C-Arm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An X-ray image intensifier (XRII) is an image intensifier that converts
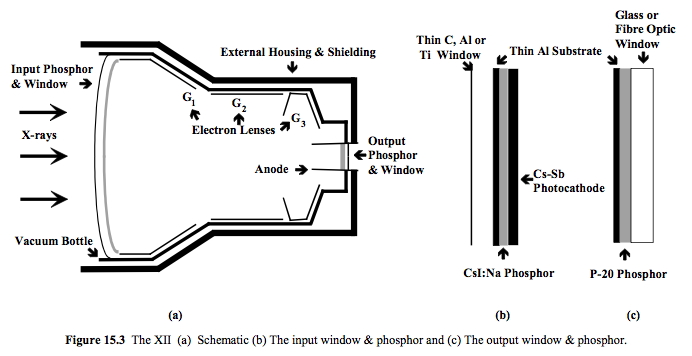 The overall function of an image intensifier is to convert incident x-ray photons to light photons of sufficient intensity to provide a viewable image. This occurs in several stages. The input window is convex is shape, made up of aluminium to minimise the scattering of X-rays. The window is 1 mm in thickness. Once X-rays pass through the aluminium windows, it encounters input phosphor that converts X-rays into light photons. The thickness of input phosphor range from 300 to 450 micrometres reach a compromise between absorption efficiency of X-rays and spatial resolution. Thicker input phosphor has higher absorption efficiency but poor spatial resoution and vice versa. Sodium activated Caesium Iodide is typically used due to its higher conversion efficiency thanks to high
The overall function of an image intensifier is to convert incident x-ray photons to light photons of sufficient intensity to provide a viewable image. This occurs in several stages. The input window is convex is shape, made up of aluminium to minimise the scattering of X-rays. The window is 1 mm in thickness. Once X-rays pass through the aluminium windows, it encounters input phosphor that converts X-rays into light photons. The thickness of input phosphor range from 300 to 450 micrometres reach a compromise between absorption efficiency of X-rays and spatial resolution. Thicker input phosphor has higher absorption efficiency but poor spatial resoution and vice versa. Sodium activated Caesium Iodide is typically used due to its higher conversion efficiency thanks to high
 A system containing an image intensifier may be used either as a fixed piece of equipment in a dedicated screening room or as mobile equipment for use in an
A system containing an image intensifier may be used either as a fixed piece of equipment in a dedicated screening room or as mobile equipment for use in an
X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s into visible light at higher intensity than the more traditional fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, ...
screens can. Such intensifiers are used in X-ray imaging systems (such as fluoroscopes) to allow low-intensity X-rays to be converted to a conveniently bright
Bright may refer to:
Common meanings
*Bright, an adjective meaning giving off or reflecting illumination; see Brightness
*Bright, an adjective meaning someone with intelligence
People
* Bright (surname)
* Bright (given name)
*Bright, the stage na ...
visible light output. The device contains a low absorbency/scatter input window, typically aluminum, input fluorescent screen, photocathode, electron optics, output fluorescent screen and output window. These parts are all mounted in a high vacuum environment within glass or, more recently, metal/ceramic. By its intensifying effect, It allows the viewer to more easily see the structure of the object being imaged than fluorescent screens alone, whose images are dim. The XRII requires lower absorbed doses due to more efficient conversion of X-ray quanta to visible light. This device was originally introduced in 1948.
Operation
 The overall function of an image intensifier is to convert incident x-ray photons to light photons of sufficient intensity to provide a viewable image. This occurs in several stages. The input window is convex is shape, made up of aluminium to minimise the scattering of X-rays. The window is 1 mm in thickness. Once X-rays pass through the aluminium windows, it encounters input phosphor that converts X-rays into light photons. The thickness of input phosphor range from 300 to 450 micrometres reach a compromise between absorption efficiency of X-rays and spatial resolution. Thicker input phosphor has higher absorption efficiency but poor spatial resoution and vice versa. Sodium activated Caesium Iodide is typically used due to its higher conversion efficiency thanks to high
The overall function of an image intensifier is to convert incident x-ray photons to light photons of sufficient intensity to provide a viewable image. This occurs in several stages. The input window is convex is shape, made up of aluminium to minimise the scattering of X-rays. The window is 1 mm in thickness. Once X-rays pass through the aluminium windows, it encounters input phosphor that converts X-rays into light photons. The thickness of input phosphor range from 300 to 450 micrometres reach a compromise between absorption efficiency of X-rays and spatial resolution. Thicker input phosphor has higher absorption efficiency but poor spatial resoution and vice versa. Sodium activated Caesium Iodide is typically used due to its higher conversion efficiency thanks to high atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
and mass attenuation coefficient The mass attenuation coefficient, or mass narrow beam attenuation coefficient of a material is the attenuation coefficient normalized by the density of the material; that is, the attenuation per unit mass (rather than per unit of distance). Thus, ...
