Brzeg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Brzeg has five public parks, three of which encircle the Old Town (''Stare Miasto''), after the area was transformed into parkland with the deconstruction of the garrison town's fortifications during the
Brzeg has five public parks, three of which encircle the Old Town (''Stare Miasto''), after the area was transformed into parkland with the deconstruction of the garrison town's fortifications during the

 Breakdown of population origin of Brzeg in 1950:
Breakdown of migrant population origin of Brzeg in 1950:
Population change:
Breakdown of population origin of Brzeg in 1950:
Breakdown of migrant population origin of Brzeg in 1950:
Population change:

 Brzeg has a total of 7,826 citizens in the potential education age group (3-24 year of age). The number of city dwellers in Brzeg that have completed
Brzeg has a total of 7,826 citizens in the potential education age group (3-24 year of age). The number of city dwellers in Brzeg that have completed
 Brzeg is located at the crossroads of the
Brzeg is located at the crossroads of the  (northbound to Namysłów and Kępno; southbound to
(northbound to Namysłów and Kępno; southbound to  (westbound to
(westbound to 
File:Brzeg Op.JPG, Most characteristic building of Brzeg, Silesian Piasts Castle
File:Brzeg Castle 06.jpg, Northern side of the castle's courtyard
File:Brzeg Op zamek 02.JPG, Southern side of the castle
File:Fragment stawu w Parku Wolności w Brzegu..jpg, Juliusz Peppel Park, the largest public park in town
File:Brzeg, Poland - panoramio (20).jpg, Long Street, main high street
File:Brzeg Marina viewed from Piastowski Bridge.jpg, Marina by the River Oder
File:Brzeg, Poland - panoramio (45).jpg, Town square and tower
File:Brzeg_town_hall.jpg, Town Hall
File:Brzeg, Kościół św. Mikołaja - fotopolska.eu (261406).jpg, St. Nicholas Church and Brzeski Dom Kultury cultural centre
File:Brzeg kosciol sw Mikolaja 04.jpg, Interior of the church
File:Brzeg, Poland - panoramio (1).jpg, Holy Cross Church
File:1225m Brzeg, kościół św. Krzyża. Foto Barbara Maliszewska.jpg, Interior of the Holy Cross Church
File:Poland Brzeg - Johann Kuben art in Feast of the Cross church.jpg, Church ceiling
::By : Gotthard Deutsch & A. M. Friedenberg
Forum Brzeg
*
Dziennik Brzeski
Foto Brzeg
Komornik Brzeg
Jewish Community in Brzeg
on Virtual Shtetl
{{Authority control Cities in Silesia Cities and towns in Opole Voivodeship Brzeg County Holocaust locations in Poland Province of Upper Silesia
Brzeg (;
 The locality in and around present-day Brzeg has been settled by people since the
The locality in and around present-day Brzeg has been settled by people since the
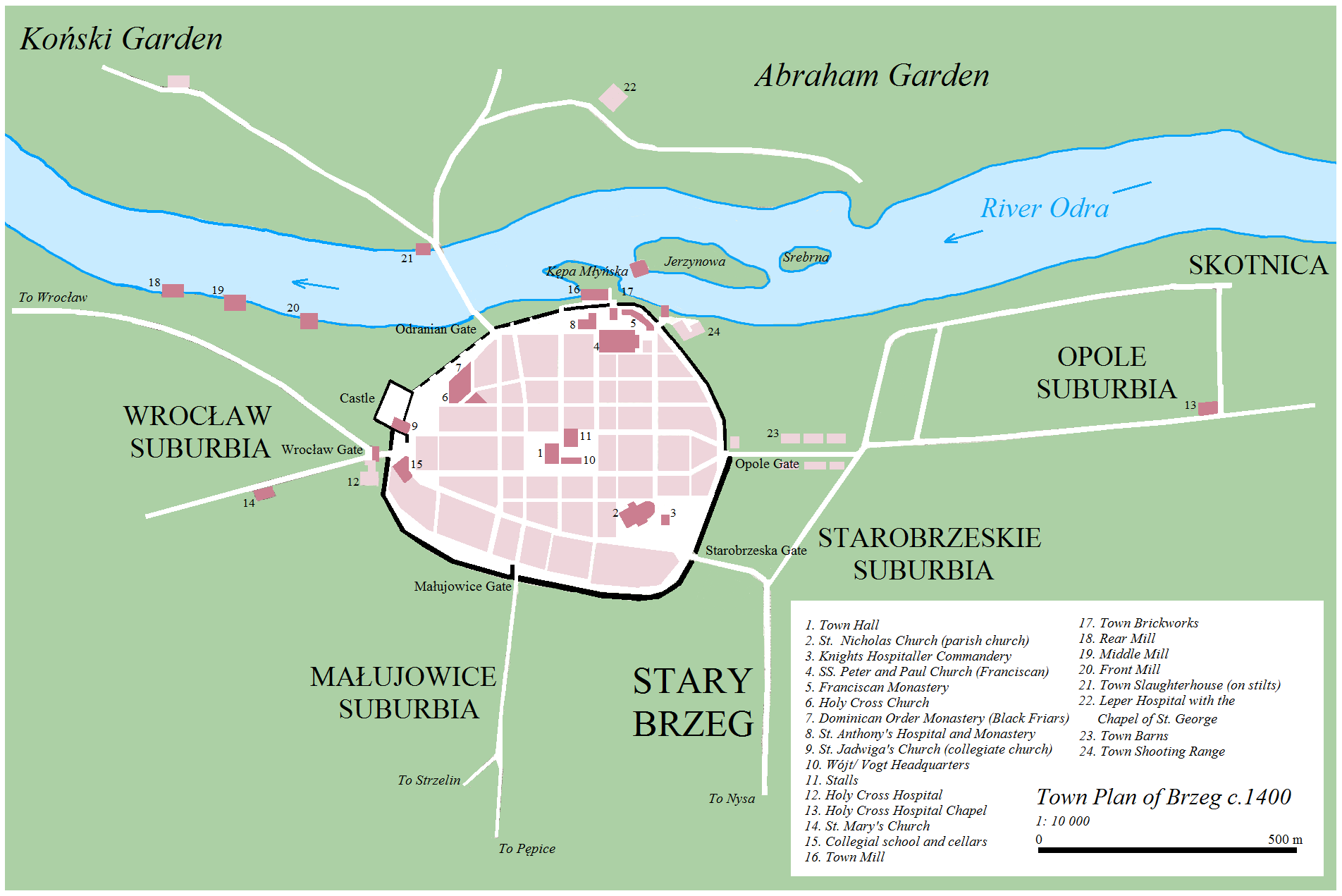
 The most favourable area for the settlement of Brzeg is located between the Castle Square (''Plac Zamkowy''), with elevated ground extending south-east towards the Square of the American Polonia (''Plac Polonii Amerykańskiej''). Before the town's foundation, three separate settlements existed in its modern-day territory, with "Wysoki Brzeg" (''Alta ripa'') bearing the main administrative role in the region. Between the late-twelfth and early-thirteen century, the Dukes of Wrocław set up a
The most favourable area for the settlement of Brzeg is located between the Castle Square (''Plac Zamkowy''), with elevated ground extending south-east towards the Square of the American Polonia (''Plac Polonii Amerykańskiej''). Before the town's foundation, three separate settlements existed in its modern-day territory, with "Wysoki Brzeg" (''Alta ripa'') bearing the main administrative role in the region. Between the late-twelfth and early-thirteen century, the Dukes of Wrocław set up a
 The town received German town law in 1250 from the
The town received German town law in 1250 from the
 In 1537 the duke
In 1537 the duke
 From the late 19th century the then German town of Brieg had expanded into a traditional military
From the late 19th century the then German town of Brieg had expanded into a traditional military
 As the town was situated on the commercial route to Wrotizla, in which a colony of Jews had long resided,
As the town was situated on the commercial route to Wrotizla, in which a colony of Jews had long resided,
 Brzeg, as the regional capital of Brzeg County (''Powiat Brzeski''), is located in the west of the Opole Voivodeship, in the south-east of Poland. The settlement is located in the
Brzeg, as the regional capital of Brzeg County (''Powiat Brzeski''), is located in the west of the Opole Voivodeship, in the south-east of Poland. The settlement is located in the
as opposed to Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
: ''Alta Ripa'', German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
: ''Brieg'', Silesian German
Silesian (Silesian: ', german: Schlesisch), Silesian German or Lower Silesian is a nearly extinct German dialect spoken in Silesia. It is part of the East Central German language area with some West Slavic and Lechitic influences. Silesian G ...
