Chandravati on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chandravati, popularly known as Chandroti, is a village situated near
 Archeological excavations suggested that there was a large settlement at the place before the establishment of Chandravati by
Archeological excavations suggested that there was a large settlement at the place before the establishment of Chandravati by
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the
Abu Road
Abu Road is a city and sub-district in Sirohi district of Rajasthan state in western India, lies on the bank of West Banas River. It is the tehsil and sub-district headquarters. Its railway station is an important stop on the main Indian Railwa ...
on the bank of the West Banas River
The West Banas is a river in western India. It originates from the southern Aravalli Range, in Sirohi District of the state of Rajasthan. It flows south, draining the valley between Mount Abu on the west and the easterly ridge of the Aravallis on ...
in the India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
n state of Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
. In ancient times it was an extensive town, and present villages such as Dattani, Kiverli, Kharadi and Santpura were its suburbs. The old ruins, such as temples, torans and images scattered over the large area, bear testimony to its past glory.
History
 Archeological excavations suggested that there was a large settlement at the place before the establishment of Chandravati by
Archeological excavations suggested that there was a large settlement at the place before the establishment of Chandravati by Paramara
The Paramara dynasty ( IAST: Paramāra) was an Indian dynasty that ruled Malwa and surrounding areas in west-central India between 9th and 14th centuries. They belonged to the Parmara clan of the Rajputs.
The dynasty was established in either ...
s. Chandravati was ruled by the Paramaras of Abu. The first Paramara ruler of the area was Sindhuraja
Sindhuraja (IAST: Sindhurāja) was an Indian king from the Paramara dynasty, who ruled the Malwa region in the late 10th century. He was the younger brother of Munja, and the father of Bhoja.
Background
No inscriptions issued by Sindhuraja ...
in the early tenth century.Mathur, Vijayendra Kumar: Aitihasik Sthanavali (Hindi), Vaigyanik tatha Takaniki Shabdawali Ayog, Government of India, 1990, p.319
Chandravati was the major city in past said to once been eighteen miles in circuit. Its prosperity seems to have lasted from the seventh to the beginning of the fifteenth century. Tradition gives it an earlier origin than Dhar
Dhar is a city located in Dhar district of the Malwa region in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. The city is the administrative headquarters of the Dhar district. Before Indian independence from Great Britain, it was the capital of the Dh ...
, making it the metropolis of Western India, when the Parmara
Parmar is a Rajput clan found in Northern and Central India, especially in Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Kutch, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and North Maharashtra.
See also
* Paramara Dynasty
* Panwar Dynasty
* Pawar
P ...
was paramount lord to whom the nine castles of the desert were the grand subordinate fiefs. In the seventh century,
then subordinate to Dhar, it proved a place of refuge to Raja Bhoj, when, by some northern invader, he was forced to flee from his capital. From the Parmars it was wrested by the Chauhan chieftains of Sirohi
Sirohi is a city, located in Sirohi district in southern Rajasthan state in western India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sirohi District and was formerly the capital of the princely state of Sirohi ruled by Deora Chauhan Rajput rul ...
, and, on the establishment of the Chaulukya dynasty
The Chaulukya dynasty (), also Solanki dynasty, was a dynasty that ruled parts of what are now Gujarat and Rajasthan in north-western India, between and . Their capital was located at Anahilavada (modern Patan). At times, their rule extend ...
of Anhilwad Patan
Patan () is the administrative seat of Patan District in the Indian state of Gujarat and is an administered municipality. It was the capital of Gujarat's Chavda and Chaulukya dynasties in medieval times, and is also known as Anhilpur-Patan ...
(942) the rulers of Chandravati became its vassals. The remains at Chandravati and on mount Abu seem to point to the eleventh and twelfth centuries as the time of greatest wealth and splendour. The materials recovered by excavation suggested that it was established around 7th century and expanded into a large settlement (about 50 hectare) around 10th or 11th century when it was a capital township.
In 1024 AD, Chandravati was attacked and plundered by Mahmud Ghazni when he passed through Rajasthan to attack Anhilwad Patan
Patan () is the administrative seat of Patan District in the Indian state of Gujarat and is an administered municipality. It was the capital of Gujarat's Chavda and Chaulukya dynasties in medieval times, and is also known as Anhilpur-Patan ...
. After defeating Prithviraj III in 1192 AD, the Muslim army also attacked Chandravati.
In 1197, its rulers Prahladan and Dharavarsh, as feudatories to Bhimdev II (1178 - 1243) of Anhilwad, encamping near Abu, attempted to hold the entrance into Gujarat against Kutb-ud-din Aibak (1192 -1210). Notwithstanding their strong position they were attacked, defeated, and put to flight. Great wealth fell into the victor'shands, and, as he passed on and took Anhilvada, it is probable that, on his way, he plundered Chandravati. Kutb-ud-din's expedition was little more than a passing raid, and Dharavarsh's son succeeded
him. He, or his successor, was about 1270 defeated and driven out by the Chauhans of Nadol. In about 1315 AD Chandravati passed into the hands of Deora Chauhans
Chauhan, historically ''Chahamana'', is a clan name historically associated with the various ruling Rajput families during the Medieval India in Rajasthan.