, when compared to zinc-cadmium sulfide. The input phosphor are arranged into small tubes, to allow photons to pass through the tube, without scattering, this improving the spatial resolution. The light photons are then converted to electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s by a photocathode. The photocathode is made up of antimony caesium, which is to match the photons produced from input phosphor, thus maximise the efficiency of producing photoelectrons. The photocathode has a thickness of 20 nm with absorption efficacy of 10 to 15%.
A potential difference
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to m ...
(25-35 kilovolts) created between the anode and photocathode then accelerates these photoelectrons while electron lens
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a g ...
es focus the beam down to the size of the output window. The output window is typically made of silver-activated zinc-cadmium sulfide and converts incident electrons back to visible light photons. At the input and output phosphors the number of photons is multiplied by several thousands, so that overall there is a large brightness gain. This gain makes image intensifiers highly sensitive to X-rays such that relatively low doses can be used for fluoroscopic procedures.
History
X-ray image intensifiers became available in the early 1950s and were viewed through a microscope. Viewing of the output was via mirrors and optical systems until the adaption of television systems in the 1960s. Additionally, the output was able to be captured on systems with a 100mm cut film camera using pulsed outputs from an X-ray tube similar to a normal radiographic exposure; the difference being the II rather than a film screen cassette provided the image for the film to record. The input screens range from 15–57 cm, with the 23 cm, 33 cm and 40 cm being among the most common. Within each image intensifier, the actual field size can be changed using the voltages applied to the internal electron optics to achieve magnification and reduced viewing size. For example, the 23 cm commonly used in cardiac applications can be set to a format of 23, 17, and 13 cm. Because the output screen remains fixed in size, the output appears to "magnify" the input image. High-speed digitalisation with analogue video signal came about in the mid-1970s, with pulsed fluoroscopy developed in the mid-1980s harnessing low dose rapid switching X-ray tubes. In the late 1990s image intensifiers began being replaced with flat panel detectors (FPDs) on fluoroscopy machines giving competition to the image intensifiers.Clinical applications
"C-arm" mobile fluoroscopy machines are often colloquially referred to as image intensifiers (or IIs), however strictly speaking the image intensifier is only one part of the machine (namely the detector). Fluoroscopy, using an X-ray machine with an image intensifier, has applications in many areas of medicine. Fluoroscopy allows live images to be viewed so thatimage-guided surgery Image-guided surgery (IGS) is any surgical procedure where the surgeon uses tracked surgical instruments in conjunction with preoperative or intraoperative images in order to directly or indirectly guide the procedure. Image guided surgery systems u ...
is feasible. Common uses include orthopedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal ...
, gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- “belly”, -énteron “intestine”, and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract ...
and cardiology
Cardiology () is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular h ...
. Less common applications can include dentistry.
Configurations
operating theatre
An operating theater (also known as an operating room (OR), operating suite, or operation suite) is a facility within a hospital where surgical operations are carried out in an aseptic environment.
Historically, the term "operating theater" refe ...
. A mobile fluoroscopy unit generally consists of two units, the X-ray generator
An X-ray generator is a device that produces X-rays. Together with an X-ray detector, it is commonly used in a variety of applications including medicine, X-ray fluorescence, electronic assembly inspection, and measurement of material thicknes ...
and image detector (II) on a moveable C-arm, and a separate workstation unit used to store and manipulate the images. The patient is positioned between the two arms, typically on a radiolucent
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypod ...
bed. Fixed systems may have a c-arm mounted to a ceiling gantry, with a separate control area. Most systems arranged as c-arms can have the image intensifier positioned above or below the patient (with the X-ray tube below or above respectively), although some static in room systems may have fixed orientations. From a radiation protection
Radiation protection, also known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". Expos ...
standpoint, under-couch (X-ray tube) operation is preferable as it reduces the amount of scattered radiation on operators and workers. Smaller "mini" mobile c-arms are also available, primarily used to image extremities, for example for minor hand surgery.
Flat panel detectors
Flat Detectors are an alternative to Image Intensifiers. The advantages of this technology include: lower patient dose and increased image quality because the X-rays are always pulsed, and no deterioration of the image quality over time. Despite FPD being at a higher cost than II/TV systems, the noteworthy changes in the physical size and accessibility for the patients is worth it, especially when dealing with paediatric patients.Feature comparison of II/TV and FPD Systems
See also
* *References
{{DEFAULTSORT:X-Ray Image Intensifier Image Radiography Image Medical imaging