Cell growth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cell growth refers to an increase in the total
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total  In
In
 Wee1 protein is a tyrosine kinase that normally phosphorylates the Cdc2 cell cycle regulatory protein (the homolog of CDK1 in humans), a cyclin-dependent kinase, on a tyrosine residue. Cdc2 drives entry into mitosis by phosphorylating a wide range of targets. This
Wee1 protein is a tyrosine kinase that normally phosphorylates the Cdc2 cell cycle regulatory protein (the homolog of CDK1 in humans), a cyclin-dependent kinase, on a tyrosine residue. Cdc2 drives entry into mitosis by phosphorylating a wide range of targets. This
Table of cell sizes
��Dense populations of a giant sulfur bacterium in Namibian shelf sediments�
) In the rod-shaped bacteria ''E. coli'', ''Caulobacter crescentus'' and ''B. subtilis'' cell size is controlled by a simple mechanisms in which cell division occurs after a constant volume has been added since the previous division. By always growing by the same amount, cells born smaller or larger than average naturally converge to an average size equivalent to the amount added during each generation.

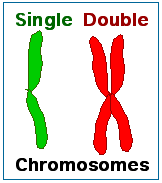 Immediately after DNA replication a human cell will have 46 "double chromosomes". In each double chromosome there are two copies of that chromosome's DNA molecule. During mitosis the double chromosomes are split to produce 92 "single chromosomes", half of which go into each daughter cell. During meiosis, there are two chromosome separation steps which assure that each of the four daughter cells gets one copy of each of the 23 types of chromosome.
Immediately after DNA replication a human cell will have 46 "double chromosomes". In each double chromosome there are two copies of that chromosome's DNA molecule. During mitosis the double chromosomes are split to produce 92 "single chromosomes", half of which go into each daughter cell. During meiosis, there are two chromosome separation steps which assure that each of the four daughter cells gets one copy of each of the 23 types of chromosome.
A comparison of generational and exponential models of cell population growth
Local Growth in an Array of Disks
''Wolfram Demonstrations Project'' Cell cycle Cellular processes
 Cell growth refers to an increase in the total
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different ele ...
of a cell, including both cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
ic, nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation (the destruction of biomolecules via the proteasome, lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane p ...
or autophagy, or catabolism).
Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
or the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
, which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation, where a cell, known as the mother cell, grows and divides to produce two daughter cells. Importantly, cell growth and cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
can also occur independently of one another. During early embryonic development ( cleavage of the zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
to form a morula and blastoderm A blastoderm (germinal disc, blastodisc) is a single layer of embryonic epithelial tissue that makes up the blastula. It encloses the fluid filled blastocoel. Gastrulation follows blastoderm formation, where the tips of the blastoderm begins the fo ...
), cell divisions
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there are ...
occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
or without any progression of the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
, such as growth of neurons during axonal pathfinding in nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes ...
development.
 In
In multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
organisms, tissue growth
Tissue growth is the process by which ''a tissue increases its size''. In animals, tissue growth occurs during embryonic development, post-natal growth, and tissue regeneration. The fundamental cellular basis for tissue growth is the process ...
rarely occurs solely through cell growth without cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
, but most often occurs through cell proliferation. This is because a single cell with only one copy of the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
in the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
can perform biosynthesis and thus undergo cell growth at only half the rate of two cells. Hence, two cells grow (accumulate mass) at twice the rate of a single cell, and four cells grow at 4-times the rate of a single cell. This principle leads to an exponential increase of tissue growth
Tissue growth is the process by which ''a tissue increases its size''. In animals, tissue growth occurs during embryonic development, post-natal growth, and tissue regeneration. The fundamental cellular basis for tissue growth is the process ...
rate (mass accumulation) during cell proliferation, owing to the exponential increase in cell number.
Cell size depends on both cell growth and cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
, with a disproportionate increase in the rate of cell growth leading to production of larger cells and a disproportionate increase in the rate of cell division leading to production of many smaller cells. Cell proliferation typically involves balanced cell growth and cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
rates that maintain a roughly constant cell size in the exponentially proliferating population of cells.
