Caesium fluoride on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Caesium fluoride or cesium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CsF and it is a
 Caesium fluoride can be prepared by the reaction of
Caesium fluoride can be prepared by the reaction of
.
www.hazard.com
.'' MSDS Date: April 27, 1993. Retrieved on September 7, 2007. Contact with acid should be avoided, as this forms highly toxic/corrosive hydrofluoric acid. The caesium
."
www.jtbaker.com
'' MSDS Date: January 16, 2006. Retrieved on September 7, 2007.
hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substan ...
white salt. Caesium fluoride can be used in organic synthesis as a source of the fluoride anion. Caesium also has the highest electropositivity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
of all non-radioactive elements and fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all known elements.
Synthesis and properties
 Caesium fluoride can be prepared by the reaction of
Caesium fluoride can be prepared by the reaction of caesium hydroxide
Caesium hydroxide is a strong base (pKa= 15.76) containing the highly reactive alkali metal caesium, much like the other alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. Caesium hydroxide is corrosive enough to quickly ...
(CsOH) with hydrofluoric acid (HF) and the resulting salt can then be purified by recrystallization. The reaction is shown below:
:CsOH + HF → CsF + H2O
Using the same reaction, another way to create caesium fluoride is to treat caesium carbonate
Caesium carbonate or cesium carbonate is a white crystalline solid compound. Caesium carbonate has a high solubility in polar solvents such as water, alcohol and DMF. Its solubility is higher in organic solvents compared to other carbonates l ...
(Cs2CO3) with hydrofluoric acid and again, the resulting salt can then be purified by recrystallization. The reaction is shown below:
:Cs2CO3 + 2 HF → 2 CsF + H2O + CO2
CsF is more soluble than sodium fluoride
Sodium fluoride (NaF) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is used in trace amounts in the fluoridation of drinking water, in toothpaste, in metallurgy, and as a flux. It is a colorless or white solid that is readily soluble in water. I ...
or potassium fluoride
Potassium fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula KF. After hydrogen fluoride, KF is the primary source of the fluoride ion for applications in manufacturing and in chemistry. It is an alkali halide and occurs naturally as the rare ...
in organic solvents. It is available in its anhydrous form, and if water has been absorbed, it is easy to dry by heating at 100 °C for two hours ''in vacuo
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often di ...
''. CsF reaches a vapor pressure
Vapor pressure (or vapour pressure in English-speaking countries other than the US; see spelling differences) or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phas ...
of 1 kilopascal
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI), and is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is defined a ...
at 825 °C, 10 kPa at 999 °C, and 100 kPa at 1249 °C.
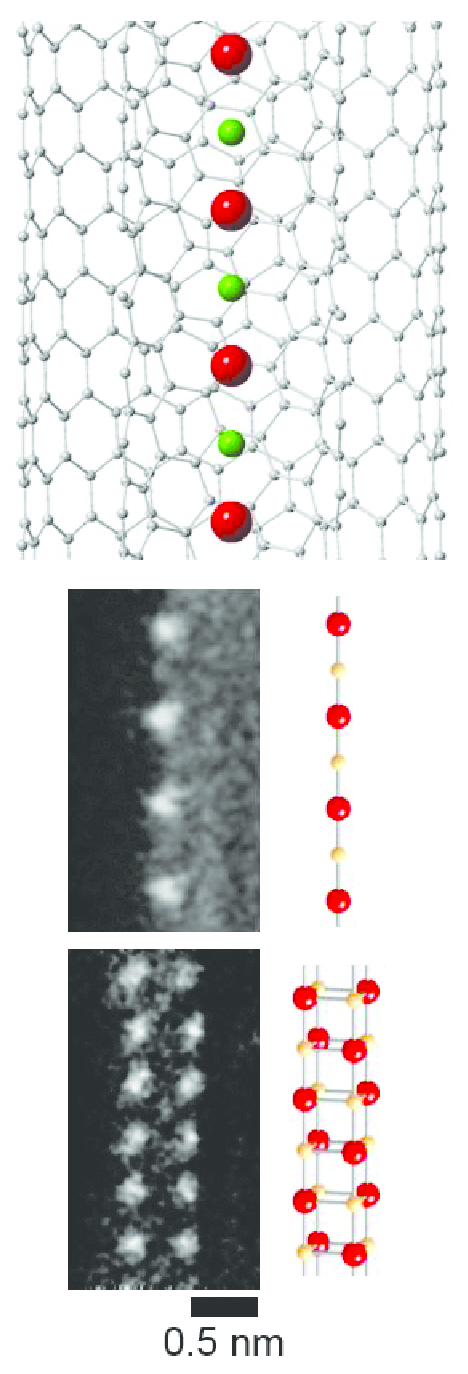
CsF chains with a thickness as small as one or two atoms can be grown inside carbon nanotubes.
