Caloocan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Caloocan, officially the City of Caloocan ( fil, Lungsod ng Caloocan; ), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in
 Originally, Caloocan was the area where the old town of Tondo and Tambobong met, located along the shores of Dagat-Dagatan, a crescent-shaped inland lagoon to the west. The settlement along the shore was called "Aromahan", or "Espina" to the Spaniards, and was separated from Manila Bay by a narrow ridge from Tondo towards an opening in Kinabutasan leading to the sea.
By the late 1700s, the fishermen of Aromahan has expanded towards a hill east of Dagat-Dagatan. This naturally stony hill was called "Kaloogan", meaning "interior territory", which evolved from the old Tagalog word "loog" (synonymous with "loob" or "inside"). The "g" sound could have shifted to the "k" sound in Tagalog phonetics (e.g. baksak > bagsak) leading to the present name of the city. With Aromahan relegated to the periphery, this hilltop area was also settled by oppressed people from Tondo, becoming the new center of the community by 1802. To the east was a vast stretch of cogon-covered land. Eventually called "Kalaanan", meaning flat grassland in old Tagalog, this area is now generally known as Grace Park.
Caloocan became a municipality when it was separated from Tondo in 1815. Its original territory extended to the foothills of Marikina, San Mateo and Montalban to the east; Tinajeros,
Originally, Caloocan was the area where the old town of Tondo and Tambobong met, located along the shores of Dagat-Dagatan, a crescent-shaped inland lagoon to the west. The settlement along the shore was called "Aromahan", or "Espina" to the Spaniards, and was separated from Manila Bay by a narrow ridge from Tondo towards an opening in Kinabutasan leading to the sea.
By the late 1700s, the fishermen of Aromahan has expanded towards a hill east of Dagat-Dagatan. This naturally stony hill was called "Kaloogan", meaning "interior territory", which evolved from the old Tagalog word "loog" (synonymous with "loob" or "inside"). The "g" sound could have shifted to the "k" sound in Tagalog phonetics (e.g. baksak > bagsak) leading to the present name of the city. With Aromahan relegated to the periphery, this hilltop area was also settled by oppressed people from Tondo, becoming the new center of the community by 1802. To the east was a vast stretch of cogon-covered land. Eventually called "Kalaanan", meaning flat grassland in old Tagalog, this area is now generally known as Grace Park.
Caloocan became a municipality when it was separated from Tondo in 1815. Its original territory extended to the foothills of Marikina, San Mateo and Montalban to the east; Tinajeros,  In 1899, the people of Caloocan showed resistance to coming to terms with the Americans, who were bent on extending their supremacy over the country. The men of Caloocan fought the new invaders on February 23, 1899, however victory eluded the local troops on the pretext of
In 1899, the people of Caloocan showed resistance to coming to terms with the Americans, who were bent on extending their supremacy over the country. The men of Caloocan fought the new invaders on February 23, 1899, however victory eluded the local troops on the pretext of
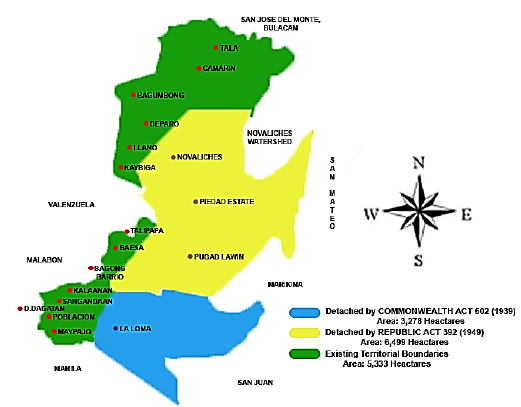 Caloocan once encompassed a much larger, contiguous area. The districts of Balintawak, La Loma and
Caloocan once encompassed a much larger, contiguous area. The districts of Balintawak, La Loma and
 South Caloocan, where most commercial and industrial establishments are found, lies on generally flat and highly accessible land, with slopes ranging from 0-3%. The topography gradually changes into gently to moderately sloping to rolling along the North Luzon Expressway, with slopes ranging from 3-18%. The highest point at above sea level can be found in this area, while the lowest point is in the southern part of Dagat-Dagatan at about above mean sea level.
North Caloocan is characterized with gently to steeply undulating to rolling topography with slopes ranging from 3-18%, mostly seen in the northern and central portion, gradually transforming into a southward trend of flat lands down to the southwestern tip of the boundary. Being accessible to major roads, many industrial and residential subdivisions have been developed in this near-level land.
South Caloocan, where most commercial and industrial establishments are found, lies on generally flat and highly accessible land, with slopes ranging from 0-3%. The topography gradually changes into gently to moderately sloping to rolling along the North Luzon Expressway, with slopes ranging from 3-18%. The highest point at above sea level can be found in this area, while the lowest point is in the southern part of Dagat-Dagatan at about above mean sea level.
North Caloocan is characterized with gently to steeply undulating to rolling topography with slopes ranging from 3-18%, mostly seen in the northern and central portion, gradually transforming into a southward trend of flat lands down to the southwestern tip of the boundary. Being accessible to major roads, many industrial and residential subdivisions have been developed in this near-level land.

 The LRT Line 1 has two stations in the southern part of the city, namely: Monumento and
The LRT Line 1 has two stations in the southern part of the city, namely: Monumento and
 The city's most celebrated landmark is the
The city's most celebrated landmark is the
 The city's one public university is the
The city's one public university is the
File:BonifacioMonumentjf9889 04.JPG,
* {{Authority control Cities in Metro Manila Populated places established in 1815 1815 establishments in the Philippines Highly urbanized cities in the Philippines Enclaves and exclaves
Metropolitan Manila
Metropolitan Manila (often shortened as Metro Manila; fil, Kalakhang Maynila), officially the National Capital Region (NCR; fil, link=no, Pambansang Punong Rehiyon), is the seat of government and one of three defined metropolitan areas in ...
, Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 1,661,584 people making it the fourth-most populous city in the Philippines.
Caloocan is divided into two geographical locations with a total combined area of . It was formerly part of the Province of Rizal of the Philippines' Southern Luzon Region. It comprises what is known as the CAMANAVA area along with cities Malabon, Navotas
Navotas, officially the City of Navotas ( fil, Lungsod ng Navotas), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 247,543 people.