Some special cells can grow to very large sizes via an unusual endoreplication
Endoreduplication (also referred to as endoreplication or endocycling) is replication of the nuclear genome in the absence of mitosis, which leads to elevated nuclear gene content and polyploidy. Endoreplication can be understood simply as a vari ...
cell cycle in which the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
is replicated during S-phase but there is no subsequent mitosis ( M-phase) or cell division (cytokinesis
Cytokinesis () is the part of the cell division process during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division in mitosis and mei ...
). These large endoreplicating cells have many copies of the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
, so are highly polyploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than one pair of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei ( eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes, where each set conta ...
.
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female ...
s can be unusually large cells in species for which embryonic development takes place away from the mother's body within an egg that is laid externally. The large size of some eggs can be achieved either by pumping in cytosolic components from adjacent cells through cytoplasmic bridges named ring canals (''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...
'') or by internalisation of nutrient storage granules (yolk granules) by endocytosis (frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-f ...
s).
Mechanisms of cell growth control
Cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
can grow by increasing the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis such that production of biomolecules exceeds the overall rate of cellular degradation of biomolecules via the proteasome, lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane p ...
or autophagy.
Biosynthesis of biomolecules is initiated by expression of genes which encode RNAs and/or proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
, including enzymes that catalyse synthesis of lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
and carbohydrates.
Individual genes are generally expressed via transcription into messenger RNA (mRNA) and translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
into protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s, and the expression of each gene occurs to various different levels in a cell-type specific fashion (in response to gene regulatory networks).
To drive cell growth, the global rate of gene expression can be increased by enhancing the overall rate of transcription by RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of euka ...
(for active genes) or the overall rate of mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
into protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
by increasing the abundance of ribosomes and tRNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino ...
, whose biogenesis depends on RNA polymerase I and RNA polymerase III. The Myc transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
is an example of a regulatory protein that can induce the overall activity of RNA polymerase I, RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of euka ...
and RNA polymerase III to drive global transcription and translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
and thereby cell growth.
In addition, the activity of individual ribosomes can be increased to boost the global efficiency of mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
via regulation of translation initiation factors, including the 'translational elongation initiation factor 4E' ( eIF4E) complex, which binds to and caps the 5' end of mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
s. The protein TOR, part of the TORC1 complex, is an important upstream regulator of translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
initiation as well as ribosome biogenesis
Ribosome biogenesis is the process of making ribosomes. In prokaryotes, this process takes place in the cytoplasm with the transcription of many ribosome gene operons. In eukaryotes, it takes place both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleolu ...
. TOR is a serine/threonine kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
that can directly phosphorylate and inactivate a general inhibitor of eIF4E, named 4E-binding protein (4E-BP), to promote translation efficiency. TOR also directly phosphorylates and activates the ribosomal protein S6-kinase ( S6K), which promotes ribosome biogenesis
Ribosome biogenesis is the process of making ribosomes. In prokaryotes, this process takes place in the cytoplasm with the transcription of many ribosome gene operons. In eukaryotes, it takes place both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleolu ...
.
To inhibit cell growth, the global rate of gene expression can be decreased or the global rate of biomolecular degradation can be increased by increasing the rate of autophagy. TOR normally directly inhibits the function of the autophagy inducing kinase Atg1/ULK1. Thus, reducing TOR activity both reduces the global rate of translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
and increases the extent of autophagy to reduce cell growth.
Cell growth regulation in animals
Many of the signal molecules that control of cellular growth are called growth factors, many of which induce signal transduction via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which includes upstream lipid kinase PI3K and the downstream serine/threonine proteinkinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
Akt, which is able to activate another protein kinase TOR, which promotes translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
and inhibits autophagy to drive cell growth.
Nutrient availability influences production of growth factors of the Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
/ IGF-1 family, which circulate as hormones in animals to activate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in cells to promote TOR activity so that when animals are well fed they will grow rapidly and when they are not able to receive sufficient nutrients they will reduce their growth rate. Recently it has been also demonstrated that cellular bicarbonate metabolism, which is responsible for cell growth, can be regulated by mTORC1 signaling.
In addition, the availability of amino acids to individual cells also directly promotes TOR activity, although this mode of regulation is more important in single-celled organisms than in multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
organisms such as animals that always maintain an abundance of amino acids in circulation.
