Capture of Combles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Capture of Combles (25 September 1916) was a tactical incident that took place during the Battle of Morval, part of the Battle of the Somme, during the
 On 22 July, reconnaissance aircraft from 9 Squadron Royal Flying Corps (RFC) flew over the German defences from Combles to Gueudecourt and reported that they were formidable but unoccupied. The village was bombarded with shells on the night of and next day an ammunition train in the station was hit and blew up. Late on 2 September, troops of the 111th Division, at readiness in Combles, were called forward to counter-attack towards Guillemont. The French Sixth Army attacked on the north bank of the Somme, from and I Corps with the 1st Division (Général de Riols de Fonclare) and the 2nd Division (Général Guignadaudet) on the northern flank, next to the British Fourth Army, took high ground south of Combles and established a foothold in Bois Douage. On 4 September, German counter-attacks on the Combles ravine, south-west of the village, were repulsed and I Corps made a slight advance north-east, from Le Forêt towards Rancourt. The British capture of Falfemont Farm on 5 September enabled the two armies to link across the Combles ravine. French patrols advanced south-east of the village and captured Ferme de l'Hôpital, just east of Le Forêt.
Rainstorms, disorganisation behind the front line and chronic supply difficulties, forced the Sixth Army to stop operations until 12 September, during which many French divisions were relieved. The I Corps commander, General
On 22 July, reconnaissance aircraft from 9 Squadron Royal Flying Corps (RFC) flew over the German defences from Combles to Gueudecourt and reported that they were formidable but unoccupied. The village was bombarded with shells on the night of and next day an ammunition train in the station was hit and blew up. Late on 2 September, troops of the 111th Division, at readiness in Combles, were called forward to counter-attack towards Guillemont. The French Sixth Army attacked on the north bank of the Somme, from and I Corps with the 1st Division (Général de Riols de Fonclare) and the 2nd Division (Général Guignadaudet) on the northern flank, next to the British Fourth Army, took high ground south of Combles and established a foothold in Bois Douage. On 4 September, German counter-attacks on the Combles ravine, south-west of the village, were repulsed and I Corps made a slight advance north-east, from Le Forêt towards Rancourt. The British capture of Falfemont Farm on 5 September enabled the two armies to link across the Combles ravine. French patrols advanced south-east of the village and captured Ferme de l'Hôpital, just east of Le Forêt.
Rainstorms, disorganisation behind the front line and chronic supply difficulties, forced the Sixth Army to stop operations until 12 September, during which many French divisions were relieved. The I Corps commander, General
 The British conformed to the French preference for afternoon attacks, which meant that the final bombardment would take place in daylight. The British preferred dawn attacks to avoid the attacking infantry waiting for too long in the front-line, vulnerable to German counter-bombardment. Tank policy had been decided at a meeting on 19 September, where the vulnerability of tanks waiting in advanced positions from dawn to zero hour, led to a decision by the Fourth Army commander, General Henry Rawlinson to keep them in reserve, ready to advance if they were needed. The XIV Corps commander,
The British conformed to the French preference for afternoon attacks, which meant that the final bombardment would take place in daylight. The British preferred dawn attacks to avoid the attacking infantry waiting for too long in the front-line, vulnerable to German counter-bombardment. Tank policy had been decided at a meeting on 19 September, where the vulnerability of tanks waiting in advanced positions from dawn to zero hour, led to a decision by the Fourth Army commander, General Henry Rawlinson to keep them in reserve, ready to advance if they were needed. The XIV Corps commander,
 The French Sixth Army planned to attack from the Somme north to Combles, in which I Corps would capture Frégicourt and Sailly-Saillisel and XXXII Corps would take Rancourt, the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and Saillisel. The 56th Division was to mask Bouleaux Wood and reach trenches to the north-east and the right-hand brigade of the
The French Sixth Army planned to attack from the Somme north to Combles, in which I Corps would capture Frégicourt and Sailly-Saillisel and XXXII Corps would take Rancourt, the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and Saillisel. The 56th Division was to mask Bouleaux Wood and reach trenches to the north-east and the right-hand brigade of the
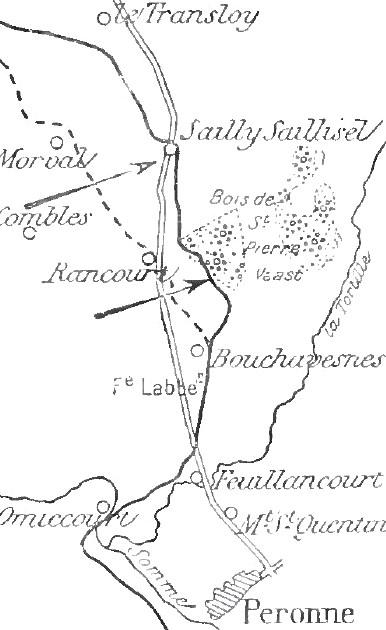
 On the German right flank the XXVI Reserve Corps took over the Combles area on 3 September, with the 52nd Reserve Division on the right, the 51st Reserve Division held Morval with the Reserve Infantry Regiment 236 and the ground further south with Reserve Infantry Regiment 235. Reserve Infantry Regiment 234 held the village but losses had reduced the front line strength of the division to with a few machine-guns. Allied bombardments had destroyed trenches, dug outs, barbed wire and communications links and to avoid observation by aircraft the German troops had dispersed among shell-holes. During the day, Allied artillery directed by the crews of artillery-observation aircraft overwhelmed the artillery batteries and guns in the area. There were no rear defence lines and the transport of supplies to the front line could only take place at night. The divisional commander Wilhem Balck, stressed that the defenders should co-operate closely with flanking units and the artillery and use hasty counter-attacks to recover lost ground and requested frequent reports delivered by all means possible. A new trench line was dug on a reverse slope east of Frégicourt and Rancourt, connecting Morval with the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and covering Sailly-Saillisel and from the wood south-east to Tortille river at Allaines.
The cessation of German attacks at Verdun, ordered by the new supreme command of Chief of the General Staff, Field Marshal von Hindenburg and General Erich Ludendorff, when they superseded Falkenhayn and the reinforcement of the Somme front, reduced the German inferiority in guns and aircraft on the Somme during September. Field artillery reduced its barrage frontage from per battery and increased its accuracy by using one air artillery flight per division, using the aircraft reinforcements from the Verdun front. Colonel Fritz von Loßberg, Chief of Staff of the 2nd Army, was also able to establish (relief divisions) behind the battlefield, ready to replace front divisions. Loßberg established new positions based on depth, dispersal and camouflage, rather than continuous lines of trenches. Rigid defence of the front-line continued but with as few soldiers as possible, relying on the firepower of machine-guns firing from behind the front-line and from the flanks. Artillery reduced its counter-battery fire and area bombardments before Anglo-French attacks and used the reinforcements from Verdun for destructive fire, observed from balloons and aircraft.
The area behind the front-line was defended by support and reserve units dispersed on reverse slopes, in undulations and in any cover that could be found, so that they could open machine-gun fire by surprise, from unseen positions and then counter-attack swiftly, before the Anglo-French infantry could consolidate captured ground. Local, corps and army reserves were held back, in lines about apart, to make progressively stronger counter-attacks. Before an attack the garrison tried to move forwards into shell-holes, to avoid Allied artillery-fire and surprise attacking infantry with machine-gun fire. Opposite the French the Germans dug new defences on a reverse slope between the Tortille stream at Allaines to the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and from there to Morval, connected to a new fourth position from Sailly Saillissel to Morval and along the Péronne–Bapaume road. After the Anglo-French attacks in mid-September a "wholesale relief" of the front-line divisions had been possible. The largest German counter-attacks of the Somme battle took place from from the Somme north to St Pierre Vaast Wood and were "destroyed" by French artillery fire. Ludendorff created "new" divisions by combing-out troops at depots and by removing regiments from existing divisions, of which the 212th, 213th and 214th divisions replaced exhausted divisions opposite the French Tenth and Sixth armies.
On the German right flank the XXVI Reserve Corps took over the Combles area on 3 September, with the 52nd Reserve Division on the right, the 51st Reserve Division held Morval with the Reserve Infantry Regiment 236 and the ground further south with Reserve Infantry Regiment 235. Reserve Infantry Regiment 234 held the village but losses had reduced the front line strength of the division to with a few machine-guns. Allied bombardments had destroyed trenches, dug outs, barbed wire and communications links and to avoid observation by aircraft the German troops had dispersed among shell-holes. During the day, Allied artillery directed by the crews of artillery-observation aircraft overwhelmed the artillery batteries and guns in the area. There were no rear defence lines and the transport of supplies to the front line could only take place at night. The divisional commander Wilhem Balck, stressed that the defenders should co-operate closely with flanking units and the artillery and use hasty counter-attacks to recover lost ground and requested frequent reports delivered by all means possible. A new trench line was dug on a reverse slope east of Frégicourt and Rancourt, connecting Morval with the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and covering Sailly-Saillisel and from the wood south-east to Tortille river at Allaines.
