Cadmium hydride on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cadmium is a
 Naturally occurring cadmium is composed of eight
Naturally occurring cadmium is composed of eight
 Cadmium (
Cadmium (
 Cadmium makes up about 0.1 ppm of
Cadmium makes up about 0.1 ppm of
File:Cadmium - world production trend.svg, History of the world production of cadmium
File:2022cadmium.png, Cadmium production in 2010
 In 2009, 86% of cadmium was used in batteries, predominantly in rechargeable nickel–cadmium batteries. Nickel–cadmium cells have a nominal cell potential of 1.2 V. The cell consists of a positive nickel hydroxide
In 2009, 86% of cadmium was used in batteries, predominantly in rechargeable nickel–cadmium batteries. Nickel–cadmium cells have a nominal cell potential of 1.2 V. The cell consists of a positive nickel hydroxide
 Cadmium
Cadmium

 Various cadmium salts are used in paint pigments, with CdS as a yellow pigment being the most common.
Various cadmium salts are used in paint pigments, with CdS as a yellow pigment being the most common.
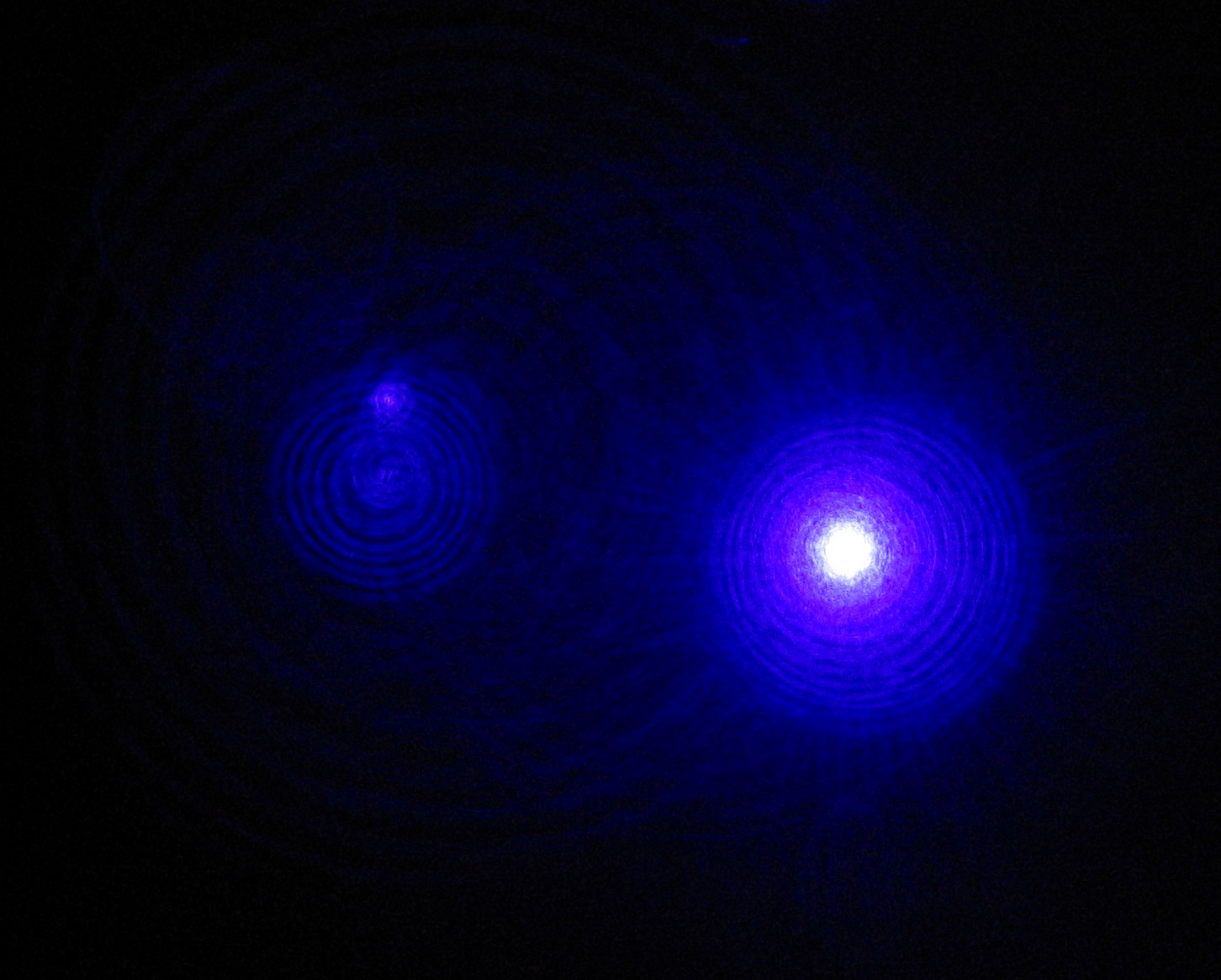 Helium–cadmium lasers are a common source of blue or ultraviolet laser light. Lasers at wavelengths of 325, 354 and 442 nm are made using this
Helium–cadmium lasers are a common source of blue or ultraviolet laser light. Lasers at wavelengths of 325, 354 and 442 nm are made using this
Can Heavy Metal in Foods, Cosmetics Spur Breast Cancer Spread?
