Boidae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Boidae, commonly known as boas or boids, are a
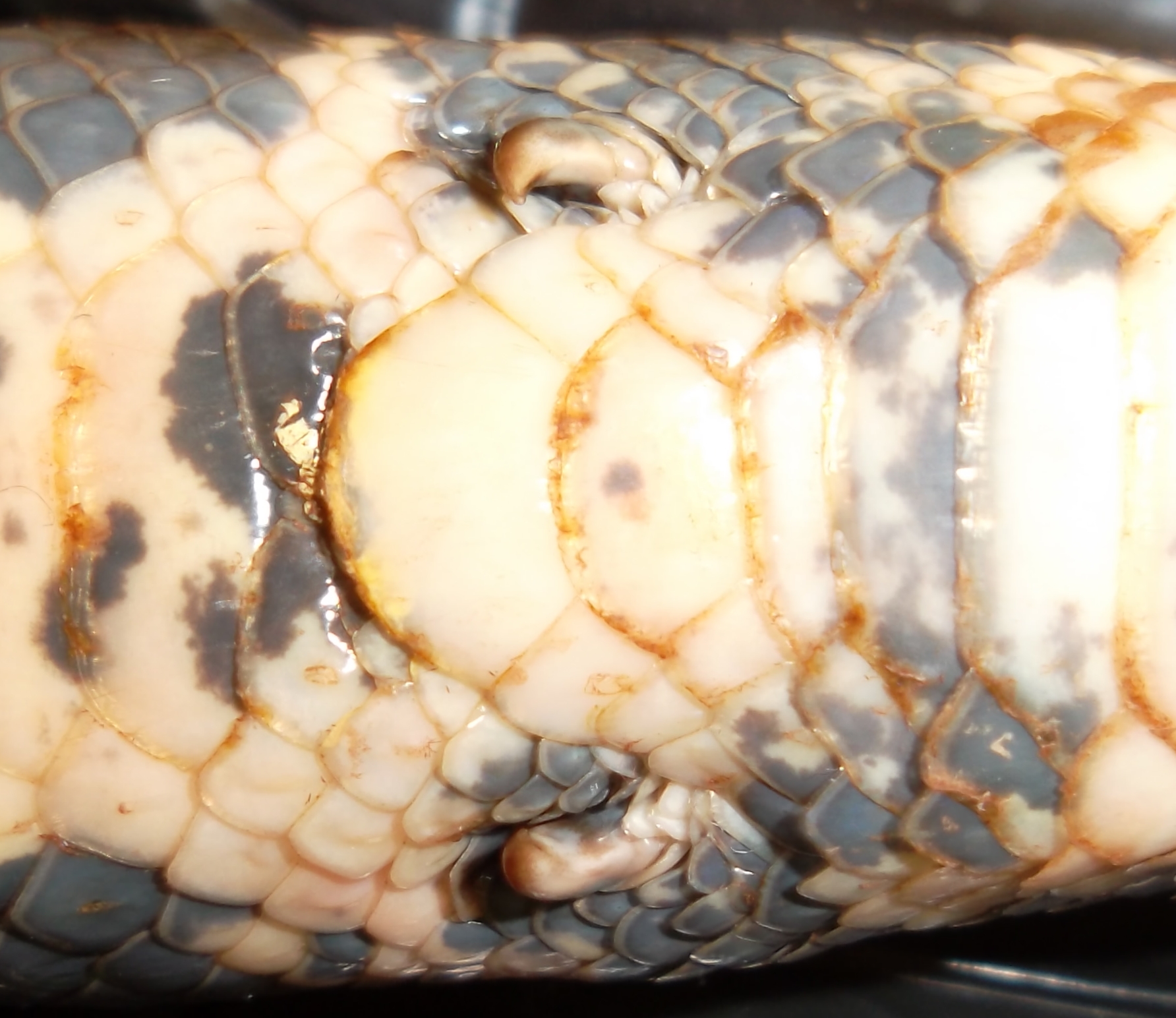 Both families share a number of primitive characteristics. Nearly all have a relatively rigid lower jaw with a coronoid element, as well as a vestigial
Both families share a number of primitive characteristics. Nearly all have a relatively rigid lower jaw with a coronoid element, as well as a vestigial Boidae
a
VMNH
Accessed 15 July 2008. Boids are, however, distinguished from the pythons in that none has postfrontal bones or premaxillary teeth, and that they give birth to live young. When labial pits are present, these are located between the scales as opposed to on them. Also, their geographical distributions are almost entirely mutually exclusive. In the few areas where they do coexist, the tendency is for them to occupy different habitats. Formerly, boas were said to be found in the
PDF
a
University of Michigan Library
Accessed 8 July 2008.
