Camille Pissarro on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro ( , ; 10 July 1830 – 13 November 1903) was a Danish-French
 Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro was born on 10 July 1830 on the island of St. Thomas to Frederick Abraham Gabriel Pissarro and Rachel Manzano-Pomié. His father was of
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro was born on 10 July 1830 on the island of St. Thomas to Frederick Abraham Gabriel Pissarro and Rachel Manzano-Pomié. His father was of
 During this period Pissarro began to understand and appreciate the importance of expressing on canvas the beauties of nature without adulteration. After a year in Paris, he therefore began to leave the city and paint scenes in the countryside to capture the daily reality of village life. He found the French countryside to be "picturesque," and worthy of being painted. It was still mostly agricultural and sometimes called the "golden age of the peasantry". Pissarro later explained the technique of painting outdoors to a student:
:"Work at the same time upon sky, water, branches, ground, keeping everything going on an equal basis and unceasingly rework until you have got it. Paint generously and unhesitatingly, for it is best not to lose the first impression."
Corot would complete his paintings back in his studio, often revising them according to his preconceptions. Pissarro, however, preferred to finish his paintings outdoors, often at one sitting, which gave his work a more realistic feel. As a result, his art was sometimes criticised as being "vulgar," because he painted what he saw: "rutted and edged hodgepodge of bushes, mounds of earth, and trees in various stages of development." According to one source, such details were equivalent to today's art showing garbage cans or beer bottles on the side of a street. This difference in style created disagreements between Pissarro and Corot.
During this period Pissarro began to understand and appreciate the importance of expressing on canvas the beauties of nature without adulteration. After a year in Paris, he therefore began to leave the city and paint scenes in the countryside to capture the daily reality of village life. He found the French countryside to be "picturesque," and worthy of being painted. It was still mostly agricultural and sometimes called the "golden age of the peasantry". Pissarro later explained the technique of painting outdoors to a student:
:"Work at the same time upon sky, water, branches, ground, keeping everything going on an equal basis and unceasingly rework until you have got it. Paint generously and unhesitatingly, for it is best not to lose the first impression."
Corot would complete his paintings back in his studio, often revising them according to his preconceptions. Pissarro, however, preferred to finish his paintings outdoors, often at one sitting, which gave his work a more realistic feel. As a result, his art was sometimes criticised as being "vulgar," because he painted what he saw: "rutted and edged hodgepodge of bushes, mounds of earth, and trees in various stages of development." According to one source, such details were equivalent to today's art showing garbage cans or beer bottles on the side of a street. This difference in style created disagreements between Pissarro and Corot.
 In 1859, while attending the free school, the Académie Suisse, Pissarro became friends with a number of younger artists who likewise chose to paint in the more realistic style. Among them were
In 1859, while attending the free school, the Académie Suisse, Pissarro became friends with a number of younger artists who likewise chose to paint in the more realistic style. Among them were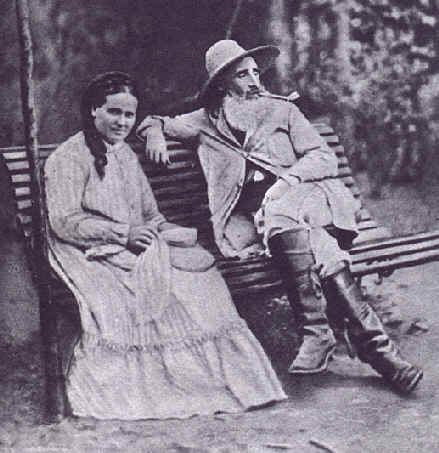  Another writer tries to describe elements of Pissarro's style:
:"The brightness of his palette envelops objects in atmosphere ... He paints the smell of the earth."
And though, on orders from the hanging Committee and the Marquis de Chennevières, Pissarro's paintings of Pontoise for example had been skyed, hung near the ceiling, this did not prevent Jules-Antoine Castagnary from noting that the qualities of his paintings had been observed by art lovers. At the age of thirty-eight, Pissarro had begun to win himself a reputation as a landscapist to rival Corot and Daubigny.
In the late 1860s or early 1870s, Pissarro became fascinated with Japanese prints, which influenced his desire to experiment in new compositions. He described the art to his son Lucien:
:"It is marvelous. This is what I see in the art of this astonishing people ... nothing that leaps to the eye, a calm, a grandeur, an extraordinary unity, a rather subdued radiance ..."
Another writer tries to describe elements of Pissarro's style:
:"The brightness of his palette envelops objects in atmosphere ... He paints the smell of the earth."
And though, on orders from the hanging Committee and the Marquis de Chennevières, Pissarro's paintings of Pontoise for example had been skyed, hung near the ceiling, this did not prevent Jules-Antoine Castagnary from noting that the qualities of his paintings had been observed by art lovers. At the age of thirty-eight, Pissarro had begun to win himself a reputation as a landscapist to rival Corot and Daubigny.
In the late 1860s or early 1870s, Pissarro became fascinated with Japanese prints, which influenced his desire to experiment in new compositions. He described the art to his son Lucien:
:"It is marvelous. This is what I see in the art of this astonishing people ... nothing that leaps to the eye, a calm, a grandeur, an extraordinary unity, a rather subdued radiance ..."
 After the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, having only Danish nationality and being unable to join the army, he moved his family to Norwood, then a village on the edge of London. However, his style of painting, which was a forerunner of what was later called "Impressionism", did not do well. He wrote to his friend, Théodore Duret, that "my painting doesn't catch on, not at all ..."
Pissarro met the Paris art dealer Paul Durand-Ruel, in London, who became the dealer who helped sell his art for most of his life. Durand-Ruel put him in touch with Monet who was likewise in London during this period. They both viewed the work of British landscape artists John Constable and
After the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, having only Danish nationality and being unable to join the army, he moved his family to Norwood, then a village on the edge of London. However, his style of painting, which was a forerunner of what was later called "Impressionism", did not do well. He wrote to his friend, Théodore Duret, that "my painting doesn't catch on, not at all ..."
Pissarro met the Paris art dealer Paul Durand-Ruel, in London, who became the dealer who helped sell his art for most of his life. Durand-Ruel put him in touch with Monet who was likewise in London during this period. They both viewed the work of British landscape artists John Constable and
 When Pissarro returned to his home in France after the war, he discovered that of the 1,500 paintings he had done over 20 years, which he was forced to leave behind when he moved to London, only 40 remained. The rest had been damaged or destroyed by the soldiers, who often used them as floor mats outside in the mud to keep their boots clean. It is assumed that many of those lost were done in the Impressionist style he was then developing, thereby "documenting the birth of
When Pissarro returned to his home in France after the war, he discovered that of the 1,500 paintings he had done over 20 years, which he was forced to leave behind when he moved to London, only 40 remained. The rest had been damaged or destroyed by the soldiers, who often used them as floor mats outside in the mud to keep their boots clean. It is assumed that many of those lost were done in the Impressionist style he was then developing, thereby "documenting the birth of
 Pissarro showed five of his paintings, all landscapes, at the exhibit, and again Émile Zola praised his art and that of the others. In the Impressionist exhibit of 1876, however, art critic Albert Wolff complained in his review, "Try to make M. Pissarro understand that trees are not violet, that sky is not the color of fresh butter ..." Journalist and art critic Octave Mirbeau on the other hand, writes, "Camille Pissarro has been a revolutionary through the revitalized working methods with which he has endowed painting".
According to Rewald, Pissarro had taken on an attitude more simple and natural than the other artists. He writes:
:"Rather than glorifying—consciously or not—the rugged existence of the peasants, he placed them without any 'pose' in their habitual surroundings, thus becoming an objective chronicler of one of the many facets of contemporary life."
In later years, Cézanne also recalled this period and referred to Pissarro as "the first Impressionist". In 1906, a few years after Pissarro's death, Cézanne, then 67 and a role model for the new generation of artists, paid Pissarro a debt of gratitude by having himself listed in an exhibition catalogue as "Paul Cézanne, pupil of Pissarro".
Pissarro, Degas, and American impressionist Mary Cassatt planned a journal of their original prints in the late 1870s, a project that nevertheless came to nothing when Degas withdrew. Art historian and the artist's great-grandson Joachim Pissarro notes that they "professed a passionate disdain for the Salons and refused to exhibit at them." Together they shared an "almost militant resolution" against the Salon, and through their later correspondences it is clear that their mutual admiration "was based on a kinship of ethical as well as aesthetic concerns".
Cassatt had befriended Degas and Pissarro years earlier when she joined Pissarro's newly formed French Impressionist group and gave up opportunities to exhibit in the United States. She and Pissarro were often treated as "two outsiders" by the Salon since neither were French or had become French citizens. However, she was "fired up with the cause" of promoting Impressionism and looked forward to exhibiting "out of solidarity with her new friends". Towards the end of the 1890s she began to distance herself from the Impressionists, avoiding Degas at times as she did not have the strength to defend herself against his "wicked tongue". Instead, she came to prefer the company of "the gentle Camille Pissarro", with whom she could speak frankly about the changing attitudes toward art. She once described him as a teacher "that could have taught the stones to draw correctly."
Pissarro showed five of his paintings, all landscapes, at the exhibit, and again Émile Zola praised his art and that of the others. In the Impressionist exhibit of 1876, however, art critic Albert Wolff complained in his review, "Try to make M. Pissarro understand that trees are not violet, that sky is not the color of fresh butter ..." Journalist and art critic Octave Mirbeau on the other hand, writes, "Camille Pissarro has been a revolutionary through the revitalized working methods with which he has endowed painting".
According to Rewald, Pissarro had taken on an attitude more simple and natural than the other artists. He writes:
:"Rather than glorifying—consciously or not—the rugged existence of the peasants, he placed them without any 'pose' in their habitual surroundings, thus becoming an objective chronicler of one of the many facets of contemporary life."
In later years, Cézanne also recalled this period and referred to Pissarro as "the first Impressionist". In 1906, a few years after Pissarro's death, Cézanne, then 67 and a role model for the new generation of artists, paid Pissarro a debt of gratitude by having himself listed in an exhibition catalogue as "Paul Cézanne, pupil of Pissarro".
Pissarro, Degas, and American impressionist Mary Cassatt planned a journal of their original prints in the late 1870s, a project that nevertheless came to nothing when Degas withdrew. Art historian and the artist's great-grandson Joachim Pissarro notes that they "professed a passionate disdain for the Salons and refused to exhibit at them." Together they shared an "almost militant resolution" against the Salon, and through their later correspondences it is clear that their mutual admiration "was based on a kinship of ethical as well as aesthetic concerns".
Cassatt had befriended Degas and Pissarro years earlier when she joined Pissarro's newly formed French Impressionist group and gave up opportunities to exhibit in the United States. She and Pissarro were often treated as "two outsiders" by the Salon since neither were French or had become French citizens. However, she was "fired up with the cause" of promoting Impressionism and looked forward to exhibiting "out of solidarity with her new friends". Towards the end of the 1890s she began to distance herself from the Impressionists, avoiding Degas at times as she did not have the strength to defend herself against his "wicked tongue". Instead, she came to prefer the company of "the gentle Camille Pissarro", with whom she could speak frankly about the changing attitudes toward art. She once described him as a teacher "that could have taught the stones to draw correctly."
