Blankenburg am Harz on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Blankenburg (Harz) is a
§ 15, April 2021. * Börnecke * Cattenstedt *

 The first traces of settlement date to the
The first traces of settlement date to the 
 The dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg turned the place into a secondary residence in the 17th century and it enjoyed its heyday under Duke Louis Rudolf (1690–1731), the second son of Anthony Ulrich of Wolfenbüttel. Rudolf was given Blankenburg in 1707 as a '' paragium''. At the same time the County of Blankenburg was elevated to the status of an imperial principality ('' Reichsfürstentum'') which was ruled independently until 1731, but then, because Louis Rudolf became a duke, was reunited with Brunswick where it remained. The present-day Little Castle with its terraced garden and Baroque pleasure garden stems from that period. From 1807 to 1813 Blankenburg belonged to the
The dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg turned the place into a secondary residence in the 17th century and it enjoyed its heyday under Duke Louis Rudolf (1690–1731), the second son of Anthony Ulrich of Wolfenbüttel. Rudolf was given Blankenburg in 1707 as a '' paragium''. At the same time the County of Blankenburg was elevated to the status of an imperial principality ('' Reichsfürstentum'') which was ruled independently until 1731, but then, because Louis Rudolf became a duke, was reunited with Brunswick where it remained. The present-day Little Castle with its terraced garden and Baroque pleasure garden stems from that period. From 1807 to 1813 Blankenburg belonged to the
 On 25 May 2009 the title ''Ort der Vielfalt'' ("Place of Variety") was conferred on the town by the federal government.
On 25 May 2009 the title ''Ort der Vielfalt'' ("Place of Variety") was conferred on the town by the federal government.


 * Above the town to the south on the hill of Blankenstein (334 m) is Blankenburg Castle
* The Little Castle (''Kleine Schloss'') with its Baroque gardens belongs to the network of Saxony-Anhalt Garden Dreams. The gardens are checkpoint 78 in the
* Above the town to the south on the hill of Blankenstein (334 m) is Blankenburg Castle
* The Little Castle (''Kleine Schloss'') with its Baroque gardens belongs to the network of Saxony-Anhalt Garden Dreams. The gardens are checkpoint 78 in the ''Stempelstelle 78 / Barocke Gärten''
at www.harzer-wandernadel.de. Retrieved 1 Nov 2017. * The town hall stems from the
 In the Great Castle is a theatre which is to be restored again.
In the Great Castle is a theatre which is to be restored again.
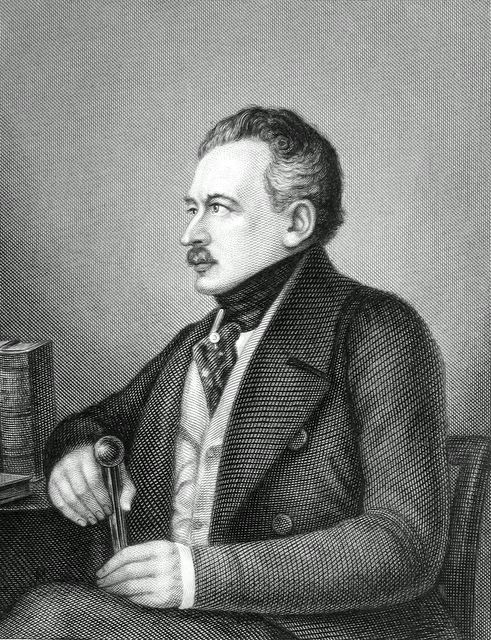 *
*
town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an ori ...
and health resort
A destination spa or health resort is a resort centered on a spa, such as a mineral spa. Historically, many such spas were developed at the location of natural hot springs or mineral springs; in the era before modern biochemical knowledge and ...
in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it th ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, at the north foot of the Harz Mountains
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German ...
, southwest of Halberstadt
Halberstadt ( Eastphalian: ''Halverstidde'') is a town in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt, the capital of Harz district. Located north of the Harz mountain range, it is known for its old town center that was greatly destroyed by Allied bomb ...
