Alsace (, ; ;
Low Alemannic German
Low Alemannic German (german: Niederalemannisch) is a branch of Alemannic German, which is part of Upper German. Its varieties are only partly intelligible to non-Alemannic speakers.
Subdivisions
*Lake Constance Alemannic ( de)
**Northern Vorar ...
/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a
territorial collectivity
A territorial collectivity (french: collectivité territoriale, previously '), or territorial authority, is a chartered subdivision of France with recognized governing authority. It is the generic name for any subdivision (subnational entity) wi ...
in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had a population of 1,898,533. Alsatian culture is characterized by a blend of Germanic and French influences.
Until 1871, Alsace included the area now known as the
Territoire de Belfort
The Territoire de Belfort () is a department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region, eastern France. It had a population of 141,318 in 2019.[région
France is divided into eighteen administrative regions (french: régions, singular ), of which thirteen are located in metropolitan France (in Europe), while the other five are overseas regions (not to be confused with the overseas collec ...]
'' in
metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
, consisting of the
Bas-Rhin
Bas-Rhin (; Alsatian: ''Unterelsàss'', ' or '; traditional german: links=no, Niederrhein; en, Lower Rhine) is a department in Alsace which is a part of the Grand Est super-region of France. The name means 'Lower Rhine', referring to its lo ...
and
Haut-Rhin
Haut-Rhin (, ; Alsatian: ''Owerelsàss'' or '; german: Oberelsass, ) is a department in the Grand Est region of France, bordering both Germany and Switzerland. It is named after the river Rhine. Its name means '' Upper Rhine''. Haut-Rhin is t ...
departments
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
. Territorial reform passed by the French Parliament in 2014 resulted in the merger of the Alsace administrative region with
Champagne-Ardenne
Champagne-Ardenne () is a former administrative region of France, located in the northeast of the country, bordering Belgium. Mostly corresponding to the historic province of Champagne, the region is known for its sparkling white wine of the ...
and
Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Gra ...
to form
Grand Est
Grand Est (; gsw-FR, Grossa Oschta; Moselle Franconian/ lb, Grouss Osten;
Rhine Franconian: ''Groß Oschte''; german: Großer Osten ; en, "Great East") is an administrative region in Northeastern France. It superseded three former administr ...
. On 1 January 2021, the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the new
European Collectivity of Alsace
The European Collectivity of Alsace (french: Collectivité européenne d'Alsace; gsw-FR, D'Europäischa Gebiatskärwerschàft Elsàss; german: Europäische Gebietskörperschaft Elsass) is a territorial collectivity in the Alsace region of France. ...
but remained part of the region Grand Est.
Alsatian is an
Alemannic dialect closely related to
Swabian
Swabian or Schwabian, or ''variation'', may refer to:
* the German region of Swabia (German: "''Schwaben''")
* Swabian German, a dialect spoken in Baden-Württemberg in south-west Germany and adjoining areas (German:"''Schwäbisch''")
* Danube S ...
, although since World War II most
Alsatians primarily speak French. Internal and international migration since 1945 has also changed the ethnolinguistic composition of Alsace. For more than 300 years, from the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
to
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the political status of Alsace was heavily contested between France and various German states in wars and diplomatic conferences. The economic and cultural capital of Alsace, as well as its largest city, is
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
, which sits on the contemporary German international border. The city is the seat of
several international organizations and bodies.
Etymology
The name ''Alsace'' can be traced to the
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old Hig ...
or ''Elisaz'', meaning "foreign domain". An alternative explanation is from a
Germanic ''Ell-sass'', meaning "seated on the
Ill ILL may refer to:
* ''I Love Lucy'', a landmark American television sitcom
* Illorsuit Heliport (location identifier: ILL), a heliport in Illorsuit, Greenland
* Institut Laue–Langevin, an internationally financed scientific facility
* Interlibrar ...
", a river in Alsace.
History
In prehistoric times, Alsace was inhabited by nomadic hunters. Later the province became a diffuse border region between the French and the German cultures and languages. After the end of the
Thirty Years War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battl ...
, southern Alsace was annexed by France in 1648, with most of the remainder conquered later in the century. In contrast to other parts of France, Protestants were permitted to practice their faith in Alsace even after the
Edict of Fontainebleau
The Edict of Fontainebleau (22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to practice their religion without ...
of 1685 that abolished their privileges in the rest of France.
After the 1870–71
Franco-Prussian War, Alsace was annexed by Germany and became a part of the 1871
unified German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
as a formal "Emperor's Land". After
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
the victorious Allies detached it from Germany and the province became part of the
Third French Republic
The French Third Republic (french: Troisième République, sometimes written as ) was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 194 ...
. After having been occupied and annexed by Germany during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, it was returned to France by the Allies at the end of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
Pre-Roman Alsace
The presence of hominids can be traced back 600,000 years ago.
By 1500 BC,
Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
s began to settle in Alsace, clearing and cultivating the land. Alsace is a plain surrounded by the
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
mountains (west) and the
Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is ...
mountains (east). It creates
Foehn wind
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the lee (downwind side) of a mountain range.
It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of ...
s which, along with natural irrigation, contribute to the fertility of the soil. In a world of agriculture, Alsace has always been a rich region which explains why it has suffered so many invasions and annexations in its history.
Roman Alsace
By 58 BC, the
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
had invaded and established Alsace as a center of
viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for '' vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of '' Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, r ...
. To protect this highly valued industry, the Romans built fortifications and military camps that evolved into various communities which have been inhabited continuously to the present day. While part of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
, Alsace was part of
Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesontio ...
.
Alemannic and Frankish Alsace
In 357 AD, Germanic tribes attempted to conquer Alsace but they were rebuffed by the Romans.
With the
decline of the Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
, Alsace became the territory of the Germanic
Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
. The Alemanni were agricultural people, and their Germanic language formed the basis of modern-day dialects spoken along the Upper Rhine (
Alsatian, Alemannian, Swabian, Swiss).
Clovis and the
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
defeated the Alemanni during the 5th century AD, culminating with the
Battle of Tolbiac
The Battle of Tolbiac was fought between the Franks, who were fighting under Clovis I, and the Alamanni, whose leader is not known. The date of the battle has traditionally been given as 496, though other accounts suggest it may either have been ...
, and Alsace became part of the
Kingdom of Austrasia. Under Clovis'
Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gaul ...
successors the inhabitants were Christianized. Alsace remained under Frankish control until the
Frankish realm
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks duri ...
, following the
Oaths of Strasbourg
The Oaths of Strasbourg were a military pact made on 14 February 842 by Charles the Bald and Louis the German against their older brother Lothair I, the designated heir of Louis the Pious, the successor of Charlemagne. One year later the T ...
of 842, was formally dissolved in 843 at the
Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
; the grandsons of
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
divided the realm into three parts. Alsace formed part of the
Middle Francia
Middle Francia ( la, Francia media) was a short-lived Frankish kingdom which was created in 843 by the Treaty of Verdun after an intermittent civil war between the grandsons of Charlemagne resulted in division of the united empire. Middle Franc ...
, which was ruled by the eldest grandson
Lothar I
Lothair I or Lothar I (Dutch and Medieval Latin: ''Lotharius''; German: ''Lothar''; French: ''Lothaire''; Italian: ''Lotario'') (795 – 29 September 855) was emperor (817–855, co-ruling with his father until 840), and the governor of Bavar ...
.
Lothar died early in 855 and his realm was divided into three parts. The part known as
Lotharingia
Lotharingia ( la, regnum Lotharii regnum Lothariense Lotharingia; french: Lotharingie; german: Reich des Lothar Lotharingien Mittelreich; nl, Lotharingen) was a short-lived medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire. As a more durable ...
, or Lorraine, was given to Lothar's son. The rest was shared between Lothar's brothers
Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (french: Charles le Chauve; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a se ...
(ruler of the
West Frankish
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about ...
realm) and
Louis the German
Louis the German (c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany and Louis II of East Francia, was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the P ...
(ruler of the
East Frankish realm). The Kingdom of Lotharingia was short-lived, however, becoming the
stem duchy
A stem duchy (german: Stammesherzogtum, from '' Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Bavarians and Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the German Empire at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dynasty (death of ...
of
Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Gra ...
in Eastern Francia after the
Treaty of Ribemont in 880. Alsace was united with the other Alemanni east of the Rhine into the stem
duchy of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia (German: ''Herzogtum Schwaben'') was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.
While the ...
.
Alsace within the Holy Roman Empire
At about this time, the surrounding areas experienced recurring fragmentation and reincorporations among a number of
feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
secular and ecclesiastical lordships, a common process in the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
. Alsace experienced great prosperity during the 12th and 13th centuries under
Hohenstaufen emperors.

Frederick I Frederick I may refer to:
* Frederick of Utrecht or Frederick I (815/16–834/38), Bishop of Utrecht.
* Frederick I, Duke of Upper Lorraine (942–978)
* Frederick I, Duke of Swabia (1050–1105)
* Frederick I, Count of Zoll ...
set up Alsace as a province (a ''
procuratio'', not a ''
provincia
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
'') to be ruled by
ministeriales
The ''ministeriales'' (singular: ''ministerialis'') were a class of people raised up from serfdom and placed in positions of power and responsibility in the High Middle Ages in the Holy Roman Empire.
The word and its German translations, ''Minist ...
, a non-noble class of civil servants. The idea was that such men would be more tractable and less likely to alienate the
fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
from the crown out of their own greed. The province had a single provincial court (''
Landgericht ''Landgericht'' may refer to:
* Landgericht (Germany), a mid-level court in the present-day judicial system of Germany
*: For example,
** Landgericht Berlin
** Landgericht Bremen
* Landgericht (medieval) The ''Landgericht'' (plural: ''Landgerichte ...
'') and a central administration with its seat at
Hagenau.
Frederick II designated the
Bishop of Strasbourg
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
These persons were bishop, archbishop or prince-bishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Strasbourg (including historically Prince-Bishopric of Strasbourg):
Bishops and prince-bishops
* Amandus
*Justinus ...
to administer Alsace, but the authority of the bishop was challenged by Count
Rudolf of Habsburg
Rudolf I (1 May 1218 – 15 July 1291) was the first King of Germany from the House of Habsburg. The first of the count-kings of Germany, he reigned from 1273 until his death.
Rudolf's election marked the end of the Great Interregnum whic ...
, who received his rights from Frederick II's son
Conrad IV
Conrad (25 April 1228 – 21 May 1254), a member of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, was the only son of Emperor Frederick II from his second marriage with Queen Isabella II of Jerusalem. He inherited the title of King of Jerusalem (as Conrad II) up ...
. Strasbourg began to grow to become the most populous and commercially important town in the region.
In 1262, after a long struggle with the ruling bishops, its citizens gained the status of
free imperial city
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
. A stop on the Paris-
Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
-
Orient
The Orient is a term for the East in relation to Europe, traditionally comprising anything belonging to the Eastern world. It is the antonym of '' Occident'', the Western World. In English, it is largely a metonym for, and coterminous with, the ...
trade route, as well as a port on the Rhine route linking
southern Germany
Southern Germany () is a region of Germany which has no exact boundary, but is generally taken to include the areas in which Upper German dialects are spoken, historically the stem duchies of Bavaria and Swabia or, in a modern context, Bavaria ...
and Switzerland to the Netherlands, England and
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
, it became the political and economic center of the region. Cities such as
Colmar
Colmar (, ; Alsatian: ' ; German during 1871–1918 and 1940–1945: ') is a city and commune in the Haut-Rhin department and Grand Est region of north-eastern France. The third-largest commune in Alsace (after Strasbourg and Mulhouse), it i ...
and
Hagenau also began to grow in economic importance and gained a kind of autonomy within the "
Décapole
The Décapole (''Dekapolis'' or german: Zehnstädtebund) was an alliance formed in 1354 by ten Imperial cities of the Holy Roman Empire in the Alsace region to maintain their rights. It was disbanded in 1679.
In 1354 Emperor Charles IV of Luxembo ...
" (or "Zehnstädtebund"), a federation of ten free towns.
Though little is known about the early history of the
Jews of Alsace, there is a lot of information from the 12th century onwards. They were successful as moneylenders and had the favor of the Emperor. As in much of Europe, the prosperity of Alsace was brought to an end in the 14th century by a series of harsh winters, bad harvests, and the
Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
. These hardships were blamed on Jews, leading to the
pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russian ...
s of 1336 and 1339. In 1349, Jews of Alsace were accused of poisoning the wells with
plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
, leading to the massacre of thousands of Jews during the
Strasbourg pogrom. Jews were subsequently forbidden to settle in the town. An additional natural disaster was the
Rhine rift
The Upper Rhine Plain, Rhine Rift Valley or Upper Rhine Graben (German: ''Oberrheinische Tiefebene'', ''Oberrheinisches Tiefland'' or ''Oberrheingraben'', French: ''Vallée du Rhin'') is a major rift, about and on average , between Basel in the s ...
earthquake of 1356, one of Europe's worst which made ruins of
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (B ...
. Prosperity returned to Alsace under
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
administration during the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
.