It is known as the ...
and Valenzuela Valenzuela may refer to:
Places
* Valenzuela, Paraguay
* Valenzuela, Metro Manila, Philippines
* Valenzuela, Spain
* Valenzuela de Calatrava, Spain
* Valenzuela, Louisiana
Other uses
* Valenzuela (surname), including a list of people with the n ...
.
South Caloocan is bordered by Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
, Quezon City
Quezon City (, ; fil, Lungsod Quezon ), also known as the City of Quezon and Q.C. (read in Filipino as Kyusi), is the most populous city in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 2,960,048 people. It was fou ...
, Malabon, Navotas and Valenzuela. Presence of commercial and industrial activities combined with residential areas make it a highly urbanized central business district and a major urban center in the Northern District of Metropolitan Manila. North Caloocan shares its border with Quezon City and Valenzuela, Marilao
Marilao, officially the Municipality of Marilao ( tgl, Bayan ng Marilao), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 254,453 people.
With the continuous expansion of ...
, Meycauayan
Meycauayan, officially the City of Meycauayan ( fil, Lungsod ng Meycauayan), is a 3rd class component city in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 225,673 people. It is one of the oldest t ...
and San Jose del Monte
San Jose del Monte, officially the City of San Jose del Monte (abbreviated as SJDM or CSJDM; fil, Lungsod ng San Jose del Monte), is a 1st class component city in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a po ...
in the province of Bulacan, and Rodriguez in the province of Rizal. It is composed of mostly residential subdivisions and extensive resettlement areas with scattered distribution of industrial estates mostly within road transit points and intersections.
Etymology
Caloocan as atoponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
comes from the Tagalog root word ''lo-ok''; ''kalook-lookan'' (or ''kaloob-looban'') means "innermost area". The city's name is colloquially spelled as Kalookan.
There is a mixed preference over the preferred spelling of the city's name. Variation, and the apparent confusion over the spelling, came about during the early 1970s, when a resolution was adopted by the municipal board, requiring the city departments to use the name "Kalookan." The execution of the said resolution was interrupted when the country was placed under martial law
Martial law is the imposition of direct military control of normal civil functions or suspension of civil law by a government, especially in response to an emergency where civil forces are overwhelmed, or in an occupied territory.
Use
Marti ...
in September 1972. After the restoration of city and municipal councils, in 1988, then-councilor Aurora Asistio-Henson filed Resolution No. 006, amending the previous resolution and seeking to promote Filipino nationalism
Filipino nationalism refers to the establishment and support of a political identity associated with the modern nation-state of the Philippines, leading to a wide-ranging campaign for political, social, and economic freedom in the Philippines. ...
by requiring all residents and all offices and establishments in the city, "whether public or private," to spell the name of the city as "Kalookan." According to Henson, the "Filipinized spelling" provides essence and significance to the city's history, and she added that it should be used "in the city hall, the barangay halls, public markets, and other places for the information and guidance of all concerned." Nevertheless, this change in spelling was denounced by the city residents, business owners, and officials. Former representative and mayor Virgilio Robles declared the move illegal because it lacked congressional approval. He added that the city's name is spelled as "Caloocan" as shown in the city charter. The general inclination of spelling in the city is "Caloocan" and not "Kalookan," despite the existing city ordinance, although confusion has led to varied spelling choices of many businesses throughout the city. The official logo has the city's name spelled as "Caloocan," and such spelling is favored by many barangays and public and private schools in the city. "Kalookan" is preferred by the Makati
Makati ( ), officially the City of Makati ( fil, Lungsod ng Makati), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines.
Makati is the financial center of the Philippines; it has the highest concentration ...
-based Directories of the Philippines Corporation (DPC), while many national newspapers and magazines, and mapmakers like the Mandaluyong-based HYDN Publishing favor "Caloocan."
History
 Originally, Caloocan was the area where the old town of Tondo and Tambobong met, located along the shores of Dagat-Dagatan, a crescent-shaped inland lagoon to the west. The settlement along the shore was called "Aromahan", or "Espina" to the Spaniards, and was separated from Manila Bay by a narrow ridge from Tondo towards an opening in Kinabutasan leading to the sea.
By the late 1700s, the fishermen of Aromahan has expanded towards a hill east of Dagat-Dagatan. This naturally stony hill was called "Kaloogan", meaning "interior territory", which evolved from the old Tagalog word "loog" (synonymous with "loob" or "inside"). The "g" sound could have shifted to the "k" sound in Tagalog phonetics (e.g. baksak > bagsak) leading to the present name of the city. With Aromahan relegated to the periphery, this hilltop area was also settled by oppressed people from Tondo, becoming the new center of the community by 1802. To the east was a vast stretch of cogon-covered land. Eventually called "Kalaanan", meaning flat grassland in old Tagalog, this area is now generally known as Grace Park.
Caloocan became a municipality when it was separated from Tondo in 1815. Its original territory extended to the foothills of Marikina, San Mateo and Montalban to the east; Tinajeros,
Originally, Caloocan was the area where the old town of Tondo and Tambobong met, located along the shores of Dagat-Dagatan, a crescent-shaped inland lagoon to the west. The settlement along the shore was called "Aromahan", or "Espina" to the Spaniards, and was separated from Manila Bay by a narrow ridge from Tondo towards an opening in Kinabutasan leading to the sea.
By the late 1700s, the fishermen of Aromahan has expanded towards a hill east of Dagat-Dagatan. This naturally stony hill was called "Kaloogan", meaning "interior territory", which evolved from the old Tagalog word "loog" (synonymous with "loob" or "inside"). The "g" sound could have shifted to the "k" sound in Tagalog phonetics (e.g. baksak > bagsak) leading to the present name of the city. With Aromahan relegated to the periphery, this hilltop area was also settled by oppressed people from Tondo, becoming the new center of the community by 1802. To the east was a vast stretch of cogon-covered land. Eventually called "Kalaanan", meaning flat grassland in old Tagalog, this area is now generally known as Grace Park.