The cessation of German attacks at Verdun, ordered by the new supreme command of Chief of the General Staff, Field Marshal von Hindenburg and General Erich Ludendorff, when they superseded Falkenhayn and the reinforcement of the Somme front, reduced the German inferiority in guns and aircraft on the Somme during September. Field artillery reduced its barrage frontage from per battery and increased its accuracy by using one air artillery flight per division, using the aircraft reinforcements from the Verdun front. Colonel Fritz von Loßberg, Chief of Staff of the 2nd Army, was also able to establish (relief divisions) behind the battlefield, ready to replace front divisions. Loßberg established new positions based on depth, dispersal and camouflage, rather than continuous lines of trenches. Rigid defence of the front-line continued but with as few soldiers as possible, relying on the firepower of machine-guns firing from behind the front-line and from the flanks. Artillery reduced its counter-battery fire and area bombardments before Anglo-French attacks and used the reinforcements from Verdun for destructive fire, observed from balloons and aircraft.
The area behind the front-line was defended by support and reserve units dispersed on reverse slopes, in undulations and in any cover that could be found, so that they could open machine-gun fire by surprise, from unseen positions and then counter-attack swiftly, before the Anglo-French infantry could consolidate captured ground. Local, corps and army reserves were held back, in lines about apart, to make progressively stronger counter-attacks. Before an attack the garrison tried to move forwards into shell-holes, to avoid Allied artillery-fire and surprise attacking infantry with machine-gun fire. Opposite the French the Germans dug new defences on a reverse slope between the Tortille stream at Allaines to the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and from there to Morval, connected to a new fourth position from Sailly Saillissel to Morval and along the Péronne–Bapaume road. After the Anglo-French attacks in mid-September a "wholesale relief" of the front-line divisions had been possible. The largest German counter-attacks of the Somme battle took place from from the Somme north to St Pierre Vaast Wood and were "destroyed" by French artillery fire. Ludendorff created "new" divisions by combing-out troops at depots and by removing regiments from existing divisions, of which the 212th, 213th and 214th divisions replaced exhausted divisions opposite the French Tenth and Sixth armies.
 During the night of the British-French bombardment increased and at on 25 September a hurricane bombardment began as the infantry attacked. The French Sixth Army attacked with seven divisions but the I Corps divisions next to the British Fourth Army involved in the attack on Combles, were held up for most of the day by German machine-gun fire on the left flank south-east of the village. The French reached the Maurepas–Frégicourt road in the centre and on the right flank of I Corps, the 42nd Division of XXXII Corps forced back the 213th Division, closed up to Frégicourt and captured Rancourt in the afternoon; further south the French attacks were repulsed by massed artillery and machine-gun fire.
Anglo-French attacks had been expected by the defenders on 23 September and the timing of the attack for the afternoon of 25 September achieved a measure of surprise. The 51st and 52nd Reserve divisions were quickly pushed back, Reserve Infantry Regiment 239 was broken through and the III Battalion surrounded. Part of Reserve Infantry Regiment 236 was destroyed at the tram line north of Bouleaux Wood, which left Reserve Infantry Regiment 235 west of Combles and Reserve Infantry Regiment 234 in the village, vulnerable to encirclement by the British from the north and the French in the south.
The 56th Division next to the French I Corps, attacked on the front of the 168th Brigade, seven minutes after zero hour, to give time for the 5th Division battalions of the 95th and 15th brigades on the left to draw level. The 1/4th London and the London Scottish advanced behind a creeping barrage fired by batteries in Angle Wood Valley in enfilade towards Bouleaux Wood, which was particularly accurate. The 1/4th London and the London Scottish began to advance steadily at with C Company leading in two waves fifty paces apart, followed by D Company in similar formation. B Company was to conform to the advance and protect the Brigade right flank, against a German riposte from the southern half of Bouleaux Wood. A Company was held in reserve to move forward to the vacant trenches of the assaulting companies. The 1/4th London reached its objectives in the northern fringe of the wood with little opposition and few casualties, killing a large number of Germans in shell hole positions on the western edge. German troops ran back over the open hillside near Combles, only to be shot down from the left flank, by Lewis gunners of the London Scottish. Consolidation of strong points began but was hampered by sniper fire, from farther south in the wood, which continued through the night, as the 167th Brigade on the right flank had not advanced all the way through the wood.
During the night of the British-French bombardment increased and at on 25 September a hurricane bombardment began as the infantry attacked. The French Sixth Army attacked with seven divisions but the I Corps divisions next to the British Fourth Army involved in the attack on Combles, were held up for most of the day by German machine-gun fire on the left flank south-east of the village. The French reached the Maurepas–Frégicourt road in the centre and on the right flank of I Corps, the 42nd Division of XXXII Corps forced back the 213th Division, closed up to Frégicourt and captured Rancourt in the afternoon; further south the French attacks were repulsed by massed artillery and machine-gun fire.
Anglo-French attacks had been expected by the defenders on 23 September and the timing of the attack for the afternoon of 25 September achieved a measure of surprise. The 51st and 52nd Reserve divisions were quickly pushed back, Reserve Infantry Regiment 239 was broken through and the III Battalion surrounded. Part of Reserve Infantry Regiment 236 was destroyed at the tram line north of Bouleaux Wood, which left Reserve Infantry Regiment 235 west of Combles and Reserve Infantry Regiment 234 in the village, vulnerable to encirclement by the British from the north and the French in the south.
The 56th Division next to the French I Corps, attacked on the front of the 168th Brigade, seven minutes after zero hour, to give time for the 5th Division battalions of the 95th and 15th brigades on the left to draw level. The 1/4th London and the London Scottish advanced behind a creeping barrage fired by batteries in Angle Wood Valley in enfilade towards Bouleaux Wood, which was particularly accurate. The 1/4th London and the London Scottish began to advance steadily at with C Company leading in two waves fifty paces apart, followed by D Company in similar formation. B Company was to conform to the advance and protect the Brigade right flank, against a German riposte from the southern half of Bouleaux Wood. A Company was held in reserve to move forward to the vacant trenches of the assaulting companies. The 1/4th London reached its objectives in the northern fringe of the wood with little opposition and few casualties, killing a large number of Germans in shell hole positions on the western edge. German troops ran back over the open hillside near Combles, only to be shot down from the left flank, by Lewis gunners of the London Scottish. Consolidation of strong points began but was hampered by sniper fire, from farther south in the wood, which continued through the night, as the 167th Brigade on the right flank had not advanced all the way through the wood.
 North of the 56th Division, the 95th Brigade of the 5th Division was delayed by enfilade machine-gun fire from the embankment north of the tram line in the 56th Division area and a strong point on the Ginchy–Morval road, until bombed from the north. The 95th Brigade then resumed its advance up the far slope and rushed the German trench running south from Morval, as the 15th Brigade overran the trench further north, just short of the village, taking many more prisoners. After another halt to reorganise, the village was occupied by the 15th Brigade at . The final objective from the windmill south to the 56th Division area was consolidated by nightfall. Several weak German counter-attacks were defeated and the 95th Brigade began working its way south towards the French at Frégicourt.
The London Scottish captured a trench from the wood to the light railway and were then engaged by German troops in the railway embankment, until the position was rushed by the 5th Division from the north and the London Scottish arrived to join in the mopping-up of the survivors in dugouts. By the area had been cleared and taken from Reserve Infantry Regiment 236. The London Scottish pressed on and captured another trench, which had only been discovered on air reconnaissance photographs the day before and from which was an excellent view over the Combles–Morval valley. No sign was yet seen of French troops moving north from the area of Frégicourt, who were to join with British troops at the crossroads east of Morval and patrols further forward were limited by the British protective barrage. By the XIV Corps divisions had overrun the last of the German defensive lines on a frontage of and artillery observers reported that German field artillery batteries and parties of German soldiers were retreating eastwards, from the area either side of Morval as the 5th Division occupied a spur east of the village. Reports from contact patrol aircraft reached the Fourth Army headquarters by giving the approximate position of the attacking troops and after thirty minutes Cavan contradicted French claims to have captured Frégicourt.
