Greek alphabet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the
Greek Unicode Issues: Punctuation
". 2005. Accessed 7 Oct 2014.
 During the
During the  Greek initially took over all of the 22 letters of Phoenician. Five were reassigned to denote vowel sounds: the glide consonants ('' yodh'') and ('' waw'') were used for (خ™, '' iota'') and (خ¥, '' upsilon'') respectively; the glottal stop consonant ('' aleph'') was used for (خ‘, '' alpha''); the pharyngeal ('' ت؟ayin'') was turned into (خں, '' omicron''); and the letter for ('' he'') was turned into (خ•, '' epsilon''). A doublet of waw was also borrowed as a consonant for (دœ, digamma). In addition, the Phoenician letter for the emphatic glottal (''
Three of the original Phoenician letters dropped out of use before the alphabet took its classical shape: the letter د؛ ('' san''), which had been in competition with خ£ ('' sigma'') denoting the same phoneme /s/; the letter دک (''
Greek initially took over all of the 22 letters of Phoenician. Five were reassigned to denote vowel sounds: the glide consonants ('' yodh'') and ('' waw'') were used for (خ™, '' iota'') and (خ¥, '' upsilon'') respectively; the glottal stop consonant ('' aleph'') was used for (خ‘, '' alpha''); the pharyngeal ('' ت؟ayin'') was turned into (خں, '' omicron''); and the letter for ('' he'') was turned into (خ•, '' epsilon''). A doublet of waw was also borrowed as a consonant for (دœ, digamma). In addition, the Phoenician letter for the emphatic glottal (''
Three of the original Phoenician letters dropped out of use before the alphabet took its classical shape: the letter د؛ ('' san''), which had been in competition with خ£ ('' sigma'') denoting the same phoneme /s/; the letter دک (''
 There were initially numerous local (epichoric) variants of the Greek alphabet, which differed in the use and non-use of the additional vowel and consonant symbols and several other features. Epichoric alphabets are commonly divided into four major types according to their different treatments of additional consonant letters for the aspirated consonants (/pت°, kت°/) and consonant clusters (/ks, ps/) of Greek. These four types are often conventionally labelled as "green", "red", "light blue" and "dark blue" types, based on a colour-coded map in a seminal 19th-century work on the topic, ''Studien zur Geschichte des griechischen Alphabets'' by
There were initially numerous local (epichoric) variants of the Greek alphabet, which differed in the use and non-use of the additional vowel and consonant symbols and several other features. Epichoric alphabets are commonly divided into four major types according to their different treatments of additional consonant letters for the aspirated consonants (/pت°, kت°/) and consonant clusters (/ks, ps/) of Greek. These four types are often conventionally labelled as "green", "red", "light blue" and "dark blue" types, based on a colour-coded map in a seminal 19th-century work on the topic, ''Studien zur Geschichte des griechischen Alphabets'' by * Upsilon is also derived from waw ( ).
The classical twenty-four-letter alphabet that is now used to represent the Greek language was originally the local alphabet of Ionia. By the late fifth century BC, it was commonly used by many Athenians. In 403 BC, at the suggestion of the archon
).
The classical twenty-four-letter alphabet that is now used to represent the Greek language was originally the local alphabet of Ionia. By the late fifth century BC, it was commonly used by many Athenians. In 403 BC, at the suggestion of the archon

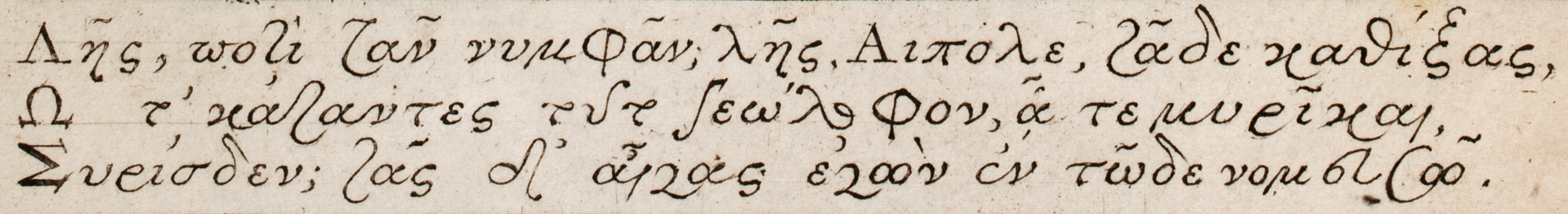 Like Latin and other alphabetic scripts, Greek originally had only a single form of each letter, without a distinction between uppercase and lowercase. This distinction is an innovation of the modern era, drawing on different lines of development of the letter shapes in earlier handwriting.
The oldest forms of the letters in antiquity are majuscule forms. Besides the upright, straight inscriptional forms (capitals) found in stone carvings or incised pottery, more fluent writing styles adapted for handwriting on soft materials were also developed during antiquity. Such handwriting has been preserved especially from papyrus manuscripts in
Like Latin and other alphabetic scripts, Greek originally had only a single form of each letter, without a distinction between uppercase and lowercase. This distinction is an innovation of the modern era, drawing on different lines of development of the letter shapes in earlier handwriting.
The oldest forms of the letters in antiquity are majuscule forms. Besides the upright, straight inscriptional forms (capitals) found in stone carvings or incised pottery, more fluent writing styles adapted for handwriting on soft materials were also developed during antiquity. Such handwriting has been preserved especially from papyrus manuscripts in

 The Greek alphabet was the model for various others:
* The Etruscan alphabet;
* The Latin alphabet, together with various other ancient scripts in Italy, adopted from an archaic form of the Greek alphabet brought to Italy by Greek colonists in the late 8th century BC, via Etruscan;
* The Gothic alphabet, devised in the 4th century AD to write the Gothic language, based on a combination of Greek and Latin uncial models;
* The
The Greek alphabet was the model for various others:
* The Etruscan alphabet;
* The Latin alphabet, together with various other ancient scripts in Italy, adopted from an archaic form of the Greek alphabet brought to Italy by Greek colonists in the late 8th century BC, via Etruscan;
* The Gothic alphabet, devised in the 4th century AD to write the Gothic language, based on a combination of Greek and Latin uncial models;
* The
 * Turkish spoken by Orthodox Christians ('' Karamanlides'') was often written in Greek script, and called '' Karamanlidika''.