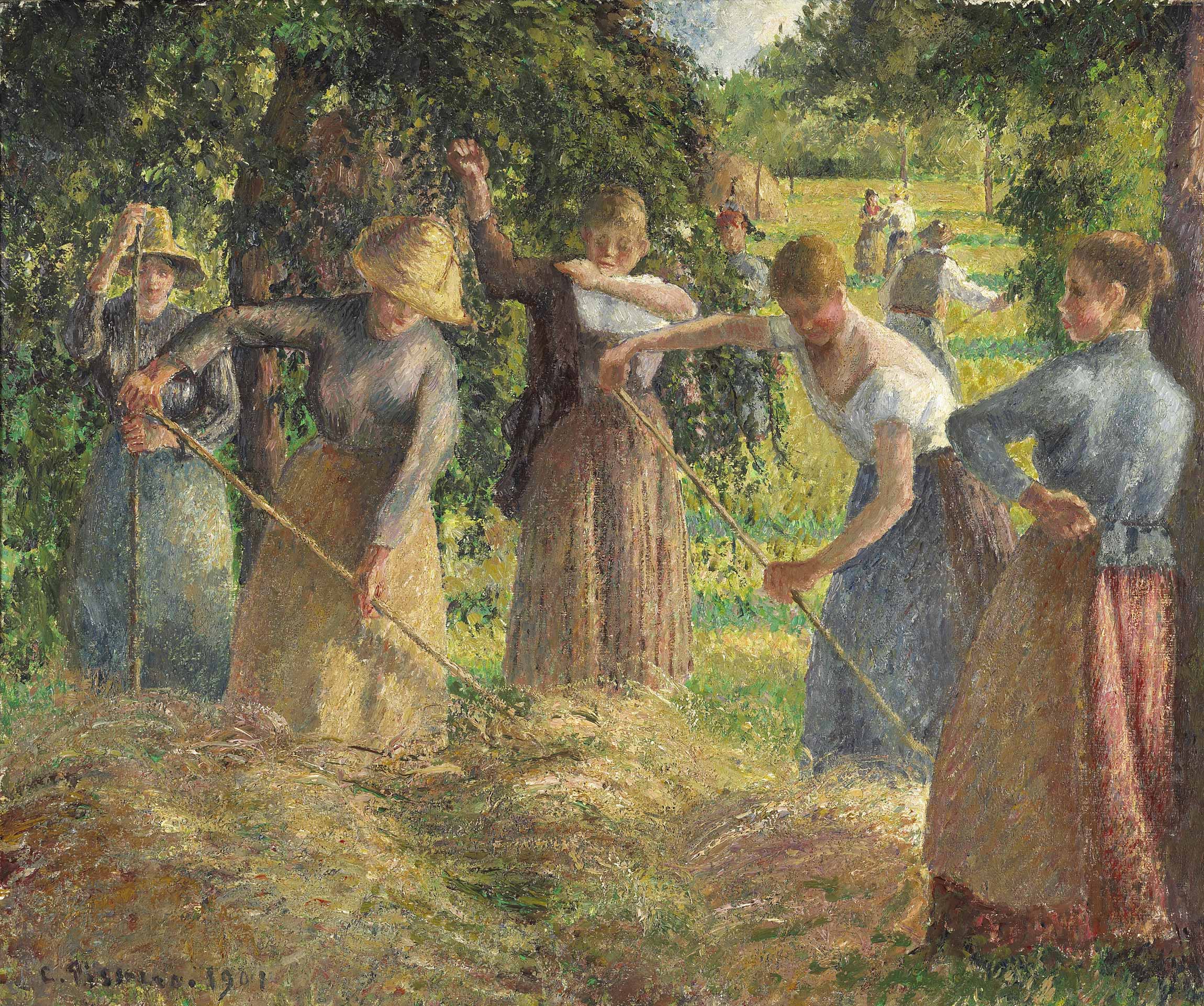

 By the 1880s, Pissarro began to explore new themes and methods of painting to break out of what he felt was an artistic "mire". As a result, Pissarro went back to his earlier themes by painting the life of country people, which he had done in Venezuela in his youth. Degas described Pissarro's subjects as "peasants working to make a living".
However, this period also marked the end of the Impressionist period due to Pissarro's leaving the movement. As Joachim Pissarro points out:
"Once such a die-hard Impressionist as Pissarro had turned his back on Impressionism, it was apparent that Impressionism had no chance of surviving ..."
It was Pissarro's intention during this period to help "educate the public" by painting people at work or at home in realistic settings, without idealising their lives.
By the 1880s, Pissarro began to explore new themes and methods of painting to break out of what he felt was an artistic "mire". As a result, Pissarro went back to his earlier themes by painting the life of country people, which he had done in Venezuela in his youth. Degas described Pissarro's subjects as "peasants working to make a living".
However, this period also marked the end of the Impressionist period due to Pissarro's leaving the movement. As Joachim Pissarro points out:
"Once such a die-hard Impressionist as Pissarro had turned his back on Impressionism, it was apparent that Impressionism had no chance of surviving ..."
It was Pissarro's intention during this period to help "educate the public" by painting people at work or at home in realistic settings, without idealising their lives.
 Pissarro eventually turned away from Neo-Impressionism, claiming its system was too artificial. He explains in a letter to a friend:
:"Having tried this theory for four years and having then abandoned it ... I can no longer consider myself one of the neo-impressionists ... It was impossible to be true to my sensations and consequently to render life and movement, impossible to be faithful to the effects, so random and so admirable, of nature, impossible to give an individual character to my drawing, hatI had to give up."
However, after reverting to his earlier style, his work became, according to Rewald, "more subtle, his color scheme more refined, his drawing firmer ... So it was that Pissarro approached old age with an increased mastery."
But the change also added to Pissarro's continual financial hardship which he felt until his 60s. His "headstrong courage and a tenacity to undertake and sustain the career of an artist", writes Joachim Pissarro, was due to his "lack of fear of the immediate repercussions" of his stylistic decisions. In addition, his work was strong enough to "bolster his morale and keep him going", he writes. His Impressionist contemporaries, however, continued to view his independence as a "mark of integrity", and they turned to him for advice, referring to him as "Père Pissarro" (father Pissarro).
Pissarro eventually turned away from Neo-Impressionism, claiming its system was too artificial. He explains in a letter to a friend:
:"Having tried this theory for four years and having then abandoned it ... I can no longer consider myself one of the neo-impressionists ... It was impossible to be true to my sensations and consequently to render life and movement, impossible to be faithful to the effects, so random and so admirable, of nature, impossible to give an individual character to my drawing, hatI had to give up."
However, after reverting to his earlier style, his work became, according to Rewald, "more subtle, his color scheme more refined, his drawing firmer ... So it was that Pissarro approached old age with an increased mastery."
But the change also added to Pissarro's continual financial hardship which he felt until his 60s. His "headstrong courage and a tenacity to undertake and sustain the career of an artist", writes Joachim Pissarro, was due to his "lack of fear of the immediate repercussions" of his stylistic decisions. In addition, his work was strong enough to "bolster his morale and keep him going", he writes. His Impressionist contemporaries, however, continued to view his independence as a "mark of integrity", and they turned to him for advice, referring to him as "Père Pissarro" (father Pissarro).
 In his older age Pissarro suffered from a recurring eye infection that prevented him from working outdoors except in warm weather. As a result of this disability, he began painting outdoor scenes while sitting by the window of hotel rooms. He often chose hotel rooms on upper levels to get a broader view. He moved around northern France and painted from hotels in Rouen, Paris, Le Havre and Dieppe. On his visits to London, he would do the same.
Pissarro died in Paris on 13 November 1903 and was buried in Père Lachaise Cemetery.
In his older age Pissarro suffered from a recurring eye infection that prevented him from working outdoors except in warm weather. As a result of this disability, he began painting outdoor scenes while sitting by the window of hotel rooms. He often chose hotel rooms on upper levels to get a broader view. He moved around northern France and painted from hotels in Rouen, Paris, Le Havre and Dieppe. On his visits to London, he would do the same.
Pissarro died in Paris on 13 November 1903 and was buried in Père Lachaise Cemetery.
 During the period Pissarro exhibited his works, art critic Armand Silvestre had called Pissarro the "most real and most naive member" of the Impressionist group.Kelder, Diane. ''The Great Book of French Impressionism'', Abbeville Press (1980) pp. 127, 135 His work has also been described by art historian Diane Kelder as expressing "the same quiet dignity, sincerity, and durability that distinguished his person." She adds that "no member of the group did more to mediate the internecine disputes that threatened at times to break it apart, and no one was a more diligent proselytizer of the new painting."
According to Pissarro's son, Lucien, his father painted regularly with Cézanne beginning in 1872. He recalls that Cézanne walked a few miles to join Pissarro at various settings in Pontoise. While they shared ideas during their work, the younger Cézanne wanted to study the countryside through Pissarro's eyes, as he admired Pissarro's landscapes from the 1860s. Cézanne, although only nine years younger than Pissarro, said that "he was a father for me. A man to consult and a little like the good Lord."
Lucien Pissarro was taught painting by his father, and described him as a "splendid teacher, never imposing his personality on his pupil."
During the period Pissarro exhibited his works, art critic Armand Silvestre had called Pissarro the "most real and most naive member" of the Impressionist group.Kelder, Diane. ''The Great Book of French Impressionism'', Abbeville Press (1980) pp. 127, 135 His work has also been described by art historian Diane Kelder as expressing "the same quiet dignity, sincerity, and durability that distinguished his person." She adds that "no member of the group did more to mediate the internecine disputes that threatened at times to break it apart, and no one was a more diligent proselytizer of the new painting."
According to Pissarro's son, Lucien, his father painted regularly with Cézanne beginning in 1872. He recalls that Cézanne walked a few miles to join Pissarro at various settings in Pontoise. While they shared ideas during their work, the younger Cézanne wanted to study the countryside through Pissarro's eyes, as he admired Pissarro's landscapes from the 1860s. Cézanne, although only nine years younger than Pissarro, said that "he was a father for me. A man to consult and a little like the good Lord."
Lucien Pissarro was taught painting by his father, and described him as a "splendid teacher, never imposing his personality on his pupil."
 During the early 1930s throughout Europe, Jewish owners of numerous fine art masterpieces found themselves forced to give up or sell off their collections for minimal prices due to anti-Jewish laws created by the new Nazi regime. Many Jews were forced to flee Germany starting in 1933, and then, as the Nazis expanded their hold over all of Europe, Austria, France, Holland, Poland, Italy and other countries. The Nazis created special looting organizations like the Reichsleiter Rosenberg Taskforce whose mission it was to seize Jewish property notably valuable artworks. When those forced into exile or deported to extermination camps owned valuables, including artwork, they were often sold to finance the Nazi war effort, sent to Hitler's personal museum, traded or seized by officials for personal gain. Several artworks by Pissarro were looted from their Jewish owners in Germany, France and elsewhere by the Nazis.
Pissarro's '' Shepherdess Bringing Home the Sheep'' (La Bergère Rentrant des Moutons") was looted from the Jewish art collectors Yvonne et Raoul Meyer in France in 1941 and transited via Switzerland and New York before entering the Fred Jones Jr Museum at the University of Oklahoma. In 2014, Meyer's daughter, Léonie-Noëlle Meyer filed a restitution claim which resulted in years of court battle. The lawsuit resulted in the recognition of Meyer's ownership and its transfer to France for five years, coupled with an agreement to shuttle the painting back and forth between Paris and Oklahoma every three years after that. However, in 2020 Meyer filed suit in a French court to challenge the accord. After Fred Jones Jr Museum sued Meyer requesting heavy financial penalties, the Holocaust survivor abandoned her effort to recover the Pissarro, saying, "I have no other choice.