.
It has been in large part rebuilt since a fire in 1836, and possesses a castle, with various collections, a museum of antiquities, an old town hall and churches. There are pine-needle baths and a psychiatric hospital. Gardening is a speciality. The nearby ridge of rocks called the ''Teufelsmauer'' (Devils Wall) offers views across the plain and into the deep gorges of the Harz.
Geography
The town of Blankenburg (Harz) lies on the northern edge of theHarz mountains
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German ...
at a height of about 234 metres. It is located west of Quedlinburg
Quedlinburg () is a town situated just north of the Harz mountains, in the district of Harz in the west of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. As an influential and prosperous trading centre during the early Middle Ages, Quedlinburg became a center of in ...
, south of Halberstadt
Halberstadt ( Eastphalian: ''Halverstidde'') is a town in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt, the capital of Harz district. Located north of the Harz mountain range, it is known for its old town center that was greatly destroyed by Allied bomb ...
and east of Wernigerode
Wernigerode () is a town in the district of Harz, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Until 2007, it was the capital of the district of Wernigerode. Its population was 35,041 in 2012.
Wernigerode is located southwest of Halberstadt, and is picturesquely s ...
. The stream known as the Goldbach flows through the district of Oesig northwest of the town centre.
Divisions
The town Blankenburg (Harz) consists of Blankenburg proper and the following ''Ortschaften'' or municipal divisions:Hauptsatzung der Stadt Blankenburg (Harz)§ 15, April 2021. * Börnecke * Cattenstedt *
Derenburg
Derenburg is a town in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it has been part of the Blankenburg am Harz municipality.
Geography
The settlement is situated in the northern foothills of the Harz mountain range ...
* Heimburg
Heimburg is a village and a former municipality in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Blankenburg am Harz.
On a hilltop above the village are the ruins of the old Heimburg Castle which, ...
* Hüttenrode
Hüttenrode is a village and a former municipality in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Blankenburg am Harz
Blankenburg (Harz) is a town and health resort in the Harz (district), distr ...
* Timmenrode
Timmenrode is a village and a former municipality in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Blankenburg am Harz
Blankenburg (Harz) is a town and health resort in the Harz (district), distri ...
* Wienrode
Wienrode is a village and a former municipality in the Harz (district), district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Blankenburg am Harz.
Former municipalities in Saxony-Anhalt
Blankenburg (Harz)
Duc ...
In addition there are the following unofficial names for localities in the town:
* Gehren
* Helsungen
* Michaelstein
* Oesig
* Regenstein
* Sonnenbreite
Neighbouring settlements
Clockwise from the north: * Municipality of Nordharz * District town ofHalberstadt
Halberstadt ( Eastphalian: ''Halverstidde'') is a town in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt, the capital of Harz district. Located north of the Harz mountain range, it is known for its old town center that was greatly destroyed by Allied bomb ...
* Town of Thale
Thale () is a town in the Harz district in Saxony-Anhalt in central Germany. Located at the steep northeastern rim of the Harz mountain range, it is known for the scenic Bode Gorge stretching above the town centre.
Geography
The town is situated ...
* Municipality of Oberharz am Brocken
Oberharz am Brocken () is a town in the Harz District, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It was formed on 1 January 2010 by the merger of the town of Elbingerode with the municipalities of the former ''Verwaltungsgemeinschaft'' ("collective municipal ...
* Town of Wernigerode
Wernigerode () is a town in the district of Harz, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Until 2007, it was the capital of the district of Wernigerode. Its population was 35,041 in 2012.
Wernigerode is located southwest of Halberstadt, and is picturesquely s ...
History

 The first traces of settlement date to the
The first traces of settlement date to the Old Stone Age
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός '' palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
, but the first recorded mention of Blankenburg goes back to 1123. The Saxon duke, Lothair of Supplinburg, installed Poppo, a nephew of Bishop Reinhard of Halberstadt, as count at the castle, which stood on a bare limestone rock on the site of the present castle. The name of the town derives from this castle.
