Bukharian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bukharan Jews ( Bukharian: יהודיאני בוכארא/яҳудиёни Бухоро, ''Yahudiyoni Bukhoro''; he, יהודי בוכרה, ''Yehudey Bukhara''), in modern times also called Bukharian Jews ( Bukharian: יהודיאני בוכארי/яҳудиёни бухорӣ, ''Yahudiyoni Bukhorī''; he, יהודים בוכרים, ''Yehudim Bukharim''), are an ethnoreligious
 The Bukharan Jews originally called themselves Bnei Israel (children of the
The Bukharan Jews originally called themselves Bnei Israel (children of the
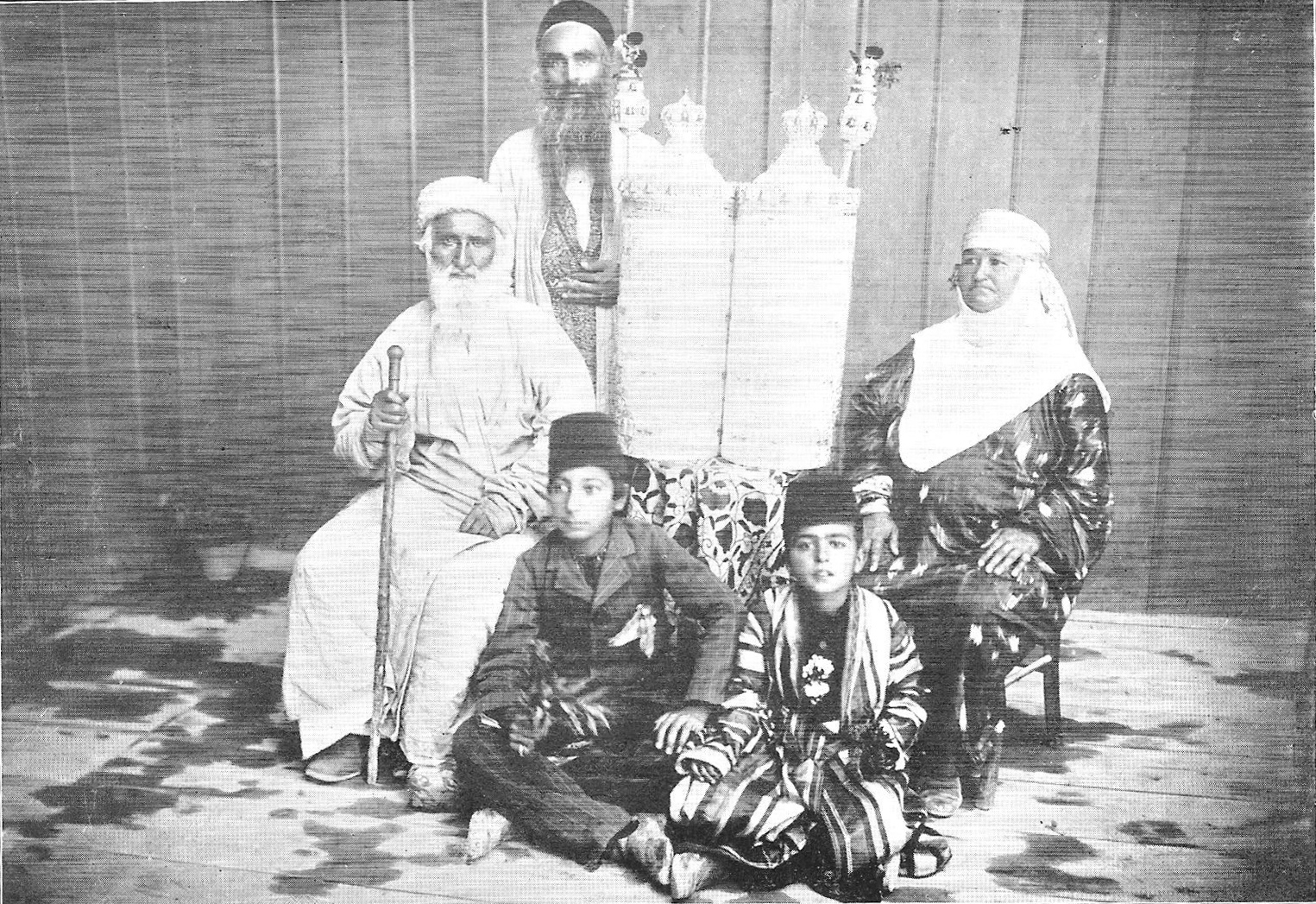

 During the 18th century, Bukharan Jews faced considerable discrimination and persecution. Jewish centers were closed down, the Muslims of the region usually forced conversion on the Jews, and the Bukharan Jewish population dramatically decreased to the point where they were almost extinct. Due to pressures to convert to
During the 18th century, Bukharan Jews faced considerable discrimination and persecution. Jewish centers were closed down, the Muslims of the region usually forced conversion on the Jews, and the Bukharan Jewish population dramatically decreased to the point where they were almost extinct. Due to pressures to convert to
 In 1793, a missionary kabbalist named Rabbi Yosef Maimon, who was a
In 1793, a missionary kabbalist named Rabbi Yosef Maimon, who was a 
"The Silk Road Leads to Queens"
''

 Currently, Bukharan Jews are mostly concentrated in the U.S. in
Currently, Bukharan Jews are mostly concentrated in the U.S. in
"Bukharan Jews now in Queens recreate their Sukkot memories"
''
"A Lost Tribe...Found in Queens"
, '' In December 1999, the First Congress of the Bukharian Jews of the United States and Canada convened in Queens. In 2007, Bukharan-American Jews initiated lobbying efforts on behalf of their community.Ruby, Walte
In December 1999, the First Congress of the Bukharian Jews of the United States and Canada convened in Queens. In 2007, Bukharan-American Jews initiated lobbying efforts on behalf of their community.Ruby, Walte
"The Bukharian Lobby"
, ''
 The Bukharan Jews have a distinct musical tradition called
The Bukharan Jews have a distinct musical tradition called
 Bukharan cuisine consists of many unique dishes, distinctly influenced by ethnic dishes historically and currently found along the
Bukharan cuisine consists of many unique dishes, distinctly influenced by ethnic dishes historically and currently found along the
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
sub-group of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
that historically spoke Bukharian, a Judeo-Tajik dialect of the Tajik language
Tajik (Tajik: , , ), also called Tajiki Persian (Tajik: , , ) or Tajiki, is the variety of Persian spoken in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan by Tajiks. It is closely related to neighbouring Dari with which it forms a continuum of mutually intelligi ...
