Bukharim quarter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Bukharan Quarter ( he, שכונת הבוכרים, ''Shkhunat HaBukharim''), also HaBukharim Quarter or Bukharim Quarter, is a neighborhood in the center of
The Bukharan Quarter ( he, שכונת הבוכרים, ''Shkhunat HaBukharim''), also HaBukharim Quarter or Bukharim Quarter, is a neighborhood in the center of
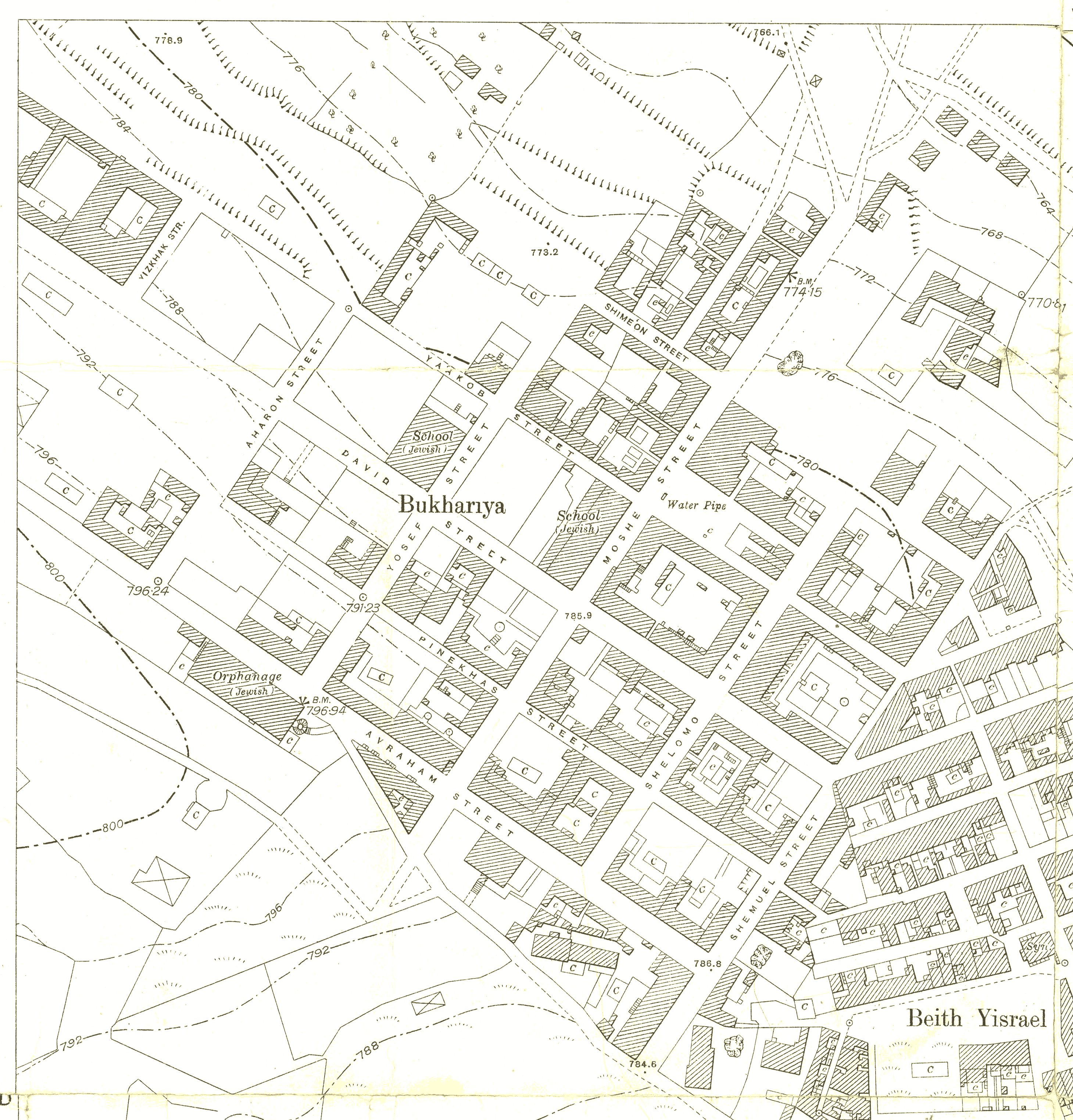 The first immigrants of Bukharan Jews from
The first immigrants of Bukharan Jews from Bukharan Quarter
/ref> In 1905-1908, a dairy was opened and cotton fields were planted on the outskirts of the neighborhood.
