Celite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Diatomaceous earth (), diatomite (), or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft,
Diatomaceous earth (), diatomite (), or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft, 
File:KieselgurNeuohe4-2.jpg, c. 1900–1910 Diatomaceous earth pit at Neuohe
File:KieselgurNeuohe3-2.jpg, c. 1900–1910 a drying area: one firing pile is being prepared; another is under way
File:KieselgurNeuohe2-2.jpg, 1913: Staff at the Neuohe factory, with male workers and a female cook in front of a drying shed
Until

Occupational exposure to crystalline silica and autoimmune disease.
Diatomite: Statistics and Information – USGS
Citat: "...A diatomaceous earth consisting of opaline silica..."
{{DEFAULTSORT:Diatomaceous Earth Sedimentary rocks Inorganic insecticides Swimming pools Water treatment Soil Soil improvers Fodder Microfossils Biomineralization Industrial minerals Sustainable agriculture
 Diatomaceous earth (), diatomite (), or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft,
Diatomaceous earth (), diatomite (), or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size
Particle size is a notion introduced for comparing dimensions of solid particles ('' flecks''), liquid particles ('' droplets''), or gaseous particles ('' bubbles''). The notion of particle size applies to particles in colloids, in ecology, in ...
ranging from more than 3 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Uni ...
to less than 1 mm, but typically 10 to 200 μm. Depending on the granularity
Granularity (also called graininess), the condition of existing in granules or grains, refers to the extent to which a material or system is composed of distinguishable pieces. It can either refer to the extent to which a larger entity is sub ...
, this powder can have an abrasive
An abrasive is a material, often a mineral, that is used to shape or finish a workpiece through rubbing which leads to part of the workpiece being worn away by friction. While finishing a material often means polishing it to gain a smooth, reflec ...
feel, similar to pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular v ...
powder, and has a low density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematicall ...
as a result of its high porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measur ...
. The typical chemical composition of oven-dried diatomaceous earth is 80–90% silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
, with 2–4% alumina (attributed mostly to clay mineral
Clay minerals are hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates (e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4), sometimes with variable amounts of iron, magnesium, alkali metals, alkaline earths, and other cations found on or near some planetary surfaces.
