C70 fullerene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
C70 fullerene is the
 C70 can undergo six reversible, one-electron reductions to , whereas
C70 can undergo six reversible, one-electron reductions to , whereas
fullerene
A fullerene is an allotrope of carbon whose molecule consists of carbon atoms connected by single and double bonds so as to form a closed or partially closed mesh, with fused rings of five to seven atoms. The molecule may be a hollow sphere, ...
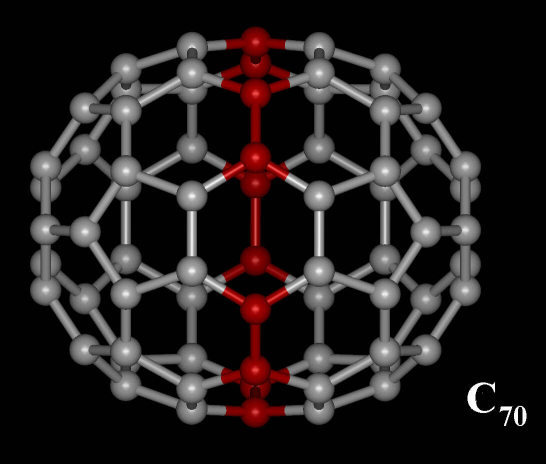
molecule consisting of 70 carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
atoms. It is a cage-like fused-ring structure which resembles a rugby ball, made of 25 hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A '' regular hexagon'' has ...
s and 12 pentagons, with a carbon atom at the vertices of each polygon and a bond along each polygon edge. A related fullerene molecule, named buckminsterfullerene (C60 fullerene), consists of 60 carbon atoms.
It was first intentionally prepared in 1985 by Harold Kroto
Sir Harold Walter Kroto (born Harold Walter Krotoschiner; 7 October 1939 – 30 April 2016), known as Harry Kroto, was an English chemist. He shared the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Robert Curl and Richard Smalley for their discovery o ...
, James R. Heath
James R. Heath (born 1962) is an American chemist and the president and professor of Institute of Systems Biology. Previous to this, he was the Elizabeth W. Gilloon Professor of Chemistry at the California Institute of Technology, after having move ...
, Sean O'Brien, Robert Curl
Robert Floyd Curl Jr. (August 23, 1933 – July 3, 2022) was an American chemist who was Pitzer–Schlumberger Professor of Natural Sciences and Professor of Chemistry at Rice University. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1996 for ...
and Richard Smalley
Richard Errett Smalley (June 6, 1943 – October 28, 2005) was an American chemist who was the Gene and Norman Hackerman Professor of Chemistry, Physics, and Astronomy at Rice University. In 1996, along with Robert Curl, also a professor of c ...
at Rice University
William Marsh Rice University (Rice University) is a private research university in Houston, Texas. It is on a 300-acre campus near the Houston Museum District and adjacent to the Texas Medical Center. Rice is ranked among the top universities ...
. Kroto, Curl and Smalley were awarded the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
for their roles in the discovery of cage-like fullerenes. The name is a homage to Buckminster Fuller
Richard Buckminster Fuller (; July 12, 1895 – July 1, 1983) was an American architect, systems theorist, writer, designer, inventor, philosopher, and futurist. He styled his name as R. Buckminster Fuller in his writings, publishing mo ...
, whose geodesic domes these molecules resemble.
History
Theoretical predictions of buckyball molecules appeared in the late 1960s to early 1970s,Katz, 363 but they went largely unnoticed. In the early 1970s, the chemistry of unsaturated carbon configurations was studied by a group at theUniversity of Sussex
, mottoeng = Be Still and Know
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £14.4 million (2020)
, budget = £319.6 million (2019–20)
, chancellor = Sanjeev Bhaskar
, vice_chancellor = Sasha Roseneil
, ...
, led by Harry Kroto and David Walton. In the 1980s a technique was developed by Richard Smalley and Bob Curl at Rice University
William Marsh Rice University (Rice University) is a private research university in Houston, Texas. It is on a 300-acre campus near the Houston Museum District and adjacent to the Texas Medical Center. Rice is ranked among the top universities ...
