Blagoveshchensk on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Blagoveshchensk ( rus, Благове́щенск, p=bləgɐˈvʲeɕːɪnsk, meaning ''City of the Annunciation'') is a
(Amur Oblast - the History. The peoples of the Amur Land)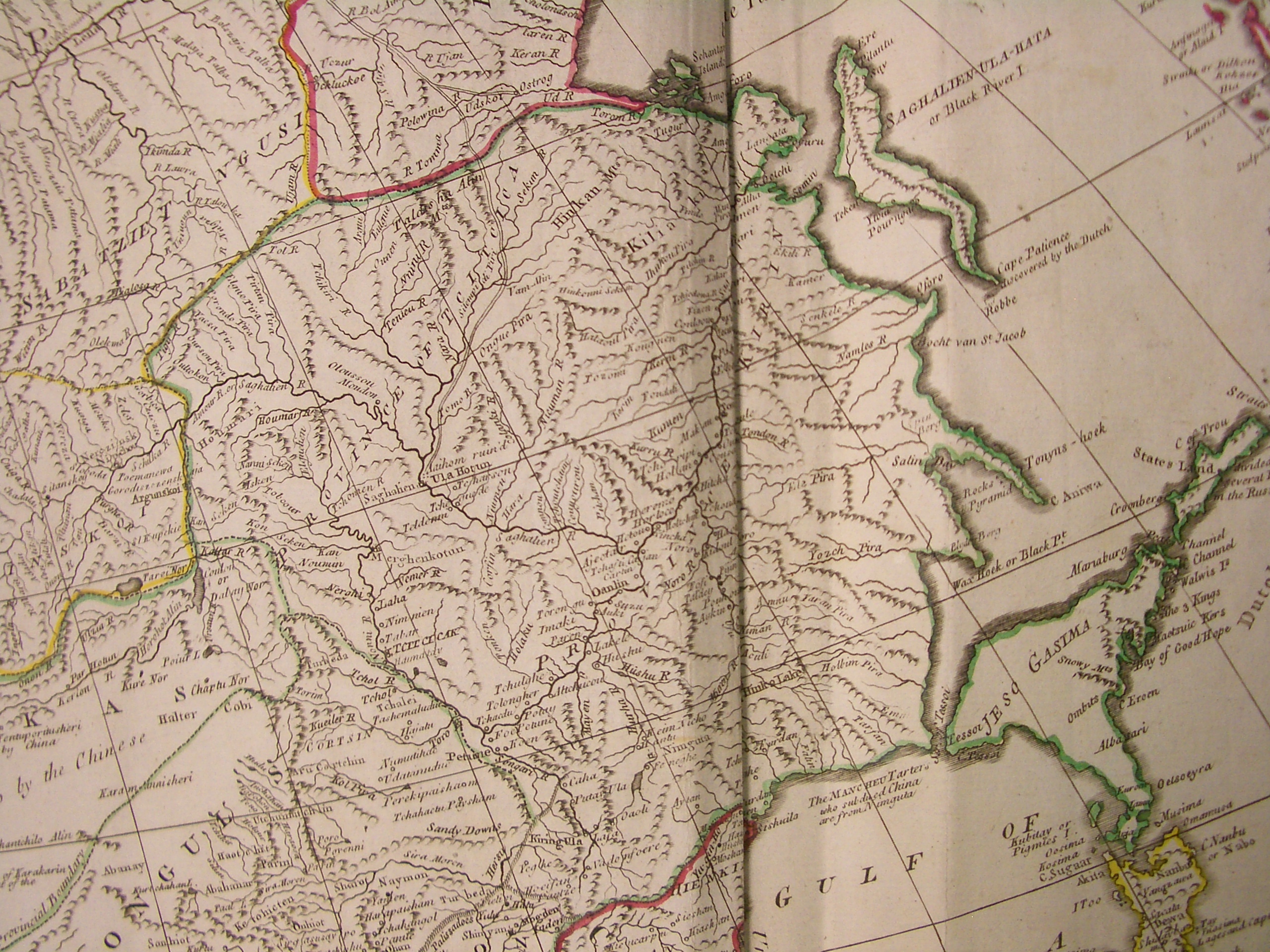 As the Russians tried to assert their control over the region, the Ducher town was probably vacated when the Duchers were evacuated by the
As the Russians tried to assert their control over the region, the Ducher town was probably vacated when the Duchers were evacuated by the
"Российско-китайские отношения в Приамурье (сер. XIX – нач. XX вв.)"
