Camelback locomotive on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A camelback locomotive (also known as a Mother Hubbard or a center-cab locomotive) is a type of
 The
The 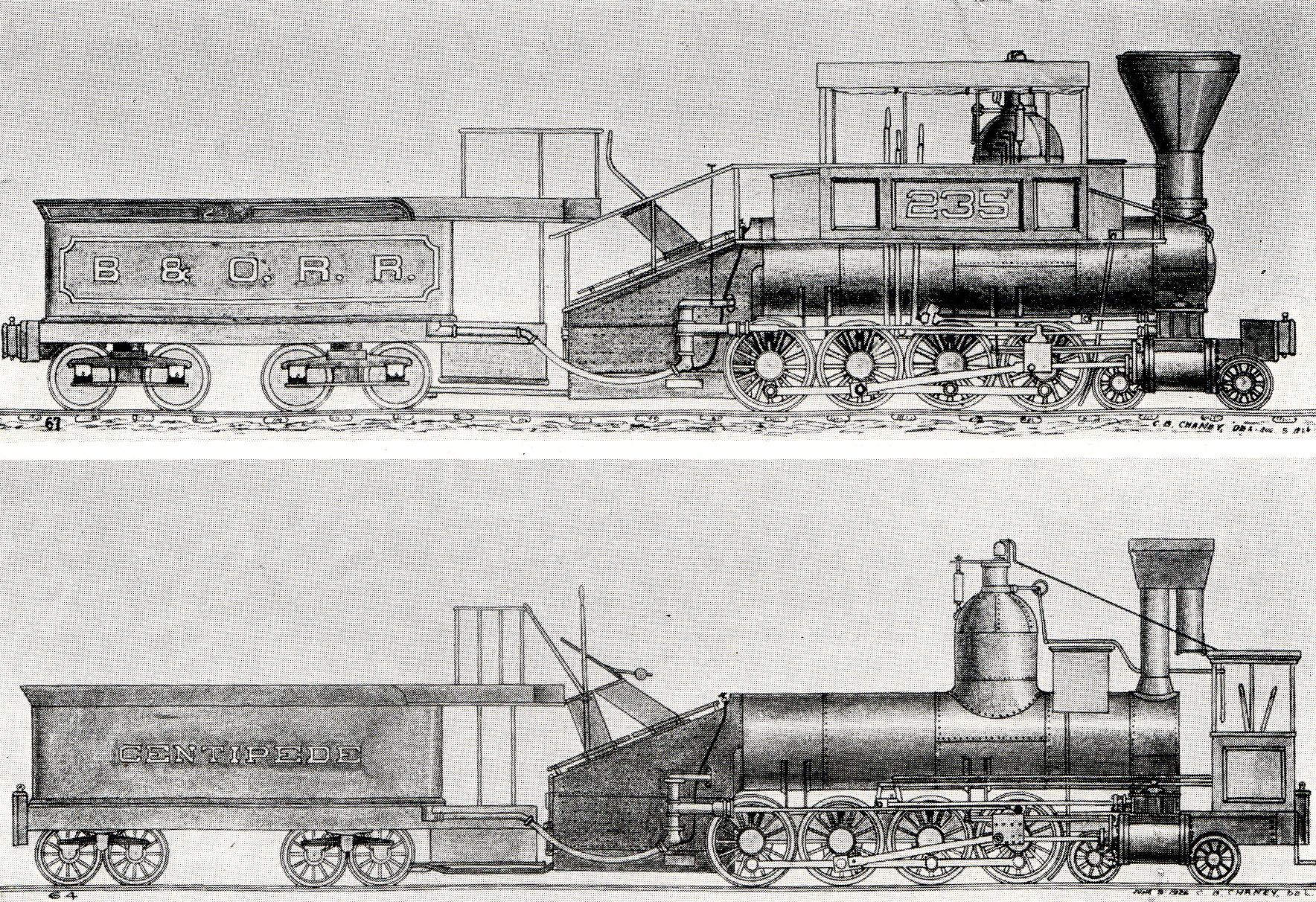 In 1853 Ross Winans, who had designed the "muddiggers", built the first of a series of
In 1853 Ross Winans, who had designed the "muddiggers", built the first of a series of
 John E. Wootten developed the Wootten
John E. Wootten developed the Wootten
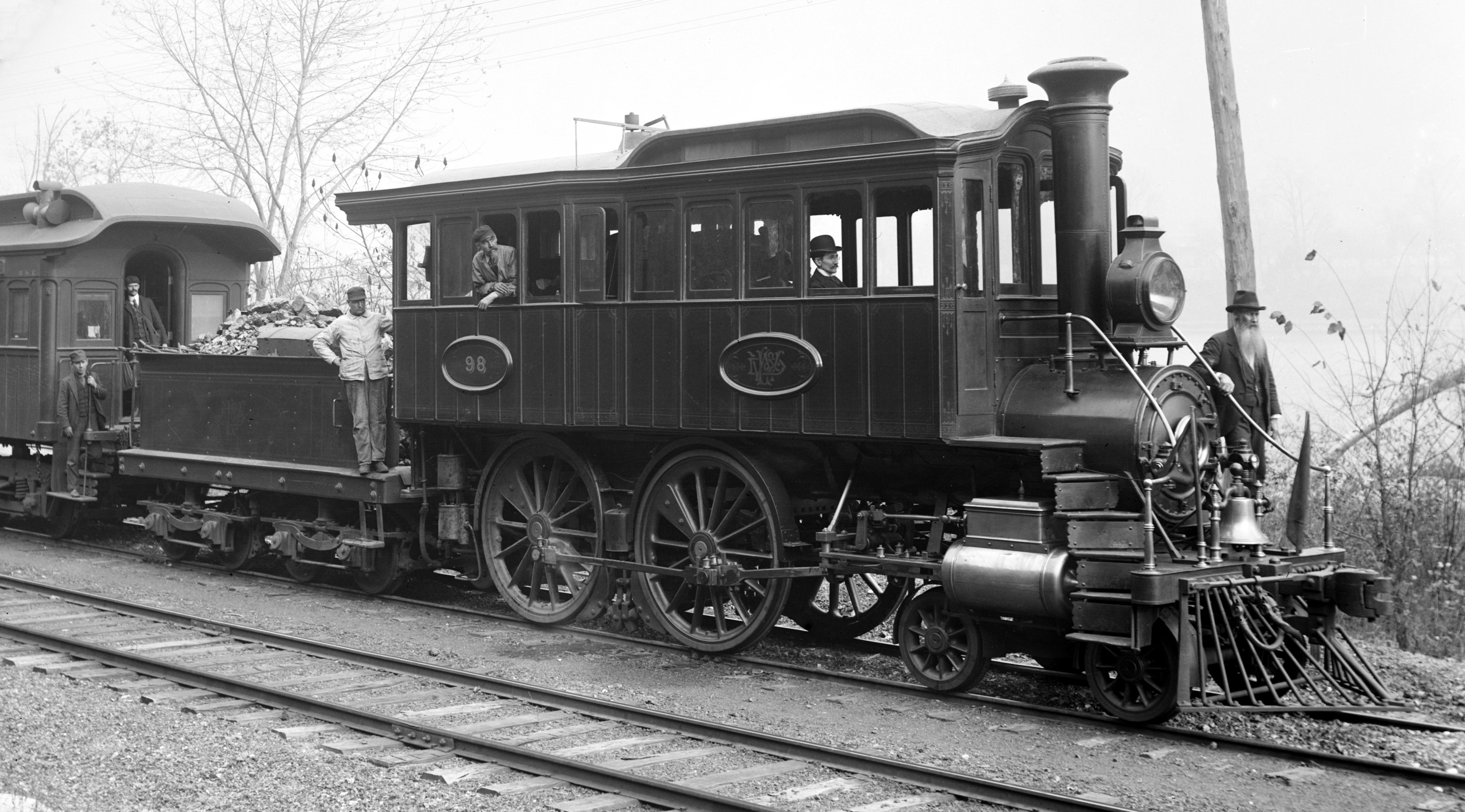 The Camelback's cab astride the boiler design raised concerns for its crew. The separation of engineer and fireman limited their ability to communicate with each other. Also, the engineer was perched above the side-rods of the locomotive, vulnerable to swinging and flying metal if anything rotating below should break; in many cases, the fireman was exposed to the elements at the rear.
While several states attempted to ban camelback engines, they were overturned due to Federal supremacy regarding railroad safety. The ICC held hearings on banning camelbacks, but they were never actually banned because by the time the hearings were held, the camelback was an obsolete design and were no longer being produced.