HealthDayBy via Yahoo There have been a few instances of general population poisoning as the result of long-term exposure to cadmium in contaminated food and water. Research into an estrogen mimicry that may induce breast cancer is ongoing, . In the decades leading up to
There have been a few instances of general population poisoning as the result of long-term exposure to cadmium in contaminated food and water. Research into an estrogen mimicry that may induce breast cancer is ongoing, . In the decades leading up to
Cadmium
at ''
ATSDR Case Studies in Environmental Medicine: Cadmium Toxicity
U.S.
chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
; it has symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
Cd and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
48. This soft, silvery-white metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
+2 in most of its compounds, and like mercury, it has a lower melting point than the transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinid ...
s in groups 3 through 11. Cadmium and its congeners in group 12 are often not considered transition metals, in that they do not have partly filled ''d'' or ''f'' electron shells in the elemental or common oxidation states. The average concentration of cadmium in Earth's crust is between 0.1 and 0.5 parts per million (ppm). It was discovered in 1817 simultaneously by Stromeyer and Hermann, both in Germany, as an impurity in zinc carbonate
Zinc carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula ZnCO3. It is a white solid that is insoluble in water. It exists in nature as the mineral smithsonite. It is prepared by treating cold solutions of zinc sulfate with potassium bicarbonat ...
.
Cadmium occurs as a minor component in most zinc ores and is a byproduct of zinc production. It was used for a long time in the 1900s as a corrosion-resistant plating on steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
, and cadmium compounds are used as red, orange, and yellow pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
s, to color glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
, and to stabilize plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
. Cadmium's use is generally decreasing because it is toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
(it is specifically listed in the European Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive 2002/95/EC (RoHS 1), short for Directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, was adopted in February 2003 by the European Uni ...
) and nickel–cadmium batteries have been replaced with nickel–metal hydride and lithium-ion
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible Intercalation (chemistry), intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically Electrical conductor, conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are c ...
batteries. Because it is a neutron poison
In applications such as nuclear reactors, a neutron poison (also called a neutron absorber or a nuclear poison) is a substance with a large neutron absorption cross-section. In such applications, absorbing neutrons is normally an undesirable ef ...
, cadmium is also used as a component of control rod
Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing ...
s in nuclear fission reactors. One of its few new uses is in cadmium telluride
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a stable crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is mainly used as the semiconducting material in cadmium telluride photovoltaics and an infrared optical window. It is usually sandwiched with ...
solar panel
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. These electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct ...
s.
Although cadmium has no known biological function in higher organisms, a cadmium-dependent carbonic anhydrase
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) () form a family of enzymes that catalyst, catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the Dissociation (chemistry), dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate a ...
has been found in marine diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma'') is any member of a large group comprising several Genus, genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of Earth's B ...
s.
Characteristics
Physical properties
Cadmium is a soft,malleable
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic deformation, which is reversi ...
, ductile
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic deformation, which is reversi ...
, silvery-white divalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an atom is a measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Valence is generally understood to be the number of chemica ...
metal. It is similar in many respects to zinc but forms complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
compounds.
Unlike most other metals, cadmium is resistant to corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
and is used as a protective plate on other metals. As a bulk metal, cadmium is insoluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solub ...
in water and is not flammable
A combustible material is a material that can burn (i.e., sustain a flame) in air under certain conditions. A material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort ...
; however, in its powdered form it may burn and release toxic fumes.
Chemical properties
Although cadmium usually has anoxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons ...
of +2, it also exists in the +1 state. Cadmium and its congeners are not always considered transition metals, in that they do not have partly filled d or f electron shells in the elemental or common oxidation states. Cadmium burns in air to form brown amorphous cadmium oxide
Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers. It occurs natur ...
(CdO); the crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
line form of this compound is a dark red which changes color when heated, similar to zinc oxide
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the Chemical formula, formula . It is a white powder which is insoluble in water. ZnO is used as an additive in numerous materials and products including cosmetics, Zinc metabolism, food supplements, rubbe ...
. Hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
, sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
, and nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
dissolve cadmium by forming cadmium chloride
Cadmium chloride is a white crystalline compound of cadmium and chloride, with the formula CdCl2. This salt is a hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The crystal structure of cadmium chloride (describe ...
(), cadmium sulfate (), and cadmium nitrate
Cadmium nitrate describes any of the related members of a family of inorganic compounds with the general formula . The most commonly encountered form being the tetrahydrate.The anhydrous form is volatile, but the others are colourless crystalline ...
() respectively. The oxidation state +1 can be produced by dissolving cadmium in a mixture of cadmium chloride and aluminium chloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms a hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are col ...
, forming the cation as cadmium(I) tetrachloroaluminate, which is similar to the cation in mercury(I) chloride
Mercury(I) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula Hg2Cl2. Also known as the mineral calomel (a rare mineral) or mercurous chloride, this dense white or yellowish-white, odorless solid is the principal example of a mercury(I) compoun ...
.
:
The structures of many cadmium complexes with nucleobase
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nuc ...
s, amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s, and vitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, ...
s have been determined.
Isotopes
 Naturally occurring cadmium is composed of eight
Naturally occurring cadmium is composed of eight isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
s. Two of them are radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
, and three are expected to decay
Decay may refer to:
Science and technology
* Bit decay, in computing
* Decay time (fall time), in electronics
* Distance decay, in geography
* Software decay, in computing
Biology
* Decomposition of organic matter
* Mitochondrial decay, in g ...
but have not measurably done so under laboratory conditions. The two natural radioactive isotopes are 113Cd (beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron ...
, half-life is ) and 116Cd (two-neutrino double beta decay
In nuclear physics, double beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which two neutrons are simultaneously transformed into two protons, or vice versa, inside an atomic nucleus. As in single beta decay, this process allows the atom to move cl ...
, half-life is ). The other three are 106Cd, 108Cd (both double electron capture
Double electron capture is a decay mode of an atomic nucleus. For a nuclide (''A'', ''Z'') with a number of nucleons ''A'' and atomic number ''Z'', double electron capture is only possible if the mass of the nuclide (''A'', ''Z''−2) is lower.
