Bremenium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Bremenium is an ancient
Bremenium is an ancient
BREMENIVM Roman Fort and Marching CampsBremenium Dedication Slab
Roman fortifications in England Roman sites in Northumberland Rochester, Northumberland




 Bremenium is an ancient
Bremenium is an ancient Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
(castrum
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a po ...
) located at Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
, Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey.
It is bordered by land ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
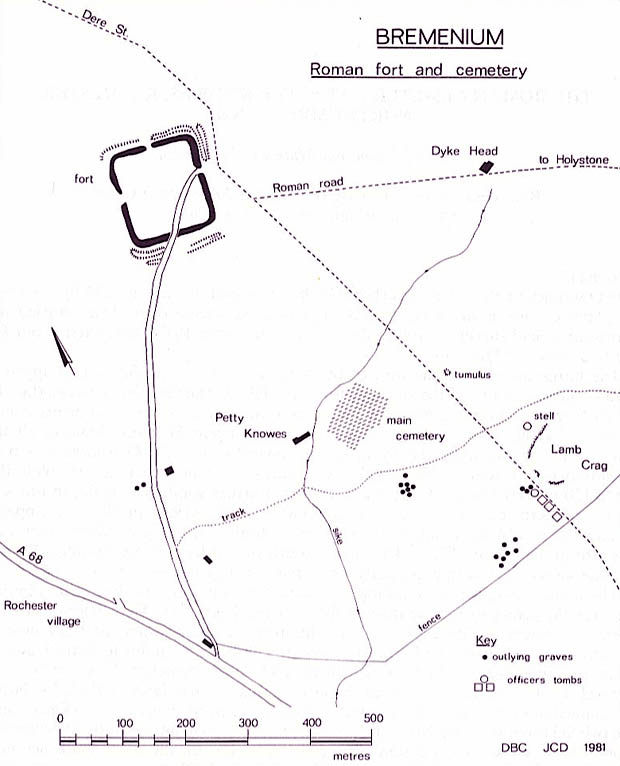
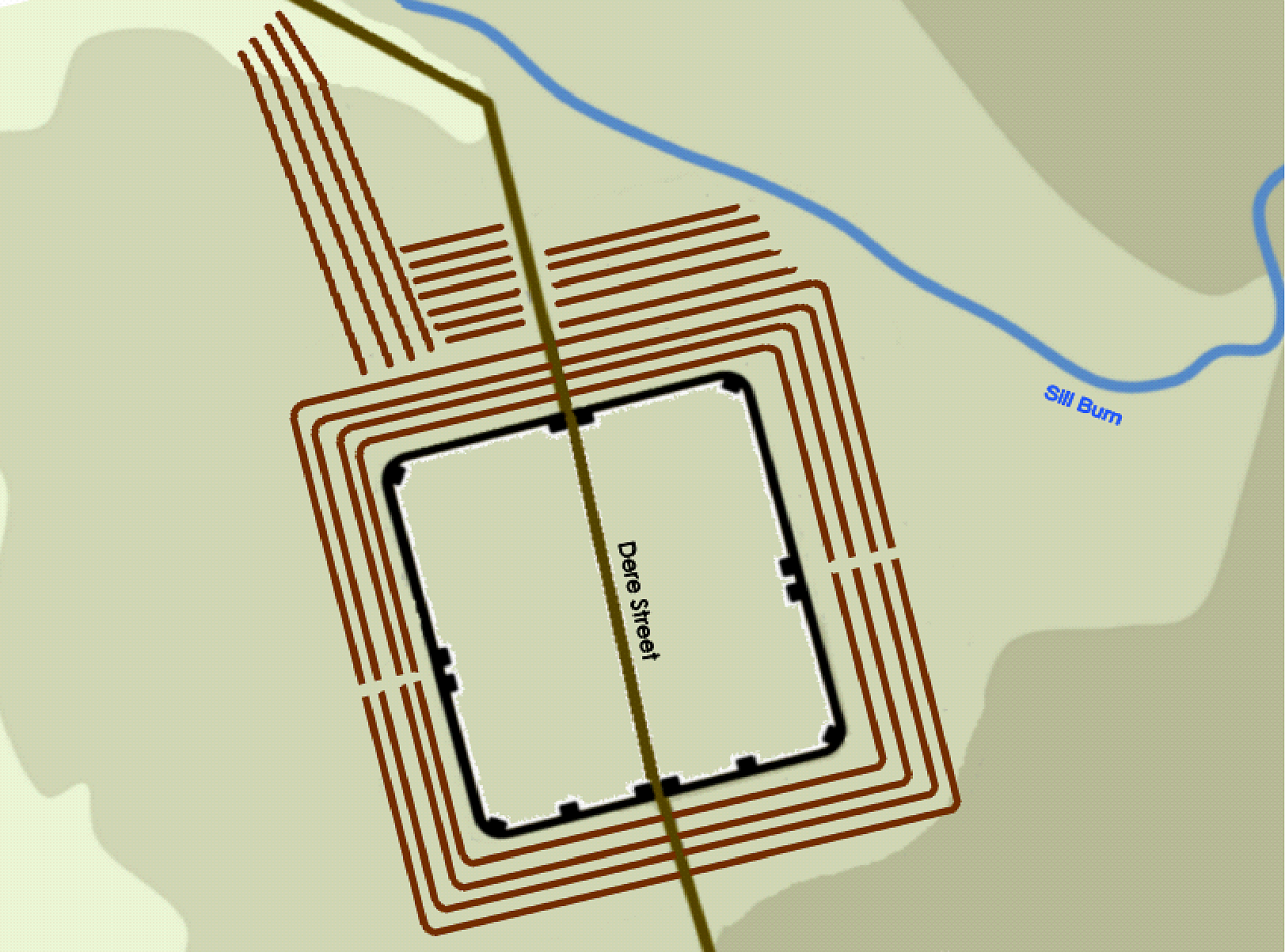
. The fort is one of the defensive structures built along Dere Street
Dere Street or Deere Street is a modern designation of a Roman road which ran north from Eboracum (York), crossing the Stanegate at Corbridge (Hadrian's Wall was crossed at the Portgate, just to the north) and continuing beyond into what is n ...
, a Roman road running from York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
to Corbridge
Corbridge is a village in Northumberland, England, west of Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle and east of Hexham. Villages nearby include Halton, Northumberland, Halton, Acomb, Northumberland, Acomb, Aydon and Sandhoe.
Etymology
Corbridge was kno ...
and onwards to Melrose. Significantly the fort is a long way north of Hadrian's Wall. It was one of the last forts north of Hadrian's wall to remain occupied until the 270s.
The fort's name, ''Bremenium'', is mentioned in the Ravenna Cosmography
The ''Ravenna Cosmography'' ( la, Ravennatis Anonymi Cosmographia, "The Cosmography of the Unknown Ravennese") is a list of place-names covering the world from India to Ireland, compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around 700 AD. Textu ...
, the Antonine Itinerary and Ptolemy's ''Geographia
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, com ...
''.
A separate Roman road ran eastwards from Bremenium to the Roman fort at Learchild, where it joined up with the Devil's Causeway