(''Russian-Chinese relations in the Amur region, mid-19th - early 20th centuries''). Part 1. Blagoveshchensk, 2003. which served in 1683-1685 as a base for the Manchus' campaign against the Russian fort of Albazin further north. After the capture of Albazin in 1685 or 1686, the Chinese relocated their town, to a new site on the right (southwestern, i.e. presently Chinese) bank of the Amur, about downstream from the original site; it later became known as
The Russians on the Amur
'. London (1861), pg. 48. The series of conflicts between Russians and China ended with Russia's recognition of the Chinese sovereignty over both sides of the Amur by the
 Although Russian settlers had lived in the area as early as 1644 and was known as ()., the present-day city began in 1856 as the military outpost of ''Ust-Zeysky''; this name means ''settlement at the mouth of the Zeya River'' in Russian.
Although Russian settlers had lived in the area as early as 1644 and was known as ()., the present-day city began in 1856 as the military outpost of ''Ust-Zeysky''; this name means ''settlement at the mouth of the Zeya River'' in Russian.
 Blagoveshchensk is the
Blagoveshchensk is the
Blagoveshchensk and Heihe partner cities
Official website of Blagoveshchensk
Blagoveshchensk Business Directory
Video: Tornado in Blagoveshchensk, July 31, 2011
{{Authority control Amur Oblast (Russian Empire) Russian Far East China–Russia border crossings Populated places established in 1856 1856 establishments in China
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
and the administrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ...
of Amur Oblast
Amur Oblast ( rus, Аму́рская о́бласть, r=Amurskaya oblast, p=ɐˈmurskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers in the Russian Far East. The administrat ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
. It is located at the confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
of the Amur
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China (Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
and the Zeya Rivers, opposite to the Chinese city of Heihe
Heihe (; ; Russian: Хэйхэ) is a prefecture-level city of northern Heilongjiang province, China, located on the Russian border, on the south bank of the Amur (Heilong) River, across the river from Blagoveshchensk. At the 2020 census, 1 ...
. Population:
The Amur has formed Russia's border with China since the 1858 Aigun Treaty and the 1860 Treaty of Peking
The Convention of Peking or First Convention of Peking is an agreement comprising three distinct treaties concluded between the Qing dynasty of China and Great Britain, France, and the Russian Empire in 1860. In China, they are regarded as ...
. The area north of the Amur belonged to the Manchu Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
by the Treaty of Nerchinsk
The Treaty of Nerchinsk () of 1689 was the first treaty between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing dynasty of China. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as far as the Stanovoy Range and kept the area between the Argun River ...
of 1689 until it was ceded to Russia by the Aigun Treaty in 1858.
History
Early history of the region
The early residents of both sides of the Amur in the region of today's Blagoveshchensk were theDaurs
The Daur people (Khalkha Mongolian: Дагуур, ''Daguur''; ) are a Mongolic people in Northeast China. The Daur form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognised in the People's Republic of China. They numbered 131,992 according to the la ...
and Duchers. An early settlement in the area of today's Blagoveshchensk was the Ducher town whose name was reported by the Russian explorer Yerofey Khabarov as Aytyun in 1652, as Aigun from 1683 to 1685, and as Aigun Old Town from 1685 until the massacre in 1900, which known to Russian archaeologists as the Grodekovo site, after the nearby village of Grodekovo some southeast of Blagoveshchensk. The Grodekovo site is thought by archaeologists to have been populated since ca. 1000 CE.Амурская область: История. Народы Амурской земли(Amur Oblast - the History. The peoples of the Amur Land)
 As the Russians tried to assert their control over the region, the Ducher town was probably vacated when the Duchers were evacuated by the
As the Russians tried to assert their control over the region, the Ducher town was probably vacated when the Duchers were evacuated by the Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
to the Sungari
The Songhua or Sunghwa River (also Haixi or Xingal, russian: Сунгари ''Sungari'') is one of the primary rivers of China, and the longest tributary of the Amur. It flows about from the Changbai Mountains on the China–North Korea bor ...