I ...
), and 114Cd (double beta decay); only lower limits on these half-lives have been determined. At least three isotopes – 110Cd, 111Cd, and 112Cd – are stable. Among the isotopes that do not occur naturally, the most long-lived are 109Cd with a half-life of 462.6 days, and 115Cd with a half-life of 53.46 hours. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives of less than 2.5 hours, and the majority have half-lives of less than 5 minutes. Cadmium has 8 known meta state
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives of 10−9 s ...
s, with the most stable being 113mCd (''t''1⁄2 = 14.1 years), 115mCd (''t''1⁄2 = 44.6 days), and 117mCd (''t''1⁄2 = 3.36 hours).
The known isotopes of cadmium range in atomic mass
Atomic mass ( or ) is the mass of a single atom. The atomic mass mostly comes from the combined mass of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with minor contributions from the electrons and nuclear binding energy. The atomic mass of atoms, ...
from 94.950 u (95Cd) to 131.946 u (132Cd). For isotopes lighter than 112 u, the primary decay mode
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
is electron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. Th ...
and the dominant decay product
In nuclear physics, a decay product (also known as a daughter product, daughter isotope, radio-daughter, or daughter nuclide) is the remaining nuclide left over from radioactive decay. Radioactive decay often proceeds via a sequence of steps ( d ...
is element 47 (silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
). Heavier isotopes decay mostly through beta emission
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron t ...
producing element 49 (indium
Indium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol In and atomic number 49. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal and one of the softest elements. Chemically, indium is similar to gallium and thallium, and its properties are la ...
).
One isotope of cadmium, 113Cd, absorbs neutrons with high selectivity: With very high probability, neutrons with energy below the ''cadmium cut-off'' will be absorbed; those higher than the ''cut-off will be transmitted''. The cadmium cut-off is about 0.5 eV, and neutrons below that level are deemed slow neutron
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with ...
s, distinct from intermediate and fast neutron
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with ...
s.
Cadmium is created via the s-process
The slow neutron-capture process, or ''s''-process, is a series of nuclear reactions, reactions in nuclear astrophysics that occur in stars, particularly asymptotic giant branch stars. The ''s''-process is responsible for the creation (nucleosynt ...
in low- to medium-mass stars with masses of 0.6 to 10 solar masses
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies ...
, over thousands of years. In that process, a silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
atom captures a neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nucle ...
and then undergoes beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron), transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron ...
.
History
 Cadmium (
Cadmium (Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''cadmia'', Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
''καδμεία'' meaning "calamine
Calamine, also known as calamine lotion, is a medication made from powdered calamine (mineral), calamine mineral that is used to treat mild itchiness. Conditions treated include sunburn, insect bites, Toxicodendron radicans, poison ivy, poiso ...
", a cadmium-bearing mixture of minerals that was named after the Greek mythological character Κάδμος, Cadmus
In Greek mythology, Cadmus (; ) was the legendary Phoenician founder of Boeotian Thebes, Greece, Thebes. He was, alongside Perseus and Bellerophon, the greatest hero and slayer of monsters before the days of Heracles. Commonly stated to be a ...
, the founder of Thebes) was discovered
Discovery is the act of detecting something new, or something previously unrecognized as meaningful, "portal". In sciences and academic disciplines, discovery is the observation of new phenomena, new actions, or new events and involves providin ...
in contaminated zinc compounds sold in pharmacies in Germany in 1817 by Friedrich Stromeyer
Friedrich Stromeyer FRS(For) FRSE (2 August 1776 – 18 August 1835) was a German chemist. He was the discoverer of cadmium.
From 1982, the Friedrich Stromeyer Prize has been awarded for chemical achievement in Germany.
Biography
He was born i ...
. Karl Samuel Leberecht Hermann simultaneously investigated the discoloration in zinc oxide and found an impurity, first suspected to be arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, because of the yellow precipitate with hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
. Additionally Stromeyer discovered that one supplier sold zinc carbonate instead of zinc oxide. Stromeyer found the new element as an impurity in zinc carbonate
Zinc carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula ZnCO3. It is a white solid that is insoluble in water. It exists in nature as the mineral smithsonite. It is prepared by treating cold solutions of zinc sulfate with potassium bicarbonat ...
(calamine), and, for 100 years, Germany remained the only important producer of the metal. The metal was named after the Latin word for calamine, because it was found in this zinc ore. Stromeyer noted that some impure samples of calamine changed color when heated but pure calamine did not. He was persistent in studying these results and eventually isolated cadmium metal by roasting
Roasting is a cooking method that uses dry heat where hot air covers the food, cooking it evenly on all sides with temperatures of at least from an open flame, oven, or other heat source. Roasting can enhance the flavor through caramelizat ...
and reducing the sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
. The potential for cadmium yellow as pigment was recognized in the 1840s, but the early scarcity of cadmium limited this application.
Even though cadmium and its compounds are toxic in certain forms and concentrations, the British Pharmaceutical Codex from 1907 states that cadmium iodide
Cadmium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds ...
was used as a medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
to treat "enlarged joints, scrofulous
The disease mycobacterial cervical lymphadenitis, also known historically as scrofula and the king's evil, involves a lymphadenitis of the cervical (neck) lymph nodes associated with tuberculosis as well as nontuberculous (atypical) mycobacteria ...
glands, and chilblains
Chilblains, also known as pernio, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to capillary beds in the skin, most often in the hands or feet, when blood perfuses into the nearby tissue, resulting in redness, itching, inflammation, and possibly ...
".
