Château de Chambord on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Château de Chambord () in

 Châteaux in the 16th century departed from castle architecture; . Indeed, while they were off-shoots of castles, with features commonly associated with them, they did not have serious defences. Extensive gardens and water features, such as a moat, were common amongst châteaux from this period. Chambord is no exception to this pattern. The layout is reminiscent of a typical castle with a
Châteaux in the 16th century departed from castle architecture; . Indeed, while they were off-shoots of castles, with features commonly associated with them, they did not have serious defences. Extensive gardens and water features, such as a moat, were common amongst châteaux from this period. Chambord is no exception to this pattern. The layout is reminiscent of a typical castle with a 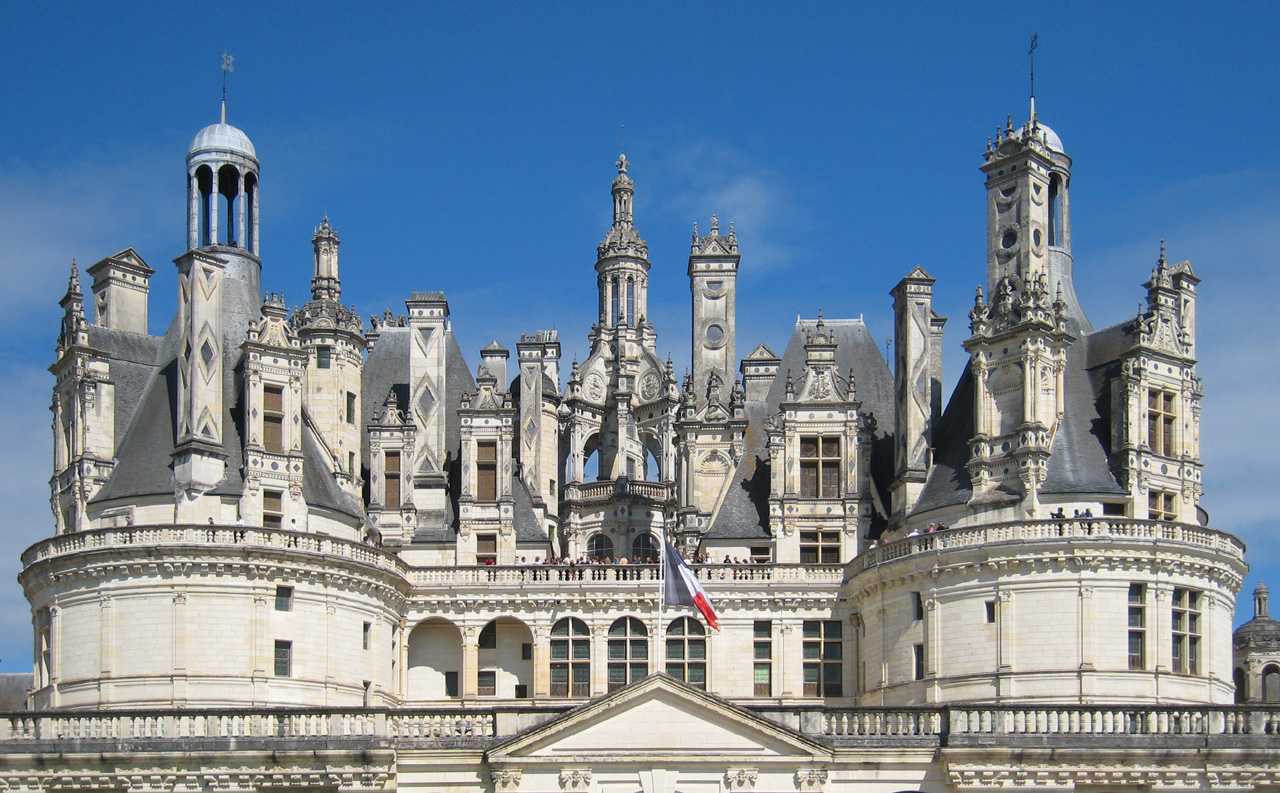 The roofscape of Chambord contrasts with the masses of its masonry and has often been compared with the skyline of a town: it shows eleven kinds of towers and three types of chimneys, without symmetry, framed at the corners by the massive towers. The design parallels are north Italian and Leonardesque. Writer
The roofscape of Chambord contrasts with the masses of its masonry and has often been compared with the skyline of a town: it shows eleven kinds of towers and three types of chimneys, without symmetry, framed at the corners by the massive towers. The design parallels are north Italian and Leonardesque. Writer  One of the architectural highlights is the spectacular open double-spiral staircase that is the centrepiece of the château. The two spirals ascend the three floors without ever meeting, illuminated from above by a sort of light house at the highest point of the château. There are suggestions that Leonardo da Vinci may have designed the staircase, but this has not been confirmed. Writer
One of the architectural highlights is the spectacular open double-spiral staircase that is the centrepiece of the château. The two spirals ascend the three floors without ever meeting, illuminated from above by a sort of light house at the highest point of the château. There are suggestions that Leonardo da Vinci may have designed the staircase, but this has not been confirmed. Writer
 The château was built to act as a hunting lodge for King Francis I; however, the king spent barely seven weeks there in total, that time consisting of short hunting visits. As the château had been constructed with the purpose of short stays, it was not practical to live in on a longer-term basis. The massive rooms, open windows and high ceilings meant heating was impractical. Similarly, as the château was not surrounded by a village or estate, there was no immediate source of food other than game. This meant that all food had to be brought with the group, typically numbering up to 2,000 people at a time.
