Cell death on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as

disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
s, localized injury
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, o ...
, or the death of the organism of which the cells are part. Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
or Type I cell-death, and autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent re ...
or Type II cell-death are both forms of programmed cell death, while necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury.
Programmed cell death
Programmed cell death (PCD) is cell death mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingersapoptose
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes includ ...
; the result is that the digits separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
(multicellular animals) tissue development.
Apoptosis

Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
is the process of programmed cell death (PCD) that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology an ...
events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
DNA fragmentation. It is now thought that – in a developmental context – cells are induced to positively commit suicide whilst in a homeostatic context; the absence of certain survival factors may provide the impetus for suicide. There appears to be some variation in the morphology and indeed the biochemistry of these suicide pathways; some treading the path of "apoptosis", others following a more generalized pathway to deletion, but both usually being genetically and synthetically motivated. There is some evidence that certain symptoms of "apoptosis" such as endonuclease activation can be spuriously induced without engaging a genetic cascade, however, presumably true apoptosis and programmed cell death must be genetically mediated. It is also becoming clear that mitosis and apoptosis are toggled or linked in some way and that the balance achieved depends on signals received from appropriate growth or survival factors.

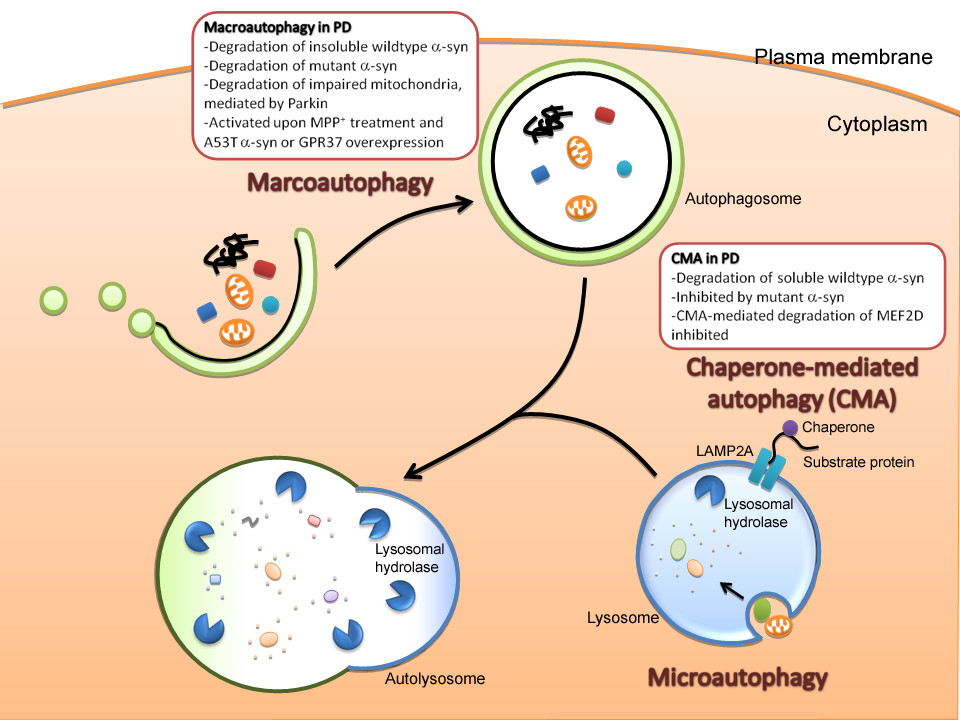
Autophagy
Autophagy is ''cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
ic'', characterized by the formation of large vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic m ...
s that eat away organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
s in a specific sequence prior to the destruction of the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
. Macroautophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent r ...
, often referred to as autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent re ...
, is a catabolic
Catabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that breaks down molecules into smaller units that are either oxidized to release energy or used in other anabolic reactions. Catabolism breaks down large molecules (such as polysaccharides, lip ...
process that results in the autophagosomic- lysosomal degradation of bulk cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
ic contents, abnormal protein aggregates, and excess or damaged organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
s. Autophagy is generally activated by conditions of nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excre ...
deprivation but has also been associated with physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
s, stress, infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
.
Other variations of PCD
Other pathways of programmed cell death have been discovered. Called "non-apoptotic programmed cell-death" (or "caspase
Caspases (cysteine-aspartic proteases, cysteine aspartases or cysteine-dependent aspartate-directed proteases) are a family of protease enzymes playing essential roles in programmed cell death. They are named caspases due to their specific cyste ...
-independent programmed cell-death"), these alternative routes to death are as efficient as apoptosis and can function as either backup mechanisms or the main type of PCD.
Some such forms of programmed cell death are anoikis, almost identical to apoptosis except in its induction; cornification
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, hor ...
, a form of cell death exclusive to the eyes; excitotoxicity; ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is a type of programmed cell death dependent on iron and characterized by the accumulation of lipid peroxides, and is genetically and biochemically distinct from other forms of regulated cell death such as apoptosis. Ferroptosis is init ...
, an iron-dependent form of cell death and Wallerian degeneration.
Plant cells undergo particular processes of PCD similar to autophagic cell death. However, some common features of PCD are highly conserved in both plants and metazoa.