Clay minera ...
s), and 0.5–2% iron oxide
Iron oxides are chemical compounds composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. All are black magnetic solids. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of wh ...
.
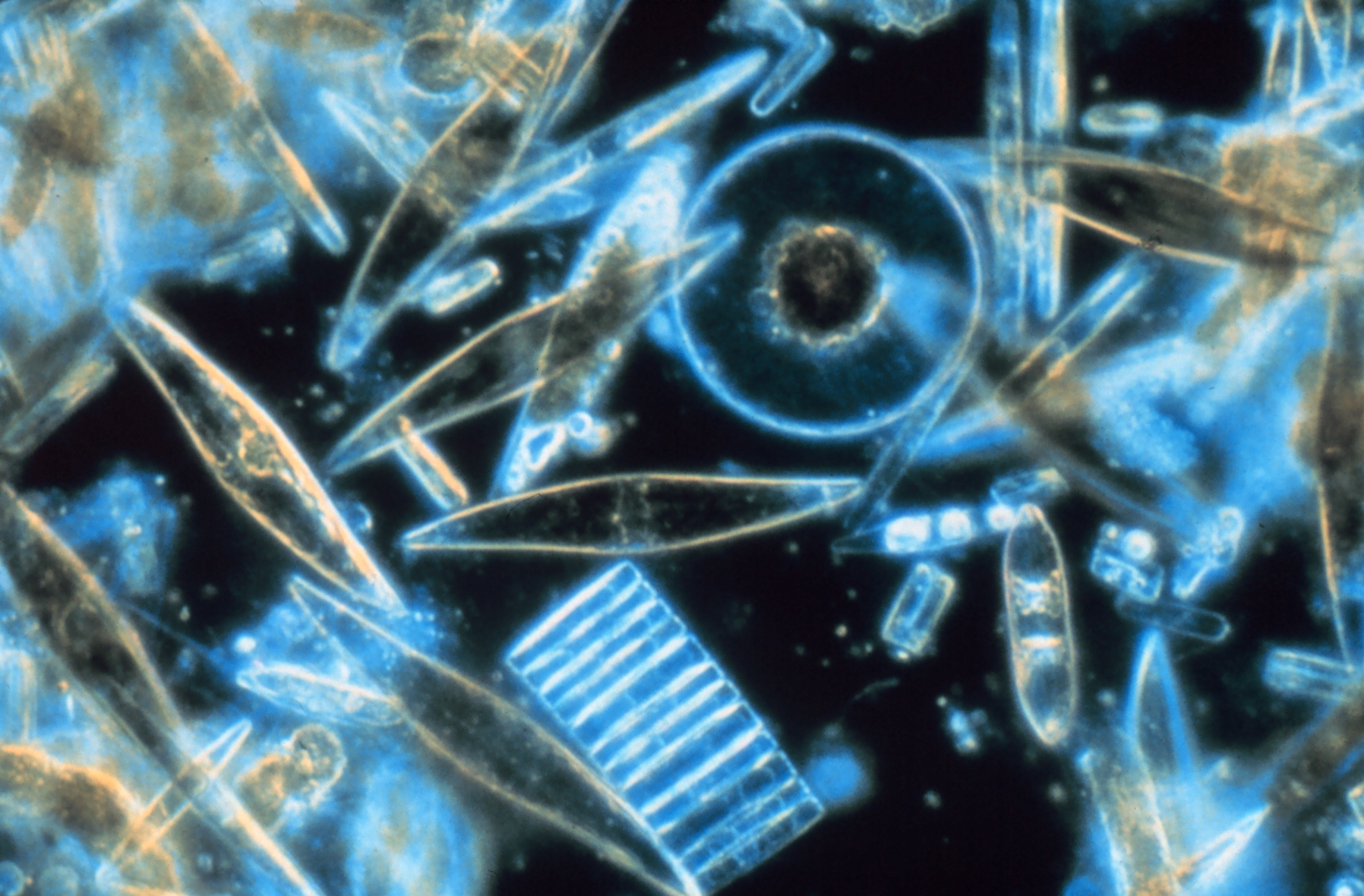
Diatomaceous earth consists of the fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
ized remains of diatom
A diatom ( Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising se ...
s, a type of hard-shelled microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist indiv ...
. It is used as a filtration
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a ''filter medium'' that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter ...
aid, mild abrasive in products including metal polishes and toothpaste
Toothpaste is a paste or gel dentifrice used with a toothbrush to clean and maintain the aesthetics and health of teeth. Toothpaste is used to promote oral hygiene: it is an abrasive that aids in removing dental plaque and food from the teeth, ...
, mechanical insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed t ...
, absorbent for liquids, matting agent for coatings, reinforcing filler in plastics and rubber, anti-block in plastic films, porous support for chemical catalysts, cat litter
A litter box, also known as a sandbox, cat box, litter tray, cat pan, potty, pot or litter pan, is an indoor feces and urine collection box for cats, as well as rabbits, ferrets, miniature pigs, small dogs, and other pets that instinctively or ...
, activator in coagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism ...
studies, a stabilizing component of dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents (such as powdered shells or clay), and stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern Germany, and patented in 1867. It rapidl ...
, a thermal insulator, and a soil for potted plants and trees as in the art of bonsai
Bonsai ( ja, 盆栽, , tray planting, ) is the Japanese art of growing and training miniature trees in pots, developed from the traditional Chinese art form of '' penjing''. Unlike ''penjing'', which utilizes traditional techniques to produc ...
.

Composition
Each deposit of diatomaceous earth is different, with varying blends of pure diatomaceous earth combined with other natural clays and minerals. The diatoms in each deposit contain different amounts of silica, depending on the sedimentation conditions, on the presence of other sediments (clay, sand, volcanic ashes), and on the age of the deposit (diagenesis
Diagenesis () is the process that describes physical and chemical changes in sediments first caused by water-rock interactions, microbial activity, and compaction after their deposition. Increased pressure and temperature only start to play a ...
, silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
(SiO2) dissolution/precipitation, diatoms tests ageing). The species of diatom may also differ among deposits. The species of diatom is dependent upon the age and paleoecology
Paleoecology (also spelled palaeoecology) is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs ...
of the deposit. In turn, the shape of a diatom is determined by its species.
Many deposits throughout British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, for ...
, such as Red Lake Earth, are from the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
epoch and contain a species of diatom known as ''Melosira granulata''. These diatoms are approximately 12 to 13 million years old and have a small globular shape. A deposit containing diatoms from this epoch can provide certain benefits over others. For example, diatoms from the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', ...
epoch (approximately 40 to 50 million years old) are not as effective in their ability to absorb fluids because as older diatoms recrystallize, their small pores become filled with silica.
Formation
Diatomite forms by the accumulation of theamorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek language, Gr ...
silica (opal
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silica (SiO2·''n''H2O); its water content may range from 3 to 21% by weight, but is usually between 6 and 10%. Due to its amorphous property, it is classified as a mineraloid, unlike crystalline form ...
, ) remains of dead diatoms (microscopic single-celled algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
) in lake sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand a ...
or marine sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mai ...
s. The fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
remains consist of a pair of symmetrical shells or frustule
A frustule is the hard and porous cell wall or external layer of diatoms. The frustule is composed almost purely of silica, made from silicic acid, and is coated with a layer of organic substance, which was referred to in the early literature on ...
s. Marine diatomites are found in association with a wide variety of other rock types but lacustrine diatomites are almost always associated with volcanic rock. Diatomaceous chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a ...
consists of diatomite that has been cemented with silica.
Diatoms are able to extract silica from water that is less than 1% saturated in amorphous silica (saturation index (SI): -2). Their frustules remain undissolved because they are surrounded by an organic matrix. Clay minerals may also precipitate on the frustules and protect them from dissolution in sea water. When the diatom dies, the frustule is stripped of its organic layer and exposed to sea water. As a result, only 1% to 10% of frustules survive long enough to be buried under sediments and some of this is dissolved within the sediments. Only an estimated 0.05% to 0.15% of the original amount of silica produced by diatoms is preserved in the sedimentary record.
Discovery
In 1836 or 1837, German peasant Peter Kasten discovered diatomaceous earth (German: ''Kieselgur'') when sinking a well on the northern slopes of the Haußelberg hill, in theLüneburg Heath
Lüneburg Heath (german: Lüneburger Heide) is a large area of heath, geest, and woodland in the northeastern part of the state of Lower Saxony in northern Germany. It forms part of the hinterland for the cities of Hamburg, Hanover and Bremen ...
in North Germany
Northern Germany (german: link=no, Norddeutschland) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony an ...
.
The extraction site on the Lüneburg Heath was 1863–1994 Neuohe, while the storage sites were:
The deposits are up to thick and are all of freshwater diatomaceous earth.
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, almost the entire worldwide production of diatomaceous earth was from this region.
Other deposits
In Poland diatomaceous earth deposits are found in Jawornik, and are composed mostly of diatomaceous skeletons (frustules) In Germany, diatomaceous earth was also extracted at Altenschlirf on theVogelsberg
The is a large volcanic mountain range in the German Central Uplands in the state of Hesse, separated from the Rhön Mountains by the Fulda river valley.
Emerging approximately 19 million years ago, the Vogelsberg is Central Europe's largest ...
(Upper Hesse
The term Upper Hesse (german: Provinz Oberhessen) originally referred to the southern possessions of the Landgraviate of Hesse, which were initially geographically separated from the more northerly Lower Hesse by the .
Later, it became the name o ...
) and at Klieken
Klieken is a village and a former municipality in the district of Wittenberg, Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lo ...
(Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making i ...
).
There is a layer of diatomaceous earth more than thick in the nature reserve of Soos Soos or SOOS may refer to:
People Surname
* Frank Soos, American short story writer
* Ricky Soos, English retired middle-distance runner
* Rozalia Șooș, Romanian former handballer
Places
* Soos, Iran, a village in Qazvin Province, Iran
* Sooß, ...
in the Czech Republic.
