Capetian House of Anjou on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Capetian House of Anjou or House of Anjou-Sicily, was a royal house and
 A younger son of
A younger son of  Charles had fully solidified his rule over Durazzo by 1272, creating a small Kingdom of Albania for himself, out of previously Despotate of Epirus territory; he was well received by local chiefs.
Charles had fully solidified his rule over Durazzo by 1272, creating a small Kingdom of Albania for himself, out of previously Despotate of Epirus territory; he was well received by local chiefs.
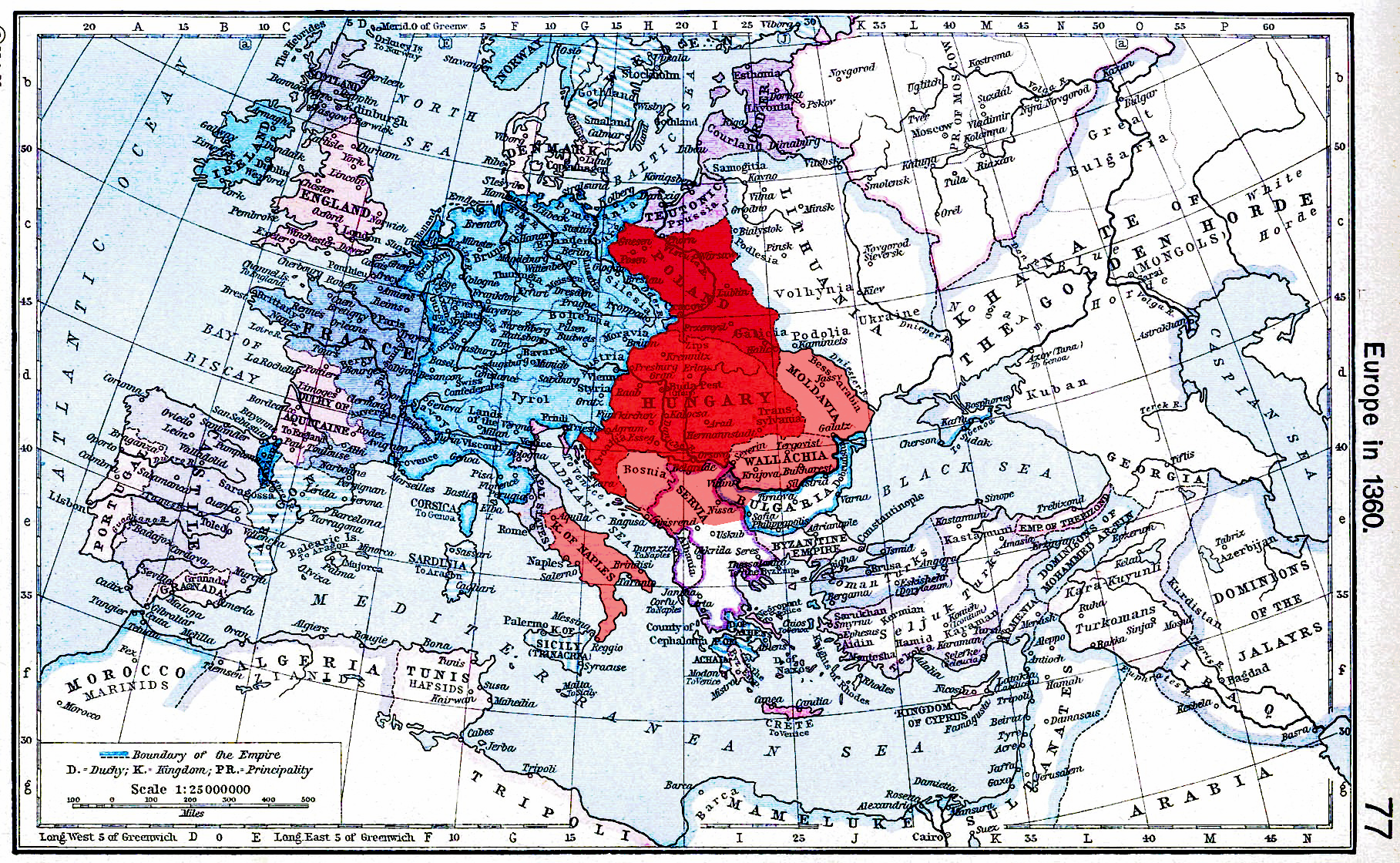 Charles was driven out of Sicily in 1282, but his successors ruled Naples until 1435.
Charles was driven out of Sicily in 1282, but his successors ruled Naples until 1435.
cadet branch
In history and heraldry, a cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets— realm, tit ...
of the direct French House of Capet
The House of Capet (french: Maison capétienne) or the Direct Capetians (''Capétiens directs''), also called the House of France (''la maison de France''), or simply the Capets, ruled the Kingdom of France from 987 to 1328. It was the most ...
, part of the Capetian dynasty. It is one of three separate royal houses referred to as ''Angevin'', meaning "from Anjou" in France. Founded by Charles I of Anjou, the youngest son of Louis VIII of France
Louis VIII (5 September 1187 – 8 November 1226), nicknamed The Lion (french: Le Lion), was King of France from 1223 to 1226. As prince, he invaded England on 21 May 1216 and was excommunicated by a papal legate on 29 May 1216. On 2 June 1216 ...
, the Capetian king first ruled the Kingdom of Sicily during the 13th century. Later the War of the Sicilian Vespers
The War of the Sicilian Vespers or just War of the Vespers was a conflict that started with the insurrection of the Sicilian Vespers against Charles of Anjou in 1282 and ended in 1302 with the Peace of Caltabellotta. It was fought in Sicily, C ...
forced him out of the island of Sicily, leaving him with the southern half of the Italian Peninsula — the Kingdom of Naples. The house and its various branches would go on to influence much of the history of Southern and Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, until becoming defunct in 1435.
Historically, the House ruled the counties of Anjou Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
* County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
**Duk ...
, Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
, Touraine
Touraine (; ) is one of the traditional provinces of France. Its capital was Tours. During the political reorganization of French territory in 1790, Touraine was divided between the departments of Indre-et-Loire, :Loir-et-Cher, Indre and Vien ...
, Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bor ...
and Forcalquier
Forcalquier (; oc, Forcauquier, ) is a commune in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in southeastern France.
Forcalquier is located between the Lure and Luberon mountain ranges, about south of Sisteron and west of the Durance river. D ...
, the principalities of Achaea and Taranto
Taranto (, also ; ; nap, label= Tarantino, Tarde; Latin: Tarentum; Old Italian: ''Tarento''; Ancient Greek: Τάρᾱς) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Taranto, serving as an important com ...