, in turn a variety of the Persian language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken an ...
. Their name comes from the former Central Asian Emirate of Bukhara
The Emirate of Bukhara ( fa, , Amārat-e Bokhārā, chg, , Bukhārā Amirligi) was a Muslim polity in Central Asia that existed from 1785 to 1920 in what is modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan. It occupied the land ...
(now primarily Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
), which once had a sizable Jewish population. Bukharan Jews comprise Persian-speaking Jewry along with the Jews of Iran, Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, and the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
.
Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
, the great majority have immigrated to Israel or to the United States while others have immigrated to Europe or Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
. Bukharan Jews are Mizrahi Jews
Mizrahi Jews ( he, יהודי המִזְרָח), also known as ''Mizrahim'' () or ''Mizrachi'' () and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or ''Edot HaMizrach'' (, ), are a grouping of Jewish communities comprising those who remained ...
.Goodman, Peter. "Bukharian Jews find homes on Long Island", ''Newsday
''Newsday'' is an American daily newspaper that primarily serves Nassau and Suffolk counties on Long Island, although it is also sold throughout the New York metropolitan area. The slogan of the newspaper is "Newsday, Your Eye on LI", and fo ...
'', September 2004.
Name and language
 The Bukharan Jews originally called themselves Bnei Israel (children of the
The Bukharan Jews originally called themselves Bnei Israel (children of the northern Kingdom of Israel
The Kingdom of Israel (), or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an Israelite kingdom in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. The kingdom controlled the areas of Samaria, Galilee and parts of Transjordan. Its capital, for the most part, was Sama ...
), which relates specifically to the Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
of Assyrian captivity
The Assyrian captivity (or the Assyrian exile) is the period in the history of ancient Israel and Judah during which several thousand Israelites from the Kingdom of Israel were forcibly relocated by the Neo-Assyrian Empire. This is one of the man ...
. The term ''Bukharan'' was coined by Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an travellers who visited Central Asia around the 16th century. Since most of the Jewish community at the time lived under the Emirate of Bukhara
The Emirate of Bukhara ( fa, , Amārat-e Bokhārā, chg, , Bukhārā Amirligi) was a Muslim polity in Central Asia that existed from 1785 to 1920 in what is modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan. It occupied the land ...
, they came to be known as ''Bukharan'' Jews. The name by which the community called itself is " Bnei Isro'il" (Israelites of the Northern Kingdom of Israel). Their Muslim neighbors would call them Yahudi, which is misidentification, since it is specific to the southern Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah ( he, , ''Yəhūdā''; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒁕𒀀𒀀 ''Ya'údâ'' 'ia-ú-da-a-a'' arc, 𐤁𐤉𐤕𐤃𐤅𐤃 ''Bēyt Dāwīḏ'', " House of David") was an Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. C ...
, but the Bnei Israel self-designation emphasizes their Israelite origins from the northern Kingdom of Israel
The Kingdom of Israel (), or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an Israelite kingdom in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. The kingdom controlled the areas of Samaria, Galilee and parts of Transjordan. Its capital, for the most part, was Sama ...
.
Bukharan Jews used Bukharian or '' Bukhori'', a Jewish dialect of the Tajik language
Tajik (Tajik: , , ), also called Tajiki Persian (Tajik: , , ) or Tajiki, is the variety of Persian spoken in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan by Tajiks. It is closely related to neighbouring Dari with which it forms a continuum of mutually intelligi ...
(in turn a variety of Persian) with linguistic elements of Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, to communicate among themselves. This language was used for all cultural and educational life among the Jews. It was used widely until Central Asia was "Russified
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
" by the Russians and the dissemination of "religious" information was halted. The elderly Bukharian generation used ''Bukhori'' as their primary language but largely speak Russian (sometimes with a slight Bukharian accent). The younger generation use Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
as their primary language, but often do understand or speak Bukharian.
The first primary written account of Jews in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
dates to the beginning of the 4th century CE. It is recalled in the Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
by Rabbi Shmuel bar Bisna, a member of the Talmudic academy in Pumbeditha, who traveled to Margiana (present-day Merv
Merv ( tk, Merw, ', مرو; fa, مرو, ''Marv''), also known as the Merve Oasis, formerly known as Alexandria ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρεια), Antiochia in Margiana ( grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐν τῇ Μαργιανῇ) and ...
in Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
). The presence of Jewish communities in Merv is also proven by Jewish writings on ossuaries from the 5th and 6th centuries, uncovered between 1954 and 1956.
History
While some Bukharan Jews relate their own ancestry to the period of theAssyrian captivity
The Assyrian captivity (or the Assyrian exile) is the period in the history of ancient Israel and Judah during which several thousand Israelites from the Kingdom of Israel were forcibly relocated by the Neo-Assyrian Empire. This is one of the man ...
and exiles from the tribes of Naphtali
According to the Book of Genesis, Naphtali (; ) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Bilhah (Jacob's sixth son). He was the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Naphtali.
Some biblical commentators have suggested that the name ''Naphtali ...
and Issachar
Issachar () was, according to the Book of Genesis, the fifth of the six sons of Jacob and Leah (Jacob's ninth son), and the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Issachar. However, some Biblical scholars view this as an eponymous metaphor pro ...
, basing this assumption on a reading of "Habor" at II Kings 17:6 as a reference to Bukhara, Bukharan Jewish tradition generally associates their establishment in the country with the emigration of Persian Jews, fleeing the persecutions of King Peroz I
Peroz I ( pal, 𐭯𐭩𐭫𐭥𐭰, Pērōz) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II (), he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III (), eventually seizing the throne after ...
(458–485 CE). In the opinion of some scholars, Jews settled in Central Asia in the sixth century, but it is certain that during the eighth to ninth centuries they lived in Central Asian cities such as Balkh, Khwarezm, and Merv. At that time, and until approximately the sixteenth century, Bukharan Jews formed a group continuous with Jews of Iran and Afghanistan.
The Bukharan Jews are considered one of the oldest ethno-religious groups of Central Asia and over the years they have developed their own distinct culture. Throughout the years, Jews from other Eastern countries such as Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and ...
, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, and Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to A ...
migrated into Central Asia (by way of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
).
