for his garrison and the town's inhabitants. Greene refused and formed a brigade under Mordecai Gist to counter British forays. Charlestown was finally evacuated by the British in December 1782. Greene presented the British leaders of the town with the Moultrie Flag.
Antebellum era (1783–1861)
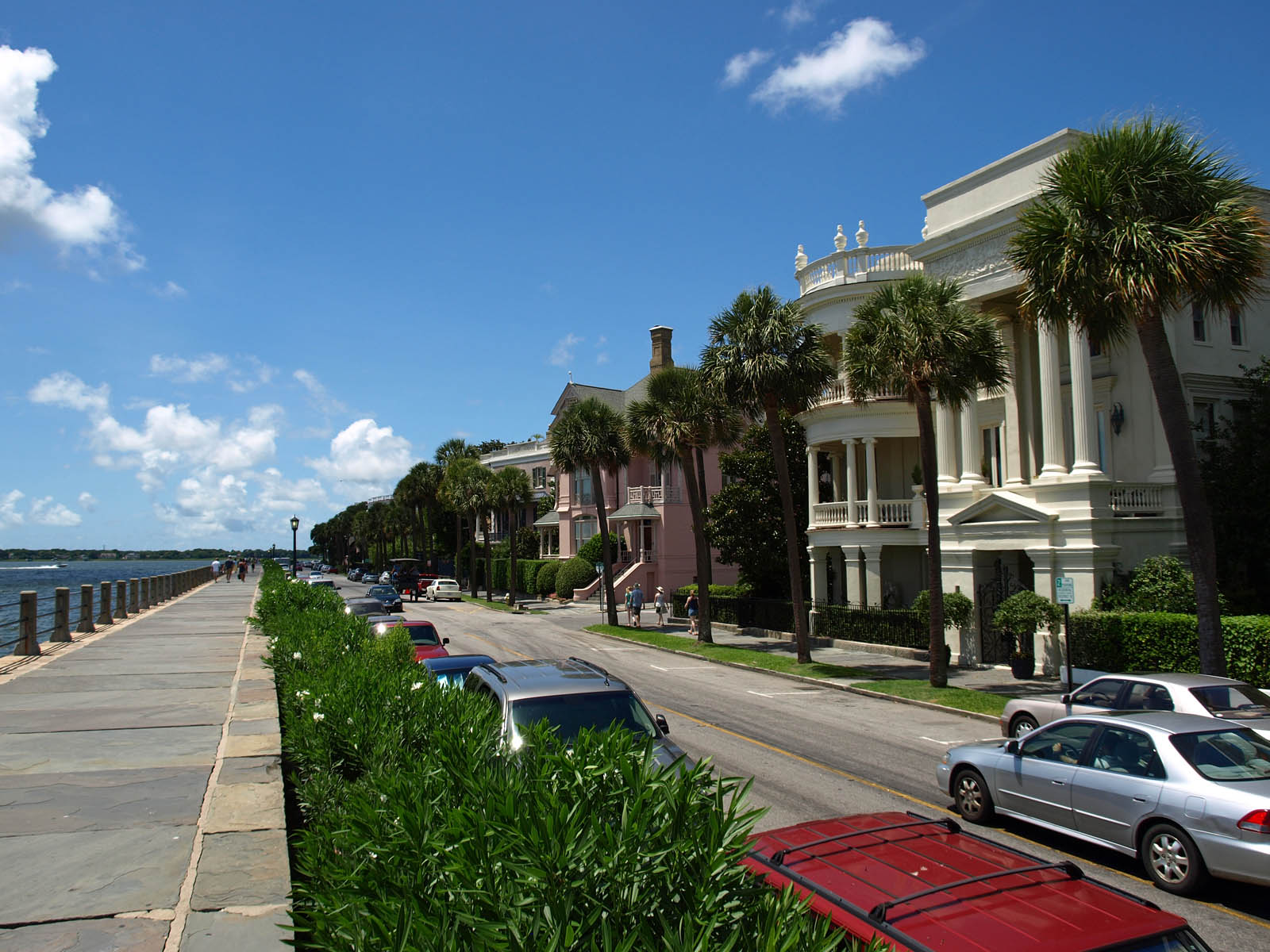


 Between the Revolutionary War and the Civil War, Charleston experienced an economic boom, at least for the top strata of society. The expansion of cotton as a cash crop in the South both led to huge wealth for a small segment of society and funded impressive architecture and culture but also escalated the importance of slaves and led to greater and greater restrictions on Black Charlestonians.
By 1783, the growth of the city had reached a point where a municipal government because desirable; therefore on August 13, 1783, an act of incorporation for the city of Charleston was ratified. The act originally specified the city's name as "Charles Ton," as opposed to the previous Charlestown, but the spelling "Charleston" quickly came to dominate.
Although
Between the Revolutionary War and the Civil War, Charleston experienced an economic boom, at least for the top strata of society. The expansion of cotton as a cash crop in the South both led to huge wealth for a small segment of society and funded impressive architecture and culture but also escalated the importance of slaves and led to greater and greater restrictions on Black Charlestonians.
By 1783, the growth of the city had reached a point where a municipal government because desirable; therefore on August 13, 1783, an act of incorporation for the city of Charleston was ratified. The act originally specified the city's name as "Charles Ton," as opposed to the previous Charlestown, but the spelling "Charleston" quickly came to dominate.
Although Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region i ...
had replaced it as the state capital in 1788, Charleston became even more prosperous as Eli Whitney's 1793 invention of the cotton gin sped the processing of the crop over 50 times. United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Britain's Industrial Revolution#Textile manufacture, Industrial Revolution—initially built upon its Textile industry#Industrial revolution, textile industry—took up the extra production ravenously and cotton became Charleston's major export commodity in the 19th century.
The Bank of South Carolina, the second-oldest building in the nation to be constructed as a bank, was established in 1798; branches of the First Bank of the United States, First and Second Bank of the United States were also located in Charleston in 1800 and 1817.
Throughout the Antebellum South, Antebellum Period, Charleston continued to be the only major American city with a majority-slave population.[ The city widespread use of slaves as workers was a frequent subject of writers and visitors: a merchant from Liverpool noted in 1834 that "almost all the working population are Negroes, all the servants, the carmen & porters, all the people who see at the stalls in Market, and most of the Journeymen in trades".]Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and ...
Slave Trade Act of 1794, in 1794 and all importation of slaves was banned Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves, in 1808, but American merchantmen frequently refused to permit Blockade of Africa, British inspection for enslaved cargo, and smuggling remained common. Much more important was the domestic slave trade, which boomed as the Deep South was developed in new cotton plantations. As a result of the trade, there was a forced migration of more than one million slaves from the Upper South to the Lower South in the antebellum years. During the early 19th century, the first dedicated slave markets were founded in Charleston, mostly near Chalmers and State streets.[ Many domestic slavers used Charleston as a port in what was called the coastwise trade, traveling to such ports as Mobile and New Orleans.
Slave ownership was the primary marker of class and even the town's freedmen and free people of color typically kept slaves if they had the wealth to do so. Visitors commonly remarked on the sheer number of Blacks in Charleston and their seeming freedom of movement, though in fact—mindful of the ]Stono Rebellion
The Stono Rebellion (also known as Cato's Conspiracy or Cato's Rebellion) was a slave revolt that began on 9 September 1739, in the colony of South Carolina. It was the largest slave rebellion in the Southern Colonies, with 25 colonists and 35 t ...
and the Haitian Revolution, slave revolution that established Haiti—the whites closely regulated the behavior of both slaves and free people of color. Wages and hiring practices were fixed, identifying badges were sometimes required, and even work songs were sometimes censored. Punishment was handled out of sight by the city's workhouse, whose fees provided the municipal government with thousands a year.[
The effects of slavery were pronounced on white society as well. The high cost of 19th-century slaves and their high rate of return combined to institute an oligarchic society controlled by about ninety interrelated families, where 4% of the free population controlled half of the wealth, and the lower half of the free population—unable to compete with owned or rented slaves—held no wealth at all.][ The white middle class was minimal: Charlestonians generally disparaged hard work as the lot of slaves.][ Frederick Law Olmsted, Olmsted considered their civic elections "entirely contests of money and personal influence" and the oligarchs dominated civic planning: the lack of public parks and amenities was noted, as was the abundance of private gardens in the wealthy's walled estates.