The Philadelphia and Reading's crews referred to these locomotives as Mother Hubbards. The B&O crews, who had co-use of the Reading's line from Philadelphia to Bound Brook NJ (the Reading's junction with the Central RR of New Jersey's line to Jersey City across from New York City) called the Camelbacks "Snappers" in reference to a possible side rod snapping and flailing into the cab. Many Camelbacks were converted into end-cab locomotives. The advent of the
The Camelback's cab astride the boiler design raised concerns for its crew. The separation of engineer and fireman limited their ability to communicate with each other. Also, the engineer was perched above the side-rods of the locomotive, vulnerable to swinging and flying metal if anything rotating below should break; in many cases, the fireman was exposed to the elements at the rear.
While several states attempted to ban camelback engines, they were overturned due to Federal supremacy regarding railroad safety. The ICC held hearings on banning camelbacks, but they were never actually banned because by the time the hearings were held, the camelback was an obsolete design and were no longer being produced.
The Philadelphia and Reading's crews referred to these locomotives as Mother Hubbards. The B&O crews, who had co-use of the Reading's line from Philadelphia to Bound Brook NJ (the Reading's junction with the Central RR of New Jersey's line to Jersey City across from New York City) called the Camelbacks "Snappers" in reference to a possible side rod snapping and flailing into the cab. Many Camelbacks were converted into end-cab locomotives. The advent of the
steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the loco ...
with the driving cab placed in the middle, astride the boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central ...
. Camelbacks were fitted with wide fireboxes which would have severely restricted driver visibility from the normal cab location at the rear.
Development
The camel and the camelback design were developed separately by two different railroads in different eras. Though the name is often incorrectly used interchangeably, they had little in common other than the placement of the cab. Unlike the later Camelbacks, Camels had cabs that rode atop the boiler. Ross Winans wanted to put as much weight on the driving wheels as possible to increase traction. Camelbacks have a cab that straddles the boiler. While Camelbacks have the same idea of moving the cab forward, they had it for different reasons. Camelbacks were developed to allow for the use of larger fireboxes, such as the Wootten, which would obstruct the engineer's view from a conventionally placed cab. Camelbacks were particularly known for being used on the Central Railroad of New Jersey and the Reading Railroad.Early use
 The
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of ...
began to look into developing high-powered steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the loco ...
s in the early 1840s, and in 1844–1847 built a series of locomotives nicknamed "muddiggers". As with many early B&O locomotives, a spur gear drive was used to connect the main shaft to the driving wheels. The long 0-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and no trailing wheels. Locomotives of this type are also referr ...
wheelbase pushed this connection to the back of the locomotive and caused the floor of the cab to be lifted up above the whole assembly.
 In 1853 Ross Winans, who had designed the "muddiggers", built the first of a series of
In 1853 Ross Winans, who had designed the "muddiggers", built the first of a series of 0-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and no trailing wheels. Locomotives of this type are also referr ...
camel locomotives. These had long cabs that ran from the back of the smokebox
A smokebox is one of the major basic parts of a steam locomotive exhaust system. Smoke and hot gases pass from the firebox through tubes where they pass heat to the surrounding water in the boiler. The smoke then enters the smokebox, and is e ...
to the front of the firebox
Firebox may refer to:
* Firebox (steam engine), the area where the fuel is burned in a steam engine
* Firebox (architecture), the part of a fireplace where fuel is combusted
*Firebox Records, a Finnish 8101705801record label
* Firebox.com, an elect ...
. The firebox itself sloped back on the earliest models. The fireman worked from a large platform on the tender, and in some cases had a chute to allow him to deliver coal to the front of the grate.
Also in 1853, Samuel Hayes, the Master of Machinery for the railroad, had built a series of camel 4-6-0
A 4-6-0 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, has four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the ...
locomotives for passenger service. The layout of the locomotive was roughly the same as for Winans' freight locomotives, except for the addition of the four-wheel leading bogie
A bogie ( ) (in some senses called a truck in North American English) is a chassis or framework that carries a wheelset, attached to a vehicle—a modular subassembly of wheels and axles. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transp ...
. Copies and variations on these locomotives were built into the 1870s, with the last retirements coming in the 1890s. These were called the "Hayes Ten-Wheelers".
