Crimean Tatar people on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the
(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.114) , region11 = , pop11 = , langs = , rels = Sunni Islam , related = Dobrujan Tatars,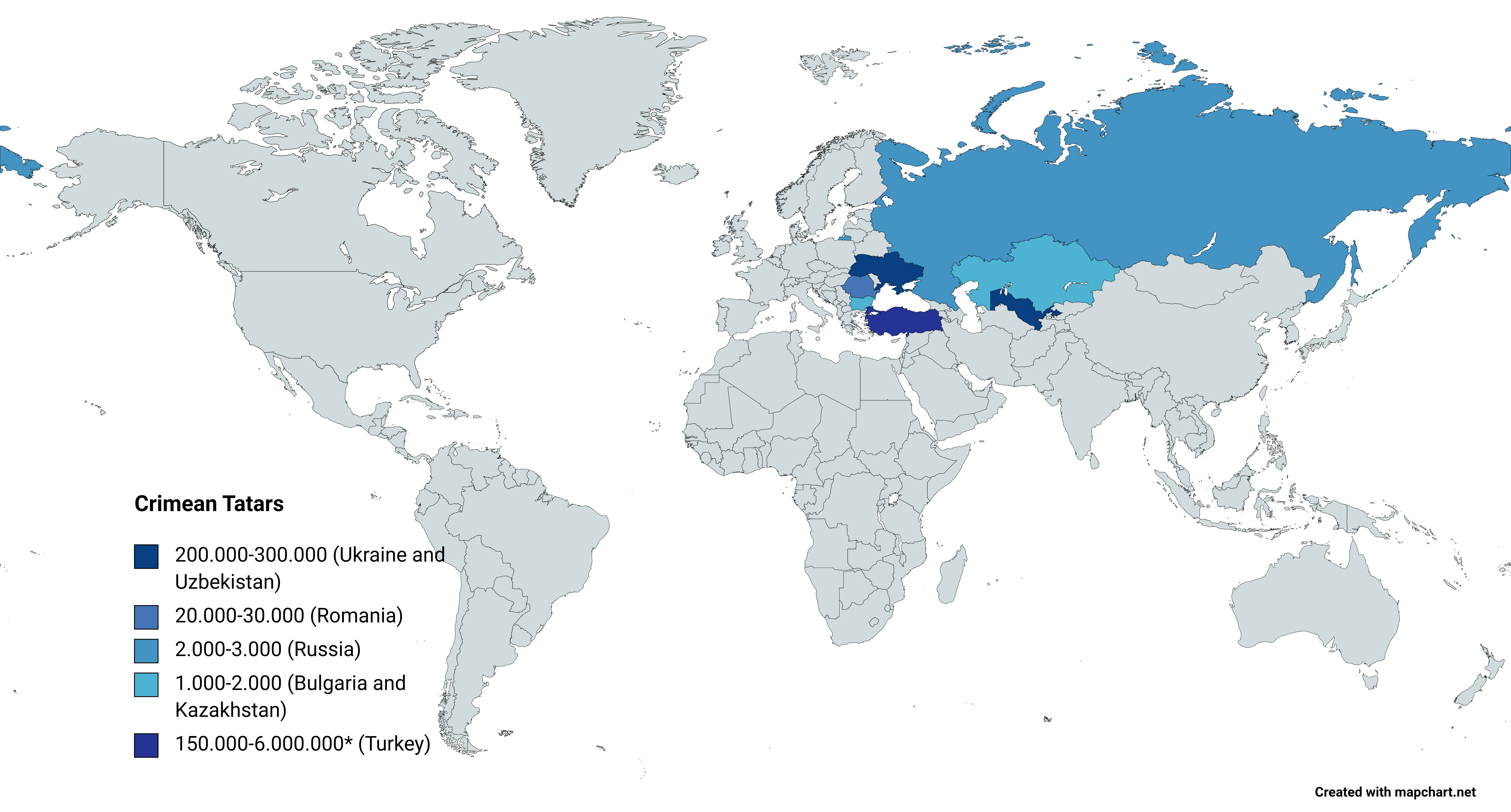 Crimean Tatars ( crh, Къырымтатарлар, translit=Qırımtatarlar) or Crimeans ( crh, Къырымлар/Къырымлылар, translit=Qırımlar/Qırımlılar) are a Turkic ethnic group and
Crimean Tatars ( crh, Къырымтатарлар, translit=Qırımtatarlar) or Crimeans ( crh, Къырымлар/Къырымлылар, translit=Qırımlar/Qırımlılar) are a Turkic ethnic group and
Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine. *the ''Noğays'' (not to be confused with related
"Historical fate of the Crimean Tatars"
Over several centuries, on the basis of
 At the beginning of the 13th century, the Crimea, the majority of the population of which was already composed of a
At the beginning of the 13th century, the Crimea, the majority of the population of which was already composed of a  In 1441, an embassy from the representatives of several strongest clans of the Crimea, including the Golden Horde clans Shırın and Barın and the Cumanic clan — Kıpçak, went to the
In 1441, an embassy from the representatives of several strongest clans of the Crimea, including the Golden Horde clans Shırın and Barın and the Cumanic clan — Kıpçak, went to the  The main population of the Crimean khanate were Crimean Tatars, along with them in the Crimean khanate lived significant communities of Karaites,
The main population of the Crimean khanate were Crimean Tatars, along with them in the Crimean khanate lived significant communities of Karaites,
Крымское ханство
— A. V. Vinogradov, S. F. Faizov Until the beginning of the 18th century, Crimean Nogays were known for frequent, at some periods almost annual,
Warfare, State and Society on the Black Sea Steppe
'. pp. 15–26. Routledge. For a long time, until the late 18th century, the Crimean Khanate maintained a massive
p. 26.
/ref> The 17th century Ottoman writer and traveller

 The Russo-Turkish War (1768–74) resulted in the defeat of the Ottomans by the Russians, and according to the
The Russo-Turkish War (1768–74) resulted in the defeat of the Ottomans by the Russians, and according to the
 As a part of the
As a part of the
 Following news of Crimea's independence
Following news of Crimea's independence  Some Crimean Tatars fled to Mainland
Some Crimean Tatars fled to Mainland
''

in JSTOR
* Williams, Brian Glyn. "The Crimean Tatar exile in Central Asia: a case study in group destruction and survival." ''Central Asian Survey'' 17.2 (1998): 285–317. * Williams, Brian Glyn. "The Ethnogenesis of the Crimean Tatars. An Historical Reinterpretation" ''Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society'' (2001) 11#3 pp. 329–34
in JSTOR
* Williams, Brian G.,
', Leyden: Brill, 2001.
, Simferopol (four volumes). * Smirnov V D, 1886, ''Krymskoe khanstvo'' * Campana (Aurélie), Dufaud (Grégory) and Tournon (Sophie) (ed.), ''Les Déportations en héritage. Les peuples réprimés du Caucase et de Crimée, hier et aujourd'hui'', Rennes: Presses universitaires de Rennes, 2009. * *
Official website of Qirim Tatar Cultural Association of Canada
Official web-site of Bizim QIRIM International Nongovernmental Organization
International Committee for Crimea
UNDP Crimea Integration and Development Programme
Crimean Tatars
Crimean Tatar words (Turkish)
Crimean Tatar words (English)
* State Defense Committee Decree No. 5859ss: On Crimean Tatars (See als
Three answers to the Decree No. 5859ss
Essays on Central Asia Index
'Крымская солидарность; ВОЗВРАЩЕНИЕ ДОМОЙ. РУСТЕМ ВАИТОВ' (YouTube channel of Crimean Tatar Solidarity; story of Rustem Vaitov returning home after 5 years of jail)
{{Authority control Ethnic groups in Crimea Ethnic groups in Bulgaria Ethnic groups in Romania Ethnic groups in Russia Ethnic groups in Turkey Ethnic groups in Ukraine Ethnic groups in Uzbekistan Turkic peoples of Europe Islam in Crimea Indigenous peoples of Europe Indigenous peoples of Ukraine Islam in Russia
Khan's Palace
The Khan's Palace ( tr, Han Sarayı) or Hansaray is located in the town of Bakhchysarai, Crimea. It was built in the 16th century and became home to a succession of Crimean Khans. The walled enclosure contains a mosque, a harem, a cemetery, livi ...