*
* Turkish spoken by Orthodox Christians ('' Karamanlides'') was often written in Greek script, and called '' Karamanlidika''.
*
On the other hand, the following phonetic letters have Unicode representations separate from their Greek alphabetic use, either because their conventional typographic shape is too different from the original, or because they also have secondary uses as regular alphabetic characters in some Latin-based alphabets, including separate Latin uppercase letters distinct from the Greek ones. The symbol in Americanist phonetic notation for the voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is the Greek letter lambda , but in the IPA. The IPA symbol for the palatal lateral approximant is , which looks similar to lambda, but is actually an inverted lowercase ''y''.
Greek and Coptic
character list in Unicode
Unicode collation charts
€”including Greek and Coptic letters, sorted by shape
Examples of Greek handwriting
*
(Alan Wood)
a browser-based tool * Collection of free fonts
{{Authority control
Greek language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, خ•خ»خ»خ·خ½خ¹خ؛خ¬, Ellinikأ،, ; grc, ل¼™خ»خ»خ·خ½خ¹خ؛خ®, Hellؤ“nikل¸—) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy ( Calabria and Salento), southe ...
since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet is an alphabet (more specifically, an abjad) known in modern times from the Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean region. The name comes from the Phoenician civilization.
The Phoenician a ...
, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (len ...
as well as consonants
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced wit ...
. In Archaic and early Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BCE, the Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard and it is this version that is still used for Greek writing today.
The uppercase and lowercase forms of the 24 letters are:
: , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , /د‚, , , , , , .
The Greek alphabet is the ancestor of the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
and Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
s. Like Latin and Cyrillic, Greek originally had only a single form of each letter; it developed the letter case
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (or more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (or more formally ''minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing ...
distinction between uppercase and lowercase in parallel with Latin during the modern era. Sound values and conventional transcriptions for some of the letters differ between Ancient
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
and Modern Greek usage because the pronunciation of Greek has changed significantly between the 5th century BCE and today. Modern and Ancient Greek also use different diacritics
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacriti ...
, with modern Greek keeping only the stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
accent ( acute) and the diaeresis.
Apart from its use in writing the Greek language, in both its ancient and its modern forms, the Greek alphabet today also serves as a source of technical symbols and labels in many domains of mathematics, science, and other fields.
Letters
Sound values
In both Ancient and Modern Greek, the letters of the Greek alphabet have fairly stable and consistent symbol-to-sound mappings, making pronunciation of words largely predictable. Ancient Greek spelling was generally near-phonemic
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-west ...
. For a number of letters, sound values differ considerably between Ancient and Modern Greek, because their pronunciation has followed a set of systematic phonological shifts that affected the language in its post-classical stages.
;Examples
;Notes
Among consonant letters, all letters that denoted voiced plosive consonants () and aspirated plosives () in Ancient Greek stand for corresponding fricative sounds in Modern Greek. The correspondences are as follows:
Among the vowel symbols, Modern Greek sound values reflect the radical simplification of the vowel system of post-classical Greek, merging multiple formerly distinct vowel phonemes into a much smaller number. This leads to several groups of vowel letters denoting identical sounds today. Modern Greek orthography remains true to the historical spellings in most of these cases. As a consequence, the spellings of words in Modern Greek are often not predictable from the pronunciation alone, while the reverse mapping, from spelling to pronunciation, is usually regular and predictable.
The following vowel letters and digraphs are involved in the mergers:
Modern Greek speakers typically use the same, modern symbol–sound mappings in reading Greek of all historical stages. In other countries, students of Ancient Greek may use a variety of conventional approximations of the historical sound system in pronouncing Ancient Greek.
Digraphs and letter combinations
Several letter combinations have special conventional sound values different from those of their single components. Among them are several digraphs of vowel letters that formerly represented diphthongs but are now monophthongized. In addition to the four mentioned above (), there is also , and , pronounced . The Ancient Greek diphthongs , and are pronounced , and in Modern Greek. In some environments, they are devoiced to , and respectively. The Modern Greek consonant combinations and stand for and (or and ) respectively; stands for and stands for . In addition, both in Ancient and Modern Greek, the letter , before another velar consonant, stands for thevelar nasal
The voiced velar nasal, also known as agma, from the Greek word for 'fragment', is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is the sound of ''ng'' in English ''sing'' as well as ''n'' before velar consonants as in ''Englis ...
; thus and are pronounced like English . In analogy to and , is also used to stand for . There are also the combinations and .
Diacritics
In thepolytonic orthography
Greek orthography has used a variety of diacritics starting in the Hellenistic period. The more complex polytonic orthography ( el, د€خ؟خ»د…د„خ؟خ½خ¹خ؛دŒ دƒدچدƒد„خ·خ¼خ± خ³دپخ±د†خ®د‚, translit=polytonikأ³ sأ½stؤ«ma grafؤ«جپs), which includes fi ...
traditionally used for ancient Greek, the stressed vowel of each word carries one of three accent marks: either the acute accent (), the grave accent (), or the circumflex accent
The circumflex () is a diacritic in the Latin and Greek scripts that is also used in the written forms of many languages and in various romanization and transcription schemes. It received its English name from la, circumflexus "bent around"a ...
( or ). These signs were originally designed to mark different forms of the phonological pitch accent in Ancient Greek. By the time their use became conventional and obligatory in Greek writing, in late antiquity, pitch accent was evolving into a single stress accent, and thus the three signs have not corresponded to a phonological distinction in actual speech ever since. In addition to the accent marks, every word-initial vowel must carry either of two so-called "breathing marks": the rough breathing
In the polytonic orthography of Ancient Greek, the rough breathing ( grc, خ´خ±دƒل½؛ د€خ½خµل؟¦خ¼خ±, dasل»³ pneأ»ma or ''daseأ®a''; la, spؤ«ritus asper) character is a diacritical mark used to indicate the presence of an sound before a vowel, ...
(), marking an sound at the beginning of a word, or the smooth breathing (), marking its absence. The letter rho (دپ), although not a vowel, also carries rough breathing in a word-initial position. If a rho was geminated within a word, the first always had the smooth breathing and the second the rough breathing (ل؟¤ل؟¥) leading to the transliteration rrh.