Deposits on the Isle of Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated b ...
, off the west coast of Scotland, were mined until 1960.
In Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the ...
and in Clark County, Nevada
Clark County is located in the U.S. state of Nevada. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,265,461. Most of the county population resides in the Las Vegas Census County Divisions, which hold 1,771,945 people as of the 2010 Census, acros ...
, United States, there are deposits that are up to several hundred meters thick in places. Marine deposits have been worked in the Sisquoc Formation
The Sisquoc Formation is a sedimentary geologic unit widespread in Southern California, both on the coast and in mountains near the coast. Overlying the Monterey Formation, it is of upper Miocene and lower Pliocene age (from about 4 to 6 mil ...
in Santa Barbara County, California
Santa Barbara County, California, officially the County of Santa Barbara, is located in Southern California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 448,229. The county seat is Santa Barbara, and the largest city is Santa Maria.
Santa Barba ...
near Lompoc
Lompoc ( ; Chumash: ''Lum Poc'') is a city in Santa Barbara County, California. Located on the Central Coast, Lompoc has a population of 43,834 as of July 2021.
Lompoc has been inhabited for thousands of years by the Chumash people, who called ...
and along the Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most populous urban ...
coast
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in n ...
. This is the world's largest deposit of diatomite. Additional marine deposits have been worked in Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean t ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
, Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
and the MoClay of Denmark. Freshwater lake deposits occur in Nevada, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
and California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
. Lake deposits also occur in interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene i ...
lakes in the eastern United States, in Canada and in Europe in Germany, France, Denmark and the Czech Republic. The worldwide association of diatomite deposits and volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plat ...
deposits suggests that the availability of silica from volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, created during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer ...
may be necessary for thick diatomite deposits.
Diatomaceous earth is sometimes found on desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
surfaces. Research has shown that the erosion of diatomaceous earth in such areas (such as the Bodélé Depression
The Bodélé Depression (), located at the southern edge of the Sahara Desert in north central Africa, is the lowest point in Chad. It is 500 km long, 150 km wide and around 160 m deep. Its bottom lies about 155 meters above sea leve ...
in the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
) is one of the most important sources of climate-affecting dust in the atmosphere.
The siliceous frustule
A frustule is the hard and porous cell wall or external layer of diatoms. The frustule is composed almost purely of silica, made from silicic acid, and is coated with a layer of organic substance, which was referred to in the early literature on ...
s of diatom
A diatom ( Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising se ...
s accumulate in fresh and brackish wetlands and lakes. Some peats and mucks contain a sufficient abundance of frustules such that they can be mined. Most of Florida's diatomaceous earths have been found in the muck of wetlands or lakes. The American Diatomite Corporation, from 1935 to 1946, refined a maximum of 145 tons per year from their processing plant near Clermont, Florida
Clermont is a city in Lake County in central Florida, United States, about west of Orlando and southeast of Leesburg. The population was 43,021 in 2020. The city is residential in character and its economy is centered in retail trade, lodging, ...
. Muck from several locations in Lake County, Florida was dried and burned (calcined
Calcination refers to thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), gener ...
) to produce the diatomaceous earth. It was formerly extracted from Lake Mývatn
() is a shallow lake situated in an area of active volcanism in the north of Iceland, not far from Krafla volcano. It has a high amount of biological activity. The lake and the surrounding wetlands provides a habitat for a number of waterbirds, e ...
in Iceland.
The commercial deposits of diatomite are restricted to Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago.
The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start ...
or Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million year ...
periods. Older deposits from as early as the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
Period are known, but are of low quality.Cummins, Arthur B., ''Diatomite'', in ''Industrial Minerals and Rocks'', 3rd ed. 1960, American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers
The American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers (AIME) is a professional association for mining and metallurgy, with over 145,000 members. It was founded in 1871 by 22 mining engineers in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, Uni ...
, pp. 303–319
Diatomite deposits rich in fossils have been located in New Zealand, but mining of the Foulden Maar
Foulden Maar is a fossil site near Middlemarch in Otago, New Zealand. The fossils were deposited in the small deep crater lake of a maar formed by a volcano in the Miocene era, around 23 million years ago. The crater lake existed for a period of ...
deposits on an industrial scale, for conversion to animal feed, has drawn strong opposition.