family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
of nonvenomous snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s primarily found in the Americas, as well as Africa, Europe, Asia, and some Pacific Islands. Boas include some of the world's largest snakes, with the green anaconda
The green anaconda (''Eunectes murinus''), also known as the giant Emerald anaconda, common anaconda, common water boa or sucuri, is a boa species found in South America. It is the heaviest and one of the longest known extant snake species. Lik ...
of South America being the heaviest and second-longest snake known; in general, adults are medium to large in size, with females usually larger than the males. Five subfamilies, comprising 12 genera and 49 species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
, are currently recognized.
The Old Tupi name for such snakes was mbói, which figures in the etymology
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the Phonological chan ...
of names such as ''jibóia'' and ''boitatá'' (the Brazilian name for the mythical giant anaconda).
Description
Like thepythons
The Pythonidae, commonly known as pythons, are a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia. Among its members are some of the largest snakes in the world. Ten genera and 42 species are currently recognized.
Distribution ...
, boas have elongated supratemporal The supratemporal bone is a paired cranial bone present in many tetrapods and tetrapodomorph fish. It is part of the temporal region (the portion of the skull roof behind the eyes), usually lying medial (inwards) relative to the squamosal and latera ...
bones. The quadrate bone
The quadrate bone is a skull bone in most tetrapods, including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, birds), and early synapsids.
In most tetrapods, the quadrate bone connects to the quadratojugal and squamosal bones in the skull, and forms upper pa ...
s are also elongated, but not as much, while both are capable of moving freely so when they swing sideways to their maximum extent, the distance between the hinges of the lower jaw is greatly increased.Parker HW, Grandison AGC. 1977. Snakes – a natural history. Second Edition. British Museum (Natural History) and Cornell University Press. 108 pp. 16 plates. LCCCN 76-54625. (cloth), (paper).
 Both families share a number of primitive characteristics. Nearly all have a relatively rigid lower jaw with a coronoid element, as well as a vestigial
Both families share a number of primitive characteristics. Nearly all have a relatively rigid lower jaw with a coronoid element, as well as a vestigial pelvic girdle
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The p ...
with hind limbs that are partially visible as a pair of spurs, one on either side of the vent
Vent or vents may refer to:
Science and technology Biology
*Vent, the cloaca region of an animal
* Vent DNA polymerase, a thermostable DNA polymerase
Geology
*Hydrothermal vent, a fissure in a planet's surface from which geothermally heated wate ...
. In males, these anal spurs are larger and more conspicuous than in females. A long row of palatal teeth is present, and most species have a functional left lung that can be up to 75% as large as the right lung.a
VMNH
Accessed 15 July 2008. Boids are, however, distinguished from the pythons in that none has postfrontal bones or premaxillary teeth, and that they give birth to live young. When labial pits are present, these are located between the scales as opposed to on them. Also, their geographical distributions are almost entirely mutually exclusive. In the few areas where they do coexist, the tendency is for them to occupy different habitats. Formerly, boas were said to be found in the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
and pythons in the Old World. While this is true of boine boas, other boid species are present in Africa, much of southern Eurasia, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
, and the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
, so this is not accurate. However, they seem more abundant in evolutionarily isolated areas. South America was isolated until a few million years ago, with a fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as ''Biota (ecology ...
that included marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
s and other distinctive mammals. With the formation of the Panamanian land bridge to North America about three million years ago, boines have migrated north as colubrids (and various Nearctic
The Nearctic realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting the Earth's land surface.
The Nearctic realm covers most of North America, including Greenland, Central Florida, and the highlands of Mexico. The parts of North America ...
mammals) have migrated south, as part of the Great American Interchange.
Distribution and habitat
Most species are found in North, Central, and South America, as well as the Caribbean, while a few are found in southeastern Europe andAsia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, Northern, Central and East Africa, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, the Arabian Peninsula, Central and southwestern Asia, India and Sri Lanka, the Moluccas
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located ...
, and New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torr ...
through to Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
and Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
.
Feeding
Prey is killed byconstriction
Constriction is a method used by various snake species to kill or subdue their prey. Although some species of venomous and mildly venomous snakes do use constriction to subdue their prey, most snakes which use constriction lack venom. The snake i ...