North of the 56th Division, the 95th Brigade of the 5th Division was delayed by enfilade machine-gun fire from the embankment north of the tram line in the 56th Division area and a strong point on the Ginchy–Morval road, until bombed from the north. The 95th Brigade then resumed its advance up the far slope and rushed the German trench running south from Morval, as the 15th Brigade overran the trench further north, just short of the village, taking many more prisoners. After another halt to reorganise, the village was occupied by the 15th Brigade at . The final objective from the windmill south to the 56th Division area was consolidated by nightfall. Several weak German counter-attacks were defeated and the 95th Brigade began working its way south towards the French at Frégicourt.
The London Scottish captured a trench from the wood to the light railway and were then engaged by German troops in the railway embankment, until the position was rushed by the 5th Division from the north and the London Scottish arrived to join in the mopping-up of the survivors in dugouts. By the area had been cleared and taken from Reserve Infantry Regiment 236. The London Scottish pressed on and captured another trench, which had only been discovered on air reconnaissance photographs the day before and from which was an excellent view over the Combles–Morval valley. No sign was yet seen of French troops moving north from the area of Frégicourt, who were to join with British troops at the crossroads east of Morval and patrols further forward were limited by the British protective barrage. By the XIV Corps divisions had overrun the last of the German defensive lines on a frontage of and artillery observers reported that German field artillery batteries and parties of German soldiers were retreating eastwards, from the area either side of Morval as the 5th Division occupied a spur east of the village. Reports from contact patrol aircraft reached the Fourth Army headquarters by giving the approximate position of the attacking troops and after thirty minutes Cavan contradicted French claims to have captured Frégicourt.
 The 1/1st London skirmished with the German garrison in the wood around a derelict tank and further to the right the 1/5th London (Rifle Brigade) and the 1/9th London (Queen Victoria's Rifles) kept the German troops in the sunken road to Combes and Combles Trench pinned down. Two tanks attached to the 56th Division, remained at an assembly point in a dip west of Leuze Wood and the three allotted to the 5th Division followed up the advance but two bogged down and the third was sent back from Morval. By midnight the 168th Brigade had established observation posts with an excellent view over the northern exits of Combles and the brigade was directed to work round the north side of Combles and cut off the route to Morval. The 167th Brigade had advanced past the derelict tank and entered the wood and all the sunken road and Combles Trench had been captured by the 169th Brigade.
At a party from the London Scottish began to probe south along the light railway towards Combles and by dawn was within . At the Rifle Brigade entered Combles and met French troops and as dawn broke the 56th Division began to consolidate a new line east of Combles, with the Germans beyond in Mutton Trench. A further attack was planned with tank support then cancelled when the tanks failed to appear. A narrow gap remained through which the German garrison could escape and for the rest of the night, the 56th Division artillery fired a barrage at the exit to catch the fleeing troops. The German garrison began to withdraw from the village at and by most of the troops had escaped and improvised a new line west of Sailly.
The 1/1st London skirmished with the German garrison in the wood around a derelict tank and further to the right the 1/5th London (Rifle Brigade) and the 1/9th London (Queen Victoria's Rifles) kept the German troops in the sunken road to Combes and Combles Trench pinned down. Two tanks attached to the 56th Division, remained at an assembly point in a dip west of Leuze Wood and the three allotted to the 5th Division followed up the advance but two bogged down and the third was sent back from Morval. By midnight the 168th Brigade had established observation posts with an excellent view over the northern exits of Combles and the brigade was directed to work round the north side of Combles and cut off the route to Morval. The 167th Brigade had advanced past the derelict tank and entered the wood and all the sunken road and Combles Trench had been captured by the 169th Brigade.
At a party from the London Scottish began to probe south along the light railway towards Combles and by dawn was within . At the Rifle Brigade entered Combles and met French troops and as dawn broke the 56th Division began to consolidate a new line east of Combles, with the Germans beyond in Mutton Trench. A further attack was planned with tank support then cancelled when the tanks failed to appear. A narrow gap remained through which the German garrison could escape and for the rest of the night, the 56th Division artillery fired a barrage at the exit to catch the fleeing troops. The German garrison began to withdraw from the village at and by most of the troops had escaped and improvised a new line west of Sailly.
 25 September dawned bright and cloudless, with a ground haze but reports from contact patrol observers were notably accurate, as the infantry advanced to their objectives on the Fourth Army front, from Morval to Gueudecourt and around Flers. Ground at the south-east edge of Morval was captured in the evening, completing the occupation of the ground on the main ridge and making Combles untenable, although British balloon observers could see that the French advance from the south had been delayed at Frégicourt. After a captured German officer disclosed that Combles was to be evacuated during the night, British artillery bombarded the valley to the east of the village. In the early hours of the morning, British troops entered the north end of Combles as French troops advanced from the south. The position of the ground forces was reported at noon by a reconnaissance crew, who returned at to observe the position of the new line but at were hit by an anti-aircraft shell and blown up.
A French aviator flying above Combles reported that
25 September dawned bright and cloudless, with a ground haze but reports from contact patrol observers were notably accurate, as the infantry advanced to their objectives on the Fourth Army front, from Morval to Gueudecourt and around Flers. Ground at the south-east edge of Morval was captured in the evening, completing the occupation of the ground on the main ridge and making Combles untenable, although British balloon observers could see that the French advance from the south had been delayed at Frégicourt. After a captured German officer disclosed that Combles was to be evacuated during the night, British artillery bombarded the valley to the east of the village. In the early hours of the morning, British troops entered the north end of Combles as French troops advanced from the south. The position of the ground forces was reported at noon by a reconnaissance crew, who returned at to observe the position of the new line but at were hit by an anti-aircraft shell and blown up.
A French aviator flying above Combles reported that
 German reinforcements had arrived on the Somme front during September and conducted the big counter-attacks on both sides of the Somme from to regain the ground lost since 12 September. The attacks were costly failures and Ludendorff called the fighting of the biggest engagement of the battle. Much German equipment was captured in Combles, including two million rounds of ammunition, shells and many hand-grenades. The battle of Morval had been a considerable Anglo-French victory. The objective was one German trench system, the original third line, which was less well-developed than the German defences on 15 September and was subjected to greater weight of shellfire. Rainfall from and the tempo of attacks had made it difficult for the Germans to improve their defences before the attack. French attacks in the south beyond Combles had less success, being confronted by a much larger amount of shell-fire. The 5th Division was relieved on the night of 26 September by the 20th Division, which was replaced by French troops after twenty-four hours, during the army boundary changes.
German reinforcements had arrived on the Somme front during September and conducted the big counter-attacks on both sides of the Somme from to regain the ground lost since 12 September. The attacks were costly failures and Ludendorff called the fighting of the biggest engagement of the battle. Much German equipment was captured in Combles, including two million rounds of ammunition, shells and many hand-grenades. The battle of Morval had been a considerable Anglo-French victory. The objective was one German trench system, the original third line, which was less well-developed than the German defences on 15 September and was subjected to greater weight of shellfire. Rainfall from and the tempo of attacks had made it difficult for the Germans to improve their defences before the attack. French attacks in the south beyond Combles had less success, being confronted by a much larger amount of shell-fire. The 5th Division was relieved on the night of 26 September by the 20th Division, which was replaced by French troops after twenty-four hours, during the army boundary changes.
 During the evening of 26 September, the 1/4th London was relieved in Bouleaux Wood by the 1/13th London (The Kensingtons) and withdrew to Bully and Beef trenches. During 27 September, trenches held by the 1/4th London were bombarded but there was no German counter-attack. In the evening the 168th Brigade handed over to the 2nd French Division and the 1/4th London, without relief in Bully and Beef trenches, withdrew to Casement Trench. The casualties of the 1/4th London were and rest of the 56th Division was relieved by the 20th and 6th divisions, as the inter-army boundary was moved north during 27 September. I Corps advanced a short distance against the 213th Division, east of the Frégicourt–Le Transloy road. A new attack from towards the German defences between Haïe Wood and St Pierre Vaast Wood, was delayed. Mutton Trench on the left flank was attacked at by the British; the French attack managed to advance on the flanks but was held up in the centre around Sailly.
During the evening of 26 September, the 1/4th London was relieved in Bouleaux Wood by the 1/13th London (The Kensingtons) and withdrew to Bully and Beef trenches. During 27 September, trenches held by the 1/4th London were bombarded but there was no German counter-attack. In the evening the 168th Brigade handed over to the 2nd French Division and the 1/4th London, without relief in Bully and Beef trenches, withdrew to Casement Trench. The casualties of the 1/4th London were and rest of the 56th Division was relieved by the 20th and 6th divisions, as the inter-army boundary was moved north during 27 September. I Corps advanced a short distance against the 213th Division, east of the Frégicourt–Le Transloy road. A new attack from towards the German defences between Haïe Wood and St Pierre Vaast Wood, was delayed. Mutton Trench on the left flank was attacked at by the British; the French attack managed to advance on the flanks but was held up in the centre around Sailly.
