Black Sea Germans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
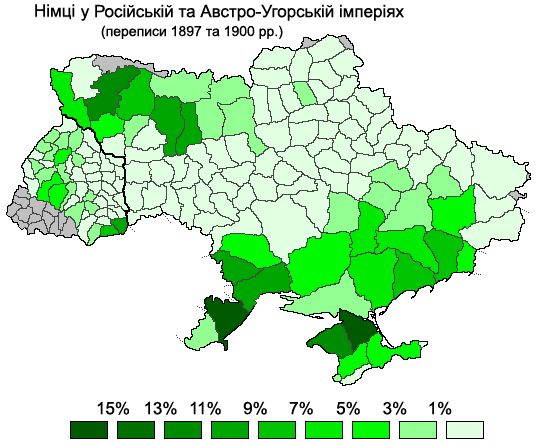
 The Black Sea Germans (german: Schwarzmeerdeutsche; russian: черноморские немцы; uk, чорноморські німці) are ethnic Germans who left their homelands (starting in the late-18th century, but mainly in the early-19th century at the behest of Emperor
The Black Sea Germans (german: Schwarzmeerdeutsche; russian: черноморские немцы; uk, чорноморські німці) are ethnic Germans who left their homelands (starting in the late-18th century, but mainly in the early-19th century at the behest of Emperor
 After the
After the
 With the defeat of the German Army at Stalingrad in the winter of 1942–1943, the Soviet
With the defeat of the German Army at Stalingrad in the winter of 1942–1943, the Soviet
and their daughter colonies: :* Hoffnungstal (today
 * Strassburg (today part of Kuchurhan/Кучурган)
* Selz (today part of Lymanske/Лиманське)
* Kandel (today part of Lymanske/Лиманське)
*
* Strassburg (today part of Kuchurhan/Кучурган)
* Selz (today part of Lymanske/Лиманське)
* Kandel (today part of Lymanske/Лиманське)
*
as well as the daughter colonies: :* Friedensfeld (today Syliwka/Силівка) :* Neu-Freudental (today Marynowe/Маринове)
as well as the daughter colonies: :* Alexanderfeld (today Berezivka/Березівка) :* Felsenburg (today Welidariwka/Велідарівка) :* Gnadenfeld (today Nejkowe/Нейкове) :* Halbstadt (today Nowoseliwka/Новоселівка) :* Neu Karlsruhe (today Tscherwona Sirka/Червона Зірка) :* Neu Rastadt (today part of Poritschtschja) :* Friedrichstal (destroyed) :* Stuttgart (destroyed)

 * Alt-Montal (today Samoschne/Заможне)
* Alt-Nassau (today Wynohradne/Виноградне)
* Blumental (today Riwne/Рівне)
* Durlach (destroyed, south of Tschapajewka/Чапаєвка)
* Friedrichsfeld (today Rosdol/Роздол)
* Grüntal (destroyed, at Tschornosemne/Чорноземне)
* Heidelberg (today Nowohoriwka/Новогорівка)
* Hochheim (today Komsomolske/Комсомольське)
* Hochstädt (today Wyssoke/Високе)
* Hoffental (today in the northern part of Wynohradne)
* Karlsruhe (today Sraskowe/Зразкове)
* Kostheim (today Pokasne/Показне)
* Kronsfeld (today Marjaniwka/Мар'янівка)
* Leiterhausen (today Traktorne/Тракторне)
* Neu-Montal (today Peremoschne/Переможне)
* Neu-Nassau (today Suwore/Суворе)
* Prischib (largely destroyed in the northern part of Wynohradne)
* Reichenfeld (today Plodorodne/Плодородне)
* Rosental (today
* Alt-Montal (today Samoschne/Заможне)
* Alt-Nassau (today Wynohradne/Виноградне)
* Blumental (today Riwne/Рівне)
* Durlach (destroyed, south of Tschapajewka/Чапаєвка)
* Friedrichsfeld (today Rosdol/Роздол)
* Grüntal (destroyed, at Tschornosemne/Чорноземне)
* Heidelberg (today Nowohoriwka/Новогорівка)
* Hochheim (today Komsomolske/Комсомольське)
* Hochstädt (today Wyssoke/Високе)
* Hoffental (today in the northern part of Wynohradne)
* Karlsruhe (today Sraskowe/Зразкове)
* Kostheim (today Pokasne/Показне)
* Kronsfeld (today Marjaniwka/Мар'янівка)
* Leiterhausen (today Traktorne/Тракторне)
* Neu-Montal (today Peremoschne/Переможне)
* Neu-Nassau (today Suwore/Суворе)
* Prischib (largely destroyed in the northern part of Wynohradne)
* Reichenfeld (today Plodorodne/Плодородне)
* Rosental (today
Black Sea German Research
American Historical Society of Germans from Russia
Germans from Russia Settlement Locations Google Map
{{National minorities of Ukraine German diaspora in Europe Ethnic groups in Ukraine German diaspora in Ukraine
 The Black Sea Germans (german: Schwarzmeerdeutsche; russian: черноморские немцы; uk, чорноморські німці) are ethnic Germans who left their homelands (starting in the late-18th century, but mainly in the early-19th century at the behest of Emperor