In 1907, the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
defined the international ångström
The angstrom (; ) is a unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten- billionth of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre, 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814� ...
in terms of a red cadmium spectral line (1 wavelength = 6438.46963 Å). This was adopted by the 7th General Conference on Weights and Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures (abbreviated CGPM from the ) is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established in 1875 under the terms of the Metre C ...
in 1927. In 1960, the definitions of both the metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
and ångström were changed to use krypton
Krypton (from 'the hidden one') is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless noble gas that occurs in trace element, trace amounts in the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere and is of ...
.
After the industrial scale production of cadmium started in the 1930s and 1940s, the major application of cadmium was the coating of iron and steel to prevent corrosion; in 1944, 62% and in 1956, 59% of the cadmium in the United States was used for plating
Plating is a finishing process in which a metal is deposited on a surface. Plating has been done for hundreds of years; it is also critical for modern technology. Plating is used to decorate objects, for corrosion inhibition, to improve solderab ...
.
In 1956, 24% of the cadmium in the United States was used for a second application in red, orange and yellow pigments from sulfides and selenides of cadmium.
The stabilizing effect of cadmium chemicals like the carboxylates cadmium laurate and cadmium stearate on PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons o ...
led to an increased use of those compounds in the 1970s and 1980s. The demand for cadmium in pigments, coatings, stabilizers, and alloys declined as a result of environmental and health regulations in the 1980s and 1990s; in 2006, only 7% of total cadmium consumption was used for plating, and only 10% was used for pigments.
At the same time, these decreases in consumption were compensated by a growing demand for cadmium for nickel–cadmium batteries, which accounted for 81% of the cadmium consumption in the United States in 2006.
Occurrence
 Cadmium makes up about 0.1 ppm of
Cadmium makes up about 0.1 ppm of Earth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
and is the 65th most abundant element. It is much rarer than zinc, which makes up about 65 ppm. No significant deposits of cadmium-containing ores are known. The only cadmium mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
of importance, greenockite (Cd S), is nearly always associated with sphalerite
Sphalerite is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hoste ...
(ZnS). This association is caused by geochemical similarity between zinc and cadmium, with no geological process likely to separate them. Thus, cadmium is produced mainly as a byproduct of mining, smelting, and refining sulfidic ores of zinc, and, to a lesser degree, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
. Small amounts of cadmium, about 10% of consumption, are produced from secondary sources, mainly from dust generated by recycling iron and steel scrap. Production in the United States began in 1907, but wide use began after World War I.
Metallic cadmium can be found in the Vilyuy River
The Vilyuy ( rus, Вилю́й, p=vʲɪˈlʲʉj; , ''Bülüü'', ) is a river in Russia, the longest tributary of the Lena. About long, it flows mostly within the Sakha Republic. Its basin covers about .
History
The river is first mentioned in ...
basin in Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
.
Rocks mined for phosphate fertilizers contain varying amounts of cadmium, resulting in a cadmium concentration of as much as 300 mg/kg in the fertilizers and a high cadmium content in agricultural soils. Coal can contain significant amounts of cadmium, which ends up mostly in coal fly ash
Coal combustion products (CCPs), also called coal combustion wastes (CCWs) or coal combustion residuals (CCRs), are byproducts of burning coal. They are categorized in four groups, each based on physical and chemical forms derived from coal combust ...
.
Cadmium in soil can be absorbed by crops such as rice and cocoa. In 2002, the Chinese ministry of agriculture measured that 28% of rice it sampled had excess lead and 10% had excess cadmium above limits defined by law. ''Consumer Reports
Consumer Reports (CR), formerly Consumers Union (CU), is an American nonprofit consumer organization dedicated to independent product testing, investigative journalism, consumer-oriented research, public education, and consumer advocacy.
Founded ...
'' tested 28 brands of dark chocolate
Dark chocolate is a form of chocolate made from cocoa solids, cocoa butter and sugar. It has a higher cocoa percentage than white chocolate, milk chocolate, and semisweet chocolate. Dark chocolate is valued for claimed—though unsupported— ...
sold in the United States in 2022, and found cadmium in all of them, with 13 exceeding the California Maximum Allowable Dose level.
Some plants such as willow trees
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, of the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 350 species (plus numerous hybrids) of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions.
Most species are known ...
and poplars
''Populus'' is a genus of 25–30 species of deciduous flowering plants in the family Salicaceae, native to most of the Northern Hemisphere. English names variously applied to different species include poplar (), aspen, and cottonwood.
The we ...
have been found to clean both lead and cadmium from soil.
Typical background concentrations of cadmium do not exceed 5 ng/m3 in the atmosphere; 2 mg/kg in soil; 1 μg/L in freshwater and 50 ng/L in seawater. Concentrations of cadmium above 10 μg/L may be stable in water having low total solute concentrations and ''p'' H and can be difficult to remove by conventional water treatment processes.
Production
Cadmium is a common impurity inzinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
ores, and it is most often isolated during the production of zinc. Some zinc ores concentrates from zinc sulfate
Zinc sulfate is an inorganic compound with the formula ZnSO4. It forms hydrates ZnSO4·''n''H2O, where ''n'' can range from 0 to 7. All are colorless solids. The most common form includes water of crystallization as the heptahydrate, with the che ...
ores contain up to 1.4% of cadmium.
In the 1970s, the output of cadmium was per ton of zinc. Zinc sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
ores are roasted in the presence of oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
, converting the zinc sulfide to the oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
. Zinc metal is produced either by smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron-making, iron, copper extraction, copper ...
the oxide with carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
or by electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
in sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, ...
. Cadmium is isolated from the zinc metal by vacuum distillation
Vacuum distillation or distillation under reduced pressure is a type of distillation performed under reduced pressure, which allows the purification of compounds not readily distilled at ambient pressures or simply to save time or energy. This te ...
if the zinc is smelted, or cadmium sulfate is precipitate
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the "sedimentation of a solid material (a precipitate) from a liquid solution". The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemic ...
d from the electrolysis solution.