One disputed theory proposes that many different mammalian cells undergo size-dependent transitions during the cell cycle. These transitions are controlled by the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1. Though the proteins that control Cdk1 are well understood, their connection to mechanisms monitoring cell size remains elusive.
A postulated model for mammalian size control situates mass as the driving force of the cell cycle. A cell is unable to grow to an abnormally large size because at a certain cell size or cell mass, the S phase is initiated. The S phase starts the sequence of events leading to mitosis and cytokinesis. A cell is unable to get too small because the later cell cycle events, such as S, G2, and M, are delayed until mass increases sufficiently to begin S phase.
Cell populations
Cell populations go through a particular type ofexponential growth
Exponential growth is a process that increases quantity over time. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a ...
called doubling or cell proliferation. Thus, each generation of cells should be twice as numerous as the previous generation. However, the number of generations only gives a maximum figure as not all cells survive in each generation. Cells can reproduce in the stage of Mitosis, where they double and split into two genetically equal cells.
Cell size
Cell size is highly variable among organisms, with some algae such as ''Caulerpa taxifolia
''Caulerpa taxifolia'' is a species of green seaweed, an alga of the genus ''Caulerpa'', native to tropical waters of the Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean, and Caribbean Sea. The species name ''taxifolia'' arises from the resemblance of its leaf-lik ...
'' being a single cell several meters in length. Plant cells are much larger than animal cells, and protists such as '' Paramecium'' can be 330 μm long, while a typical human cell might be 10 μm. How these cells "decide" how big they should be before dividing is an open question. Chemical gradients are known to be partly responsible, and it is hypothesized that mechanical stress detection by cytoskeletal
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compo ...
structures is involved. Work on the topic generally requires an organism whose cell cycle is well-characterized.
Yeast cell size regulation
The relationship between cell size andcell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
has been extensively studied in yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
. For some cells, there is a mechanism by which cell division is not initiated until a cell has reached a certain size. If the nutrient supply is restricted (after time t = 2 in the diagram, below), and the rate of increase in cell size is slowed, the time period between cell divisions is increased. Yeast cell-size mutants were isolated that begin cell division before reaching a normal/regular size (''wee'' mutants).
 Wee1 protein is a tyrosine kinase that normally phosphorylates the Cdc2 cell cycle regulatory protein (the homolog of CDK1 in humans), a cyclin-dependent kinase, on a tyrosine residue. Cdc2 drives entry into mitosis by phosphorylating a wide range of targets. This
Wee1 protein is a tyrosine kinase that normally phosphorylates the Cdc2 cell cycle regulatory protein (the homolog of CDK1 in humans), a cyclin-dependent kinase, on a tyrosine residue. Cdc2 drives entry into mitosis by phosphorylating a wide range of targets. This covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
modification of the molecular structure of Cdc2 inhibits the enzymatic activity of Cdc2 and prevents cell division. Wee1 acts to keep Cdc2 inactive during early G2 when cells are still small. When cells have reached sufficient size during G2, the phosphatase Cdc25 removes the inhibitory phosphorylation, and thus activates Cdc2 to allow mitotic entry. A balance of Wee1 and Cdc25 activity with changes in cell size is coordinated by the mitotic entry control system. It has been shown in Wee1 mutants, cells with weakened Wee1 activity, that Cdc2 becomes active when the cell is smaller. Thus, mitosis occurs before the yeast reach their normal size. This suggests that cell division may be regulated in part by dilution of Wee1 protein in cells as they grow larger.