, and the kingdoms of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
, Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
, and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
.
Rise of Charles I and his sons
 A younger son of
A younger son of House of Capet
The House of Capet (french: Maison capétienne) or the Direct Capetians (''Capétiens directs''), also called the House of France (''la maison de France''), or simply the Capets, ruled the Kingdom of France from 987 to 1328. It was the most ...
king Louis VIII of France
Louis VIII (5 September 1187 – 8 November 1226), nicknamed The Lion (french: Le Lion), was King of France from 1223 to 1226. As prince, he invaded England on 21 May 1216 and was excommunicated by a papal legate on 29 May 1216. On 2 June 1216 ...
''the Lion'', Charles was first given a noble title by his brother Louis IX of France who succeeded to the French throne in 1226. Charles was named Count of Anjou
The Count of Anjou was the ruler of the County of Anjou, first granted by Charles the Bald in the 9th century to Robert the Strong. Ingelger and his son, Fulk the Red, were viscounts until Fulk assumed the title of Count of Anjou. The Robertians ...
and Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
; the feudal County of Anjou was a western vassal state of the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period ...
, which the Capetians had wrested from the House of Plantagenet only a few decades earlier. Charles married the heiress of the County of Provence
The land of Provence has a history quite separate from that of any of the larger nations of Europe. Its independent existence has its origins in the frontier nature of the dukedom in Merovingian Gaul. In this position, influenced and affected by ...
named Beatrice of Provence, she was a member of the House of Barcelona
The House of Barcelona was a medieval dynasty that ruled the County of Barcelona continuously from 878 and the Crown of Aragon from 1137 (as kings from 1162) until 1410. They descend from the Bellonids, the descendants of Wifred the Hairy. Th ...
; this meant Charles' holdings were growing as Count of Provence
The land of Provence has a history quite separate from that of any of the larger nations of Europe. Its independent existence has its origins in the frontier nature of the dukedom in Merovingian Gaul. In this position, influenced and affected by ...
. After fighting in the Seventh Crusade, Charles was offered by Pope Clement IV
Pope Clement IV ( la, Clemens IV; 23 November 1190 – 29 November 1268), born Gui Foucois ( la, Guido Falcodius; french: Guy de Foulques or ') and also known as Guy le Gros (French for "Guy the Fat"; it, Guido il Grosso), was bishop of Le Pu ...
the Kingdom of Sicily — which at the time included not only the island of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
but also the southern half of the Italian Peninsula. The reason for Charles being offered the kingdom was because of a conflict between the Papacy and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, the latter of whom were represented by the ruling House of Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynast ...
.
It was at the Battle of Benevento
The Battle of Benevento was a major medieval battle fought on 26 February 1266, near Benevento in present-day Southern Italy, between the forces of Charles I of Anjou and those of King Manfred of Sicily. Manfred's defeat and death resulted in Ch ...
that the ''Guelph
Guelph ( ; 2021 Canadian Census population 143,740) is a city in Southwestern Ontario, Canada. Known as "The Royal City", Guelph is roughly east of Kitchener and west of Downtown Toronto, at the intersection of Highway 6, Highway 7 and Wel ...
'' Capetians gained the Sicilian kingdom from the ''Ghibelline'' Swabians, this was cemented after victory at Tagliacozzo
Tagliacozzo ( Marsicano: ') is a town and ''comune'' in the province of L'Aquila, Abruzzo, central Italy.
History
Tagliacozzo lies in an area inhabited in early historic times by the Aequi and the Marsi, although the first mentions of the town ...
. In keeping with the political landscape of the period, Charles is described by scholars as shrewd, energetic and highly ambitious. He signed the Treaty of Viterbo
The Treaty of Viterbo (or the Treaties of Viterbo) was a pair of agreements made by Charles I of Sicily with Baldwin II of Constantinople and William II Villehardouin, Prince of Achaea, on 24 and 27 May 1267, which transferred much of the rights to ...
in 1267 with Baldwin II of Courtenay and William II of Villehardouin
William of Villehardouin (french: Guillaume de Villehardouin; Kalamata, 1211 – 1 May 1278) was the fourth prince of Achaea in Frankish Greece, from 1246 to 1278. The younger son of Prince Geoffrey I, he held the Barony of Kalamat ...
, the political alliance gave many of the rights of the Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzant ...
to Charles and a marriage alliance for his daughter Beatrice of Sicily.Hazzard, '' The Fourteenth and Fifteenth Centuries'', 35. The Byzantines had taken back the city of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
in 1261 and this was a plan to take it back from Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( el, Μιχαὴλ Δούκας Ἄγγελος Κομνηνὸς Παλαιολόγος, Mikhaēl Doukas Angelos Komnēnos Palaiologos; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as the co-emperor of the Empire ...
. It also recognised Charles' possession of Corfu and cities in the Balkans such as Durazzo, as well as giving him suzerainty over the Principality of Achaea
The Principality of Achaea () or Principality of Morea was one of the three vassal states of the Latin Empire, which replaced the Byzantine Empire after the capture of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade. It became a vassal of the Kingdom ...
and sovereignty of the Aegean islands aside from those already held by the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
. For a while Charles was preoccupied helping his French brother in the unsuccessful Eighth Crusade
The Eighth Crusade was the second Crusade launched by Louis IX of France, this one against the Hafsid dynasty in Tunisia in 1270. It is also known as the Crusade of Louis IX against Tunis or the Second Crusade of Louis. The Crusade did not see any ...
on Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
. After this he once again focused on Constantinople, but his fleet was wrecked in a freak storm off the coast of Trapani
Trapani ( , ; scn, Tràpani ; lat, Drepanum; grc, Δρέπανον) is a city and municipality (''comune'') on the west coast of Sicily, in Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Trapani. Founded by Elymians, the city is still an imp ...
.Hazzard, '' The Fourteenth and Fifteenth Centuries'', 37. With the elevation of Pope Gregory X
Pope Gregory X ( la, Gregorius X; – 10 January 1276), born Teobaldo Visconti, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1 September 1271 to his death and was a member of the Secular Franciscan Order. He was ...
, there was a truce between Charles and Michael in the form of the Council of Lyons, as Christians focused on improving ecumenical relations, with hopes of regaining the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establish ...
back from the Muslims.
 Charles had fully solidified his rule over Durazzo by 1272, creating a small Kingdom of Albania for himself, out of previously Despotate of Epirus territory; he was well received by local chiefs.
Charles had fully solidified his rule over Durazzo by 1272, creating a small Kingdom of Albania for himself, out of previously Despotate of Epirus territory; he was well received by local chiefs.
 Charles was driven out of Sicily in 1282, but his successors ruled Naples until 1435.