(?). Construction of the quarter continued into the early 1950s. A total of 200 houses were built. During
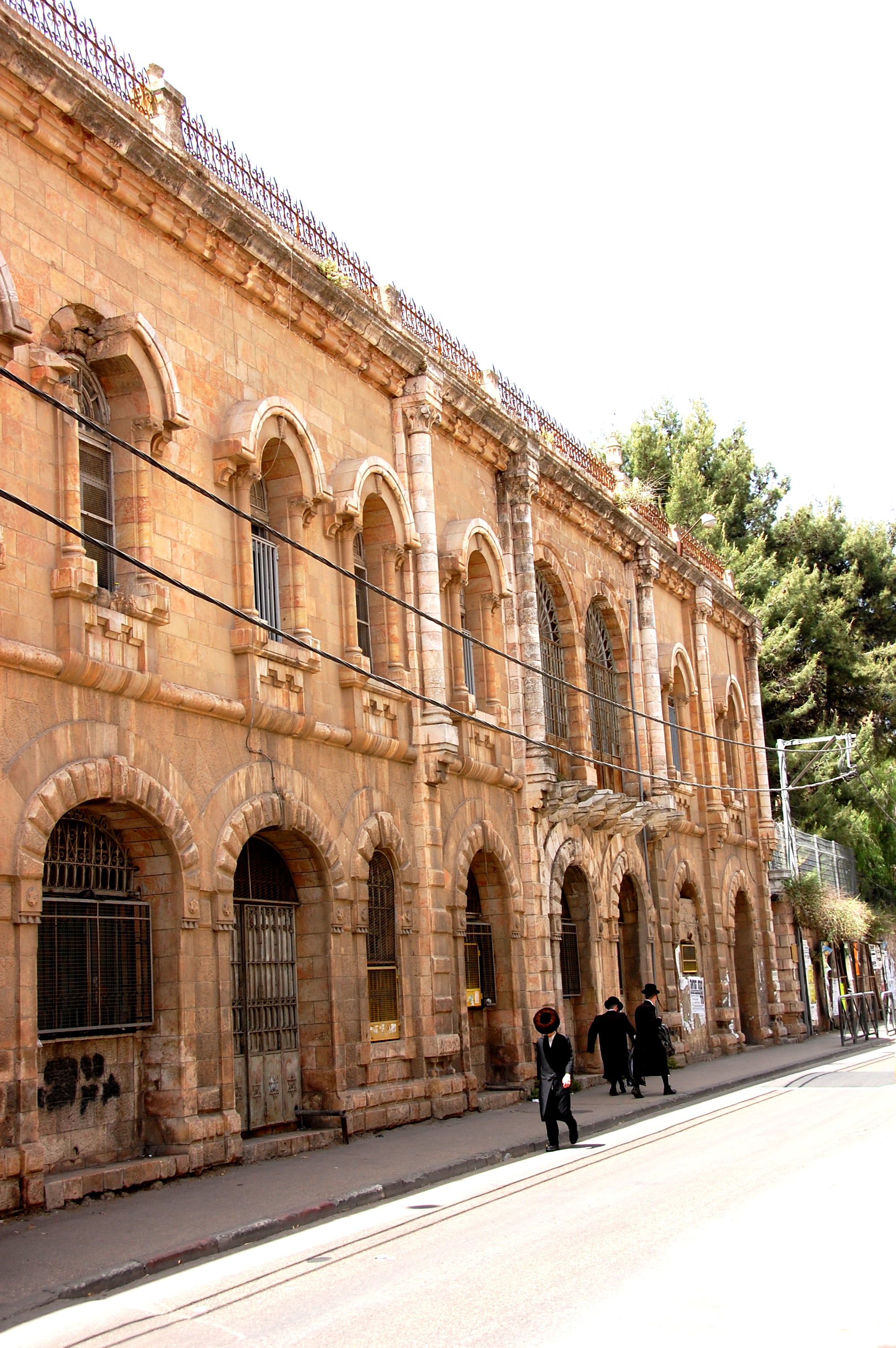
 Between 1905–1914 Bukharan merchant Elisha Yehudayoff and his son-in-law, Yisrael Haim Hefetz, built the ''Armon'' (lit. "palace") using local limestone and Italian marble with Italian-baroque ornaments. The "Armon" hosted many of the leading figures of the time. During World War I, the Ottoman army had its headquarters there. When the British captured Jerusalem in 1917, a celebratory reception was held in the "Armon". 200 Jewish soldiers serving in the British army attended a Passover Seder there. In 1921, the founding convention of the
Between 1905–1914 Bukharan merchant Elisha Yehudayoff and his son-in-law, Yisrael Haim Hefetz, built the ''Armon'' (lit. "palace") using local limestone and Italian marble with Italian-baroque ornaments. The "Armon" hosted many of the leading figures of the time. During World War I, the Ottoman army had its headquarters there. When the British captured Jerusalem in 1917, a celebratory reception was held in the "Armon". 200 Jewish soldiers serving in the British army attended a Passover Seder there. In 1921, the founding convention of the
 The Davidoff House (10, HaBukharim Street) was built in 1906 as an opulent Italian-style mansion for Joseph Davidoff, after the
The Davidoff House (10, HaBukharim Street) was built in 1906 as an opulent Italian-style mansion for Joseph Davidoff, after the
 The Bukharan Quarter ( he, שכונת הבוכרים, ''Shkhunat HaBukharim''), also HaBukharim Quarter or Bukharim Quarter, is a neighborhood in the center of