, poptime =
, popplace =
, region1 =
, pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000
, ref1 =
, region2 =
*
, pop2 = 248,193
, ref2 =
, region3 =
, pop3 = 239,000
, ref3 =
, region4 =
, pop4 = 24,137
, ref4 =
, region5 =
, pop5 = 2,449
, ref5 =
, region7 =
, pop7 = 1,803
, ref7 =
, region8 =
, pop8 = 1,532
, ref8 =
, region9 =
*()
, pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.114) , region11 = , pop11 = , langs = , rels = Sunni Islam , related = Dobrujan Tatars,
Nogais
The Nogais ( Nogai: Ногай, , Ногайлар, ) are a Turkic ethnic group who live in the North Caucasus region. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia and Astrakhan Oblast; some als ...
, Volga Tatars
The Volga Tatars or simply Tatars ( tt-Cyrl, татарлар, tatarlar) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of Russia. They are subdivided into various subgroups. Volga Tatars are Russia's second-largest ethnicity after ...
, Lipka Tatars, Crimean Karaites
The Crimean Karaites or Krymkaraylar (Crimean Karaim: Кърымкъарайлар, ''Qrımqaraylar'', singular къарай, ''qaray''; Trakai dialect: ''karajlar'', singular ''karaj''; he, קראי מזרח אירופה; crh, Qaraylar; ), a ...
 Crimean Tatars ( crh, Къырымтатарлар, translit=Qırımtatarlar) or Crimeans ( crh, Къырымлар/Къырымлылар, translit=Qırımlar/Qırımlılar) are a Turkic ethnic group and
Crimean Tatars ( crh, Къырымтатарлар, translit=Qırımtatarlar) or Crimeans ( crh, Къырымлар/Къырымлылар, translit=Qırımlar/Qırımlılar) are a Turkic ethnic group and nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective Identity (social science), identity of a group of people unde ...
who are an indigenous people of Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
. The formation and ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
of Crimean Tatars occurred during the 13th–17th centuries, uniting Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
, who appeared in Crimea in the 10th century, with other peoples who had inhabited Crimea since ancient times and gradually underwent Tatarization, including Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
, and many others.
Crimean Tatars constituted the majority of Crimea's population from the time of ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
until the mid-19th century, and the largest ethnic population until the end of the 19th century. Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
attempted to purge through a combination of physical violence, intimidation, forced resettlement, and legalized forms of discrimination between 1783 and 1900. Between Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 1783 and 1800, somewhere between 100,000 and 300,000 Crimean Tatars emigrated. However, this did not result in the complete eradication of Crimean Tatar cultural elements (at least not under the Romanov dynasty
The House of Romanov (also transcribed Romanoff; rus, Романовы, Románovy, rɐˈmanəvɨ) was the reigning imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after the Tsarina, Anastasia Romanova, was married to ...
; however, under the Soviets, the Crimean Tatars were almost completely driven from the Crimean peninsula).Almost immediately after retaking of Crimea from Axis forces
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
, in May 1944, the USSR State Defense Committee ordered the deportation of all of the Crimean Tatars from Crimea, including the families of Crimean Tatars who had served in the Soviet Army. The deportees were transported in trains and boxcars to Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, primarily to Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
. The Crimean Tatars lost 18 to 46 percent of their population as a result of the deportations. Starting in 1967, a few were allowed to return and in 1989 the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union condemned the removal of Crimean Tatars from their motherland as inhumane and lawless, but only a tiny percent were able to return before the full right of return became policy in 1989.
The European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
and international indigenous groups do not dispute their status as an indigenous people and they have been officially recognized as an indigenous people of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
as of 2014. The current Russian administration considers them a "national minority", but not an indigenous people, and continues to deny that they are titular
Titular may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Title character in a narrative work, the character referred to in its title
Religion
* Titular (Catholicism), a cardinal who holds a titulus, one of the main churches of Rome
** Titular bisho ...
people of Crimea, even though the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
considered them indigenous before their deportation and the subsequent dissolution of the Crimean Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
During the existence of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, different governments existed within the Crimean Peninsula. From 1921 to 1936, the government in the Crimean Peninsula was known as the Crimean Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic ...
(Crimean ASSR). Today, Crimean Tatars constitute approximately 15% of the population of Crimea. There remains a Crimean Tatar diaspora
The Crimean Tatar diaspora dates back to the annexation of Crimea by Russia in 1783, after which Crimean Tatars emigrated in a series of waves spanning the period from 1783 to 1917. The diaspora was largely the result of the destruction of their so ...
in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
and Uzbekistan.
The Crimean Tatars have been members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization
The Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization, or simply UNPO is an international organization established to facilitate the voices of unrepresented and marginalised nations and peoples worldwide. It was formed on 11 February 1991 in The Ha ...
(UNPO) since 1991.
Distribution
In the Ukrainian census of 2001, 248,200 Ukrainian citizens identified themselves as Crimean Tatars with 98% (or about 243,400) of them living in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. An additional 1,800 (or about 0.7%) lived in the city ofSevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
, also on the Crimean peninsula
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
, but outside the border of the autonomous republic.
About 150,000 remain in exile in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, mainly in Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
. The official number of Crimean Tatars in Turkey is 150,000 with some Crimean Tatar activists estimating a figure as high as 6 million. The activists reached this number by taking one million Tatar immigrants to Turkey as a starting point and multiplying this number by the birth rate in the span of the last hundred years. Crimean Tatars in Turkey mostly live in Eskişehir Province
Eskişehir Province ( tr, ) is a province in northwestern Turkey. Its adjacent provinces are Bilecik to the northwest, Kütahya to the west, Afyon to the southwest, Konya to the south, Ankara to the east, and Bolu to the north. The provincia ...
, descendants of those who emigrated in the late 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries. The Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, Добруджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the Balkans that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria and Romania. I ...
region of Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
is home to more than 27,000 Crimean Tatars, with the majority in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
and approximately 3,000 on the Bulgarian side of the border.
Sub-ethnic groups
The Crimean Tatars are subdivided into three sub-ethnic groups: *the '' Tats'' (not to be confused with the Iranic Tat people, living in theCaucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
region) who used to inhabit the mountainous Crimea before 1944 predominantly are Cumans, Greeks, Goths and other people, as Tats in Crimea also were called Hellenic Urum people
The Urums, singular Urum (, ; el, Ουρούμ, ''Urúm''; Turkish and Crimean Tatar: ''Urum,'' ) are several groups of Turkic-speaking Greek Orthodox people in Crimea and Georgia. History
There are two main theories covering how the Urums m ...
(Greeks settled in Crimea) who were deported by the Imperial Russia to the area around Mariupol
Mariupol (, ; uk, Маріу́поль ; russian: Мариу́поль) is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast ( Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius River. Prior to the 2022 Russia ...
; The term ''Tat'' appears already in the 8th century Orkhon inscriptions denoting "a subjected foreign people". In the 17th century Crimean context, it probably denoted various peoples of foreign (ie. non-Turkic) origin living under the khan's rule, especially the Greeks, Italians, and the remnants of Goths and Alans inhabiting the mountainous southern section of Crimea.
*the ''Yaliboylu
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace
...
'' who lived on the southern coast of the peninsula before 1944 and practiced Christianity until the 14th century;Crimean Tatars (КРИМСЬКІ ТАТАРИ)Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine. *the ''Noğays'' (not to be confused with related
Nogai people
The Nogais ( Nogai: Ногай, , Ногайлар, ) are a Turkic ethnic group who live in the North Caucasus region. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia and Astrakhan Oblast; some als ...
, living now in Southern Russia) — former inhabitants of the Crimean steppe.
Historians suggest that inhabitants of the mountainous parts of Crimea lying to the central and southern parts (the Tats), and those of the Southern coast of Crimea (the Yalıboyu) were the direct descendants of the Pontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks ( pnt, Ρωμαίοι, Ρωμίοι, tr, Pontus Rumları or , el, Πόντιοι, or , , ka, პონტოელი ბერძნები, ), also Pontian Greeks or simply Pontians, are an ethnically Greek group i ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
, Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
(Crimean Goths
The Crimean Goths were Greuthungi-Gothic tribes who remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the longest-lasting of the Gothic communities. Their existence is well attested through the ages, though the exact p ...