The vowel letters carry an additional diacritic in certain words, the so-called iota subscript
The iota subscript is a diacritic mark in the Greek alphabet shaped like a small vertical stroke or miniature iota placed below the letter. It can occur with the vowel letters eta , omega , and alpha . It represents the former presence of an o ...
, which has the shape of a small vertical stroke or a miniature below the letter. This iota represents the former offglide of what were originally long diphthongs, (i.e. ), which became monophthongized during antiquity.
Another diacritic used in Greek is the diaeresis (), indicating a hiatus.
This system of diacritics was first developed by the scholar Aristophanes of Byzantium ( 257 –  185/180 BC), who worked at the Musaeum
The Musaeum or Mouseion of Alexandria ( grc, خœخ؟د…دƒخµل؟–خ؟خ½ د„ل؟†د‚ ل¼ˆخ»خµخ¾خ±خ½خ´دپخµخ¯خ±د‚; ), which arguably included the Great Library of Alexandria, was an institution said to have been founded by Ptolemy I Soter and his son Ptolemy II Ph ...
in Alexandria during the third century BC. Aristophanes of Byzantium also was the first to divide poems into lines, rather than writing them like prose, and also introduced a series of signs for textual criticism. In 1982, a new, simplified orthography, known as "monotonic", was adopted for official use in Modern Greek by the Greek state. It uses only a single accent mark, the acute (also known in this context as ''tonos'', i.e. simply "accent"), marking the stressed syllable of polysyllabic words, and occasionally the diaeresis to distinguish diphthongal from digraph readings in pairs of vowel letters, making this monotonic system very similar to the accent mark system used in Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
. The polytonic system is still conventionally used for writing Ancient Greek, while in some book printing and generally in the usage of conservative writers it can still also be found in use for Modern Greek.
Although it is not a diacritic, the comma has a similar function as a silent letter
In an alphabetic writing system, a silent letter is a letter that, in a particular word, does not correspond to any sound in the word's pronunciation. In linguistics, a silent letter is often symbolised with a null sign . Null is an unprono ...
in a handful of Greek words, principally distinguishing (''أ³,ti'', "whatever") from (''أ³ti'', "that").Nicolas, Nick.Greek Unicode Issues: Punctuation
". 2005. Accessed 7 Oct 2014.
Romanization
There are many different methods of rendering Greek text or Greek names in the Latin script. The form in which classical Greek names are conventionally rendered in English goes back to the way Greek loanwords were incorporated into Latin in antiquity. In this system, is replaced with , the diphthongs and are rendered as and (or ) respectively; and and are simplified to and respectively. Smooth breathing marks are usually ignored and rough breathing marks are usually rendered as the letter . In modern scholarly transliteration of Ancient Greek, will usually be rendered as , and the vowel combinations as respectively. The letters and are generally rendered as and ; as either or ; and word-initial as . Transcription conventions for Modern Greek differ widely, depending on their purpose, on how close they stay to the conventional letter correspondences of Ancient Greek-based transcription systems, and to what degree they attempt either an exact letter-by-letter transliteration or rather a phonetically-based transcription. Standardized formal transcription systems have been defined by theInternational Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Art ...
(as ISO 843
ISO 843 is a system for the transliteration and/or transcription of Greek characters into Latin characters.
), by the United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names
The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names (UNGEGN) is one of the nine expert groups of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) and deals with the national and international standardization of geographical names. Ev ...
, by the Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The library ...
, and others.
History
Origins
Mycenaean period
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland ...
, from around the sixteenth century to the twelfth century BC, Linear B was used to write the earliest attested form of the Greek language, known as Mycenaean Greek
Mycenaean Greek is the most ancient attested form of the Greek language, on the Greek mainland and Crete in Mycenaean Greece (16th to 12th centuries BC), before the hypothesised Dorian invasion, often cited as the '' terminus ad quem'' for th ...
. This writing system, unrelated to the Greek alphabet, last appeared in the thirteenth century BC. In the late ninth century BC or early eighth century BC, the Greek alphabet emerged. The period between the use of the two writing systems, during which no Greek texts are attested, is known as the Greek Dark Ages. The Greeks adopted the alphabet from the earlier Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet is an alphabet (more specifically, an abjad) known in modern times from the Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean region. The name comes from the Phoenician civilization.
The Phoenician a ...
, one of the closely related scripts used for the West Semitic languages, calling it خ¦خ؟خ¹خ½خ¹خ؛خ®خ¹خ± خ³دپخ¬خ¼خ¼خ±د„خ± 'Phoenician letters'. However, the Phoenician alphabet is limited to consonants. When it was adopted for writing Greek, certain consonants were adapted to express vowels. The use of both vowels and consonants makes Greek the first alphabet in the narrow sense, as distinguished from the abjads used in Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigra ...
, which have letters only for consonants.
 Greek initially took over all of the 22 letters of Phoenician. Five were reassigned to denote vowel sounds: the glide consonants ('' yodh'') and ('' waw'') were used for (خ™, '' iota'') and (خ¥, '' upsilon'') respectively; the glottal stop consonant ('' aleph'') was used for (خ‘, '' alpha''); the pharyngeal ('' ت؟ayin'') was turned into (خں, '' omicron''); and the letter for ('' he'') was turned into (خ•, '' epsilon''). A doublet of waw was also borrowed as a consonant for (دœ, digamma). In addition, the Phoenician letter for the emphatic glottal (''
Greek initially took over all of the 22 letters of Phoenician. Five were reassigned to denote vowel sounds: the glide consonants ('' yodh'') and ('' waw'') were used for (خ™, '' iota'') and (خ¥, '' upsilon'') respectively; the glottal stop consonant ('' aleph'') was used for (خ‘, '' alpha''); the pharyngeal ('' ت؟ayin'') was turned into (خں, '' omicron''); and the letter for ('' he'') was turned into (خ•, '' epsilon''). A doublet of waw was also borrowed as a consonant for (دœ, digamma). In addition, the Phoenician letter for the emphatic glottal (''heth
Heth, sometimes written Chet, but more accurately ل¸¤et, is the eighth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician ل¸¤ؤ“t ًگ¤‡ , Hebrew ل¸¤ؤ“th , Aramaic ل¸¤ؤ“th , Syriac ل¸¤ؤ“ل¹¯ ـڑ, Arabic ل¸¤ؤپ' , and Maltese ؤ¦, ؤ§.