The British Geological Survey
The British Geological Survey (BGS) is a partly publicly funded body which aims to advance Earth science, geoscientific knowledge of the United Kingdom landmass and its continental shelf by means of systematic surveying, monitoring and research. ...
reports that in 2001, China was the top producer of cadmium with almost one-sixth of the world's production, closely followed by South Korea and Japan.
Applications
Cadmium is a common component of electric batteries,pigments
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
, coatings, and electroplating.
Batteries
 In 2009, 86% of cadmium was used in batteries, predominantly in rechargeable nickel–cadmium batteries. Nickel–cadmium cells have a nominal cell potential of 1.2 V. The cell consists of a positive nickel hydroxide
In 2009, 86% of cadmium was used in batteries, predominantly in rechargeable nickel–cadmium batteries. Nickel–cadmium cells have a nominal cell potential of 1.2 V. The cell consists of a positive nickel hydroxide electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
and a negative cadmium electrode plate separated by an alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The ...
electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
(potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
). The European Union put a limit on cadmium in electronics in 2004 of 0.01%, with some exceptions, and in 2006 reduced the limit on cadmium content to 0.002%. Another type of battery based on cadmium is the silver–cadmium battery
A silver–cadmium battery is a type of rechargeable battery using cadmium metal as its negative terminal, silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous tran ...
.
Electroplating
 Cadmium
Cadmium electroplating
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the redox, reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct current, direct electric cur ...
, consuming 6% of the global production, is used in the aircraft industry to reduce corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
of steel components. This coating is passivated by chromate salts. A limitation of cadmium plating is hydrogen embrittlement
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE), also known as hydrogen-assisted cracking or hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC), is a reduction in the ductility of a metal due to absorbed hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms are small and can Permeation, permeate solid metals. O ...
of high-strength steels from the electroplating process. Therefore, steel parts heat-treated to tensile strength above 1300 MPa (200 ksi) should be coated by an alternative method (such as special low-embrittlement cadmium electroplating processes or physical vapor deposition).
Titanium embrittlement from cadmium-plated tool residues resulted in banishment of those tools (and the implementation of routine tool testing to detect cadmium contamination) in the A-12/SR-71, U-2, and subsequent aircraft programs that use titanium.
Nuclear technology
Cadmium is used in thecontrol rod
Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing ...
s of nuclear reactors, acting as a very effective neutron poison
In applications such as nuclear reactors, a neutron poison (also called a neutron absorber or a nuclear poison) is a substance with a large neutron absorption cross-section. In such applications, absorbing neutrons is normally an undesirable ef ...
to control neutron flux
The neutron flux is a scalar quantity used in nuclear physics and nuclear reactor physics. It is the total distance travelled by all free neutrons per unit time and volume. Equivalently, it can be defined as the number of neutrons travelling ...
in nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactiv ...
. When cadmium rods are inserted in the core of a nuclear reactor, cadmium absorbs neutrons, preventing them from creating additional fission events, thus controlling the amount of reactivity. The pressurized water reactor
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions being the UK, Japan, India and Canada).
In a PWR, water is used both as ...
designed by Westinghouse Electric Company
Westinghouse Electric Company LLC is an American nuclear power company formed in 1999 from the nuclear power division of the original Westinghouse Electric Corporation. It offers nuclear products and services to utilities internationally, includ ...
uses an alloy consisting of 80% silver, 15% indium, and 5% cadmium.
Televisions
QLED TVs have been starting to include cadmium in construction. Some companies have been looking to reduce the environmental impact of human exposure and pollution of the material in televisions during production.Anticancer drugs
Complexes based on cadmium and other heavy metals have potential for the treatment of cancer, but their use is often limited due to toxic side effects.Compounds

Cadmium oxide
Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers. It occurs natur ...
was used in black and white television phosphors and in the blue and green phosphors of color television cathode ray tubes. Cadmium sulfide
Cadmium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdS. Cadmium sulfide is a yellow salt.Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001''Inorganic Chemistry'' Elsevier It occurs in nature with two different crystal structures as the rare min ...
(CdS) is used as a photoconductive surface coating for photocopier drums.
 Various cadmium salts are used in paint pigments, with CdS as a yellow pigment being the most common.
Various cadmium salts are used in paint pigments, with CdS as a yellow pigment being the most common. Cadmium selenide
Cadmium selenide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd Se. It is a black to red-black solid that is classified as a II-VI semiconductor of the n-type. It is a pigment, but applications are declining because of environmental concerns.
...
is a red pigment, commonly called ''cadmium red''. To painters who work with the pigment, cadmium provides the most brilliant and durable yellows, oranges, and reds – so much so that during production, these colors are significantly toned down before they are ground with oils and binders or blended into watercolor
Watercolor (American English) or watercolour (Commonwealth English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences), also ''aquarelle'' (; from Italian diminutive of Latin 'water'), is a painting metho ...
s, gouache
Gouache (; ), body color, or opaque watercolor is a water-medium paint consisting of natural pigment, water, a binding agent (usually gum arabic or dextrin), and sometimes additional inert material. Gouache is designed to be opaque. Gouach ...
s, acrylics, and other paint and pigment formulations. Because these pigments are potentially toxic, for safety users normally use a barrier cream
A barrier cream is a Topical medication, topical formulation used in industrial applications and as a cosmetic to place a physical barrier between the skin and contaminants that may irritate the skin (contact dermatitis or occupational dermatitis ...
on the hands to prevent absorption through the skin even though the amount of cadmium absorbed into the body through the skin is reported to be less than 1%.
In PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons o ...
, cadmium was used as heat, light, and weathering stabilizers. Currently, cadmium stabilizers have been completely replaced with barium-zinc, calcium-zinc and organo-tin stabilizers. Cadmium is used in many kinds of solder
Solder (; North American English, NA: ) is a fusible alloy, fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. Solder is melted in order to wet the parts of the joint, where it adheres to and connects the pieces aft ...
and bearing alloys, because it has a low coefficient of friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of t ...
and fatigue resistance. It is also found in some of the lowest-melting alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s, such as Wood's metal
Wood's metal, also known as Lipowitz's alloy or by the commercial names Cerrobend, Bendalloy, Pewtalloy and MCP 158, is a fusible metal alloy (having a low melting point) that is useful for soldering and making custom metal parts. The alloy is n ...
.
Semiconductors
Cadmium is an element in somesemiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
materials. Cadmium sulfide, cadmium selenide, and cadmium telluride
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a stable crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is mainly used as the semiconducting material in cadmium telluride photovoltaics and an infrared optical window. It is usually sandwiched with ...
are used in some photodetectors
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical c ...
and solar cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect.
s. HgCdTe
Hg1−''x''Cd''x''Te or mercury cadmium telluride (also cadmium mercury telluride, MCT, MerCad Telluride, MerCadTel, MerCaT or CMT) is a chemical compound of cadmium telluride (CdTe) and mercury telluride (HgTe) with a tunable bandgap spanning th ...
detectors are sensitive to mid-infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
light and used in some motion detectors.
Laboratory uses
 Helium–cadmium lasers are a common source of blue or ultraviolet laser light. Lasers at wavelengths of 325, 354 and 442 nm are made using this
Helium–cadmium lasers are a common source of blue or ultraviolet laser light. Lasers at wavelengths of 325, 354 and 442 nm are made using this gain medium
The active laser medium (also called a gain medium or lasing medium) is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of photons through electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from ...
; some models can switch between these wavelengths. They are notably used in fluorescence microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. A fluorescence micro ...
as well as various laboratory uses requiring laser light at these wavelengths.
Cadmium selenide quantum dot
Quantum dots (QDs) or semiconductor nanocrystals are semiconductor particles a few nanometres in size with optical and electronic properties that differ from those of larger particles via quantum mechanical effects. They are a central topic i ...
s emit bright luminescence
Luminescence is a spontaneous emission of radiation from an electronically or vibrationally excited species not in thermal equilibrium with its environment. A luminescent object emits ''cold light'' in contrast to incandescence, where an obje ...
under UV excitation (He–Cd laser, for example). The color of this luminescence can be green, yellow or red depending on the particle size. Colloidal solutions of those particles are used for imaging of biological tissues and solutions with a fluorescence microscope
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. A fluorescence micro ...
.
In molecular biology, cadmium is used to block voltage-dependent calcium channels from fluxing calcium ions, as well as in hypoxia research to stimulate proteasome
Proteasomes are essential protein complexes responsible for the degradation of proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are found inside all e ...
-dependent degradation of Hif-1α.
Cadmium-selective sensors based on the fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with se ...
BODIPY
BODIPY is the technical common name of a chemical compound with formula , whose molecule consists of a boron difluoride group joined to a dipyrromethene group ; specifically, the compound 4,4-difluoro-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-''s''-indacene in the ...
have been developed for imaging and sensing of cadmium in cells. One powerful method for monitoring cadmium in aqueous environments involves electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between Electric potential, electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve Electron, electrons moving via an electronic ...
. By employing a self-assembled monolayer
Self-assembled monolayers (SAM) are assemblies of organic molecules that form spontaneously on surfaces by adsorption and organize themselves into more or less distinct domains (head group, chain/backbone, and tail/end group). In some cases, mole ...
one can obtain a cadmium selective electrode with a ppt-level sensitivity.
Biological role
Cadmium has no known function in higher organisms and is considered toxic. Cadmium is considered an environmental pollutant hazardous to living organisms. A cadmium-dependentcarbonic anhydrase
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) () form a family of enzymes that catalyst, catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the Dissociation (chemistry), dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate a ...
has been found in some marine diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma'') is any member of a large group comprising several Genus, genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of Earth's B ...
s, which live in environments with low zinc concentrations.
Exposure to cadmium leads to raised levels in the blood cells for a number of months.
In vertebrates cadmium is preferentially absorbed in the kidneys but also in the liver and bones. Up to about 30 mg of cadmium is commonly inhaled throughout human childhood and adolescence.
Cadmium is eliminated from the body in very small amounts and mainly through urine resulting in a biological half-life of 20 to 40 years.
Cadmium is under research for its potential toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacteria, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect o ...
to increase the risk of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
, and osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
.
Environmental impact
Thebiogeochemistry
Biogeochemistry is the Branches of science, scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemistry, chemical, physics, physical, geology, geological, and biology, biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natu ...
of cadmium and its release to the environment is under research.
Safety
Individuals and organizations have been reviewing cadmium's bioinorganic aspects for its toxicity. The most dangerous form of occupational exposure to cadmium is inhalation of fine dust and fumes, or ingestion of highly soluble cadmium compounds. Inhalation of cadmium fumes can result initially inmetal fume fever
Metal fume fever, also known as brass founders' ague, brass shakes, zinc shakes, galvie flu, galvo poisoning, metal dust fever, welding shivers, or Monday morning fever, is an illness primarily caused by exposure to chemicals such as zinc oxide (Zn ...
, but may progress to chemical pneumonitis
Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris (e.g., animal dander), aspiration, herbicide ...
, pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness ...