As a result of all the above, the château was completely unfurnished during this period. All furniture, wall coverings, eating implements and so forth were brought specifically for each hunting trip, a major logistical exercise. It is for this reason that much furniture from the era was built to be disassembled to facilitate transportation. After Francis died of a heart attack in 1547, the château was not used for almost a century.
For more than 80 years after the death of King Francis I, French kings abandoned the château, allowing it to fall into decay. Finally, in 1639
The château was built to act as a hunting lodge for King Francis I; however, the king spent barely seven weeks there in total, that time consisting of short hunting visits. As the château had been constructed with the purpose of short stays, it was not practical to live in on a longer-term basis. The massive rooms, open windows and high ceilings meant heating was impractical. Similarly, as the château was not surrounded by a village or estate, there was no immediate source of food other than game. This meant that all food had to be brought with the group, typically numbering up to 2,000 people at a time.
As a result of all the above, the château was completely unfurnished during this period. All furniture, wall coverings, eating implements and so forth were brought specifically for each hunting trip, a major logistical exercise. It is for this reason that much furniture from the era was built to be disassembled to facilitate transportation. After Francis died of a heart attack in 1547, the château was not used for almost a century.
For more than 80 years after the death of King Francis I, French kings abandoned the château, allowing it to fall into decay. Finally, in 1639 
 In 1792, the
In 1792, the  In 1939, shortly before the outbreak of World War II, the art collections of the Louvre and Compiègne museums (including the
In 1939, shortly before the outbreak of World War II, the art collections of the Louvre and Compiègne museums (including the 
Copy
at
World History Encyclopedia - Chateau de ChambordChâteau de ChambordProgramme archéologique de ChambordRendez-vous at the National Domain of Chambord
– Official website for tourism in France (in English)
360° Panoramas of Le Château de Chambord'
by the Media Center for Art History, Columbia University {{DEFAULTSORT:Chateau De Chambord
Chambord Chambord can refer to:
* Chambord (liqueur), a brand of raspberry-flavored liqueur
* Château de Chambord, a French ''château'' built in the 16th century
* Chambord, Loir-et-Cher, the French commune where the ''château'' is located
* Chambord, ...