The Devil's Causeway is a Roman road in Northumberland, in North East England. It branches off Dere Street north of Corbridge and can be traced through Northumberland for about north to Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Description
The Devil's Causeway is ...
Roman road to Berwick upon Tweed
Berwick-upon-Tweed (), sometimes known as Berwick-on-Tweed or simply Berwick, is a town and civil parish in Northumberland, England, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, and the northernmost town in England. The 2011 United Kingdom census recor ...
.
Location
The fort is situated in the village ofRochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
, north-west of Otterburn on the A68 road between Corbridge and Jedburgh.
It was one of the forts along Dere Street
Dere Street or Deere Street is a modern designation of a Roman road which ran north from Eboracum (York), crossing the Stanegate at Corbridge (Hadrian's Wall was crossed at the Portgate, just to the north) and continuing beyond into what is n ...
, and positioned to defend this main supply and transit route to the north.
Historical background
In 79 AD Agricola moved against the Brigantes of northern England and theSelgovae
The Selgovae (Common Brittonic: *''Selgowī'') were a Celtic tribe of the late 2nd century AD who lived in what is now the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright and Dumfriesshire, on the southern coast of Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ' ...
along the southern coast of Scotland, using overwhelming military power to establish Roman control., ''Life of Agricola'', Ch. 20–21 He built a network of military roads and forts to secure the Roman occupation and Bremenium was built around 80 AD. Existing forts were strengthened and new ones planted in northeastern Scotland along the Highland Line, consolidating control of the glens that provided access to and from the Scottish Highlands. The line of military communication and supply across southeastern Scotland and northeastern England was Dere Street (on which Bremenium was located) which was well-fortified.
After Agricola was recalled from Britain in 84 AD the Romans retired to a more defensible line along the Forth–Clyde isthmus. In the 120s Hadrian established the frontier further south by building his wall, and Bremeniun remained outside it as an "outpost" fort.