Holy Roman Empire central power had begun to decline following years of imperial adventures in Italian lands, often ceding hegemony in Western Europe to France, which had long since centralized power. France began an aggressive policy of expanding eastward, first to the rivers
Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
and
Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a ...
, and when those borders were reached, aiming for the Rhine. In 1299 the French proposed a marriage alliance between
Blanche (sister of
Philip IV of France
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (french: Philippe le Bel), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre as Philip I from ...
) and
Rudolf (son of
Albert I of Germany
Albert I of Habsburg (german: Albrecht I.) (July 12551 May 1308) was a Duke of Austria and Styria from 1282 and King of Germany from 1298 until his assassination. He was the eldest son of King Rudolf I of Germany and his first wife Gertrude o ...
), with Alsace to be the dowry; however, the deal never came off. In 1307, the town of
Belfort
Belfort (; archaic german: Beffert/Beffort) is a city in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in Northeastern France, situated between Lyon and Strasbourg, approximately from the France–Switzerland border. It is the prefecture of the Terri ...
was first chartered by the Counts of
Montbéliard
Montbéliard (; traditional ) is a town in the Doubs department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in eastern France, about from the border with Switzerland. It is one of the two subprefectures of the department.
History
Montbéliard is ...
. During the next century, France was to be militarily shattered by the
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagen ...
, which prevented for a time any further tendencies in this direction. After the conclusion of the war, France was again free to pursue its desire to reach the Rhine and in 1444 a French army appeared in Lorraine and Alsace. It took up winter quarters, demanded the submission of
Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand ...
and
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
and launched an attack on
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (B ...
.
In 1469, following the , Upper Alsace was sold by Archduke
Sigismund of Austria to
Charles the Bold
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477. ...
, Duke of Burgundy. Although Charles was the nominal landlord, taxes were paid to
Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick III (German: ''Friedrich III,'' 21 September 1415 – 19 August 1493) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1452 until his death. He was the fourth king and first emperor of the House of Habsburg. He was the penultimate emperor to be crowne ...
. The latter was able to use this tax and a dynastic marriage to his advantage to gain back full control of Upper Alsace (apart from the free towns, but including Belfort) in 1477 when it became part of the demesne of the Habsburg family, who were also rulers of the empire. The town of Mulhouse joined the
Swiss Confederation
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
in 1515, where it was to remain until 1798.
By the time of the
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
in the 16th century, Strasbourg was a prosperous community, and its inhabitants accepted Protestantism in 1523.
Martin Bucer
Martin Bucer ( early German: ''Martin Butzer''; 11 November 1491 – 28 February 1551) was a German Protestant reformer based in Strasbourg who influenced Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican doctrines and practices. Bucer was originally a me ...
was a prominent Protestant reformer in the region. His efforts were countered by the Roman Catholic Habsburgs who tried to eradicate heresy in Upper Alsace. As a result, Alsace was transformed into a mosaic of Catholic and Protestant territories. On the other hand,
Mömpelgard (Montbéliard) to the southwest of Alsace, belonging to the Counts of
Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Württ ...
since 1397, remained a Protestant enclave in France until 1793.
German ''Land'' within the Kingdom of France
This situation prevailed until 1639, when most of Alsace was conquered by France to keep it out of the hands of the
Spanish Habsburgs
Habsburg Spain is a contemporary historiographical term referring to the huge extent of territories (including modern-day Spain, a piece of south-east France, eventually Portugal, and many other lands outside of the Iberian Peninsula) ruled b ...
, who by
secret treaty
A secret treaty is a treaty ( international agreement) in which the contracting state parties have agreed to conceal the treaty's existence or substance from other states and the public.Helmut Tichy and Philip Bittner, "Article 80" in Olivier D ...
in 1617 had gained a clear road to their valuable and rebellious possessions in the
Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands ( Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the ...
, the
Spanish Road
The Spanish Road ( Spanish: ''Camino Español'', German: ''Spanische Straße'') was a military road and trade route in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries, linking the Duchy of Milan, the Franche-Comté and the Spanish Netherlands, ...
. Beset by enemies and seeking to gain a free hand in
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
, the Habsburgs sold their
Sundgau
Sundgau ( or ; ) is a geographical territory in the southern Alsace region ( Haut Rhin and Belfort), on the eastern edge of France. The name is derived from Alemannic German ''Sunt- gowe'' ("South shire"), denoting an Alemannic county in the Old ...
territory (mostly in Upper Alsace) to France in 1646, which had occupied it, for the sum of 1.2 million
Thaler
A thaler (; also taler, from german: Taler) is one of the large silver coins minted in the states and territories of the Holy Roman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy during the Early Modern period. A ''thaler'' size silver coin has a diameter o ...
s. When hostilities were concluded in 1648 with the
Treaty of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought ...
, most of Alsace was recognized as part of France, although some towns remained independent. The treaty stipulations regarding Alsace were complex. Although the French king gained sovereignty, existing rights and customs of the inhabitants were largely preserved. France continued to maintain its customs border along the
Vosges mountains
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
where it had been, leaving Alsace more economically oriented to neighbouring German-speaking lands. The German language remained in use in local administration, in schools, and at the (Lutheran)
University of Strasbourg
The University of Strasbourg (french: Université de Strasbourg, Unistra) is a public research university located in Strasbourg, Alsace, France, with over 52,000 students and 3,300 researchers.
The French university traces its history to the ea ...
, which continued to draw students from other German-speaking lands. The 1685
Edict of Fontainebleau
The Edict of Fontainebleau (22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to practice their religion without ...
, by which the French king ordered the suppression of
French Protestantism, was not applied in Alsace. France did endeavour to promote Catholicism.
Strasbourg Cathedral
Strasbourg Cathedral or the Cathedral of Our Lady of Strasbourg (french: Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Strasbourg, or ''Cathédrale de Strasbourg'', german: Liebfrauenmünster zu Straßburg or ''Straßburger Münster''), also known as Strasbourg ...
, for example, which had been Lutheran from 1524 to 1681, was returned to the Catholic Church. However, compared to the rest of France, Alsace enjoyed a climate of religious tolerance.

France consolidated its hold with the 1679
Treaties of Nijmegen, which brought most remaining towns under its control. France seized Strasbourg in 1681 in an unprovoked action. These territorial changes were recognised in the 1697
Treaty of Ryswick
The Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Gran ...
that ended the
War of the Grand Alliance
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between Kingdom of France, France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by t ...
.
But Alsace still contained islands of territory nominally under the sovereignty of German princes and an independent city-state at Mulhouse. These enclaves were established by law, prescription and international consensus.
From French Revolution to the Franco-Prussian War

The year 1789 brought the French Revolution and with it the first division of Alsace into the départements of
Haut- and
Bas-Rhin
Bas-Rhin (; Alsatian: ''Unterelsàss'', ' or '; traditional german: links=no, Niederrhein; en, Lower Rhine) is a department in Alsace which is a part of the Grand Est super-region of France. The name means 'Lower Rhine', referring to its lo ...
. Alsatians played an active role in the French Revolution. On 21 July 1789, after receiving news of the
Storming of the Bastille
The Storming of the Bastille (french: Prise de la Bastille ) occurred in Paris, France, on 14 July 1789, when revolutionary insurgents stormed and seized control of the medieval armoury, fortress, and political prison known as the Bastille. At ...
in Paris, a crowd of people stormed the Strasbourg city hall, forcing the city administrators to flee and putting symbolically an end to the feudal system in Alsace. In 1792,
Rouget de Lisle
Claude Joseph Rouget de Lisle (), sometimes spelled de l'Isle or de Lile (10 May 1760 – 26 June 1836), was a French army officer of the French Revolutionary Wars. He is known for writing the words and music of the ''Chant de guerre pour l'armé ...
composed in Strasbourg the Revolutionary marching song "
La Marseillaise
"La Marseillaise" is the national anthem of France. The song was written in 1792 by Claude Joseph Rouget de Lisle in Strasbourg after the declaration of war by France against Austria, and was originally titled "Chant de guerre pour l'Armée du R ...
" (as ''Marching song for the Army of the Rhine''), which later became the anthem of France. "La Marseillaise" was played for the first time in April of that year in front of the
mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well ...
of Strasbourg
Philippe-Frédéric de Dietrich. Some of the most famous generals of the French Revolution also came from Alsace, notably
Kellermann, the victor of
Valmy
Valmy () is a commune in the Marne department in north-eastern France.
Geography
The town stands on the west flank of the Argonne massif, midway between Verdun and Paris, near Vouziers.
History
Valmy provided the setting for the Battle of Val ...
,
Kléber, who led the armies of the French Republic in
Vendée
Vendée (; br, Vande) is a department in the Pays de la Loire region in Western France, on the Atlantic coast. In 2019, it had a population of 685,442. and
Westermann, who also fought in the Vendée.
Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning '' mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin department, in the Grand Est region, eastern France, close to the Swiss and German borders. It is the largest city in Haut-Rhin and second largest in Alsace a ...
(a city in southern Alsace), which had been part of Switzerland since 1466, joined France in 1798.
At the same time, some Alsatians were in opposition to the
Jacobins
, logo = JacobinVignette03.jpg
, logo_size = 180px
, logo_caption = Seal of the Jacobin Club (1792–1794)
, motto = "Live free or die"(french: Vivre libre ou mourir)
, successor = P ...
and sympathetic to the restoration of the monarchy pursued by the invading forces of
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
who sought to crush the nascent
revolutionary republic. Many of the residents of the
Sundgau
Sundgau ( or ; ) is a geographical territory in the southern Alsace region ( Haut Rhin and Belfort), on the eastern edge of France. The name is derived from Alemannic German ''Sunt- gowe'' ("South shire"), denoting an Alemannic county in the Old ...
made "pilgrimages" to places like
Mariastein Abbey
Mariastein Abbey (Kloster Mariastein) is a Benedictine monastery in Metzerlen-Mariastein in the Canton of Solothurn, Switzerland.
Mariastein, after Einsiedeln, is the second most important place of pilgrimage in Switzerland. Over the Chapel o ...
, near
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (B ...
, in Switzerland, for baptisms and weddings. When the
French Revolutionary Army
The French Revolutionary Army (french: Armée révolutionnaire française) was the French land force that fought the French Revolutionary Wars from 1792 to 1804. These armies were characterised by their revolutionary fervour, their poor equipme ...
of the Rhine was victorious, tens of thousands fled east before it. When they were later permitted to return (in some cases not until 1799), it was often to find that their lands and homes had been confiscated. These conditions led to emigration by hundreds of families to newly vacant lands in the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
in 1803–4 and again in 1808. A poignant retelling of this event based on what
Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as tr ...
had personally witnessed can be found in his long poem ''
Hermann and Dorothea''.
In response to the
"hundred day" restoration of
Napoleon I of France
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
in 1815, Alsace along with other frontier provinces of France was occupied by foreign forces from 1815 to 1818, including over 280,000 soldiers and 90,000 horses in Bas-Rhin alone. This had grave effects on trade and the economy of the region since former overland trade routes were switched to newly opened
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
and
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
seaports.
The population grew rapidly, from 800,000 in 1814 to 914,000 in 1830 and 1,067,000 in 1846. The combination of economic and demographic factors led to hunger, housing shortages and a lack of work for young people. Thus, it is not surprising that people left Alsace, not only for Paris – where the Alsatian community grew in numbers, with famous members such as
Georges-Eugène Haussmann
Georges-Eugène Haussmann, commonly known as Baron Haussmann (; 27 March 180911 January 1891), was a French official who served as prefect of Seine (1853–1870), chosen by Emperor Napoleon III to carry out a massive urban renewal programme of n ...
– but also for more distant places like Russia and the
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
, to take advantage of the new opportunities offered there: Austria had conquered lands in Eastern Europe from the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
and offered generous terms to colonists as a way of consolidating its hold on the new territories. Many Alsatians also began to sail to the United States, settling in many areas from 1820 to 1850. In 1843 and 1844, sailing ships bringing immigrant families from Alsace arrived at the port of New York. Some settled in Texas and Illinois, many to farm or to seek success in commercial ventures: for example, the sailing ships ''Sully'' (in May 1843) and ''Iowa'' (in June 1844) brought families who set up homes in northern Illinois and northern Indiana. Some Alsatian immigrants were noted for their roles in 19th-century American economic development. Others ventured to Canada to settle in southwestern
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, notably
Waterloo County
Waterloo County was a county in the Canadian province of Ontario from 1853 until 1973. It was the direct predecessor of the Regional Municipality of Waterloo.
Situated on a subset of land within the Haldimand Tract, the traditional territory of ...
.
Alsatian Jews
In contrast to the rest of France, the Jews in Alsace had not been expelled during the Middle Ages. By 1790, the
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
population of Alsace was approximately 22,500, about 3% of the provincial population. They were highly segregated and subject to long-standing
antisemitic
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Ant ...
regulations. They maintained their own customs,
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
language, and historic traditions within the tightly knit ghettos; they adhered to Jewish law. Jews were barred from most cities and instead lived in villages. They concentrated in trade, services, and especially in money lending. They financed about a third of the mortgages in Alsace. Official tolerance grew during the French Revolution, with full emancipation in 1791. However, local antisemitism also increased and Napoleon turned hostile in 1806, imposing a one-year moratorium on all debts owed to Jews. In the 1830–1870 era, most Jews moved to the cities, where they integrated and acculturated, as antisemitism sharply declined. By 1831, the state began paying salaries to official rabbis, and in 1846 a special legal oath for Jews was discontinued. Antisemitic local riots occasionally occurred, especially during the Revolution of 1848. The merger of Alsace into Germany in 1871–1918 lessened antisemitic violence. The constitution of the ''Reichsland'' of 1911 reserved one seat in the first chamber of the ''Landtag'' for a representative of the Jewish Consistory of Alsace-Lorraine (besides two seats respectively for the two main Christian denominations).
Struggle between France and united Germany