Subclans
Khichi, Hada, Songara, Bhadauria, Devda etc. are the branches or subclan ...
.
Then (1304) came Alauddin Khalji
Alaud-Dīn Khaljī, also called Alauddin Khilji or Alauddin Ghilji (), born Ali Gurshasp, was an emperor of the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrativ ...
's final conquest of Gujarat, and Chandravati, with Anhilwad as the centre of Muslim power, lost almost all independence. Another hundred years completed its ruin. In the beginning of the fifteenth century, by the founding of Sirohi (1405), Chandravati ceased to be the seat of a Hindu chief, and, a few years later (1411 - 1412), its buildings and skilled craftsmen were carried off to enrich the new capital of Sultan Ahmed Shah I
Ahmad Shah I, born Ahmad Khan, was a ruler of the Muzaffarid dynasty, who reigned over the Gujarat Sultanate from 1411 until his death in 1442. He was the grandson of Sultan Muzaffar Shah who has been variously described as a Tank Rajput or a ...
(1411 - 1443) of Gujarat Sultanate
The Gujarat Sultanate (or the Sultanate of Guzerat), was a Medieval Indian kingdom established in the early 15th century in Western India, primarily in the present-day state of Gujarat, India. The dynasty was founded by Sultan Zafar Khan Mu ...
. Since then Chandravati has remained
forsaken and desolate. Even its ruins, sold and carried off as building materials, have all but disappeared. Though some are more modern, most of the Chandravati remains belong to the eleventh and twelfth centuries, the best period of Abu architecture (1032-1247).
Sahasamala Devada shifted his capital to Sirohi
Sirohi is a city, located in Sirohi district in southern Rajasthan state in western India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sirohi District and was formerly the capital of the princely state of Sirohi ruled by Deora Chauhan Rajput rul ...
around 1450 AD, and from then on Chandravati lost its glory.
In 1824 Sir Charles Colville
General Sir Charles Colville (7 August 1770 – 27 March 1843) was a British Army officer who served during the Napoleonic Wars. He was an ensign in 1781. He served in the West Indies from 1791 to 1797 and while serving there was promoted to li ...
and his party, the first European visitors to Chandravati, found twenty marble edifices of different sizes. One Brahmanic temple was adorned with rich, very well executed sculptured figures and ornaments in high relief, many of the figures almost quite detached. The chief images were of Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp ...
, two Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one o ...
, Mahishasuramardini, Yama
Yama (Devanagari: यम) or Yamarāja (यमराज), is a deity of death, dharma, the south direction, and the underworld who predominantly features in Hindu and Buddhist religion, belonging to an early stratum of Rigvedic Hindu deities. ...
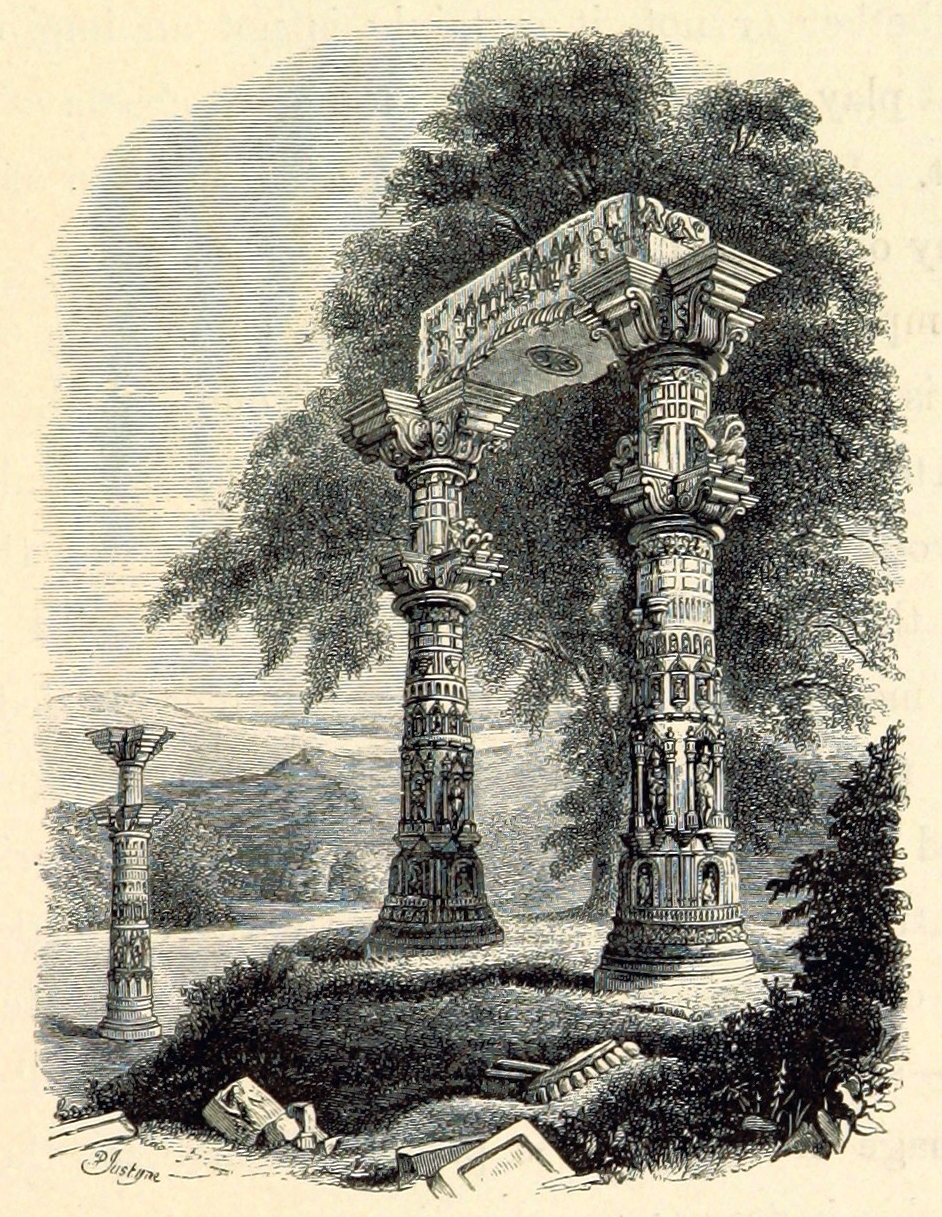
. The best executed were the dancing nymphs, with garlands and musical instruments, many of them extremely graceful. Except the roof of the domes, whoso outer marble cover was gone, the temple was white marble throughout, the lustre of tho prominent part undimmed. Near the temple, two richly carved columns, supporting an entablature and sculptured pediment, are probably triumphal pillars, ''kirti stambh'', like those at Sidhpur