16th to 18th centuries

 During the 18th century, Bukharan Jews faced considerable discrimination and persecution. Jewish centers were closed down, the Muslims of the region usually forced conversion on the Jews, and the Bukharan Jewish population dramatically decreased to the point where they were almost extinct. Due to pressures to convert to
During the 18th century, Bukharan Jews faced considerable discrimination and persecution. Jewish centers were closed down, the Muslims of the region usually forced conversion on the Jews, and the Bukharan Jewish population dramatically decreased to the point where they were almost extinct. Due to pressures to convert to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
, persecution, and isolation from the rest of the Jewish world, the Jews of Bukhara began to lack knowledge and practice of their Jewish religion. By the middle of the 18th century, practically all Bukharan Jews lived in the Bukharan Emirate
The Emirate of Bukhara ( fa, , Amārat-e Bokhārā, chg, , Bukhārā Amirligi) was a Muslim polity in Central Asia that existed from 1785 to 1920 in what is modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan. It occupied the land ...
.
Rabbi Yosef Maimon
 In 1793, a missionary kabbalist named Rabbi Yosef Maimon, who was a
In 1793, a missionary kabbalist named Rabbi Yosef Maimon, who was a Sephardic
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
Jew originally from Tetuan, Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to A ...
, travelled to Bukhara
Bukhara ( Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and the city ...
to collect/solicit money from Jewish patrons. Prior to Maimon's arrival, the native Jews of Bukhara followed the Persian religious tradition. Maimon staunchly demanded that the native Jews of Bukhara adopt Sephardic
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
traditions. Many of the native Jews were opposed to this and the community split into two factions. The followers of the Maimon clan eventually won the struggle for religious authority over the native Bukharans, and Bukharan Jewry forcefully switched to Sephardi customs. The supporters of the Maimon clan, in the conflict, credit Maimon with causing a revival of Jewish practice among Bukharan Jews which they claim was in danger of dying out. However, there is evidence that there were Torah scholars present upon his arrival to Bukhara, but because they followed the Persian rite their practices were aggressively rejected as incorrect by Maimon. Maimon is an ancestor of Shlomo Moussaieff, author Jeffrey Moussaieff Masson
Jeffrey Moussaieff Masson (born March 28, 1941 as Jeffrey Lloyd Masson) is an American author. Masson is best known for his conclusions about Sigmund Freud and psychoanalysis. In his ''The Assault on Truth'' (1984), Masson argues that Freud may ...
, and the former First Lady of Iceland Dorrit Moussaieff
Dorrit Moussaieff ( he, דורית מוסאיוף, born 12 January 1950) is an Israeli jewellery designer, editor, and businesswoman who was the First Lady of Iceland from 2003 to 2016. She became engaged to President Ólafur Ragnar Grímsson ...
.

19th century
In 1843 the Bukharan Jews were visited by the so-called "Eccentric Missionary",Joseph Wolff
Joseph Wolff (1795 – 2 May 1862) was a Jewish Christian missionary born in Weilersbach, near Bamberg, Germany, named Wolff after his paternal grandfather. He travelled widely, and was known as "the missionary to the world". He published sev ...
, a Jewish convert to Christianity who had set himself the broad task of finding the Lost Tribes of Israel
The ten lost tribes were the ten of the Twelve Tribes of Israel that were said to have been exiled from the Kingdom of Israel after its conquest by the Neo-Assyrian Empire BCE. These are the tribes of Reuben, Simeon, Dan, Naphtali, Gad, As ...
and the narrow one of seeking two British officers who had been captured by the Emir, Nasrullah Khan. Wolff wrote prolifically of his travels, and the journals of his expeditions provide valuable information about the life and customs of the peoples he travelled amongst, including the Bukharan Jews. In 1843, for example, they collected 10,000 silver '' tan'ga'' and purchased land in Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, known as '' Makhallai Yakhudion'', close to Registon.
In the middle of the 19th century, Bukharan Jews began to move to Palestine. The land on which they settled in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
was named the Bukharan quarter (Sh'hunat HaBucharim) and still exists today.
In 1865, Russian troops took over Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2 ...
, and there was a large influx of Jews to the newly created Turkestan
Turkestan, also spelled Turkistan ( fa, ترکستان, Torkestân, lit=Land of the Turks), is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the regions of Transoxiana and Xinjiang.
Overview
Known as Turan to the Persians, western Turk ...
Region. From 1876 to 1916, Jews were free to practice Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
. Dozens of Bukharan Jews held prestigious jobs in medicine, law, and government, and many Jews prospered. Many Bukharan Jews became successful and well-respected actors, artists, dancers, musicians, singers, film producers, and sportsmen. Several Bukharan entertainers became artists of merit and gained the title "People's Artist of Uzbekistan", "People's Artist of Tajikistan", and even (in the Soviet era) "People's Artist of the Soviet Union
People's Artist of the USSR ( rus, Народный артист СССР, Narodny artist SSSR), also sometimes translated as National Artist of the USSR, was an honorary title granted to artists of the Soviet Union.
Nomenclature and significan ...
". Jews succeeded in the world of sport also, with several Bukharan Jews in Uzbekistan becoming renowned boxers and winning many medals for the country. Still, Bukharan Jews were forbidden to ride in the streets and had to wear distinctive costumes. They were relegated to a ghetto, and often fell victim to persecution from the Muslim majority.
Soviet era
By the time of theRussian revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
, the Bukharan Jews were one of the most isolated Jewish communities in the world.Moskin, Julia"The Silk Road Leads to Queens"
''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'', January 18, 2006.
Following the Soviet capture of Bukhara, synagogues were destroyed or closed down, and were replaced by Soviet institutions. Consequently many Bukharan Jews fled to the West
West is a cardinal direction or compass point.
West or The West may also refer to:
Geography and locations
Global context
* The Western world
* Western culture and Western civilization in general
* The Western Bloc, countries allied with NATO ...
. The route they undertook went through Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, as the neighbouring country had many possibilities to the west. Consequently, Central Asian Jews in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
had an Afghan nationality while a minority of them were born in Afghanistan. For instance many Jewish families with the Afghan nationality were born in Kokand
Kokand ( uz, Qo‘qon/Қўқон/قوقان, ; russian: Кока́нд; fa, خوقند, Xuqand; Chagatai: خوقند, ''Xuqand''; ky, Кокон, Kokon; tg, Хӯқанд, Xöqand) is a city in Fergana Region in eastern Uzbekistan, at the so ...
. Soviet doctrines, ideology and nationalities policy had a large impact on the everyday life, culture and identity of the Bukharan Jews. The remaining community attempted to preserve their traditions while displaying loyalty to the new government.