Heth origin ...
'') was borrowed in two different functions by different dialects of Greek: as a letter for /h/ (خ—, heta) by those dialects that had such a sound, and as an additional vowel letter for the long (خ—, eta) by those dialects that lacked the consonant. Eventually, a seventh vowel letter for the long (خ©, omega) was introduced.
Greek also introduced three new consonant letters for its aspirated plosive sounds and consonant clusters: خ¦ (''phi
Phi (; uppercase خ¦, lowercase د† or د•; grc, د•خµل؟– ''pheأ®'' ; Modern Greek: ''fi'' ) is the 21st letter of the Greek alphabet.
In Archaic and Classical Greek (c. 9th century BC to 4th century BC), it represented an aspirated voicele ...
'') for , خ§ ('' chi'') for and خ¨ ('' psi'') for . In western Greek variants, خ§ was instead used for and خ¨ for . The origin of these letters is a matter of some debate.
qoppa
Koppa or qoppa (; as a modern numeral sign: ) is a letter that was used in early forms of the Greek alphabet, derived from Phoenician qoph (). It was originally used to denote the sound, but dropped out of use as an alphabetic character in fav ...
''), which was redundant with خڑ ('' kappa'') for /k/, and دœ ('' digamma''), whose sound value /w/ dropped out of the spoken language before or during the classical period.
Greek was originally written predominantly from right to left, just like Phoenician, but scribes could freely alternate between directions. For a time, a writing style with alternating right-to-left and left-to-right lines (called '' boustrophedon'', literally "ox-turning", after the manner of an ox ploughing a field) was common, until in the classical period the left-to-right writing direction became the norm. Individual letter shapes were mirrored depending on the writing direction of the current line.
Archaic variants
Adolf Kirchhoff
Johann Wilhelm Adolf Kirchhoff (6 January 1826 – 26 February 1908) was a German classical scholar and epigraphist.
Biography
The son of historical painter Johann Jakob Kirchhoff, he was born in Berlin, and educated there. He then taught in va ...
(1867).
The "green" (or southern) type is the most archaic and closest to the Phoenician. The "red" (or western) type is the one that was later transmitted to the West and became the ancestor of the Latin alphabet, and bears some crucial features characteristic of that later development. The "blue" (or eastern) type is the one from which the later standard Greek alphabet emerged. Athens
Athens ( ; el, خ‘خ¸خ®خ½خ±, Athأna ; grc, ل¼ˆخ¸ل؟†خ½خ±خ¹, Athأھnai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
used a local form of the "light blue" alphabet type until the end of the fifth century BC, which lacked the letters خ and خ¨ as well as the vowel symbols خ— and خ©. In the Old Attic alphabet, stood for and for . was used for all three sounds (correspondinة، to classical respectively), and was used for all of (corresponding to classical respectively). The letter (heta) was used for the consonant . Some variant local letter forms were also characteristic of Athenian writing, some of which were shared with the neighboring (but otherwise "red") alphabet of Euboia
Evia (, ; el, خ•دچخ²خ؟خ¹خ± ; grc, خ•ل½”خ²خ؟خ¹خ± ) or Euboia (, ) is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest p ...
: a form of that resembled a Latin ''L'' () and a form of that resembled a Latin ''S'' ().
Eucleides
Eucleides ( grc-gre, خ•ل½گخ؛خ»خµخ¯خ´خ·د‚) was archon of Athens towards the end of the fifth century BC. He contributed towards the re-establishment of democracy during his years in office (403–402 BC). He is also believed to have contributed to ...
, the Athenian Assembly formally abandoned the Old Attic alphabet and adopted the Ionian alphabet as part of the democratic reforms after the overthrow of the Thirty Tyrants. Because of Eucleides's role in suggesting the idea to adopt the Ionian alphabet, the standard twenty-four-letter Greek alphabet is sometimes known as the "Eucleidean alphabet". Roughly thirty years later, the Eucleidean alphabet was adopted in Boeotia and it may have been adopted a few years previously in Macedonia. By the end of the fourth century BC, it had displaced local alphabets across the Greek-speaking world to become the standard form of the Greek alphabet.
Letter names
When the Greeks adopted the Phoenician alphabet, they took over not only the letter shapes and sound values but also the names by which the sequence of the alphabet could be recited and memorized. In Phoenician, each letter name was a word that began with the sound represented by that letter; thus '' ت¾aleph'', the word for "ox", was used as the name for the glottal stop , '' bet'', or "house", for the sound, and so on. When the letters were adopted by the Greeks, most of the Phoenician names were maintained or modified slightly to fit Greek phonology; thus, ''ت¾aleph, bet, gimel'' became ''alpha, beta, gamma''. The Greek names of the following letters are more or less straightforward continuations of their Phoenician antecedents. Between Ancient and Modern Greek, they have remained largely unchanged, except that their pronunciation has followed regular sound changes along with other words (for instance, in the name of ''beta'', ancient /b/ regularly changed to modern /v/, and ancient /ة›ثگ/ to modern /i/, resulting in the modern pronunciation ''vita''). The name of lambda is attested in early sources as besides ; in Modern Greek the spelling is often , reflecting pronunciation. Similarly, iota is sometimes spelled in Modern Greek ( is conventionally transcribed word-initially and intervocalically before back vowels and ). In the tables below, the Greek names of all letters are given in their traditional polytonic spelling; in modern practice, like with all other words, they are usually spelled in the simplified monotonic system. In the cases of the three historical sibilant letters below, the correspondence between Phoenician and Ancient Greek is less clear, with apparent mismatches both in letter names and sound values. The early history of these letters (and the fourth sibilant letter, obsolete san) has been a matter of some debate. Here too, the changes in the pronunciation of the letter names between Ancient and Modern Greek are regular. In the following group of consonant letters, the older forms of the names in Ancient Greek were spelled with , indicating an original pronunciation with ''-ؤ“''. In Modern Greek these names are spelled with . The following group of vowel letters were originally called simply by their sound values as long vowels: ؤ“, إچ, إ«, and . Their modern names contain adjectival qualifiers that were added during the Byzantine period, to distinguish between letters that had become confusable. Thus, the letters and , pronounced identically by this time, were called ''o mikron'' ("small o") and ''o mega'' ("big o") respectively. The letter was called ''e psilon'' ("plain e") to distinguish it from the identically pronounced digraph , while, similarly, , which at this time was pronounced , was called ''y psilon'' ("plain y") to distinguish it from the identically pronounced digraph . Some dialects of the Aegean and Cypriot have retained long consonants and pronounce and ; also, has come to be pronounced in Cypriot.Letter shapes

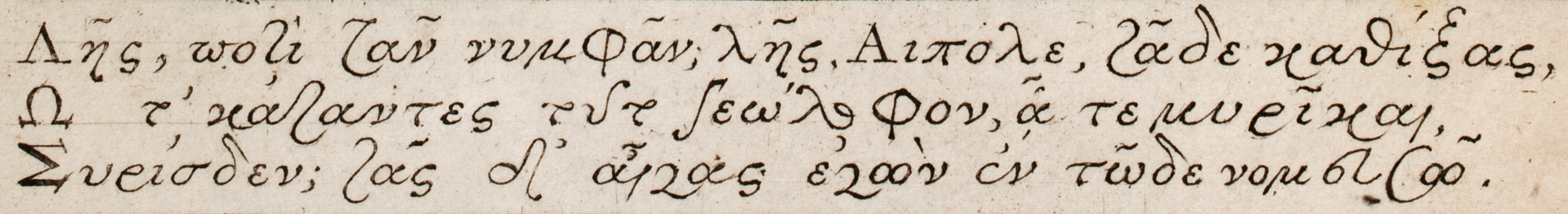 Like Latin and other alphabetic scripts, Greek originally had only a single form of each letter, without a distinction between uppercase and lowercase. This distinction is an innovation of the modern era, drawing on different lines of development of the letter shapes in earlier handwriting.