or Hurka in the mid-1650s. Since 1673, the Chinese re-used the site for their fort ("Old Aigun", in modern literature),Олег Анатольевич Тимофеев (Oleg Anatolyevich Timofeyev)"Российско-китайские отношения в Приамурье (сер. XIX – нач. XX вв.)"
(''Russian-Chinese relations in the Amur region, mid-19th - early 20th centuries''). Part 1. Blagoveshchensk, 2003. which served in 1683-1685 as a base for the Manchus' campaign against the Russian fort of Albazin further north. After the capture of Albazin in 1685 or 1686, the Chinese relocated their town, to a new site on the right (southwestern, i.e. presently Chinese) bank of the Amur, about downstream from the original site; it later became known as
Aigun
Aigun (; Manchu language, Manchu: ''aihūn hoton''; ) was a historic China, Chinese Town (China), town in northern Manchuria, situated on the right bank of the Amur River, some south (downstream) from the central urban area of Heihe (which is a ...
. E. G. Ravenstein, The Russians on the Amur
'. London (1861), pg. 48. The series of conflicts between Russians and China ended with Russia's recognition of the Chinese sovereignty over both sides of the Amur by the
Nerchinsk Treaty
The Treaty of Nerchinsk () of 1689 was the first treaty between the Tsardom of Russia and the Qing dynasty of China. The Russians gave up the area north of the Amur River as far as the Stanovoy Range and kept the area between the Argun River ...
of 1689.
Russian settlement
As the balance of power in the region had changed by the mid-19th century, theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
was able to take over the left (generally northern, but around Blagoveshchensk, eastern) bank of the Amur from China. Since the 1858 Aigun Treaty and the 1860 Treaty of Peking
The Convention of Peking or First Convention of Peking is an agreement comprising three distinct treaties concluded between the Qing dynasty of China and Great Britain, France, and the Russian Empire in 1860. In China, they are regarded as ...
, the river has remained the border between the countries, although the Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
subjects were allowed to continue to live in the so-called Sixty-Four Villages east of the Amur and the Zeya (i.e., within today's Blagoveshchensk's eastern suburbs).
 Although Russian settlers had lived in the area as early as 1644 and was known as ()., the present-day city began in 1856 as the military outpost of ''Ust-Zeysky''; this name means ''settlement at the mouth of the Zeya River'' in Russian.
Although Russian settlers had lived in the area as early as 1644 and was known as ()., the present-day city began in 1856 as the military outpost of ''Ust-Zeysky''; this name means ''settlement at the mouth of the Zeya River'' in Russian. Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
Alexander II gave approval for the founding of the city in 1858 as the seat of government for the Amur region, to be named Blagoveshchensk (literally "the city of good news") after the parish church which was dedicated to the Annunciation
The Annunciation (from Latin '), also referred to as the Annunciation to the Blessed Virgin Mary, the Annunciation of Our Lady, or the Annunciation of the Lord, is the Christian celebration of the biblical tale of the announcement by the ang ...
. According to Blagoveshchensk authorities, by 1877 the city had some 8,000 residents, with merely 15 foreigners (presumably, Chinese) among them.
The city was an important river port and trade center during the late 19th century, with growth further fueled by a gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
rush early in the 20th century and by its position on the Chinese border opposite the city of Heihe
Heihe (; ; Russian: Хэйхэ) is a prefecture-level city of northern Heilongjiang province, China, located on the Russian border, on the south bank of the Amur (Heilong) River, across the river from Blagoveshchensk. At the 2020 census, 1 ...
.
Local historians noted the pre-eminence of Blagoveshchensk in the economy of the late 19th century Russian Far East
The Russian Far East (russian: Дальний Восток России, r=Dal'niy Vostok Rossii, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in Northeast Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent; and is admin ...