Stalin's decision to end Lenin's New Economic Policy
The New Economic Policy (NEP) () was an economic policy of the Soviet Union proposed by Vladimir Lenin in 1921 as a temporary expedient. Lenin characterized the NEP in 1922 as an economic system that would include "a free market and capitalism, ...
and initiate the First five-year plan
The first five-year plan (russian: I пятилетний план, ) of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) was a list of economic goals, created by Communist Party General Secretary Joseph Stalin, based on his policy of socialism in ...
in the late 1920s resulted in a drastic deterioriation of living conditions for the Bukharan Jews. By the time Soviet authorities established their hold over the borders in Central Asia in the mid 1930s, many tens of thousands of households from Central Asia had crossed the border into Iran and Afghanistan, amongst them some 4,000 Bukharan Jews (comprising about one tenth of the total number of Bukharan Jews in Central Asia), who were heading towards Palestine.
Bukharan Jews who had put efforts into creating a Bukharan Jewish Soviet culture and national identity were charged during Stalin's Great Purge
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Yezhov'), was Soviet General Secreta ...
, or, as part of the Soviet Union's nationalities policies and nation building campaigns, were forced to assimilate into the larger Soviet Uzbek or Soviet Tajik national identities.
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
brought a lot of Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
Jewish refugees from the European regions of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
through Uzbekistan.
Starting in 1972, one of the largest Bukharan Jewish emigrations in history occurred as the Jews of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan immigrated to Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, due to looser restrictions on immigration. In the late 1980s to the early 1990s, almost all of the remaining Bukharan Jews left Central Asia for the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, or Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
in the last mass emigration of Bukharan Jews from their resident lands.
After 1991
With the disintegration of theSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
and foundation of the independent Republic of Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
in 1991, some feared growth of nationalistic policies in the country. The resurgence of Islamic fundamentalism
Islamic fundamentalism has been defined as a puritanical, revivalist, and reform movement of Muslims who aim to return to the founding scriptures of Islam. Islamic fundamentalists are of the view that Muslim-majority countries should return ...
in Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
and Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
prompted an increase in the level of emigration of Jews (both Bukharan and Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
). Before the collapse of the USSR, there were 45,000 Bukharan Jews in Central Asia.
Today, there are about 150,000 Bukharan Jews in Israel (mainly in the Tel Aviv metropolitan area including the neighborhoods of Tel Kabir, Shapira, Kiryat Shalom
, wiktionary:בית, :he:בית, house
*
*
*
*
E
, wiktionary:עין, spring, fountain
*
*
, wiktionary:עמק, :he:עמק, valley
*
G
, wiktionary:גן, :he:גן, "garden"
*
, wiktionary:גבעה, :he:גבעה, ...
, HaTikvah and cities like Or Yehuda
Or Yehuda ( he, אוֹר יְהוּדָה, ar, أور يهوده ) is a town in the Tel Aviv District of Gush Dan, Israel. In it had a population of .
History Prehistory
Human settlement back to the Chalcolithic has been found on the site.
, Ramla
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
, and Holon
Holon ( he, חוֹלוֹן ) is a city on the central coastal strip of Israel, south of Tel Aviv. Holon is part of the metropolitan Gush Dan area. In it had a population of . Holon has the second-largest industrial zone in Israel, after Haifa ...
) and 60,000 in the United States (especially Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
—a borough of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
that is widely known as the "melting pot" of the United States due to its ethnic diversity)—with smaller communities in the USA like Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
, South Florida
South Florida is the southernmost region of the U.S. state of Florida. It is one of Florida's three most commonly referred to directional regions; the other two are Central Florida and North Florida. South Florida is the southernmost part of ...
, Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,7 ...
, San Diego, Los Angeles, Seattle, and Denver. Only a few thousand still remain in Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
. About 500 live in Canada (mainly Toronto, Ontario and Montreal, Quebec). Almost no Bukharan Jews remain in Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
(compared to the 1989 Jewish population of 15,000 in Tajikistan).
Immigrant populations

Tajikistan
In early 2006, the still-activeDushanbe Synagogue
The Dushanbe Synagogue (russian: Душанбинская синагога), also known as the Bukharian Synagogue (russian: Бухарская синагога), located in Dushanbe, the capital of Tajikistan, was constructed in the 19th century ...
in Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
as well as the city's mikveh
Mikveh or mikvah (, ''mikva'ot'', ''mikvoth'', ''mikvot'', or (Yiddish) ''mikves'', lit., "a collection") is a bath used for the purpose of ritual immersion in Judaism to achieve ritual purity.
Most forms of ritual impurity can be purifi ...
(ritual bath), kosher
(also or , ) is a set of dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed kosher ( in English, yi, כּשר), fro ...
butcher, and Jewish schools were demolished by the government (without compensation to the community) to make room for the new Palace of Nations. After an international outcry, the government of Tajikistan announced a reversal of its decision and publicly claimed that it would permit the synagogue to be rebuilt on its current site. However, in mid-2008, the government of Tajikistan destroyed the whole synagogue and started construction of the Palace of Nations. The Dushanbe synagogue was Tajikistan's only synagogue and the community were therefore left without a centre or a place to pray. As a result, the majority of Bukharan Jews from Tajikistan living in Israel and the United States have very negative views towards the Tajik government and many have cut off all ties they had with the country. In 2009, the Tajik government reestablished the synagogue in a different location for the small Jewish community.
United States
 Currently, Bukharan Jews are mostly concentrated in the U.S. in
Currently, Bukharan Jews are mostly concentrated in the U.S. in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
. In Forest Hills, Queens
Forest Hills is a mostly residential neighborhood in the central portion of the borough of Queens in New York City. It is adjacent to Corona to the north, Rego Park and Glendale to the west, Forest Park to the south, Kew Gardens to the southeas ...
, 108th Street, often referred to as "Bukharan Broadway""Bukharan Broadway":
* Foner, Nancy. ''New immigrants in New York", ''Columbia University Press
Columbia University Press is a university press based in New York City, and affiliated with Columbia University. It is currently directed by Jennifer Crewe (2014–present) and publishes titles in the humanities and sciences, including the fie ...
, 2001, , p. 133. "Since the 1970s, more than 35,000 "Bukharan" émigrés have created a bustling community in Forest Hills, with restaurants, barbershops, food stores and synagogue that together have given 108th street the nickname 'Bukharan Broadway'".
* Morel, Linda"Bukharan Jews now in Queens recreate their Sukkot memories"
''
J. The Jewish News of Northern California
''J. The Jewish News of Northern California'', formerly known as ''Jweekly'', is a weekly print newspaper in Northern California, with its online edition updated daily. It is owned and operated by San Francisco Jewish Community Publications In ...
'' (''Jewish Telegraphic Agency
The Jewish Telegraphic Agency (JTA) is an international news agency and wire service, founded in 1917, serving Jewish community newspapers and media around the world as well as non-Jewish press, with about 70 syndication clients listed on its we ...