The
Franco-Prussian War, which
started in July 1870, saw France defeated in May 1871 by the
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
and other German states. The end of the war led to the
unification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of t ...
.
Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of ...
annexed Alsace and northern Lorraine to the new
German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
in 1871. France ceded more than 90% of Alsace and one-fourth of Lorraine, as stipulated in the
treaty of Frankfurt;
Belfort
Belfort (; archaic german: Beffert/Beffort) is a city in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in Northeastern France, situated between Lyon and Strasbourg, approximately from the France–Switzerland border. It is the prefecture of the Terri ...
, the largest Alsatian town south of Mulhouse, remained French. Unlike other member states of the German federation, which had governments of their own, the new ''Imperial territory of Alsace-Lorraine'' was under the sole authority of the
Kaiser
''Kaiser'' is the German word for "emperor" (female Kaiserin). In general, the German title in principle applies to rulers anywhere in the world above the rank of king (''König''). In English, the (untranslated) word ''Kaiser'' is mainly ap ...
, administered directly by the imperial government in Berlin. Between 100,000 and 130,000 Alsatians (of a total population of about a million and a half) chose to remain French citizens and leave ''Reichsland Elsaß-Lothringen'', many of them resettling in
French Algeria
French Algeria (french: Alger to 1839, then afterwards; unofficially , ar, الجزائر المستعمرة), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of French colonisation of Algeria. French rule in the region began in 1830 with the ...
as
Pieds-Noirs
The ''Pieds-Noirs'' (; ; ''Pied-Noir''), are the people of French and other European descent who were born in Algeria during the period of French rule from 1830 to 1962; the vast majority of whom departed for mainland France as soon as Alger ...
. Only in 1911 was Alsace-Lorraine granted some measure of autonomy, which was manifested also in a flag and an anthem (
Elsässisches Fahnenlied
The Elsässisches Fahnenlied (the "Hymn to the Alsatian Flag") was written by Emil Woerth (1870-1926) in German language, German when Alsace-Lorraine was part of the German Empire (1871-1918). It was adopted as the official anthem of Alsace-Lorrai ...
). In 1913, however, the
Saverne Affair
The Zabern or Saverne Affair was a crisis of domestic policy which occurred in the German Empire at the end of 1913. It was caused by political unrest in Zabern (now Saverne) in Alsace-Lorraine, where two battalions of the Prussian were garris ...
(''French'': Incident de Saverne) showed the limits of this new tolerance of the Alsatian identity.
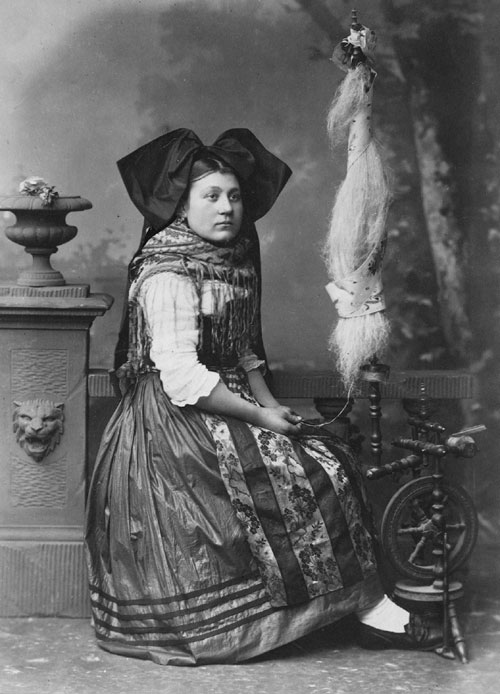

During the First World War, to avoid ground fights between brothers, many Alsatians served as sailors in the
Kaiserliche Marine
{{italic title
The adjective ''kaiserlich'' means "imperial" and was used in the German-speaking countries to refer to those institutions and establishments over which the ''Kaiser'' ("emperor") had immediate personal power of control.
The term wa ...
and took part in the Naval mutinies that led to the abdication of the Kaiser in November 1918, which left Alsace-Lorraine without a nominal head of state. The sailors returned home and tried to found an independent republic. While
Jacques Peirotes
Jacques Peirotes (1869, Strasbourg - 1935) was a French and German politician, mayor of Strasbourg from 1919 to 1929.
Biography
The young Jacques Peirotes, son of a carpenter working at the locomotives factory of Graffenstaden, learned the jo ...
, at this time deputy at the ''Landrat Elsass-Lothringen'' and just elected
mayor of Strasbourg, proclaimed the forfeiture of the German Empire and the advent of the
French Republic
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, a self-proclaimed government of Alsace-Lorraine declared its independence as the "
Republic of Alsace-Lorraine". French troops entered Alsace less than two weeks later to quash the worker strikes and remove the newly established Soviets and revolutionaries from power. With the arrival of the French soldiers, many Alsatians and local Prussian/German administrators and bureaucrats cheered the re-establishment of order.
Although U.S. President
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
had insisted that the ''région'' was self-ruling by legal status, as its constitution had stated it was bound to the sole authority of the Kaiser and not to the German state, France would allow no plebiscite, as granted by the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
to some eastern German territories at this time, because the French regarded the Alsatians as Frenchmen liberated from German rule. Germany ceded the region to France under the
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
.
Policies forbidding the use of German and requiring French were promptly introduced. In order not to antagonize the Alsatians, the region was not subjected to some legal changes that had occurred in the rest of France between 1871 and 1919, such as the
1905 French law on the separation of Church and State
The 1905 French law on the Separation of the Churches and State (French: ) was passed by the Chamber of Deputies on 9 December 1905. Enacted during the Third Republic, it established state secularism in France. France was then governed by the ''B ...
.

Alsace-Lorraine was occupied by Germany in 1940 during the Second World War. Although it was never formally annexed, Alsace-Lorraine was incorporated into the
Greater German Reich, which had been restructured into
Reichsgau
A (plural ) was an administrative subdivision created in a number of areas annexed by Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945.
Overview
The term was formed from the words (realm, empire) and , the latter a deliberately medieval-sounding word w ...
. Alsace was merged with
Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
, and Lorraine with the
Saarland
The Saarland (, ; french: Sarre ) is a state of Germany in the south west of the country. With an area of and population of 990,509 in 2018, it is the smallest German state in area apart from the city-states of Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg, a ...
, to become part of a planned
Westmark. During the war, 130,000 young men from Alsace and Lorraine were conscripted into the German armies against their will (
malgré-nous
The term Malgré-nous (, or more figuratively 'we who are forced against our will') refers to men from Alsace–Lorraine who were conscripted into the German military after the region's annexation from France during World War II. The female term ...
). There were some volunteers for the
Waffen SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with volunteers and conscripts from both occupied and unoccupied lands.
The grew from th ...
., although they were outnumbered by conscripts of the 1926–1927 classes. Thirty of said Waffen SS were involved in the
Oradour-sur-Glane massacre
On 10 June 1944, four days after D-Day, the village of Oradour-sur-Glane in Haute-Vienne in Nazi-occupied France was destroyed when 643 civilians, including non-combatant women and children, were massacred by a German Waffen-SS company.
A ne ...
(29 conscripts, one volunteer). A third of the malgré-nous perished on the Eastern front. In July 1944, 1500
malgré-nous
The term Malgré-nous (, or more figuratively 'we who are forced against our will') refers to men from Alsace–Lorraine who were conscripted into the German military after the region's annexation from France during World War II. The female term ...
were released from Soviet captivity and sent to
Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
, where they joined the
Free French Forces
__NOTOC__
The French Liberation Army (french: Armée française de la Libération or AFL) was the reunified French Army that arose from the merging of the Armée d'Afrique with the prior Free French Forces (french: Forces françaises libres, l ...
.
After World War II
Today, the territory is in certain areas subject to some laws that are significantly different from the rest of France – this is known as the
local law
A local ordinance is a law issued by a local government. such as a municipality, county, parish, prefecture, or the like.
China
In Hong Kong, all laws enacted by the territory's Legislative Council remain to be known as ''Ordinances'' () af ...
.
In more recent years, the Alsatian language is again being promoted by local, national, and European authorities as an element of the region's identity. Alsatian is taught in schools (but not mandatory) as one of the regional languages of France. German is also taught as a foreign language in local
kindergarten
Kindergarten is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally made in the late 18th cen ...
s and schools. There is a growing network of schools proposing full immersion in Alsatian dialect and in Standard German, called ''
ABCM-Zweisprachigkeit'' (ABCM -> French
acronym
An acronym is a word or name formed from the initial components of a longer name or phrase. Acronyms are usually formed from the initial letters of words, as in ''NATO'' (''North Atlantic Treaty Organization''), but sometimes use syllables, as ...
for "Association for Bilingualism in the Classroom from Kindergarten onwards", Zweisprachigkeit -> German for "Bilingualism"). However, the
Constitution of France
The current Constitution of France was adopted on 4 October 1958. It is typically called the Constitution of the Fifth Republic , and it replaced the Constitution of the Fourth Republic of 1946 with the exception of the preamble per a Consti ...
still requires that French be the only official language of the Republic.
Timeline
Geography
Topography
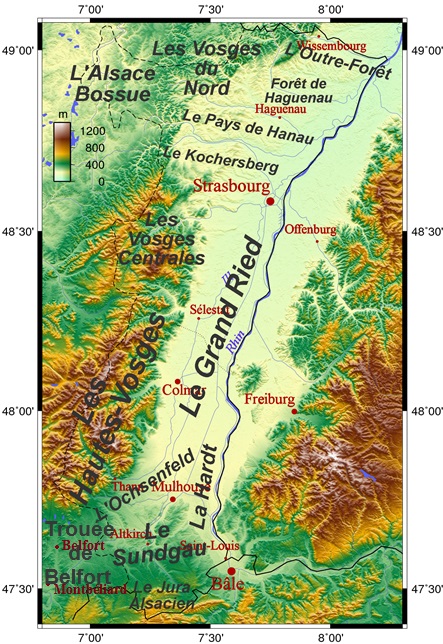
Alsace has an area of 8,283 km
2, making it the smallest ''
région
France is divided into eighteen administrative regions (french: régions, singular ), of which thirteen are located in metropolitan France (in Europe), while the other five are overseas regions (not to be confused with the overseas collec ...
'' of
metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
. It is almost four times longer than it is wide, corresponding to a plain between the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
in the east and the
Vosges mountains
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
in the west.
It includes the ''
départements
A department (, ) is an administrative or political division in several countries. Departments are the first-level divisions of 11 countries, nine in the Americas and two in Africa. An additional 10 countries use departments as second-level div ...
'' of
Haut-Rhin
Haut-Rhin (, ; Alsatian: ''Owerelsàss'' or '; german: Oberelsass, ) is a department in the Grand Est region of France, bordering both Germany and Switzerland. It is named after the river Rhine. Its name means '' Upper Rhine''. Haut-Rhin is t ...
and
Bas-Rhin
Bas-Rhin (; Alsatian: ''Unterelsàss'', ' or '; traditional german: links=no, Niederrhein; en, Lower Rhine) is a department in Alsace which is a part of the Grand Est super-region of France. The name means 'Lower Rhine', referring to its lo ...
(known previously as
Sundgau
Sundgau ( or ; ) is a geographical territory in the southern Alsace region ( Haut Rhin and Belfort), on the eastern edge of France. The name is derived from Alemannic German ''Sunt- gowe'' ("South shire"), denoting an Alemannic county in the Old ...
and
Nordgau). It borders Germany on the north and the east, Switzerland and
Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté (, ; ; Frainc-Comtou: ''Fraintche-Comtè''; frp, Franche-Comtât; also german: Freigrafschaft; es, Franco Condado; all ) is a cultural and historical region of eastern France. It is composed of the modern departments of Doubs, ...
on the south and
Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Gra ...
on the west.
Several
valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams ove ...
s are also found in the ''région''. Its highest point is the
Grand Ballon in
Haut-Rhin
Haut-Rhin (, ; Alsatian: ''Owerelsàss'' or '; german: Oberelsass, ) is a department in the Grand Est region of France, bordering both Germany and Switzerland. It is named after the river Rhine. Its name means '' Upper Rhine''. Haut-Rhin is t ...
, which reaches a height of 1426 m. It contains many forests, primarily in the
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
and in
Bas-Rhin
Bas-Rhin (; Alsatian: ''Unterelsàss'', ' or '; traditional german: links=no, Niederrhein; en, Lower Rhine) is a department in Alsace which is a part of the Grand Est super-region of France. The name means 'Lower Rhine', referring to its lo ...
(Haguenau Forest).
The
ried lies along the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
.
Geology

Alsace is the part of the plain of the Rhine located at the west of the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
, on its left bank. It is a
rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
or
graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic conte ...
, from the
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but t ...
epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided ...
, associated with its
horsts: the
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
and the
Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is ...
.
The
Jura Mountains
The Jura Mountains ( , , , ; french: Massif du Jura; german: Juragebirge; it, Massiccio del Giura, rm, Montagnas da Jura) are a sub-alpine mountain range a short distance north of the Western Alps and mainly demarcate a long part of the Fre ...
, formed by slip (induced by the alpine uplift) of the
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
cover on the
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest per ...
formations, goes through the area of
Belfort
Belfort (; archaic german: Beffert/Beffort) is a city in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in Northeastern France, situated between Lyon and Strasbourg, approximately from the France–Switzerland border. It is the prefecture of the Terri ...
.
Climate
Alsace has a
semi-continental climate at low altitude and a
continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing so ...
at high altitude. There is fairly low precipitation because the
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
protect it from the west. The city of
Colmar
Colmar (, ; Alsatian: ' ; German during 1871–1918 and 1940–1945: ') is a city and commune in the Haut-Rhin department and Grand Est region of north-eastern France. The third-largest commune in Alsace (after Strasbourg and Mulhouse), it i ...
has a
sunny microclimate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. The term may refer to areas as small as a few squ ...
; it is the second driest city in France, with an annual precipitation of 600 mm, making it ideal for ''
vin d'Alsace'' (''Alsatian wine'').
Governance
Since 2021, Alsace is a
territorial collectivity
A territorial collectivity (french: collectivité territoriale, previously '), or territorial authority, is a chartered subdivision of France with recognized governing authority. It is the generic name for any subdivision (subnational entity) wi ...
called the
European Collectivity of Alsace
The European Collectivity of Alsace (french: Collectivité européenne d'Alsace; gsw-FR, D'Europäischa Gebiatskärwerschàft Elsàss; german: Europäische Gebietskörperschaft Elsass) is a territorial collectivity in the Alsace region of France. ...
(''collectivité européenne d'Alsace'').
Administrative divisions
The European Collectivity of Alsace is divided into 2
departmental constituencies (''circonscriptions départementales''), 9
departmental arrondissements, 40
cantons, and 880
communes
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of social cohesion and teamwork from the start. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, relig ...
.