Pissarro's Picking Peas (La Cueillette) was looted from Jewish businessman Simon Bauer, in addition to 92 other artworks seized in 1943 by the Vichy collaborationist regime in France.
Pissarro's ''Sower And Ploughman,'' was owned by Dr Henri Hinrichsen, a Jewish music publisher from Leipzig, until 11 January 1940, when he was forced to relinquish the painting to Hildebrand Gurlitt in Nazi-occupied Brussels, before being murdered in Auschwitz in September 1942.
Pissarro's “Le Quai Malaquais, Printemps”, owned by German Jewish publisher
During the early 1930s throughout Europe, Jewish owners of numerous fine art masterpieces found themselves forced to give up or sell off their collections for minimal prices due to anti-Jewish laws created by the new Nazi regime. Many Jews were forced to flee Germany starting in 1933, and then, as the Nazis expanded their hold over all of Europe, Austria, France, Holland, Poland, Italy and other countries. The Nazis created special looting organizations like the Reichsleiter Rosenberg Taskforce whose mission it was to seize Jewish property notably valuable artworks. When those forced into exile or deported to extermination camps owned valuables, including artwork, they were often sold to finance the Nazi war effort, sent to Hitler's personal museum, traded or seized by officials for personal gain. Several artworks by Pissarro were looted from their Jewish owners in Germany, France and elsewhere by the Nazis.
Pissarro's '' Shepherdess Bringing Home the Sheep'' (La Bergère Rentrant des Moutons") was looted from the Jewish art collectors Yvonne et Raoul Meyer in France in 1941 and transited via Switzerland and New York before entering the Fred Jones Jr Museum at the University of Oklahoma. In 2014, Meyer's daughter, Léonie-Noëlle Meyer filed a restitution claim which resulted in years of court battle. The lawsuit resulted in the recognition of Meyer's ownership and its transfer to France for five years, coupled with an agreement to shuttle the painting back and forth between Paris and Oklahoma every three years after that. However, in 2020 Meyer filed suit in a French court to challenge the accord. After Fred Jones Jr Museum sued Meyer requesting heavy financial penalties, the Holocaust survivor abandoned her effort to recover the Pissarro, saying, "I have no other choice.
Pissarro's Picking Peas (La Cueillette) was looted from Jewish businessman Simon Bauer, in addition to 92 other artworks seized in 1943 by the Vichy collaborationist regime in France.
Pissarro's ''Sower And Ploughman,'' was owned by Dr Henri Hinrichsen, a Jewish music publisher from Leipzig, until 11 January 1940, when he was forced to relinquish the painting to Hildebrand Gurlitt in Nazi-occupied Brussels, before being murdered in Auschwitz in September 1942.
Pissarro's “Le Quai Malaquais, Printemps”, owned by German Jewish publisher
File:Pissarro Camille - Boulevard Montmartre à Paris.jpg, ''Boulevard Montmartre à Paris'', 1897.
File:Camille Pissarro - A Plaza in Caracas.jpg, ''A Plaza in Caracas'', c. 1850–52, oil on canvas. Colección Patricia Phelps de Cisneros
File:Camille Pissarro - Allée dans une fôret (sur 1859).jpg, ''Allée dans une forêt'' (Road in a Forest), 1859, oil on canvas
File:LE LABOURAGE, BÉRELLES.PNG, ''Working at Bérelles'' (Le Labourage, Bérelles), c. 1860, oil on panel
File:Camille Pissarro - Châtaigniers à Louveciennes - 1879.jpg, ''Châtaignier à
File:Camille Pissarro - La Guaira.jpg, ''La Guaira'', 1852–54, graphite and ink on paper
File:Camille Pissarro - View from Upper Norwood.jpg, ''View from Upper Norwood'', c. 1870, pen and brown ink over pencil on paper. Ashmolean Museum
File:LES POMMIERS, PONTOISE.PNG, ''Apple Trees at Pontoise'', c. 1872, pastel on paper
File:Piette by Pissarro.jpg, ''Portrait of Ludovic Piette'', c. 1875, pastel on paper. Wildenstein Institute
File:The Woods at L'Hermitage, Pontoise MET DP108213.jpg, ''The Woods at L'Hermitage, Pontoise'', 1879, softground etching, aquatint, and drypoint on china paper (sixth state).
Camille Pissarro Protests Alfred Dreyfus' Conviction: Original Letter
Shapell Manuscript Foundation
Photograph of Pissarro's mausoleum at Cimetière Père Lachaise, Paris
(
''Pissarro's People'', exhibition held at the Sterling and Francine Clark Art Institute, Williamstown MA, 12 June – 2 October 2011
Union List of Artist Names, Getty Vocabularies.
ULAN Full Record Display for Camille Pissarro. Getty Vocabulary Program, Getty Research Institute. Los Angeles, California. *
Exhibition Pissarro dans les ports, 2013, Museum of modern art André Malraux – MuMa
Camille Pissarro Personal Manuscripts
Camille Pissarro at The Jewish Museum
''Pissarro Paintings and Works on Paper at the Art Institute of Chicago''
one of the Art Institute of Chicago'
digital scholarly catalogues
*Jennifer A. Thompson,
''L’île Lacroix, Rouen (The Effect of Fog)'' by Camille Pissarro (cat. 1060)
” in
The John G. Johnson Collection: A History and Selected Works
', a Philadelphia Museum of Art free digital publication
An artwork by Camille Pissarro
at th
Ben Uri
site {{DEFAULTSORT:Pissarro, Camille 1830 births 1903 deaths 19th-century Danish painters 19th-century Danish male artists 20th-century Danish painters 20th-century Danish male artists 19th-century French painters 19th-century French male artists 20th-century French painters 20th-century French male artists Danish male painters French male painters People from the Danish West Indies People from Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands Danish Sephardi Jews French expatriates in England French Impressionist painters 19th-century French Sephardi Jews Jewish painters École des Beaux-Arts alumni School of Paris Jewish School of Paris Burials at Père Lachaise Cemetery French people of Portuguese-Jewish descent French people of Creole descent Danish people of French descent Danish people of Portuguese-Jewish descent United States Virgin Islands Jews
Impressionist
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passag ...
and Neo-Impressionist painter born on the island of St Thomas (now in the US Virgin Islands, but then in the Danish West Indies). His importance resides in his contributions to both Impressionism and Post-Impressionism
Post-Impressionism (also spelled Postimpressionism) was a predominantly French art movement that developed roughly between 1886 and 1905, from the last Impressionist exhibition to the birth of Fauvism. Post-Impressionism emerged as a reaction ...
. Pissarro studied from great forerunners, including Gustave Courbet
Jean Désiré Gustave Courbet ( , , ; 10 June 1819 – 31 December 1877) was a French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. Committed to painting only what he could see, he rejected academic convention and ...
and Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot. He later studied and worked alongside Georges Seurat and Paul Signac when he took on the Neo-Impressionist style at the age of 54.
In 1873 he helped establish a collective society of fifteen aspiring artists, becoming the "pivotal" figure in holding the group together and encouraging the other members. Art historian John Rewald called Pissarro the "dean of the Impressionist painters", not only because he was the oldest of the group, but also "by virtue of his wisdom and his balanced, kind, and warmhearted personality". Paul Cézanne
Paul Cézanne ( , , ; ; 19 January 1839 – 22 October 1906) was a French artist and Post-Impressionist painter whose work laid the foundations of the transition from the 19th-century conception of artistic endeavour to a new and radically d ...
said "he was a father for me. A man to consult and a little like the good Lord", and he was also one of Paul Gauguin
Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin (, ; ; 7 June 1848 – 8 May 1903) was a French Post-Impressionist artist. Unappreciated until after his death, Gauguin is now recognized for his experimental use of colour and Synthetist style that were distinct fr ...
's masters. Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (; 25 February 1841 – 3 December 1919) was a French artist who was a leading painter in the development of the Impressionism, Impressionist style. As a celebrator of beauty and especially femininity, feminine sensuality ...
referred to his work as "revolutionary", through his artistic portrayals of the "common man", as Pissarro insisted on painting individuals in natural settings without "artifice or grandeur".
Pissarro is the only artist to have shown his work at all eight Paris Impressionist exhibitions, from 1874 to 1886. He "acted as a father figure not only to the Impressionists" but to all four of the major Post-Impressionists, Cézanne, Seurat, Gauguin, and van Gogh
Vincent Willem van Gogh (; 30 March 185329 July 1890) was a Dutch Post-Impressionist painter who posthumously became one of the most famous and influential figures in Western art history. In a decade, he created about 2,100 artworks, inc ...
.
Early years
 Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro was born on 10 July 1830 on the island of St. Thomas to Frederick Abraham Gabriel Pissarro and Rachel Manzano-Pomié. His father was of
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro was born on 10 July 1830 on the island of St. Thomas to Frederick Abraham Gabriel Pissarro and Rachel Manzano-Pomié. His father was of Portuguese Jewish
Spanish and Portuguese Jews, also called Western Sephardim, Iberian Jews, or Peninsular Jews, are a distinctive sub-group of Sephardic Jews who are largely descended from Jews who lived as New Christians in the Iberian Peninsula during the ...
descent and held French nationality. His mother was from a French-Jewish family from the island of St. Thomas. His father was a merchant who came to the island from France to deal with the hardware store of a deceased uncle, Isaac Petit, and married his widow. The marriage caused a stir within St. Thomas's small Jewish community because she was previously married to Frederick's uncle and according to Jewish law a man is forbidden from marrying his aunt. In subsequent years his four children attended the all-black primary school. Upon his death, his will specified that his estate be split equally between the synagogue and St. Thomas' Protestant church.
When Pissarro was twelve his father sent him to boarding school in France. He studied at the Savary Academy in Passy near Paris. While a young student, he developed an early appreciation of the French art masters. Monsieur Savary himself gave him a strong grounding in drawing and painting and suggested he draw from nature when he returned to St. Thomas.
After his schooling, Pissarro returned to St. Thomas at the age of sixteen or seventeen, where his father advocated Pissarro to work in his business as a port clerk. Nevertheless, Pissarro took every opportunity during those next five years at the job to practice drawing during breaks and after work.
Visual theorist Nicholas Mirzoeff claims that the young Pissarro was inspired by the artworks of James Gay Sawkins, a British painter and geologist who lived in Charlotte Amalie, St. Thomas circa 1847. Pissarro may have attended art classes taught by Sawkins and seen Sawkins's paintings of Mitla, Mexico. Mirzoeff states, "A formal analysis suggests that awkins'swork influenced the young Pissarro, who had just returned to the island from his school in France. Soon afterward, Pissarro began his own drawings of the local African population in apparent imitation of Sawkins," creating "sketches for a postslavery imagination."
When Pissarro turned twenty-one, Danish artist Fritz Melbye, then living on St. Thomas, inspired him to take on painting as a full-time profession, becoming his teacher and friend. Pissarro then chose to leave his family and job and live in Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, where he and Melbye spent the next two years working as artists in Caracas and La Guaira. He drew everything he could, including landscapes, village scenes, and numerous sketches, enough to fill up multiple sketchbooks.
Life in France
In 1855, Pissarro moved back to Paris where he began working as an assistant toAnton Melbye
Daniel Herman Anton Melbye (13 February 1818, Copenhagen – 10 January 1875, Paris) was a Danish painter and photographer who specialized in maritime scenes. He was the brother of painters Vilhelm and Fritz Melbye.
