Ethnic groups in Belarus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The demographics of Belarus is about the demographic features of the
The demographics of Belarus is about the demographic features of the
, BelStat Originally a highly agrarian country with nearly 80% of its population in rural areas, Belarus has been undergoing a process of continuous
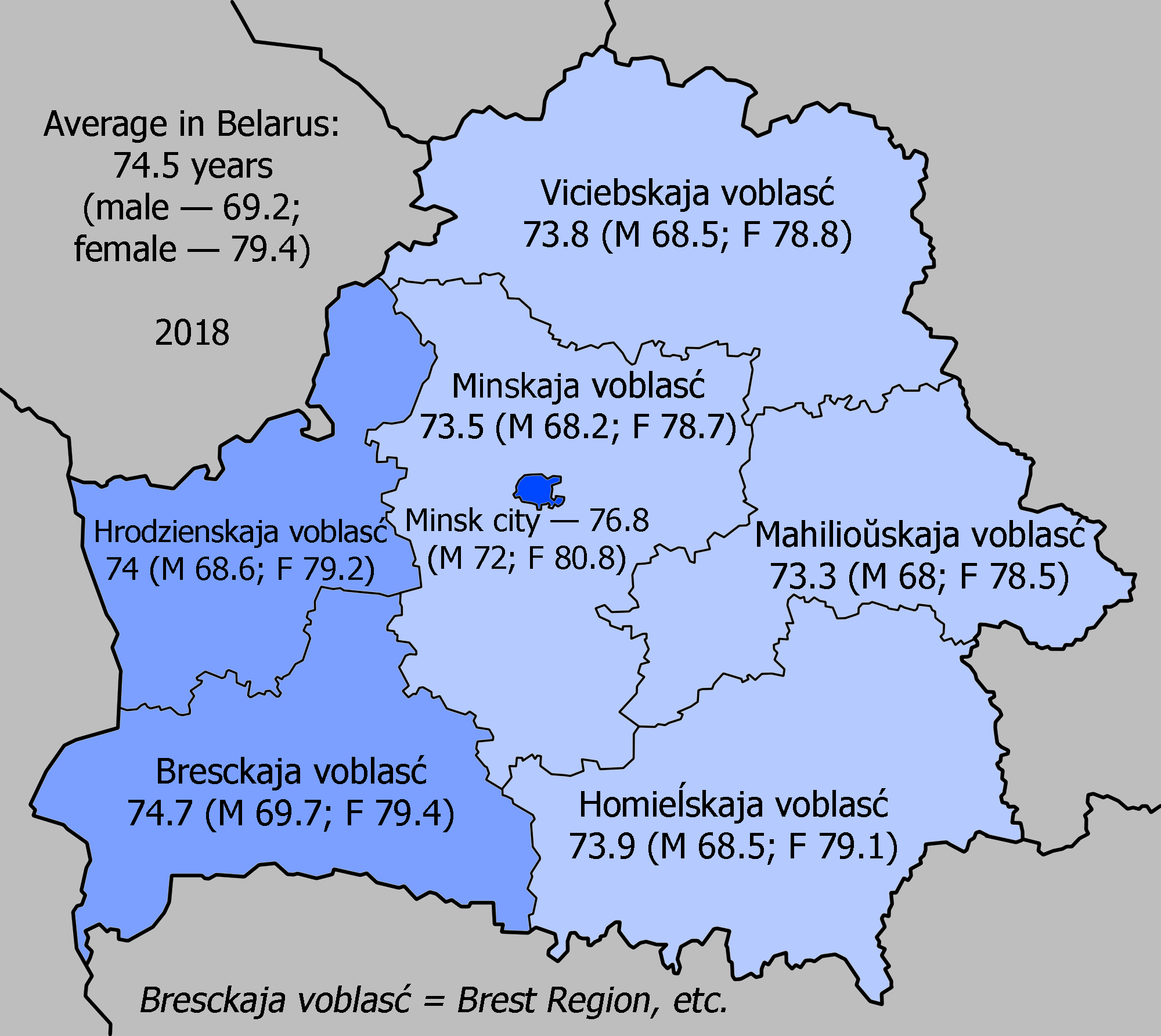 :''Total population:'' 72.15 years
:''country comparison to the world:'' 138
:''Male:'' 66.53 years
:''Female:'' 78.1 years (2014 est.)