Bas-Rhin
Bas-Rhin (; Alsatian: ''Unterelsàss'', ' or '; traditional german: links=no, Niederrhein; en, Lower Rhine) is a department in Alsace which is a part of the Grand Est super-region of France. The name means 'Lower Rhine', referring to its lo ...
*
Arrondissement of Haguenau-Wissembourg
The arrondissement of Haguenau-Wissembourg (french: Arrondissement de Hanguenau-Wissembourg; gsw-FR, Arrondissement Hàwenau-Waisseburch) is an Arrondissements of France, arrondissement of France in the Bas-Rhin Departments of France, department ...
*
Arrondissement of Molsheim
The Arrondissement of Molsheim (french: Arrondissement de Molsheim; gsw-FR, Arrondissement Molse) is an arrondissement of France in the Bas-Rhin department in the Grand Est region. It has 77 communes. Its population is 103,633 (2016), and its ...
*
Arrondissement of Saverne
*
Arrondissement of Sélestat-Erstein
*
Arrondissement of Strasbourg
The arrondissement of Strasbourg (french: Arrondissement de Strasbourg; gsw-FR, Arrondissement Strossburi) is an arrondissement of France in the Bas-Rhin department in the Grand Est region. It has 33 communes. Its population is 494,089 (2017), an ...

Haut-Rhin
Haut-Rhin (, ; Alsatian: ''Owerelsàss'' or '; german: Oberelsass, ) is a department in the Grand Est region of France, bordering both Germany and Switzerland. It is named after the river Rhine. Its name means '' Upper Rhine''. Haut-Rhin is t ...
*
Arrondissement of Altkirch
*
Arrondissement of Colmar-Ribeauvillé
The arrondissement of Colmar-Ribeauvillé is an arrondissement of France in the Haut-Rhin department in the Grand Est region. It has 98 communes. Its population is 211,312 (2017), and its area is .
Composition
The communes of the arrondissement ...
*
Arrondissement of Guebwiller
The arrondissement of Guebwiller is a former arrondissement of France in the Haut-Rhin department in the Alsace region. In 2015 it was disbanded, and most of its communes were assigned to the new arrondissement of Thann-Guebwiller, some to the a ...
*
Arrondissement of Mulhouse
The arrondissement of Mulhouse is an arrondissement of France in the Haut-Rhin department in the Grand Est region. It has 79 communes. Its population is 351,012 (2016), and its area is .
Composition
The communes of the arrondissement of Mulhou ...
*
Arrondissement of Thann-Guebwiller
The arrondissement of Thann-Guebwiller is an arrondissement of France in the Haut-Rhin department in the Grand Est region. It has 81 communes. Its population is 130,270 (2016), and its area is .
Composition
The communes of the arrondissement ...
Society
Demographics
Alsace's population increased to 1,872,949 in 2014. It has regularly increased over time, except in wartime, by both natural growth and
migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
. This growth has even accelerated at the end of the 20th century.
INSEE estimates that its population will grow 8.5% to 14.5% between 1999 and 2030.
Immigration
Religion
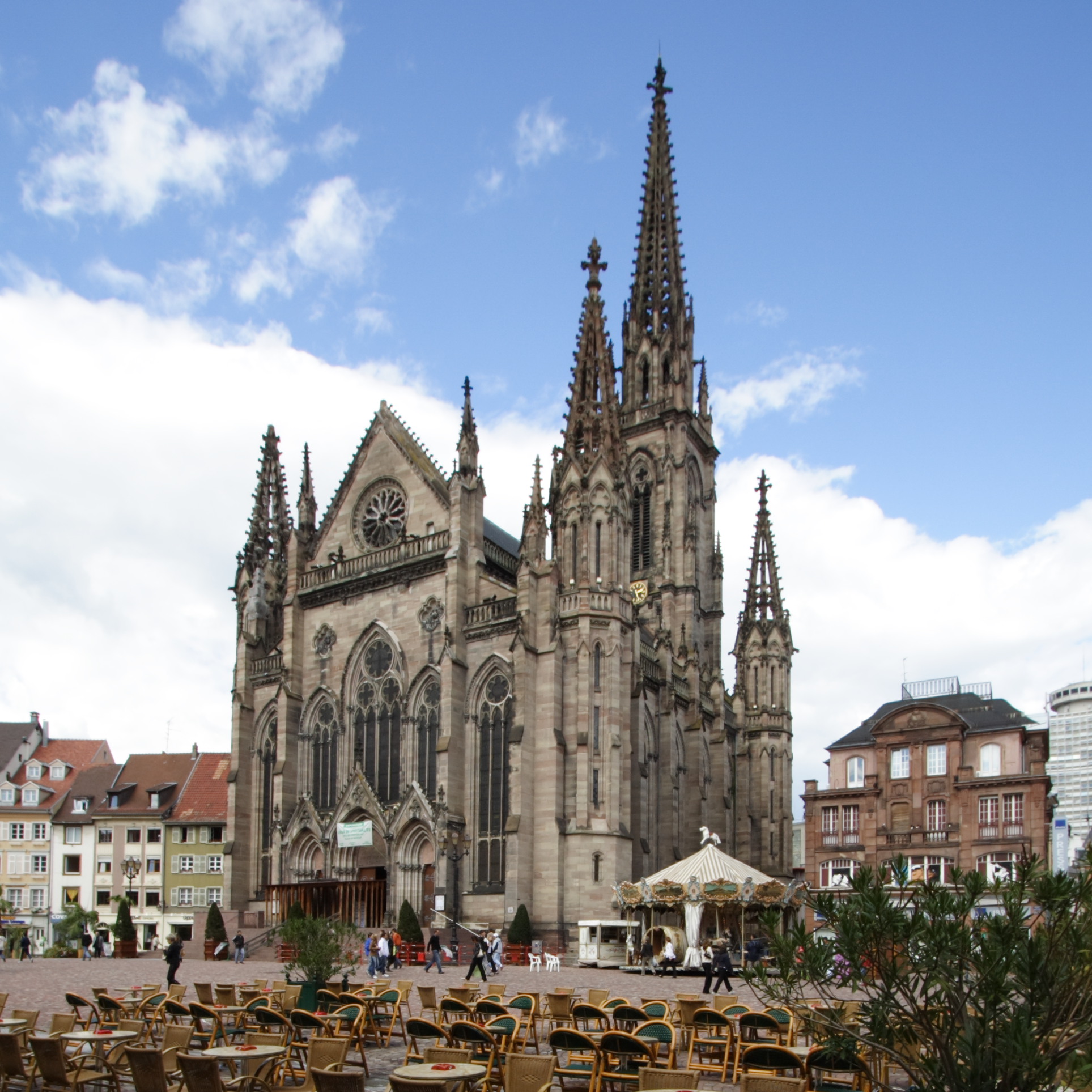

Alsace is generally seen as the most religious of all the French regions. Most of the Alsatian population is
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
, but, largely because of the region's
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
heritage, a significant
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
community also exists: today, the
EPCAAL
The Protestant Church of the Augsburg Confession of Alsace and Lorraine (french: Église protestante de la Confession d’Augsbourg d’Alsace et de Lorraine, ''EPCAAL''; german: Protestantische Kirche Augsburgischen Bekenntnisses von Elsass und ...
(a Lutheran church) is France's second largest Protestant church, also forming an administrative union (
UEPAL) with the much smaller Calvinist
EPRAL. Unlike the rest of France, the
Local law in Alsace-Moselle
The territory of the former Alsace-Lorraine, legally known as Alsace-Moselle, is a region in the eastern part of France, bordering with Germany. Its principal cities are Metz and Strasbourg. Alsace-Moselle was part of the German Empire from 1871 ...
still provides for the
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
ic
Concordat of 1801
The Concordat of 1801 was an agreement between Napoleon Bonaparte and Pope Pius VII, signed on 15 July 1801 in Paris. It remained in effect until 1905, except in Alsace-Lorraine, where it remains in force. It sought national reconciliation ...
and the
organic articles
The Organic Articles (French: ''"Les Articles Organiques"'') was a law administering public worship in France.
History
The Articles were originally presented by Napoléon Bonaparte, and consisted of 77 Articles relating to Catholicism and 44 ...
, which provides public subsidies to the Roman Catholic,
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
, and
Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John C ...
churches, as well as to Jewish synagogues; religion classes in one of these faiths is compulsory in public schools. This divergence in policy from the French majority is due to the region having been part of
Imperial Germany
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
when the
1905 law separating the French church and state was instituted (for a more comprehensive history, see:
Alsace-Lorraine). Controversy erupts periodically on the appropriateness of this legal disposition, as well as on the exclusion of other religions from this arrangement.
Following the
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
, promoted by local reformer
Martin Bucer
Martin Bucer ( early German: ''Martin Butzer''; 11 November 1491 – 28 February 1551) was a German Protestant reformer based in Strasbourg who influenced Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican doctrines and practices. Bucer was originally a me ...
, the principle of ''
cuius regio, eius religio
() is a Latin phrase which literally means "whose realm, their religion" – meaning that the religion of the ruler was to dictate the religion of those ruled. This legal principle marked a major development in the collective (if not individual ...
'' led to a certain amount of religious diversity in the highlands of northern Alsace. Landowners, who as "local lords" had the right to decide which religion was allowed on their land, were eager to entice populations from the more attractive lowlands to settle and develop their property. Many accepted without discrimination Catholics, Lutherans, Calvinists, Jews and
Anabaptist
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
s.
Multiconfessional
Multiconfessional countries have a power sharing arrangement between people of different faiths, usually three or more significant confessional groups within the same jurisdiction. Examples of modern countries deemed multiconfessional are Lebano ...
villages appeared, particularly in the region of
Alsace bossue
The Alsace bossue ( Alemannic and Frankish: ''S'Gromme/S'Krumme Elsass'', German: ''das krumme Elsass/ Krummes Elsass''), is a territory of Bas-Rhin in Alsace, which includes the three former cantons of Sarre-Union, Drulingen and La Petite-Pierre ...
. Alsace became one of the French regions boasting a thriving Jewish community, and the only region with a noticeable Anabaptist population.
Philipp Jakob Spener
Philipp Jakob Spener (23 January 1635 – 5 February 1705), was a German Lutheran theologian who essentially founded what would become to be known as Pietism. He was later dubbed the "Father of Pietism". A prolific writer, his two main works, ' ...
who founded
Pietism
Pietism (), also known as Pietistic Lutheranism, is a movement within Lutheranism that combines its emphasis on biblical doctrine with an emphasis on individual piety and living a holy Christian life, including a social concern for the needy an ...
was born in Alsace. The schism of the
Amish
The Amish (; pdc, Amisch; german: link=no, Amische), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptist Christian church fellowships with Swiss German and Alsatian origins. They are closely related to Mennonite churc ...
under the lead of
Jacob Amman
Jakob Ammann (also Jacob Amman, Amann; 12 February 1644 – between 1712 and 1730) was an Anabaptist leader and namesake of the Amish religious movement.
Personal life
The full facts about the personal life of Jacob Ammann are incomplete ...
from the
Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the R ...
s occurred in 1693 in
Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines
Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines (; ; Alsatian: ''Màrkìrisch'') is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department and Grand Est region of north-eastern France.
Geography
Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines is located in the massif of the Vosges Mountains, where it occupie ...
. The strongly Catholic
Louis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
tried in vain to drive them from Alsace. When
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
imposed military conscription without religious exception, most emigrated to the American continent.
In 1707, the
simultaneum forced many Reformed and Lutheran church buildings to also allow Catholic services. About 50 such "simultaneous churches" still exist in modern Alsace, though with the Catholic church's general lack of priests they tend to hold Catholic services only occasionally.
Culture
Alsace historically was part of the Holy Roman Empire and the German realm of culture. Since the 17th century, the region has passed between German and French control numerous times, resulting in a cultural blend. German traits remain in the more traditional, rural parts of the culture, such as the
cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
and architecture, whereas modern institutions are totally dominated by French culture.
Symbolism