Biography
His father was ...
, Fritz Melbye's brother and also a painter.''Camille Pissarro'', Art Gallery of New South Wales, (2005) He also studied paintings by other artists whose style impressed him: Courbet, Charles-François Daubigny
Charles-François Daubigny ( , , ; 15 February 181719 February 1878) was a French painter, one of the members of the Barbizon school, and is considered an important precursor of impressionism.
He was also a prolific printmaker, mostly in etch ...
, Jean-François Millet, and Corot. He also enrolled in various classes taught by masters, at schools such as École des Beaux-Arts and Académie Suisse. But Pissarro eventually found their teaching methods "stifling," states art historian John Rewald. This prompted him to search for alternative instruction, which he requested and received from Corot.
Paris Salon and Corot's influence
His initial paintings were in accord with the standards at the time to be displayed at the ParisSalon
Salon may refer to:
Common meanings
* Beauty salon, a venue for cosmetic treatments
* French term for a drawing room, an architectural space in a home
* Salon (gathering), a meeting for learning or enjoyment
Arts and entertainment
* Salon ( ...
, the official body whose academic traditions dictated the kind of art that was acceptable. The Salon's annual exhibition was essentially the only marketplace for young artists to gain exposure. As a result, Pissarro worked in the traditional and prescribed manner to satisfy the tastes of its official committee.
In 1859 his first painting was accepted and exhibited. His other paintings during that period were influenced by Camille Corot
Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot ( , , ; July 16, 1796 – February 22, 1875), or simply Camille Corot, is a French landscape and portrait painter as well as a printmaker in etching. He is a pivotal figure in landscape painting and his vast o ...
, who tutored him. He and Corot both shared a love of rural scenes painted from nature. It was by Corot that Pissarro was inspired to paint outdoors, also called "plein air
''En plein air'' (; French for 'outdoors'), or ''plein air'' painting, is the act of painting outdoors.
This method contrasts with studio painting or academic rules that might create a predetermined look. The theory of 'En plein air' painting ...
" painting. Pissarro found Corot, along with the work of Gustave Courbet
Jean Désiré Gustave Courbet ( , , ; 10 June 1819 – 31 December 1877) was a French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. Committed to painting only what he could see, he rejected academic convention and ...
, to be "statements of pictorial truth," writes Rewald. He discussed their work often. Jean-François Millet was another whose work he admired, especially his "sentimental renditions of rural life".
Use of natural outdoor settings
 During this period Pissarro began to understand and appreciate the importance of expressing on canvas the beauties of nature without adulteration. After a year in Paris, he therefore began to leave the city and paint scenes in the countryside to capture the daily reality of village life. He found the French countryside to be "picturesque," and worthy of being painted. It was still mostly agricultural and sometimes called the "golden age of the peasantry". Pissarro later explained the technique of painting outdoors to a student:
:"Work at the same time upon sky, water, branches, ground, keeping everything going on an equal basis and unceasingly rework until you have got it. Paint generously and unhesitatingly, for it is best not to lose the first impression."
Corot would complete his paintings back in his studio, often revising them according to his preconceptions. Pissarro, however, preferred to finish his paintings outdoors, often at one sitting, which gave his work a more realistic feel. As a result, his art was sometimes criticised as being "vulgar," because he painted what he saw: "rutted and edged hodgepodge of bushes, mounds of earth, and trees in various stages of development." According to one source, such details were equivalent to today's art showing garbage cans or beer bottles on the side of a street. This difference in style created disagreements between Pissarro and Corot.
During this period Pissarro began to understand and appreciate the importance of expressing on canvas the beauties of nature without adulteration. After a year in Paris, he therefore began to leave the city and paint scenes in the countryside to capture the daily reality of village life. He found the French countryside to be "picturesque," and worthy of being painted. It was still mostly agricultural and sometimes called the "golden age of the peasantry". Pissarro later explained the technique of painting outdoors to a student:
:"Work at the same time upon sky, water, branches, ground, keeping everything going on an equal basis and unceasingly rework until you have got it. Paint generously and unhesitatingly, for it is best not to lose the first impression."
Corot would complete his paintings back in his studio, often revising them according to his preconceptions. Pissarro, however, preferred to finish his paintings outdoors, often at one sitting, which gave his work a more realistic feel. As a result, his art was sometimes criticised as being "vulgar," because he painted what he saw: "rutted and edged hodgepodge of bushes, mounds of earth, and trees in various stages of development." According to one source, such details were equivalent to today's art showing garbage cans or beer bottles on the side of a street. This difference in style created disagreements between Pissarro and Corot.
With Monet, Cézanne, and Guillaumin
 In 1859, while attending the free school, the Académie Suisse, Pissarro became friends with a number of younger artists who likewise chose to paint in the more realistic style. Among them were
In 1859, while attending the free school, the Académie Suisse, Pissarro became friends with a number of younger artists who likewise chose to paint in the more realistic style. Among them were Claude Monet
Oscar-Claude Monet (, , ; 14 November 1840 – 5 December 1926) was a French painter and founder of impressionist painting who is seen as a key precursor to modernism, especially in his attempts to paint nature as he perceived it. During ...
, Armand Guillaumin
Armand Guillaumin (; February 16, 1841 – June 26, 1927) was a French impressionist painter and lithographer.
Biography Early years
Born Jean-Baptiste Armand Guillaumin in Paris, he worked at his uncle's lingerie shop while attending even ...
and Paul Cézanne
Paul Cézanne ( , , ; ; 19 January 1839 – 22 October 1906) was a French artist and Post-Impressionist painter whose work laid the foundations of the transition from the 19th-century conception of artistic endeavour to a new and radically d ...
. What they shared in common was their dissatisfaction with the dictates of the Salon. Cézanne's work had been mocked at the time by the others in the school, and, writes Rewald, in his later years Cézanne "never forgot the sympathy and understanding with which Pissarro encouraged him." As a part of the group, Pissarro was comforted from knowing he was not alone, and that others similarly struggled with their art.
Pissarro agreed with the group about the importance of portraying individuals in natural settings, and expressed his dislike of any artifice or grandeur in his works, despite what the Salon demanded for its exhibits. In 1863 almost all of the group's paintings were rejected by the Salon, and French Emperor Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A neph ...
instead decided to place their paintings in a separate exhibit hall, the Salon des Refusés
The Salon des Refusés, French for "exhibition of rejects" (), is generally known as an exhibition of works rejected by the jury of the official Paris Salon, but the term is most famously used to refer to the Salon des Refusés of 1863.
Today, b ...
. However, only works of Pissarro and Cézanne were included, and the separate exhibit brought a hostile response from both the officials of the Salon and the public.
In subsequent Salon exhibits of 1865 and 1866, Pissarro acknowledged his influences from Melbye and Corot, whom he listed as his masters in the catalogue. But in the exhibition of 1868 he no longer credited other artists as an influence, in effect declaring his independence as a painter. This was noted at the time by art critic and author Émile Zola, who offered his opinion:
:"Camille Pissarro is one of the three or four true painters of this day ... I have rarely encountered a technique that is so sure."
 Another writer tries to describe elements of Pissarro's style:
:"The brightness of his palette envelops objects in atmosphere ... He paints the smell of the earth."
And though, on orders from the hanging Committee and the Marquis de Chennevières, Pissarro's paintings of Pontoise for example had been skyed, hung near the ceiling, this did not prevent Jules-Antoine Castagnary from noting that the qualities of his paintings had been observed by art lovers. At the age of thirty-eight, Pissarro had begun to win himself a reputation as a landscapist to rival Corot and Daubigny.
In the late 1860s or early 1870s, Pissarro became fascinated with Japanese prints, which influenced his desire to experiment in new compositions. He described the art to his son Lucien:
:"It is marvelous. This is what I see in the art of this astonishing people ... nothing that leaps to the eye, a calm, a grandeur, an extraordinary unity, a rather subdued radiance ..."
Another writer tries to describe elements of Pissarro's style:
:"The brightness of his palette envelops objects in atmosphere ... He paints the smell of the earth."
And though, on orders from the hanging Committee and the Marquis de Chennevières, Pissarro's paintings of Pontoise for example had been skyed, hung near the ceiling, this did not prevent Jules-Antoine Castagnary from noting that the qualities of his paintings had been observed by art lovers. At the age of thirty-eight, Pissarro had begun to win himself a reputation as a landscapist to rival Corot and Daubigny.
In the late 1860s or early 1870s, Pissarro became fascinated with Japanese prints, which influenced his desire to experiment in new compositions. He described the art to his son Lucien:
:"It is marvelous. This is what I see in the art of this astonishing people ... nothing that leaps to the eye, a calm, a grandeur, an extraordinary unity, a rather subdued radiance ..."
Marriage and children
In 1871 inCroydon
Croydon is a large town in south London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a local government district of Greater London. It is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an exten ...
, England, he married his mother's maid, Julie Vellay, a vineyard grower's daughter, with whom he had seven children, six of which would become painters: Lucien Pissarro (1863–1944), Georges Henri Manzana Pissarro (1871–1961), Félix Pissarro (1874–1897), (1878–1952), (1881–1948), and Paul-Émile Pissarro (1884–1972). They lived outside Paris in Pontoise and later in Louveciennes
Louveciennes () is a commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. It is located in the western suburbs of Paris, between Versailles and Saint-Germain-en-Laye, and adjacent to Marly-le-Roi.
Populat ...
, both of which places inspired many of his paintings including scenes of village life, along with rivers, woods, and people at work. He also kept in touch with the other artists of his earlier group, especially Monet, Renoir, Cézanne, and Frédéric Bazille
Jean Frédéric Bazille (December 6, 1841 – November 28, 1870) was a French Impressionist painter. Many of Bazille's major works are examples of figure painting in which he placed the subject figure within a landscape painted '' en plein air'' ...
.
The London years
 After the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, having only Danish nationality and being unable to join the army, he moved his family to Norwood, then a village on the edge of London. However, his style of painting, which was a forerunner of what was later called "Impressionism", did not do well. He wrote to his friend, Théodore Duret, that "my painting doesn't catch on, not at all ..."
Pissarro met the Paris art dealer Paul Durand-Ruel, in London, who became the dealer who helped sell his art for most of his life. Durand-Ruel put him in touch with Monet who was likewise in London during this period. They both viewed the work of British landscape artists John Constable and
After the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, having only Danish nationality and being unable to join the army, he moved his family to Norwood, then a village on the edge of London. However, his style of painting, which was a forerunner of what was later called "Impressionism", did not do well. He wrote to his friend, Théodore Duret, that "my painting doesn't catch on, not at all ..."
Pissarro met the Paris art dealer Paul Durand-Ruel, in London, who became the dealer who helped sell his art for most of his life. Durand-Ruel put him in touch with Monet who was likewise in London during this period. They both viewed the work of British landscape artists John Constable and J. M. W. Turner
Joseph Mallord William Turner (23 April 177519 December 1851), known in his time as William Turner, was an English Romantic painter, printmaker and watercolourist. He is known for his expressive colouring, imaginative landscapes and turbul ...
, which confirmed their belief that their style of open air painting gave the truest depiction of light and atmosphere, an effect that they felt could not be achieved in the studio alone. Pissarro's paintings also began to take on a more spontaneous look, with loosely blended brushstrokes and areas of impasto, giving more depth to the work.