Count Poppo I of Blankenburg Blankenburg may refer to:
Places
* Blankenburg am Harz, a German town in the district of Harz, Saxony-Anhalt
* Blankenburg Castle (Harz), the castle in Blankenburg am Harz (see above)
* Bad Blankenburg, a German town in the Saalfeld-Rudolstadt dis ...
very probably came from the Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
noble family of Reginbodonen. His descendants were also subject to the nearby Regenstein Castle. This was a fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
from the Bishopric of Halberstadt
The Diocese of Halberstadt was a Roman Catholic diocese (german: Bistum Halberstadt) from 804 until 1648.
like the County of Blankenburg, also called the ''Hartingau''.
In 1180–82 Frederick Barbarossa had Blankenburg devastated because it had pledged "sole allegiance" to the Welf Welf is a Germanic first name that may refer to:
*Welf (father of Judith), 9th century Frankish count, father-in-law of Louis the Pious
*Welf I, d. bef. 876, count of Alpgau and Linzgau
*Welf II, Count of Swabia, died 1030, supposed descendant of W ...
, Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
. In 1386 Blankenburg suffered heavy destruction again.
Following the death of the last count of Regenstein
The County of Regenstein was a mediaeval State of the Holy Roman Empire, statelet of the Holy Roman Empire. It was ruled by the Duchy of Saxony, Saxon comital House of Regenstein, named after their residence at Regenstein Castle near Blankenburg (H ...
, John Ernest, the county went in 1599 as an agreed enfeoffment (') back to the dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg.
During the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
Blankenburg was hard pressed by Wallenstein
Albrecht Wenzel Eusebius von Wallenstein () (24 September 1583 – 25 February 1634), also von Waldstein ( cs, Albrecht Václav Eusebius z Valdštejna), was a Bohemian military leader and statesman who fought on the Catholic side during the Th ...
and was occupied in 1625. Nine cannonballs embedded in the walls of the town hall evince this difficult time.

 The dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg turned the place into a secondary residence in the 17th century and it enjoyed its heyday under Duke Louis Rudolf (1690–1731), the second son of Anthony Ulrich of Wolfenbüttel. Rudolf was given Blankenburg in 1707 as a '' paragium''. At the same time the County of Blankenburg was elevated to the status of an imperial principality ('' Reichsfürstentum'') which was ruled independently until 1731, but then, because Louis Rudolf became a duke, was reunited with Brunswick where it remained. The present-day Little Castle with its terraced garden and Baroque pleasure garden stems from that period. From 1807 to 1813 Blankenburg belonged to the
The dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg turned the place into a secondary residence in the 17th century and it enjoyed its heyday under Duke Louis Rudolf (1690–1731), the second son of Anthony Ulrich of Wolfenbüttel. Rudolf was given Blankenburg in 1707 as a '' paragium''. At the same time the County of Blankenburg was elevated to the status of an imperial principality ('' Reichsfürstentum'') which was ruled independently until 1731, but then, because Louis Rudolf became a duke, was reunited with Brunswick where it remained. The present-day Little Castle with its terraced garden and Baroque pleasure garden stems from that period. From 1807 to 1813 Blankenburg belonged to the Kingdom of Westphalia
The Kingdom of Westphalia was a kingdom in Germany, with a population of 2.6 million, that existed from 1807 to 1813. It included territory in Hesse and other parts of present-day Germany. While formally independent, it was a vassal state of the ...
.
In the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
the absolute neutrality of the town made it a safe refuge for the Brunswick court. Louis XVIII also stayed in Blankenburg under the name of Count of Lille
Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France region, the prefecture of the N ...
from 24 August 1796 to 10 February 1798, after his escape from Dillingen.