Strasbourg

Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
's arms are the colours of the shield of the
Bishop of Strasbourg
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
These persons were bishop, archbishop or prince-bishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Strasbourg (including historically Prince-Bishopric of Strasbourg):
Bishops and prince-bishops
* Amandus
*Justinus ...
(a band of red on a white field, also considered an inversion of the arms of the diocese) at the end of a revolt of the burghers during the Middle Ages who took their independence from the teachings of the Bishop. It retains its power over the surrounding area.
Flags


There is controversy around the recognition of the Alsatian flag. The authentic historical flag is the ''Rot-un-Wiss''; Red and White are commonly found on the coat of arms of Alsatian cities (Strasbourg, Mulhouse, Sélestat...) and of many Swiss cities, especially in
Basel's region. The German region
Hesse
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are ...
uses a flag similar to the Rot-un-Wiss. As it underlines the Germanic roots of the region, it was ''replaced'' in 1949 by a new "Union jack-like" flag representing the union of the two départements. It has, however, no real historical relevance. It has been since replaced again by a slightly different one, also representing the two départements. With the purpose of "Francizing" the region, the Rot-un-Wiss has not been recognized by Paris. Some overzealous statesmen have called it a Nazi invention – while its origins date back to the 11th century and the Red and White banner of
Gérard de Lorraine (aka. d'Alsace). The Rot-un-Wiss flag is still known as the real historical emblem of the region by most of the population and the départements' parliaments and has been widely used during protests against the creation of a new "super-region" gathering
Champagne-Ardennes
Champagne-Ardenne () is a former administrative region of France, located in the northeast of the country, bordering Belgium. Mostly corresponding to the historic province of Champagne, the region is known for its sparkling white wine of th ...
,
Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Gra ...
and Alsace, namely on Colmar's statue of liberty.
Language

Although German dialects were spoken in Alsace for most of its history, the dominant language in Alsace today is French.
The traditional language of the ''région'' is
Alsatian, an
Alemannic dialect of
Upper German
Upper German (german: Oberdeutsch ) is a family of High German dialects spoken primarily in the southern German-speaking area ().
History
In the Old High German time, only Alemannic and Bairisch are grouped as Upper German. In the Middle High ...
spoken on both sides of the Rhine and closely related to
Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , gsw, Schwiizerdütsch, Schwyzerdütsch, Schwiizertüütsch, Schwizertitsch Mundart,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no defined orthography for any of them, many different spelling ...
. Some
Frankish dialects of
West Central German
West Central German (german: Westmitteldeutsch) belongs to the Central, High German dialect family of German. Its dialects are Franconian and comprise the parts of the Rhinelandic continuum located south of the Benrath line isogloss, including ...
are also spoken in "Alsace Bossue" and in the extreme north of Alsace.
As is customary for
regional language
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
s in France, neither Alsatian nor the Frankish dialects have any form of official status, although both are now recognized as
languages of France
Of the languages of France, French is the sole official language according to the second article of the French Constitution. French, a Gallo-Romance language, is spoken by nearly the entire population of France.
In addition to French, several ...
and can be chosen as subjects in
lycées
In France, secondary education is in two stages:
* ''Collèges'' () cater for the first four years of secondary education from the ages of 11 to 15.
* ''Lycées'' () provide a three-year course of further secondary education for children betwee ...
.
Although Alsace has been part of France multiple times in the past, the region had no direct connection with the French state for several centuries. From the end of the Roman Empire (5th century) to the French annexation (17th century), Alsace was politically part of the German world.
During the
Lutheran Reform, the towns of Alsace were the first to adopt the German language as their official language instead of
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
. It was in Strasbourg that German was first used for the liturgy. It was also in Strasbourg that the first German Bible was published in 1466.
From the annexation of Alsace by France in the 17th century and the language policy of the French Revolution up to 1870, knowledge of French in Alsace increased considerably. With the education reforms of the 19th century, the middle classes began to speak and write French well. The French language never really managed, however, to win over the masses, the vast majority of whom continued to speak their German dialects and write in German (which we would now call "standard German").
Between 1870 and 1918, Alsace was annexed by the German Empire in the form of an imperial province or Reichsland, and the mandatory official language, especially in schools, became High German. French lost ground to such an extent that it has been estimated that only 2% of the population spoke French fluently and only 8% had some knowledge of it (Maugue, 1970).
After 1918, French was the only language used in schools, and particularly primary schools. After much argument and discussion and after many temporary measures, a memorandum was issued by Vice-Chancellor Pfister in 1927 and governed education in primary schools until 1939.
During a reannexation by Germany (1940–1945), High German was reinstated as the language of education. The population was forced to speak German and 'French' family names were Germanized. Following the Second World War, the 1927 regulation was not reinstated and the teaching of German in primary schools was suspended by a provisional rectorial decree, which was supposed to enable French to regain lost ground. The teaching of German became a major issue, however, as early as 1946. Following World War II, the French government pursued, in line with its traditional
language policy
Language policy is an interdisciplinary academic field. Some scholars such as Joshua Fishman and Ofelia García consider it as part of sociolinguistics. On the other hand, other scholars such as Bernard SpolskyRobert B. Kaplanand Joseph Lo Bianc ...
, a campaign to suppress the use of German as part of a wider
Francization
Francization (in American English, Canadian English, and Oxford English) or Francisation (in other British English), Frenchification, or Gallicization is the expansion of French language use—either through willful adoption or coercion—by more ...
campaign.
In 1951, Article 10 of the
Deixonne Law (''Loi Deixonne'') on the teaching of local languages and dialects made provision for
Breton,
Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
,
Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
and old
Provençal, but not for
Corsican,
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
(
West Flemish
West Flemish (''West-Vlams'' or ''West-Vloams'' or ''Vlaemsch'' (in French-Flanders), nl, West-Vlaams, french: link=no, flamand occidental) is a collection of Dutch dialects spoken in western Belgium and the neighbouring areas of France and ...
) or Alsatian in Alsace and
Moselle
The Moselle ( , ; german: Mosel ; lb, Musel ) is a river that rises in the Vosges mountains and flows through north-eastern France and Luxembourg to western Germany. It is a left bank tributary of the Rhine, which it joins at Koblenz. A ...
. However, in a Decree of 18 December 1952, supplemented by an Order of 19 December of the same year, optional teaching of the German language was introduced in elementary schools in Communes where the language of habitual use was the Alsatian dialect.
In 1972, the Inspector General of German, Georges Holderith, obtained authorization to reintroduce German into 33 intermediate classes on an experimental basis. This teaching of German, referred to as the Holderith Reform, was later extended to all pupils in the last two years of elementary school. This reform is still largely the basis of German teaching (but not Alsatian) in elementary schools today.
It was not until 9 June 1982, with the ''Circulaire sur la langue et la culture régionales en Alsace'' (Memorandum on regional language and culture in Alsace) issued by the Vice-Chancellor of the Académie Pierre Deyon, that the teaching of German in primary schools in Alsace really began to be given more official status. The Ministerial Memorandum of 21 June 1982, known as the Circulaire Savary, introduced financial support, over three years, for the teaching of regional languages in schools and universities. This memorandum was, however, implemented in a fairly lax manner.
Both Alsatian and Standard German were for a time banned from public life (including street and city names, official administration, and educational system). Though the ban has long been lifted and street signs today are often bilingual, Alsace-Lorraine is today predominantly French in language and culture. Few young people speak Alsatian today, although there do still exist one or two enclaves in the
Sundgau
Sundgau ( or ; ) is a geographical territory in the southern Alsace region ( Haut Rhin and Belfort), on the eastern edge of France. The name is derived from Alemannic German ''Sunt- gowe'' ("South shire"), denoting an Alemannic county in the Old ...
region where some older inhabitants cannot speak French, and where Alsatian is still used as the mother tongue. A related
Alemannic German
Alemannic, or rarely Alemannish (''Alemannisch'', ), is a group of High German dialects. The name derives from the ancient Germanic tribal confederation known as the Alamanni ("all men").
Distribution
Alemannic dialects are spoken by approxi ...
survives on the opposite bank of the Rhine, in
Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
, and especially in Switzerland. However, while French is the major language of the region, the Alsatian dialect of French is heavily influenced by German and other languages such as Yiddish in phonology and vocabulary.
This situation has spurred a movement to preserve the Alsatian language, which is perceived as endangered, a situation paralleled in other ''régions'' of France, such as
Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
or
Occitania
Occitania ( oc, Occitània , , or ) is the historical region in Western and Southern Europe where the Occitan language was historically spoken and where it is sometimes still used as a second language. This cultural area roughly encompasse ...
. Alsatian is now taught in French high schools. Increasingly, French is the only language used at home and at work, whereas a growing number of people have a good knowledge of
standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
as a foreign language learned in school.
The constitution of the Fifth Republic states that French alone is the official language of the Republic. However, Alsatian, along with other regional languages, are recognized by the French government in the official list of languages of France.
Although the French government signed the
European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, th ...
in 1992, it never ratified the treaty and therefore no legal basis exists for any of the regional languages in France. However, visitors to Alsace can see indications of renewed political and cultural interest in the language – in Alsatian signs appearing in car-windows and on hoardings, and in new official bilingual street signs in Strasbourg and Mulhouse.
A 1999 INSEE survey, included in the 1999 Census, the majority of the population in Alsace speak
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
as their first language, 39.0% (or 500,000 people) of the population speak
Alsatian, 16.2% (or 208,000 people) speak
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, 75,200 people speak
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
(or 5.9%) and 27,600 people speak
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
.
The survey counted 548,000 adult speakers of Alsatian in France, making it the second most-spoken regional language in the country (after
Occitan). Like all regional languages in France, however, the transmission of Alsatian is on the decline. While 39% of the adult population of Alsace speak Alsatian, only one in four children speak it, and only one in ten children uses it regularly.
Architecture

The traditional habitat of the Alsatian lowland, like in other regions of Germany and Northern Europe, consists of houses constructed with walls in
timber framing
Timber framing (german: Holzfachwerk) and "post-and-beam" construction are traditional methods of building with heavy timbers, creating structures using squared-off and carefully fitted and joined timbers with joints secured by large woode ...
and cob and roofing in flat tiles. This type of construction is abundant in adjacent parts of Germany and can be seen in other areas of France, but their particular abundance in Alsace is owed to several reasons:
# The proximity to the
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
where the wood can be found.
# During periods of war and bubonic plague, villages were often burned down, so to prevent the collapse of the upper floors, ground floors were built of stone and upper floors built in half-timberings to prevent the spread of fire.
# During most of the part of its history, a great part of Alsace was flooded by the Rhine every year. Half-timbered houses were easy to knock down and to move around during those times (a day was necessary to move it and a day to rebuild it in another place).
However, half-timbering was found to increase the risk of fire, which is why from the 19th century, it began to be rendered. In recent times, villagers started to paint the rendering white in accordance with Beaux-Arts movements. To discourage this, the region's authorities gave financial grants to the inhabitants to paint the rendering in various colours, in order to return to the original style and many inhabitants accepted (more for financial reasons than by firm belief).
Cuisine
 Alsatian cuisine
Alsatian cuisine, somewhat based on German culinary traditions, is marked by the use of pork in various forms. It is perhaps mostly known for the region's wines and beers. Traditional dishes include ''
baeckeoffe
Baeckeoffe (English: "bake oven") is a casserole dish that is typical in the French region of Alsace, situated on the border with Germany.
In the Alsatian dialect, Baeckeoffe means "baker's oven". It is a mix of sliced potatoes, sliced onions, ...
'', ''
flammekueche
Flammekueche ( Alsatian; Standard German: ''Flammkuchen''), or tarte flambée (French), is a speciality of the region of Alsace, German-speaking Moselle, Baden and the Palatinate. It is composed of bread dough rolled out very thinly in the sha ...
'', ''
choucroute'', and ''
fleischnacka
FleischschnackasSpelling of Alsatian words depends on the geographic area. () ( Alsatian word) are an Alsatian dish made from cooked meat stuffing (usually the remainders of pot-au-feu), eggs, onions, parsley, salt, pepper rolled in a fresh egg p ...
''. Southern Alsace, also called the
Sundgau
Sundgau ( or ; ) is a geographical territory in the southern Alsace region ( Haut Rhin and Belfort), on the eastern edge of France. The name is derived from Alemannic German ''Sunt- gowe'' ("South shire"), denoting an Alemannic county in the Old ...
, is characterized by ''
carpe frite'' (that also exists in
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
tradition).
Food