, Centre-Val de Loire
Centre-Val de Loire (, , ,In isolation, ''Centre'' is pronounced . ) or Centre Region (french: région Centre, link=no, ), as it was known until 2015, is one of the eighteen administrative regions of France. It straddles the middle Loire Valley ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, is one of the most recognisable château
A château (; plural: châteaux) is a manor house or residence of the lord of the manor, or a fine country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally, and still most frequently, in French-speaking regions.
Nowaday ...
x in the world because of its very distinctive French Renaissance architecture
French Renaissance architecture is a style which was prominent between the late 15th and early 17th centuries in the Kingdom of France. It succeeded French Gothic architecture. The style was originally imported from Italy after the Hundred Years ...
which blends traditional French medieval forms with classical Renaissance structures. The building, which was never completed, was constructed by the king of France, Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
.
Chambord is the largest château in the Loire Valley; it was built to serve as a hunting lodge for Francis I, who maintained his royal residences at the Château de Blois
A château (; plural: châteaux) is a manor house or residence of the lord of the manor, or a fine country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally, and still most frequently, in French-speaking regions.
Nowaday ...
and Amboise
Amboise (; ) is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department in central France. Today a small market town, it was once home of the French royal court.
Geography
Amboise lies on the banks of the river Loire, east of Tours. It is also about away ...
. The original design of the Château de Chambord is attributed to Italian architect Domenico da Cortona
Domenico da Cortona called "''Boccador''" (ca 1465 – ca 1549) was an Italian architect, a pupil of Giuliano da Sangallo. he was brought to France by Charles VIII and remained in the service of François I. His design for the royal Château ...
; Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
may also have been involved or influenced the design.
Chambord was altered considerably during the twenty-eight years of its construction (1519–1547), during which it was overseen on-site by Pierre Neveu. With the château nearing completion, Francis showed off his enormous symbol of wealth and power by hosting his old archrival, Emperor Charles V
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) ...
, at Chambord.
In 1792, in the wake of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
, some of the furnishings were sold and timber removed. For a time the building was left abandoned, though in the 19th century some attempts were made at restoration. During the Second World War, art works from the collections of the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central l ...
and the Château de Compiègne
The Château de Compiègne is a French château, a royal residence built for Louis XV and restored by Napoleon. Compiègne was one of three seats of royal government, the others being Versailles and Fontainebleau. It is located in Compiègne ...
were moved to the Château de Chambord. The château is now open to the public, receiving 700,000 visitors in 2007. Flooding in June 2016 damaged the grounds but not the château itself.
Architecture

 Châteaux in the 16th century departed from castle architecture; . Indeed, while they were off-shoots of castles, with features commonly associated with them, they did not have serious defences. Extensive gardens and water features, such as a moat, were common amongst châteaux from this period. Chambord is no exception to this pattern. The layout is reminiscent of a typical castle with a
Châteaux in the 16th century departed from castle architecture; . Indeed, while they were off-shoots of castles, with features commonly associated with them, they did not have serious defences. Extensive gardens and water features, such as a moat, were common amongst châteaux from this period. Chambord is no exception to this pattern. The layout is reminiscent of a typical castle with a keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
, corner towers, and defended by a moat. Built in Renaissance style
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman thought a ...
, the internal layout is an early example of the French and Italian style of grouping rooms into self-contained suites, a departure from the medieval style of corridor rooms. The massive château is composed of a central keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
with four immense bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
towers at the corners. The keep also forms part of the front wall of a larger compound with two larger towers. Bases for a possible further two towers are found at the rear, but these were never developed, and remain the same height as the wall. The château features 440 rooms, 282 fireplaces, and 84 staircases. Four rectangular vault
Vault may refer to:
* Jumping, the act of propelling oneself upwards
Architecture
* Vault (architecture), an arched form above an enclosed space
* Bank vault, a reinforced room or compartment where valuables are stored
* Burial vault (enclosure ...
ed hallways on each floor form a cross-shape.