In the 1810s, the town's churches intensified their discrimination against their Black parishioners, culminating in Bethel Methodist Church (Charleston, South Carolina), Bethel Methodist's 1817 construction of a hearse house over its Black burial ground. 4,376 Black Methodists joined Morris Brown in establishing Hampstead Church, the African Methodist Episcopal church now known as Emanuel African Methodist Episcopal Church, Mother Emanuel.][ State and city laws prohibited Black literacy, limited Black worship to daylight hours, and required a majority of any church's parishioners be white. In June 1818, 140 Black church members at Hampstead Church were arrested and eight of its leaders given fines and ten lashes; police raided the church again in 1820 and pressured it in 1821.][ and carpenter who had bought his freedom after winning a lottery, planned an Denmark Vesey's Rebellion, uprising and escape to Haiti—initially for Bastille Day—that failed when one slave revealed the plot to his master. Over the next month, the city's intendant (mayor) James Hamilton Jr. organized a militia for regular patrols, initiated a secret and extrajudicial tribunal to investigate, and hanged 35 and exiled 35][ or 37 slaves to Spanish Cuba for their involvement.][ and erected a South Carolina State Arsenal, new arsenal. This structure later was the basis of The Citadel, The Military College of South Carolina, the Citadel's first campus. The AME congregation built a new church but in 1834 the city banned it and all Black worship services, following Nat Turner's Nat Turner's slave rebellion, 1831 rebellion in Virginia. The estimated 10% of slaves who came to America as Islam in the United States, Muslims never had a separate mosque. Slaveholders sometimes provided them with beef rations in place of pork in recognition of religious traditions.
The registered tonnage of Charleston shipping in 1829 was 12,410. In 1832, South Carolina passed an ordinance of Nullification (U.S. Constitution), nullification, a procedure by which a state could, in effect, repeal a federal law; it was directed against the most recent tariff acts. Soon, federal soldiers were dispensed to Charleston's forts, and five United States Coast Guard cutters were detached to Charleston Harbor "to take possession of any vessel arriving from a foreign port, and defend her against any attempt to dispossess the Customs Officers of her custody until all the requirements of law have been complied with." This federal action became known as the Charleston incident. The state's politicians worked on a compromise law in Washington to gradually reduce the tariffs.
Charleston's embrace of classical architecture began after a devastating fire leveled much of the city. On April 27, 1838, Charleston suffered a catastrophic fire that burned more than 1000 buildings and caused about $3 million in damage at the time. The damaged buildings amounted to about one-fourth of all the businesses in the main part of the city. When the many homes and business were rebuilt or repaired, a great cultural awakening occurred. Previous to the fire, only a few homes were styled as Greek Revival; many residents decided to construct new buildings in that style after the conflagration. This tradition continued and made Charleston one of the foremost places to view Greek Revival architecture. The Gothic Revival also made a significant appearance in the construction of many churches after the fire that exhibited picturesque forms and reminders of devout European religion.
By 1840, the Market Hall and Sheds, where fresh meat and produce were brought daily, became a hub of commercial activity. The slave trade also depended on the port of Charleston, where ships could be unloaded and the slaves bought and sold. The legal importation of African slaves had ended in 1808, although smuggling was significant. However, the domestic trade was booming. More than one million slaves were transported from the Upland South, Upper South to the Deep South in the antebellum years, as cotton plantations were widely developed through what became known as the Black Belt (region of Alabama), Black Belt. Many slaves were transported in the coastwise slave trade, with slave ships stopping at ports such as Charleston.
]
Civil War (1861–1865)


 Charleston played a major part in the Civil War. As a pivotal city, both the Union and Confederate Armies vied for control of it. The Civil War began in
Charleston played a major part in the Civil War. As a pivotal city, both the Union and Confederate Armies vied for control of it. The Civil War began in Charleston Harbor
The Charleston Harbor is an inlet (8 sq mi/20.7 km²) of the Atlantic Ocean at Charleston, South Carolina. The inlet is formed by the junction of Ashley and Cooper rivers at . Morris and Sullivan's Islands shelter the entrance. Charleston ...
in 1861, and ended mere months after the Union forces took control of Charleston in 1865.
Following 1860 US presidential election, the election of Abraham Lincoln, the South Carolina General Assembly voted on December 20, 1860, to secession, secede from the Union (American Civil War), Union. South Carolina was the first state to secede. On December 27, Castle Pinckney was surrendered by its garrison to the state militia and, on January 9, 1861, The Citadel, The Military College of South Carolina, Citadel cadets opened fire on the USS''Star of the West'' as it entered Charleston Harbor.
The first full battle of the American Civil War occurred on April 12, 1861, when shore batteries under the command of Pierre G. T. Beauregard, General Beauregard opened fire on the held Fort Sumter in Charleston Harbor. After a 34-hour bombardment, Major Robert Anderson surrendered the fort.
On December 11, 1861, an enormous fire burned over of the city.
Union control of the sea permitted the repeated bombardment of the city, causing vast damage.[ Although Admiral Du Pont's naval assault on the town's forts in April 1863 failed, the Union navy's blockade shut down most commercial traffic. Over the course of the war, some Blockade runners of the American Civil War, blockade runners got through but not a single one made it into or out of the Charleston Harbor between August 1863 and March 1864.][Craig L. Symonds, ''The Civil War at Sea'' (2009) p. 57] The early submarine ''H. L. Hunley (submarine), H.L. Hunley'' made a night attack on the on February 17, 1864.
General Gillmore's land assault in July 1864 was unsuccessful but the fall of Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region i ...
and advance of General William T. Sherman's army through the state prompted the Confederates to evacuate the town on February 17, 1865, burning the public buildings, cotton warehouses, and other sources of supply before their departure. Union Army, Union troops moved into the city within the month. The War Department recovered what federal property remained and also confiscated the campus of the Citadel Military Academy and used it as a federal garrison for the next 17 years. The facilities were finally returned to the state and reopened as a military college in 1882 under the direction of Lawrence E. Marichak.
Postbellum (1865–1945)
Reconstruction
After the defeat of the Confederacy, federal forces remained in Charleston during Reconstruction Era, Reconstruction. The war had shattered the city's prosperity, but the African-American population surged (from 17,000 in 1860 to over 27,000 in 1880) as freedmen moved from the countryside to the major city.[Jeffrey G. Strickland, ''Ethnicity And Race In The Urban South: German Immigrants And African-Americans In Charleston, South Carolina During Reconstruction'', 2003, p. 11, Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations. Paper 1541](_blank)
Blacks quickly left the Southern Baptist Church and resumed open meetings of the African Methodist Episcopal Church, African Methodist Episcopal and AME Zion churches. They purchased dogs, guns, liquor, and better clothes—all previously banned—and ceased yielding the sidewalks to whites.[Melinda Meeks Hennessy, "Racial Violence During Reconstruction: The 1876 Riots in Charleston and Cainhoy"](_blank)
''South Carolina Historical Magazine'', Vol. 86, No. 2, (April 1985), 104–106 In the 1876 election cycle, two major riots between black Republicans and white Democrats occurred in the city, in September and the day after the election in November, as well as a violent incident in Cainhoy at an October joint discussion meeting.[Reconstruction as Armed Insurgency: Cainhoy](_blank)
, ''South Carolina during Reconstruction'', 2010–2012, accessed October 27, 2014 The Red Shirts were instrumental in suppressing the black Republican vote in some areas in 1876 and narrowly electing Wade Hampton III, Wade Hampton as governor, and taking back control of the state legislature. Another riot occurred in Charleston the day after the election, when a prominent Republican leader was mistakenly reported killed.
Politics
In the early 20th century strong political machines emerged in the city reflecting economic, class, racial, and ethnic tensions. The factions nearly all opposed U.S. Senator Benjamin Tillman, Ben Tillman who repeatedly attacked and ridiculed the city in the name of upstate poor farmers. Well organized factions within the Democratic Party in Charleston gave the voters clear choices and played a large role in state politics.
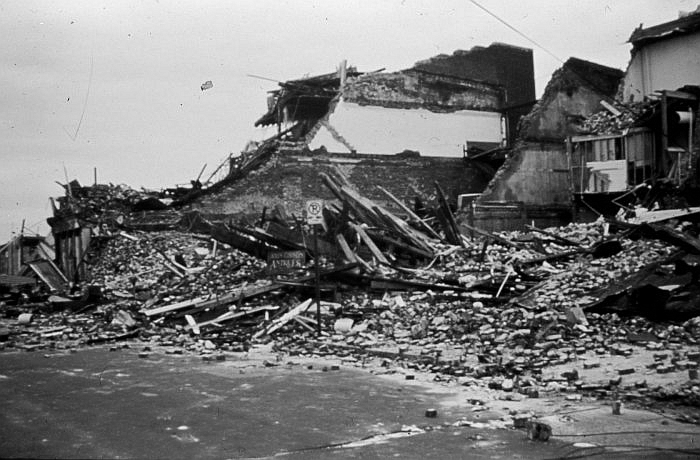
1886 earthquake
On August 31, 1886, Charleston experienced a strong 1886 Charleston earthquake, earthquake. The shock was estimated to have a moment magnitude scale, moment magnitude of 7.0 and a maximum Mercalli intensity scale, Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). It was felt as far away as Boston to the north, Chicago and Milwaukee to the northwest, as far west as New Orleans, as far south as Cuba, and as far east as Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = "Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, es ...
. It damaged 2,000 buildings in Charleston and caused $6 million worth of damage ($ million in dollars), at a time when all the city's buildings were valued around $24 million ($ million in dollars).
Charleston race riots
The Charleston race riot of 1919 took place on the night of Saturday, May 10, between members of the US Navy and the local black population. They attacked black individuals, businesses, and homes killing six and injuring dozens.
