Castle Hill, Newfoundland and Labrador on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Castle Hill is an area containing the remains of both
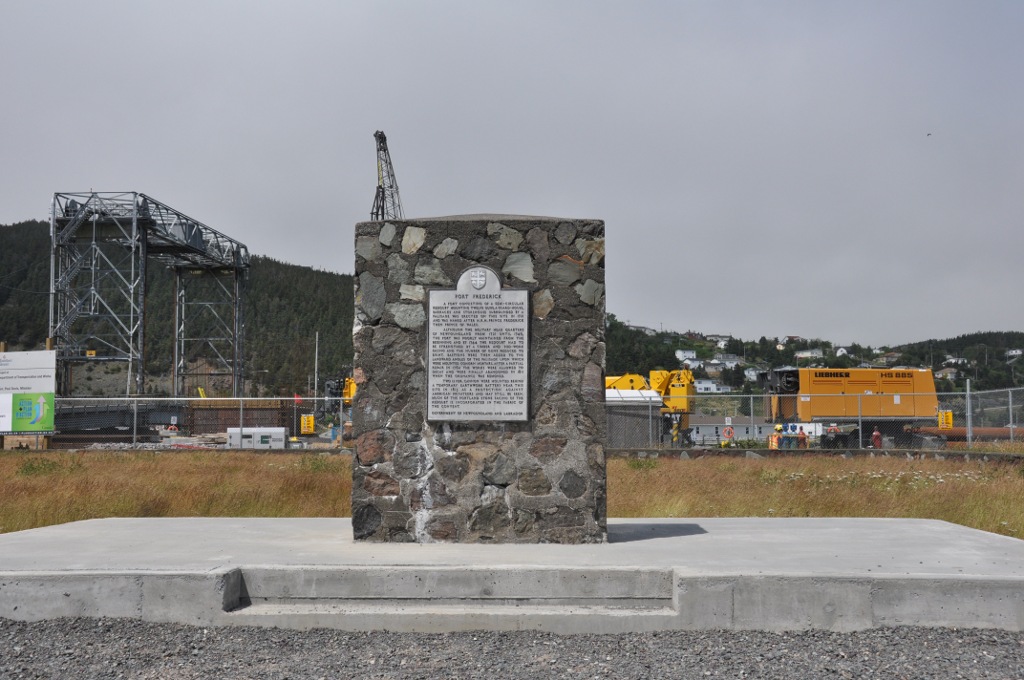

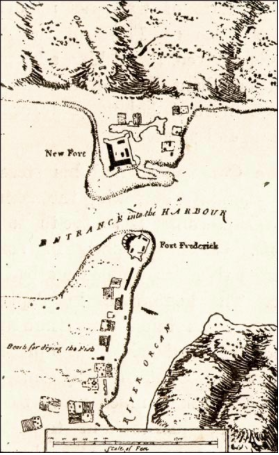 After briefly occupying Fort Louis, under the command of Samuel Gledhill, the British built the redoubt Fort Frederick (Newfoundland) to help fortify their acquisition of Placentia. It served as the military headquarters for Newfoundland from 1721 to 1746. There was a report that the Mi'kmaq were involved in a raid of Pleasance during Father Rale's War in which they were said to have killed 200 English. Governor Drummer did not believe the report.
By the 1740s, the British began construction of New Fort which overlaid the former Fort Louis.
After briefly occupying Fort Louis, under the command of Samuel Gledhill, the British built the redoubt Fort Frederick (Newfoundland) to help fortify their acquisition of Placentia. It served as the military headquarters for Newfoundland from 1721 to 1746. There was a report that the Mi'kmaq were involved in a raid of Pleasance during Father Rale's War in which they were said to have killed 200 English. Governor Drummer did not believe the report.
By the 1740s, the British began construction of New Fort which overlaid the former Fort Louis.
Castle Hill National Historic Site
– official site {{coord, 47, 15, 3.88, N, 53, 58, 17.31, W, region:CA, name=Castle Hill, display=title Military history of Newfoundland History museums in Canada Battles involving Canada Military forts in Newfoundland and Labrador Museums in Newfoundland and Labrador Open-air museums in Canada French forts in Canada National Historic Sites in Newfoundland and Labrador Forts or trading posts on the National Historic Sites of Canada register
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and British fortifications, overlooking the town of Placentia (French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
: ''Plaisance'') in Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, Canada. The site was originally established in order to protect the French fishing interests in Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
and the approaches to the French colony of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
.
King William's War
In order to protect the bay, there was one fort erected, Fort Plaisance (1662) (also known as Vieux Fort) between 1662 and 1690. DuringKing William's War
King William's War (also known as the Second Indian War, Father Baudoin's War, Castin's War, or the First Intercolonial War in French) was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War (1688–1697), also known as the War of the Grand Alli ...
, on 25 February 1690, 45 British freebooters from Ferryland led by Herman Williamson attacked Plaisance by land. After killing two soldiers and wounding governor Louis de Pastour de Costebelle, they took possession of the town and destroyed the fort. The population was imprisoned in the church for six weeks, until the English left on 5 April with the colony's supplies.
The French replaced former Fort Plaisance with Fort Saint-Louis (1691), with 50 French soldiers. In the fall of 1692, in the Battle of Placentia (1692), under the command of Commodore Thomas Gillam (Williams), five English ships armed with 62 cannon and 800 men. The English damaged several houses with cannon fire, and on 23 September the fleet withdrew. The French made attacks on St. John's in 1692 and 1694.