Paintings
Through the paintings Pissarro completed at this time, he records Sydenham and the Norwoods at a time when they were just recently connected by railways, but prior to the expansion of suburbia. One of the largest of these paintings is a view of ''St. Bartholomew's Church'' at Lawrie Park Avenue, commonly known as '' The Avenue, Sydenham'', in the collection of theNational Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director ...
in London. Twelve oil paintings date from his stay in Upper Norwood and are listed and illustrated in the catalogue raisonné prepared jointly by his fifth child Ludovic-Rodolphe Pissarro and Lionello Venturi and published in 1939. These paintings include ''Norwood Under the Snow'', and '' Lordship Lane Station'', views of The Crystal Palace
The Crystal Palace was a cast iron and plate glass structure, originally built in Hyde Park, London, Hyde Park, London, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. The exhibition took place from 1 May to 15 October 1851, and more than 14,000 exhibit ...
relocated from Hyde Park, '' Dulwich College'', '' Sydenham Hill'', ''All Saints Church Upper Norwood'', and a lost painting of St. Stephen's Church.
Returning to France, Pissarro lived in Pontoise from 1872 to 1884. In 1890 he again visited England and painted some ten scenes of central London. He came back again in 1892, painting in Kew Gardens and Kew Green, and also in 1897, when he produced several oils described as being of Bedford Park, Chiswick, but in fact all being of the nearby Stamford Brook
Stamford Brook was a tributary of the Tideway stretch of the River Thames in west London supplied by three headwaters. Historically used as an irrigation ditch or dyke the network of small watercourses had four lower courses and mouths.
Histo ...
area except for one of Bath Road, which runs from Stamford Brook along the south edge of Bedford Park.
French Impressionism
 When Pissarro returned to his home in France after the war, he discovered that of the 1,500 paintings he had done over 20 years, which he was forced to leave behind when he moved to London, only 40 remained. The rest had been damaged or destroyed by the soldiers, who often used them as floor mats outside in the mud to keep their boots clean. It is assumed that many of those lost were done in the Impressionist style he was then developing, thereby "documenting the birth of
When Pissarro returned to his home in France after the war, he discovered that of the 1,500 paintings he had done over 20 years, which he was forced to leave behind when he moved to London, only 40 remained. The rest had been damaged or destroyed by the soldiers, who often used them as floor mats outside in the mud to keep their boots clean. It is assumed that many of those lost were done in the Impressionist style he was then developing, thereby "documenting the birth of Impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passa ...
." Armand Silvestre, a critic, went so far as to call Pissarro "basically the inventor of this mpressionistpainting"; however, Pissarro's role in the Impressionist movement was "less that of the great man of ideas than that of the good counselor and appeaser ..." "Monet ... could be seen as the guiding force."
He soon reestablished his friendships with the other Impressionist artists of his earlier group, including Cézanne, Monet, Manet, Renoir, and Degas. Pissarro now expressed his opinion to the group that he wanted an alternative to the Salon
Salon may refer to:
Common meanings
* Beauty salon, a venue for cosmetic treatments
* French term for a drawing room, an architectural space in a home
* Salon (gathering), a meeting for learning or enjoyment
Arts and entertainment
* Salon ( ...
so their group could display their own unique styles.
To assist in that endeavour, in 1873 he helped establish a separate collective, called the "Société Anonyme des Artistes, Peintres, Sculpteurs et Graveurs," which included fifteen artists. Pissarro created the group's first charter and became the "pivotal" figure in establishing and holding the group together. One writer noted that with his prematurely grey beard, the forty-three-year-old Pissarro was regarded as a "wise elder and father figure" by the group. Yet he was able to work alongside the other artists on equal terms due to his youthful temperament and creativity. Another writer said of him that "he has unchanging spiritual youth and the look of an ancestor who remained a young man".
Impressionist exhibitions that shocked the critics
The following year, in 1874, the group held their first 'Impressionist' Exhibition, which shocked and "horrified" the critics, who primarily appreciated only scenes portraying religious, historical, or mythological settings. They found fault with the Impressionist paintings on many grounds: *The subject matter was considered "vulgar" and "commonplace," with scenes of street people going about their everyday lives. Pissarro's paintings, for instance, showed scenes of muddy, dirty, and unkempt settings; *The manner of painting was too sketchy and looked incomplete, especially compared to the traditional styles of the period. The use of visible and expressive brushwork by all the artists was considered an insult to the craft of traditional artists, who often spent weeks on their work. Here, the paintings were often done in one sitting and the paints were applied wet-on-wet; *The use of color by the Impressionists relied on new theories they developed, such as having shadows painted with the reflected light of surrounding, and often unseen, objects.A "revolutionary" style
 Pissarro showed five of his paintings, all landscapes, at the exhibit, and again Émile Zola praised his art and that of the others. In the Impressionist exhibit of 1876, however, art critic Albert Wolff complained in his review, "Try to make M. Pissarro understand that trees are not violet, that sky is not the color of fresh butter ..." Journalist and art critic Octave Mirbeau on the other hand, writes, "Camille Pissarro has been a revolutionary through the revitalized working methods with which he has endowed painting".
According to Rewald, Pissarro had taken on an attitude more simple and natural than the other artists. He writes:
:"Rather than glorifying—consciously or not—the rugged existence of the peasants, he placed them without any 'pose' in their habitual surroundings, thus becoming an objective chronicler of one of the many facets of contemporary life."
In later years, Cézanne also recalled this period and referred to Pissarro as "the first Impressionist". In 1906, a few years after Pissarro's death, Cézanne, then 67 and a role model for the new generation of artists, paid Pissarro a debt of gratitude by having himself listed in an exhibition catalogue as "Paul Cézanne, pupil of Pissarro".
Pissarro, Degas, and American impressionist Mary Cassatt planned a journal of their original prints in the late 1870s, a project that nevertheless came to nothing when Degas withdrew. Art historian and the artist's great-grandson Joachim Pissarro notes that they "professed a passionate disdain for the Salons and refused to exhibit at them." Together they shared an "almost militant resolution" against the Salon, and through their later correspondences it is clear that their mutual admiration "was based on a kinship of ethical as well as aesthetic concerns".
Cassatt had befriended Degas and Pissarro years earlier when she joined Pissarro's newly formed French Impressionist group and gave up opportunities to exhibit in the United States. She and Pissarro were often treated as "two outsiders" by the Salon since neither were French or had become French citizens. However, she was "fired up with the cause" of promoting Impressionism and looked forward to exhibiting "out of solidarity with her new friends". Towards the end of the 1890s she began to distance herself from the Impressionists, avoiding Degas at times as she did not have the strength to defend herself against his "wicked tongue". Instead, she came to prefer the company of "the gentle Camille Pissarro", with whom she could speak frankly about the changing attitudes toward art. She once described him as a teacher "that could have taught the stones to draw correctly."
Pissarro showed five of his paintings, all landscapes, at the exhibit, and again Émile Zola praised his art and that of the others. In the Impressionist exhibit of 1876, however, art critic Albert Wolff complained in his review, "Try to make M. Pissarro understand that trees are not violet, that sky is not the color of fresh butter ..." Journalist and art critic Octave Mirbeau on the other hand, writes, "Camille Pissarro has been a revolutionary through the revitalized working methods with which he has endowed painting".
According to Rewald, Pissarro had taken on an attitude more simple and natural than the other artists. He writes:
:"Rather than glorifying—consciously or not—the rugged existence of the peasants, he placed them without any 'pose' in their habitual surroundings, thus becoming an objective chronicler of one of the many facets of contemporary life."
In later years, Cézanne also recalled this period and referred to Pissarro as "the first Impressionist". In 1906, a few years after Pissarro's death, Cézanne, then 67 and a role model for the new generation of artists, paid Pissarro a debt of gratitude by having himself listed in an exhibition catalogue as "Paul Cézanne, pupil of Pissarro".
Pissarro, Degas, and American impressionist Mary Cassatt planned a journal of their original prints in the late 1870s, a project that nevertheless came to nothing when Degas withdrew. Art historian and the artist's great-grandson Joachim Pissarro notes that they "professed a passionate disdain for the Salons and refused to exhibit at them." Together they shared an "almost militant resolution" against the Salon, and through their later correspondences it is clear that their mutual admiration "was based on a kinship of ethical as well as aesthetic concerns".
Cassatt had befriended Degas and Pissarro years earlier when she joined Pissarro's newly formed French Impressionist group and gave up opportunities to exhibit in the United States. She and Pissarro were often treated as "two outsiders" by the Salon since neither were French or had become French citizens. However, she was "fired up with the cause" of promoting Impressionism and looked forward to exhibiting "out of solidarity with her new friends". Towards the end of the 1890s she began to distance herself from the Impressionists, avoiding Degas at times as she did not have the strength to defend herself against his "wicked tongue". Instead, she came to prefer the company of "the gentle Camille Pissarro", with whom she could speak frankly about the changing attitudes toward art. She once described him as a teacher "that could have taught the stones to draw correctly."
Neo-Impressionist period

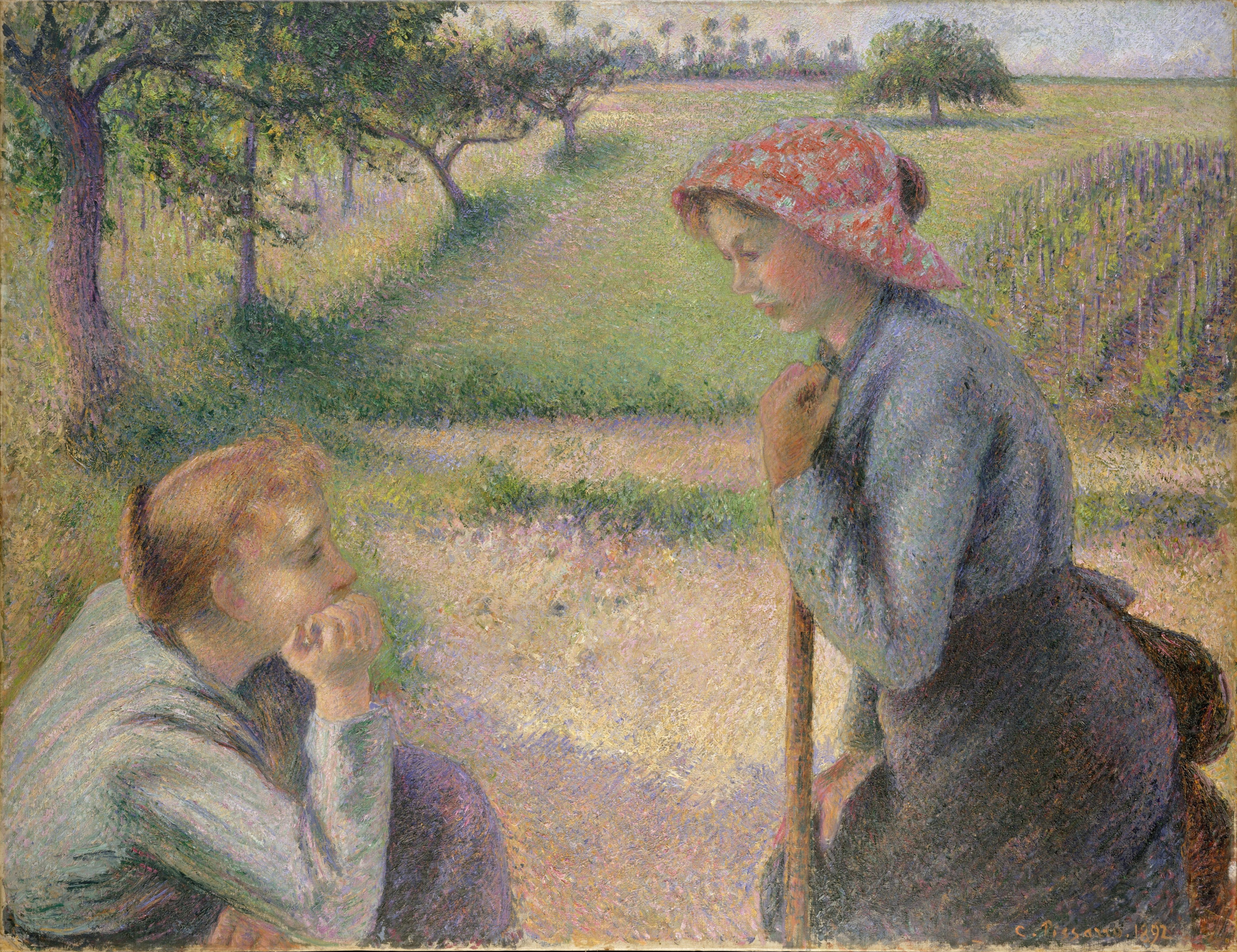
 By the 1880s, Pissarro began to explore new themes and methods of painting to break out of what he felt was an artistic "mire". As a result, Pissarro went back to his earlier themes by painting the life of country people, which he had done in Venezuela in his youth. Degas described Pissarro's subjects as "peasants working to make a living".
