Ethnic groups in Italy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This article is about the
This article is about the
 Demographic statistics according to the World Population Review in 2022.
*One birth every 6 minutes
*One death every 4 minutes
*Net loss of one person every 16 minutes
*One net migrant every 45 minutes
Demographic statistics according to the World Population Review in 2022.
*One birth every 6 minutes
*One death every 4 minutes
*Net loss of one person every 16 minutes
*One net migrant every 45 minutes
 Sources:
Sources:
 The
The  In 2021 this was 1.47 children born/woman.
Mother's mean age at first birth; 31.1 years (2017 est.)
In 2021 this was 1.47 children born/woman.
Mother's mean age at first birth; 31.1 years (2017 est.)

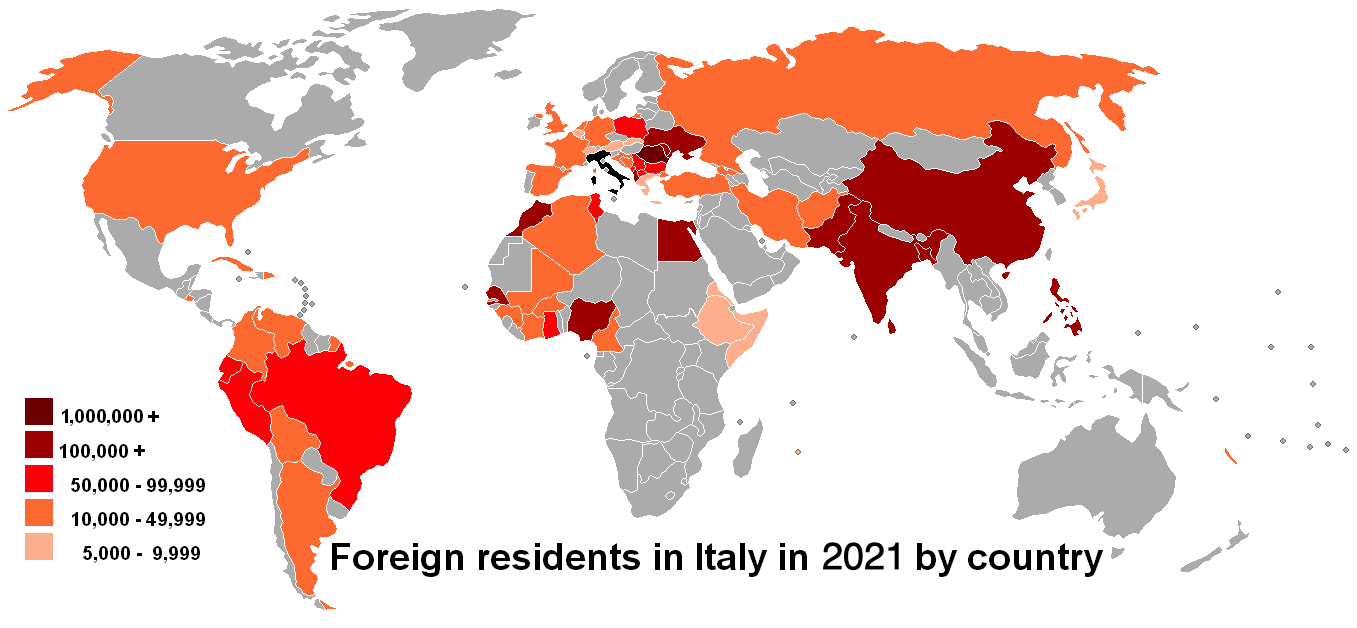 There are, as of 2021, 6,262,207 Foreign-born residents, accounting for 10.6% of the total population.
Their distribution by country of origin was as follows:
There are, as of 2021, 6,262,207 Foreign-born residents, accounting for 10.6% of the total population.
Their distribution by country of origin was as follows:
 Italy's official language is Italian;
Italy's official language is Italian;
– Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2005. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International. Online version Italian, adopted by the central state after the
 Even though the main Christian denomination in Italy is Roman Catholicism, there are some minorities of
Even though the main Christian denomination in Italy is Roman Catholicism, there are some minorities of
 The
The
Demographic page
Allianz Knowledge {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics of Italy Demographics of Italy,
 This article is about the
This article is about the demographic
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as ed ...
features of the population of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, including population density
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopu ...
, ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations Religious identity is a specific type of identity formation. Particularly, it is the sense of group membership to a religion and the importance of this group membership as it pertains to one's self-concept. Religious identity is not necessarily the ...
and other aspects of the population.