Many camelback locomotives used anthracite
Anthracite, also known as hard coal, and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic luster. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the hig ...
.
The B&O examples burned conventional bituminous coal
Bituminous coal, or black coal, is a type of coal containing a tar-like substance called bitumen or asphalt. Its coloration can be black or sometimes dark brown; often there are well-defined bands of bright and dull material within the seams. It ...
. The large fireboxes of these locomotives were made obsolete by better boiler design.
The B&O Railroad Museum has recently restored their Camel Locomotive and returned it to display. It now is in its original colors and markings for the first time since it left the Mt. Clare Shops in 1869. The Museum also has a Central of New Jersey Camelback, the
No. 592, which was donated to the Museum in the 1950s.
The Wootten firebox
 John E. Wootten developed the Wootten
John E. Wootten developed the Wootten firebox
Firebox may refer to:
* Firebox (steam engine), the area where the fuel is burned in a steam engine
* Firebox (architecture), the part of a fireplace where fuel is combusted
*Firebox Records, a Finnish 8101705801record label
* Firebox.com, an elect ...
to effectively burn culm, anthracite
Anthracite, also known as hard coal, and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic luster. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the hig ...
waste, which was a plentiful, cheap source of fuel. Wootten determined that a large, wide firebox would work best. As the successful trailing truck used to support large fireboxes had not yet been developed, Wootten instead mounted his huge firebox above the locomotive's driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled ...
s.
First Camelbacks
Originally Wooten firebox engines were built with the cab sitting upon the top of the firebox, in the rear. The first Wooten firebox locomotives 4-6-0 "Ten Wheeler" types were built in early 1877 by the P&R'sReading, Pennsylvania
Reading ( ; Pennsylvania Dutch: ''Reddin'') is a city in and the county seat of Berks County, Pennsylvania, United States. The city had a population of 95,112 as of the 2020 census and is the fourth-largest city in Pennsylvania after Philade ...
shops. However they were not a "camelback" design. The Wooten firebox proved a success; the fuel cost saving was about $2,000 a year (approx. $30,000 now). A Wooten firebox engine, P&R 412 was exhibited at the 1879 International Technological Exhibition in Paris, where it won a silver medal. Following the exhibition it toured Europe, first to sell anthracite coal and later to sell Wooten firebox engines. The engine could not demonstrate on European lines because, due to the cab sitting on top of the firebox, it was too tall to fit under bridges and through tunnels. The 412's engineer C. Gilbert Steffe came up with a solution. In a French railroad yard, he had the cab removed from the firebox and placed forward of the firebox on the running boards, creating the first camelback locomotive. The engine demonstrated in France and Italy through 1879 and was returned to the U.S. in 1880. Because the camelback design allowed for a taller firebox, the design was used by many of the railroads operating in the anthracite regions of Pennsylvania. By the time of World War 1, the diameter of locomotive boilers had increased to the point the cab astride the boiler was no longer practical and railroads stopped building camelbacks and subsequent Wooten firebox engines were built with conventional end cabs. Camelback engines were constructed with many different wheel arrangements, 0-4-0, 0-6-0, 0-8-0, 2-6-0, 2-8-0, 2-8-2, 4-4-0, and 4-6-0 were the most common wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement or wheel configuration is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed under a locomotive. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and c ...
s. The largest ones had a 0-8-8-0
In the Whyte notation for classifying the wheel arrangement of steam locomotives, an 0-8-8-0 is a locomotive with two sets of eight driving wheels and neither leading wheels nor trailing wheels. Two sets of driving wheels would give far too lon ...
arrangement and were the only articulated
An articulated vehicle is a vehicle which has a permanent or semi-permanent pivot joint in its construction, allowing it to turn more sharply. There are many kinds, from heavy equipment to buses, trams and trains. Steam locomotives were sometim ...
Camelbacks built.
Later Camelbacks
By the 1920s, many Camelback Ten Wheelers with boiler pressure at 200psi were in daily use pulling passenger trains on the Lehigh Valley, the Philadelphia and Reading, and the Central Railroad of New Jersey, particularly the last two. For their relatively small size, they were powerful, quick to accelerate, very stable at speed, and could be operated as fast as 90 miles per hour such as on the Reading's Atlantic City line. Some continued in service into the 1950s.Safety Concerns
 The Camelback's cab astride the boiler design raised concerns for its crew. The separation of engineer and fireman limited their ability to communicate with each other. Also, the engineer was perched above the side-rods of the locomotive, vulnerable to swinging and flying metal if anything rotating below should break; in many cases, the fireman was exposed to the elements at the rear.
