Terrorism by year on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war against non-combatants (mostly civilians and neutral country, neutral military personnel). The terms "terrorist" and "terrorism" originated during the French Revolution of the late 18th century but became widely used internationally and gained worldwide attention in the 1970s during The Troubles, the Troubles in Northern Ireland, the Basque conflict, and the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. The increased use of suicide attacks from the 1980s onwards was typified by the 2001 September 11 attacks in the United States.
There are various different definitions of terrorism, with no universal agreement about it. Terrorism is a Loaded language, charged term. It is often used with the connotation of something that is "morally wrong". Governments and non-state groups use the term to abuse or denounce opposing groups. Varied political organizations have been accused of using terrorism to achieve their objectives. These include Left-wing terrorism, left-wing and Right-wing terrorism, right-wing political organizations, Nationalist terrorism, nationalist groups, Religious terrorism, religious groups, Revolutionary terror, revolutionaries and State terrorism, ruling governments. Anti-terrorism legislation, Legislation declaring terrorism a crime has been adopted in many states. When terrorism is perpetrated by nation states, it is not considered terrorism by the state conducting it, making legality a largely grey-area issue. There is no consensus as to whether terrorism should be regarded as a war crime.
The Global Terrorism Database, maintained by the University of Maryland, College Park, has recorded more than 61,000 incidents of non-state terrorism, resulting in at least 140,000 deaths, between 2000 and 2014.
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war against non-combatants (mostly civilians and neutral country, neutral military personnel). The terms "terrorist" and "terrorism" originated during the French Revolution of the late 18th century but became widely used internationally and gained worldwide attention in the 1970s during The Troubles, the Troubles in Northern Ireland, the Basque conflict, and the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. The increased use of suicide attacks from the 1980s onwards was typified by the 2001 September 11 attacks in the United States.
There are various different definitions of terrorism, with no universal agreement about it. Terrorism is a Loaded language, charged term. It is often used with the connotation of something that is "morally wrong". Governments and non-state groups use the term to abuse or denounce opposing groups. Varied political organizations have been accused of using terrorism to achieve their objectives. These include Left-wing terrorism, left-wing and Right-wing terrorism, right-wing political organizations, Nationalist terrorism, nationalist groups, Religious terrorism, religious groups, Revolutionary terror, revolutionaries and State terrorism, ruling governments. Anti-terrorism legislation, Legislation declaring terrorism a crime has been adopted in many states. When terrorism is perpetrated by nation states, it is not considered terrorism by the state conducting it, making legality a largely grey-area issue. There is no consensus as to whether terrorism should be regarded as a war crime.
The Global Terrorism Database, maintained by the University of Maryland, College Park, has recorded more than 61,000 incidents of non-state terrorism, resulting in at least 140,000 deaths, between 2000 and 2014.
 The term ''terroriste'', meaning "terrorist", is first used in 1794 by the French philosopher François-Noël Babeuf, who denounces Maximilien Robespierres Jacobin regime as a dictatorship. In the years leading up to what became known as the Reign of Terror, the Brunswick Manifesto threatened Paris with an "exemplary, never to be forgotten vengeance: the city would be subjected to military punishment and total destruction" if the royal family was harmed, but this only increased the Revolution's will to abolish the monarchy. Some writers attitudes about French Revolution grew less favorable after the French monarchy was abolished in 1792. During the Reign of Terror, which began in July 1793 and lasted thirteen months, Paris was governed by the Committee of Public Safety who oversaw a regime of mass executions and public purges.
Prior to the French Revolution, ancient philosophers wrote about tyrannicide, as tyranny was seen as the greatest political threat to Greco-Roman civilization. Medieval philosophy, Medieval philosophers were similarly occupied with the concept of tyranny, though the analysis of some theologians like Thomas Aquinas drew a distinction between usurpers, who could be killed by anyone, and legitimate rulers who abused their power—the latter, in Aquinas' view, could only be punished by a public authority. John of Salisbury was the first medieval Christian scholar to defend tyrannicide.
The term ''terroriste'', meaning "terrorist", is first used in 1794 by the French philosopher François-Noël Babeuf, who denounces Maximilien Robespierres Jacobin regime as a dictatorship. In the years leading up to what became known as the Reign of Terror, the Brunswick Manifesto threatened Paris with an "exemplary, never to be forgotten vengeance: the city would be subjected to military punishment and total destruction" if the royal family was harmed, but this only increased the Revolution's will to abolish the monarchy. Some writers attitudes about French Revolution grew less favorable after the French monarchy was abolished in 1792. During the Reign of Terror, which began in July 1793 and lasted thirteen months, Paris was governed by the Committee of Public Safety who oversaw a regime of mass executions and public purges.
Prior to the French Revolution, ancient philosophers wrote about tyrannicide, as tyranny was seen as the greatest political threat to Greco-Roman civilization. Medieval philosophy, Medieval philosophers were similarly occupied with the concept of tyranny, though the analysis of some theologians like Thomas Aquinas drew a distinction between usurpers, who could be killed by anyone, and legitimate rulers who abused their power—the latter, in Aquinas' view, could only be punished by a public authority. John of Salisbury was the first medieval Christian scholar to defend tyrannicide.
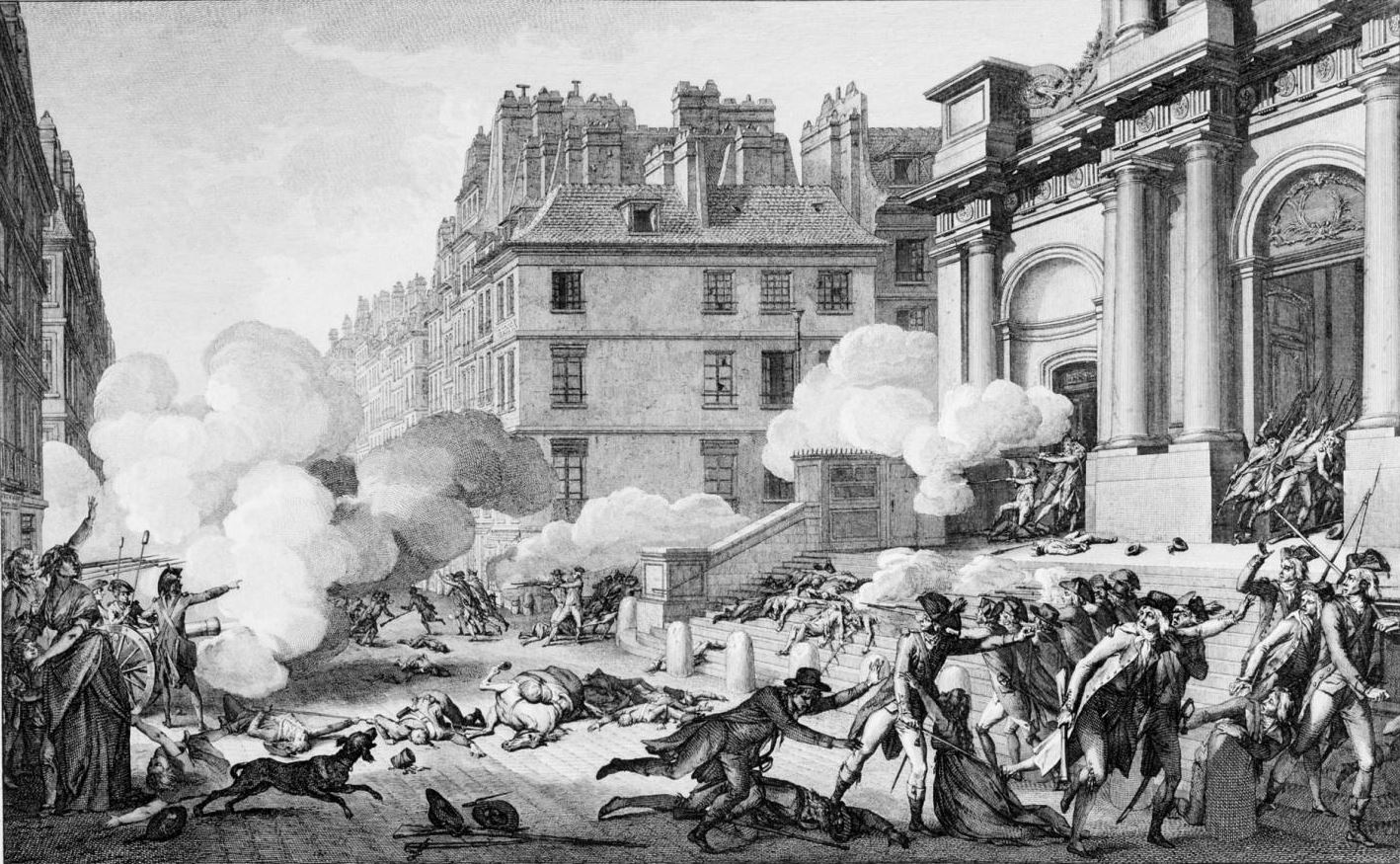 Most scholars today trace the origins of the modern tactic of terrorism to the Jewish Sicarii Zealots who attacked Romans and Jews in 1st-century Palestine (region), Palestine. They follow its development from the Persian Order of Assassins through to 19th-century anarchists. The "Reign of Terror" is usually regarded as an issue of etymology. The term terrorism has generally been used to describe violence by non-state actors rather than government violence since the 19th-century Anarchism in France, Anarchist Movement.
In December 1795, Edmund Burke used the word "Terrorists" in a description of the new French Directory, French government called 'Directory':
Most scholars today trace the origins of the modern tactic of terrorism to the Jewish Sicarii Zealots who attacked Romans and Jews in 1st-century Palestine (region), Palestine. They follow its development from the Persian Order of Assassins through to 19th-century anarchists. The "Reign of Terror" is usually regarded as an issue of etymology. The term terrorism has generally been used to describe violence by non-state actors rather than government violence since the 19th-century Anarchism in France, Anarchist Movement.
In December 1795, Edmund Burke used the word "Terrorists" in a description of the new French Directory, French government called 'Directory':

 In 2006 it was estimated that there were over 109 different definitions of terrorism.Arie W. Kruglanski and Shira Fishman ''Current Directions in Psychological Science'' Vol. 15, No. 1 (Feb. 2006), pp. 45–48 American political philosopher Michael Walzer in 2002 wrote: "Terrorism is the deliberate killing of innocent people, at random, to spread fear through a whole population and force the hand of its political leaders". Bruce Hoffman, an American scholar, has noted that it is not only individual agencies within the same governmental apparatus that cannot agree on a single definition of terrorism. Experts and other long-established scholars in the field are equally incapable of reaching a consensus.
C. A. J. Coady has written that the question of how to define terrorism is "irresolvable" because "its natural home is in polemical, ideological and propagandist contexts".
Experts disagree about "whether terrorism is wrong by definition or just wrong as a matter of fact; they disagree about whether terrorism should be defined in terms of its aims, or its methods, or both, or neither; they disagree about whether states can perpetrate terrorism; they even disagree about the importance or otherwise of ''terror'' for a definition of ''terrorism''."
In 2006 it was estimated that there were over 109 different definitions of terrorism.Arie W. Kruglanski and Shira Fishman ''Current Directions in Psychological Science'' Vol. 15, No. 1 (Feb. 2006), pp. 45–48 American political philosopher Michael Walzer in 2002 wrote: "Terrorism is the deliberate killing of innocent people, at random, to spread fear through a whole population and force the hand of its political leaders". Bruce Hoffman, an American scholar, has noted that it is not only individual agencies within the same governmental apparatus that cannot agree on a single definition of terrorism. Experts and other long-established scholars in the field are equally incapable of reaching a consensus.
C. A. J. Coady has written that the question of how to define terrorism is "irresolvable" because "its natural home is in polemical, ideological and propagandist contexts".
Experts disagree about "whether terrorism is wrong by definition or just wrong as a matter of fact; they disagree about whether terrorism should be defined in terms of its aims, or its methods, or both, or neither; they disagree about whether states can perpetrate terrorism; they even disagree about the importance or otherwise of ''terror'' for a definition of ''terrorism''."
 During the World War II, Second World War, the Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army were allied with the British, but during the Malayan Emergency, members of its successor organisation (the Malayan National Liberation Army) started campaigns against them, and were branded "terrorists" as a result. More recently, Ronald Reagan and others in the American administration frequently called the Afghan Mujahideen, mujaheddin "freedom fighters" during the Soviet–Afghan War, however twenty years later, when a new generation of Afghan men (militant groups like the Taliban and allies) were fighting against what they perceive to be a regime installed by foreign powers, their attacks were labelled terrorism by George W. Bush.
Groups accused of terrorism understandably prefer terms reflecting legitimate military or ideological action.Terrorism: concepts, causes, and conflict resolution
During the World War II, Second World War, the Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army were allied with the British, but during the Malayan Emergency, members of its successor organisation (the Malayan National Liberation Army) started campaigns against them, and were branded "terrorists" as a result. More recently, Ronald Reagan and others in the American administration frequently called the Afghan Mujahideen, mujaheddin "freedom fighters" during the Soviet–Afghan War, however twenty years later, when a new generation of Afghan men (militant groups like the Taliban and allies) were fighting against what they perceive to be a regime installed by foreign powers, their attacks were labelled terrorism by George W. Bush.
Groups accused of terrorism understandably prefer terms reflecting legitimate military or ideological action.Terrorism: concepts, causes, and conflict resolution
George Mason University Institute for Conflict Analysis and Resolution, Printed by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, Fort Belvoir, Virginia, January 2003. Leading terrorism researcher Professor Martin Rudner, director of the Canadian Centre of Intelligence and Security Studies at Ottawa's Carleton University, defines "terrorist acts" as unlawful attacks for political or other ideological goals, and said: Some groups, when involved in a "liberation" struggle, have been called "terrorists" by the Western governments or media. Later, these same persons, as leaders of the liberated nations, are called "statesmen" by similar organizations. Two examples of this phenomenon are the Nobel Peace Prize laureates Menachem Begin and Nelson Mandela. WikiLeaks editor Julian Assange has been called a "terrorist" by Sarah Palin and Joe Biden. Sometimes, states that are close allies, for reasons of history, culture and politics, can disagree over whether members of a certain organization are terrorists. For instance, some branches of the United States government refused to label members of the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) as terrorists while the IRA was using methods against one of the United States' closest allies (the United Kingdom) that the UK branded as terrorism. This was highlighted by the ''Quinn v. Robinson'' case. Media outlets who wish to convey impartiality may limit their usage of "terrorist" and "terrorism" because they are loosely defined, potentially controversial in nature, and subjective terms. The 2020 Nashville bombing#Debate over "terrorism" as a term, 2020 Nashville bombing revived a debate over the use of the word "terrorism", with critics saying it is quickly applied to attacks by Muslims but reluctantly if at all used by white Christian men, such as the Nashville bomber.
 Depending on how broadly the term is defined, the roots and practice of terrorism can be traced at least to the 1st century AD. According to the contemporary Jewish-Roman historian Josephus, after the Zealotry rebellion against Roman rule in Judea, when some prominent Jewish collaborators with Roman rule were killed, Judas of Galilee formed a small and more extreme offshoot of the Zealots, the Sicarii Zealots, in 6 AD. They were a smaller and more radical offshoot of the Zealots which was active in Judaea Province at the beginning of the 1st century AD, and they can be considered early terrorists, although this is disputed. Their terror was directed against Jewish "collaborators", including temple priests, Sadducees, Herodian dynasty, Herodians, and other wealthy elites.
The term "terrorism" itself was originally used to describe the actions of the Jacobin Club during the "Reign of Terror" in the French Revolution. "Terror is nothing other than justice, prompt, severe, inflexible", said Jacobin leader Maximilien Robespierre. In 1795, Edmund Burke denounced the Jacobins for letting "thousands of those hell-hounds called Terrorists ... loose on the people" of France.
In January 1858, Italian patriot Felice Orsini threw three bombs in an attempt to assassinate French Emperor Napoleon III.Crenshaw, Martha, ''Terrorism in Context'', p. 38. Eight bystanders were killed and 142 injured. The incident played a crucial role as an inspiration for the development of the early terrorist groups.
Arguably the first organization to use modern terrorist techniques was the Irish Republican Brotherhood, founded in 1858 as a revolutionary Irish nationalist group that carried out attacks in England. The group initiated the Fenian dynamite campaign in 1881, one of the first modern terror campaigns. Instead of earlier forms of terrorism based on political assassination, this campaign used timed explosives with the express aim of sowing fear in the very heart of Great Britain, metropolitan Britain, in order to achieve political gains.
Another early terrorist-type group was Narodnaya Volya (organization), Narodnaya Volya, founded in Russia in 1878 as a revolutionary anarchist group inspired by Sergei Nechayev and "propaganda by the deed" theorist Carlo Pisacane. The group developed ideas—such as targeted killing of the 'leaders of oppression'—that were to become the hallmark of subsequent violence by small non-state groups, and they were convinced that the developing technologies of the age—such as the invention of dynamite, which they were the first anarchist group to make widespread use of—enabled them to strike directly and with discrimination.