La prise de Combles, 26 Septembre 1916 (in French with photographs)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Combles, Capture of Conflicts in 1916 1916 in France Battle of the Somme Battles of the Western Front (World War I) Battles of World War I involving France Battles of World War I involving Germany Battles of World War I involving the United Kingdom September 1916 events
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. Combles lies north-east of Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; pcd, Anmien, or ) is a city and commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme department in the region of Hauts-de-France. In 2021, the population of ...
and east of Albert
Albert may refer to:
Companies
* Albert (supermarket), a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic
* Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands
* Albert Market, a street market in The Gambia
* Albert Productions, a record label
* Alber ...
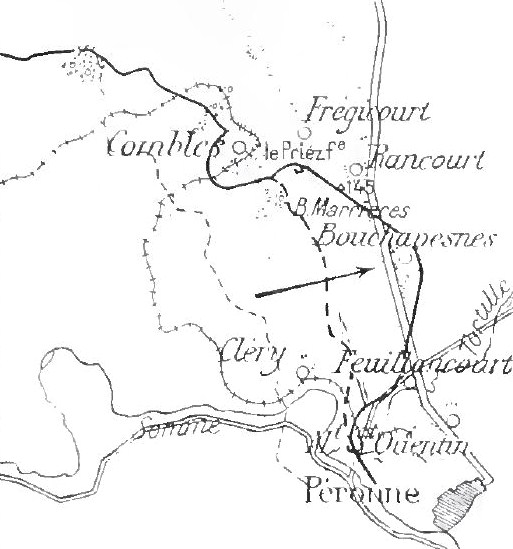
, on the D 20 Rancourt–Guillemont road, south of Bapaume, in the Combles valley a hollow between outcrops of Bazentin Ridge, between Morval to the north, Ginchy to the north-west and Falfemont Farm to the west. North of the village the valley widens into a basin, which forks north-east around the Morval Spur. In late September 1914, military operations took place in the vicinity, when the II Bavarian Corps was engaged by French Territorial divisions in an encounter battle. The French divisions were forced back and the two divisions of the II Bavarian Corps, advanced westwards on the north side of the Somme, eventually being stopped around Maricourt, Montauban and Fricourt.
Combles became a backwater until 1916, when it was used as a shelter for reserves, supplies and engineer stores and a staging area for reinforcements. the German third defensive position being built as the battle began, ran close behind the village. Combles was attacked by the British and French on 25 September, during the Battle of Morval after several delays due to rain and poor visibility. Brigades from the 56th and 5th divisions in the north, wheeled to the right to form a south-facing flank above Combles, as the French 2nd Division attacked from the south. The British attack swiftly established the defensive flank and patrols began to probe southwards. German resistance against the French attack close to the village, particularly with machine-gun fire, held back the advance.
Further to the east, the French captured Rancourt in the afternoon and closed up to Frégicourt. Prisoners taken by the British and French revealed that a retirement from the village was intended during the night. A constant Anglo-French artillery barrage was maintained on the exits. Infantry patrols probed forwards and the British and French forces met at several points in and east of the village in the early hours of 26 September. A huge amount of equipment, ammunition and engineering stores were captured in the village and on 27 September, the inter-army boundary was moved north to Morval, to assist French attacks towards Sailly-Saillisel. On 24 March 1918, Combles was recaptured by German troops, during the retreat of the 9th Division in Operation Michael
Operation Michael was a major German military offensive during the First World War that began the German Spring Offensive on 21 March 1918. It was launched from the Hindenburg Line, in the vicinity of Saint-Quentin, France. Its goal was t ...
, the German spring offensive. The village was recaptured for the last time on 29 August, by the 18th Division, during the Second Battle of Bapaume
The Second Battle of Bapaume was a battle of the First World War that took place at Bapaume in France, from 21 August 1918 to 3 September 1918. It was a continuation of the Battle of Albert and is also referred to as the second phase of that ba ...
.
Background
1914
Combles lies east of Albert on the D 20 Rancourt–Guillemont road and south of Bapaume. Morval lies to the north, Ginchy to the north-west and Falfemont Farm to the west. The village lies in a hollow between outcrops of Bazentin Ridge. On 25 September 1914, the French 11th Division advanced on the north side of the Somme towards Combles and Péronne, against increasing artillery and machine-gun fire. Next day, German attacks by the II Bavarian Corps (General Karl Ritter von Martini) attacked westwards on the north bank of the Somme, with the 4th Bavarian Division, which had pushed back French territorial divisions around Bapaume, in an encounter battle and left flank guards facing north. The division advanced through Sailly, Combles, Guilemont and Montauban. To the south, closer to the Somme, the 3rd Bavarian Division advanced through Bouchavesnes, Le Foret and Hardecourt, where the arrival of the XI Corps of the new French Tenth Army during 28 September, slowed the Bavarian advance and next day, stopped the Bavarians east of Albert.1916
 On 22 July, reconnaissance aircraft from 9 Squadron Royal Flying Corps (RFC) flew over the German defences from Combles to Gueudecourt and reported that they were formidable but unoccupied. The village was bombarded with shells on the night of and next day an ammunition train in the station was hit and blew up. Late on 2 September, troops of the 111th Division, at readiness in Combles, were called forward to counter-attack towards Guillemont. The French Sixth Army attacked on the north bank of the Somme, from and I Corps with the 1st Division (Général de Riols de Fonclare) and the 2nd Division (Général Guignadaudet) on the northern flank, next to the British Fourth Army, took high ground south of Combles and established a foothold in Bois Douage. On 4 September, German counter-attacks on the Combles ravine, south-west of the village, were repulsed and I Corps made a slight advance north-east, from Le Forêt towards Rancourt. The British capture of Falfemont Farm on 5 September enabled the two armies to link across the Combles ravine. French patrols advanced south-east of the village and captured Ferme de l'Hôpital, just east of Le Forêt.
Rainstorms, disorganisation behind the front line and chronic supply difficulties, forced the Sixth Army to stop operations until 12 September, during which many French divisions were relieved. The I Corps commander, General
On 22 July, reconnaissance aircraft from 9 Squadron Royal Flying Corps (RFC) flew over the German defences from Combles to Gueudecourt and reported that they were formidable but unoccupied. The village was bombarded with shells on the night of and next day an ammunition train in the station was hit and blew up. Late on 2 September, troops of the 111th Division, at readiness in Combles, were called forward to counter-attack towards Guillemont. The French Sixth Army attacked on the north bank of the Somme, from and I Corps with the 1st Division (Général de Riols de Fonclare) and the 2nd Division (Général Guignadaudet) on the northern flank, next to the British Fourth Army, took high ground south of Combles and established a foothold in Bois Douage. On 4 September, German counter-attacks on the Combles ravine, south-west of the village, were repulsed and I Corps made a slight advance north-east, from Le Forêt towards Rancourt. The British capture of Falfemont Farm on 5 September enabled the two armies to link across the Combles ravine. French patrols advanced south-east of the village and captured Ferme de l'Hôpital, just east of Le Forêt.
Rainstorms, disorganisation behind the front line and chronic supply difficulties, forced the Sixth Army to stop operations until 12 September, during which many French divisions were relieved. The I Corps commander, General Adolphe Guillaumat
Marie Louis Adolphe Guillaumat (4 January 1863 – 18 May 1940) was a French Army general during World War I.
Early years
Adolphe Guillaumat was born in Bourgneuf, Charente-Maritime. He graduated first from his class of 1884 at the Saint-Cyr m ...
, ordered that bogged and broken down vehicles be thrown off the roads and supplies carried forward in daylight. By 6 September, I Corps had screened Combles using the Maurepas–Frégicourt road and on 12 September, attacked Rancourt. The 2nd Division captured Bois d'Anderlou and broke into the German defences north-west of Marrières Wood, with the right flank facing Rancourt and Sailly-Saillisel
Sailly-Saillisel is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
Geography
The commune is situated some northeast of Amiens, on the N17 and D172 roads, close to the border with the Pas-de-Calais.
History
* Theatr ...
; further south, Bouchavesnes was captured by Infantry Regiment 44 (IR 44) and IR 133. On 13 September the French closed on Rancourt and Ferme du Priez between Rancourt and Combles, took the farm next day and made a small advance towards Rancourt. The I Corps artillery began a bombardment at dawn on 15 September in support of the British XIV Corps; French infantry attacked at on the left near Combles and tried to bomb into Bois Douage. On the right a small advance was made near Le Priez Farm but an attack on Rancourt was repulsed by German artillery and machine-gun fire.