The Bukharan Quarter ( he, שכונת הבוכרים, ''Shkhunat HaBukharim''), also HaBukharim Quarter or Bukharim Quarter, is a neighborhood in the center of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. The neighborhood was established by Bukharan Jews of the Old Yishuv
The Old Yishuv ( he, היישוב הישן, ''haYishuv haYashan'') were the Jewish communities of the southern Syrian provinces in the Ottoman period, up to the onset of Zionist aliyah and the consolidation of the New Yishuv by the end of Wor ...
. The neighborhood also anchored communities from modern-day Afghanistan and the Iranian city of Meshad. It belonged to the early Jewish neighborhoods built outside the Old City of Jerusalem as part of a process which began in the 1850s. Today most of the residents are Haredi Jews
Haredi Judaism ( he, ', ; also spelled ''Charedi'' in English; plural ''Haredim'' or ''Charedim'') consists of groups within Orthodox Judaism that are characterized by their strict adherence to ''halakha'' (Jewish law) and traditions, in oppos ...
.
The quarter borders Tel Arza Tel Arza ( he, תל ארזה}) is a Hareidi neighborhood in northern Jerusalem. It is bordered by Ezrat Torah on the west, Shikun Chabad on the south, the Bukharim quarter on the east, and Sanhedria on the north.
Tel Arza was established in 1931 ...
on the west, the Shmuel HaNavi neighborhood on the north, Arzei HaBira on the east, and Geula
Geula ( he, גאולה lit. ''Redemption'') is a neighborhood in the center of Jerusalem, populated mainly by Haredi Jews. Geula is bordered by Zikhron Moshe and Mekor Baruch on the west, the Bukharim neighborhood on the north, Mea Shearim on ...
on the south.