At the beginning of 2022, Italy had an estimated population of 58,9 million. Its population density, at , is higher than that of most Western European countries. However, the distribution of the population is widely uneven; the most densely populated areas are the Po Valley
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of Northern Italy. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic ex ...
(which contains about a third of the country's population) in northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative region ...
and the metropolitan areas of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
in central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half.
The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the pe ...
, while other vast areas are very sparsely populated, like the plateaus of Basilicata
it, Lucano (man) it, Lucana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
...
, the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
and Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
highlands, and the island of Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
.
The population of the country almost doubled during the twentieth century, but the pattern of growth was extremely uneven due to large-scale internal migration Internal migration or domestic migration is human migration within a country. Internal migration tends to be travel for education and for economic improvement or because of a natural disaster or civil disturbance, though a study based on the full ...
from the rural South to the industrial cities of the North, a phenomenon which happened as a consequence of the Italian economic miracle
The Italian economic miracle or Italian economic boom ( it, il miracolo economico italiano) is the term used by historians, economists, and the mass media to designate the prolonged period of strong economic growth in Italy after the Second Worl ...
of the 1950–1960s. In addition, after centuries of net emigration, from the 1980s Italy has experienced large-scale immigration for the first time in modern history. According to the Italian government, there were an estimated 5,234,000 foreign nationals resident in Italy on 1 January 2019.
High fertility and birth rates persisted until the 1970s, after which they started to dramatically decline, leading to rapid population aging. At the end of the first decade of the 21st century, one in five Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
was over 65 years old. Italy has experienced a short growth in birth rates. The total fertility rate had climbed temporary from an all-time low of 1.18 children per woman in 1995 to 1.46 in 2010. To drop again to 1.24 in 2020. Due to large scale migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
in the 2000s the total population reached its peak in 2014. Since then (lower) migration could not offset a shrinking population size, mainly due to the low birthrate, but also due to aging, the rising mortality.
Since the revised 1984 Lateran Treaty
The Lateran Treaty ( it, Patti Lateranensi; la, Pacta Lateranensia) was one component of the Lateran Pacts of 1929, agreements between the Kingdom of Italy under King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy and the Holy See under Pope Pius XI to settl ...
agreement, Italy has no official religion. However, it recognizes the role the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
plays in Italian society. In 2017, 78% of the population identified as Catholic, 15% as non-believers or atheists, 2% as other Christians and 6% adhered to other religions.
Historical overview
1861 to early 20th century
From its unification in 1861 to theItalian economic miracle
The Italian economic miracle or Italian economic boom ( it, il miracolo economico italiano) is the term used by historians, economists, and the mass media to designate the prolonged period of strong economic growth in Italy after the Second Worl ...
of the 1950s and 1960s, Italy has been a country of mass emigration. Between 1898 and 1914, the peak years of Italian diaspora
, image = Map of the Italian Diaspora in the World.svg
, image_caption = Map of the Italian diaspora in the world
, population = worldwide
, popplace = Brazil, Argentina, United States, France, Colombia, Canada, P ...
, approximately 750,000 Italians emigrated each year. As a consequence, large numbers of people with full or significant Italian ancestry are found in Brazil (25 million), Argentina (20 million), US (17.8 million), France (5 million), Venezuela (2 million), Uruguay (1.5 million), Canada (1.4 million), and Australia (800,000). In addition, Italian communities once thrived in the former African colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
of Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopi ...
(nearly 100,000 at the beginning of World War II), Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
and Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
(150,000 Italians settled in Libya, constituting about 18% of the total Libyan population).
After World War II
AfterTito
Tito may refer to:
People Mononyms
*Josip Broz Tito (1892–1980), commonly known mononymously as Tito, Yugoslav communist revolutionary and statesman
*Roberto Arias (1918–1989), aka Tito, Panamanian international lawyer, diplomat, and journal ...
's annexation of Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian and Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian, Italian and Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic betwe ...
, Kvarner
The Kvarner Gulf (, or , la, Sinus Flanaticus or ), sometimes also Kvarner Bay, is a bay in the northern Adriatic Sea, located between the Istrian peninsula and the northern Croatian Littoral mainland. The bay is a part of Croatia's internal ...