On 16 September, the artillery of the Sixth Army continued counter-battery fire and the infantry prepared to follow up in case of a German retirement. During the evening of 18 September, surprise attacks by I Corps advanced a short distance south and south-east of Combles but the relief of exhausted divisions was necessary before the main offensive was resumed with the British on 21 September (inclement weather led to postponements until 25 September). German artillery fire continued despite the rain and counter-attacks were conducted around Rancourt and Bouchavesnes. By mid-September, Combles had been outflanked on the north side by the British advance into Leuze Wood and on 20 September, the 52nd Reserve Division was pushed back further. Two days later, French troops drove back the 213th Division on the southern flank of the 51st Reserve Division and captured a sugar refinery south of the village.
Prelude
British-French offensive preparations
 The British conformed to the French preference for afternoon attacks, which meant that the final bombardment would take place in daylight. The British preferred dawn attacks to avoid the attacking infantry waiting for too long in the front-line, vulnerable to German counter-bombardment. Tank policy had been decided at a meeting on 19 September, where the vulnerability of tanks waiting in advanced positions from dawn to zero hour, led to a decision by the Fourth Army commander, General Henry Rawlinson to keep them in reserve, ready to advance if they were needed. The XIV Corps commander,
The British conformed to the French preference for afternoon attacks, which meant that the final bombardment would take place in daylight. The British preferred dawn attacks to avoid the attacking infantry waiting for too long in the front-line, vulnerable to German counter-bombardment. Tank policy had been decided at a meeting on 19 September, where the vulnerability of tanks waiting in advanced positions from dawn to zero hour, led to a decision by the Fourth Army commander, General Henry Rawlinson to keep them in reserve, ready to advance if they were needed. The XIV Corps commander, Major-General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Rudolph Cavan, put all four divisions of the corps in line, to give them narrower fronts, the easier to deploy supporting infantry. The German defences on the flanks were too close for an artillery bombardment and the corps substituted a Stokes mortar and machine-gun barrage to begin at zero hour. At on 24 September, the 1/9th Battalion London Regiment of the 169th Brigade, 56th Division, bombed down Combles Trench towards the French 73rd Regiment, as it attacked from the south-east towards the British but German reinforcements forced the bombers back to their start line.
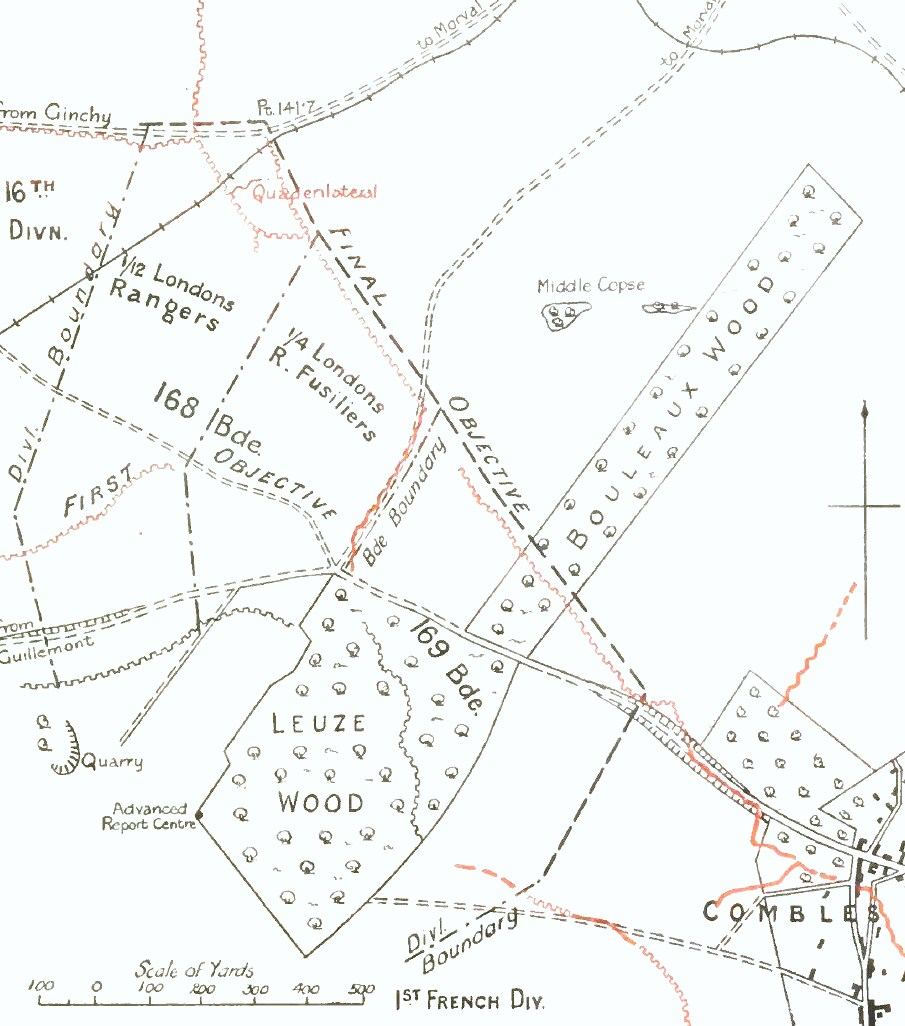
The 95th Brigade of the 5th Division held the right flank of a front from the north edge of Bouleaux Wood on the east slope of Ginchy–Telegraph Hill, on the left of the 56th Division which held the line in Bouleaux Wood. German posts had been dug on the near side of the valley and dug-outs in the light railway embankment were held by infantry and machine-guns. The 56th Division was to form a defensive flank facing south-east over Combles. During the night, two tanks allotted to the division moved forward to rendezvous in the quarry west of Leuze Wood. All three brigades of the division were in line, the 169th Brigade on the right between Combles and Leuze Wood, the 167th Brigade in the centre along Beef and Bully trenches and the 168th Brigade on the left in Middle Copse and in new trenches being dug ready to envelop Bouleaux Wood. The 1/4th London, the right-hand battalion of the 168th Brigade, was to clear the northern end of Bouleaux Wood and to establish a line of posts overlooking the ravine, while the London Scottish on the left continued the defensive flank in the direction of Morval.
From the pioneer battalion 1/5th Cheshire Regiment
The Cheshire Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army, part of the Prince of Wales' Division. The 22nd Regiment of Foot was raised by the Duke of Norfolk in 1689 and was able to boast an independent existence of over 300 years. ...
dug Gropi Trench, a connexion between Beef Trench and Middle Copse covered by the London Scottish who captured several German troops of II Battalion, Reserve Infantry Regiment 235, extended two trenches to the light railway and linked the copse to the Quadrilateral, which made a jumping-off line long facing Combles and Bouleaux Wood. At on 24 September, the 4th Battalion of the London Regiment (Royal Fusiliers) marched from Casement Trench to assembly trenches in the Gropi–Ranger system and Middle Copse. The obliteration of landmarks confused some guides but Middle Copse was eventually reached. Gropi Trench gave good cover from snipers, who were active from the direction of Bouleaux Wood during the morning. From the weather was dry, then rain fell from was dry and slight rain fell from
Franco-British plan of attack
 The French Sixth Army planned to attack from the Somme north to Combles, in which I Corps would capture Frégicourt and Sailly-Saillisel and XXXII Corps would take Rancourt, the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and Saillisel. The 56th Division was to mask Bouleaux Wood and reach trenches to the north-east and the right-hand brigade of the
The French Sixth Army planned to attack from the Somme north to Combles, in which I Corps would capture Frégicourt and Sailly-Saillisel and XXXII Corps would take Rancourt, the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and Saillisel. The 56th Division was to mask Bouleaux Wood and reach trenches to the north-east and the right-hand brigade of the 5th Division In military terms, 5th Division may refer to:
Infantry divisions
* 5th Division (Australia)
*5th Division (People's Republic of China)
* 5th Division (Colombia)
*Finnish 5th Division (Continuation War)
* 5th Light Cavalry Division (France)
*5th Mo ...
was to advance from the second objective to Morval with four halts, gaining touch with the left of the 56th Division. The 56th Division was to guard the southern flank of the Fourth Army during the attacks on Morval, Lesbœufs and Gueudecourt planned for 25 September, by capturing positions at the northern corner of Bouleaux Wood which commanded the valley north-east of Combles.