Contemporary era (1945–present)
Charleston languished economically for several decades in the 20th century, though the large federal military presence in the region helped to shore up the city's economy. Charleston's tourism boom began in earnest following the publication of Albert Simons and Samuel Lapham VI, Samuel Lapham's ''Architecture of Charleston'' in the 1920s.
The 1969 Charleston hospital strike, Charleston Hospital Strike of 1969, in which mostly black workers protested discrimination and low wages, was one of the last major events of the civil rights movement. It attracted Ralph Abernathy, Coretta Scott King, Andrew Young, and other prominent figures to march with the local leader, Mary Moultrie.
Joseph P. Riley Jr. was elected mayor in the 1970s, and helped advance several cultural aspects of the city.
Between 1989 and 1996, Charleston saw two significant economic hits. First, the eye of Hurricane Hugo came ashore at Charleston Harbor in 1989, and though the worst damage was in nearby McClellanville, South Carolina, McClellanville, three-quarters of the homes in Charleston's historic district sustained damage of varying degrees. The hurricane caused over $2.8 billion in damage. The city was able to rebound fairly quickly after the hurricane and has grown in population, reaching an estimated 124,593 residents in 2009.[David Slade, "RACIAL SHIFT: Charleston peninsula's makeup reverses in 30 years, with blacks leaving for suburbs, area becoming two-thirds white"](_blank)
, ''The Post and Courier'', March 28, 2011; accessed November 10, 2016 Many African Americans moved to the less-expensive suburbs in these decades.
Condemnation of role in the slave trade
On June 17, 2018, the Charleston City Council apologized for its role in the slave trade and condemned its "inhumane" history. It also acknowledged wrongs committed against African Americans by slavery and Jim Crow laws.
Demographics
2020 census
As of the 2020 United States census, there were 150,227 people, 58,902 households, and 31,780 families residing in the city.
Language
Given Charleston's high concentration of African Americans who spoke the Gullah language, a creole language that developed on the Sea Islands and in the Low Country, the local speech patterns were also influenced by this community. Today, Gullah is still spoken by many African American residents. However, rapid development since 1980, especially on the surrounding Sea Islands, has attracted residents from outside the area and led to a decline in Gullah's prominence.
The traditional educated Charleston accent has long been noted in the state and throughout the South. It is typically heard in wealthy European American older people who trace their families back generations in the city. It has ingliding or monophthongal long mid-vowels, raises ''ay'' and ''aw'' in certain environments, and is rhotic and non-rhotic accents, nonrhotic. Sylvester Primer of the College of Charleston wrote about aspects of the local dialect in his late 19th-century works: "Charleston Provincialisms" (1887)["Charleston Provincialisms" (1887)](_blank)
Pub. Modern Language Association of America, Vol. iii, Internet Archive and Early Journal Content on JSTOR, accessed November 5, 2014 and "The Huguenot Element in Charleston's Provincialisms", published in a German journal. He believed the accent was based on the English as it was spoken by the earliest settlers, therefore derived from Elizabethan England and preserved with modifications by Charleston speakers. The disappearing "Charleston accent" spoken mainly by older natives is still noted in the local pronunciation of the city's name. Many Charleston natives ignore the 'r' and elongate the first vowel, pronouncing the name as "Chalston".
Religion
Charleston is known as "The Holy City".Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Be ...
refugees settled in Charleston in the early 18th century. The Emanuel African Methodist Episcopal Church is the oldest African Methodist Episcopal church in the Southern United States and houses the oldest black church, black congregation south of Baltimore, Maryland.
Culture
Charleston's culture blends traditional Southern U.S., English, French, and West African elements. The downtown peninsula has a number of art, music, local cuisine, and fashion venues. Spoleto Festival USA, held annually in late spring, was founded in 1977 by Pulitzer Prize-winning composer Gian Carlo Menotti, who sought to establish a counterpart to the ''Festival dei Due Mondi'' (the Festival of Two Worlds) in Spoleto, Italy.
Charleston's oldest community theater group, the Footlight Players, has provided theatrical productions since 1931. A variety of performing arts venues includes the historic Dock Street Theatre. The annual Charleston Fashion Week held each spring in Marion Square brings in designers, journalists, and clients from across the nation. Charleston is known for its local seafood, which plays a key role in the city's renowned cuisine, comprising staple dishes such as gumbo, she-crab soup, fried oysters, Lowcountry boil, deviled crab cakes, red rice, and shrimp and grits. Rice is the staple in many dishes, reflecting the rice culture of the Low Country. The cuisine in Charleston is also strongly influenced by British and French elements.
Annual cultural events and fairs
Charleston annually hosts Spoleto Festival USA founded by Gian Carlo Menotti, a 17-day art festival featuring over 100 performances by individual artists in a variety of disciplines.
Music
The Gullah
The Gullah () are an African American ethnic group who predominantly live in the Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, and North Carolina, within the coastal plain and the Sea Islands. Their language and cultu ...
community has had a tremendous influence on music in Charleston, especially when it comes to the early development of jazz music. In turn, the music of Charleston has had an influence on that of the rest of the country. The geechee dances that accompanied the music of the dock workers in Charleston followed a rhythm that inspired Eubie Blake's "Charleston Rag" and later James P. Johnson's "Charleston (1923 song), Charleston", as well as the Charleston (dance), dance craze that defined a nation in the 1920s. "Ballin' the Jack", which was a popular dance in the years before "Charleston", was written by native Charlestonian Chris Smith (composer), Chris Smith.
The Jenkins Orphanage was established in 1891 by the Rev. Daniel J. Jenkins in Charleston. The orphanage accepted donations of musical instruments and Rev. Jenkins hired local Charleston musicians and Avery Institute Graduates to tutor the boys in music. As a result, Charleston musicians became proficient on a variety of instruments and were able to read music expertly. These traits set Jenkins musicians apart and helped land some of them positions in big bands with Duke Ellington and Count Basie. Cat Anderson, William "Cat" Anderson, Jabbo Smith, and Freddie Green are but a few of the alumni who became professional musicians. Orphanages around the country began to develop brass bands in the wake of the Jenkins Orphanage Band's success.
As many as five bands were on tour during the 1920s. The Jenkins Orphanage Band played in the inaugural parades of Presidents Theodore Roosevelt and William Howard Taft, William Taft and toured the US and Europe. The band also played on Broadway for the play "Porgy" by DuBose Heyward, DuBose and Dorothy Heyward, a stage version of their novel of the same title. The story was based in Charleston and featured the Gullah community. The Heywards insisted on hiring the real Jenkins Orphanage Band to portray themselves on stage.
Live theater
Charleston has a vibrant theater scene and is home to America's first theater. Most of the theaters are part of the League of Charleston Theatres, better known as Theatre Charleston. Some of the city's theaters include:
*The Dock Street Theatre, opened in the 1930s on the site of America's first purpose-built theater building, is home of the Charleston Stage Company, South Carolina's largest professional theater company.
*Sottile Theater is on the campus of The College of Charleston.
Museums, historical sites, and other attractions
 Charleston has many historic buildings, art and historical museums, List of parks in Charleston, South Carolina, public parks, and other attractions, including:
*Halsey Institute of Contemporary Art at the College of Charleston is free a non-collecting contemporary arts organization.
*The Calhoun Mansion, a 24,000-square-foot, 1876 Victorian home at 16 Meeting Street, is named for a grandson of John C. Calhoun who lived there with his wife, the builder's daughter. The private house is periodically open for tours.
*The Charleston Museum, America's first museum, was founded in 1773.
*The Exchange and Provost was built in 1767. It is operated as a museum by the Daughters of the American Revolution.
*The Powder Magazine (Charleston, South Carolina), Powder Magazine is a 1713 gunpowder magazine and museum. It is the oldest surviving public building in South Carolina.
*The Gibbes Museum of Art, opened in 1905, houses principally American works with a Charleston or Southern connection.
*The Fireproof Building houses the South Carolina Historical Society which has a rotating series of historical displays.
*The Nathaniel Russell House is an important federal-style house open to the public as a house museum.
*The Gov. William Aiken House, also known as the Aiken-Rhett House, is a house museum built in 1820.
*The Heyward-Washington House is a historic house museum owned and operated by the Charleston Museum. Furnished for the late 18th century, the house includes a collection of Charleston-made furniture.
*The Joseph Manigault House is a historic house museum owned and operated by the Charleston Museum. The house was designed by Gabriel Manigault and is significant for its Adam style architecture.
*The Market Hall and Sheds, also known as the City Market or simply the Market, stretch several blocks behind 188 Meeting Street. Market Hall was built in the 1841 and houses the Daughters of the Confederacy Museum. The sheds house some permanent stores, but are mainly occupied by open-air vendors.
*The Avery Research Center for African American History and Culture was established to collect, preserve, and make public the unique historical and cultural heritage of African Americans in Charleston and the South Carolina Low Country. Avery's archival collections, museum exhibitions, and public programming reflect these diverse populations, as well as the wider African Diaspora.
*Fort Sumter, site of the first shots fired in the Civil War, is located in Charleston Harbor. The National Park Service maintains a visitor center for Fort Sumter at Liberty Square (near the South Carolina Aquarium), and boat tours including the fort depart nearby.