However, this period also marked the end of the Impressionist period due to Pissarro's leaving the movement. As Joachim Pissarro points out:
"Once such a die-hard Impressionist as Pissarro had turned his back on Impressionism, it was apparent that Impressionism had no chance of surviving ..."
It was Pissarro's intention during this period to help "educate the public" by painting people at work or at home in realistic settings, without idealising their lives.
By the 1880s, Pissarro began to explore new themes and methods of painting to break out of what he felt was an artistic "mire". As a result, Pissarro went back to his earlier themes by painting the life of country people, which he had done in Venezuela in his youth. Degas described Pissarro's subjects as "peasants working to make a living".
However, this period also marked the end of the Impressionist period due to Pissarro's leaving the movement. As Joachim Pissarro points out:
"Once such a die-hard Impressionist as Pissarro had turned his back on Impressionism, it was apparent that Impressionism had no chance of surviving ..."
It was Pissarro's intention during this period to help "educate the public" by painting people at work or at home in realistic settings, without idealising their lives. Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (; 25 February 1841 – 3 December 1919) was a French artist who was a leading painter in the development of the Impressionism, Impressionist style. As a celebrator of beauty and especially femininity, feminine sensuality ...
, in 1882, referred to Pissarro's work during this period as "revolutionary," in his attempt to portray the "common man." Pissarro himself did not use his art to overtly preach any kind of political message, however, although his preference for painting humble subjects was intended to be seen and purchased by his upper class clientele. He also began painting with a more unified brushwork along with pure strokes of color.
Studying with Seurat and Signac
In 1885 he met Georges Seurat and Paul Signac, both of whom relied on a more "scientific" theory of painting by using very small patches of pure colours to create the illusion of blended colours and shading when viewed from a distance. Pissarro then spent the years from 1885 to 1888 practising this more time-consuming and laborious technique, referred to as pointillism. The paintings that resulted were distinctly different from his Impressionist works, and were on display in the 1886 Impressionist Exhibition, but under a separate section, along with works by Seurat, Signac, and his son Lucien. All four works were considered an "exception" to the eighth exhibition. Joachim Pissarro notes that virtually every reviewer who commented on Pissarro's work noted "his extraordinary capacity to change his art, revise his position and take on new challenges." One critic writes: :"It is difficult to speak of Camille Pissarro ... What we have here is a fighter from way back, a master who continually grows and courageously adapts to new theories." Pissarro explained the new art form as a "phase in the logical march of Impressionism", but he was alone among the other Impressionists with this attitude, however. Joachim Pissarro states that Pissarro thereby became the "only artist who went from Impressionism toNeo-Impressionism
Neo-Impressionism is a term coined by French art critic Félix Fénéon in 1886 to describe an art movement founded by Georges Seurat. Seurat's most renowned masterpiece, ''A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte'', marked the begi ...
".
In 1884, art dealer Theo van Gogh asked Pissarro if he would take in his older brother, Vincent
Vincent ( la, Vincentius) is a male given name derived from the Roman name Vincentius, which is derived from the Latin word (''to conquer'').
People with the given name Artists
*Vincent Apap (1909–2003), Maltese sculptor
*Vincent van Gogh ...
, as a boarder in his home. Lucien Pissarro wrote that his father was impressed by Van Gogh's work and had "foreseen the power of this artist", who was 23 years younger. Although Van Gogh never boarded with him, Pissarro did explain to him the various ways of finding and expressing light and color, ideas which he later used in his paintings, notes Lucien.
Abandoning Neo-Impressionism
 Pissarro eventually turned away from Neo-Impressionism, claiming its system was too artificial. He explains in a letter to a friend:
:"Having tried this theory for four years and having then abandoned it ... I can no longer consider myself one of the neo-impressionists ... It was impossible to be true to my sensations and consequently to render life and movement, impossible to be faithful to the effects, so random and so admirable, of nature, impossible to give an individual character to my drawing, hatI had to give up."
However, after reverting to his earlier style, his work became, according to Rewald, "more subtle, his color scheme more refined, his drawing firmer ... So it was that Pissarro approached old age with an increased mastery."
But the change also added to Pissarro's continual financial hardship which he felt until his 60s. His "headstrong courage and a tenacity to undertake and sustain the career of an artist", writes Joachim Pissarro, was due to his "lack of fear of the immediate repercussions" of his stylistic decisions. In addition, his work was strong enough to "bolster his morale and keep him going", he writes. His Impressionist contemporaries, however, continued to view his independence as a "mark of integrity", and they turned to him for advice, referring to him as "Père Pissarro" (father Pissarro).
Pissarro eventually turned away from Neo-Impressionism, claiming its system was too artificial. He explains in a letter to a friend:
:"Having tried this theory for four years and having then abandoned it ... I can no longer consider myself one of the neo-impressionists ... It was impossible to be true to my sensations and consequently to render life and movement, impossible to be faithful to the effects, so random and so admirable, of nature, impossible to give an individual character to my drawing, hatI had to give up."
However, after reverting to his earlier style, his work became, according to Rewald, "more subtle, his color scheme more refined, his drawing firmer ... So it was that Pissarro approached old age with an increased mastery."
But the change also added to Pissarro's continual financial hardship which he felt until his 60s. His "headstrong courage and a tenacity to undertake and sustain the career of an artist", writes Joachim Pissarro, was due to his "lack of fear of the immediate repercussions" of his stylistic decisions. In addition, his work was strong enough to "bolster his morale and keep him going", he writes. His Impressionist contemporaries, however, continued to view his independence as a "mark of integrity", and they turned to him for advice, referring to him as "Père Pissarro" (father Pissarro).
Later years
 In his older age Pissarro suffered from a recurring eye infection that prevented him from working outdoors except in warm weather. As a result of this disability, he began painting outdoor scenes while sitting by the window of hotel rooms. He often chose hotel rooms on upper levels to get a broader view. He moved around northern France and painted from hotels in Rouen, Paris, Le Havre and Dieppe. On his visits to London, he would do the same.
Pissarro died in Paris on 13 November 1903 and was buried in Père Lachaise Cemetery.
In his older age Pissarro suffered from a recurring eye infection that prevented him from working outdoors except in warm weather. As a result of this disability, he began painting outdoor scenes while sitting by the window of hotel rooms. He often chose hotel rooms on upper levels to get a broader view. He moved around northern France and painted from hotels in Rouen, Paris, Le Havre and Dieppe. On his visits to London, he would do the same.
Pissarro died in Paris on 13 November 1903 and was buried in Père Lachaise Cemetery.
Legacy and influence
 During the period Pissarro exhibited his works, art critic Armand Silvestre had called Pissarro the "most real and most naive member" of the Impressionist group.Kelder, Diane. ''The Great Book of French Impressionism'', Abbeville Press (1980) pp. 127, 135 His work has also been described by art historian Diane Kelder as expressing "the same quiet dignity, sincerity, and durability that distinguished his person." She adds that "no member of the group did more to mediate the internecine disputes that threatened at times to break it apart, and no one was a more diligent proselytizer of the new painting."
According to Pissarro's son, Lucien, his father painted regularly with Cézanne beginning in 1872. He recalls that Cézanne walked a few miles to join Pissarro at various settings in Pontoise. While they shared ideas during their work, the younger Cézanne wanted to study the countryside through Pissarro's eyes, as he admired Pissarro's landscapes from the 1860s. Cézanne, although only nine years younger than Pissarro, said that "he was a father for me. A man to consult and a little like the good Lord."
Lucien Pissarro was taught painting by his father, and described him as a "splendid teacher, never imposing his personality on his pupil."
During the period Pissarro exhibited his works, art critic Armand Silvestre had called Pissarro the "most real and most naive member" of the Impressionist group.Kelder, Diane. ''The Great Book of French Impressionism'', Abbeville Press (1980) pp. 127, 135 His work has also been described by art historian Diane Kelder as expressing "the same quiet dignity, sincerity, and durability that distinguished his person." She adds that "no member of the group did more to mediate the internecine disputes that threatened at times to break it apart, and no one was a more diligent proselytizer of the new painting."
According to Pissarro's son, Lucien, his father painted regularly with Cézanne beginning in 1872. He recalls that Cézanne walked a few miles to join Pissarro at various settings in Pontoise. While they shared ideas during their work, the younger Cézanne wanted to study the countryside through Pissarro's eyes, as he admired Pissarro's landscapes from the 1860s. Cézanne, although only nine years younger than Pissarro, said that "he was a father for me. A man to consult and a little like the good Lord."
Lucien Pissarro was taught painting by his father, and described him as a "splendid teacher, never imposing his personality on his pupil." Gauguin
Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin (, ; ; 7 June 1848 – 8 May 1903) was a French Post-Impressionist artist. Unappreciated until after his death, Gauguin is now recognized for his experimental use of colour and Synthetist style that were distinct fro ...
, who also studied under him, referred to Pissarro "as a force with which future artists would have to reckon". Art historian Diane Kelder notes that it was Pissarro who introduced Gauguin, who was then a young stockbroker studying to become an artist, to Degas and Cézanne. Gauguin, near the end of his career, wrote a letter to a friend in 1902, shortly before Pissarro's death:
:"If we observe the totality of Pissarro's work, we find there, despite fluctuations, not only an extreme artistic will, never belied, but also an essentially intuitive, purebred art ... He was one of my masters and I do not deny him."
The American impressionist Mary Cassatt, who at one point lived in Paris to study art, and joined his Impressionist group, noted that he was "such a teacher that he could have taught the stones to draw correctly."
Caribbean author and scholar Derek Walcott based his book-length poem, ''Tiepolo's Hound'' (2000), on Pissarro's life.