The château was never intended to provide any form of defence from enemies; consequently the walls, towers and partial moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
are decorative, and even at the time were an anachronism. Some elements of architecture—open windows, loggia
In architecture, a loggia ( , usually , ) is a covered exterior gallery or corridor, usually on an upper level, but sometimes on the ground level of a building. The outer wall is open to the elements, usually supported by a series of columns ...
s, and a vast outdoor area at the top—borrowed from the Italian Renaissance architecture
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of Ancient Greece, ancient Greek and ...
—are less practical in cold and damp northern France.
 The roofscape of Chambord contrasts with the masses of its masonry and has often been compared with the skyline of a town: it shows eleven kinds of towers and three types of chimneys, without symmetry, framed at the corners by the massive towers. The design parallels are north Italian and Leonardesque. Writer
The roofscape of Chambord contrasts with the masses of its masonry and has often been compared with the skyline of a town: it shows eleven kinds of towers and three types of chimneys, without symmetry, framed at the corners by the massive towers. The design parallels are north Italian and Leonardesque. Writer Henry James
Henry James ( – ) was an American-British author. He is regarded as a key transitional figure between literary realism and literary modernism, and is considered by many to be among the greatest novelists in the English language. He was the ...
remarked, "the towers, cupolas, the gables, the lanterns, the chimneys, look more like the spires of a city than the salient points of a single building."Quoted in
 One of the architectural highlights is the spectacular open double-spiral staircase that is the centrepiece of the château. The two spirals ascend the three floors without ever meeting, illuminated from above by a sort of light house at the highest point of the château. There are suggestions that Leonardo da Vinci may have designed the staircase, but this has not been confirmed. Writer
One of the architectural highlights is the spectacular open double-spiral staircase that is the centrepiece of the château. The two spirals ascend the three floors without ever meeting, illuminated from above by a sort of light house at the highest point of the château. There are suggestions that Leonardo da Vinci may have designed the staircase, but this has not been confirmed. Writer John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's diary, or memo ...
said of the staircase, "it is devised with four icentries or ascents, which cross one another, so that though four persons meet, they never come in sight, but by small loopholes, till they land. It consists of 274 steps (as I remember), and is an extraordinary work, but of far greater expense than use or beauty."
The château also features 128 metres of facade, more than 800 sculpted column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. ...
s and an elaborately decorated roof. When Francis I commissioned the construction of Chambord, he wanted it to look like the skyline of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
.
The château is surrounded by a wooded park and game reserve maintained with red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
, enclosed by a wall. The king's plan to divert the Loire to surround the château came about only in a novel; ''Amadis of Gaul'', which Francis had translated. In the novel the château is referred to as the ''Palace of Firm Isle''.
Chambord's towers are atypical of French contemporary design in that they lack turrets and spires. In the opinion of author Tanaka, who suggests Leonardo da Vinci influenced the château's design, they are closer in design to minaret
A minaret (; ar, منارة, translit=manāra, or ar, مِئْذَنة, translit=miʾḏana, links=no; tr, minare; fa, گلدسته, translit=goldaste) is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generall ...
s of 15th-century Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
.
History
Royal ownership
Who designed the Château de Chambord is a matter of controversy. The original design is attributed, though with several doubts, toDomenico da Cortona
Domenico da Cortona called "''Boccador''" (ca 1465 – ca 1549) was an Italian architect, a pupil of Giuliano da Sangallo. he was brought to France by Charles VIII and remained in the service of François I. His design for the royal Château ...
, whose wooden model for the design survived long enough to be drawn by André Félibien
André Félibien (May 161911 June 1695), ''sieur des Avaux et de Javercy'', was a French chronicler of the arts and official court historian to Louis XIV of France.
Biography
Félibien was born at Chartres. At the age of fourteen he went to Pa ...
in the 17th century. In the drawings of the model, the main staircase of the keep is shown with two straight, parallel flights of steps separated by a passage and is located in one of the arms of the cross. According to Jean-Guillaume, this Italian design was later replaced with the centrally located spiral staircase, which is similar to that at Blois
Blois ( ; ) is a commune and the capital city of Loir-et-Cher department, in Centre-Val de Loire, France, on the banks of the lower Loire river between Orléans and Tours.