Charles was driven out of Sicily in 1282, but his successors ruled Naples until 1435.
Charles II and division of the inheritance
This House of Anjou included the branches of Anjou-Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
, which ruled Hungary (1308–1385, 1386–1395) and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
(1370–1399), Anjou-Taranto
Taranto (, also ; ; nap, label= Tarantino, Tarde; Latin: Tarentum; Old Italian: ''Tarento''; Ancient Greek: Τάρᾱς) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Taranto, serving as an important com ...
, which ruled the remnants of the Latin Empire (1313–1374) and Anjou-Durazzo, which ruled Naples (1382–1435) and Hungary (1385–1386).
The senior line of the House of Anjou-Durazzo became extinct in the male line with the death of King Ladislaus of Naples in 1414, and totally extinct with the death of his sister Joanna II in 1435.
Branching out
Hungary
During the Middle Ages, there were several marriages between theÁrpád dynasty
The Árpád dynasty, consisted of the members of the royal House of Árpád (), also known as Árpáds ( hu, Árpádok, hr, Arpadovići). They were the ruling dynasty of the Principality of Hungary in the 9th and 10th centuries and of the King ...
and the House of Capet
The House of Capet (french: Maison capétienne) or the Direct Capetians (''Capétiens directs''), also called the House of France (''la maison de France''), or simply the Capets, ruled the Kingdom of France from 987 to 1328. It was the most ...
. Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, founder of the House of Anjou-Sicily, with his first wife, Beatrice of Provence fathered his eldest son, Charles II of Naples. (Their youngest daughter, Elizabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
was given in marriage to the future Ladislaus IV of Hungary
Ladislaus IV ( hu, IV. (Kun) László, hr, Ladislav IV. Kumanac, sk, Ladislav IV. Kumánsky; 5 August 1262 – 10 July 1290), also known as Ladislaus the Cuman, was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1272 to 1290. His mother, Elizabeth, wa ...
in 1269, but Ladislaus preferred his mistresses to her, and the marriage remained childless). In 1270, Charles II married Mary of Hungary
Mary, also known as Maria of Anjou (, , ; 137117 May 1395), reigned as Queen of Hungary and Croatia (officially 'king') between 1382 and 1385, and from 1386 until her death. She was the daughter of Louis the Great, King of Hungary and Poland ...
, daughter of Stephen V of Hungary
Stephen V ( hu, V. István, hr, Stjepan V., sk, Štefan V; before 18 October 1239 – 6 August 1272, Csepel Island) was King of Hungary and Croatia between 1270 and 1272, and Duke of Styria from 1258 to 1260. He was the oldest son of ...
and Elizabeth the Cuman
Elizabeth the Cuman (1244–1290) was the Queen consort of Stephen V of Hungary. She was regent of Hungary during the minority of her son from 1272 to 1277.
The Cumans were the western tribes of the Cuman-Kipchak confederation.
Her people follo ...
. They had fourteen children which provided the House of Anjou-Sicily with a secure position in Naples.
The childless Ladislaus IV of Hungary (1262–1290), was succeeded by Andrew III as King of Hungary. He was the son of Stephen the Posthumous, considered by Stephen's much older half-brothers (Béla IV of Hungary, Coloman of Halych, Andrew II of Halych) a bastard son of infidelity. For this reason, after the death of Ladislaus IV. some of the Árpád dynasty's cognates sought the family as extinct. In Naples, Charles Martel of Anjou
Charles Martel ( hu, Martell Károly; 8 September 1271 – 12 August 1295) of the Angevin dynasty was the eldest son of king Charles II of Naples and Mary of Hungary, the daughter of King Stephen V of Hungary.
__NOTOC__
The 18-year-old Charles Ma ...
, the eldest son of Mary of Hungary announced his claim to the Hungarian crown, backed by his mother, and the pope. He started to style himself king of Hungary, but he never managed to gain enough support from the Hungarian magnates to realize his claim.
With Andrew III's childless death (1301), the "last golden branch" of the tree of King Saint Stephen's family ended. The Hungarian diet was determined to keep the blood of Saint Stephen
Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ''Stéphanos'', meaning "wreath, crown" and by extension "reward, honor, renown, fame", often given as a title rather than as a name; c. 5 – c. 34 AD) is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first ...
(first king of Hungary) on the throne in the maternal line at least. In the upcoming years, a civil war followed between various claimants to the throne. After the short period of rule of Wenceslaus of Bohemia (1301–1305), and Otto of Bavaria (1305–1307) the civil war ended with Charles Robert's (1308–1342) victory, the son of Charles Martel of Anjou, but he was forced to continue fighting against the powerful Hungarian lords up to the early 1320s.
I. Charles I of Anjou 1226/7–1285 king of Sicily(-Naples) = Beatrice of Provence
:II. Blanche (died 1269) = Robert
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honou ...
lord of Béthune
:II. Beatrice 1252–1275 = Philip titular Latin Emperor of Constantinople
:II. Elisabeth 1261–1303 = Ladislaus IV of Hungary
Ladislaus IV ( hu, IV. (Kun) László, hr, Ladislav IV. Kumanac, sk, Ladislav IV. Kumánsky; 5 August 1262 – 10 July 1290), also known as Ladislaus the Cuman, was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1272 to 1290. His mother, Elizabeth, wa ...
:II. Charles II of Naples the Lame 1254–1309 = Mary of Hungary
Mary, also known as Maria of Anjou (, , ; 137117 May 1395), reigned as Queen of Hungary and Croatia (officially 'king') between 1382 and 1385, and from 1386 until her death. She was the daughter of Louis the Great, King of Hungary and Poland ...
::III. Charles Martel
Charles Martel ( – 22 October 741) was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish statesm ...
(1271–1295), titular King of Hungary = Clemence of Austria
Clemence of Austria (1262 – February 1293, or 1295) was a daughter of King Rudolph I of Germany and Gertrude of Hohenberg. She was a member of the House of Habsburg.
Marriage
On 8 January 1281, Clemence married Charles Martel of Anjou.
Clemenc ...
:::IV. Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
(1288–1342), King of Hungary = 1. Maria of Galicia (?), 2. Mary of Bytom, 3. Beatrice of Luxembourg
Beatrice of Luxembourg ( hu, Luxemburgi Beatrix; 1305 – 11 November 1319), was by birth member of the House of Luxembourg and by marriage Queen of Hungary.
She was the youngest child of Henry VII, Holy Roman Emperor and his wife, Margaret of B ...
, 4. Elisabeth of Poland
Elizabeth of Poland ( hu, Erzsébet, pl, Elżbieta; 1305 – 29 December 1380) was Queen of Hungary by marriage to Charles I of Hungary, and regent of Poland from 1370 to 1376 during the reign of her son Louis I.