Commercial form
Diatomaceous earth is available commercially in several formats: *granulated
Granulation is the process of forming grains or granules from a powdery or solid substance, producing a granular material. It is applied in several technological processes in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Typically, granulation invo ...
diatomaceous earth is a raw material simply crushed for convenient packaging
* milled or micronized diatomaceous earth is especially fine (10 μm to 50 μm) and used for insecticides.
* calcined
Calcination refers to thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), gener ...
diatomaceous earth is heat-treated and activated for filters.


Usages
Explosives
In 1866,Alfred Nobel
Alfred Bernhard Nobel ( , ; 21 October 1833 – 10 December 1896) was a Swedish chemist, engineer, inventor, businessman, and philanthropist. He is best known for having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prize, though he al ...
discovered that nitroglycerin
Nitroglycerin (NG), (alternative spelling of nitroglycerine) also known as trinitroglycerin (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating g ...
could be made much more stable if absorbed in diatomite (kieselguhr). This allowed a much safer transport and handling than pure nitroglycerin under the liquid form. Nobel patented this mixture as dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents (such as powdered shells or clay), and stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern Germany, and patented in 1867. It rapidl ...
in 1867; the mixture is also called guhr dynamite by reference to the German term kieselguhr.
Filtration
TheCelle
Celle () is a town and capital of the district of Celle, in Lower Saxony, Germany. The town is situated on the banks of the river Aller, a tributary of the Weser, and has a population of about 71,000. Celle is the southern gateway to the Lü ...
engineer, Wilhelm Berkefeld, recognized the ability of the diatomaceous earth to filter and developed tubular filters (known as filter candles) fired from diatomaceous earth. During the cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium '' Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting an ...
epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
in Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
in 1892, these Berkefeld filter
A Berkefeld filter is a water filter made of diatomaceous earth (''Kieselguhr''). It was invented in Germany in 1891, and by 1922 was being marketed in the United Kingdom by the Berkefeld Filter Co. Berkefeld was the name of the owner of the ...
s were used successfully.
One form of diatomaceous earth is used as a filter
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
medium, especially for swimming pools. It has a high porosity because it is composed of microscopically small, hollow particles. Diatomaceous earth (sometimes referred to by trademarked brand names such as Celite) is used in chemistry as a filtration aid, to increase flow rate, and filter very fine particles that would otherwise pass through or clog filter paper Filter paper is a semi-permeable paper barrier placed perpendicular to a liquid or air flow. It is used to separate fine solid particles from liquids or gases.
The raw materials are different Pulp (paper), paper pulps. The pulp may be made from soft ...
. It is also used to filter water, particularly in the drinking water treatment process and in fish tanks
An aquarium (plural: ''aquariums'' or ''aquaria'') is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aqu ...
, and other liquids, such as beer and wine. It can also filter syrups, sugar, and honey without removing or altering their color, taste, or nutritional properties.
Abrasive
The oldest use of diatomite is as a very mild abrasive and has been used intoothpaste
Toothpaste is a paste or gel dentifrice used with a toothbrush to clean and maintain the aesthetics and health of teeth. Toothpaste is used to promote oral hygiene: it is an abrasive that aids in removing dental plaque and food from the teeth, ...
, metal polishes, and some facial scrubs.
Pest control
Diatomite is of value as aninsecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed t ...
because of its abrasive and physico- sorptive properties. The fine powder adsorbs lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
s from the waxy outer layer of the exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
s of many species of insects; this layer acts as a barrier that resists the loss of water vapour from the insect's body. Damaging the layer increases the evaporation of water from their bodies, so that they dehydrate, often fatally.
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s die as a result of the water pressure deficiency, based on Fick's laws of diffusion
Fick's laws of diffusion describe diffusion and were derived by Adolf Fick in 1855. They can be used to solve for the diffusion coefficient, . Fick's first law can be used to derive his second law which in turn is identical to the diffusion equ ...