David C. Rapoport, David Rapoport refers to four major waves of global terrorism: "the Anarchist, the Anti-Colonial, the New Left, and the Religious. The first three have been completed and lasted around 40 years; the fourth is now in its third decade."
Depending on how broadly the term is defined, the roots and practice of terrorism can be traced at least to the 1st century AD. According to the contemporary Jewish-Roman historian Josephus, after the Zealotry rebellion against Roman rule in Judea, when some prominent Jewish collaborators with Roman rule were killed, Judas of Galilee formed a small and more extreme offshoot of the Zealots, the Sicarii Zealots, in 6 AD. They were a smaller and more radical offshoot of the Zealots which was active in Judaea Province at the beginning of the 1st century AD, and they can be considered early terrorists, although this is disputed. Their terror was directed against Jewish "collaborators", including temple priests, Sadducees, Herodian dynasty, Herodians, and other wealthy elites.
The term "terrorism" itself was originally used to describe the actions of the Jacobin Club during the "Reign of Terror" in the French Revolution. "Terror is nothing other than justice, prompt, severe, inflexible", said Jacobin leader Maximilien Robespierre. In 1795, Edmund Burke denounced the Jacobins for letting "thousands of those hell-hounds called Terrorists ... loose on the people" of France.
In January 1858, Italian patriot Felice Orsini threw three bombs in an attempt to assassinate French Emperor Napoleon III.Crenshaw, Martha, ''Terrorism in Context'', p. 38. Eight bystanders were killed and 142 injured. The incident played a crucial role as an inspiration for the development of the early terrorist groups.
Arguably the first organization to use modern terrorist techniques was the Irish Republican Brotherhood, founded in 1858 as a revolutionary Irish nationalist group that carried out attacks in England. The group initiated the Fenian dynamite campaign in 1881, one of the first modern terror campaigns. Instead of earlier forms of terrorism based on political assassination, this campaign used timed explosives with the express aim of sowing fear in the very heart of Great Britain, metropolitan Britain, in order to achieve political gains.
Another early terrorist-type group was Narodnaya Volya (organization), Narodnaya Volya, founded in Russia in 1878 as a revolutionary anarchist group inspired by Sergei Nechayev and "propaganda by the deed" theorist Carlo Pisacane. The group developed ideas—such as targeted killing of the 'leaders of oppression'—that were to become the hallmark of subsequent violence by small non-state groups, and they were convinced that the developing technologies of the age—such as the invention of dynamite, which they were the first anarchist group to make widespread use of—enabled them to strike directly and with discrimination.
David C. Rapoport, David Rapoport refers to four major waves of global terrorism: "the Anarchist, the Anti-Colonial, the New Left, and the Religious. The first three have been completed and lasted around 40 years; the fourth is now in its third decade."
File:Terrorist incidents map of the world 1970-2015.svg, Terrorist incidents, 1970–2015. A total of 157,520 incidents are plotted. : 1970–1999, : 2000–2015
File:The number of terrorist attacks 2000-2014 (Top 10 Countries).png, Top 10 Countries (2000–2014)
File:Terrorist incidents worldwide.svg, Worldwide non-state terrorist incidents 1970–2017
File:Share who are worried about vs. share of deaths from terrorism, OWID.svg, Share who are worried about vs. share of deaths from terrorism
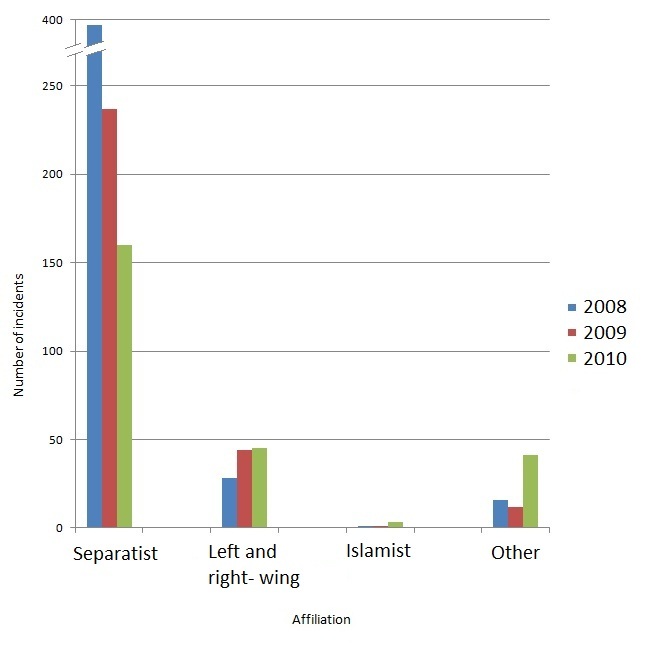
 In early 1975, the National Institute of Justice, Law Enforcement Assistant Administration in the United States formed the National Advisory Committee on Criminal Justice Standards and Goals. One of the five volumes that the committee wrote was titled ''Disorders and Terrorism'', produced by the Task Force on Disorders and Terrorism under the direction of H. H. A. Cooper, Director of the Task Force staff.
The Task Force defines terrorism as "a tactic or technique by means of which a violent act or the threat thereof is used for the prime purpose of creating overwhelming fear for coercive purposes". It classified disorders and terrorism into six categories:
* Civil disorder – A form of collective violence interfering with the peace, security, and normal functioning of the community.
* Political terrorism – Violence, Violent criminal behaviour designed primarily to generate fear in the community, or substantial segment of it, for political purposes.
* Non-Political terrorism – Terrorism that is not aimed at political purposes but which exhibits "conscious design to create and maintain a high degree of fear for coercion, coercive purposes, but the end is individual or collective gain rather than the achievement of a political objective".
* Anonymous terrorism – In the two decades prior to 2016–19, "fewer than half" of all terrorist attacks were either "claimed by their perpetrators or convincingly attributed by governments to specific terrorist groups". A number of theories have been advanced as to why this has happened.
* Quasi-terrorism – The activities incidental to the commission of crimes of violence that are similar in form and method to genuine terrorism but which nevertheless lack its essential ingredient. It is not the main purpose of the quasi-terrorists to induce terror in the immediate victim as in the case of genuine terrorism, but the quasi-terrorist uses the modalities and techniques of the genuine terrorist and produces similar consequences and reaction. For example, the fleeing felony, felon who takes hostages is a quasi-terrorist, whose methods are similar to those of the genuine terrorist but whose purposes are quite different.
* Limited political terrorism – Genuine political terrorism is characterized by a revolutionary approach; limited political terrorism refers to "acts of terrorism which are committed for ideology, ideological or political motives but which are not part of a concerted campaign to capture control of the Sovereign state, state".
* Official or state terrorism – "referring to nations whose rule is based upon fear and oppression that reach similar to terrorism or such proportions". It may be referred to as Structural Terrorism defined broadly as terrorist acts carried out by governments in pursuit of political objectives, often as part of their foreign policy.
Other sources have defined the typology of terrorism in different ways, for example, broadly classifying it into domestic terrorism and international terrorism, or using categories such as vigilante terrorism or insurgent terrorism. One way the typology of terrorism may be defined:
* Political terrorism
**Sub-state terrorism
***Revolutionary terrorism, Social revolutionary terrorism
***Nationalist terrorism, Nationalist-separatist terrorism
***Religious terrorism, Religious extremist terrorism
**** Religious fundamentalist Terrorism
**** New religions terrorism
*** Right-wing terrorism
*** Left-wing terrorism
**** Communist terrorism
** State-sponsored terrorism
** State terrorism, Regime or state terrorism
* Criminal terrorism
* Pathological terrorism
In early 1975, the National Institute of Justice, Law Enforcement Assistant Administration in the United States formed the National Advisory Committee on Criminal Justice Standards and Goals. One of the five volumes that the committee wrote was titled ''Disorders and Terrorism'', produced by the Task Force on Disorders and Terrorism under the direction of H. H. A. Cooper, Director of the Task Force staff.
The Task Force defines terrorism as "a tactic or technique by means of which a violent act or the threat thereof is used for the prime purpose of creating overwhelming fear for coercive purposes". It classified disorders and terrorism into six categories:
* Civil disorder – A form of collective violence interfering with the peace, security, and normal functioning of the community.
* Political terrorism – Violence, Violent criminal behaviour designed primarily to generate fear in the community, or substantial segment of it, for political purposes.
* Non-Political terrorism – Terrorism that is not aimed at political purposes but which exhibits "conscious design to create and maintain a high degree of fear for coercion, coercive purposes, but the end is individual or collective gain rather than the achievement of a political objective".
* Anonymous terrorism – In the two decades prior to 2016–19, "fewer than half" of all terrorist attacks were either "claimed by their perpetrators or convincingly attributed by governments to specific terrorist groups". A number of theories have been advanced as to why this has happened.
* Quasi-terrorism – The activities incidental to the commission of crimes of violence that are similar in form and method to genuine terrorism but which nevertheless lack its essential ingredient. It is not the main purpose of the quasi-terrorists to induce terror in the immediate victim as in the case of genuine terrorism, but the quasi-terrorist uses the modalities and techniques of the genuine terrorist and produces similar consequences and reaction. For example, the fleeing felony, felon who takes hostages is a quasi-terrorist, whose methods are similar to those of the genuine terrorist but whose purposes are quite different.
* Limited political terrorism – Genuine political terrorism is characterized by a revolutionary approach; limited political terrorism refers to "acts of terrorism which are committed for ideology, ideological or political motives but which are not part of a concerted campaign to capture control of the Sovereign state, state".
* Official or state terrorism – "referring to nations whose rule is based upon fear and oppression that reach similar to terrorism or such proportions". It may be referred to as Structural Terrorism defined broadly as terrorist acts carried out by governments in pursuit of political objectives, often as part of their foreign policy.
Other sources have defined the typology of terrorism in different ways, for example, broadly classifying it into domestic terrorism and international terrorism, or using categories such as vigilante terrorism or insurgent terrorism. One way the typology of terrorism may be defined:
* Political terrorism
**Sub-state terrorism
***Revolutionary terrorism, Social revolutionary terrorism
***Nationalist terrorism, Nationalist-separatist terrorism
***Religious terrorism, Religious extremist terrorism
**** Religious fundamentalist Terrorism
**** New religions terrorism
*** Right-wing terrorism
*** Left-wing terrorism
**** Communist terrorism
** State-sponsored terrorism
** State terrorism, Regime or state terrorism
* Criminal terrorism
* Pathological terrorism
audio interview summarizin
Special Report: The Psychology of Terrorism
/ref> Attacks on "collaborators" are used to intimidate people from cooperating with the state in order to undermine state control. This strategy was used in Ireland, in Kenya, in Algeria and in Cyprus during their independence struggles. Stated motives for the September 11 attacks included inspiring more fighters to join the cause of repelling the United States from Muslim countries with a successful high-profile attack. The attacks prompted some criticism from domestic and international observers regarding perceived injustices in U.S. foreign policy that provoked the attacks, but the larger practical effect was that the United States government declared a War on Terror that resulted in substantial military engagements in several Muslim-majority countries. Various commentators have inferred that al-Qaeda expected a military response, and welcomed it as a provocation that would result in more Muslims fight the United States. Some commentators believe that the resulting anger and suspicion directed toward innocent Muslims living in Western countries and the indignities inflicted upon them by security forces and the general public also contributes to radicalization of new recruits. Despite criticism that the Iraqi government had no involvement with the September 11 attacks, Bush declared the 2003 invasion of Iraq to be part of the War on Terror. The resulting backlash and instability enabled the rise of Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant and the temporary creation of an Islamic caliphate holding territory in Iraq and Syria, until ISIL lost its territory through military defeats. Attacks used to draw international attention to struggles that are otherwise unreported have included the Dawson's Field hijackings, Palestinian airplane hijackings in 1970 and the 1975 Dutch train hostage crisis.
 According to the Global Terrorism Index by the University of Maryland, College Park, religious extremism has overtaken Separatism, national separatism and become the main driver of terrorist attacks around the world. Since 9/11 there has been a five-fold increase in deaths from terrorist attacks. The majority of incidents over the past several years can be tied to groups with a religious agenda. Before 2000, it was nationalist separatist terrorist organizations such as the Provisional Irish Republican Army, IRA and Chechen rebels who were behind the most attacks. The number of incidents from nationalist separatist groups has remained relatively stable in the years since while religious extremism has grown. The prevalence of Islamist groups in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and Syria is the main driver behind these trends.
Five of the terrorist groups that have been most active since 2001 are Hamas, Boko Haram, al-Qaeda, the Taliban and Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIL. These groups have been most active in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and Syria. Eighty percent of all deaths from terrorism occurred in one of these five countries. In 2015 four Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist groups were responsible for 74% of all deaths from Islamic terrorism: Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIS, Boko Haram, the Taliban, and al-Qaeda, according to the Global Terrorism Index 2016. Since approximately 2000, these incidents have occurred on a global scale, affecting not only Muslim-majority countries, Muslim-majority states in Africa and Asia, but also states with non-Muslim majority such as Terrorism in the United States, United States, Terrorism in the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, Terrorism in France, France, Terrorism in Germany, Germany, Terrorism in Spain, Spain, Terrorist activity in Belgium, Belgium, Terrorism in Sweden, Sweden, Terrorism in Russia, Russia, Terrorism in Australia, Australia, Terrorism in Canada, Canada, Terrorism in Sri Lanka, Sri Lanka, Israel, Terrorism in China, China, Terrorism in India, India and Terrorism in the Philippines, Philippines. Such attacks have targeted both Muslims and non-Muslims, however the majority affect Muslims themselves.
Terrorism in Pakistan has become a great problem. From the summer of 2007 until late 2009, more than 1,500 people were killed in suicide attack, suicide and other attacks on civilians for reasons attributed to a number of causes—sectarian violence between Sunni and Shia Muslims; easy availability of guns and explosives; the existence of a "Kalashnikov rifle, Kalashnikov culture"; an influx of ideologically driven Muslims based AfPak, in or near Pakistan, who originated from various nations around the world and the subsequent war against the pro-Soviet Afghans in the 1980s which blew back into Pakistan; the presence of Islamist insurgent groups and forces such as the Taliban and Lashkar-e-Taiba. On July 2, 2013, in Lahore, 50 Muslim scholars of the Sunni Ittehad Council (SIC) issued a collective fatwa against suicide bombings, the killing of innocent people, bomb attacks, and targeted killings declaring them as Haraam or forbidden.
In 2015, the Southern Poverty Law Center released a report on terrorism in the United States. The report (titled ''The Age of the Wolf'') analyzed 62 incidents and found that, between 2009 and 2015, "more people have been killed in America by non-Islamic Domestic terrorism in the United States, domestic terrorists than Jihadism, jihadists." The "virulent racist and anti-semitic" ideology of the ultra-right wing Christian Identity movement is usually accompanied by anti-government sentiments.
According to the Global Terrorism Index by the University of Maryland, College Park, religious extremism has overtaken Separatism, national separatism and become the main driver of terrorist attacks around the world. Since 9/11 there has been a five-fold increase in deaths from terrorist attacks. The majority of incidents over the past several years can be tied to groups with a religious agenda. Before 2000, it was nationalist separatist terrorist organizations such as the Provisional Irish Republican Army, IRA and Chechen rebels who were behind the most attacks. The number of incidents from nationalist separatist groups has remained relatively stable in the years since while religious extremism has grown. The prevalence of Islamist groups in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and Syria is the main driver behind these trends.
Five of the terrorist groups that have been most active since 2001 are Hamas, Boko Haram, al-Qaeda, the Taliban and Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIL. These groups have been most active in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and Syria. Eighty percent of all deaths from terrorism occurred in one of these five countries. In 2015 four Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist groups were responsible for 74% of all deaths from Islamic terrorism: Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIS, Boko Haram, the Taliban, and al-Qaeda, according to the Global Terrorism Index 2016. Since approximately 2000, these incidents have occurred on a global scale, affecting not only Muslim-majority countries, Muslim-majority states in Africa and Asia, but also states with non-Muslim majority such as Terrorism in the United States, United States, Terrorism in the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, Terrorism in France, France, Terrorism in Germany, Germany, Terrorism in Spain, Spain, Terrorist activity in Belgium, Belgium, Terrorism in Sweden, Sweden, Terrorism in Russia, Russia, Terrorism in Australia, Australia, Terrorism in Canada, Canada, Terrorism in Sri Lanka, Sri Lanka, Israel, Terrorism in China, China, Terrorism in India, India and Terrorism in the Philippines, Philippines. Such attacks have targeted both Muslims and non-Muslims, however the majority affect Muslims themselves.