''), September 20, 2002. "... 108th Street, recently dubbed 'Bukharan Broadway,'..."
* Victor Wishna"A Lost Tribe...Found in Queens"
, ''
San Diego Jewish Journal
The ''San Diego Jewish Journal'', headquartered in Sorrento Valley, San Diego, California, is a Jewish magazine founded in October 2001 by Dr. Mark Moss and Mark Edelstein, and first published in December 2001. Their intent was to create a magaz ...
'', October 2003. "Leaving the bakery, we walk along what has been dubbed 'Bukharan Broadway,' where an abundance of restaurants and gift shops sit side by side." or "Bukharian Broadway", is filled with Bukharan restaurants and gift shops. Furthermore, Forest Hills is nicknamed "Bukharlem" due to the majority of the population being Bukharian. They have formed a tight-knit enclave in this area that was once primarily inhabited by Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
. Congregation Tifereth Israel in Corona, Queens
Corona is a neighborhood in the borough of Queens in New York City. It borders Flushing and Flushing Meadows–Corona Park to the east, Jackson Heights to the west, Forest Hills and Rego Park to the south, Elmhurst to the southwest, and East ...
, a synagogue founded in the early 1900s by Ashkenazi Jews, became Bukharan in the 1990s. Kew Gardens, Queens
Kew Gardens is a neighborhood in the central area of the New York City borough of Queens. Kew Gardens is bounded to the north by the Union Turnpike and the Jackie Robinson Parkway (formerly the Interboro Parkway), to the east by the Van Wyck E ...
, also has a very large population of Bukharan Jews. Author Janet Malcolm has taken an interest in Bukharan Jews in the U.S., writing at length about Jeffrey Moussaieff Masson
Jeffrey Moussaieff Masson (born March 28, 1941 as Jeffrey Lloyd Masson) is an American author. Masson is best known for his conclusions about Sigmund Freud and psychoanalysis. In his ''The Assault on Truth'' (1984), Masson argues that Freud may ...
and, in '' Iphigenia in Forest Hills: Anatomy of a Murder Trial'', about the 2007 contract murder of Daniel Malakov organized by his ex-wife Mazoltuv Borukhova. Although Bukharan Jews in Queens remain insular in some ways (living in close proximity to each other, owning and patronizing clusters of stores, and attending their own synagogue rather than other synagogues in the area), they have connections with non-Bukharans in the area.
 In December 1999, the First Congress of the Bukharian Jews of the United States and Canada convened in Queens. In 2007, Bukharan-American Jews initiated lobbying efforts on behalf of their community.Ruby, Walte
In December 1999, the First Congress of the Bukharian Jews of the United States and Canada convened in Queens. In 2007, Bukharan-American Jews initiated lobbying efforts on behalf of their community.Ruby, Walte"The Bukharian Lobby"
, ''
The Jewish Week
''The Jewish Week'' is a weekly independent community newspaper targeted towards the Jewish community of the metropolitan New York City area. ''The Jewish Week'' covers news relating to the Jewish community in NYC. In March 2016, ''The Jewish W ...
'', October 31, 2007. Zoya Maksumova, president of the Bukharan women's organization "Esther Hamalka" said "This event represents a huge leap forward for our community. Now, for the first time, Americans will know who we are." Senator Joseph Lieberman intoned, "God said to Abraham, 'You'll be an eternal people'… and now we see that the State of Israel lives, and this historic ukharancommunity, which was cut off from the Jewish world for centuries in Central Asia and suffered oppression during the Soviet Union, is alive and well in America. God has kept his promise to the Jewish people."
Culture
Dress codes
Bukharan Jews had their owndress code
A dress code is a set of rules, often written, with regard to what clothing groups of people must wear. Dress codes are created out of social perceptions and norms, and vary based on purpose, circumstances, and occasions. Different societies a ...
, similar to but also different from other cultures (mainly Turco-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century, among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these Khanates eventuall ...
) living in Central Asia. On weddings today, one can still observe the bride and the close relatives donning the traditional kaftan
A kaftan or caftan (; fa, خفتان, ) is a variant of the robe or tunic. Originating in Asia, it has been worn by a number of cultures around the world for thousands of years. In Russian usage, ''kaftan'' instead refers to a style of men's ...
(Jomah-ҷома-ג'אמה in Bukhori and Tajik).
Music
 The Bukharan Jews have a distinct musical tradition called
The Bukharan Jews have a distinct musical tradition called shashmaqam
Shashmaqam (russian: Шашмаком; uz, shashmaqom; tg, шашмақом; fa, ششمقام) is a Central Asian musical genre (typical of Tajikistan and Uzbekistan) which may have developed in the city of Bukhara. Shashmaqam means the six ...
, which is an ensemble of stringed instruments, infused with Central Asian
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the form ...
rhythms, and a considerable klezmer
Klezmer ( yi, קלעזמער or ) is an instrumental musical tradition of the Ashkenazi Jews of Central and Eastern Europe. The essential elements of the tradition include dance tunes, ritual melodies, and virtuosic improvisations played for l ...
influence as well as Muslim melodies, and even Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
chords
Chord may refer to:
* Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously
** Guitar chord a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning
* Chord (geometry), a line segment joining two points on a curve
* Chord ( ...
. The main instrument is the dayereh
Daf ( fa, دف) also known as Dâyere and Riq is a Middle Eastern (mainly Iranian) frame drum musical instrument, used in popular and classical music in South and Central Asia. It is also used in Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Tajikistan, Iran, Uzbe ...
. Shashmaqam music "reflect the mix of Hassidic vocals, Indian and Islamic instrumentals and Sufi-inspired texts and lyrical melodies." Ensemble Shashmaqam was one of the first New York-based ensembles created to showcase the music and dance of Bukharan Jews. The Ensemble was created in 1983 by Shumiel Kuyenov, a dayereh player from Queens.
Cuisine
 Bukharan cuisine consists of many unique dishes, distinctly influenced by ethnic dishes historically and currently found along the
Bukharan cuisine consists of many unique dishes, distinctly influenced by ethnic dishes historically and currently found along the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
and many parts of Central and even Southeast Asia. Shish kabob, or shashlik
Shashlik, or shashlick (russian: шашлык ''shashlyk''), is a dish of skewered and grilled cubes of meat, similar to or synonymous with shish kebab. It is known traditionally by various other names in Iran, the Caucasus, Eastern Europe and ...
, as it is often referred to in Russian, are popular, made of chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adu ...
, beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus'').