Siddhpur, also spelled Sidhpur, is a town, municipality and headquarter of Sidhpur taluka in Patan district, in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is a historical place located on the bank of the endorheic Saraswati River, which is probably a rem ...
. When visited by British explorer Burgess in 1874, of the twenty buildings not more than three or four were left.
The remains of Chandravati was destroyed further during the construction of the railway track between Malwa and Abu road before independence. It is now a small village.
Arts and literature
There were a large number of temples in Chandravati. They were mainly Shiva temples and Jain temples. Many European scholars who visited this area in the nineteenth century have written about surviving artistic specimens.James Tod
Lieutenant-Colonel James Tod (20 March 1782 – 18 November 1835) was an officer of the British East India Company and an Oriental scholar. He combined his official role and his amateur interests to create a series of works about the his ...
has given pictures of some of these temples in his ''Travels in Western India''. In 1824 Charles Colville
General Sir Charles Colville (7 August 1770 – 27 March 1843) was a British Army officer who served during the Napoleonic Wars. He was an ensign in 1781. He served in the West Indies from 1791 to 1797 and while serving there was promoted to li ...
and his party visited Chandravati and found twenty marble edifices of different sizes. One temple to Brahma was adorned with rich and finely executed sculptured figures and ornaments in high relief. Another scholar, Ferguson, found the pillars so highly ornamented in details and varieties that no two pillars are exactly alike.
At present not a single temple is in order. The pieces of old temples were removed and used in temples in distant cities. The many monuments were destroyed by contractors of Rajputana Malwa Railway before independence. The remaining were stolen or were destroyed when Abu Road industrial area was extended and Palanpur-Abu Road Highway was constructed. It divided the ancient site into two parts.
Rulers of Chandravati also patronized literature. Jain monks wrote some literary works there.
Archeology
At least three fortified enclosures were discovered during excavations. The largest fortification is spread over four hectares and is located in the valley of Banas river. Three residential complexes; six room complex in south eastern corner, six room complex in north eastern corner and the large hall with few rooms in south central part of the fort; were discovered. Several minor objects were also discovered from the complexes like terracotta beads, copper and iron objects, animal figures. The other two fortifications, a large settlement, about thirty six temples, around twelve bawaris are located in the valley of Sevarni river which is tributary of Banas.References
Notes
Bibliography
*public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired ...
:
{{Authority control
History of Rajasthan
Villages in Sirohi district
Tourist attractions in Sirohi district
Abu Road