Life Early life
She was a memb ...
::::V. (1.) Catherine
Katherine, also spelled Catherine, and other variations are feminine names. They are popular in Christian countries because of their derivation from the name of one of the first Christian saints, Catherine of Alexandria.
In the early Christ ...
(died 1355) = Henry II, Duke of Świdnica
Henry II of Świdnica, ( pl, Henryk II Świdnicki, cs, Jindřich Svídnický, german: Heinrich II. von Schweidnitz; – ), was a Duke of Świdnica from 1326 until his death (with his brother as co-ruler).
He was the second and younger son of Du ...
::::V. (4.) Charles (1321–1321/3)
::::V. (4.) Ladislaus (1324–1329)
::::V. (4.) Louis I of Hungary (1326–1382) = 1. Margaret of Bohemia, 2. Elizabeth of Bosnia
Elizabeth of Bosnia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Elizabeta Kotromanić, Елизабета Котроманић; hu, Kotromanics Erzsébet; pl, Elżbieta Bośniaczka; – January 1387) was queen consort of Hungary and Croatia, as well ...
:::::VI. (2.) Catherine (1370–1378)
:::::VI. (2.) Mary of Hungary
Mary, also known as Maria of Anjou (, , ; 137117 May 1395), reigned as Queen of Hungary and Croatia (officially 'king') between 1382 and 1385, and from 1386 until her death. She was the daughter of Louis the Great, King of Hungary and Poland ...
1371–1395 = Sigismund of Luxembourg
:::::VI. (2.) Jadwiga of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig ( hu, Hedvig), was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Grea ...
1373/4–1399 = Władysław II Jagiełło
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło ()He is known under a number of names: lt, Jogaila Algirdaitis; pl, Władysław II Jagiełło; be, Jahajła (Ягайла). See also: Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło. ...
::::V. (4.) Andrew, Duke of Calabria
Andrew, Duke of Calabria (30 October 1327 – 18 September 1345) was the first husband of Joanna I of Naples, and a son of Charles I of Hungary and brother of Louis I of Hungary.
Background and engagement
Andrew was the second of three survivin ...
(1327–1345) = Joanna I of Naples
Joanna I, also known as Johanna I ( it, Giovanna I; December 1325 – 27 July 1382), was Queen of Naples, and Countess of Provence and Forcalquier from 1343 to 1382; she was also Princess of Achaea from 1373 to 1381.
Joanna was the eldest ...
:::::VI. Charles Martel, Duke of Calabria (1345–1348)
::::V. (4.) Elizabeth (?) (b. 1327/1332) = Boleslaus II of Troppau
::::V. (4.) Stephen
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; ...
(1332–1354) duke of Slavonia = Margaret of Bavaria
Margaret of Bavaria (1363 – 23 January 1424, Dijon) was Duchess of Burgundy by marriage to John the Fearless. She was the regent of the Burgundian Low Countries during the absence of her spouse in 1404–1419 and the regent in French Burgundy ...
:::::VI. Elizabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
1352–1380 = Philip II, Prince of Taranto
Philip II (1329 – 25 November 1373) of the Angevin house, was Prince of Achaea and Taranto, and titular Latin Emperor of Constantinople (as Philip III) from 1364 to his death in 1373.
He was the son of Philip I of Taranto and Catherine ...
, titular Emperor of Constantinople
:::::VI. John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
(1354–1360), duke of Croatia, Dalmatia and Slavonia
::::V. Coloman (1317–1375), Bishop of Győr - illegitimate son with daughter of Gurke Csák
:::IV. Beatrice (1290–1354) = Jean II de La Tour du Pin, Dauphin du Viennois
:::IV. Clementia of Hungary (1293–1328) = Louis X of France
Louis X (4 October 1289 – 5 June 1316), known as the Quarrelsome (french: le Hutin), was King of France from 1314 and King of Navarre as Louis I from 1305 until his death. He emancipated serfs who could buy their freedom and readmitted Jews in ...
::III. Margaret (1273–1299) = Charles of Valois
Charles of Valois (12 March 1270 – 16 December 1325), the fourth son of King Philip III of France and Isabella of Aragon, was a member of the House of Capet and founder of the House of Valois, whose rule over France would start in 1 ...
::III. Saint Louis of Toulouse
Saint Louis of Toulouse (9 February 1274 – 19 August 1297), also known as Louis of Anjou, was a Neapolitan prince of the Capetian House of Anjou and a Catholic bishop.
Life
Louis was born in Brignoles, Provence (or in Italy, at Nocera, whe ...
(1274–1298), Bishop of Toulouse
::III. Robert the Wise
Robert of Anjou ( it, Roberto d'Angiò), known as Robert the Wise ( it, Roberto il Saggio; 1276 – 20 January 1343), was King of Naples, titular King of Jerusalem and Count of Provence and Forcalquier from 1309 to 1343, the central figure of I ...
(1275–1343), King of Naples = 1. Yolanda of Aragon, 2. Sancia of Majorca
:::IV. (1.) Charles (1298–1328), Duke of Calabria, Viceroy of Naples = 1. Catherine of Habsburg (1295–1323), 2. Marie of Valois (1309–1332)
::::V. (2.) Eloisa (1325–1325)
::::V. (2.) Joanna I of Naples
Joanna I, also known as Johanna I ( it, Giovanna I; December 1325 – 27 July 1382), was Queen of Naples, and Countess of Provence and Forcalquier from 1343 to 1382; she was also Princess of Achaea from 1373 to 1381.
Joanna was the eldest ...
(1326–1382) = Andrew, Duke of Calabria
Andrew, Duke of Calabria (30 October 1327 – 18 September 1345) was the first husband of Joanna I of Naples, and a son of Charles I of Hungary and brother of Louis I of Hungary.
Background and engagement
Andrew was the second of three survivin ...
(1327–1345)
::::V. (2.) Charles Martel (1327–1327)
::::V. (2.) Maria of Calabria
Maria of Calabria (6 May 1329 – 20 May 1366), Countess of Alba, was a Neapolitan princess of the Capetian House of Anjou whose descendants inherited the crown of Naples following the death of her older sister, Queen Joanna I.
Life
Early ye ...
(1329–1366) = 1. Charles, Duke of Durazzo 2. Robert of Baux, Count of Avellino 3. Philip II, Prince of Taranto
Philip II (1329 – 25 November 1373) of the Angevin house, was Prince of Achaea and Taranto, and titular Latin Emperor of Constantinople (as Philip III) from 1364 to his death in 1373.
