Cash and cash equivalents on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cash and cash equivalents (CCE) are the most liquid current assets found on a business's
Cash and cash equivalents (CCE) are the most liquid current assets found on a business's
 *
*
*
*
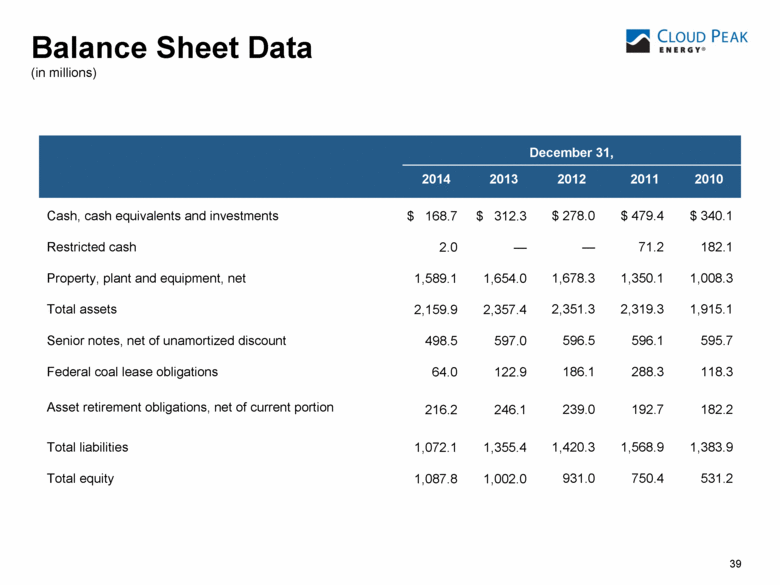 Restricted
Restricted
 Cash and cash equivalents (CCE) are the most liquid current assets found on a business's
Cash and cash equivalents (CCE) are the most liquid current assets found on a business's balance sheet
In financial accounting, a balance sheet (also known as statement of financial position or statement of financial condition) is a summary of the financial balances of an individual or organization, whether it be a sole proprietorship, a business ...
. Cash equivalents are short-term commitments "with temporarily idle cash and easily convertible into a known cash amount". An investment
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing is ...
normally counts as a cash equivalent when it has a short maturity period of 90 days or less, and can be included in the cash and cash equivalents balance from the date of acquisition when it carries an insignificant risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environm ...
of changes in the asset value. If it has a maturity of more than 90 days, it is not considered a cash equivalent. Equity investments mostly are excluded from cash equivalents, unless they are essentially cash equivalents (e.g., preferred shares with a short maturity period and a specified recovery date).
One of the company's crucial health indicators is its ability to generate cash and cash equivalents. So, a company with relatively high net assets and significantly less cash and cash equivalents can mostly be considered an indication of non-liquidity. For investors and companies cash and cash equivalents are generally counted to be "low risk and low return" investments and sometimes analysts can estimate company's ability to pay its bills in a short period of time by comparing CCE and current liabilities. Nevertheless, this can happen only if there are receivables that can be converted into cash immediately.
However, companies with a big value of cash and cash equivalents are targets for takeover
In business, a takeover is the purchase of one company (the ''target'') by another (the ''acquirer'' or ''bidder''). In the UK, the term refers to the acquisition of a public company whose shares are listed on a stock exchange, in contrast to ...
s (by other companies), since their excess cash helps buyers to finance their acquisition. High cash reserves can also indicate that the company is not effective at deploying its CCE resources, whereas for big companies it might be a sign of preparation for substantial purchases. The opportunity cost of saving up CCE is the return on equity that company could earn by investing in a new product or service or expansion of business.
Components of cash
*Currency
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins.
A more general ...
* Coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order ...
s
* Bank overdrafts normally are considered as financing activities. Nevertheless, where bank borrowings which are repayable on a demand form an integral part of company's cash management, bank overdrafts are considered to be a part of cash and cash equivalents.
* Cash in saving accounts is generally for the saving purposes so that they are not used for daily expenses.
* Cash in checking accounts
A transaction account, also called a checking account, chequing account, current account, demand deposit account, or share draft account at credit unions, is a deposit account held at a bank or other financial institution. It is available to the ...
allow to write checks and use electronic debit to access funds in the account.
* Money order
A money order is a directive to pay a pre-specified amount of money from prepaid funds, making it a more trusted method of payment than a cheque.
History
The money order system was established by a private firm in Great Britain in 1792 and was ...
is a financial instrument issued by government or financial institutions which is used by payee
A payment is the voluntary tender of money or its equivalent or of things of value by one party (such as a person or company) to another in exchange for goods, or services provided by them, or to fulfill a legal obligation. The party making the ...
to receive cash on demand. The advantage of money orders over checks is that it is more trusted since it is always prepaid. They are acceptable for payment of personal or small business's debts and can be purchased for a small fee at many locations such as post office and grocery.