) and Kipchaks along with the Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
while the latest inhabitants of the northern steppe represent the descendants of the Nogai Horde
The Nogai Horde was a confederation founded by the Nogais that occupied the Pontic–Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghuds co ...
of the Black Sea, nominally subjects of the Crimean Khan. It is largely assumed that the Tatarization process that mostly took place in the 16th century brought a sense of cultural unity through the blending of the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
and Ottoman Turks of the southern coast, Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
of the central mountains and Turkic-speaking Kipchaks and Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
of the steppe and forming of the Crimean Tatar ethnic group. However, the Cuman language
Cuman or Kuman (also called Kipchak, Qypchaq or Polovtsian) was a Kipchak Turkic language spoken by the Cumans (Polovtsy, Folban, Vallany, Kun) and Kipchaks; the language was similar to today's various languages of the Kipchak-Cuman branch. C ...
is considered the direct ancestor of the current language of the Crimean Tatars with possible incorporations of the other languages, like Crimean Gothic
Crimean Gothic was an East Germanic language spoken by the Crimean Goths in some isolated locations in Crimea until the late 18th century.
Attestation
The existence of a Germanic dialect in Crimea is noted in a number of sources from the 9th ce ...
. The fact that Crimean Tatars' ethnogenesis took place in Crimea and consisted of several stages lasting over 2500 years is proved by genetic research showing that the gene pool of the Crimean Tatars preserved both the initial components for more than 2.5 thousand years, and later in the northern steppe regions of the Crimea.
The Mongol conquest of the Kipchaks led to a merged society with a Mongol ruling class over a Kipchak speaking population which came to be dubbed Tatar and which eventually absorbed other ethnicities on the Crimean peninsula like Armenians, Italians, Greeks, and Goths to form the modern day Crimean Tatar people; up to the Soviet deportation, the Crimean Tatars could still differentiate among themselves between Tatar, Kipchak, Nogays, and the "Tat" descendants of Tatarized Goths and other Turkified peoples.
History
Origin
The Crimean Tatars were formed as a people inCrimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
and are descendants of various peoples who lived in Crimea in different historical eras. The main ethnic groups that inhabited the Crimea at various times and took part in the formation of the Crimean Tatar people are Tauri
The Tauri (; in Ancient Greek), or Taurians, also Scythotauri, Tauri Scythae, Tauroscythae (Pliny, ''H. N.'' 4.85) were an ancient people settled on the southern coast of the Crimea peninsula, inhabiting the Crimean Mountains in the 1st millenn ...
, Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
, Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
, Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, Bulgars, Khazars
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
, Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
, Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
and Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
. The consolidation of this diverse ethnic conglomerate into a single Crimean Tatar people took place over the course of centuries. The connecting elements in this process were the commonality of the territory, the Turkic language and Islamic religion
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the mai ...
.Очерки истории и культуры крымских татар. / Под. ред. Э. Чубарова. — Симферополь, Крымучпедгиз, 2005.Хайруддинов М. А. К вопросу об этногенезе крымских татар/М. А. Хайруддинов // Ученые записки Крымского государственного индустриально-педагогического института. Выпуск 2. -Симферополь, 2001.
By the end of the 15th century, the main prerequisites that led to the formation of an independent Crimean Tatar ethnic group were created: the political dominance of the Crimean Khanate was established in Crimea, the Turkic languages ( Cuman-Kipchak on the territory of the khanate) became dominant, and Islam acquired the status of a state religion throughout the Peninsula. By a preponderance Cumanian population of the Crimea acquired the name "Tatars", the Islamic religion and Turkic language, and the process of consolidating the multi-ethnic conglomerate of the Peninsula began, which has led to the emergence of the Crimean Tatar people.Vozgrin, Valer"Historical fate of the Crimean Tatars"
Over several centuries, on the basis of
Cuman language
Cuman or Kuman (also called Kipchak, Qypchaq or Polovtsian) was a Kipchak Turkic language spoken by the Cumans (Polovtsy, Folban, Vallany, Kun) and Kipchaks; the language was similar to today's various languages of the Kipchak-Cuman branch. C ...
with a noticeable Oghuz influence, the Crimean Tatar language has developed.
Golden Horde and Crimean Khanate
 At the beginning of the 13th century, the Crimea, the majority of the population of which was already composed of a
At the beginning of the 13th century, the Crimea, the majority of the population of which was already composed of a Turkic people
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose memb ...
— Cumans, became a part of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragme ...
. The Crimean Tatars mostly adopted Islam in the 14th century and thereafter Crimea became one of the centers of Islamic civilization in Eastern Europe. In the same century, trends towards separatism appeared in the Crimean Ulus of the Golden Horde. De facto independence of the Crimea from the Golden Horde may be counted since the beginning of princess (khanum) Canike's, the daughter of the powerful Khan of the Golden Horde Tokhtamysh
Tokhtamysh ( kz, Тоқтамыс, tt-Cyrl, Тухтамыш, translit=Tuqtamış, fa, توقتمش),The spelling of Tokhtamysh varies, but the most common spelling is Tokhtamysh. Tokhtamısh, Toqtamysh, ''Toqtamış'', ''Toqtamıs'', ''Toktamy ...
and the wife of the founder of the Nogai Horde
The Nogai Horde was a confederation founded by the Nogais that occupied the Pontic–Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghuds co ...
Edigey
Edigu (or Edigey) (also İdegäy or Edege Mangit) (1352–1419) was a Mongol Muslim emir of the White Horde who founded a new political entity, which came to be known as the Nogai Horde.
Edigu was from the Crimean Manghud tribe, the son of Bal ...
, reign in the peninsula. During her reign she strongly supported Hacı Giray in the struggle for the Crimean throne until her death in 1437. Following the death of Сanike, the situation of Hacı Giray in Crimea weakened and he was forced to leave Crimea for Lithuania.
The Crimean Tatars emerged as a nation at the time of the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
, an Ottoman vassal state during the 16th to 18th centuries. Russian historian, doctor of history, Professor of the Russian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across ...
Ilya Zaytsev writes that analysis of historical data shows that the influence of Turkey on the policy of the Crimea was not as high as it was reported in old Turkish sources and Imperial Russian ones. The Turkic-speaking population of Crimea had mostly adopted Islam already in the 14th century, following the conversion of Ozbeg Khan of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragme ...
. By the time of the first Russian invasion of Crimea in 1736, the Khan's archives and libraries were famous throughout the Islamic world, and under Khan Krym-Girei the city of Aqmescit was endowed with piped water, sewerage and a theatre where Molière
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin (, ; 15 January 1622 (baptised) – 17 February 1673), known by his stage name Molière (, , ), was a French playwright, actor, and poet, widely regarded as one of the greatest writers in the French language and worl ...
was performed in French, while the port of Kezlev stood comparison with Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"Ne ...
and Bakhchysarai, the capital, was described as Europe's cleanest and greenest city.Rayfield, Donald, 2014: "Dormant claims", ''Times Literary Supplement'', 9 May 2014 p 15
 In 1441, an embassy from the representatives of several strongest clans of the Crimea, including the Golden Horde clans Shırın and Barın and the Cumanic clan — Kıpçak, went to the
In 1441, an embassy from the representatives of several strongest clans of the Crimea, including the Golden Horde clans Shırın and Barın and the Cumanic clan — Kıpçak, went to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
to invite Hacı Giray to rule in the Crimea. He became the founder of the Giray dynasty
The House of Giray ( crh3, Geraylar, كرايلر, ota, آل جنكيز, Âl-i Cengiz, lit=Genghisids), also Girays, were the Genghisid/ Turkic dynasty that reigned in the Khanate of Crimea from its formation in 1431 until its downfall in 1783 ...