, most of the Julian March
Venezia Giulia, traditionally called Julian March (Serbo-Croatian, Slovene: ''Julijska krajina'') or Julian Venetia ( it, Venezia Giulia; vec, Venesia Julia; fur, Vignesie Julie; german: Julisch Venetien) is an area of southeastern Europe wh ...
as well as the Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, str ...
n city of Zara following the Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947
The Treaty of Paris between Italy and the Allied Powers was signed on 10 February 1947, formally ending hostilities between both parties. It came into general effect on 15 September 1947.
Territorial changes
* Transfer of the Adriatic islands ...
, up to 350,000 local ethnic Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
(Istrian Italians
Istrian Italians are an ethnic group from the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic region of Istria in modern northwestern Croatia and southwestern Slovenia. Istrian Italians descend from the original Latinized population of Roman Empire, Roman Istria#Early h ...
and Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro. Since the middle of the 19th century, the community, counting according to some sources nearly 20% of all Da ...
) left communist Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yugo ...
(Istrian–Dalmatian exodus
The Istrian–Dalmatian exodus (; ; ) was the post- World War II exodus and departure of local ethnic Italians ( Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) as well as ethnic Slovenes, Croats, and Istro-Romanians from the Yugoslav territory of ...
). Furthermore, all of Libya's Italians were expelled after Muammar Gaddafi's takeover in 1970.
As a result of the profound economic and social changes brought by rapid postwar economic growth, including low birth rates, an aging population and thus a shrinking workforce, by the 1970s emigration had all but stopped and Italy started to have a positive net migration rate. The nation's immigrant population reached 5 million by 2015, making up some 8% of the total population. However, the long-lasting effects of the Eurozone crisis
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies ...
double-dip recession strongly slowed down immigration rates in Italy in the 2010s.
Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic
As a direct effect of theCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
, Italy registered at least 100,000 excess deaths for 2020 only, a loss of about 1.4 years in the average life expectancy, a noticeable decrease in births rates and a marked decrease in immigration rates, the overall effect being a record natural population decline of 342,042 units in that year, the largest ever recorded since 1918 (at the time of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
).
Population
Life expectancy
Our World In Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, climate change, war, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Change Data Lab, a re ...
and the United Nations.
1871–1950
1950–2020
Source: ''UN World Population Prospects''
Fertility
total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
is the number of children born per woman. It is based on fairly good data for the entire period. Sources: Our World in Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, climate change, war, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Change Data Lab, a re ...
and Gapminder Foundation
Gapminder Foundation is a non-profit venture registered in Stockholm, Sweden, that promotes sustainable global development and achievement of the United Nations Millennium Development Goals
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eigh ...
.
 In 2021 this was 1.47 children born/woman.
Mother's mean age at first birth; 31.1 years (2017 est.)
In 2021 this was 1.47 children born/woman.
Mother's mean age at first birth; 31.1 years (2017 est.)
Age structure
:''0-14 years:'' 0–14 years: 13.45% (male 4,292,431/female 4,097,732) :''15-24 years:'' 9.61% (male 3,005,402/female 2,989,764) :''25-54 years:'' 40.86% (male 12,577,764/female 12,921,614) :''55-64 years:'' 14% (male 4,243,735/female 4,493,581) :''65 years and over:'' 22.08% (male 5,949,560/female 7,831,076) (2020 est. Median age : :total: 46.5 years. Country comparison to the world: 5th :male: 45.4 years :female: 47.5 years (2020 est.)Cities
70.4% of Italian population is classified asurban
Urban means "related to a city". In that sense, the term may refer to:
* Urban area, geographical area distinct from rural areas
* Urban culture, the culture of towns and cities
Urban may also refer to:
General
* Urban (name), a list of people ...
, a relatively low figure among developed countries. Italy's administrative boundaries have seen significant devolution
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
in recent decades; the metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually ...
was created as a new administrative unit, and major cities and metro areas now have a provincial status (similar to the concept of direct-controlled municipalities
A direct-controlled municipality is the highest level classification for cities used by unitary states, with status equal to that of the provinces in the respective countries. A direct-controlled municipality is similar to, but not the same as, a ...
in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
).
According to OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
, the largest conurbations are:
* Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
– 7.4 million
* Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
– 3.7 million
* Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
– 3.1 million
* Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
– 2.2 million
Urbanization
:
:urban population: 71% of total population (2020)
:rate of urbanization: 0.29% annual rate of change (2015–20 est.)