:''Total population:'' 72.15 years
:''country comparison to the world:'' 138
:''Male:'' 66.53 years
:''Female:'' 78.1 years (2014 est.)
Birth rate in Belarus, 2019.png, Birth rate (by district, 2019)
Death rate in Belarus, 2019.png, Mortality rate (by district, 2019)
Natural population change in Belarus, 2019.png, Rate of natural increase (by district, 2019)
 : Belarusians 84.9%,
: Belarusians 84.9%,
, 1999 Belarus Census.
Lukashenka wants to double Belarus population: will that work?
Belarus Digest {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of Belarus
 The demographics of Belarus is about the demographic features of the
The demographics of Belarus is about the demographic features of the population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
of Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, including population growth, population density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations Religious identity is a specific type of identity formation. Particularly, it is the sense of group membership to a religion and the importance of this group membership as it pertains to one's self-concept. Religious identity is not necessarily the ...
, and other aspects of the population.
Population
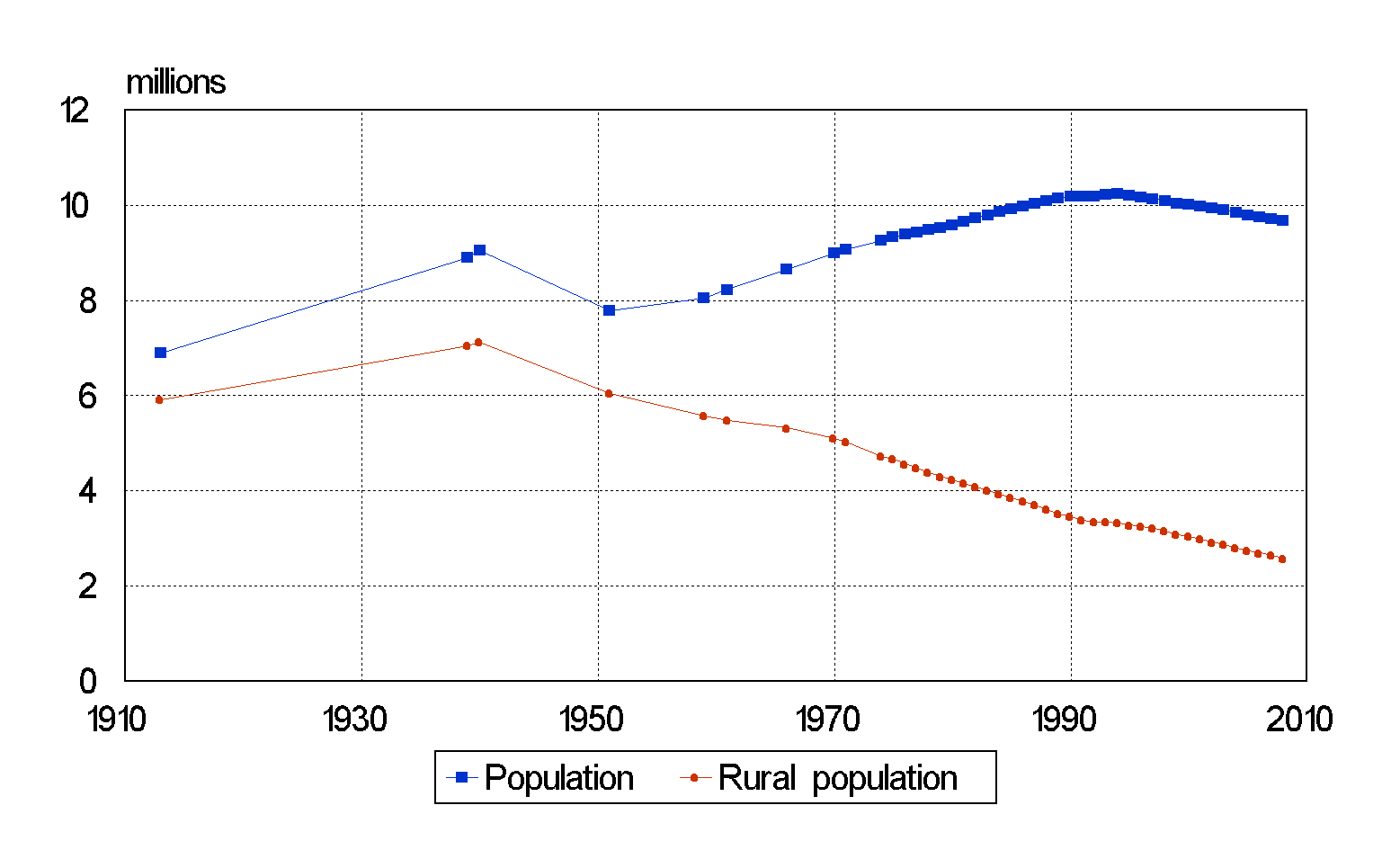
The population of Belarus suffered a dramatic decline during World War II, dropping from more than 9 million in 1940 to 7.7 million in 1951. It then resumed its long-term growth, rising to 10 million in 1999. After that the population began a steady decline, dropping to 9.7 million in 2006–2007.Population estimates 1995–2007, BelStat Originally a highly agrarian country with nearly 80% of its population in rural areas, Belarus has been undergoing a process of continuous
urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
. The rural population saw its share of the total population decrease from 70% in 1959 to less than 30% in the 2000s.
Population
:9,491,800 (January 2018 est.) :''country comparison to the world:'’ 92Age structure