, which was reflected when the heir to the Russian throne, Nicholas Alexandrovich
Nicholas Alexandrovich (russian: Николай Александрович; – ) was tsesarevich—the heir apparent—of Imperial Russia from 2 March 1855 until his death in 1865.
Early life
Grand Duke Nicholas was born on 1843, in ...
(the future Tsar Nicholas II), visited in 1891 during his grand tour of Asiatic Russia, and the locals presented him with bread and salt
Bread and salt is a welcome greeting ceremony in some Slavic, Nordic, Baltic, Balkan and other European cultures as well as in Middle Eastern cultures. It is also shared with some non-Slavic nations—Lithuanians, Latvians (both Baltic), Rom ...
on a gold tray, rather than on a silver one as in other cities of the region.
The Boxer Rebellion
In the course of theBoxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an Xenophobia, anti-foreign, anti-colonialism, anti-colonial, and Persecution of Christians#China, anti-Christian uprising in China ...
, the Qing Imperial army (made out of Manchus and Han Chinese) and Boxer insurgents shelled the city in July 1900. Chinese Honghuzi forces joined the attack against Blagoveshchensk. According to the Orthodox belief, the city was allegedly saved by a miraculous icon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. They are not simply artworks; "an icon is a sacred image used in religious devotion". The mos ...
of Our Lady of Albazin, which was prayed to continuously during the shelling which lasted almost two weeks.
On 3 July (Old Style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, this is the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various European countries between 158 ...
), a decision was made by the city's Police Chief Batarevich and the Military Governor Gribsky to deport the city's entire community of Qing subjects including ethnic Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
, Daur people and Han, numbering 4,008), who were viewed as potential fifth columnists. As cross-river shipping was interrupted by the rebellion, the question arose how to get them from the Russian to the Chinese side of the Amur. Batarevich suggested that the deportees could be first taken east of the Zeya
Zeya may refer to:
People
*Aung Zeya, full name of Alaungpaya, king of Burma in 1752–1760
* Zeya (Burmese actor) (1916–1996), Burmese actor and director
*Zeya Thaw (born 1981), alternative spelling of the name of Zayar Thaw, Burmese politici ...
, where they should obtain boats from the local Chinese villagers. The plan, however, was vetoed by the governor, and the decision was made instead to take the deportees to the ''stanitsa
A stanitsa ( rus, станица, p=stɐˈnʲitsə; uk, станиця, stanytsya) is a village inside a Cossack host ( uk, військо, viys’ko; russian: казачье войско, kazach’ye voysko, sometimes translated as "Cossack Ar ...
'' of Verkhneblagoveshchenskaya—the place where the Amur is at its narrowest—and make them leave Russia there. As the local ''ataman
Ataman (variants: ''otaman'', ''wataman'', ''vataman''; Russian: атаман, uk, отаман) was a title of Cossack and haidamak leaders of various kinds. In the Russian Empire, the term was the official title of the supreme military command ...
'' refused to provide boats to take them across the river (despite the orders of his superior), few of them made it to the Chinese side. The rest drowned in the Amur, or were shot or axed by the police, Cossacks and local volunteers, when refusing to leave the bank. Local Chinese memory holds that a massacre that took place then, at the hand of Cossacks, which killed so many that the Amur River was choked.According to Chinese sources, about 5,000 people reportedly died during these events of 4-8 July 1900.
There were 1,266 households in the city, including 900 Daurs and 4,500 Manchus until the massacre. Many Manchu villages were burned by Cossacks in the massacre according to Victor Zatsepine.
This expulsion of the local Chinese caused some hardships for Blagoveshchensk consumers. For example, during the second half of 1900 it became almost impossible to buy any green vegetables in the town, and ten eggs would cost 30-50 kopecks (and in winter, as much as a rouble), while before it had been possible to buy ten eggs for 10-15 kopecks.