The Black Sea Germans (german: Schwarzmeerdeutsche; russian: черноморские немцы; uk, чорноморські німці) are ethnic Germans who left their homelands (starting in the late-18th century, but mainly in the early-19th century at the behest of Emperor Alexander I of Russia
Alexander I (; – ) was Emperor of Russia from 1801, the first King of Congress Poland from 1815, and the Grand Duke of Finland from 1809 to his death. He was the eldest son of Emperor Paul I and Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg.
The son o ...
- ), and settled in territories off the north coast of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
, mostly in the territories of the southern Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
(including modern-day Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
).
Black Sea Germans are distinct from similar groups of settlers (the Bessarabia Germans
The Bessarabia Germans (german: Bessarabiendeutsche, ro, Germani basarabeni, uk, Бессарабські німці) were an ethnic group who lived in Bessarabia (today part of the Republic of Moldova and south-western Ukraine) between 1814 ...
, Crimea Germans
The Crimea Germans (german: Krimdeutsche) were ethnic German settlers who were invited to settle in the Crimea as part of the East Colonization.
History
From 1783 onwards, there was a systematic settlement of Russians, Ukrainians, and Germans to ...
, Dobrujan Germans The Dobrujan Germans (german: Dobrudschadeutsche) were an ethnic German group, within the larger category of Black Sea Germans, for over one hundred years. German-speaking colonists entered the approximately 23,000 km2 area of Dobruja around 18 ...
, Russian Mennonite
The Russian Mennonites (german: Russlandmennoniten it. "Russia Mennonites", i.e., Mennonites of or from the Russian Empire occasionally Ukrainian Mennonites) are a group of Mennonites who are descendants of Dutch Anabaptists who settled for abo ...
s, Volga Germans
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov a ...
, and Volhynian Germans
The German minority population in Russia, Ukraine, and the Soviet Union stemmed from several sources and arrived in several waves. Since the second half of the 19th century, as a consequence of the Russification policies and compulsory military ...
), who are separate chronologically, geographically and culturally.
History
Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
began settling in southern Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and the Crimean Peninsula
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
in the late 18th century, but the bulk of immigration and settlement occurred during the Napoleonic period, from 1800 onward, with a concentration in the years 1803 to 1805. At the time, southern Ukraine was part of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
. Designated New Russia
Novorossiya, literally "New Russia", is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later become the southern mainland of Ukraine: the region immediately north of the Black Sea and Crimea. ...
, and often colloquially South Russia (or ''Südrussland'' by its German-speaking inhabitants), these lands had been annexed by the Russian Empire during the reign of Catherine the Great after wars against the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
(1768–1774) and the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
(1783). The area of settlement was not as compact as that of the Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchm ...
territory; rather it was home to a chain of colonies. The first German settlers arrived in 1787, first from West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 177 ...