: ''Brigg'', , ) is a town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an o ...
in southwestern Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
with 34,778 inhabitants (December 2021) and the capital of Brzeg County. It is situated in Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
in the Opole Voivodeship on the left bank of the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
river.
The town of Brzeg was first mentioned as a trading and fishing settlement in the year 1234. In 1248, Silesian Duke Henry III the White
Henry III the White ( pl, Henryk III Biały) ( – 3 December 1266), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1248 until his death, as co-ruler with his brother Władysław.
Life
He was the third son of the Polish hi ...
granted the settlement Magdeburg town rights and by the late 13th century the city became fortified. Sometimes referred to as “the garden town”, the town's size greatly expanded after the construction of dwelling houses which were located on the city outskirts. From the early 14th to late 17th centuries, the town was ruled by the Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branch ...
as fiefs of the Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were a number of incorporated states in Central Europe during the medieval and early modern periods connected by feudal relations under the Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted of the Kingdom of B ...
within the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
. Later, as the result of the Silesian Wars, the town became Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
n. After the border shifts of 1945, the town's German populace was expelled and the town became part of Poland.
Etymology
In older documents, Brzeg was referred to as ''Civitas Altae Ripae'', meaning 'city on the high banks' of theOder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
River; its name is derived from Polish ''brzeg'' 'shore'.
(1841–1895), in his book of the etymology of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
n localities, states that in a Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
document from 1234 the settlement's name was ''Visoke breg'' ( pl, Wysokibrzeg, german: Wissokembreghe; literally 'high bank').
A native or resident of Brzeg is known as a ''brzeżan'', ''brzeżanin'' (male), ''brzeżanka'' (female), ''brzeżanie'' and ''brzeżaninie'' (plural).
History
Prehistory
 The locality in and around present-day Brzeg has been settled by people since the
The locality in and around present-day Brzeg has been settled by people since the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic ( Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
era, with the earliest signs of settlement between 8000 and 4200 BC, as concluded from archaeological findings in Myślibórz, Kościerzyce, Lubsza and Lipki. The early human populous left behind traces of lithic flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be ref ...
s, flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start ...
flakes and other flint related tools. The earliest signs of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
come around during the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
Era (4200–1700 BC). The Neolithic culture developed agriculture and domesticated farm animals; this lifestyle led Nomadic cultures to settle in the locality. The era saw the development of weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal ...
, pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
and mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
in the Brzeg Plain, with archaeological finds in Brzeg, Buszyce, Prędocin, Lewin Brzeski, Małujowice
Małujowice (german: Mollwitz) is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Skarbimierz, within Brzeg County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately north-west of Skarbimierz, west of Brzeg, and north-west of ...
, Lipki, Myśliborze, Mąkoszyce and Obórki.
The time period of 1300–700 BC bears the existence of the Lusatian culture of the late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
and the early Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
. The culture settled in the region and in large continued to develop agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
and the domestication of farm animals. The natural economy of the culture was based on weaving, pottery and metal works. The Lusatian culture's populous that inhabited the Brzeg Lands was identified by archaeological excavations, revealing 17 individual localities, including 3 hamlets and 8 burial sites, namely a fortified wooden settlement in Rybna and an open-pit crematory
A crematorium or crematory is a venue for the cremation of the dead. Modern crematoria contain at least one cremator (also known as a crematory, retort or cremation chamber), a purpose-built furnace. In some countries a crematorium can also b ...
in Pisarzowice (with 30 discovered burial sites).
To follow the Lusatian culture, which witnessed its declension around 500 BC, were the Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
, around 400–300 BC in Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
, as identified with archaeological findings in Lubsza and Pawłów (located in the eastern vicinity of Brzeg). Around 100 BC, the peoples of Silesia (Celtic and Germanic tribes) began trading with the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
, as evidenced through the findings of Roman currency
Roman currency for most of Roman history consisted of gold, silver, bronze, orichalcum and copper coinage. From its introduction to the Republic, during the third century BC, well into Imperial times, Roman currency saw many changes in form, denom ...
in the locality. In the 7th century Slavic peoples
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout ...
started settling in the region. At the same time Iron tools and blacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such as gates, gr ...
-based hamlets found in Kantorowice and Pępice are evidenced for the first time in this region.
Silesian period and foundation
The period of AD 500–1000 saw the establishment of the earlyfeudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
system in Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
. The era was characteristic of the establishment of gord settlements, towns and the continued development of trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct exc ...
and crafts
A craft or trade is a pastime or an occupation that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small scale pr ...
. It is believed the permanent populous around modern-day Brzeg was set up by Silesian tribes The Silesian tribes ( pl, plemiona śląskie) is a term used to refer to tribes, or groups of West Slavs that lived in the territories of Silesia in the Early Middle Ages. The territory they lived on became part of Great Moravia in 875 (now mostly i ...
. The first mention of the Silesian tribes is made in the mid-ninth-century document known as the Bavarian Geographer ( la, Geographus Bavarus), which included the Silesian gord of Ryczyn, located north-west of Brzeg, in the eastern Oława County. The Ryczyn gords became the main line of defence for the Silesians
Silesians ( szl, Ślōnzŏki or Ślůnzoki; Silesian German: ''Schläsinger'' ''or'' ''Schläsier''; german: Schlesier; pl, Ślązacy; cz, Slezané) is a geographical term for the inhabitants of Silesia, a historical region in Central Euro ...
, namely to protect the river trade routes along the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
river and the land trade route between Ryczyn (the locality's administrative centre, home to a castellan
A castellan is the title used in Medieval Europe for an appointed official, a governor of a castle and its surrounding territory referred to as the castellany. The title of ''governor'' is retained in the English prison system, as a remnant ...
) and Brzeg (being some in length). The importance of the Ryczyn gords is demonstrated by Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
's army halting their advancement before the gords in 1109.
Between the ninth and early-tenth century, the Brzeg Lands, together with all of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
, were part of Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to ...
until its demise in AD 906, after which, until 990 the region was under the rule of the Premyslids. Around the year 990, Silesia was annexed into Mieszko I's Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. During the Fragmentation of Poland (1138 – c. 1314), the area of the Brzeg Lands, along with the rest of Silesia, came under the control of King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th ...
, Bolesław III Wrymouth
Bolesław III Wrymouth ( pl, Bolesław III Krzywousty; 20 August 1086 – 28 October 1138), also known as Boleslaus the Wry-mouthed, was the duke of Lesser Poland, Silesia and Sandomierz between 1102 and 1107 and over the whole of Poland between ...
's oldest son, Władysław II the Exile : ''This article refers to the 12th century Polish monarch. For the 14th century founder of the Jagiellon dynasty, see Jogaila, and for other monarchs with similar names, see Ladislaus II (disambiguation).''
Vladislaus II the Exile ( pl, Władys ...
.
 The most favourable area for the settlement of Brzeg is located between the Castle Square (''Plac Zamkowy''), with elevated ground extending south-east towards the Square of the American Polonia (''Plac Polonii Amerykańskiej''). Before the town's foundation, three separate settlements existed in its modern-day territory, with "Wysoki Brzeg" (''Alta ripa'') bearing the main administrative role in the region. Between the late-twelfth and early-thirteen century, the Dukes of Wrocław set up a
The most favourable area for the settlement of Brzeg is located between the Castle Square (''Plac Zamkowy''), with elevated ground extending south-east towards the Square of the American Polonia (''Plac Polonii Amerykańskiej''). Before the town's foundation, three separate settlements existed in its modern-day territory, with "Wysoki Brzeg" (''Alta ripa'') bearing the main administrative role in the region. Between the late-twelfth and early-thirteen century, the Dukes of Wrocław set up a curia
Curia (Latin plural curiae) in ancient Rome referred to one of the original groupings of the citizenry, eventually numbering 30, and later every Roman citizen was presumed to belong to one. While they originally likely had wider powers, they came ...
, led by a claviger. In 1235, Henry the Bearded
Henry the Bearded ( pl, Henryk (Jędrzych) Brodaty, german: Heinrich der Bärtige; c. 1165/70 – 19 March 1238) was a Polish duke from the Piast dynasty.
He was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1201, Duke of Kraków and High Duke of all P ...
occupied the area around Oława
Oława (pronounced , , szl, Oława) is a historic town in south-western Poland with 33,029 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (from 1975–1998 it was in the former Wrocław Voivodeship), within the Wrocław m ...