The emperor Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius ( Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatori ...
advanced again in the 140s and built the Antonine Wall, when Bremenium once again became
a supply and logistical waypoint on Dere Street until about 164 when Hadrian's wall became the frontier again leaving Bremenium in hostile territory.
Description
The fort is north ofRisingham
Habitancum was an ancient Roman fort (castrum) located at Risingham, Northumberland, England. The fort was one of the defensive structures built along Dere Street, a Roman road running from York to Corbridge and onwards to Melrose in what is now ...
(Roman name ''Habitancum
Habitancum was an ancient Roman fort (castrum) located at Risingham, Northumberland, England. The fort was one of the defensive structures built along Dere Street, a Roman road running from York to Corbridge and onwards to Melrose in what is now ...
''), the next fort on Dere Street and less than a day's marching distance away. The name ''Bremenium'' means 'The Place of the Roaring Stream'. The site is in a strong position, occupying the end of a ridge with the ground falling away steeply to the north and west, and giving a clear view over the Rede Valley and beyond.
Defensive ditches can still be seen to the north and east, outside which Dere Street passes. Early temporary marching camps at Redesdale are visible across the Sills Burn from the fort.
The fort is oblong in shape, and measures north to south and east to west, giving and area of just over . There was a gate in each of the four walls, which were of stone backed by a bank of earth. It appears that an early 1st-century fort with a turf rampart occupied the site, and that it was replaced by a stone fort during the time that Quintus Lollius Urbicus
Quintus Lollius Urbicus was a Numidian Berber governor of Roman Britain between the years 139 and 142, during the reign of the Emperor Antoninus Pius. He is named in the ''Historia Augusta'', although it is not entirely historical, and his name ...
was Governor of Britain. He stayed there on his way north to build the Antonine Wall in 142 AD. The fort remained occupied even after the abandonment of the Antonine Wall in the early 160s.
The fort is unusual, in that it had 3rd-century artillery defences. The walls were thicker than most Roman forts and had stone platforms projecting back from the wall, on which were placed catapult-like machines for hurling missiles. These machines, a smaller version of the ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an ancient missile weapon that launched either bolts or stones at a distant ...
, were known as ' onagri', and derived their power from the torsion of a hair rope. From the north walls, these machines could fire missiles at anyone advancing down Dere Street from the north.
Garrison
In the 2nd century the garrison was the First Cohort ofLingones
The Lingones (Gaulish: 'the jumpers') were a Gallic tribe of the Iron Age and Roman periods. They dwelled in the region surrounding the present-day city of Langres, between the provinces of Gallia Lugdunensis and Gallia Belgica.
Name
Attes ...
(part-mounted and 500 strong), and then the First Cohort of Dalmatians (infantry). In the 3rd century the garrison was the First Cohort of Vardulians (part-mounted and one thousand strong).
Current site
The fort is now part of the village green of Rochester, but there are still remains to see. The west wall is the best preserved and consists of a nine-feet-high bank with stone facing. The west gate is complete to the springing of the arch. However, much of the stonework has been plundered over the years for local buildings.Excavations
Excavations were carried out in 1852 and 1855, but were poorly recorded. A small dig was also carried out in 1935. The excavations established that the interior of the fort was crowded with buildings, many withhypocaust
A hypocaust ( la, hypocaustum) is a system of central heating in a building that produces and circulates hot air below the floor of a room, and may also warm the walls with a series of pipes through which the hot air passes. This air can warm th ...
s.
See also
*Chew Green
Chew Green is the site of the ancient Roman encampment, commonly but erroneously called Ad Fines (Latin: The Limits) on the 1885-1900 edition of the Ordnance Survey map, in Northumberland, England, north of Rochester and west of Alwinton. The ...
* Featherwood Roman Camps
Featherwood Roman Camps are neighbouring archaeological sites in Northumberland, England, north of Featherwood and about east of Byrness. The remains of two Roman camps, near Dere Street, are scheduled monuments.
Description
The two camps, abo ...
References
* * J. Collingwood Bruce, Roman Wall (1863), Harold Hill & Son, * Frank Graham, The Roman Wall, Comprehensive History and Guide (1979), Frank Graham, * http://www.roman-britain.co.uk/places/bremenium/External links
{{Commons category, Bremenium (High Rochester)BREMENIVM Roman Fort and Marching Camps
Roman fortifications in England Roman sites in Northumberland Rochester, Northumberland