Caloocan became a municipality when it was separated from Tondo in 1815. Its original territory extended to the foothills of Marikina, San Mateo and Montalban to the east; Tinajeros, Tanza
Tanza, officially the Municipality of Tanza ( tgl, Bayan ng Tanza), formerly known as Santa Cruz de Malabón, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cavite, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 312,116 people ...
, and Tala rivers to the north; Pasig
Pasig, officially the City of Pasig ( fil, Lungsod ng Pasig), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 803,159 people.
It is located along t ...
, San Juan del Monte, San Francisco del Monte, Sampalok, Santa Cruz and Tondo in the south; and Dagat-dagatan and Aromahan to the west. The local government building was set up on the relatively well-settled portion just above Libis Espina. The old Aromahan chapel was finally abandoned and a new church was built facing the municipal hall. To escape the Spanish authorities, many from the area abandoned the town proper and sought refuge in the grasslands of Balintawak and Pugad-Lawin, in which the people fought the landlords of Hacienda de Maysilo for terrestrial rights, which went on for almost a hundred years.
Caloocan is historically significant because it was the center of activities for the Katipunan
The Katipunan, officially known as the Kataastaasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan or Kataastaasan Kagalang-galang na Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan (KKK; en, Supreme and Honorable Association of the Children of the Nation ...
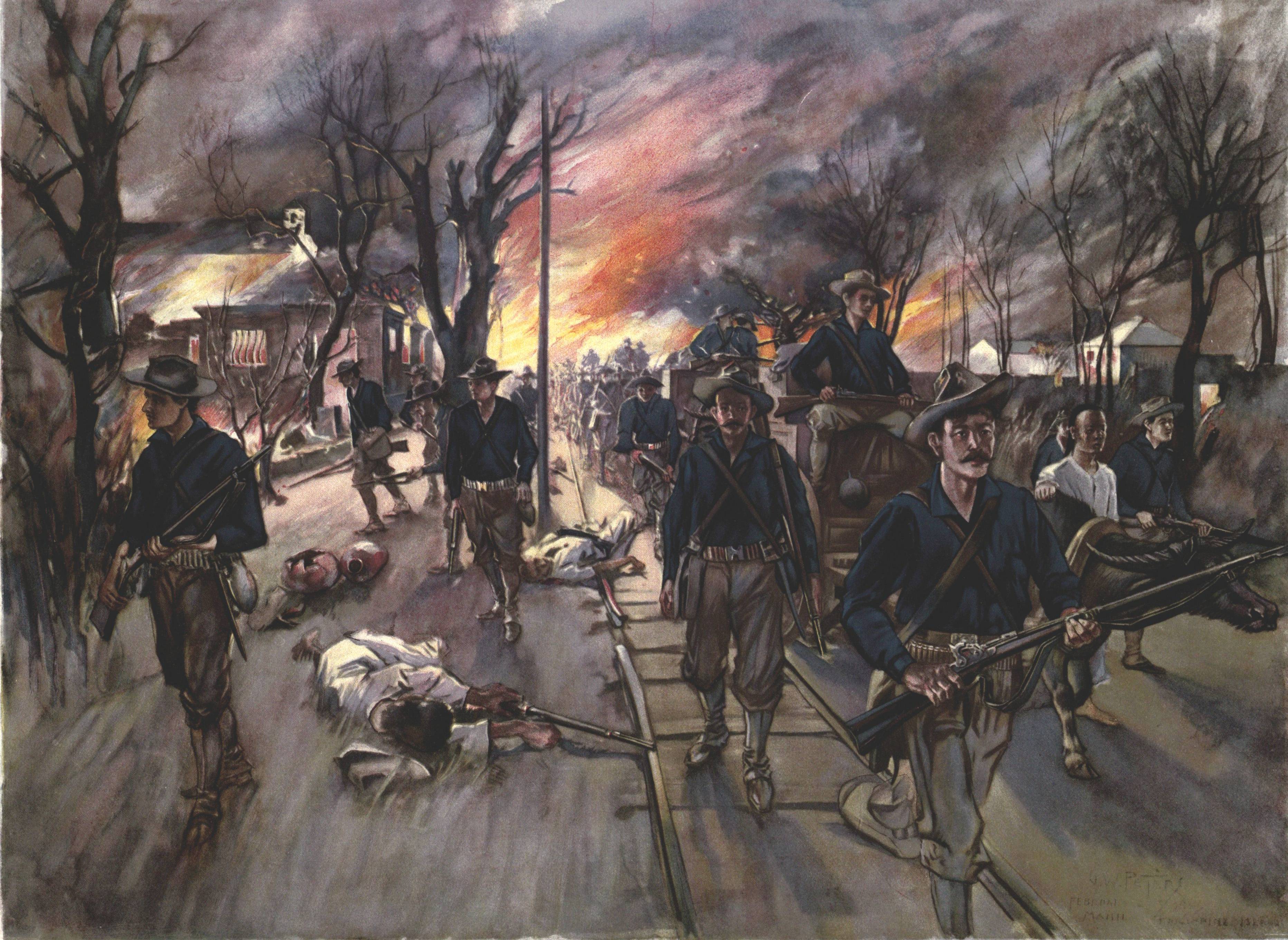
, the secret militant society that launched the Philippine Revolution during the Spanish occupation of the Philippines. In a house in Caloocan, secret meetings were held by Andrés Bonifacio and his men, and it was in the city's perimeters where the first armed encounter took place between the Katipunan and the Spaniards. The revolution erupted after the " Cry of Balintawak" led by Andres Bonifacio against their oppressors on August 30, 1896.
 In 1899, the people of Caloocan showed resistance to coming to terms with the Americans, who were bent on extending their supremacy over the country. The men of Caloocan fought the new invaders on February 23, 1899, however victory eluded the local troops on the pretext of
In 1899, the people of Caloocan showed resistance to coming to terms with the Americans, who were bent on extending their supremacy over the country. The men of Caloocan fought the new invaders on February 23, 1899, however victory eluded the local troops on the pretext of Antonio Luna
Antonio Narciso Luna de San Pedro y Novicio Ancheta (; October 29, 1866 – June 5, 1899) was a Filipino army general who fought in the Philippine–American War before his assassination in 1899.