, by which Walloons
Walloons (; french: Wallons ; wa, Walons) are a Gallo-Romance ethnic group living native to Wallonia and the immediate adjacent regions of France. Walloons primarily speak '' langues d'oïl'' such as Belgian French, Picard and Walloon. Wallo ...
had to turn over a tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conq ...
of 1 scale of grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legum ...
and of oat to the settlement of Brzeg, suggesting the existence of a granary
A granary is a storehouse or room in a barn for threshed grain or animal feed. Ancient or primitive granaries are most often made of pottery. Granaries are often built above the ground to keep the stored food away from mice and other animals ...
and other outbuildings in the curia's established headquarters.
Some two hundred m south-west from the curia
Curia (Latin plural curiae) in ancient Rome referred to one of the original groupings of the citizenry, eventually numbering 30, and later every Roman citizen was presumed to belong to one. While they originally likely had wider powers, they came ...
was the former location, on what was later to be called Mary's Hill (''Góra Marii''), of the Romanesque St. Mary's Church (''Kościół Najświętszej Marii Panny''). During the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
, the church was deconstructed, and its brickwork used for the construction of the town's fortifications. A sixteenth-century chronicle states it was "the first church", however, no more is known about the holy site. Historians believe the founder of the church may have been Bolesław I the Tall
Bolesław I the Tall ( pl, Bolesław I Wysoki) (born 1127 – died Leśnica (now part of Wrocław), 7 or 8 December 1201) was Duke of Wroclaw from 1163 until his death in 1201.
Early years
He was the eldest son of Władysław II the Exile by h ...
or Henry the Bearded
Henry the Bearded ( pl, Henryk (Jędrzych) Brodaty, german: Heinrich der Bärtige; c. 1165/70 – 19 March 1238) was a Polish duke from the Piast dynasty.
He was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1201, Duke of Kraków and High Duke of all P ...
. Around the peripheries of the settlement was the location of several hospital buildings. Towards the route to Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
in the town's west was the location of the Hospital of the Holy Ghost (''Świętego Ducha''), used both to cure the town's dwellers and as an inn for travellers along the Wrocław-Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
route the town of Brzeg was located in the middle of, with an average walking distance between each town taking one day. The area around the Holy Ghost Hospital, present-day Moniuszko Square (''Plac Moniuszki''), was the location of a major market, positioned by the cross roads of the Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
– Nysa route, east of the Wrocławska Gate. By the end of the thirteenth century, the Duke of Brzeg possessed 10 shambles
Shambles is an obsolete term for an open-air slaughterhouse and meat market.
Shambles or The Shambles may also refer to:
*The Shambles, a historic street in York, England
* Shambles Square, Manchester, England
* Shambles Glacier, Adelaide Island, ...
. The market is believed to be characteristic of other Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
n towns, commonly selling agricultural produce, namely bread, meat and shoes. Prior to the locality receiving its town charter
A city charter or town charter (generically, municipal charter) is a legal document (''charter'') establishing a municipality such as a city or town. The concept developed in Europe during the Middle Ages.
Traditionally the granting of a charter ...
in 1248 or 1250, the settlement had characteristics of a town and not of an ordinary fishing village, being referred to as "civitas" in an early Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
document, as exemplified by the existence of the curia
Curia (Latin plural curiae) in ancient Rome referred to one of the original groupings of the citizenry, eventually numbering 30, and later every Roman citizen was presumed to belong to one. While they originally likely had wider powers, they came ...
, church and a major market, allowing the settlement to develop through the exchange of produce and barter
In trade, barter (derived from ''baretor'') is a system of exchange in which participants in a transaction directly exchange goods or services for other goods or services without using a medium of exchange, such as money. Economists disti ...
.
Prior to Brzeg receiving its town charter
A city charter or town charter (generically, municipal charter) is a legal document (''charter'') establishing a municipality such as a city or town. The concept developed in Europe during the Middle Ages.
Traditionally the granting of a charter ...
, the Duke of Wrocław, Henry III the White
Henry III the White ( pl, Henryk III Biały) ( – 3 December 1266), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1248 until his death, as co-ruler with his brother Władysław.
Life
He was the third son of the Polish hi ...
, received the settlement of Małkowice, (present-day Kępa Młyńska), in exchange of his feudal rights over Zębice (south-west from Oława
Oława (pronounced , , szl, Oława) is a historic town in south-western Poland with 33,029 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (from 1975–1998 it was in the former Wrocław Voivodeship), within the Wrocław m ...
). The fishermen living in Małkowice (present-day ''ul. Rybacka''), in accordance to ancient Polish law were charged with the task of protecting the Ducal Castle along the riverside. By the turn of the thirteenth century, the defenceless populous living in the pastures of the Brzeg Plain began to relocate into the fortified ''Visoke breg'', building up a new osiedle around the present-day streets of: ''Łokietka'', ''Piastowska'' and ''Trzech Kotwic'' (extending south-east). The osiedle was documented as ''Stary Brzeg'' ( ''Antiqua Brega''; ''Alt Brieg''), to be renamed Wieś Brzeska: Brygischedorf (c. 1329) and ''villa Bregensis'' in 1339. To the west of the fortified centre of Brzeg, the settlement of Rataje (a separate village until 1975) as the former village's etymology suggests, centered around the upkeep of the ducal pastures.
Middle Ages and Early Modern period
 The town received German town law in 1250 from the
The town received German town law in 1250 from the Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
Duke Henry III the White
Henry III the White ( pl, Henryk III Biały) ( – 3 December 1266), a member of the Silesian Piasts, was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1248 until his death, as co-ruler with his brother Władysław.
Life
He was the third son of the Polish hi ...
. The foundation was carried out by the three lokators, Gerkinus of Goldberg, Ortlif and Heinrich of Reichenbach. From the emblem of Heinrich of Reichenbach the town also got its coat of arms. While in power, Henry III, granted the town (by a singular payment) the forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
around the locality of Lubsza. His successor, Henryk IV the Righteous regulated the town's church affairs, as well as renouncing his patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists su ...
over St. Mary's Church (''Kościół Św. Marii Panny''), located west of the town's western boundary. The church was granted to the Order of Saint John, subsequently founding the Church of St. Nicholas in 1292. The town was fortified
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere' ...
in 1297.
From 1311 to 1675 Brzeg was the capital of a Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the ...
n duchy ( Duchy of Brzeg) ruled by the Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branche ...
dynasty, a branch of the dukes of Lower Silesia, one of whom built a castle in 1341. The Duchy became part of the Kingdom of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
in 1329. The town was burned by the Hussites in 1428 and soon afterwards rebuilt.
In 1595 Brieg was again fortified by Joachim Frederick of Brieg and Liegnitz. In the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
it suffered greatly; in the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George ...
it was heavily bombarded by the Prussian forces; and in 1807 it was captured by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
's army. When Bohemia fell to the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
in 1526, the town fell under the overlordship of the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
s in their roles of Kings of Bohemia, although it was still ruled locally by the Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's testament, Władysław was granted Silesia as his h ...
. Upon the extinction of the last duke George William of Legnica in 1675, Brieg came under the direct rule of the Habsburgs.
Late modern and contemporary
 In 1537 the duke
In 1537 the duke Frederick II of Legnica
Frederick II, Duke of Legnica ( pl, Fryderyk II Legnicki) (12 February 1480 – 17 September 1547), also known as the Great of Legnica ( pl, Legnicki Wielki), was a Duke of Legnica from 1488 (until 1495 and 1505 with his brothers), of Brzeg from ...
concluded a treaty with Elector Joachim II of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
, whereby the Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenb ...
s of Brandenburg would inherit the duchy upon the extinction of the Silesian Piasts. On the death of George William the last duke in 1675, however, Austria refused to acknowledge the validity of the treaty and annexed the duchies and Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
of the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
used this treaty to justify his claim at the invasion of Silesia during the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George ...
in 1740. Brieg and most of Silesia were annexed by Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
in 1741 during the First Silesian War.Merriam Webster's Geographical Dictionary, Third Edition, p. 180 In 1807 the town's fortifications were pulled down by Napoleon's army. The Prussian Province of Silesia
The Province of Silesia (german: Provinz Schlesien; pl, Prowincja Śląska; szl, Prowincyjŏ Ślōnskŏ) was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1919. The Silesia region was part of the Prussian realm since 1740 and established as an official p ...
, and thus Brieg, consequently became part of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
when it was proclaimed in 1871 on the unification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was the process of building the modern German nation state with federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without multinational Austria), which commenced on 18 August 1866 with adoption of t ...
