Blood–brain barrier on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective

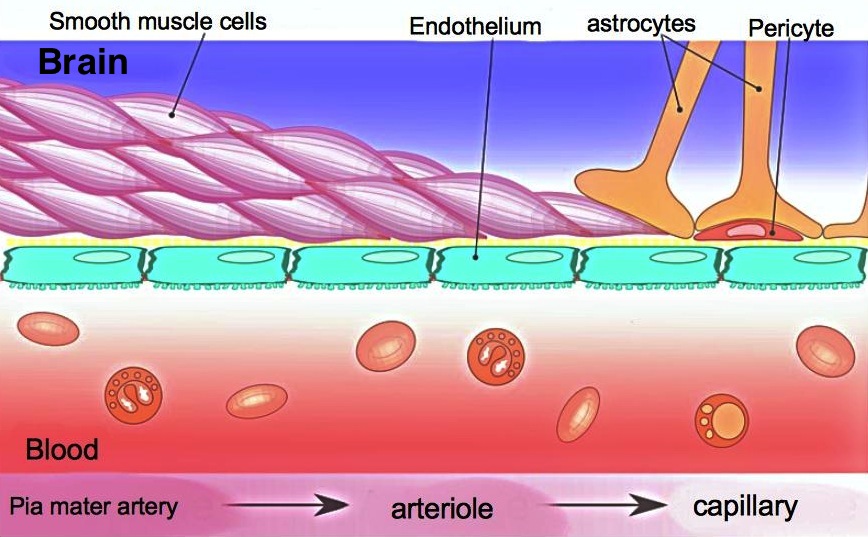 The BBB results from the selectivity of the tight junctions between the endothelial cells of brain capillaries, restricting the passage of solutes. At the interface between blood and the brain, endothelial cells are adjoined continuously by these tight junctions, which are composed of smaller subunits of
The BBB results from the selectivity of the tight junctions between the endothelial cells of brain capillaries, restricting the passage of solutes. At the interface between blood and the brain, endothelial cells are adjoined continuously by these tight junctions, which are composed of smaller subunits of
semipermeable
Semipermeable membrane is a type of biological or synthetic, polymeric membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis. The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecul ...
border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes
In chemistry, a solution is a special type of homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances. In such a mixture, a solute is a substance dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. If the attractive forces between the solven ...
in the circulating blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
where neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa ...
s reside. The blood–brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes
Pericytes (previously known as Rouget cells) are multi-functional mural cells of the microcirculation that wrap around the endothelial cells that line the capillaries throughout the body. Pericytes are embedded in the basement membrane of blood c ...
embedded in the capillary basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium an ...
. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive diffusion
Passive transport is a type of membrane transport that does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes. Instead of using cellular energy, like active transport, passive transport relies on the second law of thermodynamics to dri ...
, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
s that are crucial to neural function.
The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a g ...
s, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and large
Large means of great size.
Large may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Arbitrarily large, a phrase in mathematics
* Large cardinal, a property of certain transfinite numbers
* Large category, a category with a proper class of objects and morphisms ...
or hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are n ...
molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
, while allowing the diffusion of hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, ...
molecules (O2, CO2, hormones) and small non-polar molecules. Cells of the barrier actively transport metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
products such as glucose across the barrier using specific transport proteins. The barrier also restricts the passage of peripheral immune factors, like signaling molecules, antibodies, and immune cells, into the CNS, thus insulating the brain from damage due to peripheral immune events.
Specialized brain structures participating in sensory and secretory integration within brain neural circuits—the circumventricular organs and choroid plexus—have in contrast highly permeable capillaries.
Structure


 The BBB results from the selectivity of the tight junctions between the endothelial cells of brain capillaries, restricting the passage of solutes. At the interface between blood and the brain, endothelial cells are adjoined continuously by these tight junctions, which are composed of smaller subunits of
The BBB results from the selectivity of the tight junctions between the endothelial cells of brain capillaries, restricting the passage of solutes. At the interface between blood and the brain, endothelial cells are adjoined continuously by these tight junctions, which are composed of smaller subunits of transmembrane protein
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequent ...
s, such as occludin
Occludin is an enzyme ( EC 1.6) that oxidizes NADH. It was first identified in epithelial cells as a 65 kDa integral plasma-membrane protein localized at the tight junctions. Together with Claudins, and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), occludin has be ...
, claudins (such as Claudin-5), junctional adhesion molecule
A junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) is a protein that is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, and is expressed in a variety of different tissues, such as leukocytes, platelets, and epithelial and endothelial cells. They have been shown to ...
(such as JAM-A). Each of these tight junction proteins is stabilized to the endothelial cell membrane by another protein complex that includes scaffolding proteins such as tight junction protein 1 (ZO1) and associated proteins.