Vital statistics
In the year 2020 88,345 babies were born to at least one foreign parent which makes up 21.8% of all newborns in that year (21,024 or 5.2% were born to foreign mothers, 7,529 or 1.9% to foreign fathers and 59,792 or 14.8% to two foreign parents.Current vital statistics
Health
Obesity – adult prevalence rate : : 19.9% (2016) Country comparison to the world: 108Employment and income
Unemployment, youth ages 15–24: :total: 32.2%. Country comparison to the world: 26th :male: 30.4% :female: 34.8% (2018 est.)Immigration
Since the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989, and more recently, the2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight ...
and 2007
File:2007 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Steve Jobs unveils Apple Inc., Apple's first iPhone (1st generation), iPhone; TAM Airlines Flight 3054 overruns a runway and crashes into a gas station, killing almost 200 people; Former Pakis ...
enlargements of the European Union, Italy received growing flows of migrants from the former socialist countries of Eastern Europe (especially Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
). The second most important area of immigration to Italy has always been the neighboring North Africa (especially Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to A ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
). Furthermore, in recent years, growing migration fluxes from the Far East (notably, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
) and Latin America (Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
, Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
) have been recorded.
Italy does not collect data on ethnicity or race of the country, but does collect data on nationality of its residents.
In 2020, Istat estimated that 5,039,637 foreign citizens lived in Italy, representing about 8.4% of the total population. These figures do not include naturalized
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-citizen of a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. It may be done automatically by a statute, i.e., without any effort on the part of the in ...
foreign-born residents (121,457 foreigners acquired Italian citizenship
Italian nationality law is the law of Italy governing the acquisition, transmission and loss of Italian citizenship. Like many continental European countries it is largely based on ''jus sanguinis''. It also incorporates many elements that are ...
in 2021) as well as illegal immigrants
Illegal immigration is the migration of people into a country in violation of the immigration laws of that country or the continued residence without the legal right to live in that country. Illegal immigration tends to be financially upwa ...
, the so-called ''clandestini'', whose numbers, difficult to determine, are thought to be at least 670,000. Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Romania ...
made up the largest community in the country (1,145,718; around 10% of them being ethnic Romani people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic Itinerant groups in Europe, itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have Ro ...
), followed by Albanians
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Ser ...
(441,027) and Moroccans
Moroccans (, ) are the citizens and nationals of the Kingdom of Morocco. The country's population is predominantly composed of Arabs and Berbers (Amazigh). The term also applies more broadly to any people who are of Moroccan nationality, sh ...
(422,980).
The fourth largest, but the fastest growing, community of foreign residents in Italy was represented by the Chinese. The majority of Chinese living in Italy are from the city of Wenzhou
Wenzhou (pronounced ; Wenzhounese: Yuziou �y33–11 tɕiɤu33–32 ), historically known as Wenchow is a prefecture-level city in southeastern Zhejiang province in the People's Republic of China. Wenzhou is located at the extreme south east o ...
in the province of Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , also romanized as Chekiang) is an eastern, coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable cities include Ningbo and Wenzhou. Zhejiang is bordered by Ji ...
. Breaking down the foreign-born population by continent, in 2020 the figures were as follows: Europe (54%), Africa (22%), Asia (16%), the Americas (8%) and Oceania (0.06%). The distribution of immigrants is largely uneven in Italy: 83% of immigrants live in the northern and central parts of the country (the most economically developed areas), while only 17% live in the southern half of the peninsula.
;Net migration rate
:
: 3.21 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 34th
:
Languages
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' (stylized as ''Ethnoloɠue'') is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensi ...
has estimated that there are about 55 million speakers of Italian in the country and a further 6.7 million outside of it, primarily in the neighboring countries and in the Italian diaspora
, image = Map of the Italian Diaspora in the World.svg
, image_caption = Map of the Italian diaspora in the world
, population = worldwide
, popplace = Brazil, Argentina, United States, France, Colombia, Canada, P ...
worldwide.Ethnologue report for language code:ita (Italy)– Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2005. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International. Online version Italian, adopted by the central state after the
unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
, is a language based on the Florentine variety of Tuscan and is somewhat intermediate between the Italo-Dalmatian languages
The Italo-Dalmatian languages, or Central Romance languages, are a group of Romance languages spoken in Italy, Corsica (France), and formerly in Dalmatia (Croatia).
Italo-Dalmatian can be split into:Hammarström, Harald & Forkel, Robert & Haspe ...
and the Gallo-Romance languages
The Gallo-Romance branch of the Romance languages includes in the narrowest sense the Langues d'oïl and Franco-Provençal. However, other definitions are far broader, variously encompassing the Occitano-Romance, Gallo-Italic, and Rhaeto-Rom ...
