British People's Party (1939) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The British People's Party (BPP) was a British far-right political party founded in 1939 and led by ex- British Union of Fascists (BUF) member and Labour Party Member of Parliament John Beckett.
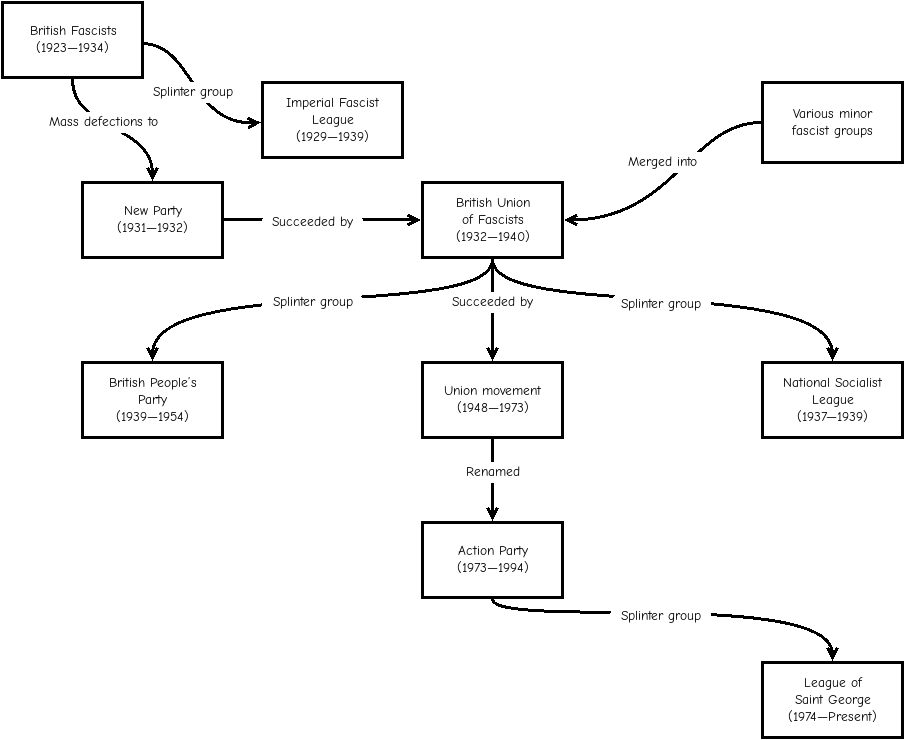 The BPP had its roots in the journal ''New Pioneer'', edited by John Beckett and effectively the mouthpiece of the
The BPP had its roots in the journal ''New Pioneer'', edited by John Beckett and effectively the mouthpiece of the
By-election results
The BPP officially disbanded in 1954.
Origins
 The BPP had its roots in the journal ''New Pioneer'', edited by John Beckett and effectively the mouthpiece of the
The BPP had its roots in the journal ''New Pioneer'', edited by John Beckett and effectively the mouthpiece of the British Council Against European Commitments
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, a co-ordinating body involving the National Socialist League
The National Socialist League (NSL) was a short-lived Nazi political movement in the United Kingdom immediately prior to the Second World War.
Formation
The NSL was formed in 1937 by William Joyce, John Beckett (politician), John Beckett and ...
(NSL), English Array and League of Loyalists. The main crux of this publication was opposition to war with Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, although it also endorsed fascism
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy an ...
and anti-Semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
. The proprietor of this journal was Viscount Lymington
A viscount ( , for male) or viscountess (, for female) is a title used in certain European countries for a noble of varying status.
In many countries a viscount, and its historical equivalents, was a non-hereditary, administrative or judicial ...
, a strong opponent of war with Germany.D. Boothroyd, ''The History of British Political Parties'', London: Politico's Publishing, 2001, p. 24 Others involved in its production included A. K. Chesterton
Arthur Kenneth Chesterton (1 May 1899 – 16 August 1973) was a British far-right journalist and political activist. From 1933 to 1938, he was a member of the British Union of Fascists (BUF). Disillusioned with Oswald Mosley, he left th ...
and the anthropologist George Henry Lane-Fox Pitt-Rivers
George Henry Lane-Fox Pitt-Rivers (22 May 1890 – 17 June 1966) was a British anthropologist and eugenicist who was one of the wealthiest men in England in the interwar period. He embraced anti-Bolshevism and anti-Semitism and became a supp ...