,necrosis and death.
Cadmium is also an environmental hazard. Human exposure is primarily from fossil fuel combustion, phosphate fertilizers, natural sources, iron and steel production, cement production and related activities, nonferrous metals production, and municipal solid waste incineration. Other sources of cadmium include bread, root crops, and vegetables.Mann, Denise (23 April 2012Can Heavy Metal in Foods, Cosmetics Spur Breast Cancer Spread?
HealthDayBy via Yahoo
 There have been a few instances of general population poisoning as the result of long-term exposure to cadmium in contaminated food and water. Research into an estrogen mimicry that may induce breast cancer is ongoing, . In the decades leading up to
There have been a few instances of general population poisoning as the result of long-term exposure to cadmium in contaminated food and water. Research into an estrogen mimicry that may induce breast cancer is ongoing, . In the decades leading up to World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, mining operations contaminated the Jinzū River
The is a river that flows from Gifu Prefecture to Toyama Prefecture in Japan. The upper reaches of the river in Gifu are called the Miya River. It is in length and has a watershed of .
Etymology
The official name for the river is "Jinzu Gawa" ( ...
in Japan with cadmium and traces of other toxic metals. As a consequence, cadmium accumulated in the rice crops along the riverbanks downstream of the mines. Some members of the local agricultural communities consumed the contaminated rice and developed itai-itai disease and renal abnormalities, including proteinuria
Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein, less than 150 mg/day; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become fo ...
and glucosuria. The victims of this poisoning were almost exclusively post-menopausal women with low iron and low body stores of other minerals. Similar general population cadmium exposures in other parts of the world have not resulted in the same health problems because the populations maintained sufficient iron and other mineral levels. Thus, although cadmium is a major factor in the itai-itai disease in Japan, most researchers have concluded that it was one of several factors.
Cadmium is one of ten substances banned by the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, which regulates hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, but allows for certain exemptions and exclusions from the scope of the law.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified cadmium and cadmium compounds as carcinogenic to humans. Although occupational exposure to cadmium is linked to lung and prostate cancer, there is still uncertainty about the carcinogenicity of cadmium in low environmental exposure. Recent data from epidemiological studies suggest that intake of cadmium through diet is associated with a higher risk of endometrial, breast, and prostate cancer as well as with osteoporosis in humans. A recent study has demonstrated that endometrial tissue is characterized by higher levels of cadmium in current and former smoking females.
Cadmium exposure is associated with a large number of illnesses including kidney disease, early atherosclerosis, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. Although studies show a significant correlation between cadmium exposure and occurrence of disease in human populations, a molecular mechanism has not yet been identified. One hypothesis holds that cadmium is an endocrine disruptor
Endocrine disruptors, sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds are chemicals that can interfere with endocrine (or hormonal) systems. These disruptions can cause ...
and some experimental studies have shown that it can interact with different hormonal
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones a ...
signaling pathways. For example, cadmium can bind to the estrogen receptor
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are proteins found in cell (biology), cells that function as receptor (biochemistry), receptors for the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). There are two main classes of ERs. The first includes the intracellular estrogen ...
alpha, and affect signal transduction along the estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
and MAPK
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflamm ...
signaling pathways at low doses.
The tobacco plant absorbs and accumulates heavy metals
upright=1.2, Crystals of lead.html" ;"title="osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead">osmium, a heavy metal nearly twice as dense as lead
Heavy metals is a controversial and ambiguous term for metallic elements with relatively h ...
such as cadmium from the surrounding soil into its leaves. Following tobacco smoke inhalation, these are readily absorbed into the body of users. Tobacco smoking is the most important single source of cadmium exposure in the general population. An estimated 10% of the cadmium content of a cigarette is inhaled through smoking. Absorption of cadmium through the lungs is more effective than through the gut. As much as 50% of the cadmium inhaled in cigarette smoke may be absorbed.
On average, cadmium concentrations in the blood of smokers is 4 to 5 times greater than non-smokers and in the kidney, 2–3 times greater than in non-smokers. Despite the high cadmium content in cigarette smoke, there seems to be little exposure to cadmium from passive smoking
Passive smoking is the inhalation of tobacco smoke, called passive smoke, secondhand smoke (SHS) or environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), by individuals other than the active Tobacco smoking, smoker. It occurs when tobacco smoke diffuses into the ...
.
In a non-smoking population, food accounts for around 90% of cadmium uptake.
High quantities of cadmium can be found in crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, mollusks
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The num ...
, offal
Offal (), also called variety meats, pluck or organ meats, is the internal organ (anatomy), organs of a butchered animal. Offal may also refer to the by-products of Milling (grinding), milled grains, such as corn or wheat.
Some cultures strong ...
, frog legs
Frog legs () are the muscular hindlimbs of frogs that are consumed as food by humans in some cuisines. Frog legs are rich in protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin A, and potassium. They are often said to taste like chicken because of the mild fl ...
, cocoa solids
Dry cocoa solids are the components of cocoa beans remaining after cocoa butter, the fatty component of the bean, is extracted from chocolate liquor, roasted cocoa beans that have been ground into a liquid state. Cocoa butter is 46% to 57% of th ...
, bitter and semi-bitter chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods.
Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocesse ...
, seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), '' Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
, fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
and algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
products. However, grains, vegetables, and starchy roots and tubers
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure that plants use as storage organs for nutrients, derived from stems or roots. Tubers help plants perennate (survive winter or dry months), provide energy and nutrients, and are a means of asexual reprod ...
are consumed in much greater quantity in the U.S., and are the source of the greatest dietary exposure there.