* Petty cash
Petty cash is a small amount of discretionary funds in the form of cash used for expenditures where it is not sensible to make any disbursement by cheque, because of the inconvenience and costs of writing, signing, and then cashing the cheque.
...
is a small amount of cash that is used for payment of insignificant expenses and the amount of it may vary depending on the organisation. For some entities $50 is adequate amount of cash, whereas for others the minimum sum should be $200. Petty cash funds must be safeguarded and recorded in order to avoid thefts. Often there is a custodian appointed who is responsible for the documentation of petty cash transactions.
Components of cash equivalents
 *
* Treasury bills
United States Treasury securities, also called Treasuries or Treasurys, are government debt instruments issued by the United States Department of the Treasury to finance government spending as an alternative to taxation. Since 2012, U.S. gov ...
, also called "T-bills", are a security issued by the U.S. Department of Treasury, where their purchase lends money to the U.S. government. T-bills are auctioned in denominations of $100, up to maximum amount of $5 million (or 35% of the auction offering if a competitive bid) and lack a coupon payment, but instead are sold at a discount, their yield being the difference between purchase price and redemption value, which is paid at maturity. Regular series Treasury bills mature in 4, 13, 26 & 52 weeks from their issue date, which may be purchased via TreasuryDirect or a licensed broker.
* Commercial paper
Commercial paper, in the global financial market, is an unsecured promissory note with a fixed maturity of rarely more than 270 days. In layperson terms, it is like an " IOU" but can be bought and sold because its buyers and sellers have some ...
is a bearer document which is used by big companies. The minimum amount permitted is £100,000 and this form of borrowing is not suitable for certain "entities". Finance companies sell 2/3 of their total commercial paper to the public, but there are also some companies which borrow less and sell their commercial paper to "paper dealers" who then re-sell the papers to the investors. A "round lot" for paper dealers is approximately £250,000.
* Marketable securities
A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument, but its legal definition varies by jurisdiction. In some countries and languages people commonly use the term "security" to refer to any f ...
make business look more liquid, since they are also included in the calculation of current ratio. These securities are mostly traded on public exchange due to their ready price availability. There are two forms of Marketable Securities: Marketable Equity Securities and Marketable Debt Securities.
* Money market fund
A money market fund (also called a money market mutual fund) is an open-ended mutual fund that invests in short-term debt securities such as US Treasury bills and commercial paper. Money market funds are managed with the goal of maintaining a ...
s are similar to checking accounts, but they mostly pay higher interest rates generated on deposited funds. Net asset Value (NAV) of Money Market funds maintains stable compared to other mutual funds and its share price is constant: $1.00 per share. For businesses, non-profit organizations and many other institutions MMF are very effective "vehicle" for cash management.
* Short-term government bond
A government bond or sovereign bond is a form of bond issued by a government to support public spending. It generally includes a commitment to pay periodic interest, called coupon payments'','' and to repay the face value on the maturity dat ...
s are mostly issued by governments to support government's spending. They are mostly issued in country's domestic currency and in the U.S government bonds include the Savings bond A savings bond is a government bond designed to provide funds for the issuer while also providing a relatively safe investment for the purchaser to save money, typically a retail investor. The earliest savings bonds were the war bond programs of Wo ...
, Treasury bond, Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities
United States Treasury securities, also called Treasuries or Treasurys, are government debt instruments issued by the United States Department of the Treasury to finance government spending as an alternative to taxation. Since 2012, U.S. go ...
and many others. Before investing into government bond investors should take into account political risk, inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
and interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, t ...
risk.
Calculation of cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are listed on balance sheet as "current assets" and its value changes when different transactions are occurred. These changes are called "cash flow
A cash flow is a real or virtual movement of money:
*a cash flow in its narrow sense is a payment (in a currency), especially from one central bank account to another; the term 'cash flow' is mostly used to describe payments that are expected ...
s" and they are recorded on accounting ledger
A ledger is a book or collection of accounts in which account transactions are recorded. Each account has an opening or carry-forward balance, and would record each transaction as either a debit or credit in separate columns, and the ending or ...
. For instance, if a company spends $300 on purchasing goods, this is recorded as $300 increase to its supplies and decrease in the value of CCE. These are few formulas that are used by analysts to calculate transactions related to cash and cash equivalents:
''Change in CCE = End of Year Cash and Cash equivalents - Beginning of Year Cash and Cash Equivalents''.