The festivities of the year's end involve the production of a great variety of biscuits and small cakes called ''
bredela'' as well as ''
pain d'épices
' or ' () is a French cake or quick bread. Its ingredients, according to ' (1694), were "rye flour, honey and spices". In Alsace, a considerable tradition incorporates a pinch of cinnamon.
According to Maguelonne Toussaint-Samat, the commercial ...
'' (
gingerbread
Gingerbread refers to a broad category of baked goods, typically flavored with ginger, cloves, nutmeg, and cinnamon and sweetened with honey, sugar, or molasses. Gingerbread foods vary, ranging from a moist loaf cake to forms nearly as cr ...
cakes) which are baked around Christmas time. The
Kugelhupf
A Gugelhupf (also ''Kugelhupf'', ''Guglhupf'', ''Gugelhopf'', and, in France, ''kouglof'', ''kougelhof'', or ''kougelhopf'') is a cake traditionally baked in a distinctive ring pan, similar to Bundt cake, but leavened with baker's yeast.
Ther ...
is also popular in Alsace, and the
Christstollen during the Christmas season.
The gastronomic symbol of the ''région'' is undoubtedly the
Choucroute, a local variety of
Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut (; , "sour cabbage") is finely cut raw cabbage that has been fermented by various lactic acid bacteria. It has a long shelf life and a distinctive sour flavor, both of which result from the lactic acid formed when the bacteria ...
. The word Sauerkraut in Alsatian has the form ''sûrkrût'', same as in other southwestern German dialects, and means "sour cabbage" as its
Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
equivalent. This word was included into the French language as ''choucroute''. To make it, the cabbage is finely shredded, layered with salt and
juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arc ...
and left to ferment in wooden barrels. Sauerkraut can be served with poultry, pork, sausage or even fish. Traditionally it is served with Strasbourg sausage or frankfurters, bacon, smoked pork or smoked
Morteau
Morteau () is a commune, in the Doubs department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region, eastern France.
300px, The road of Doubs_(river).html"_;"title="Villers-le-Lac_(D215)_along_the_Doubs_(river)">Villers-le-Lac_(D215)_along_the_Doubs_(rive ...
or
Montbéliard
Montbéliard (; traditional ) is a town in the Doubs department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in eastern France, about from the border with Switzerland. It is one of the two subprefectures of the department.
History
Montbéliard is ...
sausages, or a selection of other pork products. Served alongside are often roasted or steamed potatoes or dumplings.
Alsace is also well known for its
foie gras
Foie gras (, ; ) is a specialty food product made of the liver of a duck or goose. According to French law, foie gras is defined as the liver of a duck or goose fattened by gavage (force feeding).
Foie gras is a popular and well-known delica ...
made in the region since the 17th century. Additionally, Alsace is known for its fruit juices and mineral waters.
Wines

Alsace is an important
wine-producing ''région''. ''Vins d'Alsace'' (
Alsace wine
Alsace wine or Alsatian wine (french: Vin d'Alsace; german: Elsässer Wein; gsw, label=Haut Rhin Alsatian, d'r Wii vum Elsàss; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, de Win vum Elsàss) is produced in the Alsace region in France and is primarily w ...
s) are mostly white. Alsace produces some of the world's most noted dry
riesling
Riesling (, ; ) is a white grape variety that originated in the Rhine region. Riesling is an aromatic grape variety displaying flowery, almost perfumed, aromas as well as high acidity. It is used to make dry, semi-sweet, sweet, and sparkling wh ...
s and is the only region in France to produce mostly
varietal
A varietal wine is a wine made primarily from a single named grape variety, and which typically displays the name of that variety on the wine label.The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000.winepros.com.au. ...
wines identified by the names of the grapes used (wine from
Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The ...
is also mainly varietal, but not normally identified as such), typically from grapes also used in Germany. The most notable example is
Gewurztraminer.
Beers
Alsace is also the main beer-producing region of France, thanks primarily to
breweries
A brewery or brewing company is a business that makes and sells beer. The place at which beer is commercially made is either called a brewery or a beerhouse, where distinct sets of brewing equipment are called plant. The commercial brewing of beer ...
in and near
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
. These include those of
Fischer,
Karlsbräu,
Kronenbourg
Kronenbourg Brewery (french: Brasseries Kronenbourg, German: ''Kronenbourg Brauerei'', ) is a brewery founded in 1664 by Geronimus Hatt in the Free Imperial City of Straßburg, Holy Roman Empire (today Strasbourg, France). The name comes from ...
, and
Heineken International
Heineken N.V. () is a Dutch multinational brewing company, founded in 1864 by Gerard Adriaan Heineken in Amsterdam. , Heineken owns over 165 breweries in more than 70 countries. It produces 348 international, regional, local and speciality be ...
.
Hops
Hops are the flowers (also called seed cones or strobiles) of the hop plant '' Humulus lupulus'', a member of the Cannabaceae family of flowering plants. They are used primarily as a bittering, flavouring, and stability agent in beer, to w ...
are grown in
Kochersberg
The Kochersberg () is a natural region of the French département of Bas-Rhin in Alsace and is a part of the hills found along the eastern side of the Vosges mountains. It gave its name to the Communauté de communes du Kochersberg, a cooperation o ...
and in northern Alsace.
Schnapps
Schnapps ( or ) or schnaps is a type of alcoholic beverage that may take several forms, including distilled fruit brandies, herbal liqueurs, infusions, and "flavored liqueurs" made by adding fruit syrups, spices, or artificial flavorings to neu ...
is also traditionally made in Alsace, but it is in decline because home
distillers are becoming less common and the consumption of traditional, strong, alcoholic beverages is decreasing.
In tales

The
stork
Storks are large, long-legged, long-necked wading birds with long, stout bills. They belong to the family called Ciconiidae, and make up the order Ciconiiformes . Ciconiiformes previously included a number of other families, such as herons an ...
is a main feature of Alsace and was the subject of many
legend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived, both by teller and listeners, to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess ...
s told to children. The bird practically disappeared around 1970, but re-population efforts are continuing. They are mostly found on roofs of houses, churches and other public buildings in Alsace.
The
Easter Bunny
The Easter Bunny (also called the Easter Rabbit or Easter Hare) is a folkloric figure and symbol of Easter, depicted as a rabbit—sometimes dressed with clothes—bringing Easter eggs. Originating among German Lutherans, the "Easter Hare" ori ...
was first mentioned in
Georg Franck von Franckenau's ''De ovis paschalibus'' (About Easter eggs) in 1682 referring to an Alsace tradition of an Easter Hare bringing Easter eggs.
The term "Alsatia"
"Alsatia", the Latin form of Alsace's name, entered the
English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the ...
as "a lawless place" or "a place under no jurisdiction" prior to the 17th century as a reflection of the British perception of the region at that time. It was used into the 20th century as a term for a ramshackle marketplace, "protected by ancient custom and the independence of their patrons". The word is still in use in the 21st century among the English and Australian judiciaries to describe a place where the law cannot reach: "In setting up the
Serious Organised Crime Agency
The Serious Organised Crime Agency (SOCA) was a non-departmental public body of the Government of the United Kingdom which existed from 1 April 2006 until 7 October 2013. SOCA was a national law enforcement agency with Home Office sponsorship ...
, the state has set out to create an Alsatia – a region of executive action free of judicial oversight,"
Lord Justice Sedley in UMBS v SOCA 2007.
Derived from the above, "
Alsatia
Whitefriars is an area in the Ward of Farringdon Without in the City of London.
Until 1540, it was the site of a Carmelite monastery, from which it gets its name.
History
The area takes its name from the medieval Carmelite religious house, know ...
" was historically a
cant
Cant, CANT, canting, or canted may refer to:
Language
* Cant (language), a secret language
* Beurla Reagaird, a language of the Scottish Highland Travellers
* Scottish Cant, a language of the Scottish Lowland Travellers
* Shelta or the Cant, a la ...
term for the area near
Whitefriars, London
Whitefriars is an area in the Ward of Farringdon Without in the City of London.
Until 1540, it was the site of a Carmelite monastery, from which it gets its name.
History
The area takes its name from the medieval Carmelite religious house, know ...
, which was for a long time a
sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred place, such as a shrine. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This secondary use can be categorized into human sanctuary, a sa ...
. It is first known in print in the title of ''
The Squire of Alsatia
''The Squire of Alsatia'' is a 1688 comedy play by the English writer Thomas Shadwell. Alsatia was a nickname for the Whitefriars area of London, deriving from Alsace in northeastern France. A restoration comedy, it was performed at the Drury ...
'', a 1688 play written by
Thomas Shadwell
Thomas Shadwell ( – 19 November 1692) was an English poet and playwright who was appointed Poet Laureate in 1689.
Life
Shadwell was born at either Bromehill Farm, Weeting-with-Broomhill or Santon House, Lynford, Norfolk, and educated at Bu ...
.
Economy
According to the ''Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques'' (
INSEE), Alsace had a gross domestic product of 44.3 billion euros in 2002. With a GDP per capita of €24,804, it was the second-place ''région'' of France, losing only to
Île-de-France
The Île-de-France (, ; literally "Isle of France") is the most populous of the eighteen regions of France. Centred on the capital Paris, it is located in the north-central part of the country and often called the ''Région parisienne'' (; en, Pa ...
. 68% of its jobs are in the
services
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a p ...
; 25% are in industry, making Alsace one of France's most industrialised ''régions''.
Alsace is a ''région'' of varied economic activity, including:
*
viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for '' vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of '' Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, r ...
(mostly along the ''
Route des Vins d'Alsace'' between
Marlenheim and
Thann)
*
hop harvesting and brewing (half of French beer is produced in Alsace, especially in the vicinity of Strasbourg, notably in
Schiltigheim
Schiltigheim (, , and sometimes by non-local speakers of French; Alsatian: ''Schelige'' ; ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
The inhabitants are called ''Schilikois'' in French and ''Scheligemer'' ...
,
Hochfelden,
Saverne
Saverne (french: Saverne, ; Alsatian: ; german: Zabern ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It is situated on the Rhine-Marne canal at the foot of a pass over the Vosges Mountains, and 45 km (2 ...
and
Obernai
Obernai ( Alsatian: ''Owernah''; german: Oberehnheim) commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France. It lies on the eastern slopes of the Vosges mountains.
Obernai is a rapidly growing city, its number of inhabitants hav ...
)
* forestry development
* automobile industry (
Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning '' mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin department, in the Grand Est region, eastern France, close to the Swiss and German borders. It is the largest city in Haut-Rhin and second largest in Alsace a ...
and
Molsheim
Molsheim () is a commune and a subprefecture in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. , home town of
Bugatti
Automobiles Ettore Bugatti was a German then French manufacturer of high-performance automobiles. The company was founded in 1909 in the then-German city of Molsheim, Alsace, by the Italian-born industrial designer Ettore Bugatti. The cars ...
Automobiles)
*
life science
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy ...
s, as part of the trinational
BioValley
* tourism
*
potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt ...
(until the late 20th century) and
potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water- soluble form. mining
Alsace has many international ties and 35% of firms are foreign companies (notably German, Swiss, American, Japanese, and
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
n).
Tourism
Having been early and always densely populated, Alsace is famous for its high number of picturesque villages, churches and castles and for the various beauties of its three main towns, in spite of severe destructions suffered throughout five centuries of wars between France and Germany.
Alsace is furthermore famous for its vineyards (especially along the 170 km of the ''
Route des Vins d'Alsace'' from
Marlenheim to
Thann) and the
Vosges mountains
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
with their thick and green forests and picturesque lakes.