Linking Cdr2 to Wee1
The protein kinase Cdr2 (which negatively regulates Wee1) and the Cdr2-related kinase Cdr1 (which directly phosphorylates and inhibits Wee1 ''in vitro'') are localized to a band of cortical nodes in the middle of interphase cells. After entry into mitosis, cytokinesis factors such as myosin II are recruited to similar nodes; these nodes eventually condense to form the cytokinetic ring. A previously uncharacterized protein, Blt1, was found to colocalize with Cdr2 in the medial interphase nodes. Blt1 knockout cells had increased length at division, which is consistent with a delay in mitotic entry. This finding connects a physical location, a band of cortical nodes, with factors that have been shown to directly regulate mitotic entry, namely Cdr1, Cdr2, and Blt1. Further experimentation with GFP-tagged proteins and mutant proteins indicates that the medial cortical nodes are formed by the ordered, Cdr2-dependent assembly of multiple interacting proteins during interphase. Cdr2 is at the top of this hierarchy and works upstream of Cdr1 and Blt1. Mitosis is promoted by the negative regulation of Wee1 by Cdr2. It has also been shown that Cdr2 recruits Wee1 to the medial cortical node. The mechanism of this recruitment has yet to be discovered. A Cdr2 kinase mutant, which is able to localize properly despite a loss of function in phosphorylation, disrupts the recruitment of Wee1 to the medial cortex and delays entry into mitosis. Thus, Wee1 localizes with its inhibitory network, which demonstrates that mitosis is controlled through Cdr2-dependent negative regulation of Wee1 at the medial cortical nodes.Cell polarity factors
Cell polarity factors positioned at the cell tips provide spatial cues to limit Cdr2 distribution to the cell middle. In fission yeast '' Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' (''S. Pombe''), cells divide at a defined, reproducible size during mitosis because of the regulated activity of Cdk1. The cell polarity protein kinasePom1
Pom1 is a polarity protein kinase in fission yeast, ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' (''S. pombe''), that localizes to cell ends and regulates cell division. As the cell lengthens, the level of Pom1 in the middle declines, which triggers mitosis.Bahle ...
, a member of the dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation regulated kinase (DYRK) family of kinases, localizes to cell ends. In Pom1 knockout cells, Cdr2 was no longer restricted to the cell middle, but was seen diffusely through half of the cell. From this data it becomes apparent that Pom1 provides inhibitory signals that confine Cdr2 to the middle of the cell. It has been further shown that Pom1-dependent signals lead to the phosphorylation of Cdr2. Pom1 knockout cells were also shown to divide at a smaller size than wild-type, which indicates a premature entry into mitosis.
Pom1 forms polar gradients that peak at cell ends, which shows a direct link between size control factors and a specific physical location in the cell. As a cell grows in size, a gradient in Pom1 grows. When cells are small, Pom1 is spread diffusely throughout the cell body. As the cell increases in size, Pom1 concentration decreases in the middle and becomes concentrated at cell ends. Small cells in early G2 which contain sufficient levels of Pom1 in the entirety of the cell have inactive Cdr2 and cannot enter mitosis. It is not until the cells grow into late G2, when Pom1 is confined to the cell ends that Cdr2 in the medial cortical nodes is activated and able to start the inhibition of Wee1. This finding shows how cell size plays a direct role in regulating the start of mitosis. In this model, Pom1 acts as a molecular link between cell growth and mitotic entry through a Cdr2-Cdr1-Wee1-Cdk1 pathway. The Pom1 polar gradient successfully relays information about cell size and geometry to the Cdk1 regulatory system. Through this gradient, the cell ensures it has reached a defined, sufficient size to enter mitosis.
Other experimental systems for the study of cell size regulation
One common means to produce very large cells is by cell fusion to form syncytia. For example, very long (several inches)skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of m ...
cells are formed by fusion of thousands of myocytes. Genetic studies of the fruit fly ''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...
'' have revealed several genes that are required for the formation of multinucleated muscle cells by fusion of myoblasts. Some of the key proteins are important for cell adhesion between myocytes and some are involved in adhesion-dependent cell-to-cell signal transduction that allows for a cascade of cell fusion events.
Increases in the size of plant cell
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capab ...
s are complicated by the fact that almost all plant cells are inside of a solid cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mec ...
. Under the influence of certain plant hormones the cell wall can be remodeled, allowing for increases in cell size that are important for the growth of some plant tissues.
Most unicellular organisms are microscopic in size, but there are some giant bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
and protozoa that are visible to the naked eye. (SeTable of cell sizes
��Dense populations of a giant sulfur bacterium in Namibian shelf sediments�
) In the rod-shaped bacteria ''E. coli'', ''Caulobacter crescentus'' and ''B. subtilis'' cell size is controlled by a simple mechanisms in which cell division occurs after a constant volume has been added since the previous division. By always growing by the same amount, cells born smaller or larger than average naturally converge to an average size equivalent to the amount added during each generation.