History
 The first immigrants of Bukharan Jews from
The first immigrants of Bukharan Jews from Russian Turkestan
Russian Turkestan (russian: Русский Туркестан, Russkiy Turkestan) was the western part of Turkestan within the Russian Empire’s Central Asian territories, and was administered as a Krai or Governor-Generalship. It comprised the ...
(Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
) settled in Jerusalem in the 1870s and 1880s. In 1890, seven members of the Bukharan Jewish community formed the Hovevei Zion
Hovevei Zion ( he, חובבי ציון, lit. '' hose who areLovers of Zion''), also known as Hibbat Zion ( he, חיבת ציון), refers to a variety of organizations which were founded in 1881 in response to the Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russ ...
Association of the Jewish communities of Bukhara, Samarkand and Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2 ...
. In 1891, the association bought land and drew up a charter stating that the new quarter would be built in the style of Europe's major cities. Architect Conrad Schick
Conrad Schick (1822–1901) was a German architect, archaeologist and Protestant missionary who settled in Jerusalem in the mid-nineteenth century.Perry & Yodim (2004) For many decades he was head of the "House of Industry" at the Christ Church, ...
was employed to design the neighborhood. The streets were three times wider than even major thoroughfares in Jerusalem at the time, and spacious mansions were built with large courtyards. The homes were designed with neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
windows, European tiled roofs, neo-Moorish
Moorish Revival or Neo-Moorish is one of the exotic revival architectural styles that were adopted by architects of Europe and the Americas in the wake of Romanticist Orientalism. It reached the height of its popularity after the mid-19th centur ...
arches and Italian marble. Facades were decorated with Jewish motifs such as the Star of David and Hebrew inscriptions.
The founders named their settlement Rehovot based on a verse from the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Isaac Isaac; grc, Ἰσαάκ, Isaák; ar, إسحٰق/إسحاق, Isḥāq; am, ይስሐቅ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was th ...
) called it Rehoboth hat is Broad places or Room saying, "Now the Lord has made room for us, and we shall be fruitful in the land." (). It became also historically known as Bukhariyeh.
The neighborhood's Baba Tama Synagogue was built in 1894 and named for the Bukharan Jew who financed it.'' Isaac Isaac; grc, Ἰσαάκ, Isaák; ar, إسحٰق/إسحاق, Isḥāq; am, ይስሐቅ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was th ...
/ref> In 1905-1908, a dairy was opened and cotton fields were planted on the outskirts of the neighborhood.
(?). Construction of the quarter continued into the early 1950s. A total of 200 houses were built. During
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the Ottoman army occupied several buildings and cut down almost all of the trees.
In 1920, a factory for weaving Persian carpet
A Persian carpet ( fa, فرش ایرانی, translit=farš-e irâni ) or Persian rug ( fa, قالی ایرانی, translit=qâli-ye irâni ),Savory, R., ''Carpets'',(Encyclopaedia Iranica); accessed January 30, 2007. also known as Iranian ...
s opened, providing employment for 80 women.
Landmarks
Yehudayoff Palace ("Armon")
 Between 1905–1914 Bukharan merchant Elisha Yehudayoff and his son-in-law, Yisrael Haim Hefetz, built the ''Armon'' (lit. "palace") using local limestone and Italian marble with Italian-baroque ornaments. The "Armon" hosted many of the leading figures of the time. During World War I, the Ottoman army had its headquarters there. When the British captured Jerusalem in 1917, a celebratory reception was held in the "Armon". 200 Jewish soldiers serving in the British army attended a Passover Seder there. In 1921, the founding convention of the
Between 1905–1914 Bukharan merchant Elisha Yehudayoff and his son-in-law, Yisrael Haim Hefetz, built the ''Armon'' (lit. "palace") using local limestone and Italian marble with Italian-baroque ornaments. The "Armon" hosted many of the leading figures of the time. During World War I, the Ottoman army had its headquarters there. When the British captured Jerusalem in 1917, a celebratory reception was held in the "Armon". 200 Jewish soldiers serving in the British army attended a Passover Seder there. In 1921, the founding convention of the Chief Rabbinate
Chief Rabbi ( he, רב ראשי ''Rav Rashi'') is a title given in several countries to the recognized religious leader of that country's Jewish community, or to a rabbinic leader appointed by the local secular authorities. Since 1911, through a ...