He was the son of Philip I of Taranto and Catherine ...
:::IV. (1.) Louis (1301–1310)
:::IV. (i.) Charles d'Artois c.1300–1346, grand chamberlain for Queen Joanna I - illegitimate with Cantelma Cantelmo
:::IV. (i.) Maria d'Aquino (Boccaccio's Fiammetta) - illegitimate
:::IV. (i.) Helene - illegitimate = Andrea Thopia, Lord of Matija.
::III. Philip I Philip(p) I may refer to:
* Philip I of Macedon (7th century BC)
* Philip I Philadelphus (between 124 and 109 BC–83 or 75 BC)
* Philip the Arab (c. 204–249), Roman Emperor
* Philip I of France (1052–1108)
* Philip I (archbishop of Cologne) (1 ...
1278–1331, Prince of Taranto and Achaea = 1. Thamar Angelina Komnene
Thamar Angelina Komnene ( gr, Θαμάρ Αγγελίνα Κομνηνή; died ) was a princess consort of Taranto by marriage to Prince Philip I.
Life
Thamar was the daughter of Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas of the Despotate of Epirus and his seco ...
2. Catherine of Valois–Courtenay
:::IV. (1.) Charles of Taranto 1296–1315, vicar of Romania
:::IV. (1.) Joan of Anjou 1297–1323 = 1.Oshin of Armenia
Oshin ( hy, Օշին) (1282 – July 20, 1320) was king of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, ruling from 1307 to 1320. He was a member of the Hetoumid-family, the son of Leo II, King of Armenia and Queen Keran.
Oshin became king on the death of ...
2. Oshin of Korikos
:::IV. (1) Margarete 1298–1340 = Walter VI, Count of Brienne titular duke of Athens
:::IV. (1.) Philip, Despot of Romania 1300–1330 = Violante (daughter of James II of Aragon
James II (Catalan: ''Jaume II''; Spanish: ''Jaime II;'' 10 April 1267 – 2 or 5 November 1327), called the Just,, an, Chaime lo Chusto, es, Jaime el Justo. was the King of Aragon and Valencia and Count of Barcelona from 1291 to 1327. He ...
)
:::IV. (1.) Maria 1301/4–1368, abbess in Conversano
:::IV. (1.) Blanche 1309–1337 = Ramon Berenguer infante of Aragon, count of Prades (son of James II of Aragon
James II (Catalan: ''Jaume II''; Spanish: ''Jaime II;'' 10 April 1267 – 2 or 5 November 1327), called the Just,, an, Chaime lo Chusto, es, Jaime el Justo. was the King of Aragon and Valencia and Count of Barcelona from 1291 to 1327. He ...
)
:::IV. (1.) Beatrice = Walter II of Brienne.
:::IV. (2.) Margaret c.1325–1380 = Francis de Baux duke of Adria
:::IV. (2.) Robert, Prince of Taranto 1326–1365, titular Latin emperor of Constantinople
:::IV. (2.) Louis, Prince of Taranto 1327/8–1362, king of Naples as husband of Joanna I of Naples
Joanna I, also known as Johanna I ( it, Giovanna I; December 1325 – 27 July 1382), was Queen of Naples, and Countess of Provence and Forcalquier from 1343 to 1382; she was also Princess of Achaea from 1373 to 1381.
Joanna was the eldest ...
:::IV. (2.) Philip, Prince of Taranto 1329–1374, prince of Achaea, titular Latin emperor of Constantinople = 1. Maria of Calabria
Maria of Calabria (6 May 1329 – 20 May 1366), Countess of Alba, was a Neapolitan princess of the Capetian House of Anjou whose descendants inherited the crown of Naples following the death of her older sister, Queen Joanna I.
Life
Early ye ...
2. Elisabeth of Slavonia
Elizabeth of Slavonia (1352 – before 1380), was the heir presumptive to the Hungarian throne between 1360 and 1370.
Elizabeth was the only daughter of Stephen, Duke of Slavonia, a younger son of the Hungarian king Charles I, and member of the ...
::III. Blanche of Anjou
Blanche of Anjou (1280 – 14 October 1310) was Queen of Aragon as the second spouse of King James II of Aragon. She was a member of the Capetian House of Anjou, she is also known as Blanche of Naples. She served as Regent or "Queen-Lieutenant" o ...
(1280–1310) = James II of Aragon
James II (Catalan: ''Jaume II''; Spanish: ''Jaime II;'' 10 April 1267 – 2 or 5 November 1327), called the Just,, an, Chaime lo Chusto, es, Jaime el Justo. was the King of Aragon and Valencia and Count of Barcelona from 1291 to 1327. He ...
::III. Raymond Berengar (1281–1307), Count of Provence, Prince of Piedmont and Andria = Margaret of Clermont
::III. John (1283–1308), a priest
::III. Tristan (1284–bef. 1288)
::III. Eleanor of Anjou
Eleanor of Anjou (August 1289 – 9 August 1341) was Queen of Sicily as the wife of King Frederick II of Sicily. She was a member of the Capetian House of Anjou by birth.
She was the third daughter of King Charles II of Naples and Mary of Hunga ...
, (1289–1341) = Frederick III of Sicily
::III. Maria of Naples (1290–c. 1346) = 1. Sancho I of Majorca, 2. Jaime de Ejerica
::III. Peter Tempesta
Peter (1291 – 29 August 1315), called Tempesta (meaning "storm"), was the Count of Eboli from 1306. He was the eighth son of Charles II of Naples and Maria of Hungary (see Elizabeth of Sicily). His sobriquet came from his stormy temperamen ...
(1291–1315), Count of Gravina
::III. John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
(1276–1335), Duke of Durazzo, Prince of Achaea, and Count of Gravina = 1. Matilda of Hainaut
Matilda of Hainaut ( French: ''Mathilde de Hainaut''; November 1293 – 1331), also known as Maud and Mahaut, was Princess of Achaea from 1316 to 1321. She was the only child of Isabella of Villehardouin and Florent of Hainaut, co-rulers of Ac ...
(1293–1336), 2. Agnes of Périgord (d. 1345)
:::IV. (2.) Charles, Duke of Durazzo (1323–1348) = Maria of Calabria
Maria of Calabria (6 May 1329 – 20 May 1366), Countess of Alba, was a Neapolitan princess of the Capetian House of Anjou whose descendants inherited the crown of Naples following the death of her older sister, Queen Joanna I.
Life
Early ye ...
::::V. Joanna, Duchess of Durazzo
Joanna of Durazzo (1344 – 20 July 1387) was the eldest daughter and eldest surviving child of Charles, Duke of Durazzo, and his wife, Maria of Calabria. She succeeded as duchess on the death of her father in 1348 when she was only a child of f ...