Cell division
Cell reproduction is asexual. For most of the constituents of the cell, growth is a steady, continuous process, interrupted only briefly at M phase when the nucleus and then the cell divide in two. The process of cell division, calledcell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
, has four major parts called phases. The first part, called G1 phase is marked by synthesis of various enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s that are required for DNA replication.
The second part of the cell cycle is the S phase, where DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritan ...
produces two identical sets of chromosomes
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
. The third part is the G2 phase in which a significant protein synthesis occurs, mainly involving the production of microtubules
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 a ...
that are required during the process of division, called mitosis.
The fourth phase, M phase, consists of nuclear division ( karyokinesis) and cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis
Cytokinesis () is the part of the cell division process during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division in mitosis and mei ...
), accompanied by the formation of a new cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
. This is the physical division of mother and daughter cells. The M phase has been broken down into several distinct phases, sequentially known as prophase, prometaphase, metaphase
Metaphase ( and ) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase). These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, a ...
, anaphase and telophase leading to cytokinesis.
Cell division is more complex in eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s than in other organisms. Prokaryotic cells such as bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
l cells reproduce by binary fission, a process that includes DNA replication, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis. Eukaryotic cell division either involves mitosis or a more complex process called meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately ...
. Mitosis and meiosis are sometimes called the two nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
division processes. Binary fission is similar to eukaryote cell reproduction that involves mitosis. Both lead to the production of two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parental cell. Meiosis is used for a special cell reproduction process of diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectiv ...
organisms. It produces four special daughter cells (gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce ...
s) which have half the normal cellular amount of DNA. A male
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization.
A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to ...
and a female
Female ( symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Fema ...
gamete can then combine to produce a zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
, a cell which again has the normal amount of chromosomes.
The rest of this article is a comparison of the main features of the three types of cell reproduction that either involve binary fission, mitosis, or meiosis. The diagram below depicts the similarities and differences of these three types of cell reproduction.
Comparison of the three types of cell division
The DNA content of a cell is duplicated at the start of the cell reproduction process. Prior toDNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritan ...
, the DNA content of a cell can be represented as the amount Z (the cell has Z chromosomes). After the DNA replication process, the amount of DNA in the cell is 2Z (multiplication: 2 x Z = 2Z). During Binary fission and mitosis the duplicated DNA content of the reproducing parental cell is separated into two equal halves that are destined to end up in the two daughter cells. The final part of the cell reproduction process is cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ...
, when daughter cells physically split apart from a parental cell. During meiosis, there are two cell division steps that together produce the four daughter cells.
After the completion of binary fission or cell reproduction involving mitosis, each daughter cell has the same amount of DNA (Z) as what the parental cell had before it replicated its DNA. These two types of cell reproduction produced two daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes as the parental cell. Chromosomes duplicate prior to cell division when forming new skin cells for reproduction. After meiotic cell reproduction the four daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes that the parental cell originally had. This is the haploid amount of DNA, often symbolized as N. Meiosis is used by diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectiv ...
organisms to produce haploid gametes. In a diploid organism such as the human organism, most cells of the body have the diploid amount of DNA, 2N. Using this notation for counting chromosomes we say that human somatic cells have 46 chromosomes (2N = 46) while human sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
and eggs have 23 chromosomes (N = 23). Humans have 23 distinct types of chromosomes, the 22 autosomes and the special category of sex chromosomes. There are two distinct sex chromosomes, the X chromosome and the Y chromosome. A diploid human cell has 23 chromosomes from that person's father and 23 from the mother. That is, your body has two copies of human chromosome number 2, one from each of your parents.
 Immediately after DNA replication a human cell will have 46 "double chromosomes". In each double chromosome there are two copies of that chromosome's DNA molecule. During mitosis the double chromosomes are split to produce 92 "single chromosomes", half of which go into each daughter cell. During meiosis, there are two chromosome separation steps which assure that each of the four daughter cells gets one copy of each of the 23 types of chromosome.