, then later from Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Southwestern Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Alsace, France; as well as from the Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
area. Catholics, Lutherans, and Mennonites were all known as farmers (see Molotschna
Molotschna Colony or Molochna Colony was a Russian Mennonite settlement in what is now Zaporizhzhia Oblast in Ukraine. Today, the central village, known as Molochansk, has a population less than 10,000. The settlement is named after the Molochna ...
for Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radi ...
settlements in the Melitopol area); the Empress Catherine, herself an ethnic German, sent them a personal invitation to immigrate to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, as she felt they would make useful subjects and enrich her realm. She granted them privileges such as the free exercise of their religion and language within their largely closed communities, also exempt from military service and taxation.
Emigration to the Americas
In the late 19th century, both changing political conditions and growing hostilities towards Germans from Russia caused many Black Sea Germans, as well as Volga Germans, among other Germans from Russian communities, to begin migrating to North and South America, especially to Canada, the United States and Argentina.United States
The first Black Sea German settlements in the United States were established in 1873 near the town of Lesterville,South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large porti ...
, but they soon spread throughout both Dakotas. Lutherans and Catholics were the largest groups among the Black Sea Germans in the Dakotas. Other settlers from the Black Sea were Russian Mennonite
The Russian Mennonites (german: Russlandmennoniten it. "Russia Mennonites", i.e., Mennonites of or from the Russian Empire occasionally Ukrainian Mennonites) are a group of Mennonites who are descendants of Dutch Anabaptists who settled for abo ...
s and Hutterites
Hutterites (german: link=no, Hutterer), also called Hutterian Brethren (German: ), are a communal ethnoreligious branch of Anabaptists, who, like the Amish and Mennonites, trace their roots to the Radical Reformation of the early 16th century ...
, as well as Dobrujan Germans The Dobrujan Germans (german: Dobrudschadeutsche) were an ethnic German group, within the larger category of Black Sea Germans, for over one hundred years. German-speaking colonists entered the approximately 23,000 km2 area of Dobruja around 18 ...
who had briefly lived in southeastern Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
. By 1920, an estimated 70,000 Germans from Russia lived in North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minnesota to the east, So ...
, most of them were Black Sea Germans, in addition to Volga Germans
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov a ...
. There, most Bessarabia Germans
The Bessarabia Germans (german: Bessarabiendeutsche, ro, Germani basarabeni, uk, Бессарабські німці) were an ethnic group who lived in Bessarabia (today part of the Republic of Moldova and south-western Ukraine) between 1814 ...
, Black Sea Germans, Crimea Germans
The Crimea Germans (german: Krimdeutsche) were ethnic German settlers who were invited to settle in the Crimea as part of the East Colonization.
History
From 1783 onwards, there was a systematic settlement of Russians, Ukrainians, and Germans to ...
, and Volga Germans became wheat farmers.
Currently, it is estimated that 30-40% of North Dakota's population is of German from Russia descent, primarily Black Sea German.
Canada
Due to the increasing scarcity of farmland in the Dakotas of the United States, many Black Sea Germans resettled in the Canadian provinces ofAlberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
and Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dak ...
, where they left descendants. The Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie Provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provin ...
, especially in the province of Alberta, received Black Sea Germans, especially between 1900 and 1913, when the expansion of the railway branches made them easily accessible to new settlers. Previously, from the Black Sea region, Canada had already received Russian Mennonites. However, the forced assimilation policies implemented by Canada caused many Russian Mennonites to begin emigrating to various Latin American countries beginning in the 1920s.