With 45,898 inhabitants by 2019, Blois is the most populated city of the ...
, and a design more compatible with the French preference for spectacular grand staircases. However, "at the same time the result was also a triumph of the centralised layout—itself a wholly Italian element." In 1913 Marcel Reymond suggested that Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
, a guest of Francis at Clos Lucé
The Château du Clos Lucé (or simply Clos Lucé), formerly called Manoir du Cloux, is a large château located in the center of Amboise, in the department of Indre-et-Loire, in the Centre-Val de Loire region of France. It is located in the natur ...
near Amboise, was responsible for the original design, which reflects Leonardo's plans for a château at Romorantin
Romorantin is a traditional French variety of white wine grape, that is a sibling of Chardonnay. Once quite widely grown in the Loire, it has now only seen in the Cour-Cheverny AOC. It produces intense, minerally wines somewhat reminiscent of ...
for the King's mother, and his interests in central planning and double-spiral staircases; the discussion has not yet concluded, although many scholars now agree that Leonardo was at least responsible for the design of the central staircase.
Archaeological findings by Jean-Sylvain Caillou & Dominic Hofbauer have established that the lack of symmetry of some façades derives from an original design, abandoned shortly after the construction began, and which ground plan was organised around the central staircase following a central gyratory symmetry. Such a rotative design has no equivalent in architecture at this period of history, and appears reminiscent of Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
's works on hydraulic turbines or the helicopter. Had it been respected, it is believed that this unique building could have featured the quadruple-spiral open staircase, strangely described by John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's diary, or memo ...
and Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio ( ; ; 30 November 1508 – 19 August 1580) was an Italian Renaissance architect active in the Venetian Republic. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily Vitruvius, is widely considered to be one of th ...
, although it was never built.
Regardless of who designed the château, on 6 September 1519 Francis de Pontbriand was ordered to begin construction of the Château de Chambord. The work was interrupted by the Italian War of 1521–1526
The Italian War of 1521–1526, sometimes known as the Four Years' War, (french: Sixième guerre d'Italie) was a part of the Italian Wars. The war pitted Francis I of France and the Republic of Venice against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V ...
, and work was slowed by dwindling royal funds and difficulties in laying the structure's foundations. By 1524, the walls were barely above ground level. Building resumed in September 1526, at which point 1,800 workers were employed in building the château. At the time of the death of King Francis I in 1547, the work had cost 444,070 ''livre
LIVRE (, L), previously known as LIVRE/Tempo de Avançar (, L/TDA), is a green political party in Portugal founded in 2014.
Its founding principles are ecology, universalism, freedom, equity, solidarity, socialism and Europeanism. Its symbol i ...
s''.
 The château was built to act as a hunting lodge for King Francis I; however, the king spent barely seven weeks there in total, that time consisting of short hunting visits. As the château had been constructed with the purpose of short stays, it was not practical to live in on a longer-term basis. The massive rooms, open windows and high ceilings meant heating was impractical. Similarly, as the château was not surrounded by a village or estate, there was no immediate source of food other than game. This meant that all food had to be brought with the group, typically numbering up to 2,000 people at a time.
As a result of all the above, the château was completely unfurnished during this period. All furniture, wall coverings, eating implements and so forth were brought specifically for each hunting trip, a major logistical exercise. It is for this reason that much furniture from the era was built to be disassembled to facilitate transportation. After Francis died of a heart attack in 1547, the château was not used for almost a century.