. This also works against gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda ().
This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. T ...
s and is commonly employed in gardening to defeat slug
Slug, or land slug, is a common name for any apparently shell-less terrestrial gastropod mollusc. The word ''slug'' is also often used as part of the common name of any gastropod mollusc that has no shell, a very reduced shell, or only a ...
s. However, since slugs inhabit humid environments, efficacy is very low. Diatomaceous earth is sometimes mixed with an attractant or other additives to increase its effectiveness.
The shape of the diatoms contained in a deposit has not been proven to affect their functionality when it comes to the adsorption of lipids; however, certain applications, such as that for slugs and snails, do work best when a particularly shaped diatom is used, suggesting that lipid adsorption is not the whole story. For example, in the case of slugs and snails, large, spiny diatoms work best to lacerate the epithelium of the mollusk. Diatom shells will work to some degree on the vast majority of animals that undergo ecdysis
Ecdysis is the moulting of the cuticle in many invertebrates of the clade Ecdysozoa. Since the cuticle of these animals typically forms a largely inelastic exoskeleton, it is shed during growth and a new, larger covering is formed. The remnan ...
in shedding cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
, such as arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s or nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant- parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a bro ...
s. It also may have other effects on lophotrochozoa
Lophotrochozoa (, "crest/wheel animals") is a clade of protostome animals within the Spiralia. The taxon was established as a monophyletic group based on molecular evidence. The clade includes animals like annelids, molluscs, bryozoans, bra ...
ns, such as mollusk
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is e ...
s or annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecol ...
s.
Medical-grade diatomite has been studied for its efficacy as a deworming
Deworming (sometimes known as worming, drenching or dehelmintization) is the giving of an anthelmintic drug (a wormer, dewormer, or drench) to a human or animals to rid them of helminths parasites, such as roundworm, flukes and tapeworm. Pur ...
agent in cattle; in both studies cited the groups being treated with diatomaceous earth did not fare any better than control groups. It is commonly used in lieu of boric acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolve ...
and can be used to help control and possibly eliminate bed bugs
Bed bugs are insects from the genus ''Cimex'' that feed on blood, usually at night. Their bites can result in a number of health impacts including skin rashes, psychological effects, and allergic symptoms. Bed bug bites may lead to skin changes ...
, house dust mite, cockroach
Cockroaches (or roaches) are a paraphyletic group of insects belonging to Blattodea, containing all members of the group except termites. About 30 cockroach species out of 4,600 are associated with human habitats. Some species are well-known ...
, ant
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of ...
, and flea
Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about long, ...
infestations.
Diatomaceous earth is widely applied for insect control in grain storage.
In order to be effective as an insecticide, diatomaceous earth must be uncalcinated (i.e., it must not be heat-treated prior to application) and have a mean particle size below about 12 μm (i.e., food grade— see below).
Although considered to be relatively low-risk, pesticides containing diatomaceous earth are not exempt from regulation in the United States under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act
The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) is a United States federal law that set up the basic U.S. system of pesticide regulation to protect applicators, consumers, and the environment. It is administered and regulated by th ...
and must be registered with the Environmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale ...
.
Thermal
Its thermal properties enable it to be used as the barrier material in some fire-resistant safes. It is also used in evacuated powder insulation for use with cryogenics. Diatomaceous earth powder is inserted into the vacuum space to aid in the effectiveness of vacuum insulation. It was used in the classicalAGA cooker
The AGA cooker oven is a Swedish oven and cooker. Invented and initially produced in Sweden, since 1957 all production has been located in the UK.
History
Originally developed to burn coal or anthracite, the Aga cooker was invented in 1922 by ...
s as a thermal heat barrier.
Catalyst support
Diatomaceous earth also finds some use as asupport
Support may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Supporting character
Business and finance
* Support (technical analysis)
* Child support
* Customer support
* Income Support
Construction
* Support (structure), or lateral support, a ...
for catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
s, generally serving to maximize a catalyst's surface area
The surface area of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the definition of ...
and activity. For example, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
can be supported on the material—the combination is called Ni–Kieselguhr—to improve its activity as a hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic ...
catalyst.