, which ruled until the annexation of the Crimean Khanate by Russia in 1783. Hacı I Giray
Hacı I Giray (1397–1466, ruled circa 1441–1466) was the founder of the Crimean Khanate and the Giray dynasty of Crimea. As the Golden Horde was breaking up, he established himself in Crimea and spent most of his life fighting off other warlo ...
was a Jochid descendant of Genghis Khan and of his grandson Batu Khan
Batu Khan ( – 1255),, ''Bat haan'', tt-Cyrl, Бату хан; ; russian: хан Баты́й was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Golden Horde, a constituent of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi, thus a grandson of Genghis Kh ...
of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragme ...
. During the reign of Meñli I Giray
Meñli I Giray ( crh3, I Meñli Geray, ۱منكلى كراى) (1445–1515), also spelled as Mengli I Giray, was a ''khan'' of the Crimean Khanate (1466, 1469–1475, 1478–1515) and the sixth son of Hacı I Giray.
Biography
Struggle f ...
, Hacı's son, the army of the Great Horde
The Great Horde (''Uluğ Orda'') was a rump state of the Golden Horde that existed from the mid-15th century to 1502. It was centered at the core of the Golden Horde at Sarai. Both the Khanate of Astrakhan and the Khanate of Crimea broke away ...
that still existed then invaded the Crimea from the north, Crimean Khan won the general battle, overtaking the army of the Horde Khan in Takht-Lia, where he was killed, the Horde ceased to exist, and the Crimean Khan became the Great Khan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, 𐰴𐰍𐰣 ), or , tr, Kağan or ; ug, قاغان, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, خاقان ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
and the successor of this state. Since then, the Crimean Khanate was among the strongest powers in Eastern Europe until the beginning of the 18th century. The Khanate officially operated as a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, with great autonomy after 1580. At the same time, the Nogai hordes, not having their own khan, were vassals of the Crimean one, Muskovy and Polish-Lithuanian commonwealth paid annual tribute to the khan (until 1700
As of March 1 ( O.S. February 19), where then Julian calendar acknowledged a leap day and the Gregorian calendar did not, the Julian calendar fell one day further behind, bringing the difference to 11 days until February 28 ( O.S. February 17 ...
and 1699
Events
January–March
* January 5 – A violent Java earthquake damages the city of Batavia on the Indonesian island of Java, killing at least 28 people
* January 20 – The Parliament of England (under Tory dominance) limits the size ...
respectively). In the 17th century, the Crimean Tatars helped Ukrainian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
led by Bohdan Khmelnytsky in the struggle for independence, which allowed them to win several decisive victories over Polish troops.
In 1711, when Peter I of Russia went on a campaign
Campaign or The Campaign may refer to:
Types of campaigns
* Campaign, in agriculture, the period during which sugar beets are harvested and processed
*Advertising campaign, a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme
* Bl ...
with all his troops (80,000) to gain access to the Black Sea, he was surrounded by the army of the Crimean Khan Devlet II Giray
Devlet II Giray (1648–1718) was Khan of the Crimean Khanate from 1699 to 1702 and from 1709 to 1713. His eldest son was Selim II Giray.
First Rule (1699–1702)
Selim I Giray, after his retirement in 1699, recommended Devlet II Giray Khan ...
, finding himself in a hopeless situation. And only the betrayal of the Ottoman vizier Baltacı Mehmet Pasha
Baltacı Mehmet Pasha (also called Pakçemüezzin Baltacı Mehmet Pasha, sometimes known just as Baltacı or Baltadji; 1662, Osmancık – July 1712, Lemnos) was an Ottoman statesman who served as grand vizier of the Ottoman Empire, first fro ...
allowed Peter to get out of the encirclement of the Crimean Tatars. When Devlet II Giray protested against the vizier's decision, his response was: ''"You should know your Tatar affairs. The affairs of the Sublime Porte
The Sublime Porte, also known as the Ottoman Porte or High Porte ( ota, باب عالی, Bāb-ı Ālī or ''Babıali'', from ar, باب, bāb, gate and , , ), was a synecdoche for the central government of the Ottoman Empire.
History
The name ...
are entrusted to me. You do not have the right to interfere in them"''. Treaty of the Pruth
The Treaty of the Pruth was signed on the banks of the river Prut between the Ottoman Empire and the Tsardom of Russia on 23 July 1711 ending the Russo-Turkish War of 1710–1711. The treaty was a political victory for the Ottoman Empire.
The ...
was signed, and 10 years later, Russia declared itself an empire. In 1736, the Crimean Khan Qaplan I Giray
Qaplan I Giray was three times khan of the Crimean Khanate. He was the son of Selim I Giray and thus one of the six brothers who ruled for most the period from 1699 to 1743. During his first reign he was defeated by the Kabardians. His second r ...
was summoned by the Turkish Sultan Ahmed III to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. Understanding that Russia could take advantage of the lack of troops in Crimea, Qaplan Giray wrote to the Sultan to think twice, but the Sultan was persistent. As it was expected by Qaplan Giray, in 1736 the Russian army invaded the Crimea, led by Münnich, devastated the peninsula, killed civilians and destroyed all major cities, occupied the capital, Bakhchisaray
Bakhchysarai ( crh, Bağçasaray, italic=yes; russian: Бахчисара́й; ua, Бахчисара́й; tr, Bahçesaray) is a town in Crimea, a territory recognized by a majority of countries as part of Ukraine and annexed by Russia as the Re ...
, and burnt the Khan's palace
The Khan's Palace ( tr, Han Sarayı) or Hansaray is located in the town of Bakhchysarai, Crimea. It was built in the 16th century and became home to a succession of Crimean Khans. The walled enclosure contains a mosque, a harem, a cemetery, livi ...
with all the archives and documents, and then left the Crimea because of the epidemic that had begun in it. One year after the same was done by another Russian general — Peter Lacy
Peter Graf von Lacy (russian: link=no, Пётр Петро́вич Ла́сси, tr. ; en, Pierce Edmond de Lacy; ga, Peadar (Piarais Éamonn) de Lása; 26 September 1678 – 30 April 1751) was an Irish-born soldier who later served in the ...
.Gayvoronsky, 2007 Since then, the Crimean Khanate had not been able to recover, and its slow decline began. The Russo-Turkish War of 1768 to 1774 resulted in the defeat of the Ottomans by the Russians, and according to the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca ( tr, Küçük Kaynarca Antlaşması; russian: Кючук-Кайнарджийский мир), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on 21 July 1774, in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kayn ...
(1774) signed after the war, Crimea became independent and the Ottomans renounced their political right to protect the Crimean Khanate. After a period of political unrest in Crimea, Imperial Russia violated the treaty and annexed the Crimean Khanate in 1783.
 The main population of the Crimean khanate were Crimean Tatars, along with them in the Crimean khanate lived significant communities of Karaites,
The main population of the Crimean khanate were Crimean Tatars, along with them in the Crimean khanate lived significant communities of Karaites, Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
and Roma. In the early 16th century under the rule of the Crimean khans passed part of Nogays
The Nogais ( Nogai: Ногай, , Ногайлар, ) are a Turkic ethnic group who live in the North Caucasus region. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia and Astrakhan Oblast; some als ...
(Mangyts), who roamed outside the Crimean Peninsula
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
, moving there during periods of drought and starvation. The majority of the population professed Islam of the Hanafi stream; part of the population – Orthodox, Monotheletism, Judaism; in the 16th century. There were small Catholic communities. The Crimean Tatar population of the Crimean Peninsula was partially exempt from taxes. The Greeks paid dzhyziya, the Italians were in a privileged position due to the partial tax relief made during the reign of Meñli Geray I. By the 18 century the population of the Crimean khanate was about 500 thousand people. The territory of the Crimean khanate was divided into Kinakanta (governorships), which consisted of Kadylyk, covering a number of settlements. Great Russian EncyclopediaКрымское ханство
— A. V. Vinogradov, S. F. Faizov Until the beginning of the 18th century, Crimean Nogays were known for frequent, at some periods almost annual,
slave raids
Slave raiding is a military raid for the purpose of capturing people and bringing them from the raid area to serve as slaves. Once seen as a normal part of warfare, it is nowadays widely considered a crime. Slave raiding has occurred since ant ...
into Ukraine and Russia.Brian L. Davies (2014). Warfare, State and Society on the Black Sea Steppe
'. pp. 15–26. Routledge. For a long time, until the late 18th century, the Crimean Khanate maintained a massive
slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
with the Ottoman Empire and the Middle East which was one of the important factors of its economy. One of the most important trading ports and slave markets was Kefe. According to the Ottoman census of 1526, taxes on the sale and purchase of slaves accounted for 24% of the funds, levied in Ottoman Crimea for all activities. But in fact, there were always small raids committed by both Tatars and Cossacks, in both directions.Alan W. Fisher, ''The Russian Annexation of the Crimea 1772–1783'', Cambridge University Pressp. 26.