Regarded as one of the fiercest generals of hi ...
's rift with Emilio Aguinaldo's loyalists. The city then saw heavy fighting in the Philippine–American War, at the Battle of Caloocan
The Battle of Caloocan was one of the opening engagements of the Philippine–American War, and was fought between a U.S. force under the command of Arthur MacArthur Jr. and Filipino defenders commanded by Antonio Luna in 1899. American troops ...
and the Second Battle of Caloocan
The Second Battle of Caloocan ( fil, Ikalawang Labanan sa Caloocan, es, Segunda Batalla de Caloocan), alternately called the Second Battle of Manila, was fought from February 22 to 24, 1899, in Caloocan during the Philippine–American War. Th ...
.
In 1901, under the American regime, Caloocan, previously a part of the province of Manila, became one of the municipalities of the newly established province of Rizal. Due to the consolidation of several municipalities in 1903, Novaliches
Novaliches is a place that forms the northern areas of Quezon City, and encompasses the whole area of North Caloocan.
Etymology
The name Novaliches came from the name of the small village of Novaliches in the town of Jérica, Spain. It was ...
, then an independent municipality, became part of Caloocan pursuant to Act No. 942, as amended by Act Nos. 984 and 1008 of the Philippine Commission
The Philippine Commission was the name of two bodies, both appointed by the president of the United States, to assist with governing the Philippines.
The first Philippine Commission, also known as the Schurman Commission, was appointed by Presi ...
.
In 1942, Caloocan was one of the municipalities of Rizal merged alongside Manila and Quezon City to form the City of Greater Manila
The City of Greater Manila, also known simply as Greater Manila and sometimes Greater Manila Area (GMA), was a chartered city which existed during the World War II era. It was governed by the Commonwealth of the Philippines and was dissolved by ...
as an emergency measure by President Manuel L. Quezon. It regained its pre-war status as a municipality of Rizal when the City of Greater Manila was dissolved effective August 1, 1945.
Cityhood
In 1961, after Republic Act No. 3278 was approved by the Philippine Congress, a plebiscite was conducted. Caloocan was officially inducted into cityhood on February 16, 1962. Caloocan remained a city of the province of Rizal until November 7, 1975, when it became a part of the National Capital Region orMetro Manila
Metropolitan Manila (often shortened as Metro Manila; fil, Kalakhang Maynila), officially the National Capital Region (NCR; fil, link=no, Pambansang Punong Rehiyon), is the seat of government and one of three defined metropolitan areas in ...
, by virtue of Presidential Decree No. 824.
Territorial changes
 Caloocan once encompassed a much larger, contiguous area. The districts of Balintawak, La Loma and
Caloocan once encompassed a much larger, contiguous area. The districts of Balintawak, La Loma and Novaliches
Novaliches is a place that forms the northern areas of Quezon City, and encompasses the whole area of North Caloocan.
Etymology
The name Novaliches came from the name of the small village of Novaliches in the town of Jérica, Spain. It was ...
were once part of Caloocan. Balintawak is a historic district because it was the original site of the "Cry of Pugad Lawin" (Unang Sigaw sa Balintawak) at a location called "Kang-kong" near Tandang Sora
Melchora Aquino de Ramos (January 6, 1812 – February 19, 1919) was a Filipino revolutionary. She became known as "Tandang Sora" because of her age during the Philippine Revolution.
She was known as the "Grand Woman of the Revolution" an ...
's house. Novaliches was an expansive sector with some hillsides that served as meeting places and hideouts for Andrés Bonifacio and the ''Katipunan''.
By the 1920s, there was a consolidation of several municipalities. Caloocan annexed the neighboring town of Novaliches, as stated in the Act No. 942, as amended by Act Nos. 984 and 1008 of the Philippine Commission
The Philippine Commission was the name of two bodies, both appointed by the president of the United States, to assist with governing the Philippines.
The first Philippine Commission, also known as the Schurman Commission, was appointed by Presi ...
, bringing its total area to about . When Commonwealth Act No. 502 created Quezon City
Quezon City (, ; fil, Lungsod Quezon ), also known as the City of Quezon and Q.C. (read in Filipino as Kyusi), is the most populous city in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 2,960,048 people. It was fou ...
in 1939, Caloocan ceded 1,500 hectares of land from the barrios or sitios of Bagubantay (Bago Bantay), Balintauac (Balintawák), Balingasa
Balingasa, commonly known as Balintawak and Cloverleaf, is an administrative division in eastern Metro Manila, the Philippines. It is an urban barangay located in Quezon City, at the city's western boundary with Caloocan.
The barangay's borde ...
, Kaingin, Kangkong (present-day Apolonio Samson), La Loma, Malamig, Matalahib (present-day Santo Domingo), Masambong, Galas, San Isidro, San José, Santol and Tatalon. Instead of opposing the transfer, Caloocan residents willingly gave the land in the belief it will benefit the country's new capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
.
However, in 1949, Congress passed Republic Act No. 392, which redefined the Caloocan–Quezon City boundary. The barrios of Baesa, Sangandaan, Talipapâ, San Bartolomé, Pasong Tamó, Novaliches Proper (poblacion), Banlat (present-day Tandang Sora), Kabuyao, Pugad Lawin, Bagbag, Pasong Putik, which once belonged to Novaliches and had an area of about , were excised from Caloocan. The remaining portion of the Novaliches is now called North Caloocan. This split Caloocan into two parts: a southern section that is more urbanized, and a northern section that became suburban-rural.
Geography
Caloocan is divided into two non-contiguous areas with a total combined area of . South Caloocan, with an area of , is bordered on the south byManila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populate ...
, on the east by Quezon City
Quezon City (, ; fil, Lungsod Quezon ), also known as the City of Quezon and Q.C. (read in Filipino as Kyusi), is the most populous city in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 2,960,048 people. It was fou ...
, and on the north-northwest by Malabon, Navotas
Navotas, officially the City of Navotas ( fil, Lungsod ng Navotas), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 247,543 people.