Agriculture
Natural freshwater diatomaceous earth is used in agriculture for grain storage as ananticaking agent
An anticaking agent is an additive placed in powdered or granulated materials, such as table salt or confectioneries, to prevent the formation of lumps (caking) and for easing packaging, transport, flowability, and consumption. Caking mechanisms ...
, as well as an insecticide. It is approved by the Food and Drug Administration as a feed additive to prevent caking.
Some believe it may be used as a natural anthelmintic
Anthelmintics or antihelminthics are a group of antiparasitic drugs that expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them and without causing significant damage to the host. They may ...
(dewormer), although studies have not shown it to be effective. Some farmers add it to their livestock and poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, qu ...
feed to prevent the caking of feed. "Food-Grade Diatomaceous Earth" is widely available in agricultural feed supply stores.
Freshwater diatomite can be used as a growing medium in hydroponic
Hydroponics is a type of horticulture and a subset of hydroculture which involves growing plants, usually crops or medicinal plants, without soil, by using water-based mineral nutrient solutions in aqueous solvents. Terrestrial or aquatic plant ...
gardens.
It is also used as a growing medium in potted plants, particularly as bonsai
Bonsai ( ja, 盆栽, , tray planting, ) is the Japanese art of growing and training miniature trees in pots, developed from the traditional Chinese art form of '' penjing''. Unlike ''penjing'', which utilizes traditional techniques to produc ...
soil. Bonsai enthusiasts use it as a soil additive, or pot a bonsai tree in 100% diatomaceous earth. In vegetable gardening it is sometimes used as a soil conditioner
A soil conditioner is a product which is added to soil to improve the soil’s physical qualities, usually its fertility (ability to provide nutrition for plants) and sometimes its mechanics. In general usage, the term "soil conditioner" is often ...
, because like perlite
Perlite is an amorphous volcanic glass that has a relatively high water content, typically formed by the hydration of obsidian. It occurs naturally and has the unusual property of greatly expanding when heated sufficiently. It is an industrial ...
, vermiculite
Vermiculite is a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral which undergoes significant expansion when heated. Exfoliation occurs when the mineral is heated sufficiently, and commercial furnaces can routinely produce this effect. Vermiculite forms by the we ...
, and expanded clay, it retains water and nutrients, while draining fast and freely, allowing high oxygen circulation within the growing medium.
Marker in livestock nutrition experiments
Natural dried, not calcinated diatomaceous earth is regularly used in livestock nutrition research as a source of acid-insoluble ash (AIA), which is used as an indigestible marker. By measuring the content of AIA relative to nutrients in test diets and feces or digesta sampled from the terminal ileum (last third of the small intestine) the percentage of that nutrient digested can be calculated using the following equation: where: Natural freshwater diatomaceous earth is preferred by many researchers over chromic oxide, which has been widely used for the same purpose, the latter being a known carcinogen and, therefore, a potential hazard to research personnel.Construction
Spent diatomaceous earth from thebrewing
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains, the most popular of which is barley) in water and fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with yeast. It may be done in a brewery by a commercial brewer ...
process can be added to ceramic mass for the production of red bricks with higher open porosity.
Diatomaceous earth is considered a very prominent inorganic non-metallic material that can be utilized for the production of various ceramics, including production of porous ceramics under low temperature hydrothermal technology.
Specific varieties
* Tripolite is the variety found inTripoli, Libya
Tripoli (; ar, طرابلس الغرب, translit= Ṭarābulus al-Gharb , translation=Western Tripoli) is the capital and largest city of Libya, with a population of about 1.1 million people in 2019. It is located in the northwest of Libya o ...
.
* Bann clay is the variety found in the Lower Bann valley in Northern Ireland.
* ''Moler'' ( mo-clay) is the variety found in northwestern Denmark, especially on the islands of Fur and Mors.
* ''Freshwater-derived food grade'' diatomaceous earth is the type used in United States agriculture for grain storage, as feed supplement, and as an insecticide. It is produced uncalcinated, has a very fine particle size, and is very low in crystal silica (<2%).