/ref> The 17th century Ottoman writer and traveller
Evliya Çelebi
Derviş Mehmed Zillî (25 March 1611 – 1682), known as Evliya Çelebi ( ota, اوليا چلبى), was an Ottoman explorer who travelled through the territory of the Ottoman Empire and neighboring lands over a period of forty years, recording ...
wrote that there were 920,000 Ukrainian slaves in the Crimea but only 187,000 free Muslims. However, the Ukrainian historian Sergey Gromenko considers this testimony of Çelebi a myth popular among ultranationalists, pointing out that today it is known from the writings on economics that in the 17th century, the Crimea could feed no more than 500 thousand people. For comparison, according to the notes of the Consul of France to Qırım Giray
Khan Qırım Giray (1717–1769) was one of the most influential rulers of the Crimean Khanate. He was the patron of the Bakhchisaray Fountain and many Mosques throughout Crimea, and is also known to have extended the Bakhchisaray Palace.
Reig ...
khan Baron Totta, a hundred years later, in 1767, there were 4 million people living in the Crimean khanate, and in 1778, that is, just eleven years later, all the Christians were evicted from its territory by the Russian authorities, which turned out to be about 30 thousand, mostly Armenians and Greeks, and there were no Ukrainians among them. Also, according to more reliable modern sources than Evliya's data, slaves never constituted a significant part of the Crimean population. Russian professor Glagolev writes that there were 1.800.000 free Crimean Tatars in the Crimean Khanate in 1666, it also should be mentioned that a huge part of Ukraine was part of the Crimean Khanate, that is why Ukrainians could have been taken into account in the general population of the Khanate by Evliya (see Khan Ukraine).
Some researchers estimate that more than 2 million people were captured and enslaved during the time of the Crimean Khanate. Polish historian Bohdan Baranowski assumed that in the 17th century Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
(present-day Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
) lost an average of 20,000 yearly and as many as one million in all years combined from 1500 to 1644. In retaliation, the lands of Crimean Tatars were being raided by Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
, armed Ukrainian horsemen, who defended the steppe frontier – Wild Fields
The Wild Fields ( uk, Дике Поле, translit=Dyke Pole, russian: Дикое Поле, translit=Dikoye Polye, pl, Dzikie pola, lt, Dykra, la, Loca deserta or , also translated as "the wilderness") is a historical term used in the Polish ...
– against Tatar slave raids and often attacked and plundered the lands of Ottoman Turks and Crimean Tatars. The Don
Don, don or DON and variants may refer to:
Places
*County Donegal, Ireland, Chapman code DON
*Don (river), a river in European Russia
*Don River (disambiguation), several other rivers with the name
*Don, Benin, a town in Benin
*Don, Dang, a vill ...
Cossacks and Kalmyk Mongols also managed to raid Crimean Tatars' land. The last recorded major Crimean raid, before those in the Russo-Turkish War (1768–74)
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histor ...
took place during the reign of Peter the Great (1682–1725). However, Cossack raids continued after that time; Ottoman Grand Vizier complained to the Russian consul about raids to Crimea and Özi
Ochakiv, also known as Ochakov ( uk, Оча́ків, ; russian: Очаков; crh, Özü; ro, Oceacov and ''Vozia'', and Alektor ( in Greek), is a small city in Mykolaiv Raion, Mykolaiv Oblast, Mykolaiv Raion, Mykolaiv Oblast (region) of southe ...
in 1761. In 1769 one last major Tatar raid, which took place during the Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
, saw the capture of 20,000 slaves.
Nevertheless, some historians, including Russian historian Valery Vozgrin and Polish historian Oleksa Gayvoronsky have emphasized that the role of the slave trade in the economy of the Crimean Khanate is greatly exaggerated by modern historians, and the raiding-dependent economy is nothing but a historical myth. According to modern researches, livestock occupied a leading position in the economy of the Crimean Khanate, Crimean Khanate was one of the main wheat suppliers to the Ottoman Empire. Salt mining, viticulture and winemaking, horticulture and gardening were also developed as sources of income.
When reading the history of the Crimean Tatars, it is necessary to take into account that the historical science about the Crimean Tatars is strongly influenced by Russian historians who have rewritten the history of the Crimean Khanate to justify the annexation of the Crimea in 1783, and, especially, then by Soviet historians who distorted the history of the Crimea to justify the 1944 deportation of the Crimean Tatars
The deportation of the Crimean Tatars ( crh, Qırımtatar halqınıñ sürgünligi, Cyrillic: Къырымтатар халкъынынъ сюргюнлиги) or the Sürgünlik ('exile') was the ethnic cleansing and cultural genocide of at ...
.
In the Russian Empire

 The Russo-Turkish War (1768–74) resulted in the defeat of the Ottomans by the Russians, and according to the
The Russo-Turkish War (1768–74) resulted in the defeat of the Ottomans by the Russians, and according to the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca ( tr, Küçük Kaynarca Antlaşması; russian: Кючук-Кайнарджийский мир), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on 21 July 1774, in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kayn ...
(1774) signed after the war, Crimea became independent and the Ottomans renounced their political right to protect the Crimean Khanate. After a period of political unrest in Crimea, Russia violated the treaty and annexed the Crimean Khanate in 1783. After the annexation, the wealthier Tatars, who had exported wheat, meat, fish and wine to other parts of the Black Sea, began to be expelled and to move to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. Due to the oppression by the Russian administration and colonial politics of Russian Empire, the Crimean Tatars were forced to immigrate to the Ottoman Empire. Further expulsions followed in 1812 for fear of the reliability of the Tatars in the face of Napoleon's advance. Particularly, the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
of 1853–1856, the laws of 1860–63, the Tsarist policy and the Russo-Turkish War (1877–78)
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
caused an exodus of the Tatars; 12,000 boarded Allied ships in Sevastopol to escape the destruction of shelling, and were branded traitors by the Russian government. Of total Tatar population 300,000 of the Taurida Governorate
The Taurida Governorate (russian: Тавріическая губернія, modern spelling , ; crh, script=Latn, Tavrida guberniyası, ) or the Government of Taurida, was a historical governorate of the Russian Empire. It included the Crime ...
about 200,000 Crimean Tatars emigrated. Many Crimean Tatars perished in the process of emigration, including those who drowned while crossing the Black Sea. In total, from 1783 till the beginning of the 20th century, at least 800 thousand Tatars left Crimea. Today the descendants of these Crimeans form the Crimean Tatar diaspora
The Crimean Tatar diaspora dates back to the annexation of Crimea by Russia in 1783, after which Crimean Tatars emigrated in a series of waves spanning the period from 1783 to 1917. The diaspora was largely the result of the destruction of their so ...
in Bulgaria, Romania and Turkey.
Ismail Gasprali (1851–1914) was a renowned Crimean Tatar intellectual, influenced by the nationalist movements of the period, whose efforts laid the foundation for the modernization of Muslim culture and the emergence of the Crimean Tatar national identity. The bilingual Crimean Tatar-Russian newspaper '' Terciman-Perevodchik'' he published in 1883–1914, functioned as an educational tool through which a national consciousness and modern thinking emerged among the entire Turkic-speaking population of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
. After the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
this new elite, which included Noman Çelebicihan and Cafer Seydamet Qırımer proclaimed the first democratic republic in the Islamic world, named the Crimean People's Republic
The Crimean People's Republic ( crh, Qırım Halq Cumhuriyeti; uk, Кримська народна республіка, translit=Kryms'ka narodna respublika; russian: Крымская народная республика, translit=Krymskaya ...
on 26 December 1917. However, this republic was short-lived and abolished by the Bolshevik uprising in January 1918.