While several states attempted to ban camelback engines, they were overturned due to Federal supremacy regarding railroad safety. The ICC held hearings on banning camelbacks, but they were never actually banned because by the time the hearings were held, the camelback was an obsolete design and were no longer being produced.
The Philadelphia and Reading's crews referred to these locomotives as Mother Hubbards. The B&O crews, who had co-use of the Reading's line from Philadelphia to Bound Brook NJ (the Reading's junction with the Central RR of New Jersey's line to Jersey City across from New York City) called the Camelbacks "Snappers" in reference to a possible side rod snapping and flailing into the cab. Many Camelbacks were converted into end-cab locomotives. The advent of the
The Camelback's cab astride the boiler design raised concerns for its crew. The separation of engineer and fireman limited their ability to communicate with each other. Also, the engineer was perched above the side-rods of the locomotive, vulnerable to swinging and flying metal if anything rotating below should break; in many cases, the fireman was exposed to the elements at the rear.
While several states attempted to ban camelback engines, they were overturned due to Federal supremacy regarding railroad safety. The ICC held hearings on banning camelbacks, but they were never actually banned because by the time the hearings were held, the camelback was an obsolete design and were no longer being produced.
The Philadelphia and Reading's crews referred to these locomotives as Mother Hubbards. The B&O crews, who had co-use of the Reading's line from Philadelphia to Bound Brook NJ (the Reading's junction with the Central RR of New Jersey's line to Jersey City across from New York City) called the Camelbacks "Snappers" in reference to a possible side rod snapping and flailing into the cab. Many Camelbacks were converted into end-cab locomotives. The advent of the mechanical stoker
A mechanical stoker is a mechanical system that feeds solid fuel like coal, coke or anthracite into the furnace of a steam boiler. They are common on steam locomotives after 1900 and are also used on ships and power stations. Known now as a spre ...
which moved coal from the tender to the locomotive and its associated underfloor machinery placed cab floors and tender decks higher, and from that vantage point the engineer was safe.
Survivors
There are five known Camelback locomotives to survive today: * Central Railroad of New Jersey 4-4-2 No. 592, at theBaltimore & Ohio Railroad Museum
The B&O Railroad Museum is a museum and historic railway station exhibiting historic railroad equipment in Baltimore, Maryland. The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) company originally opened the museum on July 4, 1953, with the name of the Balt ...
in Baltimore, Maryland
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore wa ...
.
* Baltimore & Ohio Railroad 4-6-0 No. 173, at the National Museum of Transportation
The National Museum of Transportation (NMOT) is a private, 42-acre transportation museum in the Kirkwood suburb of St. Louis, Missouri. Founded in 1944, it restores, preserves, and displays a wide variety of vehicles spanning 15 decades of Amer ...
, St. Louis.
* Baltimore & Ohio Railroad 4-6-0 No. 305 (formerly No. 217), at the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad Museum in Baltimore, Maryland.
* Delaware, Lackawanna & Western 4-4-0 No. 952, at the Museum of Transportation in St. Louis, Missouri.
* Reading Company 0-4-0 No. 1187, at the Age of Steam Roundhouse
The Age of Steam Roundhouse Museum, Sugarcreek, Ohio, United States, is a museum roundhouse housing steam and diesel locomotives, passenger cars and other railroad equipment.
History
The roundhouse was built by Jerry Joe Jacobson, former CEO of ...
Museum in Sugarcreek, Ohio
Sugarcreek is a village in Tuscarawas County, Ohio. It includes the community formerly known as Shanesville. The population was 2,220 at the 2010 census. It is known as "The Little Switzerland of Ohio." In the center of town stands one of t ...
. (awaiting cosmetic restoration)
Owning railroads
*Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway
The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway , often referred to as the Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. The railroad was chartered in February 1859 to serve the cities of Atchison and Topeka, Kansas, and ...
* Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of ...
* Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canad ...