*The Battery (Charleston), The Battery is an historic defensive seawall and promenade located at the tip of the peninsula along with White Point Garden, a park featuring several memorials and Civil War-era artillery pieces.
*Rainbow Row is an iconic strip of homes along the harbor that date back to the mid-18th century. Though the homes are not open to the public, they are one of the most photographed attractions in the city and are featured heavily in local art.
*The South Carolina Aquarium includes revolving exhibits while its permanent focus is on the aquatic life of South Carolina.
*Waterfront Park (Charleston), Waterfront Park located on the Cooper River (South Carolina), Cooper River.
*Old Slave Mart museum – Located at 6 Chalmers St in the historic district is the first African American Museum. It has operated since 1938.
Charleston has many historic buildings, art and historical museums, List of parks in Charleston, South Carolina, public parks, and other attractions, including:
*Halsey Institute of Contemporary Art at the College of Charleston is free a non-collecting contemporary arts organization.
*The Calhoun Mansion, a 24,000-square-foot, 1876 Victorian home at 16 Meeting Street, is named for a grandson of John C. Calhoun who lived there with his wife, the builder's daughter. The private house is periodically open for tours.
*The Charleston Museum, America's first museum, was founded in 1773.
*The Exchange and Provost was built in 1767. It is operated as a museum by the Daughters of the American Revolution.
*The Powder Magazine (Charleston, South Carolina), Powder Magazine is a 1713 gunpowder magazine and museum. It is the oldest surviving public building in South Carolina.
*The Gibbes Museum of Art, opened in 1905, houses principally American works with a Charleston or Southern connection.
*The Fireproof Building houses the South Carolina Historical Society which has a rotating series of historical displays.
*The Nathaniel Russell House is an important federal-style house open to the public as a house museum.
*The Gov. William Aiken House, also known as the Aiken-Rhett House, is a house museum built in 1820.
*The Heyward-Washington House is a historic house museum owned and operated by the Charleston Museum. Furnished for the late 18th century, the house includes a collection of Charleston-made furniture.
*The Joseph Manigault House is a historic house museum owned and operated by the Charleston Museum. The house was designed by Gabriel Manigault and is significant for its Adam style architecture.
*The Market Hall and Sheds, also known as the City Market or simply the Market, stretch several blocks behind 188 Meeting Street. Market Hall was built in the 1841 and houses the Daughters of the Confederacy Museum. The sheds house some permanent stores, but are mainly occupied by open-air vendors.
*The Avery Research Center for African American History and Culture was established to collect, preserve, and make public the unique historical and cultural heritage of African Americans in Charleston and the South Carolina Low Country. Avery's archival collections, museum exhibitions, and public programming reflect these diverse populations, as well as the wider African Diaspora.
*Fort Sumter, site of the first shots fired in the Civil War, is located in Charleston Harbor. The National Park Service maintains a visitor center for Fort Sumter at Liberty Square (near the South Carolina Aquarium), and boat tours including the fort depart nearby.
*The Battery (Charleston), The Battery is an historic defensive seawall and promenade located at the tip of the peninsula along with White Point Garden, a park featuring several memorials and Civil War-era artillery pieces.
*Rainbow Row is an iconic strip of homes along the harbor that date back to the mid-18th century. Though the homes are not open to the public, they are one of the most photographed attractions in the city and are featured heavily in local art.
*The South Carolina Aquarium includes revolving exhibits while its permanent focus is on the aquatic life of South Carolina.
*Waterfront Park (Charleston), Waterfront Park located on the Cooper River (South Carolina), Cooper River.
*Old Slave Mart museum – Located at 6 Chalmers St in the historic district is the first African American Museum. It has operated since 1938.
Sports
 Charleston is home to a number of professional, minor league, and amateur sports teams:
*The Charleston Battery, a professional soccer team, play in the USL Championship. The Battery play at Patriots Point Soccer Complex.
*The South Carolina Stingrays, a professional hockey team, plays in the ECHL. The Stingrays play in North Charleston at the North Charleston Coliseum. The Stingrays are an affiliate of the Washington Capitals and Hershey Bears.
*The Charleston RiverDogs, a Minor League Baseball team, plays in the Low-A East and are an affiliate of the Tampa Bay Rays. The RiverDogs play at Joseph P. Riley Jr. Park.
*The Charleston Outlaws RFC is a rugby union club in the Palmetto Rugby Union, USA Rugby South, and USA Rugby. It competes in Men's Division II against the Cape Fear, Columbia, Greenville, and Charlotte "B" clubs. The club also hosts a rugby sevens tournament during Memorial Day weekend.
*The Charleston Gaelic Athletic Association is a Gaelic athletic club focusing on the sports of hurling and Gaelic football. The club competes in the Southeastern Division of the North American County Board of the Gaelic Athletic Association, GAA. The club hosts other division clubs in the Holy City Cup each spring.
*The Lowcountry Highrollers is a women's flat-track roller derby league in the Charleston area. The league is a local member of the Women's Flat Track Derby Association.
*The Family Circle Tennis Center hosts the Charleston Open, Volvo Car Open, a major Women's Tennis Association Event. The facility is located on Daniel Island.
Other notable sports venues in Charleston include Johnson Hagood Stadium (home of The Citadel Bulldogs College football, football team), McAlister Field House (home of The Citadel Bulldogs College basketball, basketball team), and TD Arena, Toronto Dominion Bank Arena at the College of Charleston, which seats 5,100 people who view the school's basketball and volleyball teams.
Charleston is home to a number of professional, minor league, and amateur sports teams:
*The Charleston Battery, a professional soccer team, play in the USL Championship. The Battery play at Patriots Point Soccer Complex.
*The South Carolina Stingrays, a professional hockey team, plays in the ECHL. The Stingrays play in North Charleston at the North Charleston Coliseum. The Stingrays are an affiliate of the Washington Capitals and Hershey Bears.
*The Charleston RiverDogs, a Minor League Baseball team, plays in the Low-A East and are an affiliate of the Tampa Bay Rays. The RiverDogs play at Joseph P. Riley Jr. Park.
*The Charleston Outlaws RFC is a rugby union club in the Palmetto Rugby Union, USA Rugby South, and USA Rugby. It competes in Men's Division II against the Cape Fear, Columbia, Greenville, and Charlotte "B" clubs. The club also hosts a rugby sevens tournament during Memorial Day weekend.
*The Charleston Gaelic Athletic Association is a Gaelic athletic club focusing on the sports of hurling and Gaelic football. The club competes in the Southeastern Division of the North American County Board of the Gaelic Athletic Association, GAA. The club hosts other division clubs in the Holy City Cup each spring.
*The Lowcountry Highrollers is a women's flat-track roller derby league in the Charleston area. The league is a local member of the Women's Flat Track Derby Association.
*The Family Circle Tennis Center hosts the Charleston Open, Volvo Car Open, a major Women's Tennis Association Event. The facility is located on Daniel Island.
Other notable sports venues in Charleston include Johnson Hagood Stadium (home of The Citadel Bulldogs College football, football team), McAlister Field House (home of The Citadel Bulldogs College basketball, basketball team), and TD Arena, Toronto Dominion Bank Arena at the College of Charleston, which seats 5,100 people who view the school's basketball and volleyball teams.
Books and films
Various books and films have been set in Charleston; some of the best known works are listed below. In addition, Charleston is a popular filming location for movies and television, both in its own right and as a stand-in for Southern and/or historic settings.
*''Porgy (novel), Porgy'' (1925), by DuBose Heyward, adapted into Porgy (play), the play in 1927. George Gershwin's folk opera ''Porgy and Bess'' (1935), based on the novel ''Porgy (novel), Porgy'', is set in Charleston and was partially written at Folly Beach, near Charleston. A Porgy and Bess (film), film version was released in 1959.
*North and South (trilogy), ''North and South'' series of books by John Jakes, was partially set in Charleston. The North and South (miniseries), ''North and South'' miniseries was partially set and filmed in Charleston.
*Part of the 1989 film ''Glory (1989 film), Glory'', starring Matthew Broderick, Denzel Washington, and Morgan Freeman, features the 1863 Second Battle of Fort Wagner on Morris Island
Morris Island is an 840-acre (3.4 km²) uninhabited island in Charleston Harbor in South Carolina, accessible only by boat. The island lies in the outer reaches of the harbor and was thus a strategic location in the American Civil War. The ...
.
*The movies ''Swamp Thing (film), Swamp Thing'' (1982) and ''The Lords of Discipline (film), The Lords of Discipline'' (1983) (based on the novel by Pat Conroy) were partly filmed in Charleston.
Economy
Commercial shipping is important to the economy. The city has two shipping terminals, of a total of five terminals owned and operated by the South Carolina Ports Authority in the Charleston metropolitan area, which are part of the fourth-largest container seaport on the East Coast and the seventh-largest container seaport in the United States.
Government
Charleston has a mayor-council government, strong mayor-council government, with the mayor acting as the chief administrator and the executive officer of the municipality. The mayor also presides over city council meetings and has a vote, the same as other council members. The current mayor, since 2016, is John Tecklenburg. The council has 12 members who are each elected from single-member districts.