In the early days of Nazi era, those who opposed the Nazi regime were persecuted and murdered. In a notorious campaign by Brunswick SS commander, Jeckeln, in September 1933, 140 communists and social democrats were herded together in the inn, ''Zur Erholung''. Here and in the ''Blankenburger Hof'' they were severely beaten, some dying as a result. During the Second World War the Blankenburg-Oesig subcamp
Subcamps (german: KZ-Außenlager), also translated as satellite camps, were outlying detention centres (''Haftstätten'') that came under the command of a main concentration camp run by the SS in Nazi Germany and German-occupied Europe. The Nazi ...
of Buchenwald concentration camp was set up in the Dr. Dasch (Harzer Werke) Monastery Works and, shortly thereafter, subordinated to Mittelbau-Dora concentration camp
Mittelbau-Dora (also Dora-Mittelbau and Nordhausen-Dora) was a Nazi concentration camp located near Nordhausen in Thuringia, Germany. It was established in late summer 1943 as a subcamp of Buchenwald concentration camp, supplying slave labour f ...
. Here some 500 prisoners had to carry out forced labour in the monastery factory and Oda Works. In addition, there was a work camp run by the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
for "half-Jew
The term Halbjude (English: Half-Jew) is a derogatory term for people with a non-Jewish and a Jewish parent. The overwhelming majority of the so-called half-Jews were legally classified as " first-degree Jewish hybrids" during the era of Nazi Germ ...
s" who were forced to do hard labour. Another camp was occupied in February 1945 by inmates of the Auschwitz subcamp of Fürstengrube and managed as Blankenburg Regenstein subcamp.
As part of the division of Germany
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
* Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
* Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division
Military
* Division (military), a formation typically consisti ...
into occupation zones in 1945, Blankenburg district was actually assigned to the British zone in accordance with the Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
and London Protocol. But because the larger eastern part of the district was linked to the rest of the British zone only by a road and a railway, the boundary was adjusted and Blankenburg incorporated into the Soviet zone. The largest part of the district thus ended up later in East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
and became part of the state of Saxony-Anhalt. The main part of the former Free State of Brunswick
The Free State of Brunswick () was a state of the German Reich in the time of the Weimar Republic. It was formed after the abolition of the Duchy of Brunswick in the course of the German Revolution of 1918–19. Its capital was Braunschweig (Bru ...
went to the British zone and thus became part of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
.
The tunnels of the Regenstein-Blankenburg facility were used from 1974 by the National People's Army
The National People's Army (german: Nationale Volksarmee, ; NVA ) were the armed forces of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) from 1956 to 1990.
The NVA was organized into four branches: the (Ground Forces), the (Navy), the (Air Force) a ...
(NVA) in the GDR as a large ammunition depot. In 1992 the Bundeswehr
The ''Bundeswehr'' (, meaning literally: ''Federal Defence'') is the armed forces of the Federal Republic of Germany. The ''Bundeswehr'' is divided into a military part (armed forces or ''Streitkräfte'') and a civil part, the military part con ...
were given the 8 km long tunnel system and established there, "the largest underground pharmacy in the world", both for routine Bundeswehr missions, but also for disaster relief around the world and for cases of serious military "operations".
On 1 January 2010 the town Blankenburg absorbed the former municipalities Cattenstedt, Derenburg
Derenburg is a town in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it has been part of the Blankenburg am Harz municipality.
Geography
The settlement is situated in the northern foothills of the Harz mountain range ...
, Heimburg
Heimburg is a village and a former municipality in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Blankenburg am Harz.
On a hilltop above the village are the ruins of the old Heimburg Castle which, ...
, Hüttenrode
Hüttenrode is a village and a former municipality in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Blankenburg am Harz
Blankenburg (Harz) is a town and health resort in the Harz (district), distr ...
, Timmenrode
Timmenrode is a village and a former municipality in the district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Blankenburg am Harz
Blankenburg (Harz) is a town and health resort in the Harz (district), distri ...
and Wienrode
Wienrode is a village and a former municipality in the Harz (district), district of Harz, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Blankenburg am Harz.
Former municipalities in Saxony-Anhalt
Blankenburg (Harz)
Duc ...
.