It is known as the ...
and Valenzuela Valenzuela may refer to:
Places
* Valenzuela, Paraguay
* Valenzuela, Metro Manila, Philippines
* Valenzuela, Spain
* Valenzuela de Calatrava, Spain
* Valenzuela, Louisiana
Other uses
* Valenzuela (surname), including a list of people with the n ...
. North Caloocan, with an area of , shares its border on the south-southeast by Quezon City
Quezon City (, ; fil, Lungsod Quezon ), also known as the City of Quezon and Q.C. (read in Filipino as Kyusi), is the most populous city in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 2,960,048 people. It was fou ...
, on the southwest by Valenzuela Valenzuela may refer to:
Places
* Valenzuela, Paraguay
* Valenzuela, Metro Manila, Philippines
* Valenzuela, Spain
* Valenzuela de Calatrava, Spain
* Valenzuela, Louisiana
Other uses
* Valenzuela (surname), including a list of people with the n ...
, on the north by Marilao
Marilao, officially the Municipality of Marilao ( tgl, Bayan ng Marilao), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 254,453 people.
With the continuous expansion of ...
, Meycauayan
Meycauayan, officially the City of Meycauayan ( fil, Lungsod ng Meycauayan), is a 3rd class component city in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 225,673 people. It is one of the oldest t ...
and San Jose del Monte
San Jose del Monte, officially the City of San Jose del Monte (abbreviated as SJDM or CSJDM; fil, Lungsod ng San Jose del Monte), is a 1st class component city in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a po ...
in the province of Bulacan, and on the northeast by Rodriguez in the province of Rizal.
Topography
 South Caloocan, where most commercial and industrial establishments are found, lies on generally flat and highly accessible land, with slopes ranging from 0-3%. The topography gradually changes into gently to moderately sloping to rolling along the North Luzon Expressway, with slopes ranging from 3-18%. The highest point at above sea level can be found in this area, while the lowest point is in the southern part of Dagat-Dagatan at about above mean sea level.
North Caloocan is characterized with gently to steeply undulating to rolling topography with slopes ranging from 3-18%, mostly seen in the northern and central portion, gradually transforming into a southward trend of flat lands down to the southwestern tip of the boundary. Being accessible to major roads, many industrial and residential subdivisions have been developed in this near-level land.
South Caloocan, where most commercial and industrial establishments are found, lies on generally flat and highly accessible land, with slopes ranging from 0-3%. The topography gradually changes into gently to moderately sloping to rolling along the North Luzon Expressway, with slopes ranging from 3-18%. The highest point at above sea level can be found in this area, while the lowest point is in the southern part of Dagat-Dagatan at about above mean sea level.
North Caloocan is characterized with gently to steeply undulating to rolling topography with slopes ranging from 3-18%, mostly seen in the northern and central portion, gradually transforming into a southward trend of flat lands down to the southwestern tip of the boundary. Being accessible to major roads, many industrial and residential subdivisions have been developed in this near-level land.
Geology
The geologic formation of the two portions of Caloocan varies in type and characteristics. and are specifically classified as quaternaryalluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. ...
, tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock ...
and tuffaceous sediment, pyroclastic flow deposit, and conglomerates. The formation on the eastern half of Metropolitan Manila extending to the coastline of Manila Bay and including a greater part of South Caloocan, is the quaternary alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. ...
- consisting of unconsolidated stream‐deposited sediments that includes sand, silt, clay or gravel.
Eastward of South Caloocan, large areas consisting of tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock ...
and tuffaceous sediment can be traced, spreading towards the whole eastern side of Metropolitan Manila. Pyroclastic flow deposit or igneous rocks formed by the lithification of ash flow are likewise present in northern fringes of South Caloocan and in most parts of North Caloocan. On the northeast borders of North Caloocan, conglomerate rocks were traced, crossing Tala Estate and extending to the province of Bulacan and the La Mesa Watershed.
Soil found in both areas of Caloocan predominantly falls under the Novaliches Series, covering 96% of the total land area of the city. The Novaliches Series is composed of reddish brown soil, friable in consistency and granular in structure. Spherical concretions are present in the subsoil and underneath are tuffaceous material of varying degrees of disintegration and weathering. Tuffaceous material is exposed by extensive erosion in some places.
Surface drainages
Caloocan has surface waters that either have natural course (creeks and rivers) or constructed to serve as drainages to remove excess water from soil surfaces. South Caloocan has about length of open drainage canals that serve mainly the reclamation area comprising Kaunlaran Village (Dagat-Dagatan Development Project) and nearly length of natural surface water coursing through the different natural river systems. These include the Tinajeros-Tullahan River along the Caloocan–Valenzuela boundary; Maligaya Creek within La Loma Cemetery and crossing Rizal Avenue Extension; Casili Creek which terminates in Estero de Maypajo, and Cantarilla/Panaca Creek along the Caloocan–Malabon boundary. In North Caloocan, all surface waters consist of natural streams, the longest being the Meycauayan-Marilao River dividing Caloocan and Bulacan. Others include the Bagong Silang River, Tala, Camarin, Pasong Malapad, and Bagumbong Creeks crossing multiple subdivisions, for length within the city's territorial boundaries.Climate
Barangays
Currently, Caloocan has 188barangay
A barangay (; abbreviated as Brgy. or Bgy.), historically referred to as barrio (abbreviated as Bo.), is the smallest administrative division in the Philippines and is the native Filipino term for a village, district, or ward. In metropolita ...
s divided into 3 legislative districts. The 1st District is composed of 59 barangays, which include Barangays 1 to 4, 77 to 85, 132 to 164 in South Caloocan and Barangays 165 to 177 in North Caloocan. The 2nd District is composed of 118 barangays, which include Barangays 5 to 76 and 86 to 131, all in South Caloocan. 3rd District, which was created in 2021, includes 11 barangays in North Caloocan that were formerly part of the 1st District, which include Barangays 178 to 188.
The city uses a hybrid system for its barangays, further dividing the cities into 16 zones. Among the cities in Metro Manila, only Manila, Pasay and Caloocan implement the so-called "Zone Systems". A zone is a group of barangays in a district. Although a zone is considered a subdivision in the local government units, the people do not elect a leader for the zone in a popular election similar to the normal barangay or local elections as the system is merely for statistical purposes. Further, all barangays have their corresponding numbers but only a few — mostly in the northern part — have corresponding names. However, names of barrios and districts do not necessarily coincide with barangay perimeters. Barangays in southern Caloocan are smaller compared to their northern counterparts.