Terrorism in Pakistan has become a great problem. From the summer of 2007 until late 2009, more than 1,500 people were killed in suicide attack, suicide and other attacks on civilians for reasons attributed to a number of causes—sectarian violence between Sunni and Shia Muslims; easy availability of guns and explosives; the existence of a "Kalashnikov rifle, Kalashnikov culture"; an influx of ideologically driven Muslims based AfPak, in or near Pakistan, who originated from various nations around the world and the subsequent war against the pro-Soviet Afghans in the 1980s which blew back into Pakistan; the presence of Islamist insurgent groups and forces such as the Taliban and Lashkar-e-Taiba. On July 2, 2013, in Lahore, 50 Muslim scholars of the Sunni Ittehad Council (SIC) issued a collective fatwa against suicide bombings, the killing of innocent people, bomb attacks, and targeted killings declaring them as Haraam or forbidden.
In 2015, the Southern Poverty Law Center released a report on terrorism in the United States. The report (titled ''The Age of the Wolf'') analyzed 62 incidents and found that, between 2009 and 2015, "more people have been killed in America by non-Islamic Domestic terrorism in the United States, domestic terrorists than Jihadism, jihadists." The "virulent racist and anti-semitic" ideology of the ultra-right wing Christian Identity movement is usually accompanied by anti-government sentiments.
. Anti-Defamation League 2017. Adherents of Christian Identity are not connected with specific Christian denominations, and they believe that White people, whites of European descent can be traced back to the "Ten Lost Tribes, Lost Tribes of Israel" and many consider Jews to be the Satanic offspring of Adam and Eve, Eve and the Serpents in the Bible, Serpent. This group has committed hate crimes, bombings and other acts of terrorism. Its influence ranges from the Ku Klux Klan and neo-Nazi groups to the anti-government Militia organizations in the United States, militia and sovereign citizen movements. Christian Identity's origins can be traced back to British Israelism, Anglo-Israelism, which held the view that the British people were descendants of ancient Israelites. However, in the United States, the ideology started to become rife with Antisemitism, anti-Semitism, and eventually Christian Identity theology diverged from the Philo-Semitism, philo-semitic Anglo-Israelism, and developed what is known as the Serpent seed, "two seed" theory. According to the two-seed theory, the Jewish people are descended from Cain and the serpent (not from Shem). The white European seedline is descended from the "lost tribes" of Israel. They hold themselves to "God's laws", not to "man's laws", and they do not feel bound to a government that they consider run by Jews and the New World Order (conspiracy theory), New World Order. The Ku Klux Klan is widely denounced by Christian denominations. Israel has had problems with Jewish religious terrorism even before independence in 1948. During Mandate for Palestine, British mandate over Palestine, the Irgun were among the Zionist groups labelled as terrorist organisations by the British authorities and United Nations, for violent terror attacks against Britons and Arabs. Another extremist group, the Lehi (militant group), Lehi, openly declared its members as "terrorists". Historian William Cleveland stated many Jews justified any action, even terrorism, taken in the cause of the creation of a Jewish state. In 1995, Yigal Amir assassinated Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin. For Amir, killing Rabin was an exemplary act that symbolized the fight against an illegitimate government that was prepared to cede Jewish Holy Land to the Palestinians.
Israel has had problems with Jewish religious terrorism even before independence in 1948. During Mandate for Palestine, British mandate over Palestine, the Irgun were among the Zionist groups labelled as terrorist organisations by the British authorities and United Nations, for violent terror attacks against Britons and Arabs. Another extremist group, the Lehi (militant group), Lehi, openly declared its members as "terrorists". Historian William Cleveland stated many Jews justified any action, even terrorism, taken in the cause of the creation of a Jewish state. In 1995, Yigal Amir assassinated Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin. For Amir, killing Rabin was an exemplary act that symbolized the fight against an illegitimate government that was prepared to cede Jewish Holy Land to the Palestinians.
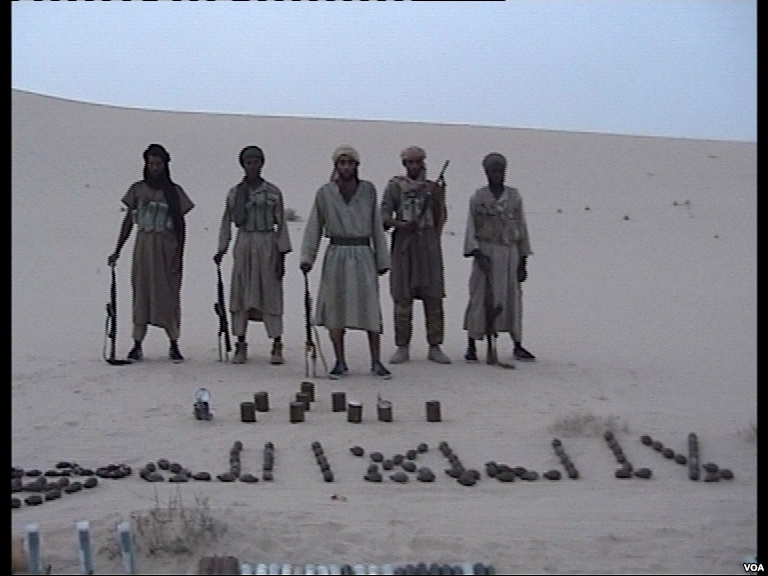 The perpetrators of acts of terrorism can be individuals, groups, or states. According to some definitions, clandestine or semi-clandestine state actors may carry out terrorist acts outside the framework of a state of war. The most common image of terrorism is that it is carried out by small and secretive Covert cell, cells, highly motivated to serve a particular cause and many of the most deadly operations in recent times, such as the September 11 attacks, the 7 July 2005 London bombings, London underground bombing, 2008 Mumbai attacks and the 2002 Bali bombing were planned and carried out by a close clique, composed of close friends, family members and other strong social networks. These groups benefited from the free flow of information and efficient telecommunications to succeed where others had failed.
Over the years, much research has been conducted to distill a terrorist profile to explain these individuals' actions through their psychology and socio-economic circumstances. Others, like Roderick Hindery, have sought to discern profiles in the propaganda tactics used by terrorists. Some security organizations designate these groups as ''violent non-state actors''. A 2007 study by economist Alan B. Krueger found that terrorists were less likely to come from an impoverished background (28 percent versus 33 percent) and more likely to have at least a high-school education (47 percent versus 38 percent). Another analysis found only 16 percent of terrorists came from impoverished families, versus 30 percent of male Palestinians, and over 60 percent had gone beyond high school, versus 15 percent of the populace.A study into the poverty-stricken conditions and whether terrorists are more likely to come from here,show that people who grew up in these situations tend to show aggression and frustration towards others. This theory is largely debated for the simple fact that just because one is frustrated,does not make them a potential terrorist.
To avoid detection, a terrorist will look, dress, and behave normally until executing the assigned mission. Some claim that attempts to profile terrorists based on personality, physical, or sociological traits are not useful. The physical and behavioral description of the terrorist could describe almost any normal person.Library of Congress
The perpetrators of acts of terrorism can be individuals, groups, or states. According to some definitions, clandestine or semi-clandestine state actors may carry out terrorist acts outside the framework of a state of war. The most common image of terrorism is that it is carried out by small and secretive Covert cell, cells, highly motivated to serve a particular cause and many of the most deadly operations in recent times, such as the September 11 attacks, the 7 July 2005 London bombings, London underground bombing, 2008 Mumbai attacks and the 2002 Bali bombing were planned and carried out by a close clique, composed of close friends, family members and other strong social networks. These groups benefited from the free flow of information and efficient telecommunications to succeed where others had failed.
Over the years, much research has been conducted to distill a terrorist profile to explain these individuals' actions through their psychology and socio-economic circumstances. Others, like Roderick Hindery, have sought to discern profiles in the propaganda tactics used by terrorists. Some security organizations designate these groups as ''violent non-state actors''. A 2007 study by economist Alan B. Krueger found that terrorists were less likely to come from an impoverished background (28 percent versus 33 percent) and more likely to have at least a high-school education (47 percent versus 38 percent). Another analysis found only 16 percent of terrorists came from impoverished families, versus 30 percent of male Palestinians, and over 60 percent had gone beyond high school, versus 15 percent of the populace.A study into the poverty-stricken conditions and whether terrorists are more likely to come from here,show that people who grew up in these situations tend to show aggression and frustration towards others. This theory is largely debated for the simple fact that just because one is frustrated,does not make them a potential terrorist.
To avoid detection, a terrorist will look, dress, and behave normally until executing the assigned mission. Some claim that attempts to profile terrorists based on personality, physical, or sociological traits are not useful. The physical and behavioral description of the terrorist could describe almost any normal person.Library of Congress
– Federal Research Division ''The Sociology and Psychology of Terrorism''. the majority of terrorist attacks are carried out by military age men, aged 16 to 40.
 Groups not part of the state apparatus of in opposition to the state are most commonly referred to as a "terrorist" in the media.
According to the Global Terrorism Database, the most active terrorist group in the period 1970 to 2010 was Shining Path (with 4,517 attacks), followed by Farabundo Marti National Liberation Front (FMLN), Provisional Irish Republican Army, Irish Republican Army (IRA), Basque Fatherland and Freedom (ETA), Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), Taliban, Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, New People's Army, National Liberation Army of Colombia (ELN), and Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK).
Groups not part of the state apparatus of in opposition to the state are most commonly referred to as a "terrorist" in the media.
According to the Global Terrorism Database, the most active terrorist group in the period 1970 to 2010 was Shining Path (with 4,517 attacks), followed by Farabundo Marti National Liberation Front (FMLN), Provisional Irish Republican Army, Irish Republican Army (IRA), Basque Fatherland and Freedom (ETA), Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), Taliban, Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, New People's Army, National Liberation Army of Colombia (ELN), and Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK).
 As with "terrorism" the concept of "state terrorism" is controversial. The Chairman of the United Nations Counter-Terrorism Committee has stated that the committee was conscious of 12 international conventions on the subject, and none of them referred to state terrorism, which was not an international legal concept. If states abused their power, they should be judged against international conventions dealing with war crimes, international human rights law, and international humanitarian law. Former United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan has said that it is "time to set aside debates on so-called 'state terrorism'. The Use of force in international law, use of force by states is already thoroughly regulated under international law". he made clear that, "regardless of the differences between governments on the question of the definition of terrorism, what is clear and what we can all agree on is that any deliberate attack on innocent civilians [or non-combatants], regardless of one's cause, is unacceptable and fits into the definition of terrorism."
State terrorism has been used to refer to terrorist acts committed by governmental agents or forces. This involves the use of state resources employed by a state's foreign policies, such as using its military to directly perform acts of terrorism. Professor of Political Science Michael Stohl cites the examples that include the German The Blitz, bombing of London, the Allies of World War II, Allied Bombing of Dresden in World War II, firebombing of Dresden, and the U.S. atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during World War II. He argues that "the use of terror tactics is common in international relations and the state has been and remains a more likely employer of terrorism within the international system than insurgents." He cites the Pre-emptive nuclear strike, first strike option as an example of the "terror of coercive diplomacy" as a form of this, which holds the world hostage with the implied threat of using nuclear weapons in "crisis management" and he argues that the institutionalized form of terrorism has occurred as a result of changes that took place following World War II. In this analysis, state terrorism exhibited as a form of foreign policy was shaped by the presence and use of Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction, and the legitimizing of such violent behavior led to an increasingly accepted form of this behavior by the state.
As with "terrorism" the concept of "state terrorism" is controversial. The Chairman of the United Nations Counter-Terrorism Committee has stated that the committee was conscious of 12 international conventions on the subject, and none of them referred to state terrorism, which was not an international legal concept. If states abused their power, they should be judged against international conventions dealing with war crimes, international human rights law, and international humanitarian law. Former United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan has said that it is "time to set aside debates on so-called 'state terrorism'. The Use of force in international law, use of force by states is already thoroughly regulated under international law". he made clear that, "regardless of the differences between governments on the question of the definition of terrorism, what is clear and what we can all agree on is that any deliberate attack on innocent civilians [or non-combatants], regardless of one's cause, is unacceptable and fits into the definition of terrorism."
State terrorism has been used to refer to terrorist acts committed by governmental agents or forces. This involves the use of state resources employed by a state's foreign policies, such as using its military to directly perform acts of terrorism. Professor of Political Science Michael Stohl cites the examples that include the German The Blitz, bombing of London, the Allies of World War II, Allied Bombing of Dresden in World War II, firebombing of Dresden, and the U.S. atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during World War II. He argues that "the use of terror tactics is common in international relations and the state has been and remains a more likely employer of terrorism within the international system than insurgents." He cites the Pre-emptive nuclear strike, first strike option as an example of the "terror of coercive diplomacy" as a form of this, which holds the world hostage with the implied threat of using nuclear weapons in "crisis management" and he argues that the institutionalized form of terrorism has occurred as a result of changes that took place following World War II. In this analysis, state terrorism exhibited as a form of foreign policy was shaped by the presence and use of Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction, and the legitimizing of such violent behavior led to an increasingly accepted form of this behavior by the state.

Charles Stewart Parnell described William Ewart Gladstone's Irish Coercion Act as terrorism in his "no-Rent manifesto" in 1881, during the Irish Land War. The concept is used to describe political repressions by governments against their own civilian populations with the purpose of inciting fear. For example, taking and executing civilian hostages or extrajudicial killing, extrajudicial elimination campaigns are commonly considered "terror" or terrorism, for example during the Red Terror or the Great Purge, Great Terror.Nicolas Werth, Karel Bartošek, Jean-Louis Panné, Jean-Louis Margolin, Andrzej Paczkowski, Stéphane Courtois, ''The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression'', Harvard University Press, 1999, hardcover, 858 pp., Such actions are often described as democide or genocide, which have been argued to be equivalent to state terrorism. Empirical studies on this have found that democracies have little democide. Western democracies, United States and state terrorism, including the United States, have supported state terrorism and mass killings, with some examples being the Indonesian mass killings of 1965–66 and Operation Condor.Mark Aarons (2007).
Justice Betrayed: Post-1945 Responses to Genocide
" In David A. Blumenthal and Timothy L.H. McCormack (eds).
The Legacy of Nuremberg: Civilising Influence or Institutionalised Vengeance? (International Humanitarian Law).
'' Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. pp
71
80–81
/ref>
, U.S. National Credit Union Administration (NCUA), 2002. Revolutionary taxes "play a secondary role as one other means of intimidating the target population". Other major sources of funding include kidnapping for ransoms, smuggling (including wildlife smuggling), fraud, and robbery. The Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant has reportedly received funding "via private donations from the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Gulf states". The Financial Action Task Force is an inter-governmental body whose mandate, since October 2001, has included combating terrorist financing.
 Terrorist attacks are often targeted to maximize fear and publicity, most frequently using explosives.
Terrorist groups usually methodically plan attacks in advance, and may train participants, plant undercover agents, and raise money from supporters or through organized crime. Communications occur through modern telecommunications, or through old-fashioned methods such as couriers. There is concern about terrorist attacks employing weapons of mass destruction. Some academics have argued that while it is often assumed terrorism is intended to spread fear, this is not necessarily true, with fear instead being a by-product of the terrorist's actions, while their intentions may be to avenge fallen comrades or destroy their perceived enemies.
Terrorism is a form of asymmetric warfare, and is more common when direct conventional warfare will not be effective because opposing forces vary greatly in power. Yuval Harari argues that the peacefulness of modern states makes them paradoxically more vulnerable to terrorism than pre-modern states. Harari argues that because modern states have committed themselves to reducing political violence to almost zero, terrorists can, by creating political violence, threaten the very foundations of the legitimacy of the modern state. This is in contrast to pre-modern states, where violence was a routine and recognised aspect of politics at all levels, making political violence unremarkable. Terrorism thus shocks the population of a modern state far more than a pre-modern one and consequently the state is forced to overreact in an excessive, costly and spectacular manner, which is often what the terrorists desire.
The type of people terrorists will target is dependent upon the ideology of the terrorists. A terrorist's ideology will create a class of "legitimate targets" who are deemed as its enemies and who are permitted to be targeted. This ideology will also allow the terrorists to place the blame on the victim, who is viewed as being responsible for the violence in the first place.
The context in which terrorist tactics are used is often a large-scale, unresolved political conflict. The type of conflict varies widely; historical examples include:
* Secession of a territory to form a new sovereign state or become part of a different state
* Dominance of territory or resources by various ethnic groups
* Imposition of a particular form of government
* Economic deprivation of a population
* Opposition to a domestic government or occupying army
* Religious fanaticism
Terrorist attacks are often targeted to maximize fear and publicity, most frequently using explosives.