The legacy of Nazi-looted Pissarros
 During the early 1930s throughout Europe, Jewish owners of numerous fine art masterpieces found themselves forced to give up or sell off their collections for minimal prices due to anti-Jewish laws created by the new Nazi regime. Many Jews were forced to flee Germany starting in 1933, and then, as the Nazis expanded their hold over all of Europe, Austria, France, Holland, Poland, Italy and other countries. The Nazis created special looting organizations like the Reichsleiter Rosenberg Taskforce whose mission it was to seize Jewish property notably valuable artworks. When those forced into exile or deported to extermination camps owned valuables, including artwork, they were often sold to finance the Nazi war effort, sent to Hitler's personal museum, traded or seized by officials for personal gain. Several artworks by Pissarro were looted from their Jewish owners in Germany, France and elsewhere by the Nazis.
Pissarro's '' Shepherdess Bringing Home the Sheep'' (La Bergère Rentrant des Moutons") was looted from the Jewish art collectors Yvonne et Raoul Meyer in France in 1941 and transited via Switzerland and New York before entering the Fred Jones Jr Museum at the University of Oklahoma. In 2014, Meyer's daughter, Léonie-Noëlle Meyer filed a restitution claim which resulted in years of court battle. The lawsuit resulted in the recognition of Meyer's ownership and its transfer to France for five years, coupled with an agreement to shuttle the painting back and forth between Paris and Oklahoma every three years after that. However, in 2020 Meyer filed suit in a French court to challenge the accord. After Fred Jones Jr Museum sued Meyer requesting heavy financial penalties, the Holocaust survivor abandoned her effort to recover the Pissarro, saying, "I have no other choice.
Pissarro's Picking Peas (La Cueillette) was looted from Jewish businessman Simon Bauer, in addition to 92 other artworks seized in 1943 by the Vichy collaborationist regime in France.
Pissarro's ''Sower And Ploughman,'' was owned by Dr Henri Hinrichsen, a Jewish music publisher from Leipzig, until 11 January 1940, when he was forced to relinquish the painting to Hildebrand Gurlitt in Nazi-occupied Brussels, before being murdered in Auschwitz in September 1942.
Pissarro's “Le Quai Malaquais, Printemps”, owned by German Jewish publisher
During the early 1930s throughout Europe, Jewish owners of numerous fine art masterpieces found themselves forced to give up or sell off their collections for minimal prices due to anti-Jewish laws created by the new Nazi regime. Many Jews were forced to flee Germany starting in 1933, and then, as the Nazis expanded their hold over all of Europe, Austria, France, Holland, Poland, Italy and other countries. The Nazis created special looting organizations like the Reichsleiter Rosenberg Taskforce whose mission it was to seize Jewish property notably valuable artworks. When those forced into exile or deported to extermination camps owned valuables, including artwork, they were often sold to finance the Nazi war effort, sent to Hitler's personal museum, traded or seized by officials for personal gain. Several artworks by Pissarro were looted from their Jewish owners in Germany, France and elsewhere by the Nazis.
Pissarro's '' Shepherdess Bringing Home the Sheep'' (La Bergère Rentrant des Moutons") was looted from the Jewish art collectors Yvonne et Raoul Meyer in France in 1941 and transited via Switzerland and New York before entering the Fred Jones Jr Museum at the University of Oklahoma. In 2014, Meyer's daughter, Léonie-Noëlle Meyer filed a restitution claim which resulted in years of court battle. The lawsuit resulted in the recognition of Meyer's ownership and its transfer to France for five years, coupled with an agreement to shuttle the painting back and forth between Paris and Oklahoma every three years after that. However, in 2020 Meyer filed suit in a French court to challenge the accord. After Fred Jones Jr Museum sued Meyer requesting heavy financial penalties, the Holocaust survivor abandoned her effort to recover the Pissarro, saying, "I have no other choice.
Pissarro's Picking Peas (La Cueillette) was looted from Jewish businessman Simon Bauer, in addition to 92 other artworks seized in 1943 by the Vichy collaborationist regime in France.
Pissarro's ''Sower And Ploughman,'' was owned by Dr Henri Hinrichsen, a Jewish music publisher from Leipzig, until 11 January 1940, when he was forced to relinquish the painting to Hildebrand Gurlitt in Nazi-occupied Brussels, before being murdered in Auschwitz in September 1942.
Pissarro's “Le Quai Malaquais, Printemps”, owned by German Jewish publisher Samuel Fischer
Samuel Fischer, later Samuel von Fischer (24 December 1859 – 15 October 1934), was a Hungarian-born German publisher, the founder of S. Fischer Verlag. Fischer was born in Liptau-Sankt-Nikolaus/Liptószentmiklós (now Liptovský Mikuláš), ...
, founder of the famous S. Fischer Verlag, passed through the hands of infamous Nazi art looter Bruno Lohse
Bruno Lohse (17 September 1911 – 19 March 2007) was a German art dealer and SS-Hauptsturmführer who, during World War II, became the chief art looter in Paris for Hermann Göring, helping the Nazi leader amass a vast collection of plundered ...
.
Pissarro's ''Le Boulevard de Montmartre, Matinée de Printemps'', owned by Max Silberberg, a German Jewish industrialist whose renowned art collection was considered "one of the best in pre-war Germany", was seized and sold in a forced auction before Silberberg and his wife Johanna were murdered in Auschwitz.
In the decades after World War II, many art masterpieces were found on display in various galleries and museums in Europe and the United States, often with false provenances and labels missing. Some, as a result of legal action, were later returned to the families of the original owners. Many of the recovered paintings were then donated to the same or other museums as a gift.
One such lost piece, Pissarro's 1897 oil painting, '' Rue St. Honoré, Apres Midi, Effet de Pluie'', was discovered hanging at Madrid's government-owned museum, the Museo Thyssen-Bornemisza
The Thyssen-Bornemisza National Museum (in Spanish, the Museo Nacional Thyssen-Bornemisza (), named after its founder), or simply the Thyssen, is an art museum in Madrid, Spain, located near the Prado Museum on one of the city's main boulevards. I ...
. In January 2011 the Spanish government denied a request by the US ambassador to return the painting. At the subsequent trial in Los Angeles, the court ruled that the Thyssen-Bornemisza Collection Foundation was the rightful owner. In 1999, Pissarro's 1897 '' Le Boulevard de Montmartre, Matinée de Printemps'' appeared in the Israel Museum in Jerusalem, its donor having been unaware of its pre-war provenance. In January 2012, ''Le Marché aux Poissons'' (The Fish Market), a color monotype, was returned after 30 years.
During his lifetime, Camille Pissarro sold few of his paintings. By the 21st century, however, his paintings were selling for millions. An auction record for the artist was set on 6 November 2007 at Christie's
Christie's is a British auction house founded in 1766 by James Christie. Its main premises are on King Street, St James's in London, at Rockefeller Center in New York City and at Alexandra House in Hong Kong. It is owned by Groupe Artémi ...
in New York, where a group of four paintings, ''Les Quatre Saisons'' (the Four Seasons), sold for $14,601,000 (estimate $12,000,000 – $18,000,000). In November 2009 ''Le Pont Boieldieu et la Gare d'Orléans, Rouen, Soleil'' sold for $7,026,500 at Sotheby's
Sotheby's () is a British-founded American multinational corporation with headquarters in New York City. It is one of the world's largest brokers of fine and decorative art, jewellery, and collectibles. It has 80 locations in 40 countries, an ...
in New York.
In February 2014 the 1897 ''Le Boulevard de Montmartre, Matinée de Printemps'', originally owned by the German industrialist and Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
victim Max Silberberg ( de), sold at Sotheby's in London for £19.9M, nearly five times the previous record.
In October 2021 Berlin's Alte Nationalgalerie restituted Pissarro's "A Square in La Roche-Guyon" (1867) to the heirs of Armand Dorville, a French Jewish art collector whose family was persecuted by the Nazis and whose paintings had been sold at a 1942 auction in Nice that was overseen by the Commissariat Général aux Questions Juives. The museum then purchased the Pissarro back.
Hermitage Museum
The State Hermitage Museum ( rus, Государственный Эрмитаж, r=Gosudarstvennyj Ermitaž, p=ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)ɨj ɪrmʲɪˈtaʂ, links=no) is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is the larges ...
File:Boulevard Montmartre- Mardi Gras (frameless).jpg, ''Boulevard Montmartre: Mardi Gras'', 1897. Hammer Museum
The Hammer Museum, which is affiliated with the University of California, Los Angeles, is an art museum and cultural center known for its artist-centric and progressive array of exhibitions and public programs. Founded in 1990 by the entrepreneur ...
File:Camille Pissarro - Boulevard Montmartre, morning, cloudy weather - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Boulevard Montmartre, morning, cloudy weather'', 1897. National Gallery of Victoria
File:The Boulevard Montmartre on a Winter Morning.JPG, ''The Boulevard Montmartre on a Winter Morning'', 1897. Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
File:Camille Pissarro - Boulevard Montmartre, Spring - Google Art Project.jpg, '' Le Boulevard de Montmartre, Matinée de Printemps'', street view from hotel window, 1897
File:Camille Pissarro - Boulevard Montmartre at Night - c 1897 - National Gallery UK.jpg, ''The Boulevard Montmartre at Night'', 1897. National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director ...
A family of painters
Camille's son Lucien was an Impressionist and Neo-impressionist painter as were his second and third sons Georges Henri Manzana Pissarro and Félix Pissarro. Lucien's daughterOrovida Pissarro
Orovida Pissarro (8 October 1893 – 8 August 1968), known for most of her life as Orovida, was a British painter and etcher. For most of her career she distanced herself from the Impressionist and Post-Impressionist styles of her father, Lucie ...
was also a painter. Camille's great-grandson, Joachim Pissarro
Joachim Pissarro (born 1959) is an art historian, theoretician, curator, educator, and director of the Hunter College Galleries and Bershad Professor of Art History at Hunter College of the City University of New York. Since 2002, Pissarro has ser ...
, became Head Curator of Drawing and Painting at the Museum of Modern Art
The Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) is an art museum located in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, on 53rd Street between Fifth and Sixth Avenues.
It plays a major role in developing and collecting modern art, and is often identified as one of t ...
in New York City and a professor in Hunter College's Art Department. Camille's great-granddaughter, Lélia Pissarro, has had her work exhibited alongside her great-grandfather. Another great-granddaughter, Julia Pissarro, a Barnard College
Barnard College of Columbia University is a private women's liberal arts college in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It was founded in 1889 by a group of women led by young student activist Annie Nathan Meyer, who petitioned Columbia ...
graduate, is also active in the art scene. From the only daughter of Camille, Jeanne Pissarro, other painters include Henri Bonin-Pissarro (1918–2003) and Claude Bonin-Pissarro (born 1921), who is the father of the Abstract artist Frédéric Bonin-Pissarro (born 1964).
The grandson of Camille Pissarro, Hugues Claude Pissarro (dit Pomié), was born in 1935 in the western section of Paris, Neuilly-sur-Seine, and began to draw and paint as a young child under his father's tutelage. During his adolescence and early twenties he studied the works of the great masters at the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
. His work has been featured in exhibitions in Europe and the United States, and he was commissioned by the White House in 1959 to paint a portrait of U.S. President Dwight Eisenhower. He now lives and paints in Donegal, Ireland, with his wife Corinne also an accomplished artist and their children.
Paintings
Louveciennes
Louveciennes () is a commune in the Yvelines department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France. It is located in the western suburbs of Paris, between Versailles and Saint-Germain-en-Laye, and adjacent to Marly-le-Roi.
Populat ...