Fire department
 The City of Charleston Fire Department consists over 300 full-time firefighters. These firefighters operate out of 21 companies located throughout the city: 16 engine companies, two tower companies, two ladder companies, a heavy rescue company, a HAZ-MAT unit and several special units. Training, Fire Marshall, Operations, and Administration are the divisions of the department. The department operates on a 24/48 schedule and is a Class 1 ISO rating. Russell (Rusty) Thomas served as Fire Chief until June 2008, and was succeeded by Chief Thomas Carr in November 2008. The department is presently led by Chief Daniel Curia.
The City of Charleston Fire Department consists over 300 full-time firefighters. These firefighters operate out of 21 companies located throughout the city: 16 engine companies, two tower companies, two ladder companies, a heavy rescue company, a HAZ-MAT unit and several special units. Training, Fire Marshall, Operations, and Administration are the divisions of the department. The department operates on a 24/48 schedule and is a Class 1 ISO rating. Russell (Rusty) Thomas served as Fire Chief until June 2008, and was succeeded by Chief Thomas Carr in November 2008. The department is presently led by Chief Daniel Curia.
Police department
The City of Charleston Police Department, with a total of 458 sworn officers, 117 civilians, and 27 reserve police officers, is South Carolina's largest police department. Luther Reynolds serves as the current Chief of Police. He follows Greg Mullen and Reuben Greenberg. Chief Reynolds is credited with continuing successful community outreach programs such as The Illumination Project and fostering a culture of mutual respect. Under Chief Reynolds, the agency has successfully withstood challenges such as the Coronavirus and downtown disturbances. Additionally, the agency continues to recruit police candidates in a competitive market.
EMS and medical centers
Emergency medical services (EMS) for the city are provided by Charleston County Emergency Medical Services (CCEMS) & Berkeley County Emergency Medical Services (BCEMS). The city is served by the EMS and 911 services of both Charleston and Berkeley counties since the city is part of both counties.
Charleston is the primary medical center for the eastern portion of the state. The city has several major hospitals located in the downtown area: MUSC Medical Center, Medical University of South Carolina Medical Center (MUSC), Ralph H. Johnson VA Medical Center, and Roper Hospital. MUSC is the state's first school of medicine, the largest medical university in the state, and the sixth-oldest continually operating school of medicine in the United States. The downtown medical district is experiencing rapid growth of biotechnology and medical research industries coupled with substantial expansions of all the major hospitals. Additionally, more expansions are planned or underway at another major hospital located in the West Ashley portion of the city: Bon Secours-St Francis Xavier Hospital. The Trident Regional Medical Center located in the North Charleston, South Carolina, City of North Charleston and East Cooper Regional Medical Center located in Mount Pleasant also serve the needs of residents of the city of Charleston.
Coast Guard Station Charleston
Coast Guard Station Charleston responds to search and rescue emergencies, conducts maritime law enforcement activities, and Ports, Waterways, and Coastal Security (PWCS) missions. Personnel from Station Charleston are highly trained professionals, composed of federal law enforcement officers, boat crewmen, and coxswains who are capable of completing a wide range of missions. In 2020, the Coast Guard announced plans to construct a "superbase" on the former Charleston Naval Shipyard complex to consolidate all its Charleston-area facilities and become the homeport for five Security cutters and additional offshore cutters.
Coast Guard Sector Charleston (District 7)
*Coast Guard Station Charleston
*Coast Guard Helicopter Air Facility, Johns Island, Charleston
*Coast Guard Reserves, Charleston
*USCGC Yellowfin, Marine Protector-class coastal patrol boat, Charleston
*USCGC Anvil, USCG inland construction tender, 75-foot inland construction tender, Charleston
*USCGC Willow, (WLB-202), Charleston
Military
*Army Corps of Engineers, Charleston District Headquarters
*U.S. Coast Guard
*Joint Base Charleston (Navy & Air Force)
Crime
The following table shows Charleston's crime rate for six crimes that Morgan Quitno uses to calculate the ranking of "America's most dangerous cities", in comparison to the national average. The statistics shown are for the number of crimes committed per 100,000 people. Since 1999, the overall crime rate of Charleston has declined markedly. The total crime index rate for Charleston in 1999 was 597.1 crimes committed per 100,000 people, while in 2011, the total crime index rate was 236.4 per 100,000.
Transportation
Airport and rail
The City of Charleston is served by the Charleston International Airport. It is located in the City of North Charleston and is about northwest of downtown Charleston. It is the busiest passenger airport in South Carolina . The airport shares runways with the adjacent Charleston Air Force Base. Charleston Executive Airport is a smaller airport located in the John's Island section of the city of Charleston and is used by noncommercial aircraft. Both airports are owned and operated by the Charleston County Aviation Authority. As of April 2019, British Airways does seasonal non-stop flights from Charleston to Heathrow Airport, London-Heathrow.
Charleston is served by two daily Amtrak trains: Palmetto (Amtrak), The Palmetto and Silver Meteor at North Charleston station, the Amtrak station located at 4565 Gaynor Avenue in the City of North Charleston located around 7.5 miles from downtown Charleston.
Interstates and highways
Interstate 26 in South Carolina, Interstate 26 (I-26) begins in downtown Charleston, with exits to the Septima Clark Expressway, the Arthur Ravenel Jr. Bridge and Meeting Street. Heading northwest, it connects the city to North Charleston
North Charleston is the third-largest city in the state of South Carolina.City Planning Department (2008-07)City of North Charleston boundary map. City of North Charleston. Retrieved January 21, 2011. On June 12, 1972, the city of North Charlest ...
, the Charleston International Airport, Interstate 95 in South Carolina, I-95, and Columbia. The Arthur Ravenel Jr. Bridge and Septima Clark Expressway are part of U.S. Route 17 in South Carolina, U.S. Route 17 (US 17), which travels east–west through the cities of Charleston and Mount Pleasant. The Mark Clark Expressway, or Interstate 526, I-526, is the Bypass (road), bypass around the city and begins and ends at US 17. U.S. Route 52 in South Carolina, US 52 is Meeting Street and its U.S. Route 52 Spur (Charleston, South Carolina), spur is East Bay Street, which becomes Morrison Drive after leaving the east side. This highway merges with King Street in the city's Neck area (industrial district). U.S. Route 78 in South Carolina, US 78 is King Street in the downtown area, eventually merging with Meeting Street.
Major highways
*Interstate 26 (eastern terminus is in Charleston)
*Interstate 526
*U.S. Route 17
*U.S. Route 52 (eastern terminus is in Charleston)
*U.S. Route 78 (eastern terminus is in Charleston)
*South Carolina Highway 7, State Highway 7 (Sam Rittenberg Boulevard)
*South Carolina Highway 30, State Highway 30 (James Island Expressway)
*South Carolina Highway 61, State Highway 61 (St. Andrews Boulevard/Ashley River Road)
*South Carolina Highway 171, State Highway 171 (Old Towne Road/Folly Road)
*South Carolina Highway 461, State Highway 461 (Paul Cantrell Boulevard/Glenn McConnell Parkway)
*South Carolina Highway 700 (Maybank Highway)
Arthur Ravenel Jr. Bridge
The Arthur Ravenel Jr. Bridge across the Cooper River (South Carolina), Cooper River opened on July 16, 2005, and was the List of longest cable-stayed bridge spans, longest cable-stayed bridge in the Americas at the time of its construction. The bridge links downtown Charleston with Mount Pleasant, and has eight lanes plus a 12-foot lane shared by pedestrians and bicycles. The height of the bridge varies, but it is estimated that it has a height of 573 feet. It replaced the John P. Grace Memorial Bridge, Grace Memorial Bridge (built in 1929) and the Silas N. Pearman Bridge (built in 1966). They were considered two of the more dangerous bridges in America and were demolished after the Ravenel Bridge opened.

City bus service
The city is also served by a bus system, operated by the Charleston Area Regional Transportation Authority (CARTA). Most of the urban area is served by regional fixed route buses, which are equipped with bike racks as part of the system's Rack and Ride program. CARTA offers connectivity to historic downtown attractions and accommodations with the Downtown Area Shuttle trolley buses, and it offers curbside pickup for disabled passengers with its Tel-A-Ride buses. A bus rapid transit system is in development, called Lowcountry Rapid Bus System, Lowcountry Rapid Transit that will connect Charleston to Summerville through North Charleston.
Rural parts of the city and metropolitan area are served by a different bus system, operated by Berkeley-Charleston-Dorchester Rural Transportation Management Association. The system is also commonly called the TriCounty Link.
Port
 The Port of Charleston, owned and operated by the South Carolina Ports Authority, is one of the largest ports in the United States, ranked seventh in the top 25 by containerization, containerized cargo volume in 2018.
The Port of Charleston, owned and operated by the South Carolina Ports Authority, is one of the largest ports in the United States, ranked seventh in the top 25 by containerization, containerized cargo volume in 2018.