In 1989, Republic Act No. 6714 called for reducing the 70 barangays constituting the first congressional district of Caloocan to only thirty (30) barangays, while the 118 barangays composing the second congressional district of Caloocan were to be reduced to thirty (30) barangays. It was presumably defeated in the plebiscite that followed.
Barangay 176 or Bagong Silang is the most populous barangay in the country with a population of 246,515 people or 16% of the total population of Caloocan. This was due to the continuous influx of informal settler families through relocation programs since the 1970s. As a result, there have been calls by residents to subdivide the Bagong Silang into seven distinct barangays.
In 1957, the sitio of Bagbaguin was separated from the barrio of Caybiga (Kaybiga) and converted into a distinct barrio known as barrio Bagbaguin.
Demographics
As of 2020, the city has a population of 1,661,584 people, which makes it the fourth largest city in the Philippines in population. Under the same census year, Caloocan South (Barangays 1 to 164) has a population of 585,091 and Caloocan North (Barangays 165 to 188) has a population of 998,887. If the two districts are treated as separate cities, they will still be among the largest in country for the 2015 census year - ranking as the 4th and 17th with the highest population. The population density of Caloocan (28,387 persons per square kilometer) surpasses that of the NCR population density. Of the country's 238 legislative districts (LDs), the 1st district of Caloocan was the biggest in terms of population size, with 1.19 million persons as of 2015. Most residents speakFilipino
Filipino may refer to:
* Something from or related to the Philippines
** Filipino language, standardized variety of 'Tagalog', the national language and one of the official languages of the Philippines.
** Filipinos, people who are citizens of th ...
and English, with considerable numbers speaking other languages and dialects.
Like many other places in the country, Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion. The city is home to the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Kalookan
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Kalookan (Lat: ''Dioecesis Kalookana'') is a diocese of the Latin Church of the Catholic Church in Metro Manila, Philippines which comprises Malabon, Navotas, and the southern portion of Caloocan.
History
The Di ...
at the southern part, while the northern part is under the Roman Catholic Diocese of Novaliches
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Novaliches (Latin: ''Dioecesis Novalichesina''; Filipino: ''Diyosesis ng Novaliches'') is a diocese of the Latin Church of the Roman Catholic Church in the Philippines. The diocese was created by Pope John Paul II ...
. There is a significant presence of Iglesia ni Cristo and other Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
churches like Church of God Caloocan located at Baesa, Caloocan.
Economy
Caloocan's 10th Avenue area is well known for the clusters of motorcycle dealers and motorcycle spare parts dealers. Among the major and famous streets are P. Zamora Street and A. Mabini Street. Numerous banks have branches in the city such as BDO, EastWest Bank, MetroBank, Maybank, Chinabank,Bank of the Philippine Islands
Bank of the Philippine Islands ( fil, Bangko ng Kapuluang Pilipinas, es, Banco de las Islas Filipinas, commonly known as BPI; ) is a universal bank in the Philippines. It is the first bank in both the Philippines and Southeast Asia. It is t ...
, UnionBank, Our Lady of Grace Credit Cooperative, etc.
The city also has a number of shopping malls and stand-alone supermarkets and hypermarkets including SM City Grand Central (formerly Ever Gotesco Grand Central), Puregold Maypajo, Monumento and Caloocan, Victory Central Mall, Araneta Square, Uniwide Warehouse Club Monumento, SM Hypermarket Monumento, and SM Center Sangandaan which are in Monumento area in the southern part. In the north, there are five shopping malls serving the residents of Bagong Silang and Camarin, namely, Zabarte Town Center, Holiday Island Mall, Metroplaza Mall, Primark Town Center Deparo, and Primark Town Center Brixton. Savemore Market have three branches which are located in Kiko Camarin (Barangay 178), Zabarte inside Zabarte Town Center, Kaybiga and Primark Deparo. Puregold
Puregold Price Club, Inc. or simply Puregold (stylized as PUREGOLD) is a chain of supermarkets in the Philippines trading goods such as consumer products (canned goods, housewares, toiletries, dry goods, and food products, among others) on a ...
Price Club also opened five branches in North Caloocan which are located in Zabarte, Bagong Silang, Deparo, Langit Road, and Quirino Highway.
Factories and industrial areas are also built in various parts of Caloocan. Manufacturers are concentrated in the northern part, particularly in Bagumbong, Kaybiga, Llano, and Tala, while plastic and steel industries are concentrated in the southern part. Tala is host to Victoria Wave Special Economic Zone, a registered zone under the Philippine Economic Zone Authority
Philippine Economic Zone Authority (PEZA) is a government agency in the Philippines attached to the Department of Trade and Industry created to help promote investments in the export-oriented manufacturing industry into the country by assisting ...
.
NLEX Corporation, the concession holder of the North Luzon Expressway, is headquartered in Caloocan. The expressway's main section and Harbor Link (through Segment 10.1 and C3– R10 section) traverse through South Caloocan.
Government
Local government
Caloocan, like othercities of the Philippines
A city ( fil, lungsod/siyudad) is one of the units of local government in the Philippines. All Philippine cities are chartered cities ( fil, nakakartang lungsod), whose existence as corporate and administrative entities is governed by their own ...
, is a local government unit whose powers and functions are specified by the Local Government Code of the Philippines. In general, as a city, Caloocan is headed by a mayor who heads the city's executive function and the vice mayor who heads the city's legislative function, which is composed of eighteen councilors, six from each of the city's three city council districts. For representation, the city has three districts, and therefore three representatives, in the country's House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
.
Elected officials
List of Mayors and Vice Mayors
;NotesInfrastructure
Transportation
 The LRT Line 1 has two stations in the southern part of the city, namely: Monumento and
The LRT Line 1 has two stations in the southern part of the city, namely: Monumento and 5th Avenue
Fifth Avenue is a major and prominent thoroughfare in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It stretches north from Washington Square Park in Greenwich Village to West 143rd Street in Harlem. It is one of the most expensive shopping stre ...