* Old towns of
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
,
Colmar
Colmar (, ; Alsatian: ' ; German during 1871–1918 and 1940–1945: ') is a city and commune in the Haut-Rhin department and Grand Est region of north-eastern France. The third-largest commune in Alsace (after Strasbourg and Mulhouse), it i ...
,
Sélestat
Sélestat (; Alsatian: ''Schlettstàdt''; German: ''Schlettstadt'') is a commune in the Grand Est region of France. An administrative division (sous-préfecture) of the Bas-Rhin department, the town lies on the Ill river, from the Rhine and t ...
,
Guebwiller
Guebwiller (french: Guebwiller, ; Alsatian: ''Gàwiller'' ; ) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est currently in north-eastern France. It was a sub-prefecture of the department until 2015.
It is situated northwest of Mulhous ...
,
Saverne
Saverne (french: Saverne, ; Alsatian: ; german: Zabern ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It is situated on the Rhine-Marne canal at the foot of a pass over the Vosges Mountains, and 45 km (2 ...
,
Obernai
Obernai ( Alsatian: ''Owernah''; german: Oberehnheim) commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France. It lies on the eastern slopes of the Vosges mountains.
Obernai is a rapidly growing city, its number of inhabitants hav ...
,
Thann
* Smaller cities and villages:
Molsheim
Molsheim () is a commune and a subprefecture in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. ,
Rosheim
Rosheim (; gsw-FR, Rose) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
It lies southwest of Strasbourg, on the eastern slopes of the Vosges mountains. It is a winemaking town on the tourist "Road of the Wines ...
,
Riquewihr
Riquewihr (; Alsatian: ; german: Reichenweier ) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
A popular tourist attraction for its historical architecture, Riquewihr is also known for the Riesling and other win ...
,
Ribeauvillé
Ribeauvillé (; Alsatian: ''Rappschwihr''; ) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It was a sub-prefecture of the department until 2015.
Its inhabitants are called ''Ribeauvillois''.
Geography
The ...
,
Kaysersberg
Kaysersberg (german: Kaisersberg ; Alsatian: ''Kaiserschbarig'') is a historical town and former commune in Alsace in northeastern France. The name is German for ''Emperor's Mountain''. The high fortress that dominates the town serves as a remi ...
,
Wissembourg
Wissembourg (; South Franconian: ''Weisseburch'' ; German: ''Weißenburg'' ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in northeastern France.
It is situated on the little river Lauter close to the border between France and Germany a ...
,
Neuwiller-lès-Saverne
Neuwiller-lès-Saverne (, literally ''Neuwiller near Saverne''; german: Neuweiler; gsw-FR, Neiwiller) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
Landmarks
The handsome 1873 synagogue survived the war.
See ...
,
Marmoutier
:''See Marmoutier Abbey (Tours) for the former abbey in Tours.''
Marmoutier (; ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin département in Grand Est in north-eastern France. The origin of the place is the former Marmoutier Abbey, of which the abbey church st ...
,
Rouffach
Rouffach (; German and Alsatian: ''Rufach'') is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
Rouffach lies along the Alsatian wine route (''Route des Vins d'Alsace'').
Its vineyards produce one of the finest ...
,
Soultz-Haut-Rhin,
Bergheim,
Hunspach
Hunspach is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. In 2020 it was voted the «Village préféré des Français» (France's favourite village).
Geography
The commune lies a short distance to the south of Wiss ...
,
Seebach,
Turckheim
Turckheim (; Alsatian: Tercka; ) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It lies west of Colmar, on the eastern slopes of the Vosges mountains.
History
Archeological finds indicate the area was alread ...
,
Eguisheim
Eguisheim (; german: Egisheim; Alsatian: ''Egsa'') is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It lies in the historical region of Alsace (german: Elsass). The village lies on the edge of the Ballons des Vo ...
,
Neuf-Brisach
Neuf-Brisach ( or ; ; gsw-FR, Nei-Brisach) is a fortified town and commune of the department of Haut-Rhin in the French region of Alsace. The fortified town was intended to guard the border between France and the Holy Roman Empire and, subsequ ...
,
Ferrette
Ferrette (; german: Pfirt ; gsw-FR, Pfìrt) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France.
It is situated close to the Swiss border. Its main attraction is the Château de Ferrette.
County of Ferrette
The County o ...
,
Niedermorschwihr and the gardens of the blue house in
Uttenhoffen
Uttenhoffen is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
History
Finds from the Neolithic Age and the Hallstatt culture period are as attested as the settlement in Roman times. After introduction of the Ref ...
* Churches (as main sights in otherwise less remarkable places):
Thann,
Andlau
Andlau ( or ; Alsatian: ''Àndlöi'') is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Alsace, Grand Est region of northeastern France.
The village owes its origin to Andlau Abbey which was founded in 880 by Richardis, the empress of Charles the Fa ...
,
Murbach
Murbach is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
Murbach Abbey is located near Murbach.
See also
* Communes of the Haut-Rhin département
The following is a list of the 366 communes of the French dep ...
,
Ebersmunster
Ebersmunster (german: Ebersmünster) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France.
It is famous for its 1727 baroque church, a work by Vorarlberg architect Peter Thumb.
Population
See also
*Communes of the Bas ...
,
Niederhaslach
Niederhaslach is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
It is noteworthy for its Gothic 13th-15th century Niederhaslach Church.
See also
* Oberhaslach, a neighbouring commune
* Communes of the Bas-Rhin de ...
,
Sigolsheim
Sigolsheim (; Alsatian: ''Sìjelse'') is a former commune in the Haut-Rhin department in north-eastern France. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune Kaysersberg Vignoble.
Children previously attended school in the École élé ...
,
Lautenbach,
Epfig,
Altorf
Altorf (; german: Altdorf; gsw-FR, Àldorf) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in the Grand Est region of northeastern France.
The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Altorfois'' or ''Altorfoises''.
The commune has been awarded one ...
,
Ottmarsheim,
Domfessel
Domfessel is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. As with other parts of Alsace and Bas-Rhin, Domfessel has had periods under German rule, and its name is Germanic. Domfessel has been part of France since ...
,
Niederhaslach
Niederhaslach is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
It is noteworthy for its Gothic 13th-15th century Niederhaslach Church.
See also
* Oberhaslach, a neighbouring commune
* Communes of the Bas-Rhin de ...
,
Marmoutier
:''See Marmoutier Abbey (Tours) for the former abbey in Tours.''
Marmoutier (; ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin département in Grand Est in north-eastern France. The origin of the place is the former Marmoutier Abbey, of which the abbey church st ...
and the fortified church at
Hunawihr
Hunawihr (; german: Hunaweier) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
The village is a member of the ''Les Plus Beaux Villages de France'' ("The most beautiful villages of France") association.
See als ...
*
Château du Haut-Kœnigsbourg
A château (; plural: châteaux) is a manor house or residence of the lord of the manor, or a fine country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally, and still most frequently, in French-speaking regions.
Nowaday ...
*
Other castles: Ortenbourg and
Ramstein (above Sélestat), Hohlandsbourg,
Fleckenstein,
Haut-Barr (above Saverne), Saint-Ulrich (above Ribeauvillé), Lichtenberg, Wangenbourg, the three Castles of
Eguisheim
Eguisheim (; german: Egisheim; Alsatian: ''Egsa'') is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It lies in the historical region of Alsace (german: Elsass). The village lies on the edge of the Ballons des Vo ...
,
Pflixbourg, Wasigenstein,
Andlau
Andlau ( or ; Alsatian: ''Àndlöi'') is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Alsace, Grand Est region of northeastern France.
The village owes its origin to Andlau Abbey which was founded in 880 by Richardis, the empress of Charles the Fa ...
, Grand Geroldseck,
Wasenbourg
Wasenbourg (german: Wasenburg), located 400 metres in height on the northwest hillside of Reisberg, is a ruined castle in the North Vosges. It is a recognized historical monument since 1898. Château fort, Château Wasenbourg Although its origins a ...
*
Cité de l'Automobile
Musée National de l’Automobile, Collection Schlumpf is an automobile museum located in Mulhouse, France, and built around the Schlumpf Collection of classic automobiles. It has the largest displayed collection of automobiles and contains the lar ...
museum in Mulhouse
*
Cité du train
The Cité du Train (English: ''City of the Train'' or ''Train City''), situated in Mulhouse, France, is one of the ten largest railway museums in the world. It is the successor to the ''musée français du chemin de fer'' (trans. French national ...
museum in Mulhouse
* The
EDF EDF may refer to:
Organisations
* Eclaireurs de France, a French Scouting association
* Education for Development Foundation, a Thai charity
* Électricité de France, a French energy company
** EDF Energy, their British subsidiary
** EDF Luminus ...
museum in Mulhouse
*
Ungersheim
Ungersheim (; gsw, Ungersche) is a Communes of France, ''commune'' in the Haut-Rhin Departments of France, ''department'' of Grand Est in eastern France. It forms part of the Mulhouse Alsace Agglomération, the inter-communal local government bo ...
's "''écomusée''" (open-air museum) and "''
Bioscope''" (leisure park about the environment, closed since September 2012)
* Musée historique in
Haguenau
Haguenau (; Alsatian language, Alsatian: or ; and historically in English: ''Hagenaw'') is a Communes of France, commune in the Bas-Rhin Département in France, department of France, of which it is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture.
...
, largest museum in Bas-Rhin outside Strasbourg
* Bibliothèque humaniste in Sélestat, one of the oldest public libraries in the world
*
Christmas market
A Christmas market, also known as ''Christkindlmarkt'' (literally: ''Christ Child Market'', but the term "Christkind" usually refers to an angel-like "spirit of Christmas" rather than literally the Christ Child), ''Christkindlesmarkt'', ''Chris ...
s in Kaysersberg, Strasbourg, Mulhouse and Colmar
* Departmental Centre of the History of Families (CDHF) in Guebwiller
* The
Maginot Line
The Maginot Line (french: Ligne Maginot, ), named after the Minister of the Armed Forces (France), French Minister of War André Maginot, is a line of concrete fortifications, obstacles and weapon installations built by French Third Republic, F ...
:
Ouvrage Schoenenbourg
Ouvrage Schoenenbourg is a Maginot Line fortification. It is located on the territory of the communes of Hunspach, Schœnenbourg and Ingolsheim, in the French ''département'' of Bas-Rhin, forming part of the Fortified Sector of Haguenau ...
*
Mount Ste Odile
*
Route des Vins d'Alsace (Alsace Wine Route)
* Mémorial d'Alsace-Lorraine in
Schirmeck
Schirmeck () is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
It is the location of the Alsace-Moselle Memorial museum.
The name of the town means "protected place". In Lorraine dialect it is called "Chermec ...
*
Natzweiler-Struthof, the only German
concentration camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simpl ...
on French territory during WWII
*
Famous mountains: Massif du Donon,
Grand Ballon, Petit Ballon,
Ballon d'Alsace
The Ballon d'Alsace german: Elsässer Belchen (el. 1247 m.), sometimes also called the Alsatian Belchen to distinguish it from other mountains named " Belchen" is a mountain at the border of Alsace, Lorraine, and Franche-Comté. From its top, vie ...
,
Hohneck,
Hartmannswillerkopf
Hartmannswillerkopf, also known as the Vieil Armand (French) or Hartmannsweiler Kopf (German; English: Hartmansweiler Head) is a pyramidal rocky spur in the Vosges mountains of the Grand Est region, France. The peak stands at overlooking the Rhin ...
*
National park
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individual ...
: Parc naturel des Vosges du Nord
*
Regional park A regional park is an area of land preserved on account of its natural beauty, historic interest, recreational use or other reason, and under the administration of a form of local government.
Definition
A regional park can be a special park distri ...
: Parc naturel régional des Ballons des Vosges (south of the
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a singl ...
)
Transportation
Roads

Most major car journeys are made on the
A35 autoroute
The A35 autoroute is a toll free motorway in northeastern France. It is also known as the ''Autoroute des cigognes'' and the ''Voie Rapide du Piémont des Vosges''. It connects the German border in the Rhine valley with the Swiss frontier via ...
, which links Saint-Louis on the Swiss border to Lauterbourg on the German border.
The
A4 toll road (towards Paris) begins northwest of
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
and the
A36 toll road towards Lyon, begins west from
Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning '' mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin department, in the Grand Est region, eastern France, close to the Swiss and German borders. It is the largest city in Haut-Rhin and second largest in Alsace a ...
.
Spaghetti junctions (built in the 1970s and 1980s) are prominent in the comprehensive system of motorways in Alsace, especially in the outlying areas of Strasbourg and Mulhouse. These cause a major buildup of traffic and are the main sources of pollution in the towns, notably in Strasbourg where the motorway traffic of the A35 was 170,000 per day in 2002.
At present, plans are being considered for building a new
dual carriageway
A dual carriageway ( BE) or divided highway ( AE) is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation (BrE) or median (AmE). Roads with two or more carriageways which are ...
west of Strasbourg, which would reduce the buildup of traffic in that area by picking up north and southbound vehicles and getting rid of the buildup outside Strasbourg. The line plans to link up the interchange of
Hœrdt to the north of Strasbourg, with
Innenheim
Innenheim (; gsw-FR, Ìnnle) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France.
Among speakers of the local language, the village is often called "Enle" or "Inle" according to the speaker's accent. The suffix "..le" ...
in the southwest. The opening is envisaged at the end of 2011, with an average usage of 41,000 vehicles a day. Estimates of the French Works Commissioner however, raised some doubts over the interest of such a project, since it would pick up only about 10% of the traffic of the A35 at Strasbourg. Paradoxically, this reversed the situation of the 1950s. At that time, the French trunk road left of the Rhine not been built, so that traffic would cross into Germany to use the Karlsruhe-Basel Autobahn.
To add to the buildup of traffic, the neighbouring German state of
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
has imposed a tax on heavy-goods vehicles using their
Autobahn
The (; German plural ) is the federal controlled-access highway system in Germany. The official German term is (abbreviated ''BAB''), which translates as 'federal motorway'. The literal meaning of the word is 'Federal Auto(mobile) Track' ...
en. Thus, a proportion of the HGVs travelling from north Germany to Switzerland or southern Alsace bypasses the
A5 on the Alsace-Baden-Württemberg border and uses the untolled French
A35 instead.
Trains