The oldest forms of the letters in antiquity are majuscule forms. Besides the upright, straight inscriptional forms (capitals) found in stone carvings or incised pottery, more fluent writing styles adapted for handwriting on soft materials were also developed during antiquity. Such handwriting has been preserved especially from papyrus manuscripts in
Like Latin and other alphabetic scripts, Greek originally had only a single form of each letter, without a distinction between uppercase and lowercase. This distinction is an innovation of the modern era, drawing on different lines of development of the letter shapes in earlier handwriting.
The oldest forms of the letters in antiquity are majuscule forms. Besides the upright, straight inscriptional forms (capitals) found in stone carvings or incised pottery, more fluent writing styles adapted for handwriting on soft materials were also developed during antiquity. Such handwriting has been preserved especially from papyrus manuscripts in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, ظ…طµط± , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
since the Hellenistic period. Ancient handwriting developed two distinct styles: uncial
Uncial is a majuscule Glaister, Geoffrey Ashall. (1996) ''Encyclopedia of the Book''. 2nd edn. New Castle, DE, and London: Oak Knoll Press & The British Library, p. 494. script (written entirely in capital letters) commonly used from the 4th to ...
writing, with carefully drawn, rounded block letters of about equal size, used as a book hand
A book hand was any of several stylized handwriting scripts used during ancient and medieval times. It was intended for legibility and often used in transcribing official documents (prior to the development of printing and similar technologies). ...
for carefully produced literary and religious manuscripts, and cursive writing, used for everyday purposes. The cursive forms approached the style of lowercase letter forms, with ascenders and descenders, as well as many connecting lines and ligatures between letters.
In the ninth and tenth century, uncial book hands were replaced with a new, more compact writing style, with letter forms partly adapted from the earlier cursive. This minuscule
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (or more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (or more formally ''minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing ...
style remained the dominant form of handwritten Greek into the modern era. During the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
, western printers adopted the minuscule letter forms as lowercase printed typefaces, while modeling uppercase letters on the ancient inscriptional forms. The orthographic practice of using the letter case distinction for marking proper names, titles, etc. developed in parallel to the practice in Latin and other western languages.
Derived alphabets
 The Greek alphabet was the model for various others:
* The Etruscan alphabet;
* The Latin alphabet, together with various other ancient scripts in Italy, adopted from an archaic form of the Greek alphabet brought to Italy by Greek colonists in the late 8th century BC, via Etruscan;
* The Gothic alphabet, devised in the 4th century AD to write the Gothic language, based on a combination of Greek and Latin uncial models;
* The
The Greek alphabet was the model for various others:
* The Etruscan alphabet;
* The Latin alphabet, together with various other ancient scripts in Italy, adopted from an archaic form of the Greek alphabet brought to Italy by Greek colonists in the late 8th century BC, via Etruscan;
* The Gothic alphabet, devised in the 4th century AD to write the Gothic language, based on a combination of Greek and Latin uncial models;
* The Glagolitic alphabet
The Glagolitic script (, , ''glagolitsa'') is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. It is generally agreed to have been created in the 9th century by Saint Cyril, a monk from Thessalonica. He and his brother Saint Methodius were sent by the Byzan ...
, devised in the 9th century AD for writing Old Church Slavonic;
* The Cyrillic script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
, which replaced the Glagolitic alphabet shortly afterwards.
* The Coptic Alphabet used for writing the Coptic language.
The Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
and Georgian alphabets are almost certainly modeled on the Greek alphabet, but their graphic forms are quite different.
Other uses
Use for other languages
Apart from the daughter alphabets listed above, which were adapted from Greek but developed into separate writing systems, the Greek alphabet has also been adopted at various times and in various places to write other languages. For some of them, additional letters were introduced.Antiquity
* Most of theIron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
alphabets of Asia Minor
Various alphabetic writing systems were in use in Iron Age Anatolia to record Anatolian languages and Phrygian. Several of these languages had previously been written with logographic and syllabic scripts.
The alphabets of Asia Minor proper s ...
were also adopted around the same time, as the early Greek alphabet was adopted from the Phoenician Alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet is an alphabet (more specifically, an abjad) known in modern times from the Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean region. The name comes from the Phoenician civilization.
The Phoenician a ...