The division was to extend the flank opposite Combles to neutralise the German defences in Bouleaux Wood, cut the tramline which looped around the north end of the wood and gain touch with the 5th Division on the left. The 168th Brigade objectives were trenches between the wood and tramline and German dugouts along the cutting and bank of the line. The 167th Brigade was to fire machine-gun and Stokes mortar barrages at the wood and the 169th Brigade was to fire on the north and north-east exists of the village. Local liaison between the 56th Division and the French 2nd Division (General Guignadaudet) was to be maintained by the divisional commander, Major-General C. P. A. Hull, for a combined attack on the village on 26 September, if necessary. Infantry supported by two tanks were to advance from Bouleaux Wood as the French advanced from the south, depending on the resistance of the German defenders.
German defensive preparations
 On the German right flank the XXVI Reserve Corps took over the Combles area on 3 September, with the 52nd Reserve Division on the right, the 51st Reserve Division held Morval with the Reserve Infantry Regiment 236 and the ground further south with Reserve Infantry Regiment 235. Reserve Infantry Regiment 234 held the village but losses had reduced the front line strength of the division to with a few machine-guns. Allied bombardments had destroyed trenches, dug outs, barbed wire and communications links and to avoid observation by aircraft the German troops had dispersed among shell-holes. During the day, Allied artillery directed by the crews of artillery-observation aircraft overwhelmed the artillery batteries and guns in the area. There were no rear defence lines and the transport of supplies to the front line could only take place at night. The divisional commander Wilhem Balck, stressed that the defenders should co-operate closely with flanking units and the artillery and use hasty counter-attacks to recover lost ground and requested frequent reports delivered by all means possible. A new trench line was dug on a reverse slope east of Frégicourt and Rancourt, connecting Morval with the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and covering Sailly-Saillisel and from the wood south-east to Tortille river at Allaines.
The cessation of German attacks at Verdun, ordered by the new supreme command of Chief of the General Staff, Field Marshal von Hindenburg and General Erich Ludendorff, when they superseded Falkenhayn and the reinforcement of the Somme front, reduced the German inferiority in guns and aircraft on the Somme during September. Field artillery reduced its barrage frontage from per battery and increased its accuracy by using one air artillery flight per division, using the aircraft reinforcements from the Verdun front. Colonel Fritz von Loßberg, Chief of Staff of the 2nd Army, was also able to establish (relief divisions) behind the battlefield, ready to replace front divisions. Loßberg established new positions based on depth, dispersal and camouflage, rather than continuous lines of trenches. Rigid defence of the front-line continued but with as few soldiers as possible, relying on the firepower of machine-guns firing from behind the front-line and from the flanks. Artillery reduced its counter-battery fire and area bombardments before Anglo-French attacks and used the reinforcements from Verdun for destructive fire, observed from balloons and aircraft.
The area behind the front-line was defended by support and reserve units dispersed on reverse slopes, in undulations and in any cover that could be found, so that they could open machine-gun fire by surprise, from unseen positions and then counter-attack swiftly, before the Anglo-French infantry could consolidate captured ground. Local, corps and army reserves were held back, in lines about apart, to make progressively stronger counter-attacks. Before an attack the garrison tried to move forwards into shell-holes, to avoid Allied artillery-fire and surprise attacking infantry with machine-gun fire. Opposite the French the Germans dug new defences on a reverse slope between the Tortille stream at Allaines to the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and from there to Morval, connected to a new fourth position from Sailly Saillissel to Morval and along the Péronne–Bapaume road. After the Anglo-French attacks in mid-September a "wholesale relief" of the front-line divisions had been possible. The largest German counter-attacks of the Somme battle took place from from the Somme north to St Pierre Vaast Wood and were "destroyed" by French artillery fire. Ludendorff created "new" divisions by combing-out troops at depots and by removing regiments from existing divisions, of which the 212th, 213th and 214th divisions replaced exhausted divisions opposite the French Tenth and Sixth armies.
On the German right flank the XXVI Reserve Corps took over the Combles area on 3 September, with the 52nd Reserve Division on the right, the 51st Reserve Division held Morval with the Reserve Infantry Regiment 236 and the ground further south with Reserve Infantry Regiment 235. Reserve Infantry Regiment 234 held the village but losses had reduced the front line strength of the division to with a few machine-guns. Allied bombardments had destroyed trenches, dug outs, barbed wire and communications links and to avoid observation by aircraft the German troops had dispersed among shell-holes. During the day, Allied artillery directed by the crews of artillery-observation aircraft overwhelmed the artillery batteries and guns in the area. There were no rear defence lines and the transport of supplies to the front line could only take place at night. The divisional commander Wilhem Balck, stressed that the defenders should co-operate closely with flanking units and the artillery and use hasty counter-attacks to recover lost ground and requested frequent reports delivered by all means possible. A new trench line was dug on a reverse slope east of Frégicourt and Rancourt, connecting Morval with the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and covering Sailly-Saillisel and from the wood south-east to Tortille river at Allaines.
The cessation of German attacks at Verdun, ordered by the new supreme command of Chief of the General Staff, Field Marshal von Hindenburg and General Erich Ludendorff, when they superseded Falkenhayn and the reinforcement of the Somme front, reduced the German inferiority in guns and aircraft on the Somme during September. Field artillery reduced its barrage frontage from per battery and increased its accuracy by using one air artillery flight per division, using the aircraft reinforcements from the Verdun front. Colonel Fritz von Loßberg, Chief of Staff of the 2nd Army, was also able to establish (relief divisions) behind the battlefield, ready to replace front divisions. Loßberg established new positions based on depth, dispersal and camouflage, rather than continuous lines of trenches. Rigid defence of the front-line continued but with as few soldiers as possible, relying on the firepower of machine-guns firing from behind the front-line and from the flanks. Artillery reduced its counter-battery fire and area bombardments before Anglo-French attacks and used the reinforcements from Verdun for destructive fire, observed from balloons and aircraft.
The area behind the front-line was defended by support and reserve units dispersed on reverse slopes, in undulations and in any cover that could be found, so that they could open machine-gun fire by surprise, from unseen positions and then counter-attack swiftly, before the Anglo-French infantry could consolidate captured ground. Local, corps and army reserves were held back, in lines about apart, to make progressively stronger counter-attacks. Before an attack the garrison tried to move forwards into shell-holes, to avoid Allied artillery-fire and surprise attacking infantry with machine-gun fire. Opposite the French the Germans dug new defences on a reverse slope between the Tortille stream at Allaines to the west end of St Pierre Vaast Wood and from there to Morval, connected to a new fourth position from Sailly Saillissel to Morval and along the Péronne–Bapaume road. After the Anglo-French attacks in mid-September a "wholesale relief" of the front-line divisions had been possible. The largest German counter-attacks of the Somme battle took place from from the Somme north to St Pierre Vaast Wood and were "destroyed" by French artillery fire. Ludendorff created "new" divisions by combing-out troops at depots and by removing regiments from existing divisions, of which the 212th, 213th and 214th divisions replaced exhausted divisions opposite the French Tenth and Sixth armies.
Battle
25 September
 During the night of the British-French bombardment increased and at on 25 September a hurricane bombardment began as the infantry attacked. The French Sixth Army attacked with seven divisions but the I Corps divisions next to the British Fourth Army involved in the attack on Combles, were held up for most of the day by German machine-gun fire on the left flank south-east of the village. The French reached the Maurepas–Frégicourt road in the centre and on the right flank of I Corps, the 42nd Division of XXXII Corps forced back the 213th Division, closed up to Frégicourt and captured Rancourt in the afternoon; further south the French attacks were repulsed by massed artillery and machine-gun fire.
Anglo-French attacks had been expected by the defenders on 23 September and the timing of the attack for the afternoon of 25 September achieved a measure of surprise. The 51st and 52nd Reserve divisions were quickly pushed back, Reserve Infantry Regiment 239 was broken through and the III Battalion surrounded. Part of Reserve Infantry Regiment 236 was destroyed at the tram line north of Bouleaux Wood, which left Reserve Infantry Regiment 235 west of Combles and Reserve Infantry Regiment 234 in the village, vulnerable to encirclement by the British from the north and the French in the south.
The 56th Division next to the French I Corps, attacked on the front of the 168th Brigade, seven minutes after zero hour, to give time for the 5th Division battalions of the 95th and 15th brigades on the left to draw level. The 1/4th London and the London Scottish advanced behind a creeping barrage fired by batteries in Angle Wood Valley in enfilade towards Bouleaux Wood, which was particularly accurate. The 1/4th London and the London Scottish began to advance steadily at with C Company leading in two waves fifty paces apart, followed by D Company in similar formation. B Company was to conform to the advance and protect the Brigade right flank, against a German riposte from the southern half of Bouleaux Wood. A Company was held in reserve to move forward to the vacant trenches of the assaulting companies. The 1/4th London reached its objectives in the northern fringe of the wood with little opposition and few casualties, killing a large number of Germans in shell hole positions on the western edge. German troops ran back over the open hillside near Combles, only to be shot down from the left flank, by Lewis gunners of the London Scottish. Consolidation of strong points began but was hampered by sniper fire, from farther south in the wood, which continued through the night, as the 167th Brigade on the right flank had not advanced all the way through the wood.