For more than 80 years after the death of King Francis I, French kings abandoned the château, allowing it to fall into decay. Finally, in 1639
The château was built to act as a hunting lodge for King Francis I; however, the king spent barely seven weeks there in total, that time consisting of short hunting visits. As the château had been constructed with the purpose of short stays, it was not practical to live in on a longer-term basis. The massive rooms, open windows and high ceilings meant heating was impractical. Similarly, as the château was not surrounded by a village or estate, there was no immediate source of food other than game. This meant that all food had to be brought with the group, typically numbering up to 2,000 people at a time.
As a result of all the above, the château was completely unfurnished during this period. All furniture, wall coverings, eating implements and so forth were brought specifically for each hunting trip, a major logistical exercise. It is for this reason that much furniture from the era was built to be disassembled to facilitate transportation. After Francis died of a heart attack in 1547, the château was not used for almost a century.
For more than 80 years after the death of King Francis I, French kings abandoned the château, allowing it to fall into decay. Finally, in 1639 King Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crown ...
gave it to his brother, Gaston d'Orléans, who saved the château from ruin by carrying out much restoration work.

King Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
had the great keep restored and furnished the royal apartments. The king then added a 1,200-horse stable, enabling him to use the château as a hunting lodge and a place to entertain a few weeks each year, for example Molière
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin (, ; 15 January 1622 (baptised) – 17 February 1673), known by his stage name Molière (, , ), was a French playwright, actor, and poet, widely regarded as one of the greatest writers in the French language and world ...
presented the premiere of his celebrated comedy, Le Bourgeois Gentilhomme here. Nonetheless, Louis XIV abandoned the château in 1685.
From 1725 to 1733, Stanislas Leszczyński Stanislav and variants may refer to:
People
* Stanislav (given name), a Slavic given name with many spelling variations (Stanislaus, Stanislas, Stanisław, etc.)
Places
* Stanislav, a coastal village in Kherson, Ukraine
* Stanislaus County, C ...
(Stanislas I), the deposed King of Poland and the father-in-law of King Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached ...
, lived at Chambord. In 1745, as a reward for valour, the king gave the château to Maurice de Saxe
Maurice, Count of Saxony (german: Hermann Moritz von Sachsen, french: Maurice de Saxe; 28 October 1696 – 20 November 1750) was a notable soldier, officer and a famed military commander of the 18th century. The illegitimate son of Augustus I ...
, Marshal of France who installed his military regiment there. Maurice de Saxe died in 1750, and once again the colossal château sat empty for many years.
French Revolution and modern history
 In 1792, the
In 1792, the Revolutionary
A revolutionary is a person who either participates in, or advocates a revolution. The term ''revolutionary'' can also be used as an adjective, to refer to something that has a major, sudden impact on society or on some aspect of human endeavor.
...
government ordered the sale of the furnishings; the wall panellings were removed and even floors were taken up and sold for the value of their timber, and, according to M de la Saussaye, the panelled doors were burned to keep the rooms warm during the sales; the empty château was left abandoned until Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
gave it to his subordinate, Louis Alexandre Berthier
Louis-Alexandre Berthier (20 November 1753 – 1 June 1815), Prince of Neuchâtel and Valangin, Prince of Wagram, was a French Marshal of the Empire who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He was twice Minister ...
. The château was subsequently purchased from his widow for the infant Duke of Bordeaux, Henri Charles Dieudonné (1820–1883) who took the title Comte de Chambord. A brief attempt at restoration and occupation was made by his grandfather King Charles X
Charles X (born Charles Philippe, Count of Artois; 9 October 1757 – 6 November 1836) was King of France from 16 September 1824 until 2 August 1830. An uncle of the uncrowned Louis XVII and younger brother to reigning kings Louis XVI and Loui ...
(1824–1830) but in 1830 both were exiled. In '' Outre-Mer: A Pilgrimage Beyond the Sea'', published in the 1830s, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (February 27, 1807 – March 24, 1882) was an American poet and educator. His original works include "Paul Revere's Ride", ''The Song of Hiawatha'', and ''Evangeline''. He was the first American to completely transl ...
remarked on the dilapidation that had set in: "all is mournful and deserted. The grass has overgrown the pavement of the courtyard, and the rude sculpture upon the walls is broken and defaced".Quoted in During the Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871) the château was used as a field hospital.