. The Lydian and Carian alphabets are generally believed to derive from the Greek alphabet, although it is not clear which variant is the direct ancestor. While some of these alphabets such as Phrygian had slight differences from the Greek counterpart, some like Carian alphabet
The Carian alphabets are a number of regional scripts used to write the Carian language of western Anatolia. They consisted of some 30 alphabetic letters, with several geographic variants in Caria and a homogeneous variant attested from the Nile ...
had mostly different values and several other characters inherited from pre-Greek local scripts. They were in use c. 800–300 BC until all the Anatolian languages were extinct due to Hellenization
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in the H ...
.
* The original Old Italic alphabets was the early Greek alphabet with only slight modifications.
* It was used in some Paleo-Balkan languages, including Thracian. For other neighboring languages or dialects, such as Ancient Macedonian, isolated words are preserved in Greek texts, but no continuous texts are preserved.
* The Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the paleohispanic scripts that present ...
was used for writing the ancient Iberian language in parts of modern Spain.
* Gaulish inscriptions (in modern France) used the Greek alphabet until the Roman conquest
* The Hebrew and Aramaic text of the Bible was written in Greek letters in Origen's Hexapla.
* The Bactrian language, an Iranian language spoken in what is now Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, ط§ظ…ط§ط±طھ ط§ط³ظ„ط§ظ…غŒ ط§ظپط؛ط§ظ†ط³طھط§ظ† is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, was written in the Greek alphabet during the Kushan Empire (65–250 AD). It adds an extra letter for the ''sh'' sound .
* The Coptic alphabet adds eight letters derived from Demotic
Demotic may refer to:
* Demotic Greek, the modern vernacular form of the Greek language
* Demotic (Egyptian), an ancient Egyptian script and version of the language
* Chل»¯ Nأ´m, the demotic script for writing Vietnamese
See also
*
* Demos (disa ...
. It is still used today, mostly in Egypt, to write Coptic, the liturgical language of Egyptian Christians. Letters usually retain an uncial form different from the forms used for Greek today. The alphabet of Old Nubian
Old Nubian (also called Middle Nubian or Old Nobiin) is an extinct Nubian language, attested in writing from the 8th to the 15th century AD. It is ancestral to modern-day Nobiin and closely related to Dongolawi and Kenzi. It was used throughou ...
is an adaptation of Coptic.
Middle Ages
* An 8th-century Arabic fragment preserves a text in the Greek alphabet, as does a 9th or 10th century psalm translation fragment. * An Old Ossetic inscription of the 10th–12th centuries found inArxyz
Arkhyz (also Nizhny Arkhyz russian: ذگر€ر…ر‹ذ·; krc, ذ«ر€ر…ر‹ذ·, ''Irxؤ±z''; "mudflows") is a village in the valley of the Bolshoy Zelenchuk River, in the Republic of Karachay–Cherkessia, Greater Caucasus, Russia, about 70 km inland from ...
, the oldest known attestation of an Ossetic language.
* The Old Nubian language
Old Nubian (also called Middle Nubian or Old Nobiin) is an extinct Nubian language, attested in writing from the 8th to the 15th century AD. It is ancestral to modern-day Nobiin and closely related to Dongolawi and Kenzi. It was used throughou ...
of Makuria (modern Sudan) adds three Coptic letters, two letters derived from Meroitic script, and a digraph of two Greek gammas used for the velar nasal
The voiced velar nasal, also known as agma, from the Greek word for 'fragment', is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is the sound of ''ng'' in English ''sing'' as well as ''n'' before velar consonants as in ''Englis ...
sound.
* Various South Slavic dialects, similar to the modern Bulgarian and Macedonian language
Macedonian (; , , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of a larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken as a first language by around two million ...
s, have been written in Greek script. The modern South Slavic languages now use modified Cyrillic alphabets.
Early modern
Tosk
Tosk ( sq-definite, toskأ«rishtja) is the southern group of dialects of the Albanian language, spoken by the ethnographic group known as Tosks. The line of demarcation between Tosk and Gheg (the northern variety) is the Shkumbin River. Tosk is t ...
Albanian was often written using the Greek alphabet, starting in about 1500. The printing press at Moschopolis published several Albanian texts in Greek script during the 18th century. It was only in 1908 that the Monastir conference standardized a Latin orthography for both Tosk and Gheg
Gheg (also spelled Geg; Gheg Albanian: ''gegnishtja'', Standard sq, gegأ«rishtja) is one of the two major varieties of Albanian, the other being Tosk. The geographic dividing line between the two varieties is the Shkumbin River, which winds ...
. Greek spelling is still occasionally used for the local Albanian dialects (Arvanitika
Arvanitika (; Arvanitika: , ; Greek: , ), also known as Arvanitic, is the variety of Albanian traditionally spoken by the Arvanites, a population group in Greece. Arvanitika is today endangered, as its speakers have been shifting to the u ...
) in Greece.
* Gagauz, a Turkic language
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languag ...
of the northeast Balkans spoken by Orthodox Christians, was apparently written in Greek characters in the late 19th century. In 1957, it was standardized on Cyrillic, and in 1996, a Gagauz alphabet
The modern Gagauz alphabet is a 31-letter Latin-based alphabet modelled on the Turkish alphabet. Previously, during Soviet rule, Gagauz's official script was Cyrillic.
Gagauz was first written in Greek letters in the late 19th century.M. Ciachi ...
based on Latin characters was adopted (derived from the Turkish alphabet).
* Surguch, a Turkic language
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languag ...
, was spoken by a small group of Orthodox Christians in northern Greece. It is now written in Latin or Cyrillic characters.
* Urum or Greek Tatar, spoken by Orthodox Christians, used the Greek alphabet.
* Judaeo-Spanish or Ladino, a Jewish dialect of Spanish, has occasionally been published in Greek characters in Greece.
* The Italian humanist Giovan Giorgio Trissino tried to add some Greek letters (ئگ خµ, ê¶ د‰) to Italian orthography
Italian orthography (writing) uses a variant of the Latin alphabet consisting of 21 letters to write the Italian language. This article focuses on the writing of Standard Italian, based historically on the Florentine dialect.
Italian orthography ...
in 1524.