During the night of the British-French bombardment increased and at on 25 September a hurricane bombardment began as the infantry attacked. The French Sixth Army attacked with seven divisions but the I Corps divisions next to the British Fourth Army involved in the attack on Combles, were held up for most of the day by German machine-gun fire on the left flank south-east of the village. The French reached the Maurepas–Frégicourt road in the centre and on the right flank of I Corps, the 42nd Division of XXXII Corps forced back the 213th Division, closed up to Frégicourt and captured Rancourt in the afternoon; further south the French attacks were repulsed by massed artillery and machine-gun fire.
Anglo-French attacks had been expected by the defenders on 23 September and the timing of the attack for the afternoon of 25 September achieved a measure of surprise. The 51st and 52nd Reserve divisions were quickly pushed back, Reserve Infantry Regiment 239 was broken through and the III Battalion surrounded. Part of Reserve Infantry Regiment 236 was destroyed at the tram line north of Bouleaux Wood, which left Reserve Infantry Regiment 235 west of Combles and Reserve Infantry Regiment 234 in the village, vulnerable to encirclement by the British from the north and the French in the south.
The 56th Division next to the French I Corps, attacked on the front of the 168th Brigade, seven minutes after zero hour, to give time for the 5th Division battalions of the 95th and 15th brigades on the left to draw level. The 1/4th London and the London Scottish advanced behind a creeping barrage fired by batteries in Angle Wood Valley in enfilade towards Bouleaux Wood, which was particularly accurate. The 1/4th London and the London Scottish began to advance steadily at with C Company leading in two waves fifty paces apart, followed by D Company in similar formation. B Company was to conform to the advance and protect the Brigade right flank, against a German riposte from the southern half of Bouleaux Wood. A Company was held in reserve to move forward to the vacant trenches of the assaulting companies. The 1/4th London reached its objectives in the northern fringe of the wood with little opposition and few casualties, killing a large number of Germans in shell hole positions on the western edge. German troops ran back over the open hillside near Combles, only to be shot down from the left flank, by Lewis gunners of the London Scottish. Consolidation of strong points began but was hampered by sniper fire, from farther south in the wood, which continued through the night, as the 167th Brigade on the right flank had not advanced all the way through the wood.
 North of the 56th Division, the 95th Brigade of the 5th Division was delayed by enfilade machine-gun fire from the embankment north of the tram line in the 56th Division area and a strong point on the Ginchy–Morval road, until bombed from the north. The 95th Brigade then resumed its advance up the far slope and rushed the German trench running south from Morval, as the 15th Brigade overran the trench further north, just short of the village, taking many more prisoners. After another halt to reorganise, the village was occupied by the 15th Brigade at . The final objective from the windmill south to the 56th Division area was consolidated by nightfall. Several weak German counter-attacks were defeated and the 95th Brigade began working its way south towards the French at Frégicourt.
The London Scottish captured a trench from the wood to the light railway and were then engaged by German troops in the railway embankment, until the position was rushed by the 5th Division from the north and the London Scottish arrived to join in the mopping-up of the survivors in dugouts. By the area had been cleared and taken from Reserve Infantry Regiment 236. The London Scottish pressed on and captured another trench, which had only been discovered on air reconnaissance photographs the day before and from which was an excellent view over the Combles–Morval valley. No sign was yet seen of French troops moving north from the area of Frégicourt, who were to join with British troops at the crossroads east of Morval and patrols further forward were limited by the British protective barrage. By the XIV Corps divisions had overrun the last of the German defensive lines on a frontage of and artillery observers reported that German field artillery batteries and parties of German soldiers were retreating eastwards, from the area either side of Morval as the 5th Division occupied a spur east of the village. Reports from contact patrol aircraft reached the Fourth Army headquarters by giving the approximate position of the attacking troops and after thirty minutes Cavan contradicted French claims to have captured Frégicourt.
North of the 56th Division, the 95th Brigade of the 5th Division was delayed by enfilade machine-gun fire from the embankment north of the tram line in the 56th Division area and a strong point on the Ginchy–Morval road, until bombed from the north. The 95th Brigade then resumed its advance up the far slope and rushed the German trench running south from Morval, as the 15th Brigade overran the trench further north, just short of the village, taking many more prisoners. After another halt to reorganise, the village was occupied by the 15th Brigade at . The final objective from the windmill south to the 56th Division area was consolidated by nightfall. Several weak German counter-attacks were defeated and the 95th Brigade began working its way south towards the French at Frégicourt.
The London Scottish captured a trench from the wood to the light railway and were then engaged by German troops in the railway embankment, until the position was rushed by the 5th Division from the north and the London Scottish arrived to join in the mopping-up of the survivors in dugouts. By the area had been cleared and taken from Reserve Infantry Regiment 236. The London Scottish pressed on and captured another trench, which had only been discovered on air reconnaissance photographs the day before and from which was an excellent view over the Combles–Morval valley. No sign was yet seen of French troops moving north from the area of Frégicourt, who were to join with British troops at the crossroads east of Morval and patrols further forward were limited by the British protective barrage. By the XIV Corps divisions had overrun the last of the German defensive lines on a frontage of and artillery observers reported that German field artillery batteries and parties of German soldiers were retreating eastwards, from the area either side of Morval as the 5th Division occupied a spur east of the village. Reports from contact patrol aircraft reached the Fourth Army headquarters by giving the approximate position of the attacking troops and after thirty minutes Cavan contradicted French claims to have captured Frégicourt.
 The 1/1st London skirmished with the German garrison in the wood around a derelict tank and further to the right the 1/5th London (Rifle Brigade) and the 1/9th London (Queen Victoria's Rifles) kept the German troops in the sunken road to Combes and Combles Trench pinned down. Two tanks attached to the 56th Division, remained at an assembly point in a dip west of Leuze Wood and the three allotted to the 5th Division followed up the advance but two bogged down and the third was sent back from Morval. By midnight the 168th Brigade had established observation posts with an excellent view over the northern exits of Combles and the brigade was directed to work round the north side of Combles and cut off the route to Morval. The 167th Brigade had advanced past the derelict tank and entered the wood and all the sunken road and Combles Trench had been captured by the 169th Brigade.
At a party from the London Scottish began to probe south along the light railway towards Combles and by dawn was within . At the Rifle Brigade entered Combles and met French troops and as dawn broke the 56th Division began to consolidate a new line east of Combles, with the Germans beyond in Mutton Trench. A further attack was planned with tank support then cancelled when the tanks failed to appear. A narrow gap remained through which the German garrison could escape and for the rest of the night, the 56th Division artillery fired a barrage at the exit to catch the fleeing troops. The German garrison began to withdraw from the village at and by most of the troops had escaped and improvised a new line west of Sailly.
The 1/1st London skirmished with the German garrison in the wood around a derelict tank and further to the right the 1/5th London (Rifle Brigade) and the 1/9th London (Queen Victoria's Rifles) kept the German troops in the sunken road to Combes and Combles Trench pinned down. Two tanks attached to the 56th Division, remained at an assembly point in a dip west of Leuze Wood and the three allotted to the 5th Division followed up the advance but two bogged down and the third was sent back from Morval. By midnight the 168th Brigade had established observation posts with an excellent view over the northern exits of Combles and the brigade was directed to work round the north side of Combles and cut off the route to Morval. The 167th Brigade had advanced past the derelict tank and entered the wood and all the sunken road and Combles Trench had been captured by the 169th Brigade.
At a party from the London Scottish began to probe south along the light railway towards Combles and by dawn was within . At the Rifle Brigade entered Combles and met French troops and as dawn broke the 56th Division began to consolidate a new line east of Combles, with the Germans beyond in Mutton Trench. A further attack was planned with tank support then cancelled when the tanks failed to appear. A narrow gap remained through which the German garrison could escape and for the rest of the night, the 56th Division artillery fired a barrage at the exit to catch the fleeing troops. The German garrison began to withdraw from the village at and by most of the troops had escaped and improvised a new line west of Sailly.