In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quantit ...
or lamb
Lamb or The Lamb may refer to:
* A young sheep
* Lamb and mutton, the meat of sheep
Arts and media Film, television, and theatre
* ''The Lamb'' (1915 film), a silent film starring Douglas Fairbanks Sr. in his screen debut
* ''The Lamb'' (1918 ...
. Pulled noodles, often thrown into a hearty stew of meat and vegetables known as ''lagman'', are similar in style to Chinese lamian
Lamian (simplified Chinese: 拉面; traditional Chinese: 拉麵; pinyin: ''Lāmiàn'') is a type of soft wheat flour Chinese noodle that is particularly common in northern China. Lamian is made by twisting, stretching and folding the dough int ...
, also traditionally served in a meat broth. ''Samsa'', pastries filled with spiced meat or vegetables, are baked in a unique, hollowed out tandoor
A tandoor ( or ) is a large urn-shaped oven, usually made of clay, originating from the Indian Subcontinent. Since antiquity, tandoors have been used to bake unleavened flatbreads, such as roti and naan, as well as to roast meat. The tandoo ...
oven, and greatly resemble the preparation and shape of Indian samosa
A samosa () or singara is a fried Indian pastry with a savory filling, including ingredients such as spiced potatoes, onions, and peas. It may take different forms, including triangular, cone, or half-moon shapes, depending on the region. Sam ...
s.
The Bukharians' Jewish identity was always preserved in the kitchen. "Even though we were in exile from Jerusalem, we observed kashruth," said Isak Masturov, another owner of Cheburechnaya. "We could not go to restaurants, so we had to learn to cook for our own community.Plov is a very popular slow-cooked
rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
dish spiced with cumin
Cumin ( or , or Article title
) (''Cuminum cyminum'') is a
Bukharian Isralites
Joseph Mammon. My Story
Official World Wide Bukharian Community Website
BJews.com
Bukharian Jewish Global Portal * Cooper, Alanna E
''Bukharan Jews and the Dynamics of Global Judaism''
Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2012.
kikayon.com * Elena Neva
"Heavenly Frogs in the Art of Bukharian Jewelers"
Kunstpedia, March 19, 2009.
''Haaretz'' (Reuters), October 21, 2009. * * * *
Bukharian Torah Lectures
by Bukharian Rabbis {{Jews and Judaism Bukharan Jews, Jewish ethnic groups Mizrahi Jews, Ethnic groups in Uzbekistan
) (''Cuminum cyminum'') is a
carrot
The carrot ('' Daucus carota'' subsp. ''sativus'') is a root vegetable, typically orange in color, though purple, black, red, white, and yellow cultivars exist, all of which are domesticated forms of the wild carrot, ''Daucus carota'', na ...
s, and in some varieties, chick peas
The chickpea or chick pea (''Cicer arietinum'') is an annual legume of the family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae. Its different types are variously known as gram" or Bengal gram, garbanzo or garbanzo bean, or Egyptian pea. Chickpea seeds are hig ...
or raisin
A raisin is a dried grape. Raisins are produced in many regions of the world and may be eaten raw or used in cooking, baking, and brewing. In the United Kingdom, Ireland, New Zealand, and Australia, the word ''raisin'' is reserved for the ...
s, and often topped with beef or lamb. Another popular dish is ''baksh'' which consists of rice, beef and liver cut into small cubes, with cilantro
Coriander (;
, which adds a shade of green to the rice once it's been cooked. Most Bukharan Jewish communities still produce their traditional breads including '' non'' (''lepyoshka'' in Russian), a circular bread with a flat center that has multiple pattern of designs, topped with black and regular sesame seed
Sesame ( or ; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a flowering plant in the genus '' Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cu ...
s, and the other, called ''non toki'', bears the dry and crusty features of traditional Jewish matzah
Matzah or matzo ( he, מַצָּה, translit=maṣṣā'','' pl. matzot or Ashk. matzos) is an unleavened flatbread that is part of Jewish cuisine and forms an integral element of the Passover festival, during which ''chametz'' ( leaven an ...
, but with a distinctly wheatier taste.
After Sabbath synagogue service, Bukharan Jews often eat steamed eggs and sweet potatoes followed by a dish of fish such as carp. Next comes the main meal called ''oshesvo''.
Genetics
A 2013 genetic study of multiple Jewish groups, including Bukharan Jews, found that Bukharan Jews clustered closely with Jewish communities from the Middle East and the Caucasus such as Iranian Jews, Mountain Jews, Georgian Jews, Kurdish Jews and Iraqi Jews, as well as other Middle Eastern and West Asian people including Kurds, Iranians, Armenians, Syrians, Druze and others; and did not cluster with their former neighbours.Notable Bukharan Jews
Afghanistan
*Zablon Simintov
Zablon Simintov (; he, זבולון סימן-טוב; born 1959), also known as Zebulon Simentov is an Afghan Jew, former carpet trader and restaurateur. Before his evacuation from Afghanistan to Israel in 2021, he was widely known as the only ...
, was the only remaining Jew in Afghanistan
United Kingdom
*Yvonne Green
Yvonne Green (born 8 April 1957) is an English poet, translator, writer and barrister.
Life and career
Green, who lives in Hendon and Herzliya, was born in Finchley, north London on 8 April 1957. She attended the Henrietta Barnett School and t ...
(née Mammon) – poet and translator
* Anthony Yadgaroff – British businessman, Jewish community leader
Israel
*Yisrael Aharoni
Yisrael Aharoni ( he, ישראל אהרוני; born July 3, 1950) :he:ישראל אהרוני (שף) is an Israeli celebrity chef.
Biography
Aharoni was born in Haifa, Israel, to Bukharan Jewish parents. Aharoni was enlisted to the Israel D ...
– Israeli chef
A chef is a trained professional cook and tradesman who is proficient in all aspects of food preparation, often focusing on a particular cuisine. The word "chef" is derived from the term ''chef de cuisine'' (), the director or head of a ki ...
and restaurateur
A restaurateur is a person who opens and runs restaurants professionally. Although over time the term has come to describe any person who owns a restaurant, traditionally it refers to a highly skilled professional who is proficient in all aspe ...
* Yoni Ben-Menachem
Yoni Ben-Menachem (born 1957) is an Israeli journalist and a Senior Researcher at the Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs
The Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs (JCPA) is an Israeli research institute specializing in public diplomacy and ...
– Israeli journalist; General Director of Israel Broadcasting Authority
* Amnon Cohen
Amnon Cohen ( he, אמנון כהן; born 1 June 1960) is an Israeli former politician. He served as a member of the Knesset for Shas from 1999 until 2015.