; after an animal has been grasped to restrain it, a number of coils are hastily wrapped around it. Then, by applying and maintaining sufficient pressure, the snake prevents its prey from inhaling, so that it eventually succumbs to asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that ca ...
tion. Recently, the pressures produced during constriction have been suggested as the cause of cardiac arrest by interfering with blood flow, but this hypothesis has not yet been confirmed.
Larger specimens usually eat animals about the size of a house cat, but larger food items are not unknown: the diet of the common anaconda, ''Eunectes murinus
The green anaconda (''Eunectes murinus''), also known as the giant Emerald anaconda, common anaconda, common water boa or sucuri, is a boa species found in South America. It is the heaviest and one of the longest known extant snake species. Li ...
'', is known to include subadult tapir
Tapirs ( ) are large, herbivorous mammals belonging to the family Tapiridae. They are similar in shape to a pig, with a short, prehensile nose trunk. Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South and Central America, with one species inh ...
s. Prey is swallowed whole, and may take several days or even weeks to fully digest. Despite their intimidating size and muscular power, they are generally not dangerous to humans.
Contrary to popular belief, even the larger species do not crush their prey to death; in fact, prey is not even noticeably deformed before it is swallowed. The speed with which the coils are applied is impressive and the force they exert may be significant, but death is caused by suffocation, with the victim not being able to move its ribs to breathe while it is being constricted.
Reproduction
Most species areovoviviparous
Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop insi ...
, with females giving birth to live young. This is in contrast to the pythons
The Pythonidae, commonly known as pythons, are a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia. Among its members are some of the largest snakes in the world. Ten genera and 42 species are currently recognized.
Distribution ...
, which all lay eggs ( oviparous).
Subfamilies
Type genus
In biological taxonomy, the type genus is the genus which defines a biological family and the root of the family name.
Zoological nomenclature
According to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, "The name-bearing type of a nominal ...
= ''Boa
Kwon Bo-ah (; born November 5, 1986), known professionally as BoA, is a South Korean singer, songwriter, dancer, record producer and actress. One of the most successful and influential Korean entertainers, she has been dubbed the " Queen of K- ...
'' – Gray, 1825
Taxonomy
Pythons
The Pythonidae, commonly known as pythons, are a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia. Among its members are some of the largest snakes in the world. Ten genera and 42 species are currently recognized.
Distribution ...
were historically classified as a subfamily of Boidae (called Pythoninae), but it was later determined that they are not closely related to boas despite having superficial similarities.
Almost all of the non-boine boids are frequently elevated to their own full family: Calabariidae/inae, Candoiidae/inae, Erycidae/inae, Charininae, Ungaliophiidae/inae, Sanziniidae/inae, and Calabariidae/inae. The taxonomy of boid snakes has long been debated, and ultimately the decision whether to assign a particular clade to a particular Linnaean rank (such as a superfamily, family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
, or subfamily) is arbitrary.
The subfamily Ungaliophiinae was formerly made up of four genera. Two of these (''Tropidophis'' and ''Trachyboa'') are actually more closely related to red pipesnakes than to boas, and are now placed in the Tropidophiidae
The Tropidophiidae, common name dwarf boas or thunder snakes, are a family of nonvenomous snakes found from Mexico and the West Indies south to southeastern Brazil. These are small to medium-sized fossorial snakes, some with beautiful and striking ...
within the Amerophidia
The Amerophidia, also known as amerophidian snakes, are a superfamily of snakes that contains two families: Aniliidae (containing a single species, ''Anilius scytale
The Aniliidae are a monotypic family created for the monotypic genus ''Ani ...
. The other two genera, ''Ungaliophis'' and ''Exiliboa'', are the sister group of the ''Charina
''Charina'' is a genus of nonvenomous boas, commonly known as rubber boas, found in North America. Two species are currently recognized''.''
Distribution and habitat
Found in North America from western Canada south through the western United St ...
- Lichanura'' clade, within Boidae.
See also
*List of boine species and subspecies
This is a list of all extant genera, species and subspecies of the snakes of the subfamily Boinae, otherwise referred to as boines or true boas. It follows the taxonomy currently provided by ITIS, which is based on the continuing work of Roy McDia ...
* List of erycine species and subspecies
References
* Kluge AG. 1991. Boine Snake Phylogeny and Research Cycles. Misc. Pub. Museum of Zoology, Univ. of Michigan No. 178a
University of Michigan Library
Accessed 8 July 2008.
External links
{{Authority control Snake families Taxa named by John Edward Gray Extant Maastrichtian first appearances