Terrorist groups usually methodically plan attacks in advance, and may train participants, plant undercover agents, and raise money from supporters or through organized crime. Communications occur through modern telecommunications, or through old-fashioned methods such as couriers. There is concern about terrorist attacks employing weapons of mass destruction. Some academics have argued that while it is often assumed terrorism is intended to spread fear, this is not necessarily true, with fear instead being a by-product of the terrorist's actions, while their intentions may be to avenge fallen comrades or destroy their perceived enemies.
Terrorism is a form of asymmetric warfare, and is more common when direct conventional warfare will not be effective because opposing forces vary greatly in power. Yuval Harari argues that the peacefulness of modern states makes them paradoxically more vulnerable to terrorism than pre-modern states. Harari argues that because modern states have committed themselves to reducing political violence to almost zero, terrorists can, by creating political violence, threaten the very foundations of the legitimacy of the modern state. This is in contrast to pre-modern states, where violence was a routine and recognised aspect of politics at all levels, making political violence unremarkable. Terrorism thus shocks the population of a modern state far more than a pre-modern one and consequently the state is forced to overreact in an excessive, costly and spectacular manner, which is often what the terrorists desire.
The type of people terrorists will target is dependent upon the ideology of the terrorists. A terrorist's ideology will create a class of "legitimate targets" who are deemed as its enemies and who are permitted to be targeted. This ideology will also allow the terrorists to place the blame on the victim, who is viewed as being responsible for the violence in the first place.
The context in which terrorist tactics are used is often a large-scale, unresolved political conflict. The type of conflict varies widely; historical examples include:
* Secession of a territory to form a new sovereign state or become part of a different state
* Dominance of territory or resources by various ethnic groups
* Imposition of a particular form of government
* Economic deprivation of a population
* Opposition to a domestic government or occupying army
* Religious fanaticism
 Responses to terrorism are broad in scope. They can include re-alignments of the political spectrum and reassessments of value system, fundamental values.
Specific types of responses include:
* Anti-terrorism legislation, Targeted laws, criminal procedures, deportations, and enhanced police powers
* Target hardening, such as locking doors or adding traffic barriers
* Preemptive strike, Preemptive or reactive military action
* Increased police intelligence, intelligence and surveillance activities
* Preemptive humanitarian activities
* More permissive interrogation and Detention (imprisonment), detention policies
The term "counter-terrorism" has a narrower connotation, implying that it is directed at terrorist actors.
Responses to terrorism are broad in scope. They can include re-alignments of the political spectrum and reassessments of value system, fundamental values.
Specific types of responses include:
* Anti-terrorism legislation, Targeted laws, criminal procedures, deportations, and enhanced police powers
* Target hardening, such as locking doors or adding traffic barriers
* Preemptive strike, Preemptive or reactive military action
* Increased police intelligence, intelligence and surveillance activities
* Preemptive humanitarian activities
* More permissive interrogation and Detention (imprisonment), detention policies
The term "counter-terrorism" has a narrower connotation, implying that it is directed at terrorist actors.
 According to a report by Dana Priest and William M. Arkin in The Washington Post, "Some 1,271 government organizations and 1,931 private companies work on programs related to counterterrorism, homeland security and intelligence in about 10,000 locations across the United States."
America's thinking on how to defeat radical Islamists is split along two very different schools of thought. Republicans, typically follow what is known as the Bush Doctrine, advocate the military model of taking the fight to the enemy and seeking to democratize the Middle East. Democrats, by contrast, generally propose the law enforcement model of better cooperation with nations and more security at home.Ankony, Robert C., "A New Strategy for America's War on Terrorism", ''Patrolling'' magazine, 75th Ranger Regiment Association, Winter 2011, 56–57. In the introduction of the ''U.S. Army / Marine Corps Counterinsurgency Field Manual'', Sarah Sewall states the need for "U.S. forces to make securing the civilian, rather than destroying the enemy, their top priority. The civilian population is the center of gravity—the deciding factor in the struggle.... Civilian deaths create an extended family of enemies—new insurgent recruits or informants—and erode support of the host nation." Sewall sums up the book's key points on how to win this battle: "Sometimes, the more you protect your force, the less secure you may be.... Sometimes, the more force is used, the less effective it is.... The more successful the counterinsurgency is, the less force can be used and the more risk must be accepted.... Sometimes, doing nothing is the best reaction." This strategy, often termed "courageous restraint", has certainly led to some success on the Middle East battlefield. However, it does not address the fact that terrorists are mostly homegrown.
According to a report by Dana Priest and William M. Arkin in The Washington Post, "Some 1,271 government organizations and 1,931 private companies work on programs related to counterterrorism, homeland security and intelligence in about 10,000 locations across the United States."
America's thinking on how to defeat radical Islamists is split along two very different schools of thought. Republicans, typically follow what is known as the Bush Doctrine, advocate the military model of taking the fight to the enemy and seeking to democratize the Middle East. Democrats, by contrast, generally propose the law enforcement model of better cooperation with nations and more security at home.Ankony, Robert C., "A New Strategy for America's War on Terrorism", ''Patrolling'' magazine, 75th Ranger Regiment Association, Winter 2011, 56–57. In the introduction of the ''U.S. Army / Marine Corps Counterinsurgency Field Manual'', Sarah Sewall states the need for "U.S. forces to make securing the civilian, rather than destroying the enemy, their top priority. The civilian population is the center of gravity—the deciding factor in the struggle.... Civilian deaths create an extended family of enemies—new insurgent recruits or informants—and erode support of the host nation." Sewall sums up the book's key points on how to win this battle: "Sometimes, the more you protect your force, the less secure you may be.... Sometimes, the more force is used, the less effective it is.... The more successful the counterinsurgency is, the less force can be used and the more risk must be accepted.... Sometimes, doing nothing is the best reaction." This strategy, often termed "courageous restraint", has certainly led to some success on the Middle East battlefield. However, it does not address the fact that terrorists are mostly homegrown.
 Mass media exposure may be a primary goal of those carrying out terrorism, to expose issues that would otherwise be ignored by the media. Some consider this to be manipulation and exploitation of the media.
The Internet has created a new way for groups to spread their messages. This has created a cycle of measures and counter measures by groups in support of and in opposition to terrorist movements. The United Nations has created its own online counter-terrorism resource.
The mass media will, on occasion, censor organizations involved in terrorism (through self-restraint or regulation) to discourage further terrorism. This may encourage organizations to perform more extreme acts of terrorism to be shown in the mass media. Conversely James F. Pastor explains the significant relationship between terrorism and the media, and the underlying benefit each receives from the other.
Former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously spoke of the close connection between terrorism and the media, calling publicity 'the oxygen of terrorism'.
Mass media exposure may be a primary goal of those carrying out terrorism, to expose issues that would otherwise be ignored by the media. Some consider this to be manipulation and exploitation of the media.
The Internet has created a new way for groups to spread their messages. This has created a cycle of measures and counter measures by groups in support of and in opposition to terrorist movements. The United Nations has created its own online counter-terrorism resource.
The mass media will, on occasion, censor organizations involved in terrorism (through self-restraint or regulation) to discourage further terrorism. This may encourage organizations to perform more extreme acts of terrorism to be shown in the mass media. Conversely James F. Pastor explains the significant relationship between terrorism and the media, and the underlying benefit each receives from the other.
Former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously spoke of the close connection between terrorism and the media, calling publicity 'the oxygen of terrorism'.
 Jones and Libicki (2008) created a list of all the terrorist groups they could find that were active between 1968 and 2006. They found 648. Of those, 136 splintered and 244 were still active in 2006. Of the ones that ended, 43 percent converted to nonviolent political actions, like the Good Friday Agreement, Irish Republican Army in Northern Ireland. Law enforcement took out 40 percent. Ten percent won. Only 20 groups, 7 percent, were destroyed by military force.
Forty-two groups became large enough to be labeled an insurgency; 38 of those had ended by 2006. Of those, 47 percent converted to nonviolent political actors. Only 5 percent were ended by law enforcement. Twenty-six percent won. Twenty-one percent succumbed to military force. Jones and Libicki concluded that military force may be necessary to deal with large insurgencies but are only occasionally decisive, because the military is too often seen as a bigger threat to civilians than the terrorists. To avoid that, the rules of engagement must be conscious of collateral damage and work to minimize it.
Another researcher, Audrey Cronin, lists six primary ways that terrorist groups end:
# Capture or killing of a group's leader. (Decapitation).
# Entry of the group into a legitimate political process. (Negotiation).
# Achievement of group aims. (Success).
# Group implosion or loss of public support. (Failure).
# Defeat and elimination through brute force. (Repression).
# Transition from terrorism into other forms of violence. (Reorientation).
Jones and Libicki (2008) created a list of all the terrorist groups they could find that were active between 1968 and 2006. They found 648. Of those, 136 splintered and 244 were still active in 2006. Of the ones that ended, 43 percent converted to nonviolent political actions, like the Good Friday Agreement, Irish Republican Army in Northern Ireland. Law enforcement took out 40 percent. Ten percent won. Only 20 groups, 7 percent, were destroyed by military force.
Forty-two groups became large enough to be labeled an insurgency; 38 of those had ended by 2006. Of those, 47 percent converted to nonviolent political actors. Only 5 percent were ended by law enforcement. Twenty-six percent won. Twenty-one percent succumbed to military force. Jones and Libicki concluded that military force may be necessary to deal with large insurgencies but are only occasionally decisive, because the military is too often seen as a bigger threat to civilians than the terrorists. To avoid that, the rules of engagement must be conscious of collateral damage and work to minimize it.
Another researcher, Audrey Cronin, lists six primary ways that terrorist groups end:
# Capture or killing of a group's leader. (Decapitation).
# Entry of the group into a legitimate political process. (Negotiation).
# Achievement of group aims. (Success).
# Group implosion or loss of public support. (Failure).
# Defeat and elimination through brute force. (Repression).
# Transition from terrorism into other forms of violence. (Reorientation).
Perspectives on Terrorism's Bibliography: Root Causes of Terrorism. 2017.
''Forecasting the Unpredictable: A Review of Forecasts on Terrorism 2000–2012'' (International Centre for Counter-Terrorism – The Hague, 2014)
* * Burleigh, Michael. ''Blood and rage: a cultural history of terrorism''. Harper, 2009. * Chaliand, Gérard and Arnaud Blin, eds. ''The history of terrorism: from antiquity to al Qaeda''. University of California Press, 2007. * Coates, Susan W., Rosenthal, Jane, and Schechter, Daniel S. ''September 11: Trauma and Human Bonds'' (New York: Taylor and Francis, Inc., 2003). * Crenshaw, Martha, ed. ''Terrorism in context''. Pennsylvania State University Press, 1995. * * Hennigfeld, Ursula/ Packard, Stephan, ed., ''Abschied von 9/11? Distanznahme zur Katastrophe''. Berlin: Frank & Timme, 2013. * Hennigfeld, Ursula, ed., ''Poetiken des Terrors. Narrative des 11. September 2001 im interkulturellen Vergleich''. Heidelberg: Winter, 2014. * Hewitt, Christopher. ''Understanding terrorism in America'' (Routledge, 2003). * Hewitt, Christopher. "Terrorism and public opinion: A five country comparison." ''Terrorism and Political Violence'' 2.2 (1990): 145-170. * Jones, Sidney.
Terrorism: myths and facts
'. Jakarta: International Crisis Group, 2013. * Land, Isaac, ed., ''Enemies of humanity: the nineteenth-century war on terrorism''. Palgrave Macmillan, 2008. * Lee, Newton. ''Counterterrorism and Cybersecurity: Total Information Awareness (2nd Edition)''. New York: Springer, 2015. * Lutz, James and Brenda Lutz. ''Terrorism : origins and evolution'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2005) * Miller, Martin A. ''The foundations of modern terrorism : state, society and the dynamics of political violence''. Cambridge University Press, 2013. * * Neria, Yuval, Gross, Raz, Marshall, Randall D., and Susser, Ezra. ''September 11, 2001: Treatment, Research and Public Mental Health in the Wake of a Terrorist Attack'' (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2006). * An open-access publication, issued since November 2020 on the International Centre for Counter-Terrorism (ICCT) website, with a chapter published each week. * Stern, Jessica. ''The Ultimate Terrorists''. (Harvard University Press 2000 reprint; 1995). 214 p. * Tausch, Arno
Estimates on the Global Threat of Islamic State Terrorism in the Face of the 2015 Paris and Copenhagen Attacks
(December 11, 2015). ''Middle East Review of International Affairs'', Rubin Center, Research in International Affairs, Idc Herzliya, Israel, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Spring 2015). *
Terrorism, Law & Democracy: 10 years after 9/11
', Canadian Institute for the Administration of Justice. .
online
* Chin, Warren. ''Britain and the war on terror: Policy, strategy and operations'' (Routledge, 2016). * Clutterbuck, Lindsay. "Countering Irish Republican terrorism in Britain: Its origin as a police function." ''Terrorism and Political Violence'' 18.1 (2006) pp: 95-118. * Greer, Steven. "Terrorism and Counter-Terrorism in the UK: From Northern Irish Troubles to Global Islamist Jihad." in ''Counter-Terrorism, Constitutionalism and Miscarriages of Justice'' (Hart Publishing, 2018) pp. 45-62. * Hamilton, Claire. "Counter-Terrorism in the UK." in ''Contagion, Counter-Terrorism and Criminology'' (Palgrave Pivot, Cham, 2019) pp. 15-47. * Hewitt, Steve. "Great Britain: Terrorism and counter-terrorism since 1968." in ''Routledge Handbook of Terrorism and Counterterrorism'' (Routledge, 2018) pp. 540-551. * Martínez-Peñas, Leandro, and Manuela Fernández-Rodríguez. "Evolution of British Law on Terrorism: From Ulster to Global Terrorism (1970–2010)." in ''Post 9/11 and the State of Permanent Legal Emergency'' (Springer, 2012) pp. 201-222. * O'Day, Alan. "Northern Ireland, Terrorism, and the British State." in ''Terrorism: Theory and Practice'' (Routledge, 2019) pp. 121-135. * Sacopulos, Peter J. "Terrorism in Britain: Threat, reality, response." ''Studies in Conflict & Terrorism'' 12.3 (1989): 153-165. * Staniforth, Andrew, and Fraser Sampson, eds. ''The Routledge companion to UK counter-terrorism'' (Routledge, 2012). * Sinclair, Georgina. "Confronting terrorism: British Experiences past and present." ''Crime, Histoire & Sociétés/Crime, History & Societies'' 18.2 (2014): 117-122
online
* Tinnes, Judith, ed. "Bibliography: Northern Ireland conflict (the troubles)." ''Perspectives on Terrorism'' 10.1 (2016): 83-110
online
* Wilkinson, Paul, ed. ''Terrorism: British Perspectives'' (Dartmouth, 1993).
Conventions on Terrorism
* United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime:
UNODC – United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime – Terrorism Prevention
Terrorism and international humanitarian law
International Committee of the Red Cross
UK Counter Terrorism Policing
{{Authority control Terrorism, Crimes Warfare by type 1790s neologisms
 Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war against non-combatants (mostly civilians and neutral country, neutral military personnel). The terms "terrorist" and "terrorism" originated during the French Revolution of the late 18th century but became widely used internationally and gained worldwide attention in the 1970s during The Troubles, the Troubles in Northern Ireland, the Basque conflict, and the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. The increased use of suicide attacks from the 1980s onwards was typified by the 2001 September 11 attacks in the United States.
There are various different definitions of terrorism, with no universal agreement about it. Terrorism is a Loaded language, charged term. It is often used with the connotation of something that is "morally wrong". Governments and non-state groups use the term to abuse or denounce opposing groups. Varied political organizations have been accused of using terrorism to achieve their objectives. These include Left-wing terrorism, left-wing and Right-wing terrorism, right-wing political organizations, Nationalist terrorism, nationalist groups, Religious terrorism, religious groups, Revolutionary terror, revolutionaries and State terrorism, ruling governments. Anti-terrorism legislation, Legislation declaring terrorism a crime has been adopted in many states. When terrorism is perpetrated by nation states, it is not considered terrorism by the state conducting it, making legality a largely grey-area issue. There is no consensus as to whether terrorism should be regarded as a war crime.
The Global Terrorism Database, maintained by the University of Maryland, College Park, has recorded more than 61,000 incidents of non-state terrorism, resulting in at least 140,000 deaths, between 2000 and 2014.
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violence during peacetime or in the context of war against non-combatants (mostly civilians and neutral country, neutral military personnel). The terms "terrorist" and "terrorism" originated during the French Revolution of the late 18th century but became widely used internationally and gained worldwide attention in the 1970s during The Troubles, the Troubles in Northern Ireland, the Basque conflict, and the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. The increased use of suicide attacks from the 1980s onwards was typified by the 2001 September 11 attacks in the United States.