. According to the Prussian census of 1905, the city of Brieg had a population of 27,486, of which 93% spoke German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, 6% spoke Polish, and 1% were bilingual.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, 60% of Brieg was destroyed and many of the town's inhabitants died during the severe winter of 1944–5 as they fled from the advancing Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
. The war had brought the most severe destruction to the town in its entire history. Some of the town's population was evacuated by the German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
who moved its population further west inside Germany for safety and declared Brieg "Festung Brieg" (Fortification Brieg). After the fall of the town to the Soviets the remaining German population were later subject to harassment and expulsion (see Expulsion of Germans after World War II
Expulsion or expelled may refer to:
General
* Deportation
* Ejection (sports)
* Eviction
* Exile
* Expeller pressing
* Expulsion (education)
* Expulsion from the United States Congress
* Extradition
* Forced migration
* Ostracism
* Persona ...
). After the war, the Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
placed Silesia, and thus the town, under Polish administration. Subsequently, Brzeg and Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the ...
were repopulated by Poles whom Soviets expelled from the eastern part of Interwar Poland.
Traditional Garrison Town
 From the late 19th century the then German town of Brieg had expanded into a traditional military
From the late 19th century the then German town of Brieg had expanded into a traditional military garrison
A garrison (from the French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip") is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a mili ...
town, from 1897 until 1919 it was the home town base to Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
Regiment No. 157 designated from 1902 the 4th Silesian Infantry Regiment No. 157 (''4. Schlesisches Infanterie-Regiment Nr. 157'') of the Royal Prussian Army
The Royal Prussian Army (1701–1919, german: Königlich Preußische Armee) served as the army of the Kingdom of Prussia. It became vital to the development of Brandenburg-Prussia as a European power.
The Prussian Army had its roots in the co ...
and respectively the Imperial German Army
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (german: Deutsches Heer), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the l ...
.Book Title: Das 4. Schlesische Infanterie-Regiment Nr. 157. Nach den amtlichen Kriegstagebüchern bearbeitet (English: The 4th Silesian Infantry Regiment No. 157. Edited according to official war diaries.), Authors: Tiede (Generalleutnant), Himer (Hauptmann) and Röhricht (Oberleutnant), 1922, Publisher: Stalling, Oldenburg, Germany, in German.Book Title: Das 4. Schlesische Infanterie-Regiment Nr. 157 im Frieden und im Kriege 1897-1919 (English: The 4th Silesian Infantry Regiment No. 157 in peacetime and in wartime 1897-1919), Author: Hans Guhr (Generalmajor), Paul Tiede (General der Infanterie), 1934, Publisher: Bernhard Sporn, Zeulenroda (Thüringen), Germany, in German. In 1914 under the regiment's last peacetime commander Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on th ...
Paul Tiede the regiment began mobilizing for the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
* Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a maj ...
at the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
as part of VI Army Corps (''VI. Armee-Korps''), 12th Division (''12. Division''), 78th Infantry Brigade (''78. Infanterie-Brigade'').
At the end of World War I the garrison barracks at Brieg remained for some years after without a stationed military regiment. The Imperial German Army Air Arm (''Luftstreitkräfte
The ''Deutsche Luftstreitkräfte'' (, German Air Force)—known before October 1916 as (Flyer Troops)—was the air arm of the Imperial German Army. In English-language sources it is usually referred to as the Imperial German Air Service, alth ...
'') military aerodrome
An aerodrome (Commonwealth English) or airdrome (American English) is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for publi ...
(''Fliegerhorst'') found in nearby ''Grüningen'' was furthermore dismantled and destroyed as part of the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
. It was not until 4 August 1930 that the 5th Squadron of Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in ...
Regiment No. 8 (''5. Schwadron Reiterregiments Nr. 8'') of the German Reichswehr
''Reichswehr'' () was the official name of the German armed forces during the Weimar Republic and the first years of the Third Reich. After Germany was defeated in World War I, the Imperial German Army () was dissolved in order to be reshape ...
arrived in Brieg from Breslau-Carlowitz, other cavalry squadrons from Militsch
Milicz (german: Militsch) is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It is the seat of Milicz County and of Gmina Milicz, part of the larger Wrocław metropolitan area.
Geography
The town is situated in the historic Lower ...
and Oels followed shortly after. This resulted in the garrison's Tiede-Barracks (named after ''Generalleutnant Paul Tiede'') located in ''Moltke-, Sedan-, Roon- und Bismarck straße'' requiring some alterations to accommodate the new arrival of horse-cavalry residents. It was from Brieg garrison, the German Cavalry Captain (''Rittmeister
__NOTOC__
(German and Scandinavian for "riding master" or "cavalry master") is or was a military rank of a commissioned cavalry officer in the armies of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Scandinavia, and some other countries. A ''Rittmeister'' is typic ...
'') Konrad Freiherr von Wangenheim
Konrad Freiherr von Wangenheim (20 August 1909 in Hanover – 28 January 1953) was a German army Cavalry officer, a horse rider who competed at the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin, securing a gold medal for the German equestrian team whilst s ...
became famous for securing a Gold medal win at the 1936 Summer Olympics
The 1936 Summer Olympics (German: ''Olympische Sommerspiele 1936''), officially known as the Games of the XI Olympiad (German: ''Spiele der XI. Olympiade'') and commonly known as Berlin 1936 or the Nazi Olympics, were an international multi-s ...
in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
for the German equestrian team whilst suffering from a broken collarbone. In 1933 an airfield located in nearby ''Hermsdorf'' was also built and thereby a much larger military aerodrome was established. The new aerodrome was occupied by Flight Reconnaissance Group 113 (''Fliegeraufklärungsgruppe 113'').
Towards the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, on 6 February 1945, the Soviet army
uk, Радянська армія
, image = File:Communist star with golden border and red rims.svg
, alt =
, caption = Emblem of the Soviet Army
, start_date ...
captured Brzeg, which resulted in moderate destruction of the town's buildings and infrastructure. After Germany's defeat in the war, Brzeg became part of Poland. Since 1950 the reconstructed town has been a part of the Opole Voivodeship.
History of the Jewish population
 As the town was situated on the commercial route to Wrotizla, in which a colony of Jews had long resided,
As the town was situated on the commercial route to Wrotizla, in which a colony of Jews had long resided, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
settled there about 1324. The Jewish community of Brieg had its separate place of worship from early times. In 1358 Jews lent money to local noblemen and the duke of Brieg, Ludwig I, who granted the Jews freedom of movement in the duchy in that year. In the 14th century the Jews of Brieg were persecuted on account of their usurious practices; one outbreak of such violence occurred in 1362. In 1392 it was claimed that all debts of the duke had been discharged by the payments to a Jew of Brieg (Jacob, the son of Moses), of a certificate of indebtedness. In 1398 the Brieg Jews bought a letter of protection from the duke, whereby they were guaranteed the peaceful possession of their privileges. But in 1401 they were driven from the city, except Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. ...
and Seman von Reichenbach, who had received a patent of protection from the duke's council for six years from May 1, 1399. In 1423, duke Ludwig II granted the Jews rights of residence on payment of an annual tax of 20 gulden, but they were expelled from the duchies of Brieg and Liegnitz
Legnica (Polish: ; german: Liegnitz, szl, Lignica, cz, Lehnice, la, Lignitium) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River (left tributary of the Oder) and the Czarna Woda. Between 1 June 1975 ...
in 1453 as a result of the inflammatory preachings of the Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
John Capistrano. Solomo, a capitalist, lent large sums of money to royal houses in the 15th century. In the 16th century, one of the local Jews served as a physician to the duke of Brieg.
With the decline of Breslau as a trade center, the Jews of Brieg became little more than an isolated community; and in modern times they shared the lot of the other Silesian Jews. They carried on insignificant trade operations as a rule. The conquest of Silesia by Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
brought but slight change in their condition.
A synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of wor ...
was built in Brieg in 1799, and a rabbi was first appointed in 1816. The Jewish population numbered 156 in 1785; 376 in 1843; 282 in 1913; 255 in 1933; and 123 in 1939. In the Kristallnacht
() or the Night of Broken Glass, also called the November pogrom(s) (german: Novemberpogrome, ), was a pogrom against Jews carried out by the Nazi Party's (SA) paramilitary and (SS) paramilitary forces along with some participation fro ...
pogroms of 1938 the interior of the synagogue was completely demolished and the Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the ...
scrolls publicly burned; numerous shops were ransacked. The community was not reestablished after the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
.