Air operations
 25 September dawned bright and cloudless, with a ground haze but reports from contact patrol observers were notably accurate, as the infantry advanced to their objectives on the Fourth Army front, from Morval to Gueudecourt and around Flers. Ground at the south-east edge of Morval was captured in the evening, completing the occupation of the ground on the main ridge and making Combles untenable, although British balloon observers could see that the French advance from the south had been delayed at Frégicourt. After a captured German officer disclosed that Combles was to be evacuated during the night, British artillery bombarded the valley to the east of the village. In the early hours of the morning, British troops entered the north end of Combles as French troops advanced from the south. The position of the ground forces was reported at noon by a reconnaissance crew, who returned at to observe the position of the new line but at were hit by an anti-aircraft shell and blown up.
A French aviator flying above Combles reported that
25 September dawned bright and cloudless, with a ground haze but reports from contact patrol observers were notably accurate, as the infantry advanced to their objectives on the Fourth Army front, from Morval to Gueudecourt and around Flers. Ground at the south-east edge of Morval was captured in the evening, completing the occupation of the ground on the main ridge and making Combles untenable, although British balloon observers could see that the French advance from the south had been delayed at Frégicourt. After a captured German officer disclosed that Combles was to be evacuated during the night, British artillery bombarded the valley to the east of the village. In the early hours of the morning, British troops entered the north end of Combles as French troops advanced from the south. The position of the ground forces was reported at noon by a reconnaissance crew, who returned at to observe the position of the new line but at were hit by an anti-aircraft shell and blown up.
A French aviator flying above Combles reported that
26 September
The French 110th Infantry Regiment entered Combles from the south and by dawn had fought through the south-east part of the village and taken The 73rd Infantry Regiment attacked from the south-west and met groups of British infantry. German infantry retreating between the village and Frégicourt were routed and engaged by machine-gun fire as they fled to Haïe Wood. At red rockets followed by one green rocket had been seen rising from the German positions west and north-west of the village, which was taken to be a signal for the German retirement and by the 1/1st London patrols had reached the Orchard unopposed. One party pushed on into the village and linked with French troops. In the 169th Brigade area to the south, the London Rifle Brigade had advanced down Combles Trench and met French troops south of Morval near the sunken road and the 167th Brigade linked with the 5th Division south of Morval. The 1/1st London had advanced along the Ginchy road and took prisoners from Reserve Infantry regiments 234 and 235; at the London Scottish had made contact with French patrols at the light railway near the north-east exit of the village. A document showed that the headquarters of I Battalion, Reserve Infantry Regiment 234 had left the village at the night previous and some German troops retreating northwards towards Morval had been seen and shot down by the London Scottish. The 56th Division troops digging-in about beyond Combles and Morval linked with the French who had captured Frégicourt just before dawn and advanced north. A French attack on the German defences from Haïe Wood to St Pierre Vaast Wood was planned for the afternoon and the 168th Brigade was ordered to attack down the German third position (Mutton Trench) between Frégicourt and Morval. Reconnaissance by aircraft discovered that German troops occupied the trench and the 1/12th London (The Rangers) of the 168th Brigade was ordered to advance behind two tanks. Both tanks ditched on the approach and the attack was postponed and eventually cancelled. The French attack began at and managed to advance on the flanks but was stopped in the centre by German machine-gun fire. The 5th Division advanced a short distance down Mutton Trench and took part of thunder Trench east of Morval and was then held up by German machine-gun fire from Sailly-Saillisel. During the afternoon the French Sixth Army and British Fourth Army staffs met to arrange a northward adjustment of the inter-army boundary, to the edge of Lesbœufs eastwards to the south of Le Transloy on the Péronne–Bapaume road. Behind the front line the new boundary was set through Guillemont and the Guillemont–Maricourt road.Aftermath
Analysis
 German reinforcements had arrived on the Somme front during September and conducted the big counter-attacks on both sides of the Somme from to regain the ground lost since 12 September. The attacks were costly failures and Ludendorff called the fighting of the biggest engagement of the battle. Much German equipment was captured in Combles, including two million rounds of ammunition, shells and many hand-grenades. The battle of Morval had been a considerable Anglo-French victory. The objective was one German trench system, the original third line, which was less well-developed than the German defences on 15 September and was subjected to greater weight of shellfire. Rainfall from and the tempo of attacks had made it difficult for the Germans to improve their defences before the attack. French attacks in the south beyond Combles had less success, being confronted by a much larger amount of shell-fire. The 5th Division was relieved on the night of 26 September by the 20th Division, which was replaced by French troops after twenty-four hours, during the army boundary changes.
German reinforcements had arrived on the Somme front during September and conducted the big counter-attacks on both sides of the Somme from to regain the ground lost since 12 September. The attacks were costly failures and Ludendorff called the fighting of the biggest engagement of the battle. Much German equipment was captured in Combles, including two million rounds of ammunition, shells and many hand-grenades. The battle of Morval had been a considerable Anglo-French victory. The objective was one German trench system, the original third line, which was less well-developed than the German defences on 15 September and was subjected to greater weight of shellfire. Rainfall from and the tempo of attacks had made it difficult for the Germans to improve their defences before the attack. French attacks in the south beyond Combles had less success, being confronted by a much larger amount of shell-fire. The 5th Division was relieved on the night of 26 September by the 20th Division, which was replaced by French troops after twenty-four hours, during the army boundary changes.
Casualties
The 5th Division suffered from and the 56th Division suffered in September. New Zealand Division suffered from October. The German 1st and 2nd armies suffered in September, which was their most costly month of the battle. Post war commentary in the German Official History and by Crown Prince Rupprecht, dwelt on the loss of so many of the German army's remaining peace-trained officers, non-commissioned officers and infantry, particularly by an increased willingness to surrender.Subsequent operations
 During the evening of 26 September, the 1/4th London was relieved in Bouleaux Wood by the 1/13th London (The Kensingtons) and withdrew to Bully and Beef trenches. During 27 September, trenches held by the 1/4th London were bombarded but there was no German counter-attack. In the evening the 168th Brigade handed over to the 2nd French Division and the 1/4th London, without relief in Bully and Beef trenches, withdrew to Casement Trench. The casualties of the 1/4th London were and rest of the 56th Division was relieved by the 20th and 6th divisions, as the inter-army boundary was moved north during 27 September. I Corps advanced a short distance against the 213th Division, east of the Frégicourt–Le Transloy road. A new attack from towards the German defences between Haïe Wood and St Pierre Vaast Wood, was delayed. Mutton Trench on the left flank was attacked at by the British; the French attack managed to advance on the flanks but was held up in the centre around Sailly.
During the evening of 26 September, the 1/4th London was relieved in Bouleaux Wood by the 1/13th London (The Kensingtons) and withdrew to Bully and Beef trenches. During 27 September, trenches held by the 1/4th London were bombarded but there was no German counter-attack. In the evening the 168th Brigade handed over to the 2nd French Division and the 1/4th London, without relief in Bully and Beef trenches, withdrew to Casement Trench. The casualties of the 1/4th London were and rest of the 56th Division was relieved by the 20th and 6th divisions, as the inter-army boundary was moved north during 27 September. I Corps advanced a short distance against the 213th Division, east of the Frégicourt–Le Transloy road. A new attack from towards the German defences between Haïe Wood and St Pierre Vaast Wood, was delayed. Mutton Trench on the left flank was attacked at by the British; the French attack managed to advance on the flanks but was held up in the centre around Sailly.
1918
Combles was recaptured by German troops on 24 March 1918, during the retreat of the 9th Division duringOperation Michael
Operation Michael was a major German military offensive during the First World War that began the German Spring Offensive on 21 March 1918. It was launched from the Hindenburg Line, in the vicinity of Saint-Quentin, France. Its goal was t ...
, the German spring offensive. The village was recaptured for the last time on by the 18th Division, during the Second Battle of Bapaume
The Second Battle of Bapaume was a battle of the First World War that took place at Bapaume in France, from 21 August 1918 to 3 September 1918. It was a continuation of the Battle of Albert and is also referred to as the second phase of that ba ...
.
Commemoration
Combles Communal Cemetery was begun by French troops in 1916, on the north-east side of the village and lies between the Frégicourt and Le Transloy roads. An Extension to the north-east was built for interments from the Frégicourt Communal Cemetery, Leuze Wood Cemetery, Longtree Dump Military Cemetery and Maurepas Military Cemetery, which were moved after the war.Notes
Footnotes
References
Books * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Theses *Further reading
* * *External links
La prise de Combles, 26 Septembre 1916 (in French with photographs)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Combles, Capture of Conflicts in 1916 1916 in France Battle of the Somme Battles of the Western Front (World War I) Battles of World War I involving France Battles of World War I involving Germany Battles of World War I involving the United Kingdom September 1916 events