There are various different definitions of terrorism, with no universal agreement about it. Terrorism is a Loaded language, charged term. It is often used with the connotation of something that is "morally wrong". Governments and non-state groups use the term to abuse or denounce opposing groups. Varied political organizations have been accused of using terrorism to achieve their objectives. These include Left-wing terrorism, left-wing and Right-wing terrorism, right-wing political organizations, Nationalist terrorism, nationalist groups, Religious terrorism, religious groups, Revolutionary terror, revolutionaries and State terrorism, ruling governments. Anti-terrorism legislation, Legislation declaring terrorism a crime has been adopted in many states. When terrorism is perpetrated by nation states, it is not considered terrorism by the state conducting it, making legality a largely grey-area issue. There is no consensus as to whether terrorism should be regarded as a war crime.
The Global Terrorism Database, maintained by the University of Maryland, College Park, has recorded more than 61,000 incidents of non-state terrorism, resulting in at least 140,000 deaths, between 2000 and 2014.
Etymology
Etymologically, the word terror is derived from the Latin verb ''Tersere'', which later becomes ''Terrere''. The latter form appears in European languages as early as the 12th century; its first known use in French is the word ''terrible'' in 1160. By 1356 the word ''terreur'' is in use. ''Terreur'' is the origin of the Middle English term ''terrour'', which later becomes the modern word "terror".Historical background
 The term ''terroriste'', meaning "terrorist", is first used in 1794 by the French philosopher François-Noël Babeuf, who denounces Maximilien Robespierres Jacobin regime as a dictatorship. In the years leading up to what became known as the Reign of Terror, the Brunswick Manifesto threatened Paris with an "exemplary, never to be forgotten vengeance: the city would be subjected to military punishment and total destruction" if the royal family was harmed, but this only increased the Revolution's will to abolish the monarchy. Some writers attitudes about French Revolution grew less favorable after the French monarchy was abolished in 1792. During the Reign of Terror, which began in July 1793 and lasted thirteen months, Paris was governed by the Committee of Public Safety who oversaw a regime of mass executions and public purges.
Prior to the French Revolution, ancient philosophers wrote about tyrannicide, as tyranny was seen as the greatest political threat to Greco-Roman civilization. Medieval philosophy, Medieval philosophers were similarly occupied with the concept of tyranny, though the analysis of some theologians like Thomas Aquinas drew a distinction between usurpers, who could be killed by anyone, and legitimate rulers who abused their power—the latter, in Aquinas' view, could only be punished by a public authority. John of Salisbury was the first medieval Christian scholar to defend tyrannicide.
The term ''terroriste'', meaning "terrorist", is first used in 1794 by the French philosopher François-Noël Babeuf, who denounces Maximilien Robespierres Jacobin regime as a dictatorship. In the years leading up to what became known as the Reign of Terror, the Brunswick Manifesto threatened Paris with an "exemplary, never to be forgotten vengeance: the city would be subjected to military punishment and total destruction" if the royal family was harmed, but this only increased the Revolution's will to abolish the monarchy. Some writers attitudes about French Revolution grew less favorable after the French monarchy was abolished in 1792. During the Reign of Terror, which began in July 1793 and lasted thirteen months, Paris was governed by the Committee of Public Safety who oversaw a regime of mass executions and public purges.
Prior to the French Revolution, ancient philosophers wrote about tyrannicide, as tyranny was seen as the greatest political threat to Greco-Roman civilization. Medieval philosophy, Medieval philosophers were similarly occupied with the concept of tyranny, though the analysis of some theologians like Thomas Aquinas drew a distinction between usurpers, who could be killed by anyone, and legitimate rulers who abused their power—the latter, in Aquinas' view, could only be punished by a public authority. John of Salisbury was the first medieval Christian scholar to defend tyrannicide.
 Most scholars today trace the origins of the modern tactic of terrorism to the Jewish Sicarii Zealots who attacked Romans and Jews in 1st-century Palestine (region), Palestine. They follow its development from the Persian Order of Assassins through to 19th-century anarchists. The "Reign of Terror" is usually regarded as an issue of etymology. The term terrorism has generally been used to describe violence by non-state actors rather than government violence since the 19th-century Anarchism in France, Anarchist Movement.
In December 1795, Edmund Burke used the word "Terrorists" in a description of the new French Directory, French government called 'Directory':
Most scholars today trace the origins of the modern tactic of terrorism to the Jewish Sicarii Zealots who attacked Romans and Jews in 1st-century Palestine (region), Palestine. They follow its development from the Persian Order of Assassins through to 19th-century anarchists. The "Reign of Terror" is usually regarded as an issue of etymology. The term terrorism has generally been used to describe violence by non-state actors rather than government violence since the 19th-century Anarchism in France, Anarchist Movement.
In December 1795, Edmund Burke used the word "Terrorists" in a description of the new French Directory, French government called 'Directory':
At length, after a terrible struggle, the [Directory] Troops prevailed over the Citizens ... To secure them further, they have a strong corps of irregular military, irregulars, ready armed. Thousands of those Hell-hounds called Terrorists, whom they had shut up in Prison on their last Revolution, as the Satellites of Tyranny, are let loose on the people.(emphasis added)The terms "terrorism" and "terrorist" gained renewed currency in the 1970s as a result of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, the The Troubles, Northern Ireland conflict, the Basque conflict, and the operations of groups such as the Red Army Faction. Leila Khaled was described as a terrorist in a 1970 issue of ''Life (magazine), Life'' magazine. A number of books on terrorism were published in the 1970s. The topic came further to the fore after the 1983 Beirut barracks bombings and again after the 2001 September 11 attacks and the 2002 Bali bombings.
Modern definitions

 In 2006 it was estimated that there were over 109 different definitions of terrorism.Arie W. Kruglanski and Shira Fishman ''Current Directions in Psychological Science'' Vol. 15, No. 1 (Feb. 2006), pp. 45–48 American political philosopher Michael Walzer in 2002 wrote: "Terrorism is the deliberate killing of innocent people, at random, to spread fear through a whole population and force the hand of its political leaders". Bruce Hoffman, an American scholar, has noted that it is not only individual agencies within the same governmental apparatus that cannot agree on a single definition of terrorism. Experts and other long-established scholars in the field are equally incapable of reaching a consensus.
C. A. J. Coady has written that the question of how to define terrorism is "irresolvable" because "its natural home is in polemical, ideological and propagandist contexts".
Experts disagree about "whether terrorism is wrong by definition or just wrong as a matter of fact; they disagree about whether terrorism should be defined in terms of its aims, or its methods, or both, or neither; they disagree about whether states can perpetrate terrorism; they even disagree about the importance or otherwise of ''terror'' for a definition of ''terrorism''."
In 2006 it was estimated that there were over 109 different definitions of terrorism.Arie W. Kruglanski and Shira Fishman ''Current Directions in Psychological Science'' Vol. 15, No. 1 (Feb. 2006), pp. 45–48 American political philosopher Michael Walzer in 2002 wrote: "Terrorism is the deliberate killing of innocent people, at random, to spread fear through a whole population and force the hand of its political leaders". Bruce Hoffman, an American scholar, has noted that it is not only individual agencies within the same governmental apparatus that cannot agree on a single definition of terrorism. Experts and other long-established scholars in the field are equally incapable of reaching a consensus.
C. A. J. Coady has written that the question of how to define terrorism is "irresolvable" because "its natural home is in polemical, ideological and propagandist contexts".
Experts disagree about "whether terrorism is wrong by definition or just wrong as a matter of fact; they disagree about whether terrorism should be defined in terms of its aims, or its methods, or both, or neither; they disagree about whether states can perpetrate terrorism; they even disagree about the importance or otherwise of ''terror'' for a definition of ''terrorism''."
State terrorism
State terrorism refers to acts of terrorism conducted by a State (polity), state against its own citizens or against another state.United Nations
In November 2004, a Secretary-General of the United Nations report described terrorism as any act "intended to cause death or serious bodily harm to civilians or non-combatants with the purpose of intimidating a population or compelling a government or an international organization to do or abstain from doing any act". The international community has been slow to formulate a universally agreed, legally binding definition of this crime. These difficulties arise from the fact that the term "terrorism" is politically and emotionally charged. In this regard, Angus Martyn, briefing the Australian parliament, stated,The international community has never succeeded in developing an accepted comprehensive definition of terrorism. During the 1970s and 1980s, the United Nations attempts to define the term floundered mainly due to differences of opinion between various members about the use of violence in the context of conflicts over national liberation and self-determination.Angus MartynThese divergences have made it impossible for the United Nations to conclude a Definition of terrorism#UN Comprehensive Convention (1997–present), Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism that incorporates a single, all-encompassing, legally binding, criminal law definition of terrorism. The international community has adopted a series of Definition of terrorism#The sectoral approach, sectoral conventions that define and criminalize various types of terrorist activities. Since 1994, the United Nations General Assembly has repeatedly condemned terrorist acts using the following political description of terrorism:
The Right of Self-Defence under International Law-the Response to the Terrorist Attacks of 11 September
Australian Law and Bills Digest Group, Parliament of Australia Web Site, February 12, 2002.
Criminal acts intended or calculated to provoke a state of terror in the public, a group of persons or particular persons for political purposes are in any circumstance unjustifiable, whatever the considerations of a political, philosophical, ideological, racial, ethnic, religious or any other nature that may be invoked to justify them.
U.S. law
Various legal systems and government agencies use different Anti-terrorism legislation, definitions of terrorism in their national legislation. U.S. Code Title 22 Chapter 38, Section 2656f(d) defines terrorism as: "Premeditated, politically motivated violence perpetrated against noncombatant targets by subnational groups or clandestine agents". 18 U.S.C. § 2331 defines "international terrorism" and "domestic terrorism" for purposes of Chapter 113B of the Code, entitled "Terrorism": "International terrorism" means activities with the following three characteristics:Media spectacle
A definition proposed by Carsten Bockstette at the George C. Marshall European Center for Security Studies, underlines the psychological and tactical aspects of terrorism: Terrorists attack national symbols, which may negatively affect a government, while increasing the prestige of the given List of designated terrorist groups, terrorist group or its ideology.Political violence
Terrorist acts frequently have a political purpose. Some official, governmental definitions of terrorism use the criterion of the illegitimacy or unlawfulness of the act. to distinguish between actions authorized by a government (and thus "lawful") and those of other actors, including individuals and small groups. For example, carrying out a strategic bombing on an enemy city, which is designed to affect civilian support for a cause, would not be considered terrorism if it were authorized by a government. This criterion is inherently problematic and is not universally accepted, because: it denies the existence of state terrorism. An associated term is violent non-state actor. According to Ali Khan, the distinction lies ultimately in a political judgment.Pejorative use
Having the connotation of "something morally wrong", the term "terrorism" is often used to abuse or denounce opposite parties, either governments or non-state groups. An example of this is the ''terruqueo'' political attack used by right-wing groups in Peru to target leftist groups or those opposed to the neoliberal ''status quo'', likening opponents to guerillas from the internal conflict in Peru. Those labeled "terrorists" by their opponents rarely identify themselves as such, and typically use other terms or terms specific to their situation, such as separatist, freedom fighter, liberator, revolutionary, vigilante, Insurgent, militant, paramilitary, guerrilla warfare, guerrilla, rebellion, rebel, patriot, or any similar-meaning word in other languages and cultures. Jihadi, mujahideen, and fedayeen are similar Arabic words that have entered the English lexicon. It is common for both parties in a conflict to describe each other as terrorists. On whether particular terrorist acts, such as killing non-combatants, can be justified as the lesser evil in a particular circumstance, philosophers have expressed different views: while, according to David Rodin, utilitarian philosophers can (in theory) conceive of cases in which the evil of terrorism is outweighed by the good that could not be achieved in a less morally costly way, in practice the "harmful effects of undermining the convention of non-combatant immunity is thought to outweigh the goods that may be achieved by particular acts of terrorism".Rodin, David (2006). "Terrorism". In E. Craig (Ed.), ''Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy''. London: Routledge. Among the non-utilitarian philosophers, Michael Walzer argued that terrorism can be morally justified in only one specific case: when "a nation or community faces the extreme threat of complete destruction and the only way it can preserve itself is by intentionally targeting non-combatants,then it is morally entitled to do so". In his book ''Inside Terrorism'' Bruce Hoffman offered an explanation of why the term ''terrorism'' becomes distorted: The pejorative connotations of the word can be summed up in the aphorism, "One man's terrorist is another man's freedom fighter". This is exemplified when a group using irregular military methods is an ally of a Sovereign state, state against a mutual enemy, but later falls out with the state and starts to use those methods against its former ally. During the World War II, Second World War, the Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army were allied with the British, but during the Malayan Emergency, members of its successor organisation (the Malayan National Liberation Army) started campaigns against them, and were branded "terrorists" as a result. More recently, Ronald Reagan and others in the American administration frequently called the Afghan Mujahideen, mujaheddin "freedom fighters" during the Soviet–Afghan War, however twenty years later, when a new generation of Afghan men (militant groups like the Taliban and allies) were fighting against what they perceive to be a regime installed by foreign powers, their attacks were labelled terrorism by George W. Bush.
Groups accused of terrorism understandably prefer terms reflecting legitimate military or ideological action.Terrorism: concepts, causes, and conflict resolution
During the World War II, Second World War, the Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army were allied with the British, but during the Malayan Emergency, members of its successor organisation (the Malayan National Liberation Army) started campaigns against them, and were branded "terrorists" as a result. More recently, Ronald Reagan and others in the American administration frequently called the Afghan Mujahideen, mujaheddin "freedom fighters" during the Soviet–Afghan War, however twenty years later, when a new generation of Afghan men (militant groups like the Taliban and allies) were fighting against what they perceive to be a regime installed by foreign powers, their attacks were labelled terrorism by George W. Bush.
Groups accused of terrorism understandably prefer terms reflecting legitimate military or ideological action.Terrorism: concepts, causes, and conflict resolutionGeorge Mason University Institute for Conflict Analysis and Resolution, Printed by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, Fort Belvoir, Virginia, January 2003. Leading terrorism researcher Professor Martin Rudner, director of the Canadian Centre of Intelligence and Security Studies at Ottawa's Carleton University, defines "terrorist acts" as unlawful attacks for political or other ideological goals, and said: Some groups, when involved in a "liberation" struggle, have been called "terrorists" by the Western governments or media. Later, these same persons, as leaders of the liberated nations, are called "statesmen" by similar organizations. Two examples of this phenomenon are the Nobel Peace Prize laureates Menachem Begin and Nelson Mandela. WikiLeaks editor Julian Assange has been called a "terrorist" by Sarah Palin and Joe Biden. Sometimes, states that are close allies, for reasons of history, culture and politics, can disagree over whether members of a certain organization are terrorists. For instance, some branches of the United States government refused to label members of the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) as terrorists while the IRA was using methods against one of the United States' closest allies (the United Kingdom) that the UK branded as terrorism. This was highlighted by the ''Quinn v. Robinson'' case. Media outlets who wish to convey impartiality may limit their usage of "terrorist" and "terrorism" because they are loosely defined, potentially controversial in nature, and subjective terms. The 2020 Nashville bombing#Debate over "terrorism" as a term, 2020 Nashville bombing revived a debate over the use of the word "terrorism", with critics saying it is quickly applied to attacks by Muslims but reluctantly if at all used by white Christian men, such as the Nashville bomber.
History
 Depending on how broadly the term is defined, the roots and practice of terrorism can be traced at least to the 1st century AD. According to the contemporary Jewish-Roman historian Josephus, after the Zealotry rebellion against Roman rule in Judea, when some prominent Jewish collaborators with Roman rule were killed, Judas of Galilee formed a small and more extreme offshoot of the Zealots, the Sicarii Zealots, in 6 AD. They were a smaller and more radical offshoot of the Zealots which was active in Judaea Province at the beginning of the 1st century AD, and they can be considered early terrorists, although this is disputed. Their terror was directed against Jewish "collaborators", including temple priests, Sadducees, Herodian dynasty, Herodians, and other wealthy elites.
The term "terrorism" itself was originally used to describe the actions of the Jacobin Club during the "Reign of Terror" in the French Revolution. "Terror is nothing other than justice, prompt, severe, inflexible", said Jacobin leader Maximilien Robespierre. In 1795, Edmund Burke denounced the Jacobins for letting "thousands of those hell-hounds called Terrorists ... loose on the people" of France.
In January 1858, Italian patriot Felice Orsini threw three bombs in an attempt to assassinate French Emperor Napoleon III.Crenshaw, Martha, ''Terrorism in Context'', p. 38. Eight bystanders were killed and 142 injured. The incident played a crucial role as an inspiration for the development of the early terrorist groups.
Arguably the first organization to use modern terrorist techniques was the Irish Republican Brotherhood, founded in 1858 as a revolutionary Irish nationalist group that carried out attacks in England. The group initiated the Fenian dynamite campaign in 1881, one of the first modern terror campaigns. Instead of earlier forms of terrorism based on political assassination, this campaign used timed explosives with the express aim of sowing fear in the very heart of Great Britain, metropolitan Britain, in order to achieve political gains.