, Texas to isolate these substances. They used laser vaporization
Vaporization (or vaporisation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomenon ...
of a suitable target to produce clusters of atoms. Kroto realized that by using a graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
target.Katz, 368
C70 was discovered in 1985 by Robert Curl, Harold Kroto and Richard Smalley. Using laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fi ...
evaporation of graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
they found C''n'' clusters (for even ''n'' with ''n'' > 20) of which the most common were C60 and C70. For this discovery they were awarded the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. The discovery of buckyballs was serendipitous, as the scientists were aiming to produce carbon plasmas to replicate and characterize unidentified interstellar matter
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar ...
. Mass spectrometry analysis of the product indicated the formation of spheroidal carbon molecules.
Synthesis
In 1990, K. Fostiropoulos, W. Krätchmer and D. R. Huffman developed a simple and efficient method of producing fullerenes in gram and even kilogram amounts which boosted fullerene research. In this technique, carbon soot is produced from two high-purity graphite electrodes by igniting an arc discharge between them in an inert atmosphere (helium gas). Alternatively, soot is produced by laser ablation of graphite orpyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''py ...
of aromatic hydrocarbon
Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The parent member of aromatic compounds is benzene. The word "aromatic" originates from the past groupin ...
s. Fullerenes are extracted from the soot using a multistep procedure. First, the soot is dissolved in appropriate organic solvents. This step yields a solution containing up to 70% of C60 and 15% of C70, as well as other fullerenes. These fractions are separated using chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system ( ...
.
Properties
Molecule
The C70 molecule has a D5h symmetry and contains 37 faces (25 hexagons and 12 pentagons) with a carbon atom at the vertices of each polygon and a bond along each polygon edge. Its structure is similar to that of C60 molecule (20 hexagons and 12 pentagons), but has a belt of 5 hexagons inserted at the equator. The molecule has eight bond lengths ranging between 0.137 and 0.146 nm. Each carbon atom in the structure is bonded covalently with 3 others. C70 can undergo six reversible, one-electron reductions to , whereas
C70 can undergo six reversible, one-electron reductions to , whereas oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
is irreversible. The first reduction requires around 1.0 V ( Fc/), indicating that C70 is an electron acceptor.
Solution
Fullerenes are sparingly soluble in many aromaticsolvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
s such as toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a colorless, water-insoluble liquid with the smell associated with paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of a methyl group (CH3) a ...
and others like carbon disulfide
Carbon disulfide (also spelled as carbon disulphide) is a neurotoxic, colorless, volatile liquid with the formula and structure . The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical n ...
, but not in water. Solutions of C70 are a reddish brown. Millimeter-sized crystals of C70 can be grown from solution.
Solid
Solid C70 crystallizes inmonoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic s ...
, hexagonal, rhombohedral
In geometry, a rhombohedron (also called a rhombic hexahedron or, inaccurately, a rhomboid) is a three-dimensional figure with six faces which are rhombi. It is a special case of a parallelepiped where all edges are the same length. It can be us ...
, and face-centered cubic (fcc) polymorphs at room temperature. The fcc phase is more stable at temperatures above 70 °C. The presence of these phases is rationalized as follows. In a solid, C70 molecules form an fcc arrangement where the overall symmetry depends on their relative orientations. The low-symmetry monoclinic form is observed when molecular rotation is locked by temperature or strain. Partial rotation along one of the symmetry axes of the molecule results in the higher hexagonal or rhombohedral symmetries, which turn into a cubic structure when the molecules start freely rotating.
All phases of C70 form brownish crystals with a bandgap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference (i ...
of 1.77 eV; they are n-type semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
s where conductivity is attributed to oxygen diffusion into the solid from atmosphere. The unit cell of fcc C70 solid contains voids at 4 octahedral and 12 tetrahedral sites.Katz, 372 They are large enough to accommodate impurity atoms. When electron-donating elements, such as alkali metals, are doped into these voids, C70 converts into a conductor with conductivity up to around 2 S/cm.
References
Bibliography
* {{Molecules detected in outer space Fullerenes