Biography
Born in Samarkand in the Soviet Union (today in Uzbekistan), Cohen made aliyah ...
– Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
i politician and member of the Knesset
The Knesset ( he, הַכְּנֶסֶת ; "gathering" or "assembly") is the unicameral legislature of Israel. As the supreme state body, the Knesset is sovereign and thus has complete control of the entirety of the Israeli government (wit ...
for Shas
Shas ( he, ש״ס) is a Haredi religious political party in Israel. Founded in 1984 under the leadership of Rabbi Ovadia Yosef, a former Israeli Sephardi chief rabbi, who remained its spiritual leader until his death in October 2013, it primarily ...
* Guy Haimov – professional football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
player
* Shimon Hakham
Rabbi Shimon Hakham ( he, שמעון חכם; 1843, Bukhara- 1910, Jerusalem) was a Bukharan rabbi residing in Jerusalem who promoted literacy by translating Hebrew religious books into Bukhori.
Rabbi Hakham was born into a religious family and ...
– Bukharan-Israeli rabbi, writer, one of the founders of the Bukharan Quarter
* Robert Ilatov – Israeli politician and member of the Knesset for Yisrael Beiteinu
Yisrael Beiteinu ( he, יִשְׂרָאֵל בֵּיתֵנוּ, russian: Наш Дом Израиль, lit. ''Israel Our Home'') is a secularist, nationalist right-wing political party in Israel. The party's base was originally secular Russia ...
* Avi Issacharoff – Israeli journalist and creator of the series ''Fauda
''Fauda'' (, from ''fawḍā'', meaning "chaos") is an Israeli television series developed by Lior Raz and Avi Issacharoff drawing on their experiences in the Israel Defense Forces. The series premiered on February 15, 2015. It tells the stor ...
''
* Lev Leviev – billionaire businessman, investor, philanthropist, president of the World Congress of Bukharian Jews
* Nitzan Kaikov – Israeli songwriter
A songwriter is a musician who professionally composes musical compositions or writes lyrics for songs, or both. The writer of the music for a song can be called a composer, although this term tends to be used mainly in the classical music ...
and music producer
A record producer is a recording project's creative and technical leader, commanding studio time and coaching artists, and in popular genres typically creates the song's very sound and structure.Virgil Moorefield"Introduction" ''The Producer as ...
* Yosef Maimon – religious leader
* Rinat Matatov – Israeli actress
* Moshe Mishaelof – professional football player
* Shlomo Moussaieff – co-founder of the Bukharan Quarter in Jerusalem
* Shlomo Moussaieff – Israeli millionaire businessman
* Dorrit Moussaieff
Dorrit Moussaieff ( he, דורית מוסאיוף, born 12 January 1950) is an Israeli jewellery designer, editor, and businesswoman who was the First Lady of Iceland from 2003 to 2016. She became engaged to President Ólafur Ragnar Grímsson ...
– former First Lady of Iceland
* Rafael Pinhasi
__NOTOC__
Rafael Pinhasi ( he, רפאל פנחסי, born 1940) is a former Israeli politician who served as Minister of Communications between 1990 and 1992.
Early life
Born in Kabul in Afghanistan, Pinhasi's family made aliyah in 1950. He was ...
– Israeli politician and member of the Knesset for Shas
* Esther Roth-Shahamorov
Esther Roth-Shahamorov ( he, אסתר רוט-שחמורוב; born April 16, 1952) is a former Israeli track and field athlete. She specialized in the 100-meter hurdles and the 100-meter sprint.
Early and personal life
Esther Shahamorov was bo ...
– Israeli former track and field
Track and field is a sport that includes athletic contests based on running, jumping, and throwing skills. The name is derived from where the sport takes place, a running track and a grass field for the throwing and some of the jumping eve ...
athlete
* Eson Kandov – Singer and Honored People's Artist of the USSR
* Gideon Sa'ar
Gideon Moshe Sa'ar ( he, גִּדְעוֹן סַעַר; born 9 December 1966) is an Israeli politician who has served as Minister of Justice since June 2021. Sa'ar was previously a member of the Knesset for the Likud between 2003 and 2014, as De ...
– Israeli politician who served as a member of Knesset for New Hope
* Yulia Shamalov-Berkovich
Yulia Shamalov-Berkovich ( he, יוליה שמאלוב-ברקוביץ', born 1 April 1964) is an Israeli politician who served as a member of the Knesset for Kadima between 2009 and 2013.
Biography
Born in the Soviet Union, Shamalov-Berkovich ...
– Israeli politician who served as a member of the Knesset for Kadima
Kadima ( he, קדימה, lit=''Forward'') was a centrist and liberal political party in Israel. It was established on 24 November 2005 by moderates from Likud largely following the implementation of Ariel Sharon's unilateral disengagement pl ...
from 2009-2013
* Idan Yaniv
Idan Yaniv ( he, עידן יניב; born October 18, 1986) is an Israeli singer born in Tel Aviv.
He has successfully recorded five albums with many popular singles. His debut single was "Hoshev Aleha" and it was a hit that generated a lot of a ...
– Israeli singer, "2007 Israeli Artist of the Year"
* Benjamin Yusupov Benjamin Yusupov ( he, בנימין יוסופוב; born November 22, 1962 in Dushanbe, Tajikistan) is a classical composer, conductor and pianist.
Biography
Born in Dushanbe, Tajikistan in 1962. Yusupov studied piano, composition and conductin ...
– Israeli classical composer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and Def ...
, conductor and pianist
A pianist ( , ) is an individual musician who plays the piano. Since most forms of Western music can make use of the piano, pianists have a wide repertoire and a wide variety of styles to choose from, among them traditional classical music, ja ...
United States
*Jacob Arabov
Jacob Arabo (born Yakov Arabov or Jacob Arabov on June 3, 1965; also frequently known as "Jacob the Jeweler") is an American jewelry and watch designer who founded Jacob & Company in 1986 and grew it to become an international luxury brand. He beg ...
– proprietor of Jacob & Co.
* Michael Aronov
Michael Aronov (born May 4, 1976) is an American actor who has worked in film, television and theatre. In 2017, he won the Tony Award for Best Featured Actor in a Play for his role as Uri Savir in the Broadway play ''Oslo''. He is also known for p ...
– American actor and playwright, Tony Award winner
* Boris Kandov
Boris Kandov is the President of the Bukharian Jewish Congress in the United States and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and no ...
– President of the Bukharian Jewish Congress of the US and Canada
* Jeffrey Moussaieff Masson
Jeffrey Moussaieff Masson (born March 28, 1941 as Jeffrey Lloyd Masson) is an American author. Masson is best known for his conclusions about Sigmund Freud and psychoanalysis. In his ''The Assault on Truth'' (1984), Masson argues that Freud may ...