Jewish life in Blankenburg
At end of the 12th century, the abbess of Quedlinburg pledged estates to Blankenburg Jews. These appear at the time to have been both in Blankenburg and in Quedlinburg. Whether there was a synagogue in Blankenburg in the Middle Ages, is not clear. In modern times, there was no longer a synagogue in Blankenburg. On Saturdays several Jewish families met at ''Chrons'' for the Sabbath, including the families of the businessmen Alexander Meyer, Moritz Westfeld and Conrad Hesse, as well as Anna Ewh and Lydia Rhynarsewsky. In the wake of ''Kristallnacht
() or the Night of Broken Glass, also called the November pogrom(s) (german: Novemberpogrome, ), was a pogrom against Jews carried out by the Nazi Party's (SA) paramilitary and (SS) paramilitary forces along with some participation fro ...
'' on 9 November 1938, Jews were deported from Blankenburg to different camps. In the census on 17 May 1939 there were still twelve Jewish citizens registered, including five men.
Politics
 On 25 May 2009 the title ''Ort der Vielfalt'' ("Place of Variety") was conferred on the town by the federal government.
On 25 May 2009 the title ''Ort der Vielfalt'' ("Place of Variety") was conferred on the town by the federal government.
Town council
Since the local elections on 11 April 2010 the town council has been composed as follows: * CDU: 10 seats * The Left: 5 seats * Wählergruppe Pro Blankenburg: 3 seats *SPD
The Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, ; SPD, ) is a centre-left social democratic political party in Germany. It is one of the major parties of contemporary Germany.
Saskia Esken has been t ...
: 3 seats
* FDP: 2 seats
* Wählergemeinschaft für umweltfreundliche Landwirtschaft Derenburg WUL: 2 seats
* Wählergemeinschaft Timmenrode WGT: 2 seats
* Bürgeraktiv Wienrode BAW: 2 seats
* Interessengemeinschaft Pro Heimburg IGPH: 1 seat
* Gemeinsam für Kinder und Jugendliche /IG Kultur Derenburg GfKJ/IG-K: 1 seat
* Freiwillige Feuerwehr Derenburg: 1 seat
* Freie Wählergemeinschaft Harz FWH: 1 seat
* Einzelbewerber Frank Schade: 1 seat
* Wählergemeinschaft Cattenstedt WGC: 1 seat
* Alliance '90/The Greens: 1 seat
Economy and infrastructure
The most important economic factors for Blankenburg (Harz) are tourism and facilities for spa and health industry. In addition there are several small to medium sized businesses. The largest industrial concern in the town is the ''Harzer Werke Motorentechnik'' with about 60 employees, which grew out of a grey iron foundry founded in about 1870.Transport


Blankenburg (Harz) station
Blankenburg (Harz) station is the most important station in Blankenburg in the Saxony-Anhalt district of Harz in central Germany.
Location
The station lies in the north of the town. Whilst this simplified its accessibility from Halberstadt to t ...
is a terminus
Terminus may refer to:
* Bus terminus, a bus station serving as an end destination
* Terminal train station or terminus, a railway station serving as an end destination
Geography
*Terminus, the unofficial original name of Atlanta, Georgia, United ...
and has a bypass for goods traffic. There are connexions to Elbingerode (Rübeland Railway) (goods trains only) and Halberstadt
Halberstadt ( Eastphalian: ''Halverstidde'') is a town in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt, the capital of Harz district. Located north of the Harz mountain range, it is known for its old town center that was greatly destroyed by Allied bomb ...
. The Harz-Elbe Express has worked the line to Halberstadt since 15 December 2005. In the 20th century there was a line to Thale and Quedlinburg.
Blankenburg (Harz) is located next to the B 6n, a newly built dual carriageway, and is linked to it over two junctions: Blankenburg Ost and Blankenburg Zentrum. In addition the B 27 federal road runs southwest and the B 81 north to south through Blankenburg (Harz).