''Value of Cash and Cash Equivalents at the end of period = Net Cash Flow + Value of CCE at the period of beginning''
Liquidity measurement ratios
*Current ratio The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures whether a firm has enough resources to meet its short-term obligations. It compares a firm's current assets to its current liabilities, and is expressed as follows:-
:
The current ratio is an ...
is generally used to estimate company's liquidity by "deriving the proportion of current assets available to cover current liabilities". The main idea behind this concept is to decide whether current assets which also include cash and cash equivalents are available pay off its short term liabilities (taxes, notes payable, etc.) The higher current ratio is, the better is for the organisation.*
Quick ratio
In finance, the quick ratio, also known as the acid-test ratio is a type of liquidity ratio, which measures the ability of a company to use its ''near cash'' or quick assets to extinguish or retire its current liabilities immediately. It is defi ...
is liquidity indicator that defines current ratio by measuring the most liquid current assets in the company that are available to cover liabilities. Unlike to the current ratio, inventories and other assets that are difficult to convert into the cash are excluded from the calculation of quick ratio
In finance, the quick ratio, also known as the acid-test ratio is a type of liquidity ratio, which measures the ability of a company to use its ''near cash'' or quick assets to extinguish or retire its current liabilities immediately. It is defi ...
.*
Cash ratio
Reserve requirements are central bank regulations that set the minimum amount that a commercial bank must hold in liquid assets. This minimum amount, commonly referred to as the commercial bank's reserve, is generally determined by the centra ...
is more restrictive than above mentioned ratios because no other current asset
In accounting, a current asset is any asset which can reasonably be expected to be sold, consumed, or exhausted through the normal operations of a business within the current fiscal year or operating cycle or financial year (whichever period is ...
s than cash can be used to pay off current debt. Most of the creditors give importance to cash ratio of the company, since it give them idea whether the entity is able to maintain stable cash balances in order to pay off their current debts as they come due.Restricted cash
 Restricted
Restricted cash
In economics, cash is money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.
In bookkeeping and financial accounting, cash is current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately or near-im ...
is the amount of cash and cash equivalent items which are restricted for withdrawal and usage. The restrictions might include legally restricted deposits
A deposit account is a bank account maintained by a financial institution in which a customer can deposit and withdraw money. Deposit accounts can be savings accounts, current accounts or any of several other types of accounts explained below.
...
, which are held as compensating balances against short-term borrowings, contracts entered into with others or entity statements of intention with regard to specific deposits; nevertheless, time deposits and short-term certificates of deposit are excluded from legally restricted deposits. Restricted cash can be also set aside for other purposes such as expansion of the entity, dividend
A dividend is a distribution of profits by a corporation to its shareholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, it is able to pay a portion of the profit as a dividend to shareholders. Any amount not distributed is taken to be re-i ...
funds
Funding is the act of providing resources to finance a need, program, or project. While this is usually in the form of money, it can also take the form of effort or time from an organization or company. Generally, this word is used when a firm use ...
or "retirement of long-term debt". Depending on its immateriality or materiality, restricted cash may be recorded as "cash" in the financial statement or it might be classified based on the date of availability disbursements. Moreover, if cash is expected to be used within one year after the balance sheet date it can be classified as "current asset
In accounting, a current asset is any asset which can reasonably be expected to be sold, consumed, or exhausted through the normal operations of a business within the current fiscal year or operating cycle or financial year (whichever period is ...
", but in a longer period of time it is mentioned as non- current asset. For example, a large machine manufacturing company receives an advance payment ( deposit) from its customer for a machine that should be produced and shipped to another country within 2 months. Based on the customer contract the manufacturer should put the deposit into separate bank account and not withdraw or use the money until the equipment is shipped and delivered. This is a restricted cash, since manufacturer has the deposit, but he can not use it for operations until the equipment
Equipment most commonly refers to a set of tools or other objects commonly used to achieve a particular objective. Different job
Work or labor (or labour in British English) is intentional activity people perform to support the needs and ...
is shipped.
See also
*Balance sheet
In financial accounting, a balance sheet (also known as statement of financial position or statement of financial condition) is a summary of the financial balances of an individual or organization, whether it be a sole proprietorship, a business ...
* Currency
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins.
A more general ...
* Inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
* Inflation hedge An inflation hedge is an investment intended to protect the investor against (hedge) a decrease in the purchasing power of money (inflation). There is no investment known to be a successful hedge in all inflationary environments, just as there is n ...
* United States Treasury security
United States Treasury securities, also called Treasuries or Treasurys, are government debt instruments issued by the United States Department of the Treasury to finance government spending as an alternative to taxation. Since 2012, U.S. go ...
References
{{Reflist, 30em Asset Cash