. Its development was also influenced by the Germanic languages of the post-Roman invaders. When Italy unified in 1861, only 3% of the population spoke Italian, even though an estimated 90% of Italians speak Italian as their L1 nowadays.
Italy is in fact one of the most linguistically diverse countries in Europe, as there are not only varieties of Italian specific to each cultural region, but also distinct regional and minority languages. The establishment of the national education system has led to the emergence of the former and a decrease in the use of the latter. The spread of Italian was further expanded in the 1950s and 1960s, because of the economic growth and the rise of mass media and television, with the state broadcaster (RAI
RAI – Radiotelevisione italiana (; commercially styled as Rai since 2000; known until 1954 as Radio Audizioni Italiane) is the national public broadcasting company of Italy, owned by the Ministry of Economy and Finance. RAI operates many ter ...
) setting a colloquial variety of Italian to which the population would be exposed.
As a way to distance itself from the Italianization
Italianization ( it, italianizzazione; hr, talijanizacija; french: italianisation; sl, poitaljančevanje; german: Italianisierung; el, Ιταλοποίηση) is the spread of Italian culture, language and identity by way of integration or ass ...
policies promoted because of nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
, Italy recognized twelve languages as the Country's " historical linguistic minorities", which are promoted alongside Italian in their respective territories. French is co-official in the Aosta Valley
, Valdostan or Valdotainian it, Valdostano (man) it, Valdostana (woman)french: Valdôtain (man)french: Valdôtaine (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title = Official languages
, population_blank1 = Italian French
...
as the province's prestige variety
In sociolinguistics, prestige is the level of regard normally accorded a specific language or dialect within a speech community, relative to other languages or dialects. Prestige varieties are language or dialect families which are generally cons ...
, under which the more commonly spoken Franco-Provencal dialects have been historically roofed. German has the same status in the province of South Tyrol
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol
, settlement_type = Autonomous province
, image_skyline =
, image_alt ...
as, in some parts of that province and in parts of the neighbouring Trentino
Trentino ( lld, Trentin), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento, is an autonomous province of Italy, in the country's far north. The Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous region ...
, does Ladin
Ladin may refer to:
*Ladin language, a language in northern Italy, often classified as a Rhaeto-Romance language
*Ladin people, the inhabitants of the Dolomite Alps region of northern Italy
See also
*Laden (disambiguation)
*Ladino (disambiguati ...
. Slovene and Friulian are officially recognised in the provinces of Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into pr ...
, Gorizia
Gorizia (; sl, Gorica , colloquially 'old Gorizia' to distinguish it from Nova Gorica; fur, label= Standard Friulian, Gurize, fur, label= Southeastern Friulian, Guriza; vec, label= Bisiacco, Gorisia; german: Görz ; obsolete English ''Gori ...
and Udine
Udine ( , ; fur, Udin; la, Utinum) is a city and ''comune'' in north-eastern Italy, in the middle of the Friuli Venezia Giulia region, between the Adriatic Sea and the Alps (''Alpi Carniche''). Its population was 100,514 in 2012, 176,000 with t ...
in Venezia Giulia
Venezia Giulia, traditionally called Julian March ( Serbo-Croatian, Slovene: ''Julijska krajina'') or Julian Venetia ( it, Venezia Giulia; vec, Venesia Julia; fur, Vignesie Julie; german: Julisch Venetien) is an area of southeastern Europe w ...
. In Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
, the Sardinian language
Sardinian or Sard ( , or ) is a Romance language spoken by the Sardinians on the Western Mediterranean island of Sardinia.
Many Romance linguists consider it the language that is closest to Latin among all its genealogical descendants. ...
has been the language traditionally spoken and is often regarded by linguists as constituting its own branch of Romance; in the 1990s, Sardinian has been recognized as "having equal dignity" with Italian, the introduction of which to the island officially started under the rule of the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule of ...
in the 18th century.
In these regions, official documents are either bilingual (trilingual in Ladin communities) in the co-official language(s) by default, or available as such upon request. Traffic signs are also multilingual, except in the Valle d’Aosta where French toponyms are generally used, with the exception of Aosta
Aosta (, , ; french: Aoste , formerly ; frp, Aoûta , ''Veulla'' or ''Ouhta'' ; lat, Augusta Praetoria Salassorum; wae, Augschtal; pms, Osta) is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps, north-northwest o ...
itself, which has retained its Latin form in Italian as well as English. Attempts to Italianize them, especially during the Fascist period, have been formally abandoned. Education is possible in minority languages where such schools are operating.