In mathematics and science
Greek symbols are used as symbols in mathematics,physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
and other science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
s. Many symbols have traditional uses, such as lower case epsilon (خµ) for an arbitrarily small positive number, lower case pi (د€) for the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, capital sigma (خ£) for summation, and lower case sigma (دƒ) for standard deviation. Formerly, the Greek letters were used for naming North Atlantic hurricanes if the normal list ran out. This happened only in the 2005 and 2020
2020 was heavily defined by the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to global social and economic disruption, mass cancellations and postponements of events, worldwide lockdowns and the largest economic recession since the Great Depression in t ...
hurricane seasons for a total of 15 storms, the last one being Hurricane Iota
Hurricane Iota was a devastating late-season Category 4 hurricane, Category 4 Atlantic hurricane which caused severe damage to areas of Central America already devastated by Hurricane Eta just less than two weeks prior. The 31st and final trop ...
. In May 2021 the World Health Organisations announced that the variants of SARS-CoV-2 of the virus would be named using letters of the Greek alphabet to avoid stigma and simplify communications for non-scientific audiences.
Astronomy
Greek letters are used to denote the brighter stars within each of the eighty-eight constellations. In most constellations, the brightest star is designated Alpha and the next brightest Beta etc. For example, the brightest star in the constellation ofCentaurus
Centaurus is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. ...
is known as Alpha Centauri. For historical reasons, the Greek designations of some constellations begin with a lower ranked letter.
International Phonetic Alphabet
Several Greek letters are used as phonetic symbols in theInternational Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation ...
(IPA). Several of them denote fricative consonants; the rest stand for variants of vowel sounds. The glyph shapes used for these letters in specialized phonetic fonts is sometimes slightly different from the conventional shapes in Greek typography proper, with glyphs typically being more upright and using serifs, to make them conform more with the typographical character of other, Latin-based letters in the phonetic alphabet. Nevertheless, in the Unicode encoding standard, the following three phonetic symbols are considered the same characters as the corresponding Greek letters proper:For chi and beta, separate codepoints for use in a Latin-script environment were added in Unicode versions 7.0 (2014) and 8.0 (2015) respectively: U+AB53 "Latin small letter chi" (ê“) and U+A7B5 "Latin small letter beta" (êµ). As of 2017, the International Phonetic Association still lists the original Greek codepoints as the standard representations of the IPA symbols in questioOn the other hand, the following phonetic letters have Unicode representations separate from their Greek alphabetic use, either because their conventional typographic shape is too different from the original, or because they also have secondary uses as regular alphabetic characters in some Latin-based alphabets, including separate Latin uppercase letters distinct from the Greek ones. The symbol in Americanist phonetic notation for the voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is the Greek letter lambda , but in the IPA. The IPA symbol for the palatal lateral approximant is , which looks similar to lambda, but is actually an inverted lowercase ''y''.
Use as numerals
Greek letters were also used to write numbers. In the classical Ionian system, the first nine letters of the alphabet stood for the numbers from 1 to 9, the next nine letters stood for the multiples of 10, from 10 to 90, and the next nine letters stood for the multiples of 100, from 100 to 900. For this purpose, in addition to the 24 letters which by that time made up the standard alphabet, three otherwise obsolete letters were retained or revived: digamma for 6, koppa for 90, and a rare Ionian letter for s today calledsampi
Sampi (modern: د،; ancient shapes: , ) is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet. It was used as an addition to the classical 24-letter alphabet in some eastern Ionic dialects of ancient Greek in the 6th and 5th centuries BC, to denote some t ...
, for 900. This system has remained in use in Greek up to the present day, although today it is only employed for limited purposes such as enumerating chapters in a book, similar to the way Roman numerals are used in English. The three extra symbols are today written as , and respectively. To mark a letter as a numeral sign, a small stroke called '' keraia'' is added to the right of it.
Use by student fraternities and sororities
In North America, many college fraternities and sororities are named with combinations of Greek letters, and are hence also known as "Greek letter organizations". This naming tradition was initiated by the foundation of the Phi Beta Kappa Society at the College of William and Mary in 1776. The name of this fraternal organization is an acronym for the ancient Greek phrase خ¦خ¹خ»خ؟دƒخ؟د†خ¯خ± خ’خ¯خ؟د… خڑد…خ²خµدپخ½خ®د„خ·د‚ (''Philosophia Biou Kybernؤ“tؤ“s''), which means "Love of wisdom, the guide of life" and serves as the organization's motto. Sometimes early fraternal organizations were known by their Greek letter names because the mottos that these names stood for were secret and revealed only to members of the fraternity. Different chapters within the same fraternity are almost always (with a handful of exceptions) designated using Greek letters as serial numbers. The founding chapter of each respective organization is its A chapter. As an organization expands, it establishes a B chapter, a خ“ chapter, and so on and so forth. In an organization that expands to more than 24 chapters, the chapter after خ© chapter is AA chapter, followed by AB chapter, etc. Each of these is still a "chapter Letter", albeit a double-digit letter just as 10 through 99 are double-digit numbers. The Roman alphabet has a similar extended form with such double-digit letters when necessary, but it is used for columns in a table or chart rather than chapters of an organization.Glyph variants
Some letters can occur in variant shapes, mostly inherited from medievalminuscule
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (or more formally ''majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (or more formally ''minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing ...
handwriting. While their use in normal typography of Greek is purely a matter of font styles, some such variants have been given separate encodings in Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, wh ...
.
* The symbol ("curled beta") is a cursive variant form of beta (خ²). In the French tradition of Ancient Greek typography, خ² is used word-initially, and is used word-internally.
* The letter delta has a form resembling a cursive capital letter D; while not encoded as its own form, this form is included as part of the symbol for the drachma
The drachma ( el, خ´دپخ±د‡خ¼خ® , ; pl. ''drachmae'' or ''drachmas'') was the currency used in Greece during several periods in its history:
# An ancient Greek currency unit issued by many Greek city states during a period of ten centuries, fr ...
(a خ”دپ digraph) in the Currency Symbols
A currency symbol or currency sign is a graphic symbol used to denote a currency unit. Usually it is defined by the monetary authority, like the national central bank for the currency concerned.
In formatting, the symbol can use various format ...
block, at U+20AF (₯).
* The letter epsilon can occur in two equally frequent stylistic variants, either shaped ('lunate epsilon', like a semicircle with a stroke) or (similar to a reversed number 3). The symbol دµ (U+03F5) is designated specifically for the lunate form, used as a technical symbol.