The final attempt to make use of the colossus came from the Comte de Chambord, but after the Comte died in 1883, the château was left to his sister's heirs, the titular Dukes of Parma
The Duke of Parma and Piacenza () was the ruler of the Duchy of Parma and Piacenza, a historical state of Northern Italy, which existed between 1545 and 1802, and again from 1814 to 1859.
The Duke of Parma was also Duke of Piacenza, excep ...
, then resident in Austria. First left to Robert, Duke of Parma, who died in 1907 and after him, Elias, Prince of Parma. Any attempts at restoration ended with the onset of World War I in 1914. The Château de Chambord was confiscated as enemy property in 1915, but the family of the Duke of Parma sued to recover it, and that suit was not settled until 1932; restoration work was not begun until a few years after World War II ended in 1945. The Château and surrounding areas, some , have belonged to the French state since 1930.
 In 1939, shortly before the outbreak of World War II, the art collections of the Louvre and Compiègne museums (including the
In 1939, shortly before the outbreak of World War II, the art collections of the Louvre and Compiègne museums (including the Mona Lisa
The ''Mona Lisa'' ( ; it, Gioconda or ; french: Joconde ) is a half-length portrait painting by Italian artist Leonardo da Vinci. Considered an archetypal masterpiece of the Italian Renaissance, it has been described as "the best known ...
and Venus de Milo
The ''Venus de Milo'' (; el, Αφροδίτη της Μήλου, Afrodíti tis Mílou) is an ancient Greek sculpture that was created during the Hellenistic period, sometime between 150 and 125 BC. It is one of the most famous works of ancient ...
) were stored at the Château de Chambord. An American B-24 Liberator bomber crashed onto the château lawn on 22 June 1944. The image of the château has been widely used to sell commodities from chocolate to alcohol and from porcelain to alarm clocks; combined with the various written accounts of visitors, this made Chambord one of the best known examples of France's architectural history. Today, Chambord is a major tourist attraction, and in 2007 around 700,000 people visited the château.
After unusually heavy rainfall, Chambord was closed to the public from 1 to 6 June 2016. The river Cosson
The Cosson () is a long river in central France, a right tributary of the river Beuvron. Its source is near the village of Vannes-sur-Cosson, Sologne. The Cosson flows through the following departments and communes:
* Loiret: La Ferté-Saint ...
, a tributary of the Loire
The Loire (, also ; ; oc, Léger, ; la, Liger) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the Rhône ...
, flooded its banks and the château's moat. Drone photography documented some of the peak flooding. The described effects of the flooding on Chambord's 13,000-acre property. The 20-mile wall around the château was breached at several points, metal gates were torn from their framing, and roads were damaged. Also, trees were uprooted and certain electrical and fire protection systems were put out of order. However, the château itself and its collections reportedly were undamaged. The foundation observed that paradoxically the natural disaster affected Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
's vision that Chambord appears to rise from the waters as if it were diverting the Loire. Repairs are expected to cost upwards of a quarter-million dollars.

Influence
The Château de Chambord has further influenced a number of architectural and decorative elements across Europe. Château de Chambord was the model for the reconstruction and new construction of the originalSchwerin Palace
Schwerin Castle (also known as ''Schwerin Palace'', german: Schweriner Schloss, ), is a schloss located in the city of Schwerin, the capital of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern state, Germany. It is situated on an island in the city's main lake, Lake Schwe ...
between 1845 and 1857.
Yet in the later half of the nineteenth century, the château's style is seen proliferating across the United Kingdom, influencing the Founder's Building
The Founder's Building is the original building of Royal Holloway College, University of London (RHUL), in Egham, Surrey, England. It is an example of French-Renaissance-style architecture in the United Kingdom, having been modelled on French ch ...
at Royal Holloway, University of London
Royal Holloway, University of London (RHUL), formally incorporated as Royal Holloway and Bedford New College, is a public research university and a constituent college of the federal University of London. It has six schools, 21 academic departm ...