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
and other authorities recognize a number of other languages which are not legally protected by Italian government: Piedmontese
Piedmontese (; autonym: or , in it, piemontese) is a language spoken by some 2,000,000 people mostly in Piedmont, northwestern region of Italy. Although considered by most linguists a separate language, in Italy it is often mistakenly reg ...
, Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
, Ligurian, Lombard, Emilian-Romagnolo, Neapolitan
Neapolitan means of or pertaining to Naples, a city in Italy; or to:
Geography and history
* Province of Naples, a province in the Campania region of southern Italy that includes the city
* Duchy of Naples, in existence during the Early and Hig ...
and Sicilian.
Religion
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
is by far the largest religion in the country, although the Catholic Church is no longer officially the state religion
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular, is not necessarily a t ...
. In 2006, 87.8% of Italy's population self-identified as Roman Catholic, although only about one-third of these described themselves as active members (36.8%). In 2016, 71.1% of ''Italian citizens'' self-identified as Roman Catholic. This increased again to 78% in 2018.
Most Italians believe in God, or a form of a spiritual life force. According to a Eurobarometer
Eurobarometer is a series of public opinion surveys conducted regularly on behalf of the European Commission and other EU Institutions since 1973. These surveys address a wide variety of topical issues relating to the European Union throughout i ...
Poll in 2005: 74% of Italian citizens responded that 'they believe there is a God', 16% answered that 'they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force' and 6% answered that 'they do not believe there is any sort of spirit, God, or life force'. There are no data collected through census.
Christianity
The Italian Catholic Church is part of the global Roman Catholic Church, under the leadership of the Pope,curia
Curia (Latin plural curiae) in ancient Rome referred to one of the original groupings of the citizenry, eventually numbering 30, and later every Roman citizen was presumed to belong to one. While they originally likely had wider powers, they came ...
in Rome, and the Conference of Italian Bishops
The Italian Episcopal Conference ( it, Conferenza Episcopale Italiana) or CEI is the episcopal conference of the Italian bishops of the Catholic Church, the official assembly of the bishops in Italy.
The conference was founded in 1971 and carri ...
. In addition to Italy, two other sovereign nations are included in Italian-based dioceses, San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
and Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
. There are 225 dioceses in the Italian Catholic Church, see further in this article and in the article List of the Roman Catholic dioceses in Italy
The following is the List of the Catholic dioceses in Italy. , the Catholic Church in Italy is divided into sixteen ecclesiastical regions. While they are similar to the 20 civil regions of the Italian state, there are some differences. Most eccl ...
. Even though by law Vatican City is not part of Italy, it is in Rome, and along with Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, Italian is the most spoken and second language of the Roman Curia.
Italy has a rich Catholic culture
Christian culture generally includes all the cultural practices which have developed around the religion of Christianity. There are variations in the application of Christian beliefs in different cultures and traditions.
Christian culture has i ...
, especially as numerous Catholic saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Or ...
s, martyr
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
s and popes were Italian themselves. Roman Catholic art in Italy especially flourished during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
and Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
periods, with numerous Italian artists, such as Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was ins ...
, Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on ...
, Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual ...
, Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of h ...
, Fra Angelico
Fra Angelico (born Guido di Pietro; February 18, 1455) was an Italian painter of the Early Renaissance, described by Vasari in his '' Lives of the Artists'' as having "a rare and perfect talent".Giorgio Vasari, ''Lives of the Artists''. Pengu ...
, Gian Lorenzo Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, , ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 159828 November 1680) was an Italian sculptor and architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his ...
, Sandro Botticelli
Alessandro di Mariano di Vanni Filipepi ( – May 17, 1510), known as Sandro Botticelli (, ), was an Italian Renaissance painting, Italian painter of the Early Renaissance. Botticelli's posthumous reputation suffered until the late 19th cent ...
, Tintoretto
Tintoretto ( , , ; born Jacopo Robusti; late September or early October 1518Bernari and de Vecchi 1970, p. 83.31 May 1594) was an Italian painter identified with the Venetian school. His contemporaries both admired and criticized the speed wit ...
, Titian
Tiziano Vecelli or Vecellio (; 27 August 1576), known in English as Titian ( ), was an Italians, Italian (Republic of Venice, Venetian) painter of the Renaissance, considered the most important member of the 16th-century Venetian school (art), ...
and Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto ( , ) and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/ Proto-Renaissance period. G ...