In the Soviet Union (1917–1991)
 As a part of the
As a part of the Russian famine of 1921
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
* Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and pe ...
the Peninsula suffered widespread starvation. More than 100,000 Crimean Tatars starved to death,Maria Drohobycky, ''Crimea: Dynamics, Challenges and Prospects'', Rowman & Littlefield, 1995, p.91, and tens of thousands of Tatars fled to Turkey or Romania. Thousands more were deported or killed during the collectivization
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member- ...
in 1928–29. The Soviet government's "collectivization" policies led to a major nationwide famine in 1931–33. Between 1917 and 1933, 150,000 Tatars—about 50% of the population at the time—either were killed or forced out of Crimea. During Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
's Great Purge
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Yezhov'), was Soviet General Secret ...
, statesmen and intellectuals such as Veli Ibraimov and Bekir Çoban-zade were imprisoned or executed on various charges.
In May 1944, the entire Crimean Tatar population of Crimea was exiled to Central Asia, mainly to Uzbekistan, on the orders of Joseph Stalin, the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and the Chairman of the USSR State Defense Committee. Although a great number of Crimean Tatar men served in the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
and took part in the partisan movement in Crimea during the war, the existence of a Tatar Legion in the Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
army and the collaboration of some Crimean Tatar religious and political leaders with Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
during the German occupation of Crimea provided the Soviet leadership with justification for accusing the entire Crimean Tatar population of being Nazi collaborators. Some modern researchers argue that Crimea's geopolitical position fueled Soviet perceptions of Crimean Tatars as a potential threat. This belief is based in part on an analogy with numerous other cases of deportations of non-Russians from boundary territories, as well as the fact that other non-Russian populations, such as Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
and Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely unders ...
were also removed from Crimea (see Deportation of the peoples inhabiting Crimea).
All 240,000 Crimean Tatars were deported
Deportation is the expulsion of a person or group of people from a place or country. The term ''expulsion'' is often used as a synonym for deportation, though expulsion is more often used in the context of international law, while deportation ...
''en masse'', in a form of collective punishment
Collective punishment is a punishment or sanction imposed on a group for acts allegedly perpetrated by a member of that group, which could be an ethnic or political group, or just the family, friends and neighbors of the perpetrator. Because ind ...
, on 17–18 May 1944 as "special settlers" to the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
Uzbekistan (, ) is the common English name for the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (Uzbek SSR; uz, Ўзбекистон Совет Социалистик Республикаси, Oʻzbekiston Sovet Sotsialistik Respublikasi, in Russian: Уз ...
and other distant parts of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. This event is called Sürgün in the Crimean Tatar language; the few who escaped were shot on sight or drowned in scuttled barges, and within months half their number had died of cold, hunger, exhaustion and disease. Many of them were re-located to toil as forced labourers in the Soviet GULAG
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in ...
system.
Civil rights movement
= Causes
= Starting in 1944, Crimean Tatars lived mostly in Central Asia with the designation as "special settlers", meaning that they had few rights. "Special settlers" were forbidden from leaving small designated areas and had to frequently sign in at a commandant's office. Soviet propaganda directed towards Uzbeks depicted Crimean Tatars as threats to their homeland, and as a result there were many documented hate crimes against Crimean-Tatar civilians by Uzbek Communist loyalists. In the 1950s the "special settler" regime ended, but Crimean Tatars were still kept closely tethered to Central Asia; while other deported ethnic groups like theChechens
The Chechens (; ce, Нохчий, , Old Chechen: Нахчой, ''Naxçoy''), historically also known as ''Kisti'' and ''Durdzuks'', are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group of the Nakh peoples native to the North Caucasus in Eastern Europe. "Eu ...
, Karachays
The Karachays ( krc, Къарачайлыла, Qaraçaylıla or таулула, , 'Mountaineers') are an indigenous Caucasian Turkic ethnic group in the North Caucasus. They speak Karachay-Balkar, a Turkic language. They are mostly situa ...
, and Kalmyks were fully allowed to return to their native lands during the Khrushchev thaw, economic and political reasons combined with basic misconceptions and stereotypes about Crimean Tatars led to Moscow and Tashkent being reluctant to allow Crimean Tatars the same right of return; the same decree that rehabilitated the beforementioned deported nations and restored their national republics urged Crimean Tatars who wanted a national republic to seek "national reunification" in the Tatar ASSR in lieu of restoration of the Crimean ASSR, much to the dismay of Crimean Tatars who bore no connection to or desire to "return" to Tatarstan. Moscow's refusal to allow a return was not only based out of a desire to satisfy the new Russian settlers in Crimea, who were very hostile to the idea of a return and had been subject to lots of Tatarophobic propaganda, but for economic reasons: high productivity from Crimean Tatar workers in Central Asia meant that letting the diaspora return would take a toll on Soviet industrialization goals in Central Asia. Historians have long suspected that violent resistance to confinement in exile from Chechens led to further willingness to let them return, while the non-violent Crimean Tatar movement did not lead to any desire for Crimean Tatars to leave Central Asia. In effect, the government was punishing Crimean Tatars for being Stakhanovites
The term Stakhanovite () originated in the Soviet Union and referred to workers who modeled themselves after Alexey Stakhanov. These workers took pride in their ability to produce more than was required, by working harder and more efficiently, th ...
while rewarding the deported nations that contributed less to the building of socialism, creating further resentment.
A 1967 Soviet decree removed the charges against Crimean Tatars on paper while simultaneously referring to them not by their proper ethnonym but by the euphemism that eventually became standard of "citizens of Tatar nationality who formerly lived in Crimea", angering many Crimean Tatars who realized it meant they were not even seen as Crimean Tatars by the government. In addition, the Soviet government did nothing to facilitate their resettlement in Crimea and to make reparations for lost lives and confiscated property. Before the mass return in the perestroika era, Crimean Tatars made up only 1.5% of Crimea's population, since government entities at all levels took a variety of measures beyond the already-debilitating residence permit system to keep them in Central Asia.
= Methods
= The abolition of the special settlement regime made it possible for Crimean Tatar rights activists to mobilize. The primary method of raising grievances with the government was petitioning. Many for the right of return gained over 100,000 signatures; although other methods of protest were occasionally used, the movement remained completely non-violent. When only a small percentage of Crimean Tatars were allowed to return to Crimea, those who were not granted residence permits would return to Crimea and try to live under the radar. However, the lack of a residence permit resulted in a second deportation for them. A last-resort method to avoid a second deportation was self-immolation, famously used by Crimean Tatar national hero Musa Mamut, one of those who moved to Crimea without a residence permit. He doused himself with gasoline and committed self-immolation in front of police trying to deport him on 23 June 1978. Mamut died of severe burns several days later, but expressed no regret for having committed self-immolation. Mamut posthumously became a symbol of Crimean Tatar resistance and nationhood, and remains celebrated by Crimean Tatars. Other notable self-immolations in the name of the Crimean Tatar right of return movement include that of Shavkat Yarullin, who fatally committed self-immolation in front of a government building in protest in October 1989, and Seidamet Balji who attempted self-immolation while being deported from Crimea in December that year but survived. Many other famous Crimean Tatars threatened government authorities with self-immolation if they continued to be ignored, includingHero of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union (russian: Герой Советского Союза, translit=Geroy Sovietskogo Soyuza) was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for ...
Abdraim Reshidov. In the later years of the Soviet Union, Crimean Tatar activists held picket protests in Red Square.
= Results
= After a prolonged effort of lobbying by the Crimean Tatar civil rights movement, the Soviet government established a commission in 1987 to evaluate the request for the right of return, chaired byAndrey Gromyko
Andrei Andreyevich Gromyko (russian: Андрей Андреевич Громыко; be, Андрэй Андрэевіч Грамыка; – 2 July 1989) was a Soviet communist politician and diplomat during the Cold War. He served as ...