The massacre angered the Chinese, and had ramifications for the future: the Chinese Honghuzi fought a guerilla war against Russian occupation and assisted the Japanese in the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
against the Russians in revenge. Louis Livingston Seaman mentioned the massacre as being the reason for the Chinese Honghuzi hatred towards the Russians:The Chinaman, be he Hung-hutze or peasant, in his relation to the Russians in this conflict with Japan has not forgotten the terrible treatment accorded him since the Muscovite occupation of Manchuria. He still remembers the massacre at Blagovestchensk when nearly 8,000 unarmed men, women, and children were driven at the point of the bayonet into the raging Amur, until — as one of the Russian officers who participated in that brutal murder told me at Chin-Wang-Tao in 1900 — "the execution of my orders made me almost sick, for it seemed as though I could have walked across the river on the bodies of the floating dead." Not a Chinaman escaped, except forty who were employed by a leading foreign merchant who ransomed their lives at a thousand roubles each. These, and many even worse, atrocities are remembered and now is their moment for revenge. So it was easy for Japan to enlist the sympathy of these men, especially when emphasized by liberal pay, as is now the case. It is believed that more than 10,000 of these bandits, divided into companies of from 200 to 300 each and led by Japanese officers, are now in the pay of Japan.
Civil war and the Soviet era
The city was also the site of conflict during theRussian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, with Japanese troops occupying the city in support of the White Army
The White Army (russian: Белая армия, Belaya armiya) or White Guard (russian: Бѣлая гвардія/Белая гвардия, Belaya gvardiya, label=none), also referred to as the Whites or White Guardsmen (russian: Бѣлогв� ...
. From 1920 until 1922, the city was declared part of the Far Eastern Republic
The Far Eastern Republic ( rus, Дальневосто́чная Респу́блика, ДВР, r=Dalnevostochnaya Respublika, DVR, p=dəlʲnʲɪvɐˈstotɕnəjə rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə), sometimes called the Chita Republic, was a nominally indep ...
, an area which was nominally independent, but in reality a buffer zone under control of the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
. The city became the administrative center of Amur Oblast
Amur Oblast ( rus, Аму́рская о́бласть, r=Amurskaya oblast, p=ɐˈmurskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers in the Russian Far East. The administrat ...
in 1932.
During the Cultural Revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goa ...
in China, the city was subject to Maoist
Maoism, officially called Mao Zedong Thought by the Chinese Communist Party, is a variety of Marxism–Leninism that Mao Zedong developed to realise a socialist revolution in the agricultural, pre-industrial society of the Republic of Ch ...
propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
blasted from loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A ''speaker system'', also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or ...
s across the river 24 hours a day.
Administrative and municipal status
 Blagoveshchensk is the
Blagoveshchensk is the administrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ...
of the oblast
An oblast (; ; Cyrillic (in most languages, including Russian and Ukrainian): , Bulgarian: ) is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Ukraine, as well as the Soviet Union and the Kingdo ...
Law #127-OZ and, within the framework of administrative divisions, it also serves as the administrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ...
of Blagoveshchensky District
Blagoveshchensky District is the name of several administrative and municipal districts in Russia. The name is generally derived from or related to the root "blagovesheniye" ( good news).
* Blagoveshchensky District, Altai Krai, an administrat ...
,Law #51-OZ even though it is not a part of it. As an administrative division, it is, together with six rural localities, incorporated separately as Blagoveshchensk Urban Okrug—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions ...
. As a municipal division, this administrative unit also has urban okrug status.Law #447-OZ
Politics
In July 2013, a public hearing was held at which citizens declared themselves to be in favor of a return to the direct election of the mayor. A meeting of deputies voted for rejection of the "two-headed" management. In September 2013, City Council voted for a return to theClimate
Blagoveschensk experiences a monsoon-influenced hot-summer humid continental climate ( Köppen ''Dwa''), bordering on a monsoon-influenced warm-summer humid continental climate (''Dwb'') which it had before 1990. The city features frigid, windy, but dry winters due to the influence of theSiberian high
The Siberian High (also Siberian Anticyclone; russian: Азиатский антициклон (''Aziatsky antitsiklon'')) is a massive collection of cold dry air that accumulates in the northeastern part of Eurasia from September until April. It ...