The BBB is composed of endothelial cells restricting passage of substances from the blood more selectively than endothelial cells of capillaries elsewhere in the body. Astrocyte cell projections called astrocytic feet (also known as "glia limitans
The glia limitans, or the glial limiting membrane, is a thin barrier of astrocyte foot processes associated with the parenchymal basal lamina surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost layer of neural tissue, and among its respon ...
") surround the endothelial cells of the BBB, providing biochemical support to those cells. The BBB is distinct from the quite similar blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervo ...
, which is a function of the choroidal cells of the choroid plexus, and from the blood-retinal barrier, which can be considered a part of the whole realm of such barriers.
Not all vessels in the human brain exhibit BBB properties. Some examples of this include the circumventricular organs, the roof of the third and fourth ventricles, capillaries in the pineal gland on the roof of the diencephalon
The diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic ''prosencephalon''). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic ''mesencephalon''). The diencephalon has also been known as the 'tweenbrain in o ...
and the pineal gland
The pineal gland, conarium, or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cy ...
. The pineal gland secretes the hormone melatonin
Melatonin is a natural product found in plants and animals. It is primarily known in animals as a hormone released by the pineal gland in the brain at night, and has long been associated with control of the sleep–wake cycle.
In vertebrat ...
"directly into the systemic circulation", thus melatonin is not affected by the blood–brain barrier.
Development
The BBB appears to be functional by the time of birth. P-glycoprotein, a transporter, exists already in the embryonal endothelium. Measurement of brain uptake of various blood-borne solutes showed that newborn endothelial cells were functionally similar to those in adults, indicating that a selective BBB is operative at birth. In mice, Claudin-5 loss during development is lethal and results in size-selective loosening of the BBB.Function
The blood–brain barrier acts effectively to protect brain tissue from circulatingpathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a g ...
s and other potentially toxic substances. Accordingly, blood-borne infections of the brain are rare. Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
s of the brain that do occur are often difficult to treat. Antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
are too large to cross the blood–brain barrier, and only certain antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and preventio ...
are able to pass. In some cases, a drug has to be administered directly into the cerebrospinal fluid where it can enter the brain by crossing the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervo ...
.
Circumventricular organs
Circumventricular organs (CVOs) are individual structures located adjacent to the fourth ventricle orthird ventricle
The third ventricle is one of the four connected ventricles of the ventricular system within the mammalian brain. It is a slit-like cavity formed in the diencephalon between the two thalami, in the midline between the right and left lateral ...
in the brain, and are characterized by dense capillary beds with permeable endothelial cells unlike those of the blood–brain barrier. Included among CVOs having highly permeable capillaries are the area postrema, subfornical organ, vascular organ of the lamina terminalis
The vascular organ of lamina terminalis (VOLT), organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis (OVLT), or supraoptic crest is one of the four sensory circumventricular organs of the brain, the others being the subfornical organ, the median eminence, ...
, median eminence, pineal gland
The pineal gland, conarium, or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cy ...
, and three lobes of the pituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The h ...
.
Permeable capillaries of the sensory CVOs (area postrema, subfornical organ, vascular organ of the lamina terminalis) enable rapid detection of circulating signals in systemic blood, while those of the secretory CVOs (median eminence, pineal gland, pituitary lobes) facilitate transport of brain-derived signals into the circulating blood. Consequently, the CVO permeable capillaries are the point of bidirectional blood–brain communication for neuroendocrine function.
Specialized permeable zones
The border zones between brain tissue "behind" the blood–brain barrier and zones "open" to blood signals in certain CVOs contain specialized hybrid capillaries that are leakier than typical brain capillaries, but not as permeable as CVO capillaries. Such zones exist at the border of the area postrema— nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS), and median eminence— hypothalamicarcuate nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (also known as ARH, ARC, or infundibular nucleus) is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes seve ...
. These zones appear to function as rapid transit regions for brain structures involved in diverse neural circuits—like the NTS and arcuate nucleus—to receive blood signals which are then transmitted into neural output. The permeable capillary zone shared between the median eminence and hypothalamic arcuate nucleus is augmented by wide pericapillary spaces, facilitating bidirectional flow of solutes between the two structures, and indicating that the median eminence is not only a secretory organ, but may also be a sensory organ.