, whilst individual members, especially Lymington, were close to ruralist Rolf Gardiner
Henry Rolf Gardiner (5 November 1902 – 26 November 1971) was an English rural revivalist, helping to bring back folk dance styles including Morris dancing and sword dancing. He founded groups significant in the British history of organic far ...
.
Policy and structure
Beckett split from his NSL allyWilliam Joyce
William Brooke Joyce (24 April 1906 – 3 January 1946), nicknamed Lord Haw-Haw, was an American-born fascist and Nazi propaganda broadcaster during the Second World War. After moving from New York to Ireland and subsequently to England, ...
in 1939 after Joyce intimated to the patriotic
Patriotism is the feeling of love, devotion, and sense of attachment to one's country. This attachment can be a combination of many different feelings, language relating to one's own homeland, including ethnic, cultural, political or histor ...
Beckett that were war to break out between Britain and Germany he would fight for the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
. This, along with a feeling that Joyce's virulent anti-Semitism was hamstringing the NSL, led Beckett to link up with Lord Tavistock, the heir to the Duke of Bedford
Duke of Bedford (named after Bedford, England) is a title that has been created six times (for five distinct people) in the Peerage of England. The first and second creations came in 1414 and 1433 respectively, in favour of Henry IV's third so ...
, in founding the British People's Party in 1939. The new party supported an immediate end to the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, and was vehemently opposed to usury
Usury () is the practice of making unethical or immoral monetary loans that unfairly enrich the lender. The term may be used in a moral sense—condemning taking advantage of others' misfortunes—or in a legal sense, where an interest rate is c ...
, calling to mind some of the economic policies of Hilaire Belloc
Joseph Hilaire Pierre René Belloc (, ; 27 July 187016 July 1953) was a Franco-English writer and historian of the early twentieth century. Belloc was also an orator, poet, sailor, satirist, writer of letters, soldier, and political activist. H ...
. The group also brought in elements of Social Credit
Social credit is a distributive philosophy of political economy developed by C. H. Douglas. Douglas attributed economic downturns to discrepancies between the cost of goods and the compensation of the workers who made them. To combat what he ...
, as Lord Tavistock had been a sometime activist in the Social Credit Party.
The party was controlled by an executive committee consisting of Tavistock as Chairman, Beckett as secretary and ex-Labour Party candidate Ben Greene
Ben Greene (28 December 1901 – October 1978) was a British Labour Party politician and pacifist. He was interned during the Second World War because of his fascist associations and appealed to the Judicial Committee of the House of Lords aga ...
(a noted pacifist and member of the Peace Pledge Union
The Peace Pledge Union (PPU) is a non-governmental organisation that promotes pacifism, based in the United Kingdom. Its members are signatories to the following pledge: "War is a crime against humanity. I renounce war, and am therefore determin ...
) as treasurer, with Viscount Lymington
A viscount ( , for male) or viscountess (, for female) is a title used in certain European countries for a noble of varying status.
In many countries a viscount, and its historical equivalents, was a non-hereditary, administrative or judicial ...
and former left-wing journalist John Scanlon also added. Other early members of the party included Ronald Nall-Cain, 2nd Baron Brocket, Richard St. Barbe Baker, Sydney Arnold, 1st Baron Arnold
Sydney Arnold, 1st Baron Arnold (13 January 1878 – 3 August 1945) was a radical United Kingdom, British Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party politician who later joined the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party and served as a government minister.
A so ...
, Walter Montagu Douglas Scott, 8th Duke of Buccleuch and Walter Erskine, 12th Earl of Mar
Walter may refer to:
People
* Walter (name), both a surname and a given name
* Little Walter, American blues harmonica player Marion Walter Jacobs (1930–1968)
* Gunther (wrestler), Austrian professional wrestler and trainer Walter Hahn (born 1 ...
.
Activities
The party's activities were generally limited to meetings, the publication of a journal, ''The People's Post'' and the contesting of a singleby-election
A by-election, also known as a special election in the United States and the Philippines, a bye-election in Ireland, a bypoll in India, or a Zimni election (Urdu: ضمنی انتخاب, supplementary election) in Pakistan, is an election used to f ...
in Hythe, Kent in 1939. The campaign for the 1939 Hythe by-election, in which former Labour Party member St. John Philby was the BPP candidate, was fought on an anti-war platform. Despite gaining the public support of the likes of Sir Barry Domvile
Admiral Sir Barry Edward Domvile, (5 September 1878 – 13 August 1971) was a high-ranking Royal Navy officer who was interned during the Second World War for being a Nazi sympathiser.