Schools, colleges, and universities
 Because most of the city of Charleston is located in Charleston County, it is served by the Charleston County School District. Part of the city, however, is served by the Berkeley County School District in northern portions of the city, such as the Cainhoy Industrial District, Cainhoy Historical District and Daniel Island.
Charleston is also served by a large number of independent schools, including Porter-Gaud School (K-12), Charleston Collegiate School (K-12), Ashley Hall (school), Ashley Hall (Pre K-12), Charleston Day School (K-8), First Baptist Church School (K-12), Palmetto Christian Academy (K-12), Coastal Christian Preparatory School (K-12), Mason Preparatory School (K-8), and Addlestone Hebrew Academy (K-8).
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Charleston Office of Education also operates out of the city and oversees several K-8 parochial schools, such as Blessed Sacrament School, Christ Our King School, Charleston Catholic School, Nativity School, and Divine Redeemer School, all of which are "feeder" schools into Bishop England High School, a diocesan high school within the city. Bishop England, Porter-Gaud School, and Ashley Hall (school), Ashley Hall are the city's oldest and most prominent private schools, and are a significant part of Charleston history, dating back some 150 years.
Public institutions of higher education in Charleston include the College of Charleston, The Citadel, The Military College of South Carolina, and the Medical University of South Carolina. The city is also home to private schools including the Charleston Southern University and Charleston School of Law. Charleston is also home to the Roper Hospital School of Practical Nursing, and the city has a downtown satellite campus for the region's technical school, Trident Technical College. Charleston has the only college in the country that offers bachelor's degrees in the building arts, The American College of the Building Arts.
Because most of the city of Charleston is located in Charleston County, it is served by the Charleston County School District. Part of the city, however, is served by the Berkeley County School District in northern portions of the city, such as the Cainhoy Industrial District, Cainhoy Historical District and Daniel Island.
Charleston is also served by a large number of independent schools, including Porter-Gaud School (K-12), Charleston Collegiate School (K-12), Ashley Hall (school), Ashley Hall (Pre K-12), Charleston Day School (K-8), First Baptist Church School (K-12), Palmetto Christian Academy (K-12), Coastal Christian Preparatory School (K-12), Mason Preparatory School (K-8), and Addlestone Hebrew Academy (K-8).
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Charleston Office of Education also operates out of the city and oversees several K-8 parochial schools, such as Blessed Sacrament School, Christ Our King School, Charleston Catholic School, Nativity School, and Divine Redeemer School, all of which are "feeder" schools into Bishop England High School, a diocesan high school within the city. Bishop England, Porter-Gaud School, and Ashley Hall (school), Ashley Hall are the city's oldest and most prominent private schools, and are a significant part of Charleston history, dating back some 150 years.
Public institutions of higher education in Charleston include the College of Charleston, The Citadel, The Military College of South Carolina, and the Medical University of South Carolina. The city is also home to private schools including the Charleston Southern University and Charleston School of Law. Charleston is also home to the Roper Hospital School of Practical Nursing, and the city has a downtown satellite campus for the region's technical school, Trident Technical College. Charleston has the only college in the country that offers bachelor's degrees in the building arts, The American College of the Building Arts.
Media
Broadcast television
Charleston is the nation's 89th-largest media market, Designated market area (DMA), with 332,770 households and 0.27% of the U.S. TV population. These stations are licensed in Charleston and have significant operations or viewers in the city:
*WCBD-TV (2, NBC) and (14, The CW, CW)
*WGWG (4, Heroes & Icons)
*WCSC-TV (5, CBS, Bounce TV, Grit (TV network), Grit)
*South Carolina Educational Television, WITV (7, PBS)
*WLCN-CD (18, Christian Television Network, CTN)
*WTAT, WTAT-TV (24, Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox)
*WAZS-CD (29, Azteca America Independent)
*WJNI-CD (31, America One Independent)
*WCIV (36, MyNetworkTV, American Broadcasting Company, ABC, MeTV)
Notable people
As a population and wealth center with colleges and cultural outlets, Charleston has produced List of people from Charleston, South Carolina, many notable people in all fields. Among the most notable historical and contemporary figures are:
*Jarrell Brantley (born 1996), basketball player
*Stephen Colbert, comedian and host of ''The Late Show with Stephen Colbert, The Late Show''
*Wesley Donehue, political strategist, Internet consultant, CEO
*Ann Drayton, 18th-century landowner
*Shepard Fairey, graffiti artist
*Robert F. Furchgott, recipient of Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1998)
*Thomas Gibson, actor and star of ''Criminal Minds''
*Fritz Hollings, former US Senator and Governor of South Carolina
*Lauren Hutton, model and actress, starring in ''American Gigolo'' and ''The Gambler (1974 film), The Gambler (1974)''
*Robert Jordan (James Oliver Rigney Jr.), fantasy author, notable for ''Wheel of Time'' series
*Madelyn Cline, Actress in Outer Banks (TV series), ''Outer Banks''
*John Laurens, American revolutionary lieutenant colonel in the continental army
*Peter Manigault, wealthiest person in British North America in 1770
*Denmark Vesey, revolutionary
*Robert Smalls, African American civil war hero, businessman, politician, and civil rights activist
*Joseph Wragg
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
, a pioneer of the large-scale slave trade
*Khris Middleton, NBA basketball player, gold medal Olympian
Sister cities
Charleston's sister cities are:
*Doha, Qatar
*Freetown, Sierra Leone
*Panama City, Panama
*Speightstown, Barbados
*Spoleto, Italy
The relationship with Spoleto began when Pulitzer Prize-winning Italian composer Gian Carlo Menotti selected Charleston as the city to host the American version of Spoleto's annual Festival of Two Worlds. "Looking for a city that would provide the charm of Spoleto, as well as its wealth of theaters, churches, and other performance spaces, they selected Charleston, South Carolina, as the ideal location. The historic city provided a perfect fit: intimate enough that the Festival would captivate the entire city, yet cosmopolitan enough to provide an enthusiastic audience and robust infrastructure."
See also
* List of municipalities in South Carolina
Notes
References
*
*
*
*.
*
*
Further reading
General
*Borick, Carl P. ''A Gallant Defense: The Siege of Charleston, 1780.'' University of South Carolina Press, U. of South Carolina Press, 2003. 332 pp.
*Bull, Kinloch Jr. ''The Oligarchs in Colonial and Revolutionary Charleston: Lieutenant Governor William Bull II and His Family.'' U. of South Carolina Press, 1991. 415 pp.
*Clarke, Peter. ''A Free Church in a Free Society. The Ecclesiology of John England, Bishop of Charleston, 1820–1842, a Nineteenth Century Missionary Bishop in the Southern United States.'' Charleston, South Carolina: Bagpipe, 1982. 561 pp.
*Coker, P. C., III. ''Charleston's Maritime Heritage, 1670–1865: An Illustrated History.'' Charleston, South Carolina: Coker-Craft, 1987. 314 pp.
*Doyle, Don H. ''New Men, New Cities, New South: Atlanta, Nashville, Charleston, Mobile, 1860–1910.'' University of North Carolina Press, U. of North Carolina Press, 1990. 369 pp.
*Fraser, Walter J. Jr. ''Charleston! Charleston! The History of a Southern City.'' U. of South Carolina, 1990. 542 pp. the standard scholarly history
*Gillespie, Joanna Bowen. ''The Life and Times of Martha Laurens Ramsay, 1759–1811.'' U. of South Carolina Press, 2001.
*Goloboy, Jennifer L. ''Charleston and the Emergence of Middle-Class Culture in the Revolutionary Era.'' Athens, GA; University of Georgia Press, 2016.
*Hagy, James William. ''This Happy Land: The Jews of Colonial and Antebellum Charleston.'' University of Alabama Press, U. of Alabama Press, 1993.
*Hart, Emma. ''Building Charleston: Town and Society in the Eighteenth Century British Atlantic World'' (University of Virginia Press, 2010, University of South Carolina Press 2015)
*Jaher, Frederic Cople. ''The Urban Establishment: Upper Strata in Boston, New York, Charleston, Chicago, and Los Angeles.'' University of Illinois Press, U. of Illinois Press, 1982. 777 pp.
*Pease, William H. and Pease, Jane H. ''The Web of Progress: Private Values and Public Styles in Boston and Charleston, 1828–1843. '' Oxford University Press, Oxford U. Press, 1985. 352 pp.
*Pease, Jane H. and Pease, William H. ''A Family of Women: The Carolina Petigrus in Peace and War.'' U. of North Carolina Press, 1999. 328 pp.
*Pease, Jane H. and Pease, William H. ''Ladies, Women, and Wenches: Choice and Constraint in Antebellum Charleston and Boston.'' U. of North Carolina Press, 1990. 218 pp.
*Phelps, W. Chris. ''The Bombardment of Charleston, 1863–1865.'' Gretna, La.: Pelican, 2002. 175 pp.
*Rosen, Robert N. ''Confederate Charleston: An Illustrated History of the City and the People during the Civil War.'' U. of South Carolina Press, 1994. 181 pp.