Another early terrorist-type group was Narodnaya Volya (organization), Narodnaya Volya, founded in Russia in 1878 as a revolutionary anarchist group inspired by Sergei Nechayev and "propaganda by the deed" theorist Carlo Pisacane. The group developed ideas—such as targeted killing of the 'leaders of oppression'—that were to become the hallmark of subsequent violence by small non-state groups, and they were convinced that the developing technologies of the age—such as the invention of dynamite, which they were the first anarchist group to make widespread use of—enabled them to strike directly and with discrimination.
David C. Rapoport, David Rapoport refers to four major waves of global terrorism: "the Anarchist, the Anti-Colonial, the New Left, and the Religious. The first three have been completed and lasted around 40 years; the fourth is now in its third decade."
Depending on how broadly the term is defined, the roots and practice of terrorism can be traced at least to the 1st century AD. According to the contemporary Jewish-Roman historian Josephus, after the Zealotry rebellion against Roman rule in Judea, when some prominent Jewish collaborators with Roman rule were killed, Judas of Galilee formed a small and more extreme offshoot of the Zealots, the Sicarii Zealots, in 6 AD. They were a smaller and more radical offshoot of the Zealots which was active in Judaea Province at the beginning of the 1st century AD, and they can be considered early terrorists, although this is disputed. Their terror was directed against Jewish "collaborators", including temple priests, Sadducees, Herodian dynasty, Herodians, and other wealthy elites.
The term "terrorism" itself was originally used to describe the actions of the Jacobin Club during the "Reign of Terror" in the French Revolution. "Terror is nothing other than justice, prompt, severe, inflexible", said Jacobin leader Maximilien Robespierre. In 1795, Edmund Burke denounced the Jacobins for letting "thousands of those hell-hounds called Terrorists ... loose on the people" of France.
In January 1858, Italian patriot Felice Orsini threw three bombs in an attempt to assassinate French Emperor Napoleon III.Crenshaw, Martha, ''Terrorism in Context'', p. 38. Eight bystanders were killed and 142 injured. The incident played a crucial role as an inspiration for the development of the early terrorist groups.
Arguably the first organization to use modern terrorist techniques was the Irish Republican Brotherhood, founded in 1858 as a revolutionary Irish nationalist group that carried out attacks in England. The group initiated the Fenian dynamite campaign in 1881, one of the first modern terror campaigns. Instead of earlier forms of terrorism based on political assassination, this campaign used timed explosives with the express aim of sowing fear in the very heart of Great Britain, metropolitan Britain, in order to achieve political gains.
Another early terrorist-type group was Narodnaya Volya (organization), Narodnaya Volya, founded in Russia in 1878 as a revolutionary anarchist group inspired by Sergei Nechayev and "propaganda by the deed" theorist Carlo Pisacane. The group developed ideas—such as targeted killing of the 'leaders of oppression'—that were to become the hallmark of subsequent violence by small non-state groups, and they were convinced that the developing technologies of the age—such as the invention of dynamite, which they were the first anarchist group to make widespread use of—enabled them to strike directly and with discrimination.
David C. Rapoport, David Rapoport refers to four major waves of global terrorism: "the Anarchist, the Anti-Colonial, the New Left, and the Religious. The first three have been completed and lasted around 40 years; the fourth is now in its third decade."
Infographics
Types
Depending on the country, the political system, and the time in history, the types of terrorism are varying.
 In early 1975, the National Institute of Justice, Law Enforcement Assistant Administration in the United States formed the National Advisory Committee on Criminal Justice Standards and Goals. One of the five volumes that the committee wrote was titled ''Disorders and Terrorism'', produced by the Task Force on Disorders and Terrorism under the direction of H. H. A. Cooper, Director of the Task Force staff.
The Task Force defines terrorism as "a tactic or technique by means of which a violent act or the threat thereof is used for the prime purpose of creating overwhelming fear for coercive purposes". It classified disorders and terrorism into six categories:
* Civil disorder – A form of collective violence interfering with the peace, security, and normal functioning of the community.
* Political terrorism – Violence, Violent criminal behaviour designed primarily to generate fear in the community, or substantial segment of it, for political purposes.
* Non-Political terrorism – Terrorism that is not aimed at political purposes but which exhibits "conscious design to create and maintain a high degree of fear for coercion, coercive purposes, but the end is individual or collective gain rather than the achievement of a political objective".
* Anonymous terrorism – In the two decades prior to 2016–19, "fewer than half" of all terrorist attacks were either "claimed by their perpetrators or convincingly attributed by governments to specific terrorist groups". A number of theories have been advanced as to why this has happened.
* Quasi-terrorism – The activities incidental to the commission of crimes of violence that are similar in form and method to genuine terrorism but which nevertheless lack its essential ingredient. It is not the main purpose of the quasi-terrorists to induce terror in the immediate victim as in the case of genuine terrorism, but the quasi-terrorist uses the modalities and techniques of the genuine terrorist and produces similar consequences and reaction. For example, the fleeing felony, felon who takes hostages is a quasi-terrorist, whose methods are similar to those of the genuine terrorist but whose purposes are quite different.
* Limited political terrorism – Genuine political terrorism is characterized by a revolutionary approach; limited political terrorism refers to "acts of terrorism which are committed for ideology, ideological or political motives but which are not part of a concerted campaign to capture control of the Sovereign state, state".
* Official or state terrorism – "referring to nations whose rule is based upon fear and oppression that reach similar to terrorism or such proportions". It may be referred to as Structural Terrorism defined broadly as terrorist acts carried out by governments in pursuit of political objectives, often as part of their foreign policy.
Other sources have defined the typology of terrorism in different ways, for example, broadly classifying it into domestic terrorism and international terrorism, or using categories such as vigilante terrorism or insurgent terrorism. One way the typology of terrorism may be defined:
* Political terrorism
**Sub-state terrorism
***Revolutionary terrorism, Social revolutionary terrorism
***Nationalist terrorism, Nationalist-separatist terrorism
***Religious terrorism, Religious extremist terrorism
**** Religious fundamentalist Terrorism
**** New religions terrorism
*** Right-wing terrorism
*** Left-wing terrorism
**** Communist terrorism
** State-sponsored terrorism
** State terrorism, Regime or state terrorism
* Criminal terrorism
* Pathological terrorism
In early 1975, the National Institute of Justice, Law Enforcement Assistant Administration in the United States formed the National Advisory Committee on Criminal Justice Standards and Goals. One of the five volumes that the committee wrote was titled ''Disorders and Terrorism'', produced by the Task Force on Disorders and Terrorism under the direction of H. H. A. Cooper, Director of the Task Force staff.
The Task Force defines terrorism as "a tactic or technique by means of which a violent act or the threat thereof is used for the prime purpose of creating overwhelming fear for coercive purposes". It classified disorders and terrorism into six categories:
* Civil disorder – A form of collective violence interfering with the peace, security, and normal functioning of the community.
* Political terrorism – Violence, Violent criminal behaviour designed primarily to generate fear in the community, or substantial segment of it, for political purposes.
* Non-Political terrorism – Terrorism that is not aimed at political purposes but which exhibits "conscious design to create and maintain a high degree of fear for coercion, coercive purposes, but the end is individual or collective gain rather than the achievement of a political objective".
* Anonymous terrorism – In the two decades prior to 2016–19, "fewer than half" of all terrorist attacks were either "claimed by their perpetrators or convincingly attributed by governments to specific terrorist groups". A number of theories have been advanced as to why this has happened.
* Quasi-terrorism – The activities incidental to the commission of crimes of violence that are similar in form and method to genuine terrorism but which nevertheless lack its essential ingredient. It is not the main purpose of the quasi-terrorists to induce terror in the immediate victim as in the case of genuine terrorism, but the quasi-terrorist uses the modalities and techniques of the genuine terrorist and produces similar consequences and reaction. For example, the fleeing felony, felon who takes hostages is a quasi-terrorist, whose methods are similar to those of the genuine terrorist but whose purposes are quite different.
* Limited political terrorism – Genuine political terrorism is characterized by a revolutionary approach; limited political terrorism refers to "acts of terrorism which are committed for ideology, ideological or political motives but which are not part of a concerted campaign to capture control of the Sovereign state, state".
* Official or state terrorism – "referring to nations whose rule is based upon fear and oppression that reach similar to terrorism or such proportions". It may be referred to as Structural Terrorism defined broadly as terrorist acts carried out by governments in pursuit of political objectives, often as part of their foreign policy.
Other sources have defined the typology of terrorism in different ways, for example, broadly classifying it into domestic terrorism and international terrorism, or using categories such as vigilante terrorism or insurgent terrorism. One way the typology of terrorism may be defined:
* Political terrorism
**Sub-state terrorism
***Revolutionary terrorism, Social revolutionary terrorism
***Nationalist terrorism, Nationalist-separatist terrorism
***Religious terrorism, Religious extremist terrorism
**** Religious fundamentalist Terrorism
**** New religions terrorism
*** Right-wing terrorism
*** Left-wing terrorism
**** Communist terrorism
** State-sponsored terrorism
** State terrorism, Regime or state terrorism
* Criminal terrorism
* Pathological terrorism
Causes and motivations
Choice of terrorism as a tactic
Individuals and groups choose terrorism as a tactic because it can: * Act as a form of asymmetric warfare in order to directly force a government to agree to demands * Intimidate a group of people into capitulating to the demands in order to avoid future injury * Get attention and thus political support for a cause * Directly inspire more people to the cause (such as revolutionary acts) – propaganda of the deed * Indirectly inspire more people to the cause by provoking a hostile response or over-reaction from enemies to the causeThe Psychology Of Terrorismaudio interview summarizin
Special Report: The Psychology of Terrorism
/ref> Attacks on "collaborators" are used to intimidate people from cooperating with the state in order to undermine state control. This strategy was used in Ireland, in Kenya, in Algeria and in Cyprus during their independence struggles. Stated motives for the September 11 attacks included inspiring more fighters to join the cause of repelling the United States from Muslim countries with a successful high-profile attack. The attacks prompted some criticism from domestic and international observers regarding perceived injustices in U.S. foreign policy that provoked the attacks, but the larger practical effect was that the United States government declared a War on Terror that resulted in substantial military engagements in several Muslim-majority countries. Various commentators have inferred that al-Qaeda expected a military response, and welcomed it as a provocation that would result in more Muslims fight the United States. Some commentators believe that the resulting anger and suspicion directed toward innocent Muslims living in Western countries and the indignities inflicted upon them by security forces and the general public also contributes to radicalization of new recruits. Despite criticism that the Iraqi government had no involvement with the September 11 attacks, Bush declared the 2003 invasion of Iraq to be part of the War on Terror. The resulting backlash and instability enabled the rise of Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant and the temporary creation of an Islamic caliphate holding territory in Iraq and Syria, until ISIL lost its territory through military defeats. Attacks used to draw international attention to struggles that are otherwise unreported have included the Dawson's Field hijackings, Palestinian airplane hijackings in 1970 and the 1975 Dutch train hostage crisis.
Causes motivating terrorism
Specific political or social causes have included: * Independence or separatist movements * Irredentist movements * Adoption of a particular political philosophy, such as socialism (left-wing terrorism), anarchism, or fascism (possibly through a coup or as an ideology of an independence or separatist movement) * Environmental protection (eco-terrorism) * Supremacism of a particular group ** Preventing a rival group from sharing or occupying a particular territory (such as by discouraging immigration or encouraging flight) ** Subjugation of a particular population (such as Lynching in the United States, lynching of African Americans) * Spread or dominance of a particular religion – religious terrorism * Ending perceived government oppression * Responding to a violent act (for example, tit-for-tat attacks in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, in The Troubles in Northern Ireland, or Timothy McVeigh's revenge for the Waco siege and Ruby Ridge incident) Causes for right-wing terrorism have included white nationalism, ethnonationalism, fascism, anti-socialism, the anti-abortion movement, and tax resistance. Sometimes terrorists on the same side fight for different reasons. For example, in the Chechen–Russian conflict secular Chechens using terrorist tactics fighting for national independence are allied with radical Islamist terrorists who have arrived from other countries.Personal and social factors
Various personal and social factors may influence the personal choice of whether to join a terrorist group or attempt an act of terror, including: * Identity (social science), Identity, including affiliation with a particular culture, ethnicity, or religion * Previous exposure to violence * Financial reward (for example, the Palestinian Authority Martyrs Fund) * Mental health disorder * Social isolation * Perception that the cause responds to a profound injustice or indignity A report conducted by Paul Gill, John Horgan and Paige Deckert found that for "lone wolf" terrorists: * 43% were motivated by religious beliefs * 32% had pre-existing mental health disorders, while many more are found to have mental health problems upon arrest * At least 37% lived alone at the time of their event planning and/or execution, a further 26% lived with others, and no data were available for the remaining cases * 40% were unemployed at the time of their arrest or terrorist event * 19% subjectively experienced being disrespected by others * 14% percent experienced being the victim of verbal or physical assault Ariel Merari, a psychologist who has studied the psychological profiles of suicide terrorists since 1983 through media reports that contained biographical details, interviews with the suicides' families, and interviews with jailed would-be Suicide attack, suicide attackers, concluded that they were unlikely to be psychologically abnormal. In comparison to economic theories of criminal behaviour, Scott Atran found that suicide terrorists exhibit none of the socially dysfunctional attributes—such as fatherless, friendless, jobless situations—or suicidal symptoms. By which he means, they do not kill themselves simply out of hopelessness or a sense of 'having nothing to lose'. Abrahm suggests that terrorist organizations do not select terrorism for its political effectiveness. Individual terrorists tend to be motivated more by a desire for social solidarity with other members of their organization than by political platforms or strategic objectives, which are often murky and undefined. Michael Mousseau shows possible relationships between the type of economy within a country and ideology associated with terrorism. Many terrorists have a history of domestic violence.Democracy and domestic terrorism
Terrorism is most common in nations with intermediate political freedom, and it is least common in the most democratic nations. Some examples of "terrorism" in non-democratic nations include ETA (separatist group), ETA in Spain under Francisco Franco (although the group's terrorist activities increased sharply after Franco's death), the Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists in pre-war Second Polish Republic, Poland, the Shining Path in Peru under Alberto Fujimori, the Kurdistan Workers Party when Turkey was ruled by military leaders and the African National Congress, ANC in South Africa. Democracies, such as Japan, the United Kingdom, the United States, Israel, Indonesia, India, Spain, Germany, Italy and the Philippines, have experienced domestic terrorism. While a democratic nation espousing civil liberties may claim a sense of higher moral ground than other regimes, an act of terrorism within such a state may cause a dilemma: whether to maintain its civil liberties and thus risk being perceived as ineffective in dealing with the problem; or alternatively to restrict its civil liberties and thus risk delegitimizing its claim of supporting civil liberties. For this reason, homegrown terrorism has started to be seen as a greater threat, as stated by former CIA Director Michael Hayden. This dilemma, some social theorists would conclude, may very well play into the initial plans of the acting terrorist(s); namely, to delegitimize the state and cause a systematic shift towards anarchy via the accumulation of negative sentiments towards the state system.Religious terrorism
 According to the Global Terrorism Index by the University of Maryland, College Park, religious extremism has overtaken Separatism, national separatism and become the main driver of terrorist attacks around the world. Since 9/11 there has been a five-fold increase in deaths from terrorist attacks. The majority of incidents over the past several years can be tied to groups with a religious agenda. Before 2000, it was nationalist separatist terrorist organizations such as the Provisional Irish Republican Army, IRA and Chechen rebels who were behind the most attacks. The number of incidents from nationalist separatist groups has remained relatively stable in the years since while religious extremism has grown. The prevalence of Islamist groups in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and Syria is the main driver behind these trends.
Five of the terrorist groups that have been most active since 2001 are Hamas, Boko Haram, al-Qaeda, the Taliban and Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIL. These groups have been most active in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and Syria. Eighty percent of all deaths from terrorism occurred in one of these five countries. In 2015 four Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist groups were responsible for 74% of all deaths from Islamic terrorism: Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIS, Boko Haram, the Taliban, and al-Qaeda, according to the Global Terrorism Index 2016. Since approximately 2000, these incidents have occurred on a global scale, affecting not only Muslim-majority countries, Muslim-majority states in Africa and Asia, but also states with non-Muslim majority such as Terrorism in the United States, United States, Terrorism in the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, Terrorism in France, France, Terrorism in Germany, Germany, Terrorism in Spain, Spain, Terrorist activity in Belgium, Belgium, Terrorism in Sweden, Sweden, Terrorism in Russia, Russia, Terrorism in Australia, Australia, Terrorism in Canada, Canada, Terrorism in Sri Lanka, Sri Lanka, Israel, Terrorism in China, China, Terrorism in India, India and Terrorism in the Philippines, Philippines. Such attacks have targeted both Muslims and non-Muslims, however the majority affect Muslims themselves.