1344–1387 = 1. Louis, Count of Beaumont
Louis of Évreux (also called "of Navarre"; 1341 – 1376) was the youngest son of Philip III of Navarre and Joan II of Navarre. He inherited the county of Beaumont-le-Roger from his father (1343) and became Duke of Durazzo in right of his sec ...
2. Robert IV of Artois, Count of Eu
Robert IV of Artois (1356 – 20 July 1387), son of John of Artois, Count of Eu and Isabeau of Melun, was Count of Eu from April to July 1387.
About 1376, he married Joanna of Durazzo, daughter of Charles, Duke of Durazzo. Robert IV inherit ...
::::V. Agnes of Durazzo
Agnes of Durazzo (1345 – 10 February 1383) was the wife of James of Baux, titular Latin Emperor of Constantinople. She was the last woman to claim the title of empress of the Latin Empire.
Agnes was the second daughter of Charles, Duke of D ...
1345–138 = Cansignorio della Scala lord of Verona 2. James of Baux
::::V. Margaret of Durazzo
Margaret of Durazzo ( it, Margherita di Durazzo 28 July 1347 – 6 August 1412) was Queen of Naples and Hungary and Princess of Achaea as the spouse of Charles III of Naples. She was regent of Naples from 1386 until 1393 during the minority of he ...
1347–1412 = Charles III of Naples
Charles the Short or Charles of Durazzo (1345 – 24 February 1386) was King of Naples and the titular King of Jerusalem from 1382 to 1386 as Charles II, and King of Hungary from 1385 to 1386 as Charles II. In 1381, Charles created the chivalr ...
:::IV. (2.) Louis, Count of Gravina (1324–1362) = Margaret of Sanseverino
::::V. Louis (1344–d. young)
::::V. Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person t ...
(1345–1386), king of Naples (1382–1386) and Hungary (1385–1386) = Margaret of Durazzo
Margaret of Durazzo ( it, Margherita di Durazzo 28 July 1347 – 6 August 1412) was Queen of Naples and Hungary and Princess of Achaea as the spouse of Charles III of Naples. She was regent of Naples from 1386 until 1393 during the minority of he ...
:::::VI. Joanna II of Naples 1371–1435 = 1. William, Duke of Austria
William ( – 15 July 1406), known as William the Courteous (german: Wilhelm der Freundliche), a member of the House of Habsburg and Wilhelm, was Duke of Austria from 1386. As head of the Leopoldian line, he ruled over the Inner Austrian duchie ...
2. James II, Count of La Marche
James II of Bourbon-La Marche (1370 – 1438 in Besançon) was count of La Marche. He was captured at the battle of Nicopolis in 1396, later being ransomed. In 1403, James led an attack on English soil and burned Plymouth. He married Joanna o ...
:::::VI. Ladislaus of Naples
Ladislaus the Magnanimous ( it, Ladislao, hu, László; 15 February 1377 – 6 August 1414) was King of Naples from 1386 until his death and an unsuccessful claimant to the kingdoms of Hungary and Croatia. Ladislaus was a skilled political and m ...
1377–1414 = 1. Costanza Chiaramonte Costanza Chiaramonte ( – 1423) was a queen consort of Naples in 1389-1392, married to King Ladislaus of Naples. With changing political circumstances, their marriage was annulled.
Life
Costanza was a daughter of Manfredi III Chiaramonte, count of ...
, 2. Mary of Lusignan, 3. Mary of Enghien
::::V. Agnes (1347–d. young)
:::IV. (2.) Robert of Durazzo
Robert of Durazzo (1326 – 19 September 1356, Poitiers) was the third son of John, Duke of Durazzo and Agnes de Périgord.
He was the lord of Cappacio, Muro, and Montalbano in the Kingdom of Naples. Captured in 1350 at the siege of Avers ...
(1326–1356)
::III. Beatrice (1295–c. 1321) = 1. Azzo VIII d'Este, marchese of Ferrara, 2. Bertrand III of Baux, Count of Andria (d. 1351)
:II. Philip 1256–1277, elected king of Sardinia - died childless
:II. Robert 1258–1265 - died childless
The three surviving sons of Charles Robert (Charles I of Hungary) were Louis I of Hungary (1326–1382), Andrew, Duke of Calabria
Andrew, Duke of Calabria (30 October 1327 – 18 September 1345) was the first husband of Joanna I of Naples, and a son of Charles I of Hungary and brother of Louis I of Hungary.
Background and engagement
Andrew was the second of three survivin ...
(1327-1345), and Stephen, Duke of Slavonia (1332-1354). Louis I had only two surviving daughters, Mary of Hungary
Mary, also known as Maria of Anjou (, , ; 137117 May 1395), reigned as Queen of Hungary and Croatia (officially 'king') between 1382 and 1385, and from 1386 until her death. She was the daughter of Louis the Great, King of Hungary and Poland ...
(1371-1395), who married the future Holy Roman emberor Sigismund of Luxembourg, and Hedwig of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig ( hu, Hedvig), was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Great, ...
(1373/74-1399), who was given in marriage to the Grand Duke of Lithuania Władysław II Jagiełło
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło ()He is known under a number of names: lt, Jogaila Algirdaitis; pl, Władysław II Jagiełło; be, Jahajła (Ягайла). See also: Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło. ...
, the future king of Poland. (See the section of Poland.) After Louis I's death without male heirs, Mary's husband, Sigismund of Luxembourg (1368-1437) managed to be accepted as Mary's co-ruler, by the Hungarian lords. When the queen died (1395) the Hungarian crown passed over to the House of Luxembourg.
In 1333, the six years old second son of Charles Robert, Andrew
Andrew is the English form of a given name common in many countries. In the 1990s, it was among the top ten most popular names given to boys in List of countries where English is an official language, English-speaking countries. "Andrew" is freq ...
(1327–1345) was taken to the court of Naples by his father for dynastic purposes, who put him under guardianship of Robert the Wise
Robert of Anjou ( it, Roberto d'Angiò), known as Robert the Wise ( it, Roberto il Saggio; 1276 – 20 January 1343), was King of Naples, titular King of Jerusalem and Count of Provence and Forcalquier from 1309 to 1343, the central figure of I ...
. Andrew was betrothed in 1334 to his cousin Joanna, granddaughter and heiress apparent of King Robert of Naples; Andrew's father was a fraternal nephew of King Robert. At the age of 15 he married Joanna I of Naples
Joanna I, also known as Johanna I ( it, Giovanna I; December 1325 – 27 July 1382), was Queen of Naples, and Countess of Provence and Forcalquier from 1343 to 1382; she was also Princess of Achaea from 1373 to 1381.