*Rosen, Robert. ''A Short History of Charleston.'' University of South Carolina Press, (1997). , scholarly survey
*Spence, E. Lee. ''Spence's Guide to South Carolina: diving, 639 shipwrecks (1520–1813), saltwater sport fishing, recreational shrimping, crabbing, oystering, clamming, saltwater aquarium, 136 campgrounds, 281 boat landings'' (Nelson Southern Printing, Sullivan's Island, South Carolina: Spence, ©1976) OCLC: 2846435
*Spence, E. Lee. ''Treasures of the Confederate Coast: the "real Rhett Butler" & Other Revelations'' (Narwhal Press, Charleston/Miami, ©1995) ,
Art, architecture, city planning, literature, science
*
*Cothran, James R. ''Gardens of Historic Charleston.'' U. of South Carolina Press, 1995. 177 pp.
*
*Greene, Harlan. ''Mr. Skylark: John Bennett and the Charleston Renaissance.'' University of Georgia Press, U. of Georgia Press, 2001. 372 pp.
*
*Hutchisson, James M. and Greene, Harlan, ed. ''Renaissance in Charleston: Art and Life in the Carolina Low Country, 1900–1940.'' U. of Georgia Press, 2003. 259 pp.
*Hutchisson, James M. ''DuBose Heyward: A Charleston Gentleman and the World of Porgy and Bess.'' University Press of Mississippi, U. Press of Mississippi, 2000. 225 pp.
* .
*
*McNeil, Jim. ''Charleston's Navy Yard: A Picture History.'' Charleston, South Carolina: Coker Craft, 1985. 217 pp.
*
*O'Brien, Michael and Moltke-Hansen, David, ed. ''Intellectual Life in Antebellum Charleston. '' University of Tennessee Press, U. of Tennessee Press, 1986. 468 pp.
*Poston, Jonathan H. ''The Buildings of Charleston: A Guide to the City's Architecture.'' U. of South Carolina Press, 1997. 717 pp.
*
*
*Stephens, Lester D. ''Science, Race, and Religion in the American South: John Bachman and the Charleston Circle of Naturalists, 1815–1895.'' U. of North Carolina Press, 2000. 338 pp.
*
*
* .
*Yuhl, Stephanie E. ''A Golden Haze of Memory: The Making of Historic Charleston.'' U. of North Carolina Press, 2005. 285 pp.
*Zola, Gary Phillip. ''Isaac Harby of Charleston, 1788–1828: Jewish Reformer and Intellectual.'' U. of Alabama Press, 1994. 284 pp.
*Susan Harbage Page and Juan Logan. "Prop Master at Charleston's Gibbes Museum of Art", ''Southern Spaces'', September 21, 2009.
*Nelson, Emily ''The Locket'', 2010, 207 pp. The Angel Oak tree at Johns Island near Charleston is featured prominently in the book, The Locket by Emily Nelson.
*Wilson, Thomas D. ''The Ashley Cooper Plan: The Founding of Carolina and the Origins of Southern Political Culture''. Chapel Hill, N.C.: University of North Carolina Press, 2016.
Race
*Bellows, Barbara L. ''Benevolence among Slaveholders: Assisting the Poor in Charleston, 1670–1860.'' Baton Rouge, LA: LSU Press, Louisiana State U. Press, 1993.
*Drago, Edmund L. ''Initiative, Paternalism, and Race Relations: Charleston's Avery Normal Institute.'' Athens, GA: University of Georgia Press, 1990.
*Egerton, Douglas R. ''He Shall Go Out Free: The Lives of Denmark Vesey.'' Madison House, 1999.
*Greene, Harlan; Hutchins, Harry S. Jr.; and Hutchins, Brian E. ''Slave Badges and the Slave-Hire System in Charleston, South Carolina, 1783–1865.'' McFarland, 2004. 194 pp.
*Jenkins, Wilbert L. ''Seizing the New Day: African Americans in Post-Civil War Charleston.'' Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 1998. 256 pp.
*Johnson, Michael P. and Roark, James L. ''No Chariot Let Down: Charleston's Free People of Color on the Eve of the Civil War. '' Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press, 1984.
*Kennedy, Cynthia M. ''Braided Relations, Entwined Lives: The Women of Charleston's Urban Slave Society.'' Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 2005.
*Powers, Bernard E. Jr. ''Black Charlestonians: A Social History, 1822–1885.'' University of Arkansas Press, U. of Arkansas Press, 1994.
*Strickland, Jeff.
Unequal Freedoms: Ethnicity, Race, and White Supremacy in Civil War-Era Charleston
'' Gainesville, FL: University Press of Florida, 2015.
*Wilson, Thomas D. ''The Ashley Cooper Plan: The Founding of Carolina and the Origins of Southern Political Culture''. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press, 2016.
External links
*
Charleston Tourism Guide
*
{{Authority control
Charleston, South Carolina,
Charleston–North Charleston–Summerville metropolitan area
Cities in Berkeley County, South Carolina
Cities in Charleston County, South Carolina
Cities in South Carolina
County seats in South Carolina
Former colonial and territorial capitals in the United States
Former state capitals in the United States, South Carolina
Populated coastal places in South Carolina
Populated places established in 1670
Port cities and towns of the United States Atlantic coast
Regions of South Carolina
 The incorporated city fitted into as late as the
The incorporated city fitted into as late as the  Charleston has a
Charleston has a 
 King Charles II granted the chartered
King Charles II granted the chartered  Charles Town was fortified according to a plan developed in 1704 under
Charles Town was fortified according to a plan developed in 1704 under  At the foundation of the town, the principal items of commerce were
At the foundation of the town, the principal items of commerce were  Delegates for the Continental Congress were elected in 1774, and South Carolina declared its independence from Britain on the steps of the Exchange and Provost, Exchange. Slavery was again an important factor in the city's role during the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War. The British attacked the settlement three times, assuming that the settlement had a large base of Loyalist (American Revolution), Loyalists who would rally to their cause once given some military support. The loyalty of white Southerners towards the Crown had largely been forfeited, however, by British legal cases (such as the 1772 Somerset v Stewart, Somersett case which marked the prohibition of slavery in England and Wales; a significant milestone in the Abolitionism, abolitionist struggle) and military tactics (such as Dunmore's Proclamation in 1775) that promised the emancipation of slaves owned by Patriot planters; these efforts did, however, unsurprisingly win the allegiance of thousands of Black Loyalists.
The Battle of Sullivan's Island saw the British fail to capture a partially constructed Fort Moultrie, palmetto palisade from William Moultrie, Col. Moultrie's 2nd South Carolina Regiment, militia regiment on June 28, 1776. The Liberty Flag used by Moultrie's men formed the basis of the later South Carolina flag, and the victory's anniversary continues to be commemorated as Carolina Day.
Making the capture of Charlestown their chief priority, the British sent Henry Clinton (American War of Independence), Sir Henry Clinton, who laid Siege of Charleston, siege to Charleston on April 1, 1780, with about 14,000 troops and 90 ships. Bombardment began on March 11, 1780. The Patriots, led by Benjamin Lincoln, had about 5,500 men and inadequate fortifications to repel the forces against them. After the British cut his supply lines and lines of retreat at the battles of Battle of Monck's Corner, Monck's Corner and Battle of Lenud's Ferry, Lenud's Ferry, Lincoln's surrender on May 12, 1780 became the greatest List of American Revolutionary War battles, American defeat of the war.
The British continued to hold Charlestown for over a year following Siege of Yorktown (1781), their defeat at Yorktown in 1781, although they alienated local planters by refusing to restore full civil government. Nathanael Greene had entered the state after Cornwallis's Battle of Guilford Courthouse, pyrrhic victory at Guilford Courthouse and kept the area under a kind of siege. British Army officer Alexander Leslie (British Army officer), Alexander Leslie, commanding Charlestown, requested a truce in March 1782 to purchase food for his garrison and the town's inhabitants. Greene refused and formed a brigade under Mordecai Gist to counter British forays. Charlestown was finally evacuated by the British in December 1782. Greene presented the British leaders of the town with the Moultrie Flag.
Delegates for the Continental Congress were elected in 1774, and South Carolina declared its independence from Britain on the steps of the Exchange and Provost, Exchange. Slavery was again an important factor in the city's role during the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War. The British attacked the settlement three times, assuming that the settlement had a large base of Loyalist (American Revolution), Loyalists who would rally to their cause once given some military support. The loyalty of white Southerners towards the Crown had largely been forfeited, however, by British legal cases (such as the 1772 Somerset v Stewart, Somersett case which marked the prohibition of slavery in England and Wales; a significant milestone in the Abolitionism, abolitionist struggle) and military tactics (such as Dunmore's Proclamation in 1775) that promised the emancipation of slaves owned by Patriot planters; these efforts did, however, unsurprisingly win the allegiance of thousands of Black Loyalists.
The Battle of Sullivan's Island saw the British fail to capture a partially constructed Fort Moultrie, palmetto palisade from William Moultrie, Col. Moultrie's 2nd South Carolina Regiment, militia regiment on June 28, 1776. The Liberty Flag used by Moultrie's men formed the basis of the later South Carolina flag, and the victory's anniversary continues to be commemorated as Carolina Day.