Terrorism in Pakistan has become a great problem. From the summer of 2007 until late 2009, more than 1,500 people were killed in suicide attack, suicide and other attacks on civilians for reasons attributed to a number of causes—sectarian violence between Sunni and Shia Muslims; easy availability of guns and explosives; the existence of a "Kalashnikov rifle, Kalashnikov culture"; an influx of ideologically driven Muslims based AfPak, in or near Pakistan, who originated from various nations around the world and the subsequent war against the pro-Soviet Afghans in the 1980s which blew back into Pakistan; the presence of Islamist insurgent groups and forces such as the Taliban and Lashkar-e-Taiba. On July 2, 2013, in Lahore, 50 Muslim scholars of the Sunni Ittehad Council (SIC) issued a collective fatwa against suicide bombings, the killing of innocent people, bomb attacks, and targeted killings declaring them as Haraam or forbidden.
In 2015, the Southern Poverty Law Center released a report on terrorism in the United States. The report (titled ''The Age of the Wolf'') analyzed 62 incidents and found that, between 2009 and 2015, "more people have been killed in America by non-Islamic Domestic terrorism in the United States, domestic terrorists than Jihadism, jihadists." The "virulent racist and anti-semitic" ideology of the ultra-right wing Christian Identity movement is usually accompanied by anti-government sentiments.
According to the Global Terrorism Index by the University of Maryland, College Park, religious extremism has overtaken Separatism, national separatism and become the main driver of terrorist attacks around the world. Since 9/11 there has been a five-fold increase in deaths from terrorist attacks. The majority of incidents over the past several years can be tied to groups with a religious agenda. Before 2000, it was nationalist separatist terrorist organizations such as the Provisional Irish Republican Army, IRA and Chechen rebels who were behind the most attacks. The number of incidents from nationalist separatist groups has remained relatively stable in the years since while religious extremism has grown. The prevalence of Islamist groups in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and Syria is the main driver behind these trends.
Five of the terrorist groups that have been most active since 2001 are Hamas, Boko Haram, al-Qaeda, the Taliban and Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIL. These groups have been most active in Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and Syria. Eighty percent of all deaths from terrorism occurred in one of these five countries. In 2015 four Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist groups were responsible for 74% of all deaths from Islamic terrorism: Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, ISIS, Boko Haram, the Taliban, and al-Qaeda, according to the Global Terrorism Index 2016. Since approximately 2000, these incidents have occurred on a global scale, affecting not only Muslim-majority countries, Muslim-majority states in Africa and Asia, but also states with non-Muslim majority such as Terrorism in the United States, United States, Terrorism in the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, Terrorism in France, France, Terrorism in Germany, Germany, Terrorism in Spain, Spain, Terrorist activity in Belgium, Belgium, Terrorism in Sweden, Sweden, Terrorism in Russia, Russia, Terrorism in Australia, Australia, Terrorism in Canada, Canada, Terrorism in Sri Lanka, Sri Lanka, Israel, Terrorism in China, China, Terrorism in India, India and Terrorism in the Philippines, Philippines. Such attacks have targeted both Muslims and non-Muslims, however the majority affect Muslims themselves.
Terrorism in Pakistan has become a great problem. From the summer of 2007 until late 2009, more than 1,500 people were killed in suicide attack, suicide and other attacks on civilians for reasons attributed to a number of causes—sectarian violence between Sunni and Shia Muslims; easy availability of guns and explosives; the existence of a "Kalashnikov rifle, Kalashnikov culture"; an influx of ideologically driven Muslims based AfPak, in or near Pakistan, who originated from various nations around the world and the subsequent war against the pro-Soviet Afghans in the 1980s which blew back into Pakistan; the presence of Islamist insurgent groups and forces such as the Taliban and Lashkar-e-Taiba. On July 2, 2013, in Lahore, 50 Muslim scholars of the Sunni Ittehad Council (SIC) issued a collective fatwa against suicide bombings, the killing of innocent people, bomb attacks, and targeted killings declaring them as Haraam or forbidden.
In 2015, the Southern Poverty Law Center released a report on terrorism in the United States. The report (titled ''The Age of the Wolf'') analyzed 62 incidents and found that, between 2009 and 2015, "more people have been killed in America by non-Islamic Domestic terrorism in the United States, domestic terrorists than Jihadism, jihadists." The "virulent racist and anti-semitic" ideology of the ultra-right wing Christian Identity movement is usually accompanied by anti-government sentiments.. Anti-Defamation League 2017. Adherents of Christian Identity are not connected with specific Christian denominations, and they believe that White people, whites of European descent can be traced back to the "Ten Lost Tribes, Lost Tribes of Israel" and many consider Jews to be the Satanic offspring of Adam and Eve, Eve and the Serpents in the Bible, Serpent. This group has committed hate crimes, bombings and other acts of terrorism. Its influence ranges from the Ku Klux Klan and neo-Nazi groups to the anti-government Militia organizations in the United States, militia and sovereign citizen movements. Christian Identity's origins can be traced back to British Israelism, Anglo-Israelism, which held the view that the British people were descendants of ancient Israelites. However, in the United States, the ideology started to become rife with Antisemitism, anti-Semitism, and eventually Christian Identity theology diverged from the Philo-Semitism, philo-semitic Anglo-Israelism, and developed what is known as the Serpent seed, "two seed" theory. According to the two-seed theory, the Jewish people are descended from Cain and the serpent (not from Shem). The white European seedline is descended from the "lost tribes" of Israel. They hold themselves to "God's laws", not to "man's laws", and they do not feel bound to a government that they consider run by Jews and the New World Order (conspiracy theory), New World Order. The Ku Klux Klan is widely denounced by Christian denominations.
 Israel has had problems with Jewish religious terrorism even before independence in 1948. During Mandate for Palestine, British mandate over Palestine, the Irgun were among the Zionist groups labelled as terrorist organisations by the British authorities and United Nations, for violent terror attacks against Britons and Arabs. Another extremist group, the Lehi (militant group), Lehi, openly declared its members as "terrorists". Historian William Cleveland stated many Jews justified any action, even terrorism, taken in the cause of the creation of a Jewish state. In 1995, Yigal Amir assassinated Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin. For Amir, killing Rabin was an exemplary act that symbolized the fight against an illegitimate government that was prepared to cede Jewish Holy Land to the Palestinians.
Israel has had problems with Jewish religious terrorism even before independence in 1948. During Mandate for Palestine, British mandate over Palestine, the Irgun were among the Zionist groups labelled as terrorist organisations by the British authorities and United Nations, for violent terror attacks against Britons and Arabs. Another extremist group, the Lehi (militant group), Lehi, openly declared its members as "terrorists". Historian William Cleveland stated many Jews justified any action, even terrorism, taken in the cause of the creation of a Jewish state. In 1995, Yigal Amir assassinated Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin. For Amir, killing Rabin was an exemplary act that symbolized the fight against an illegitimate government that was prepared to cede Jewish Holy Land to the Palestinians.
Perpetrators
 The perpetrators of acts of terrorism can be individuals, groups, or states. According to some definitions, clandestine or semi-clandestine state actors may carry out terrorist acts outside the framework of a state of war. The most common image of terrorism is that it is carried out by small and secretive Covert cell, cells, highly motivated to serve a particular cause and many of the most deadly operations in recent times, such as the September 11 attacks, the 7 July 2005 London bombings, London underground bombing, 2008 Mumbai attacks and the 2002 Bali bombing were planned and carried out by a close clique, composed of close friends, family members and other strong social networks. These groups benefited from the free flow of information and efficient telecommunications to succeed where others had failed.
Over the years, much research has been conducted to distill a terrorist profile to explain these individuals' actions through their psychology and socio-economic circumstances. Others, like Roderick Hindery, have sought to discern profiles in the propaganda tactics used by terrorists. Some security organizations designate these groups as ''violent non-state actors''. A 2007 study by economist Alan B. Krueger found that terrorists were less likely to come from an impoverished background (28 percent versus 33 percent) and more likely to have at least a high-school education (47 percent versus 38 percent). Another analysis found only 16 percent of terrorists came from impoverished families, versus 30 percent of male Palestinians, and over 60 percent had gone beyond high school, versus 15 percent of the populace.A study into the poverty-stricken conditions and whether terrorists are more likely to come from here,show that people who grew up in these situations tend to show aggression and frustration towards others. This theory is largely debated for the simple fact that just because one is frustrated,does not make them a potential terrorist.
To avoid detection, a terrorist will look, dress, and behave normally until executing the assigned mission. Some claim that attempts to profile terrorists based on personality, physical, or sociological traits are not useful. The physical and behavioral description of the terrorist could describe almost any normal person.Library of Congress
The perpetrators of acts of terrorism can be individuals, groups, or states. According to some definitions, clandestine or semi-clandestine state actors may carry out terrorist acts outside the framework of a state of war. The most common image of terrorism is that it is carried out by small and secretive Covert cell, cells, highly motivated to serve a particular cause and many of the most deadly operations in recent times, such as the September 11 attacks, the 7 July 2005 London bombings, London underground bombing, 2008 Mumbai attacks and the 2002 Bali bombing were planned and carried out by a close clique, composed of close friends, family members and other strong social networks. These groups benefited from the free flow of information and efficient telecommunications to succeed where others had failed.
Over the years, much research has been conducted to distill a terrorist profile to explain these individuals' actions through their psychology and socio-economic circumstances. Others, like Roderick Hindery, have sought to discern profiles in the propaganda tactics used by terrorists. Some security organizations designate these groups as ''violent non-state actors''. A 2007 study by economist Alan B. Krueger found that terrorists were less likely to come from an impoverished background (28 percent versus 33 percent) and more likely to have at least a high-school education (47 percent versus 38 percent). Another analysis found only 16 percent of terrorists came from impoverished families, versus 30 percent of male Palestinians, and over 60 percent had gone beyond high school, versus 15 percent of the populace.A study into the poverty-stricken conditions and whether terrorists are more likely to come from here,show that people who grew up in these situations tend to show aggression and frustration towards others. This theory is largely debated for the simple fact that just because one is frustrated,does not make them a potential terrorist.
To avoid detection, a terrorist will look, dress, and behave normally until executing the assigned mission. Some claim that attempts to profile terrorists based on personality, physical, or sociological traits are not useful. The physical and behavioral description of the terrorist could describe almost any normal person.Library of Congress– Federal Research Division ''The Sociology and Psychology of Terrorism''. the majority of terrorist attacks are carried out by military age men, aged 16 to 40.
Non-state groups
 Groups not part of the state apparatus of in opposition to the state are most commonly referred to as a "terrorist" in the media.
According to the Global Terrorism Database, the most active terrorist group in the period 1970 to 2010 was Shining Path (with 4,517 attacks), followed by Farabundo Marti National Liberation Front (FMLN), Provisional Irish Republican Army, Irish Republican Army (IRA), Basque Fatherland and Freedom (ETA), Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), Taliban, Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, New People's Army, National Liberation Army of Colombia (ELN), and Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK).
Groups not part of the state apparatus of in opposition to the state are most commonly referred to as a "terrorist" in the media.
According to the Global Terrorism Database, the most active terrorist group in the period 1970 to 2010 was Shining Path (with 4,517 attacks), followed by Farabundo Marti National Liberation Front (FMLN), Provisional Irish Republican Army, Irish Republican Army (IRA), Basque Fatherland and Freedom (ETA), Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), Taliban, Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam, New People's Army, National Liberation Army of Colombia (ELN), and Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK).
State sponsors
A state can sponsor terrorism by funding or harboring a terrorist group. Opinions as to which acts of violence by states consist of state-sponsored terrorism vary widely. When states provide funding for groups considered by some to be terrorist, they rarely acknowledge them as such.State terrorism
 As with "terrorism" the concept of "state terrorism" is controversial. The Chairman of the United Nations Counter-Terrorism Committee has stated that the committee was conscious of 12 international conventions on the subject, and none of them referred to state terrorism, which was not an international legal concept. If states abused their power, they should be judged against international conventions dealing with war crimes, international human rights law, and international humanitarian law. Former United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan has said that it is "time to set aside debates on so-called 'state terrorism'. The Use of force in international law, use of force by states is already thoroughly regulated under international law". he made clear that, "regardless of the differences between governments on the question of the definition of terrorism, what is clear and what we can all agree on is that any deliberate attack on innocent civilians [or non-combatants], regardless of one's cause, is unacceptable and fits into the definition of terrorism."
State terrorism has been used to refer to terrorist acts committed by governmental agents or forces. This involves the use of state resources employed by a state's foreign policies, such as using its military to directly perform acts of terrorism. Professor of Political Science Michael Stohl cites the examples that include the German The Blitz, bombing of London, the Allies of World War II, Allied Bombing of Dresden in World War II, firebombing of Dresden, and the U.S. atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during World War II. He argues that "the use of terror tactics is common in international relations and the state has been and remains a more likely employer of terrorism within the international system than insurgents." He cites the Pre-emptive nuclear strike, first strike option as an example of the "terror of coercive diplomacy" as a form of this, which holds the world hostage with the implied threat of using nuclear weapons in "crisis management" and he argues that the institutionalized form of terrorism has occurred as a result of changes that took place following World War II. In this analysis, state terrorism exhibited as a form of foreign policy was shaped by the presence and use of Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction, and the legitimizing of such violent behavior led to an increasingly accepted form of this behavior by the state.
As with "terrorism" the concept of "state terrorism" is controversial. The Chairman of the United Nations Counter-Terrorism Committee has stated that the committee was conscious of 12 international conventions on the subject, and none of them referred to state terrorism, which was not an international legal concept. If states abused their power, they should be judged against international conventions dealing with war crimes, international human rights law, and international humanitarian law. Former United Nations Secretary-General Kofi Annan has said that it is "time to set aside debates on so-called 'state terrorism'. The Use of force in international law, use of force by states is already thoroughly regulated under international law". he made clear that, "regardless of the differences between governments on the question of the definition of terrorism, what is clear and what we can all agree on is that any deliberate attack on innocent civilians [or non-combatants], regardless of one's cause, is unacceptable and fits into the definition of terrorism."
State terrorism has been used to refer to terrorist acts committed by governmental agents or forces. This involves the use of state resources employed by a state's foreign policies, such as using its military to directly perform acts of terrorism. Professor of Political Science Michael Stohl cites the examples that include the German The Blitz, bombing of London, the Allies of World War II, Allied Bombing of Dresden in World War II, firebombing of Dresden, and the U.S. atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during World War II. He argues that "the use of terror tactics is common in international relations and the state has been and remains a more likely employer of terrorism within the international system than insurgents." He cites the Pre-emptive nuclear strike, first strike option as an example of the "terror of coercive diplomacy" as a form of this, which holds the world hostage with the implied threat of using nuclear weapons in "crisis management" and he argues that the institutionalized form of terrorism has occurred as a result of changes that took place following World War II. In this analysis, state terrorism exhibited as a form of foreign policy was shaped by the presence and use of Weapon of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction, and the legitimizing of such violent behavior led to an increasingly accepted form of this behavior by the state.

Justice Betrayed: Post-1945 Responses to Genocide
" In David A. Blumenthal and Timothy L.H. McCormack (eds).
The Legacy of Nuremberg: Civilising Influence or Institutionalised Vengeance? (International Humanitarian Law).
'' Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. pp
71
80–81
/ref>
Connection with tourism
The connection between terrorism and tourism has been widely studied since the Luxor massacre in Egypt. In the 1970s, the targets of terrorists were politicians and chiefs of police while now, international tourists and visitors are selected as the main targets of attacks. The attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon on September 11, 2001, were the symbolic center, which marked a new epoch in the use of civil transport against the main power of the planet. From this event onwards, the spaces of leisure that characterized the pride of West were conceived as dangerous and frightful.Funding
State-sponsored terrorism, State sponsors have constituted a major form of funding; for example, Palestine Liberation Organization, Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine and other groups sometimes considered to be terrorist organizations, were funded by the Soviet Union. The Stern Gang received funding from Italian Fascism, Italian Fascist officers in Beirut to undermine the Mandatory Palestine, British authorities in Palestine. "Revolutionary tax" is another major form of funding, and essentially a euphemism for "protection money".Detection of Terrorist Financing, U.S. National Credit Union Administration (NCUA), 2002. Revolutionary taxes "play a secondary role as one other means of intimidating the target population". Other major sources of funding include kidnapping for ransoms, smuggling (including wildlife smuggling), fraud, and robbery. The Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant has reportedly received funding "via private donations from the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Gulf states". The Financial Action Task Force is an inter-governmental body whose mandate, since October 2001, has included combating terrorist financing.
Tactics
 Terrorist attacks are often targeted to maximize fear and publicity, most frequently using explosives.