Therapeutic research
As a drug target
The blood–brain barrier is formed by the brain capillary endothelium and excludes from the brain 100% of large-molecule neurotherapeutics and more than 98% of all small-molecule drugs. Overcoming the difficulty of delivering therapeutic agents to specific regions of the brain presents a major challenge to treatment of most brain disorders. In its neuroprotective role, the blood–brain barrier functions to hinder the delivery of many potentially important diagnostic and therapeutic agents to the brain. Therapeutic molecules and antibodies that might otherwise be effective in diagnosis and therapy do not cross the BBB in adequate amounts to be clinically effective. The BBB represents an obstacle to some drugs reaching the brain, thus to overcome this barrier some peptides able to naturally cross the BBB have been widely investigated as a drug delivery system. Mechanisms for drug targeting in the brain involve going either "through" or "behind" the BBB. Modalities for drug delivery to the brain in unit doses through the BBB entail its disruption byosmotic
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region ...
means, or biochemically by the use of vasoactive substances, such as bradykinin
Bradykinin (BK) (Greek brady-, slow; -kinin, kīn(eîn) to move) is a peptide that promotes inflammation. It causes arterioles to dilate (enlarge) via the release of prostacyclin, nitric oxide, and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor an ...
, or even by localized exposure to high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU).
Other methods used to get through the BBB may entail the use of endogenous transport systems, including carrier-mediated transporters, such as glucose and amino acid carriers, receptor-mediated transcytosis for insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
or transferrin
Transferrins are glycoproteins found in vertebrates which bind to and consequently mediate the transport of iron (Fe) through blood plasma. They are produced in the liver and contain binding sites for two Fe3+ ions. Human transferrin is encod ...
, and the blocking of active efflux transporters such as p-glycoprotein. Some studies have shown that vectors targeting BBB transporters, such as the transferrin receptor, have been found to remain entrapped in brain endothelial cells of capillaries, instead of being ferried across the BBB into the targeted area.
Nanoparticles
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal ...
is under preliminary research for its potential to facilitate the transfer of drugs across the BBB. Capillary endothelial cells and associated pericytes
Pericytes (previously known as Rouget cells) are multi-functional mural cells of the microcirculation that wrap around the endothelial cells that line the capillaries throughout the body. Pericytes are embedded in the basement membrane of blood c ...
may be abnormal in tumors and the blood–brain barrier may not always be intact in brain tumors. Other factors, such as astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of ...
, may contribute to the resistance of brain tumors to therapy using nanoparticles. Fat soluble molecules less than 400 daltons in mass can freely diffuse past the BBB through lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
mediated passive diffusion.
Damage in injury and disease
The blood–brain barrier may become damaged in select neurological diseases, as indicated byneuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Incr ...
studies of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As ...
, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
, ischemic stroke, and brain trauma, and in systemic diseases, such as liver failure. Effects such as impaired glucose transport and endothelial degeneration may lead to metabolic dysfunction within the brain, and an increased permeability of the BBB to proinflammatory factors, potentially allowing antibiotics and phagocytes to move across the BBB.
Prediction
There have been many attempts to correlate the experimental blood brain barrier permeability, with physicochemical properties. The first QSAR study of brain–blood distribution was conducted in 1988, this study reported the in vivo values in rats for a large number of H2 receptor histamine agonists. The first papers trying to model blood brain barrier permeability, identified three properties, i.e., molecular volume, lipophilicity, and hydrogen bonding potential, as contributing significantly to the transport through the blood brain barrier. Two datasets, one with numerical logBB values (1058 molecules) and the one with categorical labels (7807 molecules with 4956 BBB+ and 2851 BBB−) have been published in 2021. The categorical dataset has been used in 2022 to select four different classification models based on molecular fingerprints, MACCS166 keys and molecular descriptors.History
In 1898, Arthur Biedl and R. Kraus observed that low-concentration "bile salts" failed to affect behavior when injected into the bloodstream of animals. Thus, in theory, they had failed to enter the brain. Two years later, Max Lewandowsky coined the term "Blood–brain barrier" in 1900, referring to the hypothesized semipermeable membrane (then termed hematoencephalic barrier). All the while,bacteriologist
A bacteriologist is a microbiologist, or similarly trained professional, in bacteriology -- a subdivision of microbiology that studies bacteria, typically pathogenic ones. Bacteriologists are interested in studying and learning about bacteria, ...
Paul Ehrlich was studying staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cells), and in th ...
, a procedure that is used in many microscopy studies to make fine biological structures visible using chemical dyes. As Ehrlich injected some of these dyes (notably the aniline dyes that were then widely used), the dye stained all of the organs of some kinds of animals except for their brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
s. At that time, Ehrlich attributed this lack of staining to the brain simply not picking up as much of the dye.
However, in a later experiment in 1913, Edwin Goldmann (one of Ehrlich's students) injected the dye directly into the cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
s of animal brains. He found then the brains did become dyed, but the rest of the body did not, demonstrating the existence of a compartmentalization between the two. At that time, it was thought that the blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide awa ...
s themselves were responsible for the barrier, since no obvious membrane could be found.
See also
* * *References
{{DEFAULTSORT:blood-brain Barrier Central nervous system Neurology Animal physiology Pharmacokinetics Brain Circulatory system