* ''Salt-water-derived pool / beer / wine filter grade'' is not suitable for human consumption or effective as an insecticide. Usually calcinated before being sold to remove impurities and undesirable volatile contents, it is composed of larger particles than the freshwater version and has a high crystalline silica content (>60%).
Microbial degradation
Certain species of bacteria in oceans and lakes can accelerate the rate of dissolution of silica in dead and living diatoms by usinghydrolytic
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis i ...
enzymes to break down the organic algal material.
Climatologic importance
The Earth'sclimate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
is affected by dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ...
in the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A ...
, so locating major sources of atmospheric dust is important for climatology
Climatology (from Greek , ''klima'', "place, zone"; and , '' -logia'') or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. This modern field of stu ...
. Recent research indicates that surface deposits of diatomaceous earth play an important role. Research shows that significant dust comes from the Bodélé Depression
The Bodélé Depression (), located at the southern edge of the Sahara Desert in north central Africa, is the lowest point in Chad. It is 500 km long, 150 km wide and around 160 m deep. Its bottom lies about 155 meters above sea leve ...
in Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic ...
, where storms push diatomite gravel over dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, f ...
s, generating dust by abrasion.
Safety considerations
Inhalation of ''crystalline'' silica is harmful to the lungs, causingsilicosis
Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust. It is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs. It is a type of pneumoconiosis. Silic ...
. ''Amorphous'' silica is considered to have low toxicity, but prolonged inhalation causes changes to the lungs. Diatomaceous earth is mostly amorphous silica but contains some crystalline silica, especially in the saltwater forms. In a 1978 study of workers, those exposed to natural diatomaceous earth for over five years had no significant lung changes while 40% of those exposed to the calcined form had developed pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis is the general term for a class of interstitial lung disease where inhalation of dust ( for example, ash dust, lead particles, pollen grains etc) has caused interstitial fibrosis. The three most common types are asbestosis, silico ...
. Today's common diatomaceous earth formulations are safer to use, as they are predominantly made up of amorphous silica and contain little or no crystalline silica.
The crystalline silica content of diatomaceous earth is regulated in the United States by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration'' (OSHA ) is a large regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. Congress established the agen ...
(OSHA) and there are guidelines from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the C ...
that set maximum amounts allowable in the product (1%) and in the air near the breathing zone of workers, with a recommended exposure limit
A recommended exposure limit (REL) is an occupational exposure limit that has been recommended by the United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. The REL is a level that NIOSH believes would be protective of worker safet ...
at 6 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday. OSHA has set a permissible exposure limit
The permissible exposure limit (PEL or OSHA PEL) is a legal limit in the United States for exposure of an employee to a chemical substance or physical agent such as high level noise. Permissible exposure limits are established by the Occupationa ...
for diatomaceous earth as 20 mppcf (80 mg/m3/%SiO2). At levels of 3,000 mg/m3, diatomaceous earth is immediately dangerous to life and health.
In the 1930s, long-term occupational exposure among workers in the cristobalite diatomaceous earth industry who were exposed to high levels of airborne crystalline silica over decades were found to have an increased risk of silicosis
Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust. It is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs. It is a type of pneumoconiosis. Silic ...
.
Today, workers are required to use respiratory-protection measures when concentrations of silica exceed allowable levels.
Diatomite produced for pool filters is treated with high heat (calcination
Calcination refers to thermal treatment of a solid chemical compound (e.g. mixed carbonate ores) whereby the compound is raised to high temperature without melting under restricted supply of ambient oxygen (i.e. gaseous O2 fraction of air), gen ...
) and a fluxing agent (soda ash
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions ...
), causing the formerly harmless amorphous silicon dioxide to assume its crystalline form.
See also
* * * * * * *References
Occupational exposure to crystalline silica and autoimmune disease.
External links
*Diatomite: Statistics and Information – USGS
Citat: "...A diatomaceous earth consisting of opaline silica..."
{{DEFAULTSORT:Diatomaceous Earth Sedimentary rocks Inorganic insecticides Swimming pools Water treatment Soil Soil improvers Fodder Microfossils Biomineralization Industrial minerals Sustainable agriculture