. Roman Catholic architecture in Italy is equally as rich and impressive, with churches, basilicas and cathedrals such as St Peter's Basilica
The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter in the Vatican ( it, Basilica Papale di San Pietro in Vaticano), or simply Saint Peter's Basilica ( la, Basilica Sancti Petri), is a Church (building), church built in the Renaissance architecture, Renaissanc ...
, Florence Cathedral
Florence Cathedral, formally the (; in English Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Flower), is the cathedral of Florence, Italy ( it, Duomo di Firenze). It was begun in 1296 in the Gothic style to a design of Arnolfo di Cambio and was structurally co ...
and St Mark's Basilica
The Patriarchal Cathedral Basilica of Saint Mark ( it, Basilica Cattedrale Patriarcale di San Marco), commonly known as St Mark's Basilica ( it, Basilica di San Marco; vec, Baxéłega de San Marco), is the cathedral church of the Catholic Pa ...
. Roman Catholicism is the largest religion and denomination in Italy, with around 71.1% of Italians considering themselves Catholic. Italy is also home to the greatest number of cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
s in the world, and is the country with the greatest number of Roman Catholic churches per capita.
 Even though the main Christian denomination in Italy is Roman Catholicism, there are some minorities of
Even though the main Christian denomination in Italy is Roman Catholicism, there are some minorities of Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
, Waldensian, Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
and other Christian churches.
Immigration from Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
, Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
, and Eastern Africa at the beginning of the 21st century has increased the size of Baptist
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul c ...
, Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of t ...
, Pentecostal and Evangelical communities in Italy, while immigration from Eastern Europe has produced large Eastern Orthodox communities.
In 2006, Protestants made up 2.1% of Italy's population, and members of Eastern Orthodox churches comprised 1.2% or more than 700,000 Eastern Orthodox Christians including 180,000 Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
, 550,000 Pentecostals and Evangelists (0.8%), of whom 400,000 are members of the Assemblies of God
The Assemblies of God (AG), officially the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, is a group of over 144 autonomous self-governing national groupings of churches that together form the world's largest Pentecostal denomination."Assemblies of God". ...
, about 250,000 are Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in ...
(0.4%), 30,000 Waldensians
The Waldensians (also known as Waldenses (), Vallenses, Valdesi or Vaudois) are adherents of a church tradition that began as an ascetic movement within Western Christianity before the Reformation.
Originally known as the "Poor Men of Lyon" in ...
, 25,000 Seventh-day Adventists, 22,000 Mormons, 15,000 Baptists (plus some 5,000 Free Baptists), 7,000 Lutherans
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
, 4,000 Methodists (affiliated with the Waldensian Church).
Other religions
The longest-established religious faith in Italy is Judaism, Jews having been present inAncient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom ...
before the birth of Christ. Italy has seen many influential Italian-Jews, such as prime minister Luigi Luzzatti
Luigi Luzzatti (11 March 1841 – 29 March 1927) was an Italian financier, political economist, social philosopher, and jurist. He served as the 20th prime minister of Italy between 1910 and 1911.
Luzzatti came from a wealthy and cultured Jewis ...
, who took office in 1910, Ernesto Nathan served as mayor of Rome from 1907 to 1913 and Shabbethai Donnolo (died 982). During the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
, Italy took in many Jewish refugees from Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
Germany. However, with the creation of the Nazi-backed puppet Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic ( it, Repubblica Sociale Italiana, ; RSI), known as the National Republican State of Italy ( it, Stato Nazionale Repubblicano d'Italia, SNRI) prior to December 1943 but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò ...
, about 15% of 48,000 Italian Jews were killed. This, together with the emigration that preceded and followed the Second World War, has left only a small community of around 45,000 Jews in Italy today.
Due to immigration from around the world, there has been an increase in non-Christian religions. As of 2009, there were 1.0 million Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
in Italy forming 1.6 percent of population; independent estimates put the Islamic population in Italy anywhere from 0.8 million to 1.5 million. Only 50,000 Italian Muslims hold Italian citizenship
Italian nationality law is the law of Italy governing the acquisition, transmission and loss of Italian citizenship. Like many continental European countries it is largely based on ''jus sanguinis''. It also incorporates many elements that are ...
.