Making the capture of Charlestown their chief priority, the British sent Henry Clinton (American War of Independence), Sir Henry Clinton, who laid Siege of Charleston, siege to Charleston on April 1, 1780, with about 14,000 troops and 90 ships. Bombardment began on March 11, 1780. The Patriots, led by Benjamin Lincoln, had about 5,500 men and inadequate fortifications to repel the forces against them. After the British cut his supply lines and lines of retreat at the battles of Battle of Monck's Corner, Monck's Corner and Battle of Lenud's Ferry, Lenud's Ferry, Lincoln's surrender on May 12, 1780 became the greatest List of American Revolutionary War battles, American defeat of the war.
The British continued to hold Charlestown for over a year following Siege of Yorktown (1781), their defeat at Yorktown in 1781, although they alienated local planters by refusing to restore full civil government. Nathanael Greene had entered the state after Cornwallis's Battle of Guilford Courthouse, pyrrhic victory at Guilford Courthouse and kept the area under a kind of siege. British Army officer Alexander Leslie (British Army officer), Alexander Leslie, commanding Charlestown, requested a truce in March 1782 to purchase food for his garrison and the town's inhabitants. Greene refused and formed a brigade under Mordecai Gist to counter British forays. Charlestown was finally evacuated by the British in December 1782. Greene presented the British leaders of the town with the Moultrie Flag.


 Between the Revolutionary War and the Civil War, Charleston experienced an economic boom, at least for the top strata of society. The expansion of cotton as a cash crop in the South both led to huge wealth for a small segment of society and funded impressive architecture and culture but also escalated the importance of slaves and led to greater and greater restrictions on Black Charlestonians.
By 1783, the growth of the city had reached a point where a municipal government because desirable; therefore on August 13, 1783, an act of incorporation for the city of Charleston was ratified. The act originally specified the city's name as "Charles Ton," as opposed to the previous Charlestown, but the spelling "Charleston" quickly came to dominate.
Although
Between the Revolutionary War and the Civil War, Charleston experienced an economic boom, at least for the top strata of society. The expansion of cotton as a cash crop in the South both led to huge wealth for a small segment of society and funded impressive architecture and culture but also escalated the importance of slaves and led to greater and greater restrictions on Black Charlestonians.
By 1783, the growth of the city had reached a point where a municipal government because desirable; therefore on August 13, 1783, an act of incorporation for the city of Charleston was ratified. The act originally specified the city's name as "Charles Ton," as opposed to the previous Charlestown, but the spelling "Charleston" quickly came to dominate.
Although 

 Charleston played a major part in the Civil War. As a pivotal city, both the Union and Confederate Armies vied for control of it. The Civil War began in
Charleston played a major part in the Civil War. As a pivotal city, both the Union and Confederate Armies vied for control of it. The Civil War began in  Charleston is home to a number of professional, minor league, and amateur sports teams:
*The Charleston Battery, a professional soccer team, play in the USL Championship. The Battery play at Patriots Point Soccer Complex.
*The South Carolina Stingrays, a professional hockey team, plays in the ECHL. The Stingrays play in North Charleston at the North Charleston Coliseum. The Stingrays are an affiliate of the Washington Capitals and Hershey Bears.
*The Charleston RiverDogs, a Minor League Baseball team, plays in the Low-A East and are an affiliate of the Tampa Bay Rays. The RiverDogs play at Joseph P. Riley Jr. Park.
*The Charleston Outlaws RFC is a rugby union club in the Palmetto Rugby Union, USA Rugby South, and USA Rugby. It competes in Men's Division II against the Cape Fear, Columbia, Greenville, and Charlotte "B" clubs. The club also hosts a rugby sevens tournament during Memorial Day weekend.
*The Charleston Gaelic Athletic Association is a Gaelic athletic club focusing on the sports of hurling and Gaelic football. The club competes in the Southeastern Division of the North American County Board of the Gaelic Athletic Association, GAA. The club hosts other division clubs in the Holy City Cup each spring.
*The Lowcountry Highrollers is a women's flat-track roller derby league in the Charleston area. The league is a local member of the Women's Flat Track Derby Association.
*The Family Circle Tennis Center hosts the Charleston Open, Volvo Car Open, a major Women's Tennis Association Event. The facility is located on Daniel Island.
Other notable sports venues in Charleston include Johnson Hagood Stadium (home of The Citadel Bulldogs College football, football team), McAlister Field House (home of The Citadel Bulldogs College basketball, basketball team), and TD Arena, Toronto Dominion Bank Arena at the College of Charleston, which seats 5,100 people who view the school's basketball and volleyball teams.
Charleston is home to a number of professional, minor league, and amateur sports teams:
*The Charleston Battery, a professional soccer team, play in the USL Championship. The Battery play at Patriots Point Soccer Complex.
*The South Carolina Stingrays, a professional hockey team, plays in the ECHL. The Stingrays play in North Charleston at the North Charleston Coliseum. The Stingrays are an affiliate of the Washington Capitals and Hershey Bears.
*The Charleston RiverDogs, a Minor League Baseball team, plays in the Low-A East and are an affiliate of the Tampa Bay Rays. The RiverDogs play at Joseph P. Riley Jr. Park.
*The Charleston Outlaws RFC is a rugby union club in the Palmetto Rugby Union, USA Rugby South, and USA Rugby. It competes in Men's Division II against the Cape Fear, Columbia, Greenville, and Charlotte "B" clubs. The club also hosts a rugby sevens tournament during Memorial Day weekend.
*The Charleston Gaelic Athletic Association is a Gaelic athletic club focusing on the sports of hurling and Gaelic football. The club competes in the Southeastern Division of the North American County Board of the Gaelic Athletic Association, GAA. The club hosts other division clubs in the Holy City Cup each spring.
*The Lowcountry Highrollers is a women's flat-track roller derby league in the Charleston area. The league is a local member of the Women's Flat Track Derby Association.
*The Family Circle Tennis Center hosts the Charleston Open, Volvo Car Open, a major Women's Tennis Association Event. The facility is located on Daniel Island.
Other notable sports venues in Charleston include Johnson Hagood Stadium (home of The Citadel Bulldogs College football, football team), McAlister Field House (home of The Citadel Bulldogs College basketball, basketball team), and TD Arena, Toronto Dominion Bank Arena at the College of Charleston, which seats 5,100 people who view the school's basketball and volleyball teams.

 The Port of Charleston, owned and operated by the South Carolina Ports Authority, is one of the largest ports in the United States, ranked seventh in the top 25 by containerization, containerized cargo volume in 2018. It consists of six terminals, with the sixth having opened in April 2021. Port activity at the two terminals located in the city of Charleston is one of the city's leading sources of revenue, behind tourism.
Today, the Port of Charleston boasts the deepest water in the southeast region and regularly handles ships too big to transit through the Panama Canal. A harbor-deepening project is currently underway to take the Port of Charleston's entrance channel to 54 feet and harbor channel to 52 feet at mean low tide. With an average high tide of 6 feet, the depth clearances will become 60 feet and 58 feet, respectively.
Part of Union Pier Treminal, in the city of Charleston, is a cruise ship passenger terminal which hosted numerous cruise departures annually through 2019. Beginning in May 2019, until cruise operations were interrupted in April 2020, the Carnival Cruise Lines, Carnival Carnival Sunshine, ''Sunshine'' was permanently stationed in Charleston, offering 4, 5, and 7-day cruises to the Caribbean.
With the closure of the Naval Base and the Charleston Naval Shipyard in 1996, Detyens, Inc. signed a long-term lease. With three dry docks, one floating dock, and six piers, Detyens Shipyard, Inc. is one of the largest commercial marine repair facilities on the East Coast. Projects include military, commercial, and cruise ships.
The Port of Charleston, owned and operated by the South Carolina Ports Authority, is one of the largest ports in the United States, ranked seventh in the top 25 by containerization, containerized cargo volume in 2018. It consists of six terminals, with the sixth having opened in April 2021. Port activity at the two terminals located in the city of Charleston is one of the city's leading sources of revenue, behind tourism.
Today, the Port of Charleston boasts the deepest water in the southeast region and regularly handles ships too big to transit through the Panama Canal. A harbor-deepening project is currently underway to take the Port of Charleston's entrance channel to 54 feet and harbor channel to 52 feet at mean low tide. With an average high tide of 6 feet, the depth clearances will become 60 feet and 58 feet, respectively.
Part of Union Pier Treminal, in the city of Charleston, is a cruise ship passenger terminal which hosted numerous cruise departures annually through 2019. Beginning in May 2019, until cruise operations were interrupted in April 2020, the Carnival Cruise Lines, Carnival Carnival Sunshine, ''Sunshine'' was permanently stationed in Charleston, offering 4, 5, and 7-day cruises to the Caribbean.
With the closure of the Naval Base and the Charleston Naval Shipyard in 1996, Detyens, Inc. signed a long-term lease. With three dry docks, one floating dock, and six piers, Detyens Shipyard, Inc. is one of the largest commercial marine repair facilities on the East Coast. Projects include military, commercial, and cruise ships.