Immediately after DNA replication a human cell will have 46 "double chromosomes". In each double chromosome there are two copies of that chromosome's DNA molecule. During mitosis the double chromosomes are split to produce 92 "single chromosomes", half of which go into each daughter cell. During meiosis, there are two chromosome separation steps which assure that each of the four daughter cells gets one copy of each of the 23 types of chromosome.
Sexual reproduction
Though cell reproduction that uses mitosis can reproduce eukaryotic cells, eukaryotes bother with the more complicated process of meiosis becausesexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote th ...
such as meiosis confers a selective advantage
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the po ...
. Notice that when meiosis starts, the two copies of sister chromatids number 2 are adjacent to each other. During this time, there can be genetic recombination events. Information from the chromosome 2 DNA gained from one parent (red) will transfer over to the chromosome 2 DNA molecule that was received from the other parent (green). Notice that in mitosis the two copies of chromosome number 2 do not interact. Recombination of genetic information between homologous chromosomes during meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately ...
is a process for repairing DNA damages. This process can also produce new combinations of genes, some of which may be adaptively beneficial and influence the course of evolution. However, in organisms with more than one set of chromosomes at the main life cycle stage, sex may also provide an advantage because, under random mating, it produces homozygotes and heterozygote
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
M ...
s according to the Hardy–Weinberg ratio.
Disorders
A series of growth disorders can occur at the cellular level and these consequently underpin much of the subsequent course incancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, in which a group of cells display uncontrolled growth and division beyond the normal limits, ''invasion'' (intrusion on and destruction of adjacent tissues), and sometimes ''metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, the ...
'' (spread to other locations in the body via lymph or blood). Several key determinants of cell growth, like ploidy and the regulation of cellular metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
, are commonly disrupted in tumors. Therefore, heterogenous cell growth and pleomorphism
Pleomorphism may refer to:
* Pleomorphism (cytology), variability in the size and shape of cells and/or their nuclei
* Pleomorphism (microbiology), the ability of some bacteria to alter their shape or size in response to environmental conditions
...
is one of the earliest hallmarks of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
progression. Despite the prevalence of pleomorphism in human pathology, its role in disease progression is unclear. In epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellu ...
tissues, pleomorphism in cellular size can induce packing defects and disperse aberrant cells. But the consequence of atypical cell growth in other animal tissues is unknown.
Measurement methods
The cell growth can be detected by a variety of methods. The cell size growth can be visualized by microscopy, using suitable stains. But the increase of cells number is usually more significant. It can be measured by manual counting of cells under microscopy observation, using the dye exclusion method (i.e. trypan blue) to count only viable cells. Less fastidious, scalable, methods include the use of cytometers, while flow cytometry allows combining cell counts ('events') with other specific parameters: fluorescent probes for membranes, cytoplasm or nuclei allow distinguishing dead/viable cells, cell types, cell differentiation, expression of a biomarker such as Ki67. Beside the increasing number of cells, one can be assessed regarding the metabolic activity growth, that is, the CFDA andcalcein
Calcein, also known as fluorexon, fluorescein complex, is a fluorescent dye with excitation and emission wavelengths of 495/515 nm, respectively, and has the appearance of orange crystals. Calcein self- quenches at concentrations above 70 ...
-AM measure (fluorimetrically) not only the membrane functionality (dye retention), but also the functionality of cytoplasmic enzymes (esterases). The MTT assays (colorimetric) and the resazurin assay (fluorimetric) dose the mitochondrial redox potential.
All these assays may correlate well, or not, depending on cell growth conditions and desired aspects (activity, proliferation). The task is even more complicated with populations of different cells, furthermore when combining cell growth interferences or toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
.
See also
*Bacterial growth
250px, Growth is shown as ''L'' = log(numbers) where numbers is the number of colony forming units per ml, versus ''T'' (time.)
Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing ...
References
Books
* {{cite book , last1=Morgan , first1=David O. , title=The cell cycle: principles of control , date=2007 , publisher=Sunderland, Mass. , location=London , isbn=978-0-9539181-2-6External links
A comparison of generational and exponential models of cell population growth
Local Growth in an Array of Disks
''Wolfram Demonstrations Project'' Cell cycle Cellular processes