Structure
Caesium fluoride has the halite structure, which means that the Cs+ and F− pack in acubic closest packed
In geometry, close-packing of equal spheres is a dense arrangement of congruent spheres in an infinite, regular arrangement (or lattice). Carl Friedrich Gauss proved that the highest average density – that is, the greatest fraction of space occ ...
array as do Na+ and Cl− in sodium chloride.
Applications in organic synthesis
Being highly dissociated, CsF is a more reactive source of fluoride than related salts. CsF is an alternative totetra-n-butylammonium fluoride
Tetra-''n''-butylammonium fluoride, commonly abbreviated to TBAF and ''n''-Bu4NF, is a quaternary ammonium salt with the chemical formula (CH3CH2CH2CH2)4N+F−. It is commercially available as the white solid trihydrate and as a solution in tetra ...
(TBAF) and TAS-fluoride (TASF).
As a base
As with other soluble fluorides, CsF is moderately basic, because HF is aweak acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions ...
. The low nucleophilicity
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
of fluoride means it can be a useful base in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, ...
. CsF gives higher yields in Knoevenagel condensation
In organic chemistry, the Knoevenagel condensation () reaction is a type of chemical reaction named after German chemist Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the aldol condensation.
A Knoevenagel condensation is a nucleophilic addition o ...
reactions than KF or NaF.
Formation of Cs-F bonds
Caesium fluoride serves as a source of fluoride in organofluorine chemistry. Similarly topotassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosph ...
fluoride, CsF reacts with hexafluoroacetone
Hexafluoroacetone (HFA) is a chemical compound with the formula (CF3)2CO. It is structurally similar to acetone; however, its reactivity is markedly different. It a colourless, hygroscopic, nonflammable, highly reactive gas characterized by a mus ...
to form a stable perfluoroalkoxide salt. It will convert electron-deficient aryl chlorides to aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromaticity, aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar ...
fluorides (Halex process
In chemistry, the Halex process is used to convert aromatic chlorides to the corresponding aromatic fluorides. The process entails ''Hal''ide ''ex''change, hence the name. The reaction conditions call for hot (150-250 °C) solution of the aryl ch ...
), although potassium fluoride is more commonly used.
Deprotection agent
Due to the strength of the Si– F bond, fluoride is useful fordesilylation
Silylation is the introduction of one or more (usually) substituted silyl groups (R3Si) to a molecule. The process is the basis of organosilicon chemistry.
Of organic compounds
Alcohols, carboxylic acids, amines, thiols, and phosphates can be sily ...
reactions, i.e. cleavage of Si-O bonds in organic synthesis. CsF is commonly used for such reactions. Solutions of caesium fluoride in THF
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ...
or DMF attack a wide variety of organosilicon compounds to produce an organosilicon fluoride and a carbanion, which can then react with electrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carrie ...
s, for example:
:
Precautions
Like other soluble fluorides, CsF is moderately toxic.MSDS Listing for cesium fluoride.
www.hazard.com
.'' MSDS Date: April 27, 1993. Retrieved on September 7, 2007. Contact with acid should be avoided, as this forms highly toxic/corrosive hydrofluoric acid. The caesium
ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
(Cs+) and caesium chloride are generally not considered toxic.MSDS Listing for cesium chloride."
www.jtbaker.com
'' MSDS Date: January 16, 2006. Retrieved on September 7, 2007.
References
{{Fluorides Fluorides Caesium compounds Metal halides Alkali metal fluorides Rock salt crystal structure