There are more than 200,000 followers of faith originating in the Indian subcontinent, including some 70,000 Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The ter ...
with 22 gurdwaras
A gurdwara (sometimes written as gurudwara) ( Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ''guradu'ārā'', meaning "Door to the Guru") is a place of assembly and worship for Sikhs. Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all fai ...
across the country, 70,000 Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, and 50,000 Buddhists
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
. There are an estimated some 4,900 Bahá'ís in Italy in 2005.
Education
Literacy : : ''definition:'' age 15 and over can read and write :total population: 99.2% :male: 99.4% :female: 99% (2018 est.) School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education) : :total: 16 years :male: 16 years :female: 17 years (2018)Genetics and ethnic groups
 The
The genetic history of Italy
The genetic history of Italy is greatly influenced by geography and history. The ancestors of Italians are mostly Indo-European languages, Indo-European speakers (Italic peoples such as Latins (Italic tribe), Latins, Falisci, Picentes, Umbri, Um ...
is greatly influenced by geography and history. The ancestors of Italians are mostly Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
speakers (Italic peoples
The Italic peoples were an ethnolinguistic group identified by their use of Italic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
The Italic peoples are descended from the Indo-European speaking peoples who inhabited Italy from at lea ...
such as Latins
The Latins were originally an Italic tribe in ancient central Italy from Latium. As Roman power and colonization spread Latin culture during the Roman Republic.
Latins culturally "Romanized" or "Latinized" the rest of Italy, and the word Latin ...
, Umbrians, Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
An Oscan-speaking people, who may have originated as an offshoot of the Sabines, they f ...
, Oscans
The Osci (also called Oscans, Opici, Opsci, Obsci, Opicans) were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum before and during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the language ...
, Sicels
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the name it has held since antiquity, b ...
and Adriatic Veneti
The Veneti (also Heneti) were an Indo-European people who inhabited northeastern Italy, in an area corresponding to the modern-day region of Veneto.Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
, Iapygians
The Iapygians or Apulians (; el, Ἰάπυγες, ''Ĭāpyges''; la, Iāpyges, Iapygii, Umbrian ''Iabuscer'') were an Indo-European-speaking people, dwelling in an eponymous region of the southeastern Italian Peninsula named Iapygia (modern Apu ...
and Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
) and pre-Indo-European speakers (Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roug ...
, Ligures
The Ligures (singular Ligur; Italian: liguri; English: Ligurians) were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day north-western Italy, is named.
Ancient Liguria corresponded more or less to the current Italian regi ...
, Rhaetians and Camunni
The Camuni or Camunni were an ancient population located in Val Camonica during the Iron Age (1st millennium BC); the Latin name ''Camunni'' was attributed to them by the authors of the 1st century. They are also called ancient Camuni, to disti ...
in mainland Italy, Sicani and Elymians in Sicily and the Nuragic people in Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
). During the imperial period of Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom ...
, the city of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
was also home to people from various regions throughout the Mediterranean basin, including Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alb ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
. Based on DNA analysis, there is evidence of ancient regional genetic substructure and continuity within modern Italy dating to the pre-Roman and Roman periods.
Within the Italian population, there is enough cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.T ...
, Languages of Italy, linguistic, Genetic history of Italy, genetic and History of Italy#Unification (1814 to 1861), historical diversity for them to constitute several distinct groups throughout the peninsula.«It should be noted, then, that the Italians, though often described as a homogeneous people, are divided into several culturally, socially, and politically diverse groups throughout the peninsula.» Jeffrey Cole (edited by), ''Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia'', Santa Barbara (California), ABC-CLIO, 2011, p.204 In this regard, peoples like the Friulians, the Ladin people, Ladins, the Sardinian people, Sardinians and the South Tyrol
it, Provincia Autonoma di Bolzano – Alto Adige lld, Provinzia Autonoma de Balsan/Bulsan – Südtirol
, settlement_type = Autonomous province
, image_skyline =
, image_alt ...
eans, who also happen to constitute recognized linguistic minorities, or even the Sicilians who are not, are cases in point, attesting to such internal diversity.
See also
* List of Italians *Italian diaspora
, image = Map of the Italian Diaspora in the World.svg
, image_caption = Map of the Italian diaspora in the world
, population = worldwide
, popplace = Brazil, Argentina, United States, France, Colombia, Canada, P ...
*Italian Americans
* Italian Brazilians
* Italian Argentines
*Italian Venezuelans
* Romani people in Italy
Footnotes
References
External links
Demographic page
Allianz Knowledge {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics of Italy Demographics of Italy,