Educational establishments
* Primary schools: Am Regenstein Primary School, Martin Luther School * Secondary schools: August Bebel School, Heinrich Heine School * Grammar school: Gymnasium Am Thie * Yamaha Music School, SchickerLeisure and sports facilities
* Sportforum * "Am Thie" open-air swimming poolCulture and places of interest
 * Above the town to the south on the hill of Blankenstein (334 m) is Blankenburg Castle
* The Little Castle (''Kleine Schloss'') with its Baroque gardens belongs to the network of Saxony-Anhalt Garden Dreams. The gardens are checkpoint 78 in the
* Above the town to the south on the hill of Blankenstein (334 m) is Blankenburg Castle
* The Little Castle (''Kleine Schloss'') with its Baroque gardens belongs to the network of Saxony-Anhalt Garden Dreams. The gardens are checkpoint 78 in the Harzer Wandernadel
The Harzer Wandernadel is a system of hiking awards in the Harz mountains in central Germany. The hiker (or mountain biker) can earn awards at different levels of challenge by walking to the various checkpoints in the network and stamping his or ...
hiking network.at www.harzer-wandernadel.de. Retrieved 1 Nov 2017. * The town hall stems from the
renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
period (internally older, later converted).
* Above the town hall is the medieval parish church of St. Bartholomew. In the tower and the chancel of the church there are late Romanesque section of wall from around 1200. The statues of benefactors in the chancel, probably around 1300, belong to the other successors of the Naumburg benefactors' statues.
* The town has picturesque villas from the turn of the 20th century.
* Also worth seeing are the historic gardens (Baroque garden, castle park, pheasant garden, animal park).
* On the edge of the town lies the former robber baron castle and fortress of Regenstein
The County of Regenstein was a mediaeval State of the Holy Roman Empire, statelet of the Holy Roman Empire. It was ruled by the Duchy of Saxony, Saxon comital House of Regenstein, named after their residence at Regenstein Castle near Blankenburg (H ...
.
* Regenstein Mill (''Regenstein-Mühle'') in the woods west of Regenstein Castle, an old mill with water channels carved out of the rock (Harzer Wandernadel
The Harzer Wandernadel is a system of hiking awards in the Harz mountains in central Germany. The hiker (or mountain biker) can earn awards at different levels of challenge by walking to the various checkpoints in the network and stamping his or ...
checkpoint no. 82).
* The Teufelsmauer
The Teufelsmauer (''Devil's Wall'') is a rock formation made of hard sandstones of the Upper Cretaceous in the northern part of the Harz Foreland in central Germany. This wall of rock runs from Blankenburg (Harz) via Weddersleben and Rieder ...
(''Devil's Wall''), a bizarre sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
rock formation and geological natural monument
A natural monument is a natural or natural/cultural feature of outstanding or unique value because of its inherent rarity, representative of aesthetic qualities or cultural significance.
Under World Commission on Protected Areas guidelines, na ...
* The Ziegenkopf ridge and nature reserve.
* Remains of the Luisenburg castle.
* The sand caves of Sandhöhlen im Heers in the woods below Regenstein Castle which are also thought to be a Germanic cult site or thingstead (Harzer Wandernadel
The Harzer Wandernadel is a system of hiking awards in the Harz mountains in central Germany. The hiker (or mountain biker) can earn awards at different levels of challenge by walking to the various checkpoints in the network and stamping his or ...
checkpoint no. 81).
Theatre
 In the Great Castle is a theatre which is to be restored again.
In the Great Castle is a theatre which is to be restored again.
Museums
* The town museum for Blankenburg (Harz) is in the Little Castle, the former ducal ''Lustschloss
In Renaissance and Early Modern German architecture, a ''Lustschloss'' (french: maison de plaisance, both equating in English to "pleasure castle/house") is a small country house or palace which served the private pleasure of its owner, usuall ...
''
* Unique in Germany is the hostel museum. It contains a large collection of items, as well as a library of craft work.
* In addition there is Michaelstein Abbey with its herb garden and instrument museum.