'', 1870. Musée d'Orsay, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
File:Camille Pissarro - Allée dans le parc de Marly.jpg, ''The Woods at Marly'', 1871. Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum
File:La Route.jpg, ''The Road to Versailles, Louveciennes: Morning Frost'', 1871. Dallas Museum of Art
File:Pissaro, Camille, Still Life Apples and Pears.jpg, ''Still Life: Apples and Pears in a Round Basket'', 1872. The Henry and Rose Pearlman Collection, on long-term loan to the Princeton University Art Museum
The Princeton University Art Museum (PUAM) is the Princeton University gallery of art, located in Princeton, New Jersey. With a collecting history that began in 1755, the museum was formally established in 1882, and now houses over 113,000 works ...
File:Camille Pissarro - Paul Cézanne.jpg, Camille Pissarro, ''Portrait of Paul Cézanne
Paul Cézanne ( , , ; ; 19 January 1839 – 22 October 1906) was a French artist and Post-Impressionist painter whose work laid the foundations of the transition from the 19th-century conception of artistic endeavour to a new and radically d ...
'', 1874. National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director ...
File:Camille Pissarro A Cowherd at Valhermeil, Auvers-sur-Oise The Metropolitan Museum of Art.jpg, '' A Cowherd at Valhermeil, Auvers-sur-Oise'', 1874. Metropolitan Museum of Art
File:MuMA - Pissarro - Un carrefour à l'Hermitage, Pontoise.JPG, ''Un Carrefour à l'Hermitage, Pontoise'', 1876. Musée Malraux
File:Camille Pissarro - Red roofs, corner of a village, winter - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Toits rouges, coin d'un village, hiver'', Côte de Saint-Denis, Pontoise, 1877. Musée d'Orsay, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
Image:Camille Pissarro - The Côte des Bœufs at L'Hermitage - National Gallery London.jpg, ''The Côte des Bœufs at L'Hermitage'', 1877. National Gallery
The National Gallery is an art museum in Trafalgar Square in the City of Westminster, in Central London, England. Founded in 1824, it houses a collection of over 2,300 paintings dating from the mid-13th century to 1900. The current Director ...
Image:Camille Pissarro - Dans le jardin des Mathurins, Pontoise - 503.jpg, ''The Garden of Pontoise'', 1877
File:Camille Pissarro Washerwoman, Study The Metropolitan Museum of Art.jpg, ''Washerwoman, Study'', 1880. Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
File:Camille Pissarro - Conversation - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Conversation'', c. 1881. National Museum of Western Art
File:The Harvest, Pontoise.jpg, '' The Harvest, Pontoise'', 1881. Metropolitan Museum of Art
File:Camille Pissarro - The Harvest - Google Art Project.jpg, ''The Harvest'', 1882. Bridgestone Museum of Art
Artizon Museum , until 2018 , is an art museum in Tokyo, Japan.
The museum was founded in 1952 by the founder of Bridgestone Tire Co., Ishibashi Shojiro (his family name means stone bridge). The museum's collections include Impressionists, ...
, Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.46 ...
File:CAMILLE PISSARRO (1830-1903) Le jardin de Maubuisson, Pontoise, la mère Bellette 21 7-16 x 25 7-8 in. (54.5 x 65.7cm).jpg, ''Le jardin de Maubuisson, Pontoise'', 1882
File:The Church at Eragny Pissarro.jpg, ''The Church at Eragny'', 1884. Walters Art Museum
File:Route Enneigée avec maison, environs d'Éragny by Camille Pissarro.jpg, ''Route Enneigée avec maison, environs d'Éragny'', 1885
Image:Bergère rentrant des moutons.jpg, ''Shepherdess Bringing in Sheep (Bergère rentrant des moutons)'' 1886. University of Oklahoma
File:Camille Pissarro 019.jpg, ''Children on a Farm,'' 1887. Collection of G. Signac, Paris
Image:Camille Pissarro 016.jpg, ''Haying at Eragny'', 1889
File:Pissarro—Old Chelsea Bridge.jpg, ''Old Chelsea Bridge, London'' 1890. Smith College Museum of Arts
File:The Place du Havre, Paris.jpg, ''Place du Havre'', Paris, 1893. Art Institute of Chicago
File:Morning, An Overcast Day, Rouen MET DT1863.jpg, '' Morning, An Overcast Day, Rouen'', 1896. Metropolitan Museum of Art
File:14 oct 2014 theatre fr.jpg, ''Place du Théâtre Français: Fog Effect'', 1897. Dallas Museum of Art
File:Camille Pissarro 036.jpg, ''Rouen, Rue de l'Épicerie'', 1898
File:Camille Pissarro, The Garden of the Tuileries on a Winter Afternoon, 1899.jpg, '' The Garden of the Tuileries on a Winter Afternoon'', 1899, Metropolitan Museum of Art
File:Camille Pissarro - La Place due Théâtre Français - Google Art Project.jpg, ''La Place du Théâtre Français'', 1898. Los Angeles County Museum of Art
The Los Angeles County Museum of Art (LACMA) is an art museum located on Wilshire Boulevard in the Miracle Mile vicinity of Los Angeles. LACMA is on Museum Row, adjacent to the La Brea Tar Pits (George C. Page Museum).
LACMA was founded in 19 ...
File:Camille Pissarro (1830-1903) - 'View of Rouen', 1898.jpg, ''View of Rouen'', 1898. Honolulu Museum of Art
File:WLA_metmuseum_Camille_Pissarro_French.jpg, ''The Garden of the Tuileries on a Spring Morning'', 1899. Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
File:Camille Pissarro (1830-1903) - 'Morning, Winter Sunshine, Frost, the Pont-Neuf, the Seine, the Louvre, Soleil D'hiver Gella Blanc', ca. 1901.jpg, ''Morning, Winter Sunshine, Frost, the Pont-Neuf, the Seine, the Louvre, Soleil D'hiver Gella Blanc'', c. 1901. Honolulu Museum of Art
File:Pissarro havre.jpg, ''Ship entering the Harbor at Le Havre'', 1903. Dallas Museum of Art
File:Camille Pissarro - The Fish Market in Dieppe, Grey Weather, Morning - 1902 - Dallas Museum of Art.jpg, ''The Fish Market, Dieppe: Grey Weather, Morning'', c 1902. Dallas Museum of Art
Drawings and prints
Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
File:Camille Pissarro - Boulevard de Rochechouart, 1880. Pastel, Sterling and Francine Clark Art Institute.jpg, ''Boulevard de Rochechouart'', 1880, pastel on beige wove paper
File:Camille Pissarro - Paysage a Osny - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Landscape in Osny
Osny () is a commune in the Val-d'Oise department, in the northwestern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the center of Paris, in the "new town" of Cergy-Pontoise, created in the 1960s.
Population
Transportation
Osny is served by ...
'', 1887, etching on Holland paper. Museum of Fine Arts, Houston
File:Camille Pissarro-Faneuses d'Eragny.jpg, ''Tedders of Eragny'' (Faneuses d'Eragny), 1897, etching, aquatint and dry-point on paper. Strasbourg Museum of Modern and Contemporary Art
File:Paysanne Nouant son Foulard by Camille Pissarro.jpg, ''Paysanne Nouant son Foulard'', 1882, pastel on paper
List of paintings
*'' The Banks of the Oise near Pontoise'' 1873, Indianapolis Museum of Art *'' Pont Boieldieu in Rouen, Rainy Weather'', 1896, Art Gallery of Ontario *'' Steamboats in the Port of Rouen'', 1896, Metropolitan Museum of Art *'' Le Boulevard de Montmartre, Matinée de Printemps'', view from window, 1897, private collection * '' Hay Harvest at Éragny'', 1901, National Gallery of Canada *'' Self-portrait'', 1903, Tate Gallery, LondonReferences
Bibliography
* Rewald, John, ed., with the assistance of Lucien Pissarro: ''Camille Pissarro, Lettres à son fils Lucien'', Editions Albin Michel, Paris 1950; previously published, translated to English: ''Camille Pissarro, Letters to his son Lucien'', New York 1943 & London 1944; 3rd revised edition, Paul P Appel Publishers, 1972 * Bailly-Herzberg, Janine, ed.: ', 5 volumes, Presses Universitaires de France, Paris, 1980 & Editions du Valhermeil, Paris, 1986–1991 – – – – * * Thorold, Anne, ed.: ''The letters of Lucien to Camille Pissarro 1883–1903'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York & Oakleigh, 1993Further reading
* Clement, Russell T. and Houze, Annick, '' Neo-Impressionist Painters: A Sourcebook on Georges Seurat, Camille Pissarro, Paul Signac, Théo van Rysselberghe, Henri-Edmond Cross, Charles Angrand, Maximilien Luce, and Albert Dubois-Pillet'' (1999), Greenwood Press, * Eitner, Lorenz, ''An Outline of 19th Century European Painting: From David through Cézanne'' (1992), HarperCollins Publishers, * Nochlin, Linda, ''The Politics of Vision: Essays on Nineteenth-Century Art and Society'' (1991) Westview Press, * Rewald, John, '' The History of Impressionism'' (1961), Museum of Modern Art, * Stone, Irving, ''Depths of Glory'' (1987), Signet, * Tabarant, A., ''Pissarro'' (1925), John Lane the Bodley Head Ltd., translated by J. Lewis May''Critical Catalogue of Paintings''
In June 2006, a three-volume work of 1,500 pages was published, titled ''Pissarro: Critical Catalogue of Paintings''. It was compiled by Joachim Pissarro, descendant of the painter, and Claire Durand-Ruel Snollaerts, descendant of the French art dealer Paul Durand-Ruel. The work is the most comprehensive collection of Pissarro paintings to date. It contains accompanying images of drawings and studies, as well as photographs of Pissarro and his family that had not previously been published.External links
Camille Pissarro Protests Alfred Dreyfus' Conviction: Original Letter
Shapell Manuscript Foundation
Photograph of Pissarro's mausoleum at Cimetière Père Lachaise, Paris
(
JPG
JPEG ( ) is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image ...
)
''Pissarro's People'', exhibition held at the Sterling and Francine Clark Art Institute, Williamstown MA, 12 June – 2 October 2011
Union List of Artist Names, Getty Vocabularies.
ULAN Full Record Display for Camille Pissarro. Getty Vocabulary Program, Getty Research Institute. Los Angeles, California. *
Exhibition Pissarro dans les ports, 2013, Museum of modern art André Malraux – MuMa
Camille Pissarro Personal Manuscripts
Camille Pissarro at The Jewish Museum
''Pissarro Paintings and Works on Paper at the Art Institute of Chicago''
one of the Art Institute of Chicago'
digital scholarly catalogues
*Jennifer A. Thompson,
''L’île Lacroix, Rouen (The Effect of Fog)'' by Camille Pissarro (cat. 1060)
” in
The John G. Johnson Collection: A History and Selected Works
', a Philadelphia Museum of Art free digital publication
An artwork by Camille Pissarro
at th
Ben Uri
site {{DEFAULTSORT:Pissarro, Camille 1830 births 1903 deaths 19th-century Danish painters 19th-century Danish male artists 20th-century Danish painters 20th-century Danish male artists 19th-century French painters 19th-century French male artists 20th-century French painters 20th-century French male artists Danish male painters French male painters People from the Danish West Indies People from Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands Danish Sephardi Jews French expatriates in England French Impressionist painters 19th-century French Sephardi Jews Jewish painters École des Beaux-Arts alumni School of Paris Jewish School of Paris Burials at Père Lachaise Cemetery French people of Portuguese-Jewish descent French people of Creole descent Danish people of French descent Danish people of Portuguese-Jewish descent United States Virgin Islands Jews