Geography
Status
The shape of the town, including its neighbouring '' osiedla'', is comparable to that of a deformedrectangle
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram contain ...
, elongated north-south and west-east. The area of the town, including the village of Rataje, which was incorporated into Brzeg on January 1, 1973, is some . In comparison to Opole, with a total area of ; Nysa's and Kędzierzyn-Koźle's ; Brzeg is ranked fourth in the Opole Voivodeship by both population and area.
Topography
 Brzeg, as the regional capital of Brzeg County (''Powiat Brzeski''), is located in the west of the Opole Voivodeship, in the south-east of Poland. The settlement is located in the
Brzeg, as the regional capital of Brzeg County (''Powiat Brzeski''), is located in the west of the Opole Voivodeship, in the south-east of Poland. The settlement is located in the valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams ove ...
of the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
, located between Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
38.5 km to its east and Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
, to its north-west. The town has a predominantly flat relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
(in comparison to the river scarp on the eastern bank of the river). The River Oder, at low water levels (predominantly between June and early September) forms eyots north of Jerzynowa, Kępa and Srebrna Islands. The locality is located in the Brzeg Plain (''Rownina Brzeska''), part of the Silesian Lowlands
Silesian Lowlands (or Silesian Plains, pl, Nizina Śląska, cs, Slezská nížina, german: Schlesische Niederung) are lowlands located in Silesia, Poland in Central Europe. A small part is located in the Czech Republic. It is part of the Centra ...
. The Brzeg Plain's boundaries are outlined by the Oder river to its north, the Nysa Kłodzka Valley to its south-east, the hillocks of Grodków
Grodków (; szl, Grodkōw) is a town in Brzeg County, Opole Voivodeship in Poland, the administrative seat of Gmina Grodków. It is located in the Silesian Lowlands of the Oder basin, in the historic Upper Silesia region, about south of Brz ...
Hills and the Wawrzyszów Hills to its south. The western boundary of the Brzeg Plain is marked by the Oława
Oława (pronounced , , szl, Oława) is a historic town in south-western Poland with 33,029 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (from 1975–1998 it was in the former Wrocław Voivodeship), within the Wrocław m ...
Valley, along the Oder's mid-course.
The Brzeg Plain was formed by the Riss glaciation
The Riss glaciation, Riss Glaciation, Riss ice age, Riss Ice Age, Riss glacial or Riss Glacial (german: Riß-Kaltzeit, ', ' or (obsolete) ') is the second youngest glaciation of the Pleistocene epoch in the traditional, quadripartite glacial classi ...
period (347,000 to 128,000 years ago), leaving behind remnants of a ground moraine from the last glacial period. The ground moraines have left two equally small hills, bearing characteristics of kame
A kame, or ''knob'', is a glacial landform, an irregularly shaped hill or mound composed of sand, gravel and till that accumulates in a depression on a retreating glacier, and is then deposited on the land surface with further melting of the ...
s. The kames form the Łosiów Range (''Wał Łosiowski''), between the confluence of the River Nysa Kłodzka and the Oława Valley. Small streams, having their sources around the range, are fed directly into the Oder in the region of Nysa Kłodzka and Oława
Oława (pronounced , , szl, Oława) is a historic town in south-western Poland with 33,029 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (from 1975–1998 it was in the former Wrocław Voivodeship), within the Wrocław m ...
.Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the ...Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
, is due to the formation of a "przesieka" ("clearing"). The "clearing" was a lateral formation, extending northerly from the former Sudetes
The Sudetes ( ; pl, Sudety; german: Sudeten; cs, Krkonošsko-jesenická subprovincie), commonly known as the Sudeten Mountains, is a geomorphological subprovince in Central Europe, shared by Germany, Poland and the Czech Republic. They consi ...
Wildland to the southern foothill
Foothills or piedmont are geographically defined as gradual increases in elevation at the base of a mountain range, higher hill range or an upland area. They are a transition zone between plains and low relief hills and the adjacent topograp ...
s of the Sudetes
The Sudetes ( ; pl, Sudety; german: Sudeten; cs, Krkonošsko-jesenická subprovincie), commonly known as the Sudeten Mountains, is a geomorphological subprovince in Central Europe, shared by Germany, Poland and the Czech Republic. They consi ...
Mountains. The clearing's characteristics set it as a point for defence in the Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the ...
region, lined with barrages made out of cut down woodland. The Brzeg Plain was settled due to its fertile soil, allowing for the earliest forms of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
to develop in the locality. The locality was first settled by Silesian tribes and in later history, until 1675, by the Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branche ...
duchies of Duchy of Brzeg, Legnica
Legnica (Polish: ; german: Liegnitz, szl, Lignica, cz, Lehnice, la, Lignitium) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River (left tributary of the Oder) and the Czarna Woda. Between 1 June 197 ...
and Wołów, united under the Duchy of Legnica-Wołów-Brzeg. Presently, the region is spotted with numerous towns, including Brzeg, Grodków
Grodków (; szl, Grodkōw) is a town in Brzeg County, Opole Voivodeship in Poland, the administrative seat of Gmina Grodków. It is located in the Silesian Lowlands of the Oder basin, in the historic Upper Silesia region, about south of Brz ...
and Strzelin
Strzelin (german: Strehlen, cz, Střelín) is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in south-western Poland. It is located on the Oława river, a tributary of the Oder, about south of the region's capital Wrocław. It is part of the Wrocław me ...
, as well as villages, with agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
providing the major source of income. The development of agriculture is met with a lack of forested areas, apart from the Stobrawa Landscape Park
Stobrawa Landscape Park (''Stobrawski Park Krajobrazowy'') is a protected area ( Landscape Park) in south-western Poland, established in 1999, covering an area of in the region of the Stobrawa river.
The Park lies within Opole Voivodeship: in ...
, located 7.2 km to the north of Brzeg and the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
river. The Stobrawa woodland, agriculture and the Oder (as a form of transport) provided Brzeg the necessary diversity to remain the regional trade capital in Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
.
Brzeg's geographical position between two trade routes, running from west to east (Legnica
Legnica (Polish: ; german: Liegnitz, szl, Lignica, cz, Lehnice, la, Lignitium) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River (left tributary of the Oder) and the Czarna Woda. Between 1 June 197 ...
–Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
) and north to south (Gniezno
Gniezno (; german: Gnesen; la, Gnesna) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. One of the Piast dynasty's chief cities, ...
– Nysa) and further on into the Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia ( cs, České království),; la, link=no, Regnum Bohemiae sometimes in English literature referred to as the Czech Kingdom, was a medieval and early modern monarchy in Central Europe, the predecessor of the modern Czec ...
, additionally stimulated the town's demographic and economic expansion. Presently, Brzeg remains located between the European route E67
European route E 67 is an E-road running from Prague in the Czech Republic to Estonia and by ferry to Finland. It goes via Prague, Wrocław, Warsaw, Kaunas, Panevėžys, Riga, Tallinn, Helsinki.
The route is known as the Via Baltica ...
and E40.