Buildings
* Great Castle * Little Castle * Town hall * Church of St. Bartholomew * Michaelstein Abbey * Ruins of Regenstein Castle * Wilhelm Raabe Tower west of Blankenburg (Harz) on the EichenbergHistorical monuments
* Memorial grove forconcentration camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simpl ...
prisoners and forced labourers of various nationalities at the levelled cemetery of ''Alten Friedhof'' on ''Lühner-Tor-Platz''
* Monument stone in memory of the concentration camp inmates of the subcamp
Subcamps (german: KZ-Außenlager), also translated as satellite camps, were outlying detention centres (''Haftstätten'') that came under the command of a main concentration camp run by the SS in Nazi Germany and German-occupied Europe. The Nazi ...
near the present-day ''Diesterweg School'' in the district of ''Oesig''
* Memorial board in ''Mauerstraße 14'' to the sentencing of 63 anti-fascists in September 1933
Regular events
* Viking Festival (Easter) * Country- and Trucker Festival * Knight's Tournament (in July) * Abbey Festival * Historic weekends (railways and markets; baroque castle gardens and parks) * Michaelstein Abbey concerts (all year) * Sternthal Christmas marketNotable people
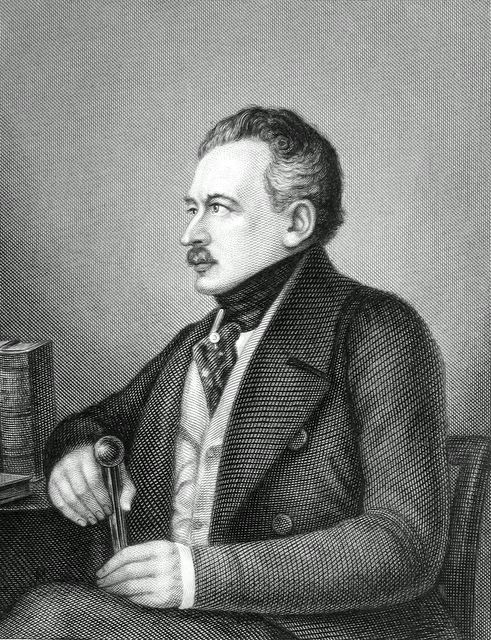 *
*Joseph von Radowitz
Joseph Maria Ernst Christian Wilhelm von Radowitz (6 February 1797 – 25 December 1853) was a conservative Prussian statesman and general famous for his proposal to unify Germany under Prussian leadership by means of a negotiated agreemen ...
, (1797-1853), general
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
and politician
A politician is a person active in party politics, or a person holding or seeking an elected office in government. Politicians propose, support, reject and create laws that govern the land and by an extension of its people. Broadly speaking ...
* Adolph von Steinwehr
Baron Adolph Wilhelm August Friedrich von Steinwehr (September 25, 1822 – February 25, 1877) was a German-Brunswick army officer who emigrated to the United States, became a geographer, cartographer, and author, and served as a Union general ...
(1822-1877), geographer, cartographer, brigadier general in the American Civil War (Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
)
*Julius Elster Julius Johann Phillipp Ludwig Elster (24 December 1854 in Blankenburg – 6 April 1920) was a teacher and physicist.
Biography
Elster and Hans Friedrich Geitel, the son of a Forester, Forstmeister who had moved to Bad Blankenburg, Blankenburg with ...
(1854-1920), physicist
*Robert Koldewey
Robert Johann Koldewey (10 September 1855 – 4 February 1925) was a German archaeologist, famous for his in-depth excavation of the ancient city of Babylon in modern-day Iraq. He was born in Blankenburg am Harz in Germany, the duchy of Brunswick, ...
, (1855-1925), architect
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
and archaeologist
*Oswald Spengler
Oswald Arnold Gottfried Spengler (; 29 May 1880 – 8 May 1936) was a German historian and philosopher of history whose interests included mathematics, science, and art, as well as their relation to his organic theory of history. He is best kno ...