TER Alsace
TER Alsace was the regional rail network serving the région of Alsace, eastern France. In 2016 it was merged into the new TER Grand Est.
Network Rail
Road
* Cernay – Sewen
* Colmar – Turckheim – Munster – Metzeral
* Colmar – Vo ...
is the rail network serving Alsace. Its network is articulated around the city of Strasbourg. It is one of the most developed rail networks in France, financially sustained partly by the French railroad
SNCF
The Société nationale des chemins de fer français (; abbreviated as SNCF ; French for "National society of French railroads") is France's national state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the country's national rail traffic ...
, and partly by the ''région'' Alsace.
Because the Vosges are surmountable only by the
Col de Saverne
The Col de Saverne (Pass of Saverne or Saverne Pass, ) is a natural pass in the north of the Vosges mountains, near Saverne, which permits travel between the départements of Bas-Rhin and Moselle, and therefore between Alsace and Lorraine.
Transp ...
and the
Belfort
Belfort (; archaic german: Beffert/Beffort) is a city in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in Northeastern France, situated between Lyon and Strasbourg, approximately from the France–Switzerland border. It is the prefecture of the Terri ...
Gap, it has been suggested that Alsace needs to open up and get closer to France in terms of its rail links. Developments already under way or planned include:
* the
TGV Est (Paris – Strasbourg) had its first phase brought into service in June 2007, bringing down the Strasbourg-Paris trip from 4 to 2 hours 20 minutes, and further reducing it to 1h 50m after the completion of the second phase in 2016.
* the
TGV Rhin-Rhône between
Dijon
Dijon (, , ) (dated)
* it, Digione
* la, Diviō or
* lmo, Digion is the prefecture of the Côte-d'Or department and of the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in northeastern France. the commune had a population of 156,920.
The earlie ...
and Mulhouse (opened in 2011)
* a tram-train system in Mulhouse (2011)
* an interconnection with the German
InterCityExpress
The Intercity Express (commonly known as ICE ()) is a system of high-speed trains predominantly running in Germany. It also serves some destinations in Austria, Denmark (ceased in 2017 but planned to resume in 2022), France, Belgium, Switzerl ...
, as far as
Kehl
Kehl (; gsw, label= Low Alemannic, Kaal) is a town in southwestern Germany in the Ortenaukreis, Baden-Württemberg. It is on the river Rhine, directly opposite the French city of Strasbourg, with which it shares some municipal servicesfor exa ...
(expected 2016)
However, the abandoned Maurice-Lemaire tunnel towards
Saint-Dié-des-Vosges
Saint-Dié-des-Vosges (; german: Sankt Didel), commonly referred to as just Saint-Dié, is a commune in the Vosges department in Grand Est in northeastern France.
It is a sub-prefecture of the department.
Geography
Saint-Dié is located in th ...
was rebuilt as a toll road.
Waterways
Port traffic of Alsace exceeds 15 million tonnes, of which about three-quarters is centred on Strasbourg, which is the second busiest French fluvial harbour. The enlargement plan of the
Rhône–Rhine Canal
The Canal du Rhône au Rhin is one of the important watershed canals of the French waterways, connecting the Rhine to the Saône and the Rhône and thereby the North Sea and the Mediterranean. As built, the canal was made up of four distinct sect ...
, intended to link up the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
and Central Europe (Rhine,
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
,
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
and
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
) was abandoned in 1998 for reasons of expense and land erosion, notably in the Doubs valley.
Air traffic
There are two international airports in Alsace:
* the international airport of Strasbourg in Entzheim
* the international EuroAirport Basel-Mulhouse-Freiburg, which is the seventh largest French airport in terms of traffic
Strasbourg is also two hours away by road from one of the largest European airports, Frankfurt Main, and 2 hours 30 minutes from Charles de Gaulle Airport through the direct TGV service, stopping in Terminal 2.
Cycling network
Crossed by three EuroVelo routes
* the EuroVelo 5 (Via Francigena from London to Rome/Brindisi),
* the EuroVelo 6 (Véloroute des fleuves from Nantes to Budapest (H)) and
* the EuroVelo 15 (Véloroute Rhin / Rhine cycle route from Andermatt (CH) to Rotterdam (NL)).
Alsace is the most bicycle-friendly region of France, with of cycle routes. The network is of a very good standard and well signposted. All the towpaths of the canals in Alsace (canal des houillères de la Sarre, canal de la Marne au Rhin, canal de la Bruche, canal du Rhône au Rhin) are tarred.
Notable people

The following is a selection of people born in Alsace who have been particularly influential or successful in their respective fields.
Arts
*Jean Arp
*Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi
*Théodore Deck
*Gustave Doré
*Sébastien Érard
*Jean-Jacques Henner
*Philip James de Loutherbourg
*Master of the Drapery Studies
*Marcel Marceau
*Sam Marx
*Charles Munch (conductor), Charles Munch
*Claude Rich
*Martin Schongauer
*Marie Tussaud
*Tomi Ungerer
*Émile Waldteufel
*Jean-Jacques Waltz (aka Hansi)
*Cora Wilburn
*William Wyler
Business
*Automobiles Ettore
Bugatti
Automobiles Ettore Bugatti was a German then French manufacturer of high-performance automobiles. The company was founded in 1909 in the then-German city of Molsheim, Alsace, by the Italian-born industrial designer Ettore Bugatti. The cars ...
*Thierry Mugler
*Schlumberger brothers
*André Koechlin
*Léopold Louis-Dreyfus
Literature
*Sebastian Brant
*August Stöber
*Gottfried von Strassburg
Military
*Alfred Dreyfus
*François Christophe de Kellermann
*Jean-Baptiste Kléber
*Jacques Paul Klein
*Jean Rapp
Nobility
*Henriette Louise de Waldner de Freundstein
*Ludwig I of Bavaria
Religion
*
Martin Bucer
Martin Bucer ( early German: ''Martin Butzer''; 11 November 1491 – 28 February 1551) was a German Protestant reformer based in Strasbourg who influenced Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican doctrines and practices. Bucer was originally a me ...
*Wolfgang Capito
*Charles de Foucauld
*Herrad of Landsberg
*Pope Leo IX
*Thomas Murner
*J. F. Oberlin
*Odile of Alsace
*Albert Schweitzer
*Philipp Spener
*Jakob Wimpfeling
Sciences
*Hans Bethe
*Charles Friedel
*Charles Frédéric Gerhardt
*Johann Hermann
*Alfred Kastler
*Erich Leo Lehmann
*Jean-Marie Lehn
*Wilhelm Philippe Schimper
*Charles Xavier Thomas
*Pierre Weiss
*Charles-Adolphe Wurtz
Sports
*Mehdi Baala
*Yann Ehrlacher
*Valérien Ismaël
*Sébastien Loeb
*Yvan Muller
*Thierry Omeyer
*Thomas Voeckler
*Arsène Wenger
Major communities
German original names in brackets if French names differ:
* Bischheim, Bas-Rhin, Bischheim
*
Colmar
Colmar (, ; Alsatian: ' ; German during 1871–1918 and 1940–1945: ') is a city and commune in the Haut-Rhin department and Grand Est region of north-eastern France. The third-largest commune in Alsace (after Strasbourg and Mulhouse), it i ...
(Kolmar)
*
Guebwiller
Guebwiller (french: Guebwiller, ; Alsatian: ''Gàwiller'' ; ) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est currently in north-eastern France. It was a sub-prefecture of the department until 2015.
It is situated northwest of Mulhous ...
(Gebweiler)
*
Haguenau
Haguenau (; Alsatian language, Alsatian: or ; and historically in English: ''Hagenaw'') is a Communes of France, commune in the Bas-Rhin Département in France, department of France, of which it is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture.
...
(Hagenau)
* Illkirch-Graffenstaden (Illkirch-Grafenstaden)
* Illzach
* Lingolsheim
*
Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning '' mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin department, in the Grand Est region, eastern France, close to the Swiss and German borders. It is the largest city in Haut-Rhin and second largest in Alsace a ...
(Mülhausen)
* Saint-Louis, Haut-Rhin, Saint-Louis (St. Ludwig)
*
Saverne
Saverne (french: Saverne, ; Alsatian: ; german: Zabern ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It is situated on the Rhine-Marne canal at the foot of a pass over the Vosges Mountains, and 45 km (2 ...
(Zabern)
*
Schiltigheim
Schiltigheim (, , and sometimes by non-local speakers of French; Alsatian: ''Schelige'' ; ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France.
The inhabitants are called ''Schilikois'' in French and ''Scheligemer'' ...
*
Sélestat
Sélestat (; Alsatian: ''Schlettstàdt''; German: ''Schlettstadt'') is a commune in the Grand Est region of France. An administrative division (sous-préfecture) of the Bas-Rhin department, the town lies on the Ill river, from the Rhine and t ...
(Schlettstadt)
*
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
(Straßburg)
* Wittenheim
Sister regions
There is an ''accord de coopération internationale'' between Alsace and the following regions:
* Vest (development region), Vest, Romania
*Gyeongsangbuk-do, South Korea
* Upper Austria, Austria
* Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Lower Silesia, Poland
*Quebec, Canada
* Jiangsu, China
* Moscow Oblast, Moscow, Russia
See also
* 2014 Alsace single territorial collectivity referendum
* Musée alsacien (Strasbourg)
* Route Romane d'Alsace
* German place names in Alsace
* Alsace independence movement
* Castroville, Texas
Notes
References
Further reading
* Assall, Paul. ''Juden im Elsass''. Zürich: Rio Verlag. .
* ''Das Elsass: Ein literarischer Reisebegleiter''. Frankfurt a. M.: Insel Verlag, 2001. .
* Erbe, Michael (Hrsg.) ''Das Elsass: Historische Landschaft im Wandel der Zeiten''. Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 2002. .
* Faber, Gustav. ''Elsass''. München: Artemis-Cicerone Kunst- und Reiseführer, 1989.
* Fischer, Christopher J. ''Alsace to the Alsatians? Visions and Divisions of Alsatian Regionalism, 1870–1939'' (Berghahn Books, 2010).
* Gerson, Daniel. ''Die Kehrseite der Emanzipation in Frankreich: Judenfeindschaft im Elsass 1778 bis 1848''. Essen: Klartext, 2006. .
* Herden, Ralf Bernd. ''Straßburg Belagerung 1870''. Norderstedt: BoD, 2007, .
* Hummer, Hans J. ''Politics and Power in Early Medieval Europe: Alsace and the Frankish Realm, 600–1000''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009.
* Kaeppelin, Charles E. R, and Mary L. Hendee.
Alsace Throughout the Ages'. Franklin, Pa: C. Miller, 1908.
* Mehling, Marianne (Hrsg.) ''Knaurs Kulturführer in Farbe Elsaß''. München: Droemer Knaur, 1984.
* Putnam, Ruth.
Alsace and Lorraine: From Cæsar to Kaiser, 58 B.C.–1871 A.D.' New York: 1915.
* Schreiber, Hermann. ''Das Elsaß und seine Geschichte, eine Kulturlandschaft im Spannungsfeld zweier Völker''. Augsburg: Weltbild, 1996.
* Schwengler, Bernard. ''Le Syndrome Alsacien: d'Letschte?'' Strasbourg: Éditions Oberlin, 1989. .
* Tomi Ungerer, Ungerer, Tomi. ''Elsass. Das offene Herz Europas''. Straßburg: Édition La Nuée Bleue, 2004. .
* Vogler, Bernard and Hermann Lersch. ''Das Elsass''. Morstadt: Éditions Ouest-France, 2000. .
External links
Official website of the Alsace regional councilAlsace : at the heart of Europe– Official French website (in English)
Visit AlsaceOfficial Alsace tourism website
* [http://www.alsatourisme.fr/ Alsatourisme] Tourism in Alsace
*
Alsace.net: Directory of Alsatian Websites
"Museums of Alsace"
Churches and chapels of Alsace(pictures only)
Medieval castles of Alsace(pictures only)
"Organs of Alsace"
''The Alsatian Library of Mutual Credit''
''The Alsatian Artists''
{{Authority control
Alsace,
NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union

 Holy Roman Empire central power had begun to decline following years of imperial adventures in Italian lands, often ceding hegemony in Western Europe to France, which had long since centralized power. France began an aggressive policy of expanding eastward, first to the rivers
Holy Roman Empire central power had begun to decline following years of imperial adventures in Italian lands, often ceding hegemony in Western Europe to France, which had long since centralized power. France began an aggressive policy of expanding eastward, first to the rivers  France consolidated its hold with the 1679 Treaties of Nijmegen, which brought most remaining towns under its control. France seized Strasbourg in 1681 in an unprovoked action. These territorial changes were recognised in the 1697
France consolidated its hold with the 1679 Treaties of Nijmegen, which brought most remaining towns under its control. France seized Strasbourg in 1681 in an unprovoked action. These territorial changes were recognised in the 1697  The year 1789 brought the French Revolution and with it the first division of Alsace into the départements of Haut- and
The year 1789 brought the French Revolution and with it the first division of Alsace into the départements of Haut- and  The Franco-Prussian War, which started in July 1870, saw France defeated in May 1871 by the
The Franco-Prussian War, which started in July 1870, saw France defeated in May 1871 by the  During the First World War, to avoid ground fights between brothers, many Alsatians served as sailors in the
During the First World War, to avoid ground fights between brothers, many Alsatians served as sailors in the  Alsace has an area of 8,283 km2, making it the smallest ''
Alsace has an area of 8,283 km2, making it the smallest '' Alsace is the part of the plain of the Rhine located at the west of the
Alsace is the part of the plain of the Rhine located at the west of the  The traditional habitat of the Alsatian lowland, like in other regions of Germany and Northern Europe, consists of houses constructed with walls in
The traditional habitat of the Alsatian lowland, like in other regions of Germany and Northern Europe, consists of houses constructed with walls in  Alsatian cuisine, somewhat based on German culinary traditions, is marked by the use of pork in various forms. It is perhaps mostly known for the region's wines and beers. Traditional dishes include ''
Alsatian cuisine, somewhat based on German culinary traditions, is marked by the use of pork in various forms. It is perhaps mostly known for the region's wines and beers. Traditional dishes include '' The festivities of the year's end involve the production of a great variety of biscuits and small cakes called '' bredela'' as well as ''
The festivities of the year's end involve the production of a great variety of biscuits and small cakes called '' bredela'' as well as '' Alsace is an important wine-producing ''région''. ''Vins d'Alsace'' (
Alsace is an important wine-producing ''région''. ''Vins d'Alsace'' ( The
The 
 * Old towns of
* Old towns of  Most major car journeys are made on the
Most major car journeys are made on the 
 The following is a selection of people born in Alsace who have been particularly influential or successful in their respective fields.
The following is a selection of people born in Alsace who have been particularly influential or successful in their respective fields.