Environment
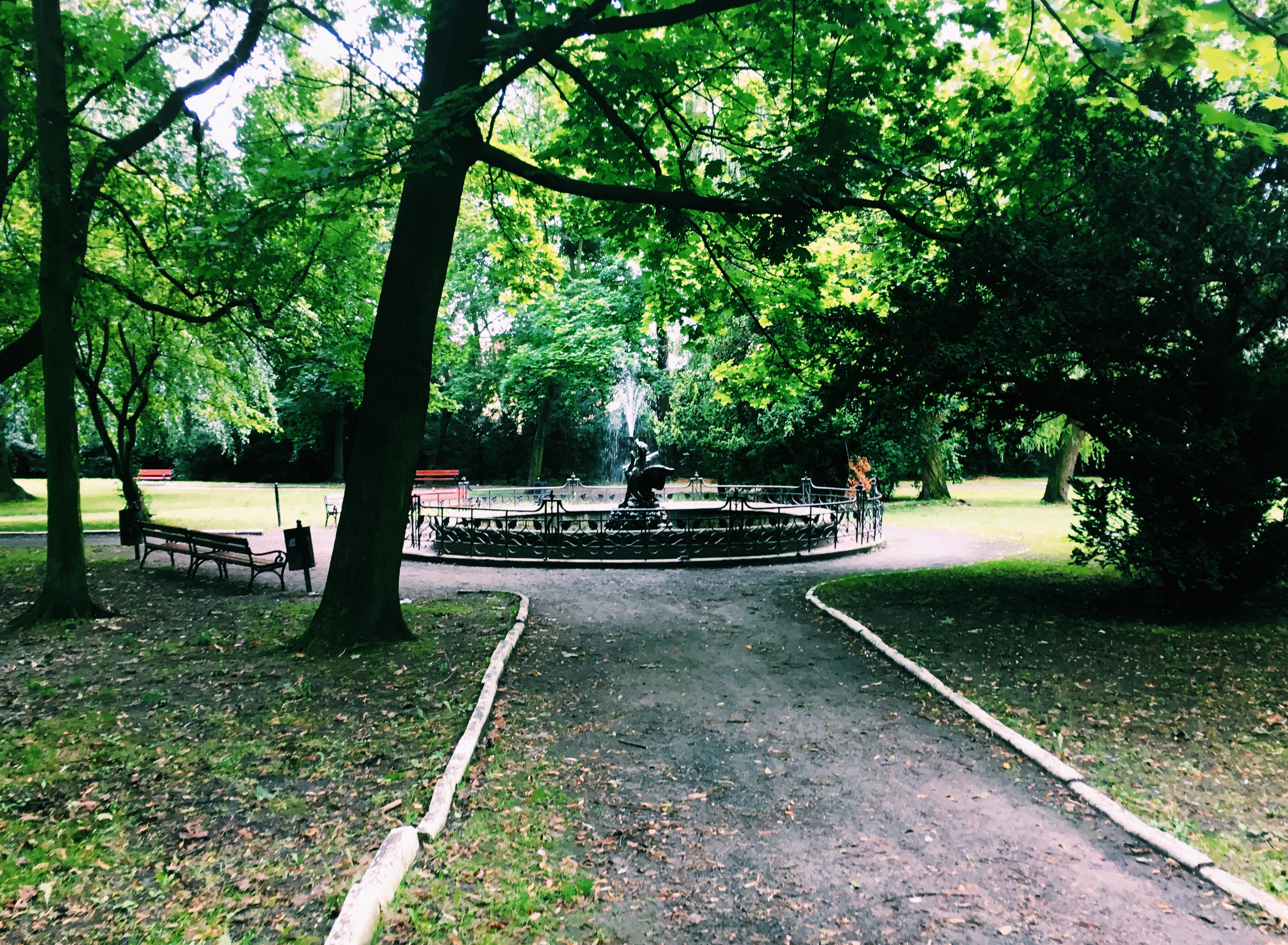
 Brzeg has five public parks, three of which encircle the Old Town (''Stare Miasto''), after the area was transformed into parkland with the deconstruction of the garrison town's fortifications during the
Brzeg has five public parks, three of which encircle the Old Town (''Stare Miasto''), after the area was transformed into parkland with the deconstruction of the garrison town's fortifications during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
in 1807. The parkland, surrounding the Old Town to its south, became known as the ''Planty''. The ''Planty'' constitute of the Central Park of J. Czajkowski (''Park Centralny im. J. Czajkowskiego''), with a total area of 6.1 ha. The Central Park contains an artificial lake
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including contr ...
and a stream, connecting its waters to the western portion of the ''Planty'', the ''Park nad Fosą''. The Park by the Moat (''Park nad Fosą''), with a total area of 3.7 ha, is located south of the Silesian Piasts' Castle. The third and largest by area parkland surrounding the Old Town is located by the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
river, the Odranian Park (''Park Nadodrzański''), with a total area of 10.9 ha. The castle, together with the town's fortification remnants, the Odrzańska Gate is located in the park.
The largest parkland in Brzeg, located in the south-west of the town is the Park of Juliusz Peppel (Park im. Juliusza Peppela) and formerly Liberty Park (''Park Wolności'') having a total area of 68.8 ha. The parkland was established after donations from the owners of Skarbimierz and the landed-elite family von Lobbecke donated the area to the town's authorities, to make way for a landscape park in the area. The smallest of the five public parks in Brzeg is the ''Park Ptasi'', located in the south of the town, west of the osiedle of Westerplatte. The park has a total area of 1 ha.
Demography
History
After 1945, the town of Brzeg was part of the population transfers of theSoviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and Polish People's Republic
The Polish People's Republic ( pl, Polska Rzeczpospolita Ludowa, PRL) was a country in Central Europe that existed from 1947 to 1989 as the predecessor of the modern Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million ne ...
's campaign to resettle Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
from Kresy (annexed by the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
) to the newly annexed territories by Poland from the defeated Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, as part of the Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement (german: Potsdamer Abkommen) was the agreement between three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union on 1 August 1945. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned th ...
. During the Polish resettlement campaign, the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
population of Brzeg was expelled to the remaining territories of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
. The newly arrived population in Brzeg predominantly came from the countryside, being former peasants. The integration of the residents came in phases: education, communal work, marriages and the provision of material goods and items left behind by the former populace. By 1975, 37.9% of the population of Brzeg had settled in the town after 1960.

 Breakdown of population origin of Brzeg in 1950:
Breakdown of migrant population origin of Brzeg in 1950:
Population change:
Breakdown of population origin of Brzeg in 1950:
Breakdown of migrant population origin of Brzeg in 1950:
Population change:
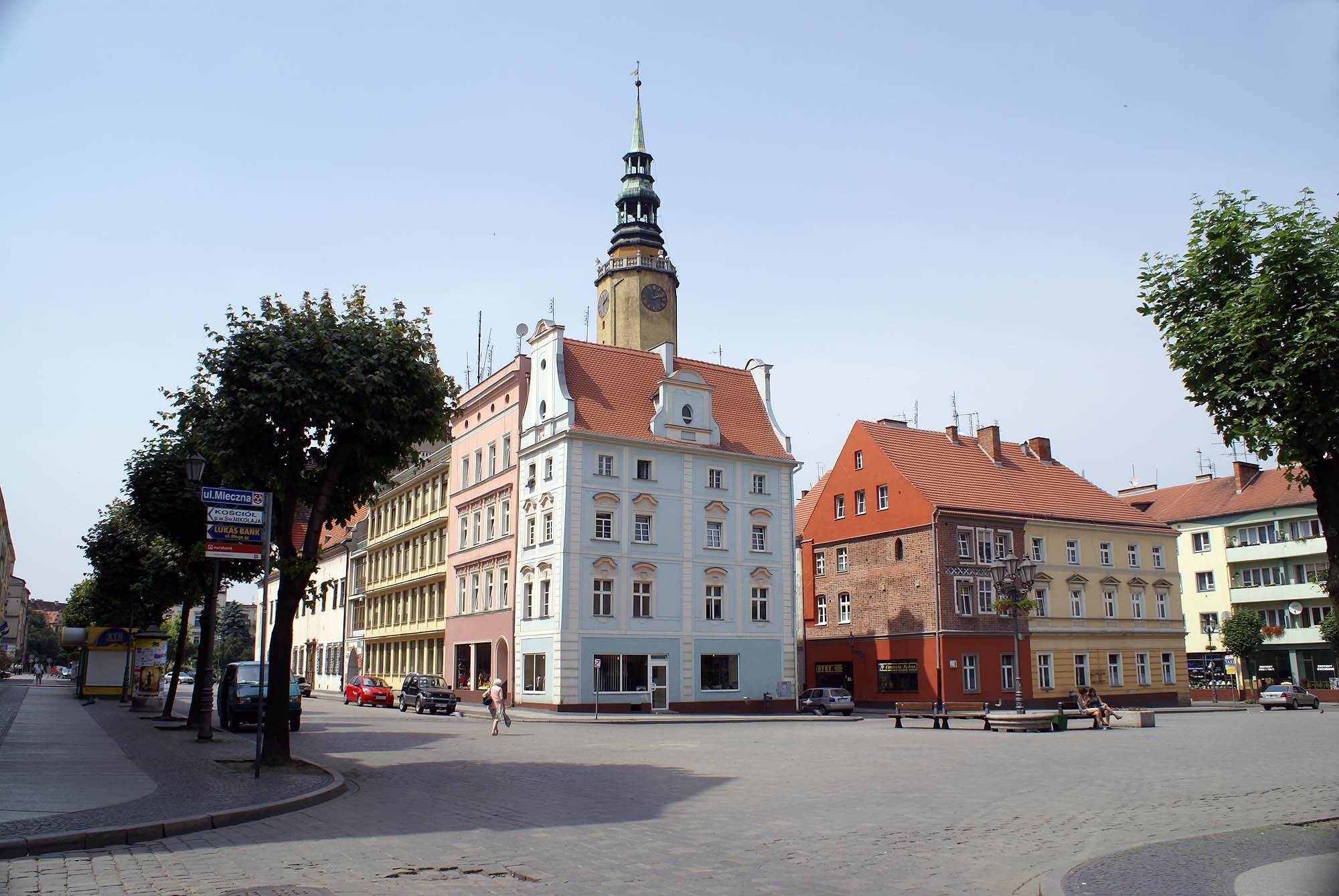
Main sights
* The Renaissance Brzeg Town Hall (Rynek), surrounded by thirteenth-century townhouses. * Old Castle (Zamek), with an interesting adorned façade, host of the Muzeum Piastów Śląskich. The Brzeg Castle is referred to as the Silesian Wawel. The castle-complex includes the Chapel of St.Jadwiga of Poland
Jadwiga (; 1373 or 137417 July 1399), also known as Hedwig ( hu, Hedvig), was the first woman to be crowned as monarch of the Kingdom of Poland. She reigned from 16 October 1384 until her death. She was the youngest daughter of Louis the Grea ...