. The railway traverses Rizal Avenue Extension and enters the City of Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
and Pasay, as well as Quezon City
Quezon City (, ; fil, Lungsod Quezon ), also known as the City of Quezon and Q.C. (read in Filipino as Kyusi), is the most populous city in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 2,960,048 people. It was fou ...
. The stretch can be traveled in about 30 minutes. Philippine National Railways also has a line, with its terminal at Samson Road, and passes through Caloocan railway station, 10th Avenue railway station
10th Avenue station (also called Asistio Avenue station) is a railway station located on the North Main Line in Caloocan, Metro Manila, Philippines, near the original Caloocan railway station.
The station was meant to be a part of a revived comm ...
, and 5th Avenue railway station
5th Avenue station (also called C-3 station) is a railway station located on the North Main Line in Caloocan, Metro Manila, Philippines. Facilities such as ramps and platforms were planned to be constructed near the level crossing with C-3 Roa ...
. The currently under construction MRT Line 7
The Metro Rail Transit Line 7, also known as MRT Line 7 or MRT-7, is a rapid transit line under construction in the Philippines. When completed, the line will be long, with 14 stations, and the first line to have a third rail electrification. ...
had also proposed two stations located at the northern part of Caloocan that will be passing at Sacred Heart and Tala.
The city has an extensive network of roads, the most prominent being Epifanio de los Santos Avenue, which begins in the Monumento area. Quirino Highway
The Quirino Highway, formerly called the El Quirino Express Road or Ipo Road, is a four-to-eight lane, secondary highway that connects Quezon City to the municipality of Norzagaray in Bulacan, Philippines. The road is a designated as National ...
, which connects Quezon City and eastern Bulacan, also traverses the northern part of Caloocan. The North Luzon Expressway's Operations and Maintenance Center and the motorway's Balintawak toll barrier are in the southern part of Caloocan. Its extension in the NLEX Harbor Link that connects it towards Navotas
Navotas, officially the City of Navotas ( fil, Lungsod ng Navotas), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 247,543 people.
It is known as the ...
and Port of Manila
The Port of Manila ( fil, Pantalan ng Maynila) refers to the collective facilities and terminals that process maritime trade function in harbors in Metro Manila. Located in the Port Area and Tondo districts of Manila, Philippines facing the M ...
also traverses Caloocan. The NLEX Connector project that will connect Harbor Link with the City of Manila and Skyway
A skyway, skybridge, skywalk, or sky walkway is an elevated type of pedway connecting two or more buildings in an urban area, or connecting elevated points within mountainous recreational zones. Urban skyways very often take the form of enclo ...
is currently under construction. The northern end of Skyway, which connects the North and South Luzon Expressways, is also found near NLEX's Balintawak toll plaza, with a possible connection to a future toll road leading to the New Manila International Airport
New Manila International Airport ( fil, Bagong Paliparang Pandaigdig ng Maynila), also known as Bulacan International Airport, is an international airport under construction on the coastal areas of Bulakan, Bulacan, north of the capital Manil ...
.
Bus line Victory Liner Incorporated has its headquarters and terminal along in Rizal Avenue Extension near the Monumento station
Monumento station is an elevated Manila Light Rail Transit (LRT) station situated on Line 1. The station serves the southern portion of Caloocan, and is named after the most famous landmark of Caloocan, the Monumento Circle, which houses the Bon ...
.
Landmarks
monument
A monument is a type of structure that was explicitly created to commemorate a person or event, or which has become relevant to a social group as a part of their remembrance of historic times or cultural heritage, due to its artistic, hist ...
to the revolutionary Andrés Bonifacio, which stands on a roundabout where EDSA, MacArthur Highway, Samson Road, and Rizal Avenue Extension intersect. The memorial was erected in 1933, and consists of an obelisk with sculptures by National Artist Guillermo Tolentino
Guillermo Estrella Tolentino (July 24, 1890 – July 12, 1976) was a Filipino sculptor and professor of the University of the Philippines. He was designated as a National Artist of the Philippines for Sculpture in 1973, three years before his de ...
. The monument marks the very first battle of the Philippine Revolution on August 3, 1896. Recent renovations have been made on the environs of the monument, including the Bonifacio Circle, its former site, and the Caloocan stretch of EDSA, which is away from the landmark. The whole area is known as 'Monumento'.
The new Caloocan City Hall stands in a rectangular lot bordered by 8th and 9th Streets and 8th and 9th Avenues in Grace Park East at the southern part of the city. The old Caloocan City Hall stands at A. Mabini Street in the southern part across from San Roque Parish Cathedral. There is also the Caloocan City Hall North serving the northern part of the city, located along Zapote Street in Camarin. The city's District Office of the Bureau of Internal Revenue is along EDSA.
Other sites of historical importance identified by the city government include a lot in P. Zamora Street where the wife of Katipunan leader Andrés Bonifacio once resided; the heritage house of Gertrudes Sevilla, the owner of which is the nephew of Gregoria de Jesús
Gregoria de Jesús y Álvarez (9 May 1875 – 15 March 1943), also known by her nickname Oriang, was the founder and vice-president of the women's chapter of the Katipunan of the Philippines. She was also the custodian of the documents and s ...
; Santa Quiteria Church in Baesa; and Our Lady of Grace Parish in 11th Avenue; La Loma Cemetery, the oldest cemetery in Manila; and Thai To Taoist Temple along 6th Avenue.
Police
The Caloocan City Police Station is under the parent agency National Capital Region Police Office's Northern Police District of the Philippine National Police. The whole Caloocan city police force was recently sacked after a series of crimes, including killings and robberies, were committed by its members. However, instead of dismissing the erring police officers, they were scheduled to be retrained by then-PNP Chief Ronald dela Rosa.Education
 The city's one public university is the
The city's one public university is the University of Caloocan City
The University of Caloocan City (abbreviated as UCC) is a public-type local university established in 1971 and formerly called ''Caloocan City Community College'' and ''Caloocan City Polytechnic College''. Its south campus is located at Biglang ...