Joanna was the eldest ...
. After the death of Robert (1343), the King of Naples, Andrew became a victim of power clashes in the court of Naples.
Robert's claim to the throne was rather tenuous and did not follow primogeniture. Andrew's grandfather, Charles Martel of Anjou
Charles Martel ( hu, Martell Károly; 8 September 1271 – 12 August 1295) of the Angevin dynasty was the eldest son of king Charles II of Naples and Mary of Hungary, the daughter of King Stephen V of Hungary.
__NOTOC__
The 18-year-old Charles Ma ...
, had died young; therefore, the throne should have passed to Andrew's father. However, due to fears of impending invasion from Sicily, it was felt that a seven-year-old heir was too risky and would not be able to hold off invasions. The throne was offered to the next son of Charles II of Naples, Louis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
, but he refused on religious grounds, and it thus passed to Robert. To recompensate Andrew's father, Charles II decided to assign him the claim to Hungary.
When King Robert died in 1343, in his last will and testament, he formally bequeathed his kingdom to his granddaughter Joanna, making no mention of Andrew and thus denying him the right to reign along with Joanna. With the approval of Pope Clement VI
Pope Clement VI ( la, Clemens VI; 1291 – 6 December 1352), born Pierre Roger, was head of the Catholic Church from 7 May 1342 to his death in December 1352. He was the fourth Avignon pope. Clement reigned during the first visitation of the Bl ...
, Joanna was crowned sole monarch of Naples in August 1344. Fearing for his life, Andrew wrote to his mother Elizabeth that he would soon flee the kingdom. She intervened, and made a state visit, before she returned to Hungary allegedly bribing Pope Clement to reverse himself and permit the coronation of Andrew.
Hearing of the Pope's reversal, a group of noble conspirators (the involvement of Queen Joanna is unproved) determined to forestall Andrew's coronation. During a hunting trip at Aversa, Andrew left his room in the middle of the night and was set upon by the conspirators. A treacherous servant barred the door behind him, and, as Joanna cowered in their bed, a terrible struggle ensued, Andrew defending himself furiously and shrieking for aid. He was finally overpowered, strangled with a cord, and flung from a window. Isolde, Andrew's Hungarian nurse took the Prince's corpse to the church of the monks, and remained with it until next morning mourning it. When the Hungarian knights arrived she told them everything in their mother tongue so no one else would learn about the truth, and soon they left Naples reporting everything to the Hungarian King.
The deed would taint the rest of Joanna's reign, although she was twice acquitted of any charge in the trials that followed. Andrew's elder brother Louis I of Hungary several times invaded the Kingdom of Naples and drove out Joanna, only to meet with reverses.
In November 1347, Louis set out for Naples with some 1,000 soldiers (Hungarians and Germans), mostly mercenaries. When he reached the border of Joanna’s kingdom, he had 2,000 Hungarian knights, 2,000 mercenary heavy cavalry, 2,000 Cuman horse archers and 6000 mercenary heavy infantry. Joanna in the meantime had married her cousin Louis of Taranto and had signed a peace with Naples' traditional enemy, the Kingdom of Sicily. The army of Naples, 2,700 knights and 5,000 infantrymen, was led by Louis of Taranto. On January 11, 1348, in the Battle of Capua, the king of Hungary defeated the army of Louis of Taranto. Four days later the queen repaired to Provence, while her husband followed soon afterwards. All the kingdom's barons swore loyalty to the new ruler as he marched to Naples from Benevento. While visiting Aversa, where his brother had been murdered, Louis had Charles of Durazzo assassinated in revenge by his condottiero. The Neapolitans, who had quickly grown unhappy with the severe Hungarian rule, called back Joan, who paid for her return expedition by selling her rights on Avignon to the popes. She landed near Naples and easily captured it, but the Hungarian commander Ulrich von Wolfart commanded a strong resistance in Apulia. Joanna and Louis would await a new trial on Andrew's assassination, to be held in Avignon. The verdict was Joanna's acquittal from any charge in January 1352, and a peace was signed with Hungary on March 23, 1352. Ultimately, 37 years later, Louis' kinsman Charles III of Naples
Charles the Short or Charles of Durazzo (1345 – 24 February 1386) was King of Naples and the titular King of Jerusalem from 1382 to 1386 as Charles II, and King of Hungary from 1385 to 1386 as Charles II. In 1381, Charles created the chivalr ...
conquered Naples with Hungarian aid and put Joanna to death.
Stephen of Anjou
Stephen ( hu, István; 20 August 1332 – 9 August 1354) was a Hungarian royal prince of the Capetian House of Anjou. He was the youngest son of Charles I of Hungary and Elizabeth of Poland, Queen of Hungary, Elizabeth of Poland to survive childh ...
(1332–1354), duke of Slavonia, the third surviving son of Charles Robert, died before his older brother. For this reason, he (and his son) had no chance to take over the rule neither in Hungary, nor in Poland. In 1350, he married Margaret of Bavaria. His marriage with a German princess made him unpopular in Poland. The Polish noblemen acknowledged Louis as Casimir III's sole heir in July 1351 only after he had promised that he would not allow Stephen to participate in the government of Poland. Margaret gave birth to a daughter Elizabeth (in 1370 she married Philip of Taranto), and a son John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
, who inherited Croatia, Dalmatia and Slavonia from his father, but he was still a child when he died in 1360.
On the death of Louis I of Hungary, Charles III of Naples
Charles the Short or Charles of Durazzo (1345 – 24 February 1386) was King of Naples and the titular King of Jerusalem from 1382 to 1386 as Charles II, and King of Hungary from 1385 to 1386 as Charles II. In 1381, Charles created the chivalr ...
, son of Louis of Durazzo (1324–1362), the great-grandson of Charles II of Naples and Mary of Hungary, claimed the Hungarian throne as the senior Angevin male, and ousted Louis' daughter Mary of Hungary in December 1385. It was not difficult for him to reach the power, as he counted with the support of several Croatian lords, and many contacts which he made during his period as Duke of Croatia and Dalmatia. However, Elizabeth of Bosnia, widow of Louis and mother of Mary, arranged to have Charles assassinated on 7 February 1386. He died of wounds at Visegrád on 24 February. His son, Ladislaus of Naples
Ladislaus the Magnanimous ( it, Ladislao, hu, László; 15 February 1377 – 6 August 1414) was King of Naples from 1386 until his death and an unsuccessful claimant to the kingdoms of Hungary and Croatia. Ladislaus was a skilled political and m ...
would try to obtain the crown of Hungary in the future, but never reached his goal.