, philosopher, (1880-1936) (The Decline of the West
''The Decline of the West'' (german: Der Untergang des Abendlandes; more literally, ''The Downfall of the Occident''), is a two-volume work by Oswald Spengler. The first volume, subtitled ''Form and Actuality'', was published in the summer of 19 ...
)
* Joachim Albrecht Eggeling, (1884-1945), Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
Gauleiter
A ''Gauleiter'' () was a regional leader of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) who served as the head of a '' Gau'' or '' Reichsgau''. ''Gauleiter'' was the third-highest rank in the Nazi political leadership, subordinate only to '' Reichsleiter'' and to ...
*Kurt Ranke
Kurt Ranke (14 April 1908 – 6 June 1985) was a German ethnologist who specialized in the study of fairy tales.
Biography
Kurt Ranke was born in Blankenburg, Germany on 14 April 1908. His father was a postal inspector. Growing up in Essen, Ranke ...
(1908-1985), folklorist, Germanist, antiquarian and narrative researcher
*Polykarp Kusch
Polykarp Kusch (January 26, 1911 – March 20, 1993) was a German-born American physicist. In 1955, the Nobel Committee gave a divided Nobel Prize for Physics, with one half going to Kusch for his accurate determination that the magnetic momen ...
, (1911-1993), co-recipient of the Nobel Prize for Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
in 1955
*Frederica of Hanover
Frederica of Hanover (''Friederike Luise''; ; 18 April 1917 – 6 February 1981) was Queen consort of Greece from 1947 until 1964 as the wife of King Paul, thereafter Queen mother during the reign of her son, King Constantine II.
Early life
...
, (1917-1981), queen consort of Paul of Greece
Paul ( el, Παύλος, ''Pávlos''; 14 December 1901 – 6 March 1964) was King of Greece from 1 April 1947 until his death in 1964. He was succeeded by his son, Constantine II.
Paul was first cousin to Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh an ...
*Susi Erdmann
Susi-Lisa Erdmann (later Plankensteiner, born 29 January 1968) is an East German-German luger and bobsledder who competed from 1977 to 1998 in luge, then since 1999 in bobsleigh. She was born in Blankenburg, Bezirk Magdeburg. Competing in five W ...
(born 1968), bob driver
* Christian Lademann (born 1975), cyclist
*Subaru Kimura
, known professionally as , is a German-Japanese actor and rapper. His best-known role is voicing Takeshi Goda in the ''Doraemon'' series, which has spawned numerous specials.
Biography
Kimura was born in Blankenburg (Harz) and raised in Japan ...
(born 1990), German-Japanese actor
Twin town
*Herdecke
Herdecke () is a town in the district of Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis, North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. It is located south of Dortmund in the Ruhr Area. Its location between the two Ruhr reservoirs Hengsteysee and Harkortsee has earned it the nickname ...
, North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inha ...
* Meerbusch
Meerbusch () is a town in Rhein-Kreis Neuss, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It has been an incorporated town since 1970. Meerbusch is the municipality with the most income millionaires in North Rhine-Westphalia.
Geography
Meerbusch is a town in ...
, North Rhine-Westphalia
* Wolfenbüttel
Wolfenbüttel (; nds, Wulfenbüddel) is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany, the administrative capital of Wolfenbüttel District. It is best known as the location of the internationally renowned Herzog August Library and for having the largest ...
, Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
* Georgsmarienhütte
Georgsmarienhütte () is a town in the district of Osnabrück, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated in the Teutoburg Forest, approx. 7 km south of Osnabrück.
History
In 1856 the company "Georgs-Marien-Bergwerks- und Hüttenverein" wa ...
, Lower Saxony
See also
*County of Blankenburg
The County of Blankenburg (german: Grafschaft Blankenburg) was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. Its capital was Blankenburg, it was located in and near the Harz mountains.
History
County of Blankenburg
About 1123 Lothair of Supplinburg, then D ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Blankenburg Am Harz Towns in the Harz 1120s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1123 establishments in Europe Populated places established in the 12th century Holocaust locations in Germany Duchy of Brunswick