* Central Railroad of New Jersey
The Central Railroad of New Jersey, also known as the Jersey Central or Jersey Central Lines , was a Class I railroad with origins in the 1830s. It was absorbed into Conrail in April 1976 along with several other prominent bankrupt railroads of ...
* Chicago and Eastern Illinois Railroad
The Chicago and Eastern Illinois Railroad was a Class I railroad that linked Chicago to southern Illinois, St. Louis, and Evansville. Founded in 1877, it grew aggressively and stayed relatively strong throughout the Great Depression and two ...
* Chicago and Indiana Coal Railroad
* Choctaw, Oklahoma and Gulf Railroad
The Choctaw, Oklahoma and Gulf Railroad (CO&G), known informally as the "Choctaw Route," was an American railroad in the states of Arkansas and Oklahoma. The company, originally known as the Choctaw Coal and Railway Company, completed its main li ...
* Delaware and Hudson Railway
The Delaware and Hudson Railway (D&H) is a railroad that operates in the Northeastern United States. In 1991, after more than 150 years as an independent railroad, the D&H was purchased by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP). CP operates D&H ...
* Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad
The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (also known as the DL&W or Lackawanna Railroad) was a U.S. Class 1 railroad that connected Buffalo, New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey (and by ferry with New York City), a distance of . Incorporated in ...
* Bath & Hammondsport Railroad
B&H Rail Corporation , formerly the Bath & Hammondsport Railroad, is a Class III shortline railroad. Initially the line served the communities of Bath, New York and Hammondsport, New York. In Bath, the railroad connected with the Erie Railroad and ...
* Erie Railroad
The Erie Railroad was a railroad that operated in the northeastern United States, originally connecting New York City — more specifically Jersey City, New Jersey, where Erie's Pavonia Terminal, long demolished, used to stand — with Lake ...
* Hecla and Torch Lake Railroad
* Lehigh and Hudson River Railway
The Lehigh and Hudson River Railway (L&HR) was the smallest of the six railroads that were merged into Conrail in 1976. It was a bridge line running northeast–southwest across northwestern New Jersey, connecting the line to the Poughkeepsie B ...
* Lehigh and New England Railroad
The Lehigh & New England Railroad was a Class I railroad located in Northeastern United States that acted as a bridge line. It was the second notable U.S. railroad to file for abandonment in its entirety, the first being the New York, Ontari ...
* Lehigh Valley Railroad
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad built in the Northeastern United States to haul anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Pennsylvania. The railroad was authorized on April 21, 1846 for freight and transportation of passengers, goods, ...
* Long Island Rail Road
The Long Island Rail Road , often abbreviated as the LIRR, is a commuter rail system in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County on Long Island. With an average week ...
* Maine Central Railroad
The Maine Central Railroad Company was a U. S. Class I railroad in central and southern Maine. It was chartered in 1856 and began operations in 1862. By 1884, Maine Central was the longest railroad in New England. Maine Central had expanded to ...
* Missouri-Kansas-Texas Railroad
* Nashville, Chattanooga and St. Louis Railway
* New York, Ontario and Western Railway
The New York, Ontario and Western Railway, more commonly known as the O&W or NYO&W, was a regional railroad with origins in 1868, lasting until March 29, 1957 (the last train ran from Norwich to Middletown, NY on this date), after which it was or ...
* New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway
The New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway (or New York, Susquehanna and Western Railroad and also known as the Susie-Q or the Susquehanna) is a Class II American freight railway operating over 400 miles (645 km) of track in t ...
* Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named ...
* Reading Railroad
The Reading Company ( ) was a Philadelphia-headquartered railroad that provided passenger and commercial rail transport in eastern Pennsylvania and neighboring states that operated from 1924 until its 1976 acquisition by Conrail.
Commonly call ...
* St. Clair Tunnel Company
* Staten Island Rapid Transit
* Southern Pacific Railroad
The Southern Pacific (or Espee from the railroad initials- SP) was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the ...
* Union Pacific Railroad
The Union Pacific Railroad , legally Union Pacific Railroad Company and often called simply Union Pacific, is a freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Paci ...
* Wheeling and Lake Erie Railroad
References
* * * * Steam locomotive types *{{cite book, last=Holton, first=James, title=The Reading Railroad: History of a Coal Age Empire, vol. 1, publisher=Garrigues House, year=1989