Poland
In 1355, the lastPiast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branche ...
king of Poland, Casimir III, designated his sororal nephew, the Angevin king Louis I of Hungary, as his heir presumptive
An heir presumptive is the person entitled to inherit a throne, peerage, or other hereditary honour, but whose position can be displaced by the birth of an heir apparent or a new heir presumptive with a better claim to the position in question.
...
by the Privilege of Buda
The Privilege of Buda (also known as the Treaty of Buda) was a set of promises and concessions made to ensure that Louis I of Hungary would succeed to his uncle Casimir III's Polish throne, thus enabling the union of Hungary and Poland.
Backgro ...
. Upon the death of Casimir (5 November 1370), who left no legitimate sons, Louis ascended the Polish throne virtually unopposed. The Polish nobility welcomed his accession, rightly believing that Louis would be an absentee king who would not take much interest in Polish affairs. He sent his mother Elizabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
, sister of Casimir III, to govern Poland as regent. Louis probably considered himself first and foremost king of Hungary; he visited his northern kingdom three times and spent there a couple of months altogether. Negotiations with the Polish nobility frequently took place in Hungary. Hungarians themselves were unpopular in Poland, as was the king's Polish mother who governed the kingdom. In 1376, ''circa'' 160 Hungarians in her retinue were massacred in Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
and the queen returned to Hungary disgraced. Louis replaced her with their relative, Vladislaus II of Opole
Vladislaus II of Opole ( pl, Władysław Opolczyk, german: Wladislaus von Oppeln, hu, Oppelni László, uk, Владислав Опольчик; ca. 1332 – 18 May 1401), nicknamed Naderspan, was Duchy of Opole, Duke of Opole from 1356, Coun ...
.
The Hungarian-Polish union fell apart after Louis died in 1382. The dissatisfied Polish '' szlachta'' demanded that his successor in Hungary, Mary
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a feminine given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religious contexts
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also calle ...
, move to Kraków and reign over Hungary and Poland from there. Mary's mother, Elizabeth of Bosnia
Elizabeth of Bosnia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Elizabeta Kotromanić, Елизабета Котроманић; hu, Kotromanics Erzsébet; pl, Elżbieta Bośniaczka; – January 1387) was queen consort of Hungary and Croatia, as well ...
(widow of Louis and grandniece of Casimir III's father, Vladislaus I), knew that the lack of supporters would render her influence at least as restricted as that of her mother-in-law and refused to move. She abandoned the idea of attempting to subdue the Polish nobility by force and agreed to send her younger surviving daughter, Hedwig Hedwig may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Hedwig (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Grzegorz Hedwig (born 1988), Polish slalom canoeist
* Johann Hedwig, (1730–1799), German botanist
* Romanus Adol ...
, to be crowned as Louis' successor in Poland.
Hedvig (known as Jadwiga in Poland) was crowned "king" in Poland's capital, Kraków, on 16 October 1384. Her coronation either reflected the Polish nobility's opposition to her intended husband, William, becoming king without further negotiation, or simply emphasized her status as queen regnant. With her mother's consent, Jadwiga's advisors opened negotiations with Jogaila, Grand Duke of Lithuania, who was still a pagan, concerning his potential marriage to Jadwiga. Jogaila signed the Union of Krewo, pledging to convert to Roman Catholicism and to promote his pagan subjects' conversion. Jogaila, who took the baptismal name Władysław, married Jadwiga on 15 February 1386. Jogaila, now in Polish styled Władysław Jagiełło, was crowned King of Poland on 4 March 1386. As Jadwiga's co-ruler, Jagiełło worked closely with his wife. Hedvig (or Jadwiga) was childless for over a decade. She became pregnant in late 1398 or early 1399. A newborn princess named Elizabeth Bonifacia was delivered on 22 June 1399 at Wawel Castle. However, the infant died after only three weeks, on 13 July 1399. 53Jadwiga, too, was on her deathbed. She died on 17 July 1399, four days after her newborn daughter. Thus, the Polish throne went over to the Jagiellonian dynasty
The Jagiellonian dynasty (, pl, dynastia jagiellońska), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty ( pl, dynastia Jagiellonów), the House of Jagiellon ( pl, Dom Jagiellonów), or simply the Jagiellons ( pl, Jagiellonowie), was the name assumed by a cad ...
of Lithuanian origin. The union of Poland and Lithuania was a decisive moment in the histories of both countries; it marked a beginning of the four centuries of shared history. By 1569 the Polish–Lithuanian union grew into a new state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and lasted until the Third Partition in 1795.
Naples
Taranto
Kingdom of Albania
The Kingdom of Albania, or '' Regnum Albaniae'', was established byCharles of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and Forcalquier (1246–48, 1256–85) ...
in the Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
n territory he conquered from the Despotate of Epirus in the year 1271. He took the title of "King of Albania" in February 1272. The kingdom extended from the region of Durrës
Durrës ( , ; sq-definite, Durrësi) is the second most populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of ...
(then known as Dyrrhachium) south along the coast to Butrint
Butrint ( el, Βουθρωτόν and Βουθρωτός, ''Bouthrōtón'', la, Buthrōtum) was an ancient Greek and later Roman city and bishopric in Epirus. "Speakers of these various Greek dialects settled different parts of Greece at differe ...
. A major attempt to advance further in direction of Constantinople, failed at the Siege of Berat (1280–1281). A Byzantine counteroffensive soon ensued, which drove the Angevins out of the interior by 1281. The Sicilian Vespers
The Sicilian Vespers ( it, Vespri siciliani; scn, Vespiri siciliani) was a successful rebellion on the island of Sicily that broke out at Easter 1282 against the rule of the French-born king Charles I of Anjou, who had ruled the Kingdom of ...
further weakened the position of Charles, and the Kingdom was soon reduced by the Epirotes
Epirus (; Epirote Greek: , ; Attic Greek: , ) was an ancient Greek kingdom, and later republic, located in the geographical region of Epirus, in north-western Greece and southern Albania. Home to the ancient Epirotes, the state was bordered by ...
to a small area around Durrës. The Angevins held out here, however, until 1368, when the city was captured by Karl Thopia
Karl Thopia ( sq, Karl Topia) was an Albanian feudal prince and warlord who ruled Albania from the middle of the 14th century until the first Ottoman conquest of Albania. Thopia usually maintained good relations with the Roman Curia.
Family ...
.
Genealogy of Capetian-Anjou
Titles
Designation and details
List of monarchs
Kingdom of Sicily
Kingdom of Naples
Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Poland
References
Sources
* * *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Capetian House Of AnjouAnjou Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
* County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
**Duk ...
Hungarian nobility
Neapolitan royal houses
Italian nobility
Neapolitan nobility