.
* St. Nicholas's Church (Gothic architectural style).
* Holy Cross Church (on old castle square), (Baroque architectural style).
* St. Jadwiga's Church, located by the castle.
* St. Luke's Church, a church built in the Neoclassical architectural style.
* Saints Peter and Paul Church, a Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
church built in the thirteen-century.
* Christ's Resurrection Church, a garrison church built in the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
architectural style.
* Baroque figures of John of Nepomuk
John of Nepomuk (or John Nepomucene) ( cs, Jan Nepomucký; german: Johannes Nepomuk; la, Ioannes Nepomucenus) ( 1345 – 20 March 1393)
was the saint of Bohemia (Czech Republic) who was drowned in the Vltava river at the behest of Wenceslaus ...
and Jude the Apostle
Jude ( grc-gre, Ἰούδας Ἰακώβου translit. Ioúdas Iakóbou) was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus according to the New Testament. He is generally identified as Thaddeus ( grc-gre, Θαδδαῖος; cop, ⲑⲁⲇⲇⲉⲟⲥ; ...
from 1722, standing by the façade of the Holy Cross Church.
* Statue of the Holy Trinity
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the central dogma concerning the nature of God in most Christian churches, which defines one God existing in three coequal, coeternal, consubstantial divine persons: God th ...
(on old castle square), raised in 1731.
* Piast Gimnasium (''Gimnazium Piastowskie'') founded in 1569.
* Odrzańska Gate, part of the former fortifications; located in the ''Park Odrzański'' (Odranian Park).
* Water tower
A water tower is an elevated structure supporting a water tank constructed at a height sufficient to pressurize a distribution system for potable water, and to provide emergency storage for fire protection. Water towers often operate in conju ...
(''Wieża ciśnień'') by Rybacka Street (''ul. Rybacka''), from 1877.
* Residential townhouses:
** Rynek 19, Renaissance façade from 1621 (reconstruction).
** Chopina 1, Renaissance from 1597.
** Jabłkowa 5, Baroque townhouse from 1715.
** Jabłkowa 7, Empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
architectural style from 1797.
* Old Garrison buildings (''Stare Koszary'') from the Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
colonisation period.
* ''Planty'' - remaining bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
fortifications around the medieval town. The fortifications were deconstructed in 1807, with the area transformed into the ''Planty'' Park.
* Synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of wor ...
from 1799.
* River Boat Station (''Brzeg Marina'') (on the east bank of the Oder), built in 2012.
Economy

Industry
Brzeg is the centre for industry and production in the Brzeg County. The town's industries include the production ofagricultural machinery
Agricultural machinery relates to the mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the countless kinds of farm implements that ...
, electric engines, margarine
Margarine (, also , ) is a spread used for flavoring, baking, and cooking. It is most often used as a substitute for butter. Although originally made from animal fats, most margarine consumed today is made from vegetable oil. The spread was or ...
and sugar production.
The largest concentration of industry in Brzeg is located in the town's eastern quarter, south of the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
, with numerous manufacturers, including: the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
Bartling GmbH (plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adapta ...
packaging company); "BESEL" ( Polish electric engine company, founded in the town in 1950), and CIK car accessories plant. All three industries are located between Ciepłownicza Street (''ul. Ciepłownicza'') and Składowa Street (''ul. Składowa'').
Brzeg is also home to one of the largest confectionary
Confectionery is the art of making confections, which are food items that are rich in sugar and carbohydrates. Exact definitions are difficult. In general, however, confectionery is divided into two broad and somewhat overlapping categorie ...
companies in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, PWC Odra S.A. (founded in 1946). Presently, the firm is part of the joint-stock company
A joint-stock company is a business entity in which shares of the company's stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their shares (certificates of ownership). Shareholders a ...
Otmuchów Group. The production plant is located by Starobrzeska Street (''ul. Starobrzeska'').
Tourism
, Brzeg had the lowest number of foreign tourists in the Opole Voivodeship, with some 95% being national tourists. Per 1000 of the population, there are 1.60–3.89 available accommodations, which is behind nine of the eleven regional capitals (being at level with Kędzierzyn-Koźle) in the Opole Voivodeship, includingOpole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
, with 3.90–5.89 tourist accommodations per 1000 of the population.
Education
 Brzeg has a total of 7,826 citizens in the potential education age group (3-24 year of age). The number of city dwellers in Brzeg that have completed
Brzeg has a total of 7,826 citizens in the potential education age group (3-24 year of age). The number of city dwellers in Brzeg that have completed higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after compl ...
is at 14.4% of the population, which is similar to the statistical average of the number of people obtaining higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after compl ...
in the Opole Voivodeship, being at 15.1%. Data from 2015 indicates that 2.5% of the population of Brzeg have completed post- lyceum (''policealne'') education, with Brzeg having two post- lyceum schools (''szkoły policealne''): Medyczne Studium Zawodowe by Ofiar Katynia Street (medical practice institution); Policealne Studium Zawodowe – Zespół Szkół Ekonomicznych by Jan Paweł II Street (higher school of economics). The population of Brzeg that is in the age of potential further education (aged 19–24) is 26.8%, out of which 27.1% are women and 26.6% are men.
Some 22.4% of the population of the town of Brzeg () has some sort of work-related further education (i.e. scholarship
A scholarship is a form of financial aid awarded to students for further education. Generally, scholarships are awarded based on a set of criteria such as academic merit, diversity and inclusion, athletic skill, and financial need.
Scholars ...
or college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offerin ...
course). In 2015, 5.3% of the town's population participated in secondary education
Secondary education or post-primary education covers two phases on the International Standard Classification of Education scale. Level 2 or lower secondary education (less commonly junior secondary education) is considered the second and final ph ...
, while some 19.6% have attended primary education
Primary education or elementary education is typically the first stage of formal education, coming after preschool/ kindergarten and before secondary school. Primary education takes place in '' primary schools'', ''elementary schools'', or ...
in that same year. The city council of Brzeg spends 33.3% of its annual budget on education, amounting to 35.2 million zlotys annually.
Post-secondary education institutions:
Public gymnasium (secondary school) institutions:
Transport
 Brzeg is located at the crossroads of the
Brzeg is located at the crossroads of the National Road
The National Road (also known as the Cumberland Road) was the first major improved highway in the United States built by the federal government. Built between 1811 and 1837, the road connected the Potomac and Ohio Rivers and was a main tran ...
Wiązów
Wiązów (german: Wansen) is a town in Strzelin County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of the administrative district ( gmina) called Gmina Wiązów. The town lies approximately east of Strzelin, and sout ...
and Strzelin
Strzelin (german: Strehlen, cz, Střelín) is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in south-western Poland. It is located on the Oława river, a tributary of the Oder, about south of the region's capital Wrocław. It is part of the Wrocław me ...
) and the National Road Oława
Oława (pronounced , , szl, Oława) is a historic town in south-western Poland with 33,029 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (from 1975–1998 it was in the former Wrocław Voivodeship), within the Wrocław m ...
, Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
, Bolesławiec and Zgorzelec; eastbound to Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
, Strzelce Opolskie, Bytom
Bytom (Polish pronunciation: ; Silesian: ''Bytōm, Bytōń'', german: Beuthen O.S.) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. Located in the Silesian Voivodeship of Poland, the city is 7 km northwest of Katowice, the regional capi ...
, Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
, Tarnów
Tarnów () is a city in southeastern Poland with 105,922 inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of 269,000 inhabitants. The city is situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship since 1999. From 1975 to 1998, it was the capital of the Tarn� ...