Fort Royal was built in 1693. French forces successfully raided British settlements during times of war while Fort Royal, atop Castle Hill, protected the colony from attack by British warships. At the end of 1693 the garrison had about 60 soldiers. Governor Jacques-François de Monbeton de Brouillan (1691–97) mobilized a frigate and eight ships to attack English Newfoundland. He took possession of about 30 fishing boats, captured prisoners and seized a large amount of fish. De Monbeton was joined on this expedition by Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville, who marched overland from Plaisance to spearhead a punishing attack on the English settlements in a famous Avalon Peninsula Campaign. A strong British relief force of 1500 troops reoccupied St. John's in the summer of 1697: they found the town abandoned, pillaged and every building destroyed. The following year construction was begun at St. John's on a well-engineered fortification - Fort William - which was completed in 1700.
Queen Anne's War
During Queen Anne's War, the arrival of Governor Daniel d'Auger de Subercase in 1702 was beneficial. By giving seniority leave, he got rid of the undisciplined soldiers, and a grievance was removed when soldiers were supplied with free uniforms. The garrison was reinforced with Mi'kmaq, and privateers provided some defence at sea. In 1705, Subercase attacked the English settlements. This expedition was a great success - only St. John's and Carbonear successfully resisted. Subercase had almost 500 regulars, French Canadians and Indians. He took the town of St. John, but the Fort William garrison held out and refused terms. After a five-week siege, Subercase retired to Placentia with all the booty his men and several hundred captive townspeople could carry. That summer, detachments of French and Indians attacked and burned out all English communities in Conception, Trinity and Bonavista Bays. Sporadic attacks continued throughout 1706, despite British reinforcement of the St. John's garrison. In 1708, England blockaded Plaisance to starve the capital, which also contained 500 English prisoners. Despite the blockade, , king's lieutenant to Philippe Pastour de Costebelle, attacked English settlements and in January 1709, with a force of 170 men, French, Canadians and Indians, he took St. John's, captured 800 prisoners and destroyed the town's defences. The garrison numbered 250 by 1711. Governor Brouillan had previously estimated that the colony needed at least 300 soldiers to ensure an effective defence. In 1713, the French gave up their right to settlement in Newfoundland and established a new stronghold atLouisbourg
Louisbourg is an unincorporated community and former town in Cape Breton Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia.
History
The French military founded the Fortress of Louisbourg in 1713 and its fortified seaport on the southwest part of the harbour ...
on Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18. ...
. British settlers replaced the French and their soldiers garrisoned the fortifications until 1811.
Father Rale's War

 After briefly occupying Fort Louis, under the command of Samuel Gledhill, the British built the redoubt Fort Frederick (Newfoundland) to help fortify their acquisition of Placentia. It served as the military headquarters for Newfoundland from 1721 to 1746. There was a report that the Mi'kmaq were involved in a raid of Pleasance during Father Rale's War in which they were said to have killed 200 English. Governor Drummer did not believe the report.
By the 1740s, the British began construction of New Fort which overlaid the former Fort Louis.
After briefly occupying Fort Louis, under the command of Samuel Gledhill, the British built the redoubt Fort Frederick (Newfoundland) to help fortify their acquisition of Placentia. It served as the military headquarters for Newfoundland from 1721 to 1746. There was a report that the Mi'kmaq were involved in a raid of Pleasance during Father Rale's War in which they were said to have killed 200 English. Governor Drummer did not believe the report.
By the 1740s, the British began construction of New Fort which overlaid the former Fort Louis.
Castle Hill National Historic Site
Designated a National Historic Site in 1968, after years of archeological projects, today the ruins of the fort are managed byParks Canada
Parks Canada (PC; french: Parcs Canada),Parks Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Parks Canada Agency (). is the agency of the Government of Canada which manages the country's 48 National Parks, th ...
, and known as Castle Hill National Historic Site.
Key elements of the site today:
* Remains of the walls of Gaillardin Redoubt (1692),
* Fort Royal (1693–1703) and detached Redoubt (1697)
* La Fontaine Battery (1697) – unexcavated remains
* remains of British blockhouse (1762)
* Horseshoe Battery – unexcavated remains
* 6 smoothbore cannons – added 1930s
The visitor center features exhibits about the history of the fort, and the lives of the fishing families and soldiers who lived there.
Legacy
On 28 June 1985 Canada Post issued 'Castle Hill, Nfld., circa 1762' one of the 20 stamps in the "Forts Across Canada Series" (1983 & 1985). The stamps are perforated x 13 mm and were printed by Ashton-Potter Limited based on the designs by Rolf P. Harder.Units at the garrison
*British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
* French Army
History
Early history
The first permanent army, paid with regular wages, instead of feudal levies, was established under Charles VII of France, Charles VII in the 1420 to 1430s. The Kings of France needed reliable troops during and after the ...
* Independent Companies of Foot (1713–1718)
* Independent Company of Artillery (1713–1726)
* Ordnance Engineers (Royal Engineers) 1714–1870
* Phillip's Regiment of Foot – Ex. Independent Coys Placentia, 40th Regiment of Foot, 1st. Battalion South Lancashire Regiment (1718–1764)
* 1st. Battalion Royal Artillery – Ex. Independent Company of Artillery (1726–1756)
References
*Environment Canada – Parks, Castle Hill National Historic Park brochure, 1987. *Canning, Jane, The Theory and Historical Development of the Fortifications at Castle Hill, 1974, manuscript on file at Castle Hill NHS. *Canadian Heritage – Parks Canada, Welcome to Castle Hill brochure, undated (2000 ?).External links
Castle Hill National Historic Site
– official site {{coord, 47, 15, 3.88, N, 53, 58, 17.31, W, region:CA, name=Castle Hill, display=title Military history of Newfoundland History museums in Canada Battles involving Canada Military forts in Newfoundland and Labrador Museums in Newfoundland and Labrador Open-air museums in Canada French forts in Canada National Historic Sites in Newfoundland and Labrador Forts or trading posts on the National Historic Sites of Canada register