* The symbol ("script theta") is a cursive form of theta (خ¸), frequent in handwriting, and used with a specialized meaning as a technical symbol.
* The symbol ("kappa symbol") is a cursive form of kappa (خ؛), used as a technical symbol.
* The symbol ("variant pi") is an archaic script form of pi (د€), also used as a technical symbol.
* The letter rho (دپ) can occur in different stylistic variants, with the descending tail either going straight down or curled to the right. The symbol (U+03F1) is designated specifically for the curled form, used as a technical symbol.
* The letter sigma, in standard orthography, has two variants: د‚, used only at the ends of words, and دƒ, used elsewhere. The form ("lunate sigma
Sigma (; uppercase خ£, lowercase دƒ, lowercase in word-final position د‚; grc-gre, دƒخ¯خ³خ¼خ±) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase خ£ is used as ...
", resembling a Latin '' c'') is a medieval stylistic variant that can be used in both environments without the final/non-final distinction.
* The capital letter upsilon (خ¥) can occur in different stylistic variants, with the upper strokes either straight like a Latin ''Y'', or slightly curled. The symbol د’ (U+03D2) is designated specifically for the curled form (), used as a technical symbol, e.g. in physics.
* The letter phi
Phi (; uppercase خ¦, lowercase د† or د•; grc, د•خµل؟– ''pheأ®'' ; Modern Greek: ''fi'' ) is the 21st letter of the Greek alphabet.
In Archaic and Classical Greek (c. 9th century BC to 4th century BC), it represented an aspirated voicele ...
can occur in two equally frequent stylistic variants, either shaped as (a circle with a vertical stroke through it) or as (a curled shape open at the top). The symbol (U+03D5) is designated specifically for the closed form, used as a technical symbol.
* The letter omega has at least three stylistic variants of its capital form. The standard is the "open omega" (خ©), resembling an open partial circle with the opening downward and the ends curled outward. The two other stylistic variants are seen more often in modern typography, resembling a raised and underscored circle (roughly oج²), where the underscore may or may not be touching the circle on a tangent (in the former case it resembles a superscript omicron similar to that found in the numero sign or masculine ordinal indicator
In written languages, an ordinal indicator is a character, or group of characters, following a numeral denoting that it is an ordinal number, rather than a cardinal number. In English orthography, this corresponds to the suffixes ''-st'', ''- ...
; in the latter, it closely resembles some forms of the Latin letter Q). The open omega is always used in symbolic settings and is encoded in Letterlike Symbols
Letterlike Symbols is a Unicode block containing 80 characters which are constructed mainly from the glyphs of one or more letters. In addition to this block, Unicode includes full styled mathematical alphabets, although Unicode does not expl ...
(U+2126) as a separate code point for backward compatibility.
Computer encodings
For computer usage, a variety of encodings have been used for Greek online, many of them documented in . The two principal ones still used today are ISO/IEC 8859-7 andUnicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, wh ...
. ISO 8859-7 supports only the monotonic orthography; Unicode supports both the monotonic and polytonic orthographies.
ISO/IEC 8859-7
For the range A0–FF (hex), it follows the Unicode range 370–3CF (see below) except that some symbols, like آ©, آ½, آ§ etc. are used where Unicode has unused locations. Like all ISO-8859 encodings, it is equal to ASCII for 00–7F (hex).Greek in Unicode
Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, wh ...
supports polytonic orthography
Greek orthography has used a variety of diacritics starting in the Hellenistic period. The more complex polytonic orthography ( el, د€خ؟خ»د…د„خ؟خ½خ¹خ؛دŒ دƒدچدƒد„خ·خ¼خ± خ³دپخ±د†خ®د‚, translit=polytonikأ³ sأ½stؤ«ma grafؤ«جپs), which includes fi ...
well enough for ordinary continuous text in modern and ancient Greek, and even many archaic forms for epigraphy. With the use of combining characters, Unicode also supports Greek philology and dialectology Dialectology (from Greek , ''dialektos'', "talk, dialect"; and , '' -logia'') is the scientific study of linguistic dialect, a sub-field of sociolinguistics. It studies variations in language based primarily on geographic distribution and their ass ...
and various other specialized requirements. Most current text rendering engines do not render diacritics well, so, though alpha with macron and acute can be ''represented'' as U+03B1 U+0304 U+0301, this rarely renders well: .
There are two main blocks of Greek characters in Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, wh ...
. The first is "Greek and Coptic" (U+0370 to U+03FF). This block is based on ISO 8859-7
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
and is sufficient to write Modern Greek. There are also some archaic letters and Greek-based technical symbols.
This block also supports the Coptic alphabet. Formerly, most Coptic letters shared codepoints with similar-looking Greek letters; but in many scholarly works, both scripts occur, with quite different letter shapes, so as of Unicode 4.1, Coptic and Greek were disunified. Those Coptic letters with no Greek equivalents still remain in this block (U+03E2 to U+03EF).
To write polytonic Greek, one may use combining diacritical mark
In digital typography, combining characters are characters that are intended to modify other characters. The most common combining characters in the Latin script are the combining diacritical marks (including combining accents).
Unicode al ...
s or the precomposed characters in the "Greek Extended" block (U+1F00 to U+1FFF).
Combining and letter-free diacritics
Combining and spacing (letter-free) diacritical marks pertaining toGreek language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, خ•خ»خ»خ·خ½خ¹خ؛خ¬, Ellinikأ،, ; grc, ل¼™خ»خ»خ·خ½خ¹خ؛خ®, Hellؤ“nikل¸—) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy ( Calabria and Salento), southe ...
:
Encodings with a subset of the Greek alphabet
IBM code pages 437, 860, 861, 862, 863, and 865 contain the letters خ“خکخ£خ¦خ©خ±خ´خµد€دƒد„د† (plus خ² as an alternative interpretation for أں).See also
* Greek Font Society * Greek ligatures * Palamedes * Romanization of GreekNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * reek translation of ''Greek: a history of the language and its speakers'', London 1997* * * * * * * – selections from the Gospels in Macedonian. * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Greek and Coptic
character list in Unicode
Unicode collation charts
€”including Greek and Coptic letters, sorted by shape
Examples of Greek handwriting
*
(Alan Wood)
a browser-based tool * Collection of free fonts
{{Authority control