– author
An author is the writer of a book, article, play, mostly written work. A broader definition of the word "author" states:
"''An author is "the person who originated or gave existence to anything" and whose authorship determines responsibility f ...
* Jacob Nasirov
Jacob Nasirov is a prominent Bukharian rabbi residing in Jamaica Estates, Queens, New York. His family originated in Bukhara and immigrated to Afghanistan in 1932. At age 5, his family made '' aliyah'' to Israel. After serving in the Israel Defe ...
– Bukharan-American rabbi from Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
(member of the Bukharian Rabbinical Counsel)
* Rus Yusupov
Rus Yusupov (born May 4, 1984) is an American designer and tech entrepreneur. He is best known as the co-founder of Vine and the co-founder and CEO of HQ Trivia.
Career
Early career
Yusupov began his career as a digital product designer at ...
– Bukharan-American Internet entrepreneur; co-founder of Vine
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themsel ...
* Iosef Yusupov
Iosef Yusupov is an American set designer who was one of the scenic designers for the George Tsypin creative team of the 2014 Winter Olympics opening ceremony in Sochi, Russia. Currently living in the United States, he has designed many shows (pl ...
– designer
A designer is a person who plans the form or structure of something before it is made, by preparing drawings or plans.
In practice, anyone who creates tangible or intangible objects, products, processes, laws, games, graphics, services, or exp ...
Other
*Ari Babakhanov Ari Babakhanov (born 1934) is an Uzbekistani musician who performs the long-necked lutes tanbur, qashqari rubab and dutar.
Biography
Babakhanov was born in Bukhara into a Jewish family which can look back on an outstanding dynasty of traditio ...
– musician
A musician is a person who composes, conducts, or performs music. According to the United States Employment Service, "musician" is a general term used to designate one who follows music as a profession. Musicians include songwriters who wr ...
from Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
* Rena Galibova
Rena Galibova (Russian: Рена Абрамовна Галибова, Tajik: Раъно Абрамовна Ғолибова) (May 24, 1915 – September 10, 1995) was a Tajik actress and opera singer who was named the People's Artist of Tajik ...
– Soviet actress, "People's Artist of Tajikistan" (an awarded title, alluding to national prominence)
* Meirkhaim Gavrielov – journalist murdered in Tajikistan in 1998
* Barno Itzhakova
Barno Iskhakova (12 May 1927 - 7 September 2001; tg, Барно Исҳоқова, fa, برنا اسحاقوا, russian: Барно Исхакова, he, ברנו יצחקובה) was a Soviet and Bukharian Jewish musician from Tajikistan.
Earl ...
– vocalist, famous for her rendition of traditional Shashmaqom songs in Tajik and Uzbek
* Malika Kalontarova
Malika Kolontarova ( tg, Малика Қаландарова, russian: Мазол (Малика) Яшуваевна Калантарова or Колонтарова; born 2 September 1950) is a Tajik–American dancer. She is known as the "Q ...
– dancer, "People's Artist of Soviet Union" (Queen of Eastern Dance)
* Fatima Kuinova
Panir Ibragimova (28 December 1926 – 28 December 2021), better known by the stage name of Fatima Kuinova ( tg, Фатима Куэнова, fa, فاطمه کوینوا), was a Bukharan Jewish Shashmakom singer. She was named "Merited Artist ...
– Soviet singer, "Merited Artist of the Soviet Union"
* Ilyas Malayev
Ilyas Malayev (January 12, 1936 – May 2, 2008) (russian: Ильяс Малаев, uz, Илёс Маллаев ) was an Uzbekistani musician and poet.
Malayev was born in Mary (then in the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic, now in Turkmenis ...
– musician and poet from Uzbekistan, "Honoured Artist of Uzbekistan"
* Shoista Mullodzhanova – Shashmakon singer, "People's Artist of Tajikistan" (Queen of Shashmakom
Shashmaqam (russian: Шашмаком; uz, shashmaqom; tg, шашмақом; fa, ششمقام) is a Central Asian musical genre (typical of Tajikistan and Uzbekistan) which may have developed in the city of Bukhara. Shashmaqam means the s ...
music)
* Gavriel Mullokandov
Gavriel Aronovich Mullokandov ( uz, Гавриэл Муллоқандов, Gavriel Mulloqandov, russian: Гавриэль Аронович Муллокандов; 8 April 1900 – 6 February 1972) is widely regarded as the greatest Bukharian Jew ...
– popular Shashmakom artist, "People's Artist of Uzbekistan"
* Suleiman Yudakov
Suleiman (Solomon) Alexandrovich Yudakov ( tg, Сулаймон Александрович Юдаков; russian: Сулейман (Соломон) Александрович Юдаков) ( – 1990) was a Soviet Bukharian composer of Bukha ...
– Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
composer and musician, "People's Artist of the Uzbek SSR"
See also
* Bukharan Jews in Israel * Bukhori dialect * Africa Israel Investments * Bais Yaakov Machon Academy *Dushanbe Synagogue
The Dushanbe Synagogue (russian: Душанбинская синагога), also known as the Bukharian Synagogue (russian: Бухарская синагога), located in Dushanbe, the capital of Tajikistan, was constructed in the 19th century ...
* Emirate of Bukhara
The Emirate of Bukhara ( fa, , Amārat-e Bokhārā, chg, , Bukhārā Amirligi) was a Muslim polity in Central Asia that existed from 1785 to 1920 in what is modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan. It occupied the land ...
* History of the Jews in Russia and the Soviet Union
* History of the Jews under Muslim Rule
* Ohr Avner Foundation
References
Notes Bibliography * Ricardo Garcia-Carcel: ''La Inquisición'', Biblioteca El Sol. Biblioteca Básica de Historia. Grupo Anaya, Madrid, Spain 1990. .External links
*Bukharian Isralites
Joseph Mammon. My Story
Official World Wide Bukharian Community Website
BJews.com
Bukharian Jewish Global Portal * Cooper, Alanna E
''Bukharan Jews and the Dynamics of Global Judaism''
Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2012.
kikayon.com * Elena Neva
"Heavenly Frogs in the Art of Bukharian Jewelers"
Kunstpedia, March 19, 2009.
''Haaretz'' (Reuters), October 21, 2009. * * * *
Bukharian Torah Lectures
by Bukharian Rabbis {{Jews and Judaism Bukharan Jews, Jewish ethnic groups Mizrahi Jews, Ethnic groups in Uzbekistan