. Gromyko's condescending attitude and failure to assure them that they would have the right of return ended up concerning members of the Crimean Tatar civil rights movement. In June 1988 he issued an official statement that rejected the request for re-establishment of a Crimean Tatar autonomy in Crimea and supported only allowing an organized return of a few more Crimean Tatars, while agreeing to allow the lower-priority requests of having more publications and school instruction in the Crimean Tatar language at the local level among areas with the deported populations. The conclusion that "no basis to renew autonomy and grant Crimean Tatars the right to return" triggered widespread protests. Less than two years after Gromyko's commission had rejected their request for autonomy and return, pogroms against the deported Meskhetian Turks were taking place in Central Asia. During the pogroms, some Crimean Tatars were targeted as well, resulting in changing attitudes towards allowing Crimean Tatars to move back to Crimea. Eventually a second commission, chaired by Gennady Yanaev and inclusive of Crimean Tatars on the board, was established in 1989 to reevaluate the issue, and it was decided that the deportation was illegal and the Crimean Tatars were granted the full right to return, revoking previous laws intended to make it as difficult as possible for Crimean Tatars to move to Crimea.
After Ukrainian independence
Today, more than 250,000 Crimean Tatars have returned to their homeland, struggling to re-establish their lives and reclaim their national and cultural rights against many social and economic obstacles. One-third of them are atheists, and over half that consider themselves religious are non-observant.2014 Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation
 Following news of Crimea's independence
Following news of Crimea's independence referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
organized with the help of Russia on 16 March 2014, the Kurultai leadership voiced concerns of renewed persecution, as commented by a U.S. official before the visit of a UN human rights team to the peninsula. At the same time, Rustam Minnikhanov
Rustam Nurgaliyevich Minnikhanov (russian: Руста́м Нургали́евич Минниха́нов, tt-Cyrl, Рөстәм Нургали улы Миңнеханов; born 1 March 1957) is a Russian politician who has served as ...
, the president of Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: Республика Татарстан, Respublika Tatarstan, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə tətɐrˈstan; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Республикасы), or simply Tatarstan (russian: Татарстан, tt ...
was dispatched to Crimea to quell Crimean Tatars' concerns and to state that "in the 23 years of Ukraine's independence the Ukrainian leaders have been using Crimean Tatars as pawns in their political games without doing them any tangible favors". The issue of Crimean Tatar persecution by Russia has since been raised regularly on an international level.
On 18 March 2014, the day Crimea was annexed by Russia, and Crimean Tatar was ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' declared one of the three official languages of Crimea. It was also announced that Crimean Tatars will be required to relinquish coastal lands on which they squatted since their return to Crimea in the early 1990s and be given land elsewhere in Crimea. Crimea stated it needed the relinquished land for "social purposes", since part of this land is occupied by the Crimean Tatars without legal documents of ownership. The situation was caused by the inability of the USSR (and later Ukraine) to sell the land to Crimean Tatars at a reasonable price instead of giving back to the Tatars the land owned before deportation, once they or their descendants returned from Central Asia (mainly Uzbekistan). As a consequence, some Crimean Tatars settled as squatters, occupying land that was and is still not legally registered.
 Some Crimean Tatars fled to Mainland
Some Crimean Tatars fled to Mainland Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
due to the Crimean crisis – reportedly around 2000 by 23 March. On 29 March 2014, an emergency meeting of the Crimean Tatars representative body, the Kurultai, voted in favor of seeking "ethnic and territorial autonomy" for Crimean Tatars using "political and legal" means. The meeting was attended by the Head of the Republic of Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: Республика Татарстан, Respublika Tatarstan, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə tətɐrˈstan; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Республикасы), or simply Tatarstan (russian: Татарстан, tt ...
and the chair of the Russian Council of Muftis. Decisions as to whether the Tatars will accept Russian passports or whether the autonomy sought would be within the Russian or Ukrainian state have been deferred pending further discussion.
The Mejlis works in emergency mode in Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Kyi ...
.
After the annexation of Crimea by Russian Federation, Crimean Tatars are reportedly persecuted and discriminated by Russian authorities, including cases of torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogational torture, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. definitions of tortur ...
, arbitrary detention
Arbitrary arrest and arbitrary detention are the arrest or detention of an individual in a case in which there is no likelihood or evidence that they committed a crime against legal statute, or in which there has been no proper due process of law ...
s, forced disappearance
An enforced disappearance (or forced disappearance) is the secret abduction or imprisonment of a person by a State (polity), state or political organization, or by a third party with the authorization, support, or acquiescence of a state or po ...
s by Russian security forces
Security forces are statutory organizations with internal security mandates. In the legal context of several nations, the term has variously denoted police and military units working in concert, or the role of military and paramilitary forces (su ...
and courts.
On 12 June 2018, Ukraine lodged a memorandum
A memorandum ( : memoranda; abbr: memo; from the Latin ''memorandum'', "(that) which is to be remembered") is a written message that is typically used in a professional setting. Commonly abbreviated "memo," these messages are usually brief and ...
consisting of 17,500 pages of text in 29 volumes to the UN's International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice (ICJ; french: Cour internationale de justice, links=no; ), sometimes known as the World Court, is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN). It settles disputes between states in accordanc ...
about racial discrimination
Racial discrimination is any discrimination against any individual on the basis of their skin color, race or ethnic origin.Individuals can discriminate by refusing to do business with, socialize with, or share resources with people of a certain g ...
against Crimean Tatars by Russian authorities in occupied Crimea and state financing of terrorism by Russian Federation in Donbas.
Culture
Yurts
A yurt (from the Turkic languages) or ger ( Mongolian) is a portable, round tent covered and insulated with skins or felt and traditionally used as a dwelling by several distinct nomadic groups in the steppes and mountains of Central Asia. ...
or nomadic tents have traditionally played an important role in the cultural history of Crimean Tatars. There are different types of yurts; some are large and collapsible, called "terme", while others are small and non-collapsible (otav).
On the Nowruz
Nowruz ( fa, نوروز, ; ), zh, 诺鲁孜节, ug, نەۋروز, ka, ნოვრუზ, ku, Newroz, he, נורוז, kk, Наурыз, ky, Нооруз, mn, Наурыз, ur, نوروز, tg, Наврӯз, tr, Nevruz, tk, Nowruz, ...
holiday, Crimean Tatars usually cook eggs, chicken soup, puff meat pie (kobete), halva, and sweet biscuits. Children put on masks and sing special songs under the windows of their neighbours, receiving sweets in return.
The songs (makam) of the nomadic steppe Crimean Tatars are characterized by diatonic, melodic simplicity and brevity. The songs of mountainous and southern coastal Crimean Tatars, called , are sung with richly ornamented melodies. Household lyricism
Lyricism is a quality that expresses deep feelings or emotions in an inspired work of art.
Often used to describe the capability of a Lyricist.
Description
Lyricism is when art is expressed in a beautiful or imaginative way, or when it has an ...
is also widespread. Occasionally, song competitions take place between young men and women during Crimean holidays and weddings. Ritual folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging ...
includes winter greetings, wedding songs, lamentations and circular dance songs (khoran). Epic stories or destans are very popular among the Crimean Tatars, particularly the destans of "Chora batyr", "Edige", " Koroglu" and others.
Today in use there are two types of alphabet: Cyrillic and Latin. Initially Crimean Tatars used Arabic script. In 1928 it was replaced with the Latin alphabet. Cyrillic was introduced in 1938 based on the Russian alphabet. The Cyrillic alphabet was the only official one between 1938 and 1997. All its letters coincide with those of the Russian alphabet. The 1990s saw the start of the gradual transition of the language to the new Latin alphabet based on the Turkish one.
Cuisine
The traditional cuisine of the Crimean Tatars has similarities with that ofGreeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
, Balkan peoples, Nogays
The Nogais ( Nogai: Ногай, , Ногайлар, ) are a Turkic ethnic group who live in the North Caucasus region. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia and Astrakhan Oblast; some als ...
, North Caucasians, and Volga Tatars
The Volga Tatars or simply Tatars ( tt-Cyrl, татарлар, tatarlar) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of Russia. They are subdivided into various subgroups. Volga Tatars are Russia's second-largest ethnicity after ...
, although some national dishes and dietary habits vary between different Crimean Tatar regional subgroups; for example, fish and produce are more popular among Yaliboylu Tatar dishes while meat and dairy is more prevalent in Steppe Tatar cuisine. Many Uzbek dishes were incorporated into Crimean Tatar national cuisine during exile in Central Asia since 1944, and these dishes have become prevalent in Crimea since the return. Uzbek samsa, laghman, and ( pilaf) are sold in most Tatar roadside cafes in Crimea as national dishes. In turn, some Crimean Tatar dishes, including chibureki, have been adopted by peoples outside Crimea, such as in Turkey and the North Caucasus.