Most plants bio-accumulate metal toxins such as cadmium and when composted to form organic fertilizers, yield a product that often can contain high amounts (e.g., over 0.5 mg) of metal toxins for every kilogram of fertilizer. Fertilizers made from animal dung (e.g., cow dung) or urban waste can contain similar amounts of cadmium. The cadmium added to the soil from fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
s (rock phosphates or organic fertilizers) become bio-available and toxic only if the soil pH
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a soil. Soil pH is a key characteristic that can be used to make informative analysis both qualitative and quantitatively regarding soil characteristics. pH is defined as the neg ...
is low (i.e., acidic soils). In the European Union, an analysis of almost 22,000 topsoil
Topsoil is the upper layer of soil. It has the highest concentration of organic matter and microorganisms and is where most of the Earth's biological soil activity occurs.
Description
Topsoil is composed of mineral particles and organic mat ...
samples with LUCAS survey concluded that 5.5% of samples have concentrations higher than 1 mg kg−1.
Zinc, copper, calcium, and iron ions, and selenium with vitamin C are used to treat cadmium intoxication, although it is not easily reversed.
Regulations
Because of the adverse effects of cadmium on the environment and human health, the supply and use of cadmium is restricted in Europe under theREACH Regulation
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is a European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006, amended on 16 December 2008 by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008. REACH addresses the production and use of che ...
.
The EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain specifies that 2.5 μg/kg body weight is a tolerable weekly intake for humans. The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives has declared 7 μg/kg body weight to be the provisional tolerable weekly intake level. The state of California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
requires a food label to carry a warning about potential exposure to cadmium on products such as cocoa powder. The European Commission has put in place the EU regulation (2019/1009) on fertilizing products (EU, 2019), adopted in June 2019 and fully applicable as of July 2022. It sets a Cd limit value in phosphate fertilizers to 60 mg kg−1 of .
The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA; ) is a regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. The United States Congress established ...
(OSHA) has set the permissible exposure limit
The permissible exposure limit (PEL or OSHA PEL) is a legal limit in the United States for exposure of an employee to a chemical substance or physical agents such as high level noise. Permissible exposure limits were established by the Occupational ...
(PEL) for cadmium at a time-weighted average (TWA) of 0.005 ppm. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the List of United States federal agencies, United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related occ ...
(NIOSH) has not set a recommended exposure limit
A recommended exposure limit (REL) is an occupational exposure limit that has been recommended by the United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. The REL is a level that NIOSH believes would be protective of worker safety ...
(REL) and has designated cadmium as a known human carcinogen. The IDLH
The term immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) is defined by the US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) as exposure to airborne contaminants that is "likely to cause death or immediate or delayed permanent adver ...
(immediately dangerous to life and health) level for cadmium is 9 mg/m3.
In addition to mercury, the presence of cadmium in some batteries has led to the requirement of proper disposal (or recycling) of batteries.
Product recalls
In May 2006, a sale of the seats fromArsenal F.C.
The Arsenal Football Club, commonly known as simply Arsenal, is a professional football club based in Islington, North London, England. They compete in the Premier League, the top tier of English football. In domestic football, Arsenal h ...
's old stadium, Highbury
Highbury is an area of North London, England, in the London Borough of Islington.
Highbury Manor
Highbury was once owned by Ranulf, brother of Ilger, and included all the areas north and east of Canonbury and Holloway Roads.
The manor hou ...
in London, England was cancelled when the seats were discovered to contain trace amounts of cadmium. Reports of high levels of cadmium use in children's jewelry in 2010 led to a US Consumer Product Safety Commission
The United States Consumer Product Safety Commission (USCPSC, CPSC, or commission) is an independent agency of the United States government. The CPSC seeks to promote the safety of consumer products by addressing "unreasonable risks" of injury ...
investigation. The U.S. CPSC issued specific recall notices for cadmium content in jewelry sold by Claire's
Claire's (formerly known as Claire's Boutiques, Claire's Boutique and Claire's Accessories) is an American retailer of accessories, jewelry, and toys primarily aimed towards tween and teen
girls, and young women. It was founded in 1961 and i ...
and Wal-Mart
Walmart Inc. (; formerly Wal-Mart Stores, Inc.) is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets (also called supercenters), discount department stores, and grocery stores in the United States and 23 other ...
stores.
In June 2010, McDonald's
McDonald's Corporation, doing business as McDonald's, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational fast food chain store, chain. As of 2024, it is the second largest by number of locations in the world, behind only the Chinese ch ...
voluntarily recalled more than 12 million promotional '' Shrek Forever After 3D'' Collectible Drinking Glasses because of the cadmium levels in paint pigments on the glassware. The glasses were manufactured by Arc International
Arc Holdings is the holding company of the Arc Group, specializing in the design and manufacturing of glass tableware. The Arc Group markets its collections in France and exports them abroad under the registered trademarks Luminarc, Arcopal, Cr ...
, of Millville, New Jersey
Millville is a city in Cumberland County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 United States census, the city's population was 27,491, a decrease of 909 (−3.2%) from the 2010 census count of 28,400, which in turn reflected an in ...
, USA.
See also
* Red List building materials *Toxic heavy metal
A toxic heavy metal is a common but misleading term for a metal-like element noted for its potential toxicity. Not all heavy metals are toxic and some toxic metals are not heavy. Elements often discussed as toxic include cadmium, mercury and ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (2012). Toxicological Profile for Cadmium. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp5.pdf *External links
Cadmium
at ''
The Periodic Table of Videos
''Periodic Videos'' (also known as ''The Periodic Table of Videos'') is a video project and YouTube channel on chemistry. It consists of a series of videos about chemical elements and the periodic table, with additional videos on other topics i ...
'' (University of Nottingham)
ATSDR Case Studies in Environmental Medicine: Cadmium Toxicity
U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...