took place at the "Armon", at which Rabbis Abraham Isaac Kook
Abraham Isaac Kook (; 7 September 1865 – 1 September 1935), known as Rav Kook, and also known by the acronym HaRaAYaH (), was an Orthodox rabbi, and the first Ashkenazi Chief Rabbi of British Mandatory Palestine. He is considered to be one ...
and Jacob Meir
Yaakov Meir CBE (1856–1939), was an Orthodox rabbi, and the first Sephardic Chief Rabbi appointed under the British Mandate of Palestine. A Talmudic scholar, fluent in Hebrew as well as five other languages, he enjoyed a reputation as one of Je ...
were elected. At the end of the British Mandate the "Armon" served as a meeting place for the Irgun
Irgun • Etzel
, image = Irgun.svg , image_size = 200px
, caption = Irgun emblem. The map shows both Mandatory Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan, which the Irgun claimed in its entirety for a future Jewish state. The acronym "Etzel" i ...
.
Davidoff House
Great War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
it became for a decade (1915-25) the home of the Hebrew Gymnasium in Jerusalem, a high school which had been founded in the neighborhood in 1909, and it currently serves as the quarter's community center.
Notable residents
*Yitzhak Ben-Zvi
Yitzhak Ben-Zvi ( he, יִצְחָק בֶּן־צְבִי ''Yitshak Ben-Tsvi''; 24 November 188423 April 1963) was a historian, Labor Zionist leader and the longest-serving President of Israel.
Biography
Born in Poltava in the Russian Empir ...
(1884–1963), historian, Labor Zionist leader, President of Israel
*Joseph Klausner
Joseph Gedaliah Klausner ( he, יוסף גדליה קלוזנר; 20 August 1874 – 27 October 1958), was a Lithuanian-born Israeli historian and professor of Hebrew literature. He was the chief redactor of the '' Encyclopedia Hebraica''. He was ...
(1874–1958), historian and professor of Hebrew literature
* Dorrit Moussaieff (born 1950), Israeli jewellery designer, former First Lady of Iceland
* Shlomo Moussaieff (1852–1922), rabbi, gemstone trader, one of the neighborhood's founders
*Moshe Sharett
Moshe Sharett ( he, משה שרת, born Moshe Chertok (Hebrew: ) 15 October 1894 – 7 July 1965) was a Russian-born Israeli politician who served as Israel's second prime minister from 1954 to 1955. A member of Mapai, Sharett's term was b ...
(1894–1965), Labor Zionist leader, Prime Minister of Israel
*Rachel Yanait
Rachel Yanait Ben-Zvi ( he, רחל ינאית בן-צבי; 1886 – 16 November 1979) was an Israeli author and educator, and a leading Labor Zionist. Ben-Zvi was the wife of the second President of Israel, Yitzhak Ben-Zvi.
Biography
Rachel Yana ...
(1886–1979), educator, leading Labor Zionist, wife of Yitzhak Ben-Zvi
See also
* Batei Saidoff, a house built in 1911 by Y. Saidoff, a Bukharan Jew, outside the Bukharan Quarter * Bukharan Jews in Israel *Expansion of Jerusalem in the 19th century
The expansion of Jerusalem in the 19th century, also referred to as the departure from the walls, was the process of building new residences outside of the Old City walls, and shifting the city center to the new neighborhoods. The process started ...
*History of Jerusalem
During its long history, Jerusalem has been attacked 52 times, captured and recaptured 44 times, besieged 23 times, and destroyed twice.. According to Eric H. Cline's tally in Jerusalem Besieged. The oldest part of the city was settled in the ...
Notes
References
{{Coord, 31, 47, 35, N, 35, 13, 8, E, display=title Neighbourhoods of Jerusalem Orthodox Jewish communities in Jerusalem Bukharan-Jewish culture in Israel