(formerly Caloocan City Community College in 1971 and Caloocan City Polytechnic College in 1975). Other educational institutions offering tertiary education include University of the East Caloocan
The University of the East, Caloocan Extension Campus (''Pamantasan ng Silangan'' and commonly abbreviated as UE Caloocan or UE Cal) is a private higher education institution in Caloocan, Philippines. It is one of the three campuses of the Unive ...
, Manila Central University, La Consolacion College-Caloocan, and La Consolacion College-Novaliches, Access Computer College Caloocan, AMA Computer College-Caloocan, STI Academic Center Caloocan, among others.
There are also several public and private schools catering to K12 such as:
* Caloocan National Science and Technology High School (North Caloocan's first-ever science and technology high school; its students are admitted if they pass a competitive examination)
*Caloocan City Science High School
Caloocan City Science High School (CCSHS, CalSci, or Kalsay), is a public secondary science school in Caloocan, Metro Manila, Philippines.
History
Caloocan City Science High School stands behind the Division Office along 10th Avenue corner P. ...
*Caloocan City Business High School
Caloocan City Business High School (CCBHS) is a business and technical-skills oriented public high school in Caloocan, Metro Manila, Philippines. It offers ABM (Accountancy, Business and Management), HUMSS (Humanities and Social Sciences), S ...
*Caloocan High School
Caloocan High School ( fil, Mataas na Paaralan ng Caloocan) abbreviated to CHS also known as CalHigh or Kalhay, is a secondary school in Caloocan, Philippines. It was the largest secondary school in Caloocan, and was established on March 22, 194 ...
*Amparo High School
*Maria Clara High School
*Philippine Cultural College
Philippine Cultural College (; abbreviated as PCC) is a Chinese Filipino school with three campuses located in Manila, Caloocan and Quezon City, Metro Manila, Philippines, established on June 27, 1923 by the Philippine Chinese Educational Ass ...
(Annex)
* Holy Infant Montessori Center
*Northern Rizal Yorklin School
*St. Mary's Academy of Caloocan City
*Notre Dame of Greater Manila
* Bagumbong High School
*Antonio Luna High School (formerly Bagumbong High School-Annex)
*Camarin High School
*Tala High School
*Manuel Luis Quezon High School
*Sampaguita High School
*Cielito Zamora High School
*Bagong Silang High School
*National Housing Corporation High School (NHC HS)
*Genesis Christian Academy of Caloocan
*Kalayaan National High School
*Deparo High School
*Escuela de Sophia of Caloocan, Inc.
*Escuela San Gabriel de Arcangel Foundation, Inc.
*Colegio de San Gabriel of Caloocan, Inc.
*Guardian Angel School
*Horacio Dela Costa Elementary School
*Horacio Dela Costa High School
*Antonio Uy Tan Senior High School
* Saint Benedict School of Novaliches
*Saint Dominic Savio School of Caloocan City
*Saint Andrew School MHANLE Inc.
*Immaculada Concepcion College
* Systems Plus Computer College
* St. Gabriel Academy
*Asian Institute of Computer Studies – Caloocan
*St. Clare College of Caloocan
*Mystical Rose School of Caloocan, Inc.
*Holy Angel School of Caloocan, Inc.
*St. Agnes Academy of Caloocan, Inc.
*St. Therese of Rose School,
*Young Achievers School of Caloocan
*St. Joseph College of Novaliches
*St. Raphaela Mary School of Caloocan
*Our Lady of Lourdes Catholic School
*Maranatha Christian Academy of Caloocan (Camarin)
*Ridgewood School of Caloocan
*Grace Park Elementary School
*Sampalukan Elementary School
*Libis Talisay Elementary School
*Kaunlaran Elementary School
*Lerma Elementary School
*Pag-Asa Elementary School
*Camarin Elementary School
*La Consolacion College
**Caloocan (South) Campus
** Novaliches (Deparo) Campus
Twin towns – sister cities
Local
* Calamba, Laguna * Malabon, Metro Manila *San Jose del Monte
San Jose del Monte, officially the City of San Jose del Monte (abbreviated as SJDM or CSJDM; fil, Lungsod ng San Jose del Monte), is a 1st class component city in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a po ...
, Bulacan
International
* Incheon, South KoreaGallery
Bonifacio Monument
The Andrés Bonifacio Monument, commonly known simply as Bonifacio Monument or Monumento, is a memorial monument in Caloocan, Philippines which was designed by National Artist Guillermo Tolentino to commemorate the Philippine revolutionary And ...
File:San Roque Cathedral, Caloocan City.jpg, San Roque Cathedral-Parish in Poblacion district
File:Old St. Pancratius Church in La Loma Cemetery, Caloocan City.jpg, Old St. Pancratius Chapel in La Loma Cemetery
02860jfCamarin City Hall Caloocan Cityfvf 04.JPG, Caloocan City Hall North
9526Complex Caloocan City Hall Landmarks 21.jpg, View of Grace Park from the new city hall
File:Cccaloocanjf.JPG, View of Barangays 15 and 16 from the old city hall
File:Xxcaloocanjf.JPG, Regional Trial Courts, Halls of Justice
File:Diocesan Shrine of Our Lady of Grace (Kalookan Diocese, the Philippines - October 2012).jpg, Vicariate of Our Lady of Grace, Diocesan Shrine of Our Lady of Grace, Roman Catholic Diocese of Kalookan
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Kalookan (Lat: ''Dioecesis Kalookana'') is a diocese of the Latin Church of the Catholic Church in Metro Manila, Philippines which comprises Malabon, Navotas, and the southern portion of Caloocan.
History
The Di ...
File:2Tala Caloocan City Buildings Church 16.jpg, Dr. Jose N. Rodriguez Memorial Hospital in Tala
File:9538Caloocan City Barangays Landmarks 17.jpg, Kalookan Cockpit Arena in Kaybiga
File:9848Caloocan City Barangays Landmarks 44.jpg, Glorieta Park
File:102Churches landmarks Buildings Camarin Area, Caloocan City 15.jpg, Caloocan City North Medical Center in Camarin
References
External links
* * Philippine Standard Geographic Codebr>History of Caloocan, Philippines* {{Authority control Cities in Metro Manila Populated places established in 1815 1815 establishments in the Philippines Highly urbanized cities in the Philippines Enclaves and exclaves