Terrorist groups usually methodically plan attacks in advance, and may train participants, plant undercover agents, and raise money from supporters or through organized crime. Communications occur through modern telecommunications, or through old-fashioned methods such as couriers. There is concern about terrorist attacks employing weapons of mass destruction. Some academics have argued that while it is often assumed terrorism is intended to spread fear, this is not necessarily true, with fear instead being a by-product of the terrorist's actions, while their intentions may be to avenge fallen comrades or destroy their perceived enemies.
Terrorism is a form of asymmetric warfare, and is more common when direct conventional warfare will not be effective because opposing forces vary greatly in power. Yuval Harari argues that the peacefulness of modern states makes them paradoxically more vulnerable to terrorism than pre-modern states. Harari argues that because modern states have committed themselves to reducing political violence to almost zero, terrorists can, by creating political violence, threaten the very foundations of the legitimacy of the modern state. This is in contrast to pre-modern states, where violence was a routine and recognised aspect of politics at all levels, making political violence unremarkable. Terrorism thus shocks the population of a modern state far more than a pre-modern one and consequently the state is forced to overreact in an excessive, costly and spectacular manner, which is often what the terrorists desire.
The type of people terrorists will target is dependent upon the ideology of the terrorists. A terrorist's ideology will create a class of "legitimate targets" who are deemed as its enemies and who are permitted to be targeted. This ideology will also allow the terrorists to place the blame on the victim, who is viewed as being responsible for the violence in the first place.
The context in which terrorist tactics are used is often a large-scale, unresolved political conflict. The type of conflict varies widely; historical examples include:
* Secession of a territory to form a new sovereign state or become part of a different state
* Dominance of territory or resources by various ethnic groups
* Imposition of a particular form of government
* Economic deprivation of a population
* Opposition to a domestic government or occupying army
* Religious fanaticism
Terrorist attacks are often targeted to maximize fear and publicity, most frequently using explosives.
Terrorist groups usually methodically plan attacks in advance, and may train participants, plant undercover agents, and raise money from supporters or through organized crime. Communications occur through modern telecommunications, or through old-fashioned methods such as couriers. There is concern about terrorist attacks employing weapons of mass destruction. Some academics have argued that while it is often assumed terrorism is intended to spread fear, this is not necessarily true, with fear instead being a by-product of the terrorist's actions, while their intentions may be to avenge fallen comrades or destroy their perceived enemies.
Terrorism is a form of asymmetric warfare, and is more common when direct conventional warfare will not be effective because opposing forces vary greatly in power. Yuval Harari argues that the peacefulness of modern states makes them paradoxically more vulnerable to terrorism than pre-modern states. Harari argues that because modern states have committed themselves to reducing political violence to almost zero, terrorists can, by creating political violence, threaten the very foundations of the legitimacy of the modern state. This is in contrast to pre-modern states, where violence was a routine and recognised aspect of politics at all levels, making political violence unremarkable. Terrorism thus shocks the population of a modern state far more than a pre-modern one and consequently the state is forced to overreact in an excessive, costly and spectacular manner, which is often what the terrorists desire.
The type of people terrorists will target is dependent upon the ideology of the terrorists. A terrorist's ideology will create a class of "legitimate targets" who are deemed as its enemies and who are permitted to be targeted. This ideology will also allow the terrorists to place the blame on the victim, who is viewed as being responsible for the violence in the first place.
The context in which terrorist tactics are used is often a large-scale, unresolved political conflict. The type of conflict varies widely; historical examples include:
* Secession of a territory to form a new sovereign state or become part of a different state
* Dominance of territory or resources by various ethnic groups
* Imposition of a particular form of government
* Economic deprivation of a population
* Opposition to a domestic government or occupying army
* Religious fanaticism
Responses
 Responses to terrorism are broad in scope. They can include re-alignments of the political spectrum and reassessments of value system, fundamental values.
Specific types of responses include:
* Anti-terrorism legislation, Targeted laws, criminal procedures, deportations, and enhanced police powers
* Target hardening, such as locking doors or adding traffic barriers
* Preemptive strike, Preemptive or reactive military action
* Increased police intelligence, intelligence and surveillance activities
* Preemptive humanitarian activities
* More permissive interrogation and Detention (imprisonment), detention policies
The term "counter-terrorism" has a narrower connotation, implying that it is directed at terrorist actors.
Responses to terrorism are broad in scope. They can include re-alignments of the political spectrum and reassessments of value system, fundamental values.
Specific types of responses include:
* Anti-terrorism legislation, Targeted laws, criminal procedures, deportations, and enhanced police powers
* Target hardening, such as locking doors or adding traffic barriers
* Preemptive strike, Preemptive or reactive military action
* Increased police intelligence, intelligence and surveillance activities
* Preemptive humanitarian activities
* More permissive interrogation and Detention (imprisonment), detention policies
The term "counter-terrorism" has a narrower connotation, implying that it is directed at terrorist actors.
Terrorism research
Terrorism research, also called terrorism studies, or terrorism and counter-terrorism research, is an interdisciplinary academic field which seeks to understand the causes of terrorism, how to prevent it as well as its impact in the broadest sense. Terrorism research can be carried out in both military and civilian contexts, for example by research centres such as the British Centre for the Study of Terrorism and Political Violence, the Norwegian Centre for Violence and Traumatic Stress Studies, and the International Centre for Counter-Terrorism (ICCT). There are several academic journals devoted to the field, including ''Perspectives on Terrorism''.International agreements
One of the agreements that promote the international legal anti-terror framework is the Code of Conduct Towards Achieving a World Free of Terrorism that was adopted at the 73rd session of the United Nations General Assembly in 2018. The Code of Conduct was initiated by Kazakhstan President Nursultan Nazarbayev. Its main goal is to implement a wide range of international commitments to counter terrorism and establish a broad global coalition towards achieving a world free of terrorism by 2045. The Code was signed by more than 70 countries.Response in the United States
 According to a report by Dana Priest and William M. Arkin in The Washington Post, "Some 1,271 government organizations and 1,931 private companies work on programs related to counterterrorism, homeland security and intelligence in about 10,000 locations across the United States."
America's thinking on how to defeat radical Islamists is split along two very different schools of thought. Republicans, typically follow what is known as the Bush Doctrine, advocate the military model of taking the fight to the enemy and seeking to democratize the Middle East. Democrats, by contrast, generally propose the law enforcement model of better cooperation with nations and more security at home.Ankony, Robert C., "A New Strategy for America's War on Terrorism", ''Patrolling'' magazine, 75th Ranger Regiment Association, Winter 2011, 56–57. In the introduction of the ''U.S. Army / Marine Corps Counterinsurgency Field Manual'', Sarah Sewall states the need for "U.S. forces to make securing the civilian, rather than destroying the enemy, their top priority. The civilian population is the center of gravity—the deciding factor in the struggle.... Civilian deaths create an extended family of enemies—new insurgent recruits or informants—and erode support of the host nation." Sewall sums up the book's key points on how to win this battle: "Sometimes, the more you protect your force, the less secure you may be.... Sometimes, the more force is used, the less effective it is.... The more successful the counterinsurgency is, the less force can be used and the more risk must be accepted.... Sometimes, doing nothing is the best reaction." This strategy, often termed "courageous restraint", has certainly led to some success on the Middle East battlefield. However, it does not address the fact that terrorists are mostly homegrown.
According to a report by Dana Priest and William M. Arkin in The Washington Post, "Some 1,271 government organizations and 1,931 private companies work on programs related to counterterrorism, homeland security and intelligence in about 10,000 locations across the United States."
America's thinking on how to defeat radical Islamists is split along two very different schools of thought. Republicans, typically follow what is known as the Bush Doctrine, advocate the military model of taking the fight to the enemy and seeking to democratize the Middle East. Democrats, by contrast, generally propose the law enforcement model of better cooperation with nations and more security at home.Ankony, Robert C., "A New Strategy for America's War on Terrorism", ''Patrolling'' magazine, 75th Ranger Regiment Association, Winter 2011, 56–57. In the introduction of the ''U.S. Army / Marine Corps Counterinsurgency Field Manual'', Sarah Sewall states the need for "U.S. forces to make securing the civilian, rather than destroying the enemy, their top priority. The civilian population is the center of gravity—the deciding factor in the struggle.... Civilian deaths create an extended family of enemies—new insurgent recruits or informants—and erode support of the host nation." Sewall sums up the book's key points on how to win this battle: "Sometimes, the more you protect your force, the less secure you may be.... Sometimes, the more force is used, the less effective it is.... The more successful the counterinsurgency is, the less force can be used and the more risk must be accepted.... Sometimes, doing nothing is the best reaction." This strategy, often termed "courageous restraint", has certainly led to some success on the Middle East battlefield. However, it does not address the fact that terrorists are mostly homegrown.
Mass media
 Mass media exposure may be a primary goal of those carrying out terrorism, to expose issues that would otherwise be ignored by the media. Some consider this to be manipulation and exploitation of the media.
The Internet has created a new way for groups to spread their messages. This has created a cycle of measures and counter measures by groups in support of and in opposition to terrorist movements. The United Nations has created its own online counter-terrorism resource.
The mass media will, on occasion, censor organizations involved in terrorism (through self-restraint or regulation) to discourage further terrorism. This may encourage organizations to perform more extreme acts of terrorism to be shown in the mass media. Conversely James F. Pastor explains the significant relationship between terrorism and the media, and the underlying benefit each receives from the other.
Former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously spoke of the close connection between terrorism and the media, calling publicity 'the oxygen of terrorism'.
Mass media exposure may be a primary goal of those carrying out terrorism, to expose issues that would otherwise be ignored by the media. Some consider this to be manipulation and exploitation of the media.
The Internet has created a new way for groups to spread their messages. This has created a cycle of measures and counter measures by groups in support of and in opposition to terrorist movements. The United Nations has created its own online counter-terrorism resource.
The mass media will, on occasion, censor organizations involved in terrorism (through self-restraint or regulation) to discourage further terrorism. This may encourage organizations to perform more extreme acts of terrorism to be shown in the mass media. Conversely James F. Pastor explains the significant relationship between terrorism and the media, and the underlying benefit each receives from the other.
Former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher famously spoke of the close connection between terrorism and the media, calling publicity 'the oxygen of terrorism'.
Outcome of terrorist groups
Databases
The following terrorism databases are or were made publicly available for research purposes, and track specific acts of terrorism: * Global Terrorism Database, an open-source database by the University of Maryland, College Park on terrorist events around the world from 1970 through 2017 with more than 150,000 cases. * MIPT Terrorism Knowledge Base * Worldwide Incidents Tracking System * Tocsearch (dynamic database) The following public report and index provides a summary of key global trends and patterns in terrorism around the world * Global Terrorism Index, produced annually by the Institute for Economics and Peace The following publicly available resources index electronic and bibliographic resources on the subject of terrorism * Human Security Gateway The following terrorism databases are maintained in secrecy by the United States Government for intelligence and counter-terrorism purposes: * Terrorist Identities Datamart Environment * Terrorist Screening Database Jones and Libicki (2008) includes a table of 268 terrorist groups active between 1968 and 2006 with their status as of 2006: still active, splintered, converted to nonviolence, removed by law enforcement or military, or won. (These data are not in a convenient machine-readable format but are available.)See also
Notes
References
* * ** * *Perspectives on Terrorism's Bibliography: Root Causes of Terrorism. 2017.
Further reading
* Bakker, Edwin''Forecasting the Unpredictable: A Review of Forecasts on Terrorism 2000–2012'' (International Centre for Counter-Terrorism – The Hague, 2014)
* * Burleigh, Michael. ''Blood and rage: a cultural history of terrorism''. Harper, 2009. * Chaliand, Gérard and Arnaud Blin, eds. ''The history of terrorism: from antiquity to al Qaeda''. University of California Press, 2007. * Coates, Susan W., Rosenthal, Jane, and Schechter, Daniel S. ''September 11: Trauma and Human Bonds'' (New York: Taylor and Francis, Inc., 2003). * Crenshaw, Martha, ed. ''Terrorism in context''. Pennsylvania State University Press, 1995. * * Hennigfeld, Ursula/ Packard, Stephan, ed., ''Abschied von 9/11? Distanznahme zur Katastrophe''. Berlin: Frank & Timme, 2013. * Hennigfeld, Ursula, ed., ''Poetiken des Terrors. Narrative des 11. September 2001 im interkulturellen Vergleich''. Heidelberg: Winter, 2014. * Hewitt, Christopher. ''Understanding terrorism in America'' (Routledge, 2003). * Hewitt, Christopher. "Terrorism and public opinion: A five country comparison." ''Terrorism and Political Violence'' 2.2 (1990): 145-170. * Jones, Sidney.
Terrorism: myths and facts
'. Jakarta: International Crisis Group, 2013. * Land, Isaac, ed., ''Enemies of humanity: the nineteenth-century war on terrorism''. Palgrave Macmillan, 2008. * Lee, Newton. ''Counterterrorism and Cybersecurity: Total Information Awareness (2nd Edition)''. New York: Springer, 2015. * Lutz, James and Brenda Lutz. ''Terrorism : origins and evolution'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2005) * Miller, Martin A. ''The foundations of modern terrorism : state, society and the dynamics of political violence''. Cambridge University Press, 2013. * * Neria, Yuval, Gross, Raz, Marshall, Randall D., and Susser, Ezra. ''September 11, 2001: Treatment, Research and Public Mental Health in the Wake of a Terrorist Attack'' (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2006). * An open-access publication, issued since November 2020 on the International Centre for Counter-Terrorism (ICCT) website, with a chapter published each week. * Stern, Jessica. ''The Ultimate Terrorists''. (Harvard University Press 2000 reprint; 1995). 214 p. * Tausch, Arno
Estimates on the Global Threat of Islamic State Terrorism in the Face of the 2015 Paris and Copenhagen Attacks
(December 11, 2015). ''Middle East Review of International Affairs'', Rubin Center, Research in International Affairs, Idc Herzliya, Israel, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Spring 2015). *
Terrorism, Law & Democracy: 10 years after 9/11
', Canadian Institute for the Administration of Justice. .
United Kingdom
* Blackbourn, Jessie. "Counter-Terrorism and Civil Liberties: The United Kingdom Experience, 1968-2008." ''Journal of the Institute of Justice and International Studies'' 8 (2008): 63+ * Bonner, David. "United Kingdom: the United Kingdom response to terrorism." ''Terrorism and Political Violence'' 4.4 (1992): 171-205online
* Chin, Warren. ''Britain and the war on terror: Policy, strategy and operations'' (Routledge, 2016). * Clutterbuck, Lindsay. "Countering Irish Republican terrorism in Britain: Its origin as a police function." ''Terrorism and Political Violence'' 18.1 (2006) pp: 95-118. * Greer, Steven. "Terrorism and Counter-Terrorism in the UK: From Northern Irish Troubles to Global Islamist Jihad." in ''Counter-Terrorism, Constitutionalism and Miscarriages of Justice'' (Hart Publishing, 2018) pp. 45-62. * Hamilton, Claire. "Counter-Terrorism in the UK." in ''Contagion, Counter-Terrorism and Criminology'' (Palgrave Pivot, Cham, 2019) pp. 15-47. * Hewitt, Steve. "Great Britain: Terrorism and counter-terrorism since 1968." in ''Routledge Handbook of Terrorism and Counterterrorism'' (Routledge, 2018) pp. 540-551. * Martínez-Peñas, Leandro, and Manuela Fernández-Rodríguez. "Evolution of British Law on Terrorism: From Ulster to Global Terrorism (1970–2010)." in ''Post 9/11 and the State of Permanent Legal Emergency'' (Springer, 2012) pp. 201-222. * O'Day, Alan. "Northern Ireland, Terrorism, and the British State." in ''Terrorism: Theory and Practice'' (Routledge, 2019) pp. 121-135. * Sacopulos, Peter J. "Terrorism in Britain: Threat, reality, response." ''Studies in Conflict & Terrorism'' 12.3 (1989): 153-165. * Staniforth, Andrew, and Fraser Sampson, eds. ''The Routledge companion to UK counter-terrorism'' (Routledge, 2012). * Sinclair, Georgina. "Confronting terrorism: British Experiences past and present." ''Crime, Histoire & Sociétés/Crime, History & Societies'' 18.2 (2014): 117-122
online
* Tinnes, Judith, ed. "Bibliography: Northern Ireland conflict (the troubles)." ''Perspectives on Terrorism'' 10.1 (2016): 83-110
online
* Wilkinson, Paul, ed. ''Terrorism: British Perspectives'' (Dartmouth, 1993).
External links
* United NationsConventions on Terrorism
* United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime:
UNODC – United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime – Terrorism Prevention
Terrorism and international humanitarian law
International Committee of the Red Cross
UK Counter Terrorism Policing
{{Authority control Terrorism, Crimes Warfare by type 1790s neologisms