, designed by William Henry Crossland and the main building of Fettes College
Fettes College () is a co-educational independent boarding and day school in Edinburgh, Scotland, with over two-thirds of its pupils in residence on campus. The school was originally a boarding school for boys only and became co-ed in 1983. In ...
in Edinburgh, designed by David Bryce
David Bryce FRSE FRIBA RSA (3 April 1803 – 7 May 1876) was a Scottish architect.
Life
Bryce was born at 5 South College Street in Edinburgh, the son of David Bryce (1763–1816) a grocer with a successful side interest in buildi ...
in 1870. Between 1874 and 1889, the country house in Buckinghamshire, Waddesdon Manor
Waddesdon Manor is a English country house, country house in the village of Waddesdon, in Buckinghamshire, England. Owned by National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust and managed by the Rothschild Foundation ...
, was built with similar architectural frameworks as the Château de Chambord, disseminated via the architect Gabriel-Hippolyte Destailleur
Hippolyte Destailleur (27 September 1822 – 17 November 1893) was a French architect, interior designer, and collector. He is noted for his designs and restoration work for great châteaux in France and in England, as well as his collection of bo ...
. For instance, the twin staircase towers, on the north facade, were inspired by the staircase tower at the Château.Girouard, Mark ''A Hundred Years at Waddesdon'', published by Rothschild Waddesdon, 1998: 24 However, following the theme of unparalleled luxury at Waddesdon, the windows of the towers at Waddesdon were glazed, unlike those of the staircase at Chambord, and were far more ornate.
References
Notes Footnotes Bibliography * * * * Félibien, André (1681). ''Mémoires pour servir à l'histoire des maisons royales'', published for the first time from the manuscript in the Bibliothèque nationale in 1874. Paris: J. BaurCopy
at
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical c ...
.
*
* Guillaume, Jean (1996). "Chambord, château of", vol. 6, pp. 415–417, in ''The Dictionary of Art
''Grove Art Online'' is the online edition of ''The Dictionary of Art'', often referred to as the ''Grove Dictionary of Art'', and part of Oxford Art Online, an internet gateway to online art reference publications of Oxford University Press, ...
'', edited by Jane Turner, reprinted with minor corrections in 1998. New York: Grove. .
*
* Hanser, David A. (2006). ''Architecture of France''. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. .
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*External links
World History Encyclopedia - Chateau de Chambord
– Official website for tourism in France (in English)
360° Panoramas of Le Château de Chambord'
by the Media Center for Art History, Columbia University {{DEFAULTSORT:Chateau De Chambord
Chambord Chambord can refer to:
* Chambord (liqueur), a brand of raspberry-flavored liqueur
* Château de Chambord, a French ''château'' built in the 16th century
* Chambord, Loir-et-Cher, the French commune where the ''château'' is located
* Chambord, ...
Chambord Chambord can refer to:
* Chambord (liqueur), a brand of raspberry-flavored liqueur
* Château de Chambord, a French ''château'' built in the 16th century
* Chambord, Loir-et-Cher, the French commune where the ''château'' is located
* Chambord, ...
Museums in Loir-et-Cher
National museums of France
Historic house museums in Centre-Val de Loire
Houses completed in 1547
Hunting museums
Hunting lodges in France
Chambord Chambord can refer to:
* Chambord (liqueur), a brand of raspberry-flavored liqueur
* Château de Chambord, a French ''château'' built in the 16th century
* Chambord, Loir-et-Cher, the French commune where the ''château'' is located
* Chambord, ...
Royal residences in France
Double spiral staircases
Stairways
Monuments historiques of Centre-Val de Loire
Ancien Régime French architecture
French Renaissance architecture
Renaissance architecture in France
1547 establishments in France
Castles in France