Throughout the 1930s, he had expressed support for Germany ...
, leader of The Link, the campaign was not a success and Philby was unable to retain his deposit. Philby claimed that he agreed with none of the BPP's views apart from their opposition to war. He was more disposed towards the Labour Party but felt they were becoming too pro-war. In Philby's mind, as well as popularly, the BPP were seen as more of a single issue anti-war party.
During the war
After the outbreak of theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
the BPP was involved in British Union of Fascists-led initiatives to forge closer links between the disparate groups on the far right, although in private Oswald Mosley
Sir Oswald Ernald Mosley, 6th Baronet (16 November 1896 – 3 December 1980) was a British politician during the 1920s and 1930s who rose to fame when, having become disillusioned with mainstream politics, he turned to fascism. He was a member ...
had a low opinion of the BPP, dismissing Beckett as a "crook", Tavistock as "woolly headed" and Greene as "not very intelligent". Beckett's internment under Defence Regulation 18B
Defence Regulation 18B, often referred to as simply 18B, was one of the Defence Regulations used by the British Government during and before the Second World War. The complete name for the rule was Regulation 18B of the Defence (General) Regula ...
in 1940 saw the party go into hibernation, although it was not subject to any government ban. The patronage of Lord Tavistock, who succeeded to the dukedom of Bedford in 1940, ensured that the BPP was exempted from proscription. The group was briefly involved in a clandestine alliance with A.K. Chesterton's National Front After Victory in 1944, a group that also attracted the interest of J.F.C. Fuller
Major-General John Frederick Charles "Boney" Fuller (1 September 1878 – 10 February 1966) was a senior British Army officer, military historian, and strategist, known as an early theorist of modern armoured warfare, including categorising pr ...
, Henry Williamson
Henry William Williamson (1 December 1895 – 13 August 1977) was an English writer who wrote novels concerned with wildlife, English social history and ruralism. He was awarded the Hawthornden Prize for literature in 1928 for his book ''Tarka ...
, Jeffrey Hamm, William Morris, 1st Viscount Nuffield
William Richard Morris, 1st Viscount Nuffield, (10 October 1877 – 22 August 1963) was an English motor manufacturer and philanthropist. He was the founder of Morris Motors Limited and is remembered as the founder of the Nuffield Foundation, ...
and Lymington (who had succeeded his father as Earl of Portsmouth
Earl of Portsmouth is a title in the Peerage of Great Britain. It was created in 1743 for John Wallop, 1st Viscount Lymington, who had previously represented Hampshire in the House of Commons. He had already been created Baron Wallop, of Fa ...
in the meantime) amongst others. However, the movement was scuppered when it was infiltrated by the Board of Deputies of British Jews, who fed information to Robert Vansittart, 1st Baron Vansittart
Robert Gilbert Vansittart, 1st Baron Vansittart, (25 June 1881 – 14 February 1957), known as Sir Robert Vansittart between 1929 and 1941, was a senior British diplomat in the period before and during the Second World War. He was Principal Pri ...
, whose speech about the dangers of a revival of fascism led to a crackdown on such movements.
Final years
The BPP name was heard again in 1945 when the party organised an unsuccessful petition for clemency for Beckett's former ally William Joyce, who was executed fortreason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplo ...
. Before long the BPP returned to wider activity after the war when party policy focused on monetary reform and the promotion of agriculture. With the Union Movement
The Union Movement (UM) was a far-right political party founded in the United Kingdom by Oswald Mosley. Before the Second World War, Mosley's British Union of Fascists (BUF) had wanted to concentrate trade within the British Empire, but the Uni ...
not appearing until 1948 the BPP initially attracted some new members, including Colin Jordan, who was invited to join in 1946 and was associated with the group for a time before concentrating his efforts on the more hardline Arnold Leese. The party contested the Combined English Universities by-election on 18 March 1946 but received only 239 votes.The BPP officially disbanded in 1954.
References
Bibliography
* * * * * {{Authority control Political parties established in 1939 Political parties disestablished in 1954 Defunct political parties in the United Kingdom 1939 establishments in the United Kingdom 1954 disestablishments in the United Kingdom Far-right political parties in the United Kingdom