:0–14 years: 15.4% (male 759,285/female 717,118) :15–24 years: 11.7% (male 575,907/female 544,170) :25–54 years: 45.5% (male 2,141,419/female 2,227,433) :55–64 years: 13.3% (male 562,639/female 716,216) :65 years and over: 14.2% (male 430,225/female 933,646) (2014 est.)Median age
:''Total:'' 39.4 years :''Male:'' 36.3 years :''Female:'' 42.4 years (2014 est.)Sex ratio
:At birth: 1.06 male(s)/female :0–14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female :15–24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female :25–54 years: 0.96 male(s)/female :55–64 years: 0.87 male(s)/female :65 years and over: 0.46 male(s)/female :Total population: 0.87 male(s)/female (2014 est.)Life expectancy at birth
 :''Total population:'' 72.15 years
:''country comparison to the world:'' 138
:''Male:'' 66.53 years
:''Female:'' 78.1 years (2014 est.)
:''Total population:'' 72.15 years
:''country comparison to the world:'' 138
:''Male:'' 66.53 years
:''Female:'' 78.1 years (2014 est.)
Total fertility rate (TFR) in Belarus by region and year
Infant mortality rate
:''Total:'' 4.0 deaths/1,000 live births for 429 death. (2010) :''Total:'' 3.9 deaths/1,000 live births for 422 death. (2011) :''Total:'' 3.4 deaths/1,000 live births for 386 death. (2012) :''Total:'' 3.5 deaths/1,000 live births for 407 death. (2013) :''Total:'' 3.5 deaths/1,000 live births for 415 death. (2014) :''Total:'' 3.5 deaths/1,000 live births for 321 death. (January–September 2014) :''Total:'' 3.2 deaths/1,000 live births for 283 death. (January–September 2015)Vital statistics
Belarusian provinces of the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
The figures below refer to the five governorates of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
( Grodno, Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest c ...
, Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
, Mogilev
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the bor ...
, Vilna
Vilnius ( , ; see also #Etymology and other names, other names) is the capital and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the munic ...
) with a Belarusian majority.