Activation-induced cell death (AICD) is a programmed cell death caused by the interaction of Fas receptor (Fas, CD95)and Fas ligand (FasL, CD95 ligand).Zhang J, Xu X, Liu Y. (2004), Activation-Induced Cell Death in T Cells and Autoimmunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 1(3):186-92 It occurs as a result of repeated stimulation of specific T-cell receptors (TCR) and it helps to maintain the periphery immune tolerance. Therefore, an alteration of the process may lead to autoimmune diseases. In the other words AICD is the negative regulator of activated T-lymphocytes.
Ischemic cell death, or oncosis, is a form of accidental, or passive cell death that is often considered a lethal injury. The process is characterized by mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
l swelling, cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
vacuolization, and swelling of the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
and cytoplasm.
Mitotic catastrophe
Mitotic Catastrophe has been defined as either a cellular mechanism to prevent potentially cancerous cells from proliferating or as a mode of cellular death that occurs following improper cell cycle progression or entrance. Mitotic catastrophe can ...
is an oncosuppressive mechanism that can lead to cell death that is due to premature or inappropriate entry of cells into mitosis. It is the most common mode of cell death in cancer cells exposed to ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
and many other anti-cancer treatments.
Immunogenic cell death Immunogenic cell death is any type of cell death eliciting an immune response. Both accidental cell death and regulated cell death can result in immune response. Immunogenic cell death contrasts to forms of cell death (apoptosis, autophagy or others ...
or immunogenic apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
is a form of cell death caused by some cytostatic agents such as anthracyclines, oxaliplatin and bortezomib, or radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Rad ...
and photodynamic therapy (PDT).
Pyroptosis Pyroptosis is a highly inflammatory form of lytic programmed cell death that occurs most frequently upon infection with intracellular pathogens and is likely to form part of the antimicrobial response. This process promotes the rapid clearance of va ...
is a highly inflammatory form of programmed cell death that occurs most frequently upon infection with intracellular pathogens and is likely to form part of the antimicrobial response in myeloid cells.
PANoptosis PANoptosis is an inflammatory cell death pathway. Consideration of the totality of biological effects from cell death in multiple studies has led to the conceptualization of PANoptosis, a unique innate immune inflammatory cell death pathway regulate ...
is a unique inflammatory cell death pathway that integrates components from other cell death pathways. The totality of biological effects in PANoptosis cannot be individually accounted for by pyroptosis, apoptosis, or necroptosis alone. PANoptosis is regulated by multifaceted macromolecular complexes termed PANoptosomes.
Necrotic cell death
Necrosis is cell death where a cell has been badly damaged through external forces such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. In necrosis, a cell undergoes swelling, followed by uncontrolled rupture of the cell membrane with cell contents being expelled. These cell contents often then go on to cause inflammation in nearby cells. A form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, has been recognized as an alternative form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis can serve as a cell-death backup to apoptosis when the apoptosis signaling is blocked by endogenous or exogenous factors such as viruses or mutations. Necroptotic pathways are associated with death receptors such as the tumor necrosis factor receptor 1.Field of study and etymology
The term "cell necrobiology" has been used to describe the life processes associated with morphological, biochemical, and molecular changes which predispose, precede, and accompany cell death, as well as the consequences and tissue response to cell death. The word is derived from the Greek νεκρό meaning "death", βìο meaning "life", and λόγος meaning "the study of". The term was initially coined to broadly define investigations of the changes that accompany cell death, detected and measured by multiparameter flow- and laser scanning- cytometry. It has been used to describe the real-time changes during cell death, detected by flow cytometry.See also
*Programmed cell death 1
Programmed cell death protein 1, also known as PD-1 and CD279 (cluster of differentiation 279), is a protein on the surface of T and B cells that has a role in regulating the immune system's response to the cells of the human body by down-regula ...
, a protein
* Tumor Necrosis Factor 1
References
{{Death Cellular processes Medical aspects of death