, Jarosław and Korczowa
Korczowa ( uk, Корчова, ''Korchova'') is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Radymno, within Jarosław County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland, close to the border with Ukraine.
The village lies approx ...
. The interchange to the Motorway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms ...
(''Węzeł Przylesie'') is located 14 km south of Brzeg.
Brzeg has well developed railway and bus transportation services. The PKP Brzeg railway station is operated by PKP Intercity
PKP Intercity is a company of PKP Group responsible for long-distance passenger transport. It runs about 350 trains daily, connecting mainly large agglomerations and smaller towns in Poland. The company also provides most international trains t ...
and Przewozy Regionalne
Polregio (formerly ''Przewozy Regionalne'') is a train operator in Poland, responsible for local and interregional passenger transportation. Each day it runs approximately 3,000 regional trains. In 2002 it carried 215 million passengers.
Th ...
. The town has direct connections to Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
, Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
, Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
, Warszawa
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
, Katowice
Katowice ( , , ; szl, Katowicy; german: Kattowitz, yi, קאַטעוויץ, Kattevitz) is the capital city of the Silesian Voivodeship in southern Poland and the central city of the Upper Silesian metropolitan area. It is the 11th most popu ...
, Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
, Szczecin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
, Zielona Góra
Zielona Góra is the largest city in Lubusz Voivodeship, located in western Poland, with 140,403 inhabitants (2021). Zielona Góra has a favourable geographical position, being close to the Polish-German border and on several international road ...
, Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
, Kielce
Kielce (, yi, קעלץ, Keltz) is a city in southern Poland, and the capital of the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship. In 2021, it had 192,468 inhabitants. The city is in the middle of the Świętokrzyskie Mountains (Holy Cross Mountains), on the ban ...
, Przemyśl
Przemyśl (; yi, פשעמישל, Pshemishl; uk, Перемишль, Peremyshl; german: Premissel) is a city in southeastern Poland with 58,721 inhabitants, as of December 2021. In 1999, it became part of the Subcarpathian Voivodeship; it was p ...
, Zamość, Nysa, and other cities. The Brzeg bus service is operated by PKS Brzeg, with ten bus lines around the town and Gmina Brzeg. The important routes are to Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
, Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
, Grodków
Grodków (; szl, Grodkōw) is a town in Brzeg County, Opole Voivodeship in Poland, the administrative seat of Gmina Grodków. It is located in the Silesian Lowlands of the Oder basin, in the historic Upper Silesia region, about south of Brz ...
, Namysłów, Nysa, Karpacz
Karpacz ( German: ''Krummhübel'') is a spa town and ski resort in Jelenia Góra County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland, and one of the most important centres for mountain hiking and skiing, including ski jumping. Its populatio ...
, Strzelin
Strzelin (german: Strehlen, cz, Střelín) is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in south-western Poland. It is located on the Oława river, a tributary of the Oder, about south of the region's capital Wrocław. It is part of the Wrocław me ...
, Wiązów
Wiązów (german: Wansen) is a town in Strzelin County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of the administrative district ( gmina) called Gmina Wiązów. The town lies approximately east of Strzelin, and sout ...
, and others. On Sunday, there is a special route to Szklarska Poręba.
In 2013, a hospital helipad
A helipad is a landing area or platform for helicopters and powered lift aircraft.
While helicopters and powered lift aircraft are able to operate on a variety of relatively flat surfaces, a fabricated helipad provides a clearly marked hard ...
was opened by Mossora Street (''ul. Mossora'').
Sports
* KS Cukierki Odra Brzeg – women's basketball team, 8th place in Sharp Torell Basket Liga in 2003/2004 seasonNotable people
* C. de Bridia (born 1247), Minorite friar, wrote the '' Tartar Relation'' (de Bridia meaning "of Brzeg") *Johann Heermann
Johann Heermann (11 October 158517 February 1647) was a German poet and hymnodist. He is commemorated in the Calendar of Saints of the Lutheran Church on 26 October with Philipp Nicolai and Paul Gerhardt.
Life
Heermann was born in Raudten ...
(1585–1647), German poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral or w ...
and hymnodist
A hymnwriter (or hymn writer, hymnist, hymnodist, hymnographer, etc.) is someone who writes the text, music, or both of hymns. In the Judeo-Christian tradition, the composition of hymns dates back to before the time of David, who composed many of ...
* Georg Gebel the younger (1709–1753), Prussian general
* Leopold Wilhelm von Dobschütz (1763–1836), Prussian general
* Wilhelm Schuppe (1836–1913), German positivist philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
* Max Friedlaender (1852–1934), German musician
A musician is a person who composes, conducts, or performs music. According to the United States Employment Service, "musician" is a general term used to designate one who follows music as a profession. Musicians include songwriters who wr ...
and composer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and Def ...
* Oskar Moll (1875-1947), German painter
* Max Obal
Max Obal (born Max David Gotthelf Sroke; 4 September 1881 – 18 May 1949) was a German actor, singer, screenwriter, and film director. He co-directed the 1927 swashbuckler '' Rinaldo Rinaldini'' featuring Hans Albers.Grange p.251
Selected filmogr ...
(1881–1949), German actor, screenwriter
A screenplay writer (also called screenwriter, scriptwriter, scribe or scenarist) is a writer who practices the craft of screenwriting, writing screenplays on which mass media, such as films, television programs and video games, are based.
...
and film director
A film director controls a film's artistic and dramatic aspects and visualizes the screenplay (or script) while guiding the film crew and actors in the fulfilment of that vision. The director has a key role in choosing the cast members, pr ...
* Alfred Kurella (1895–1975), German SED functionary
* Johannes Brockt (1901–1980), German-Austrian musicologist
Musicology (from Greek μουσική ''mousikē'' 'music' and -λογια ''-logia'', 'domain of study') is the scholarly analysis and research-based study of music. Musicology departments traditionally belong to the humanities, although some m ...
and conductor
* Franciszek Gajowniczek (1901–1995), Polish Auschwitz
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 Nazi concentration camps, concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, occupied Poland (in a portion annexed int ...
survivor
* Otto Thorbeck (1912–1976), German lawyer
* Kurt Masur
Kurt Masur (18 July 1927 – 19 December 2015) was a German conductor. Called "one of the last old-style maestros", he directed many of the principal orchestras of his era. He had a long career as the Kapellmeister of the Leipzig Gewandhaus O ...
(1927–2015), German musician and conductor
* Mieczysław Domaradzki (1949–1998), Polish archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landsca ...
and thracologist
Thracology ( bg, Тракология, Trakologiya; ro, Tracologie) is the scientific study of Ancient Thrace and Thracian antiquities and is a regional and thematic branch of the larger disciplines of ancient history and archaeology. A practition ...
* Adrian Tekliński (born 1989), Polish road
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types o ...
and track cyclist
* Kamil Bednarek (born 1991), Polish reggae
Reggae () is a music genre that originated in Jamaica in the late 1960s. The term also denotes the modern popular music of Jamaica and its diaspora. A 1968 single by Toots and the Maytals, " Do the Reggay" was the first popular song to use ...
and dancehall
Dancehall is a genre of Jamaican popular music that originated in the late 1970s. Initially, dancehall was a more sparse version of reggae than the roots style, which had dominated much of the 1970s.Barrow, Steve & Dalton, Peter (2004) "The R ...
musician and composer.
* Bartosz Białek (born 2001), Polish football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
player
Twin towns – sister cities
Brzeg is twinned with: *Beroun
Beroun (; german: Beraun) is a town in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 20,000 inhabitants. It lies at the confluence of the Berounka and Litavka rivers. Beroun creates a conurbation with Králův Dvůr, former p ...
, Czech Republic
* Bourg-en-Bresse, France
* Goslar
Goslar (; Eastphalian: ''Goslär'') is a historic town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the administrative centre of the district of Goslar and located on the northwestern slopes of the Harz mountain range. The Old Town of Goslar and the Mi ...
, Germany
Gallery
References
Bibliography of Jewish Encyclopedia
* Brann, ''Geschichte der Juden in Schlesien''; * ''Jahrbuch des Deutsch-Israelitischen Gemeindebundes'' :::By : Gotthard Deutsch & A. M. Friedenberg
External links
Forum Brzeg
*
Dziennik Brzeski
Foto Brzeg
Komornik Brzeg
Jewish Community in Brzeg
on Virtual Shtetl
{{Authority control Cities in Silesia Cities and towns in Opole Voivodeship Brzeg County Holocaust locations in Poland Province of Upper Silesia