After WWII
Source: National Statistical Committee of the Republic of BelarusCurrent vital statistics
Ethnic groups
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
7.5%, Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
3.1%, Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
1.7%, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
0.1%, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
0.1%, Lipka Tatars 0.1%, Ruska Roma
The Ruska Roma (russian: Руска́ Рома́), also known as Russian Gypsies (russian: Русские цыгане) or ''Xaladitka Roma'' (russian: Халадытка Рома, translit=Khaladytka Roma, ''i.e.'' "Roma-Soldiers"),
are the ...
0.1%, Lithuanians 0.1%, Azerbaijanis 0.1%, others 2.2% (2019 census).
Prior to the Second World War
Prior toWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
were the second largest ethnic group in Belarus, and at 400,000 in the 1926 and 1939 censuses they even exceeded the number of Russians (although admittedly by a small margin). Jews accounted for 7%–8% of the total population at that time, comprising more than 40% of the population in cities and towns, where Jews and Poles were the majority, while Belarusians mostly lived in rural areas.
The Poles were the fourth largest ethnic group in Byelorussian SSR (current Eastern portion of Belarus), before World War II, comprising 1–2% of the population in the pre-war censuses (less than 100,000).
After the Second World War
TheHolocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
decimated the Jewish population in Belarus, and after World War II, in 1959, Jews accounted for only 1.9% of the population. Since then, Jewish emigration to Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and other countries reduced the number of Jews to 0.1% of the population (13,000 in 2009).
After the war, a large number of Poles were forced to move to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. In exchange, Belarusians from the former Belastok Voblast
Belastok Voblast or Belostok Oblast ( be, Беластоцкая вобласць, Biełastockaja vobłasć, russian: Белостокская Область, pl, Obwód białostocki) was a short-lived territorial unit in the Belarusian Soviet ...
, which was returned to Poland in 1945, after being occupied in 1939 were displaced to Belarus. Due to changes in the western border of Belarus and Poland after World War II (see territorial changes of Poland
Poland is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north. The total ...
), the number of Poles in Belarus increased to more than 500,000 according to the first post-war census (1959) and to about 400,000 according to the 1999 census. Poles are now the third largest ethnic group in Belarus (see Polish minority in Belarus
The Polish minority in Belarus numbers officially 288,000 according to 2019 census.. Listing total population of Belarus with population by age and sex, marital status, education, nationality, language and livelihood ("Общая числен� ...
). There are around 15,000 of Lipka Tatars and about 10,000 of Ruska Roma
The Ruska Roma (russian: Руска́ Рома́), also known as Russian Gypsies (russian: Русские цыгане) or ''Xaladitka Roma'' (russian: Халадытка Рома, translit=Khaladytka Roma, ''i.e.'' "Roma-Soldiers"),
are the ...
(Russian Gypsies).
In the post-war period Belarus experienced an influx of workers from other parts of the Soviet Union, for example Russians and Ukrainians. The decade after independence saw a decline in the population of most of these minority groups, either by assimilation or emigration. The most significant exception to this trend has been a continued (if small-scale) net immigration of Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
and Azerbaijanis, whose numbers increased from less than 2,000 in 1959 to around 10,000 in 1999.Ethnic composition of the population, 1999 Belarus Census.
Languages
Belarusian andRussian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
are the official languages according to the Constitution of Belarus
The Constitution of the Republic of Belarus ( be, Канстытуцыя Рэспублікі Беларусь, russian: Конституция Республики Беларусь) is the ultimate law of Belarus. The Constitution is composed o ...
(Article 17). The constitution guarantees preservation of the cultural heritage of all ethnic minorities, including their languages (Article 15). Russian, and not Belarusian, is the dominant language in Belarus, spoken normally at home by 70% of the population (2009 census). Major cities such as Minsk and Brest are overwhelmingly Russian-speaking.
Religion
According to 1997 estimates, 80% of the religious population belonged to theEastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
and the others are mainly Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
, Greek Catholic, Protestants, Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, and Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
.
Urbanization
:''Urban population:'' 75% of total population (2011) :''Rate of urbanization:'' 0.21% annual rate of change (2010–2015 est.)See also
* List of cities in Belarus * Belarus Census (disambiguation)References
External links
Lukashenka wants to double Belarus population: will that work?
Belarus Digest {{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of Belarus