, and warm, wet summers, due to the East Asian monsoon
The East Asian Monsoon is a monsoonal flow that carries moist air from the Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean to East Asia. It affects approximately one-third of the global population, influencing the climate of Japan, the Korean Peninsula, Taiwan, C ...
. On 1 August 2011, it became the first city in the Russian Far East
The Russian Far East (russian: Дальний Восток России, r=Dal'niy Vostok Rossii, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in Northeast Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent; and is admin ...
to be hit by a tornado.
Economy
Since thedissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
, the city's economic focus has turned to border trade with China. The town is now home to a large Chinese expatriate community. Blagoveshchensk is part of a free trade zone which includes the Chinese city of Heihe, located on the other side of the Amur River.
Main industries in the town include metal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
and timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, w ...
processing, as well as paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distribu ...
production.
Transportation
The city is served by a branch highway and railway connecting it toBelogorsk Belogorsk or Bilohirsk (russian: Белогорск; uk, Білогірськ) is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia and Ukraine.
;Urban localities
*Belogorsk, Amur Oblast, a town in Amur Oblast; administratively incorporated as ...
on the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the ea ...
and Trans-Siberian Highway. It is also served by a river port. On the other side of the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China (Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
is Heihe
Heihe (; ; Russian: Хэйхэ) is a prefecture-level city of northern Heilongjiang province, China, located on the Russian border, on the south bank of the Amur (Heilong) River, across the river from Blagoveshchensk. At the 2020 census, 1 ...
, Heilongjiang Province
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost provinc ...
, China, which is the starting point of China National Highway 202 that goes south to Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest c ...
and Dalian
Dalian () is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China. Located on ...
. Ignatyevo Airport, located northwest of the city center, serves domestic destinations.
The Blagoveshchensk–Heihe Bridge, completed at the end of 2019, includes a 2-lane highway bridge over the Amur to link Blagoveshchensk and Heihe.
The world's first international cable car to Heihe has also been proposed to open in 2022.
Education
Universities
*Amur State Medical Academy *Amur State University
Amur State University (russian: Аму́рский госуда́рственный университе́т) is a university in Blagoveshchensk, Amur Oblast, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontin ...
* Blagoveshchensk State Pedagogical University
*Far Eastern Higher Combined Arms Command School
The Marshal of the Soviet Union K. K. Rokossovsky Far Eastern Higher Combined Arms Command School (russian: Дальневосточное высшее общевойсковое командное училище имени Маршала Сов ...
*Far Eastern State Agricultural University
*Finance University under the Government of the Russian Federation
Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation (FinU or Financial University) (Russian: Финансовый университет при Правительстве Российской Федерации) is a public unive ...
(Blagoveschensk Branch)
* Maritime State University named after admiral Gennady Nevelskoy (Blagoveschensk Branch)
*Modern University for the Humanities
The Modern University for the Humanities (MUH) (russian: Современная гуманитарная академия), established in 1992. The university has been deprived of license order No.179-07 of January 30, 2017, accreditation cancel ...
(Blagoveschensk Branch)
*Moscow Academy of Business in Association with the Government of Moscow (Blagoveschensk Branch)
Sister city
*Heihe
Heihe (; ; Russian: Хэйхэ) is a prefecture-level city of northern Heilongjiang province, China, located on the Russian border, on the south bank of the Amur (Heilong) River, across the river from Blagoveshchensk. At the 2020 census, 1 ...
, Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () Postal romanization, formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a Provinces of China, province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is th ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
See also
*Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky
Count Nikolay Nikolayevich Muravyov-Amursky (also spelled as Nikolai Nikolaevich Muraviev-Amurskiy; russian: link=no, Никола́й Никола́евич Муравьёв-Аму́рский; – ) was a Russian general, statesman and diplomat, ...
* Amur Cossacks
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * *External links
Official website of Blagoveshchensk
Blagoveshchensk Business Directory
Video: Tornado in Blagoveshchensk, July 31, 2011
{{Authority control Amur Oblast (Russian Empire) Russian Far East China–Russia border crossings Populated places established in 1856 1856 establishments in China