Crimean Tatar political parties
National Movement of Crimean Tatars
Founded by Crimean Tatar civil rights activist Yuri Osmanov, the National Movement of Crimean Tatars (NDKT) was the major opposition faction to the Dzhemilev faction during the Soviet era. The official goal of the NDKT during the Soviet era was the restoration of the Crimean ASSR under the Leninist principle of national autonomy for titular indigenous peoples in their homeland, conflicting with the desires of an independent Tatar state from the OKND, the predecessor of the Mejilis. Yuri Osmanov, founder of the organization, was highly critical of Dzhemilev, saying that the OKND, the predecessor of the Mejilis, did not sufficiently try to mend ethnic tensions in Crimea. However, the OKND decreased in popularity after Yuri Osmanov was killed.Mejlis
In 1991, the Crimean Tatar leadership founded the Kurultai, or Parliament, to act as a representative body for the Crimean Tatars which could address grievances to the Ukrainian central government, the Crimean government, and international bodies.Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People
The Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People ( crh, Къырымтатар Миллий Меджлиси - ''Qırımtatar Milliy Meclisi'') is the single highest executive-representative body of the Crimean Tatars in period between sessions of the Q ...
is the executive body of the Kurultai.
From the 1990s until October 2013, the political leader of the Crimean Tatars and the chairman of the Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People
The Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People ( crh, Къырымтатар Миллий Меджлиси - ''Qırımtatar Milliy Meclisi'') is the single highest executive-representative body of the Crimean Tatars in period between sessions of the Q ...
was former Soviet dissident
Soviet dissidents were people who disagreed with certain features of Soviet ideology or with its entirety and who were willing to speak out against them. The term ''dissident'' was used in the Soviet Union in the period from the mid-1960s until ...
Mustafa Dzhemilev
Mustafa Abduldzhemil Jemilev ( crh, Mustafa Abdülcemil Cemilev, Мустафа Абдюльджемиль Джемилев, ), also known widely with his adopted descriptive surname Qırımoğlu "Son of Crimea" ( Crimean Tatar Cyrillic: , ; born ...
. Since October 2013 the chairman of the Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People
The Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People ( crh, Къырымтатар Миллий Меджлиси - ''Qırımtatar Milliy Meclisi'') is the single highest executive-representative body of the Crimean Tatars in period between sessions of the Q ...
has been Refat Chubarov
Refat Abdurahman oglu Chubarov; Crimean Tatar Cyrillic: Рефат Абдурахман огълу Чубаров uk, Рефат Абдурахманович Чубаров, translit=Refat Abdurakhmanovych Chubarov (born 22 September 1957) is ...
.
Following the 2014 Russian annexation of Crimea
In February and March 2014, Russia invaded and subsequently annexed the Crimean Peninsula from Ukraine. This event took place in the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity and is part of the wider Russo-Ukrainian War.
The events in Kyiv th ...
, Russian authorities declared the Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People an extremist organization, and banned it on 26 April 2016.Crimean court bans Tatar ruling body in blow to minority''
The Star (Malaysia)
''The Star'' () is an English-language newspaper in Malaysia. Based in Petaling Jaya, it was established in 1971 as a regional newspaper in Penang. It is the largest paid English newspaper in terms of circulation in Malaysia, according to the ...
'' (26 April 2016)
New Milliy Firqa
In 2006, a new Crimean Tatar party in opposition to the Mejlis was founded, taking the name of the previously-defunct Milly Firqa party from the early 20th century. The party claims to be successor of the ideas of Yuri Osmanov and NDKT.UDTTMR
InRomanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
*** Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
** Romanian cuisine, tradition ...
"Uniunea Democratica a Tatarilor Turco-Musulmani din Romania, UDTTMR" in Crimean Tatar "Romanya Müslüman Tatar Türklerĭ Demokrat Bĭrlĭgĭ, RMTTDB" is an ethnic minority political party in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
representing the Tatar community.

Notable Crimean Tatars
See also
* Index of articles related to Crimean Tatars *De-Tatarization of Crimea
The de-Tatarization of Crimea ( crh, Qırımnıñ tatarsızlaştırıluvı, italics=yes; russian: Детатаризация Крыма, Detatarizatsiya Kryma) refers to the Soviet and Russian efforts to remove traces of the indigenous Crimean Tat ...
* Aqmescit Friday mosque
* Crimean legends The interest in Crimean legends started at the end of the 19th century. The legends were published with a purpose of attraction of
attracting tourism.
Field work and publications of Crimean folklore were mostly done by non-professional folklorist ...
* Tatarophobia
Tatarophobia (russian: Татарофобия, Tatarofobiya) refers to the fear of, the hatred towards, demonization of, or prejudice against people who are generally referred to as Tatars, including but not limited to Volga, Siberian, and Crimean ...
References
Footnotes
Citations
Further reading
* Conquest, Robert. 1970. ''The Nation Killers: The Soviet Deportation of Nationalities'' (London: Macmillan). () * Fisher, Alan W. 1978. ''The Crimean Tatars.'' Stanford, CA:Hoover Institution Press
The Hoover Institution (officially The Hoover Institution on War, Revolution, and Peace; abbreviated as Hoover) is an American public policy think tank and research institution that promotes personal and economic liberty, free enterprise, and ...
. ()
* Fisher, Alan W. 1998. ''Between Russians, Ottomans and Turks: Crimea and Crimean Tatars'' (Istanbul: Isis Press, 1998). ()
* Nekrich, Alexander. 1978. ''The Punished Peoples: The Deportation and Fate of Soviet Minorities at the End of the Second World War'' (New York: W. W. Norton). ()
* Quelquejay, Lemercier. "The Tatars of the Crimea, a retrospective summary." ''Central Asian Review'' 16#1 (1968): 15–25.
*
* Williams, Brian Glyn. "The hidden ethnic cleansing of Muslims in the Soviet Union: The exile and repatriation of the Crimean Tatars." ''Journal of Contemporary History'' (2002): 323–347in JSTOR
* Williams, Brian Glyn. "The Crimean Tatar exile in Central Asia: a case study in group destruction and survival." ''Central Asian Survey'' 17.2 (1998): 285–317. * Williams, Brian Glyn. "The Ethnogenesis of the Crimean Tatars. An Historical Reinterpretation" ''Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society'' (2001) 11#3 pp. 329–34
in JSTOR
* Williams, Brian G.,
', Leyden: Brill, 2001.
Other languages
* Vozgrin, Valery, 2013, ''Istoriya krymskykh tatar'', Simferopol (four volumes). * Smirnov V D, 1886, ''Krymskoe khanstvo'' * Campana (Aurélie), Dufaud (Grégory) and Tournon (Sophie) (ed.), ''Les Déportations en héritage. Les peuples réprimés du Caucase et de Crimée, hier et aujourd'hui'', Rennes: Presses universitaires de Rennes, 2009. * *
External links
Official website of Qirim Tatar Cultural Association of Canada
Official web-site of Bizim QIRIM International Nongovernmental Organization
International Committee for Crimea
UNDP Crimea Integration and Development Programme
Crimean Tatars
Crimean Tatar words (Turkish)
Crimean Tatar words (English)
* State Defense Committee Decree No. 5859ss: On Crimean Tatars (See als
Three answers to the Decree No. 5859ss
Essays on Central Asia Index
'Крымская солидарность; ВОЗВРАЩЕНИЕ ДОМОЙ. РУСТЕМ ВАИТОВ' (YouTube channel of Crimean Tatar Solidarity; story of Rustem Vaitov returning home after 5 years of jail)
{{Authority control Ethnic groups in Crimea Ethnic groups in Bulgaria Ethnic groups in Romania Ethnic groups in Russia Ethnic groups in Turkey Ethnic groups in Ukraine Ethnic groups in Uzbekistan Turkic peoples of Europe Islam in Crimea Indigenous peoples of Europe Indigenous peoples of Ukraine Islam in Russia