Argentina
The first contingents of Black Sea Germans arrived in Argentina in 1898. Volga Germans, who had begun migrating to the country 20 years earlier, outnumbered Black Sea Germans at all times. Thus, many of them joined Argentine towns where there were already Volga Germans and in other cases founded their own colonies. Many of the Black Sea Germans who arrived in Argentina came from the Black Sea colonies München, Speier/Speyer, Rastadt, Landau, Rohrbach, Manheim, Karlsruhe, Kandel, etc. They settled, mainly, in the southwest of Buenos Aires Province and in the east of La Pampa Province. In 1905, some Black Sea German families bought land in Estancia El Lucero, in Coronel Suárez Partido (Coronel Suárez Partido has been simultaneously one of the epicenters of the Volga German settlements in Argentina), Buenos Aires Province. The next year, other Black Sea German families founded Colonia Monte La Plata, in Villarino Partido, same province. Many others settled in La Pampa Province, where there were already Volga German colonies, too. In this second province, Colonia San José (in English: "Saint Joseph Colony") was one of the examples of coexistence between Volga Germans and Black Sea Germans in the country. It had been founded by Volga Germans and later several Black Sea German families joined. In its cemetery, a long central path perpendicular to its entrance divides the land in two: on one side are the graves of the Volga Germans and their descendants, and on the other are the graves of the Black Sea Germans and their descendants. Over the years, its inhabitants have migrated to other Argentine towns or cities; however, this cemetery is a testimony of the way in which both German communities have cooperated in the country, without losing their own identities. In addition, this particularity facilitates any search. Regarding the Russian Mennonites, in 1877, a small group had arrived in Argentina and settled near Olavarría, in Buenos Aires Province. However, they were not conservative and soon assimilated with Germans living in that area. Instead, in the 1980s, the first very conservative Russian Mennonite colony (Old Colony Mennonites
The name Old Colony Mennonites (German: ''Altkolonier-Mennoniten'') is used to describe that part of the Russian Mennonite movement that is descended from colonists who migrated from the Chortitza Colony in Russia (itself originally of Prussian o ...
) was founded in the country. Its inhabitants are descendants of the Russian Mennonites who had fled Canadian forced assimilation policies in the 1920s. At that time, their ancestors settled in Mexico. But then, some of the later generations considered they were also in danger of assimilation there, so they left Mexico and settled in Argentina and other countries. This colony is located in the former Estancia Remecó (in English: "Remecó Ranch"), 40 km from Guatraché, in La Pampa Province. Curiously, Guatraché is, at the same time, one of the Argentine towns where the majority of the population is made up of Volga German and Black Sea German descent. Later, other Russian Mennonite colonies were founded in other places of Argentina.
Russian Revolution and the genocide of Germans from Russia
 After the
After the Bolshevik Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key moment ...
and the formation of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, Black Sea Germans, prior to World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, were subjected to the forced starvation of man-made famines, the closure of German-language churches, schools, and community organisations, and were required to change their language of instruction from German to Russian. The 45,000 Germans in Crimea (along with other Black Sea Germans) were forced into exile in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
and Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, many into forced labour camp
A labor camp (or labour camp, see spelling differences) or work camp is a detention facility where inmates are forced to engage in penal labor as a form of punishment. Labor camps have many common aspects with slavery and with prisons (especi ...
s. Many did not survive the labor camps.
Many were deported as a result of the collectivization
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member- ...
of all Soviet agricultural land in 1930/1931 by Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
's first five-year plan. The German farmers were labelled ''kulaks
Kulak (; russian: кула́к, r=kulák, p=kʊˈlak, a=Ru-кулак.ogg; plural: кулаки́, ''kulakí'', 'fist' or 'tight-fisted'), also kurkul () or golchomag (, plural: ), was the term which was used to describe peasants who owned ov ...
'' (rich peasants) by the Communist regime, and those who did not voluntarily agree to give up their land to the Soviet farming collectives were expelled to Siberia and Central Asia. The mass deportation of the Germans was based on social and ethnic criteria, the German Russian settlements probably suffered more than any other communities. About 1.2 percent of the Soviet population was classified as ''kulak'' and deported to the ''GULag
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in ...
'', based on a total Soviet population of 147 million, according to the 1926 census. The number of ethnic Germans sent to the camps as ''kulaks'' was about 50,000 out of a German population in the Soviet Union at the time of the same census of 1.239 million, that is, about 4 percent of the German population. The Germans were not the only ethnic group deported in large numbers during the collectivization drive, as many ethnic Poles also suffered the same fate. Germans, however, comprised the single largest foreign-origin minority sent into internal exile in the Soviet Union. There appeared to have been a deep prejudice against German communities because many Soviet officials considered all German farmers ''kulaks.''
After Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941, the Soviet leadership decided to label all ethnic Germans from Russia as enemies of the USSR, and accused them of collaborating with Nazis, most were arrested, even killed or deported to labor camps. The Supreme Soviet decreed the first evacuations, which were really expulsions, as the inhabitants were never allowed to return. Action to deport every ethnic German from the Crimea began on 15 August 1941. Although the decree stated that old people would not have to leave, everyone was expelled, first to Stavropol
Stavropol (; rus, Ставрополь, p=ˈstavrəpəlʲ) is a city and the administrative centre of Stavropol Krai, Russia. As of the 2021 Census, its population was 547,820, making it one of Russia's fastest growing cities.
It was known as ...
, and then to Rostov
Rostov ( rus, Росто́в, p=rɐˈstof) is a town in Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, one of the oldest in the country and a tourist center of the Golden Ring. It is located on the shores of Lake Nero, northeast of Moscow. Population:
While ...
in southeastern Ukraine, near the Crimea, but then all were sent on to camps and special settlements in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
. Given only three or four hours to pack, the deportees were not told where they were going, how long they would stay there, or how much food to take. The result was starvation for many and, due to the confusion, the separation of many families. In all, perhaps as many as 60,000 ethnic Germans were expelled from the Crimean peninsula alone at this time. Other parts of Southern Russian were also affected.
Although the majority of the Black Sea Germans avoided deportation due to the rapid advance of the German Army, Stalin, nevertheless, had sufficient time to arrest and exile those living east of the Dnieper River
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
. Between 25 September 1941 and 10 October 1941, approximately 105,000 ethnic Germans were exiled from this region and forcibly deported to Soviet-held areas far to the east beyond the Ural mountains. In terms of total numbers deported to Siberia and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, between 15 August and 25 December 1941, the Soviet authorities expelled and exiled 856,000 German from Russia.
Because of the quick conquest of Soviet territory by the Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
in the early months of their invasion, the Soviet regime was not able to deport the majority of the ethnic Germans from the western part of the Soviet Union, that is, the area west of the Dnieper river. The German towns and villages in the Western Ukraine, in Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
, and the Black Sea region all came under Nazi German rule, first under a military government and then under that of the Nazi Party or the SS, as Reichskommissariat Ukraine
During World War II, (abbreviated as RKU) was the civilian occupation regime () of much of Nazi German-occupied Ukraine (which included adjacent areas of modern-day Belarus and pre-war Second Polish Republic). It was governed by the Reich Min ...
.
Evacuation of Ethnic Germans during World War II
 With the defeat of the German Army at Stalingrad in the winter of 1942–1943, the Soviet
With the defeat of the German Army at Stalingrad in the winter of 1942–1943, the Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
began its offensive, recapturing more and more German-occupied territory. SS Head Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
made a decision to evacuate all ethnic Germans and bring them to the Reich. Evacuations began in scattered German communities in the North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, ...
, where in February 1943, 11,000 people were transferred. Shortly thereafter, 40,000 German Russians were sent westward from the area between the Don
Don, don or DON and variants may refer to:
Places
*County Donegal, Ireland, Chapman code DON
*Don (river), a river in European Russia
*Don River (disambiguation), several other rivers with the name
*Don, Benin, a town in Benin
*Don, Dang, a vill ...
and Dnieper Rivers. When the Soviet troops neared the Dnieper River in October 1943, the ''Chortitza'' Mennonite communities, totaling about 35,000 people, had to flee. In October, 45,000 ethnic Germans from Volhynia (Western Ukraine) were also forced to leave, and, by February 1944, it became clear to the Germans in Southern Ukraine that the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
could not be stopped; thus, they began their hurried evacuation. About 135,000 fled to the West. Approximately 280,000 ethnic Germans were successfully brought out of the occupied Soviet Union, which represented almost 90 percent of the registered German population, according to the 1943 Reich census.
On the basis of the articles pertaining to the repatriation of nationals in the Yalta Agreement
The Yalta Conference (codenamed Argonaut), also known as the Crimea Conference, held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the post ...
, the United States and the Soviet Union agreed to return each other's nationals at the end of the war. Of the almost 300,000 ethnic Germans who were evacuated by the Germans from the Soviet Union, about 200,000 were caught and sent to the labor camps by the Red Army, either as they fled from the Warthegau
The ''Reichsgau Wartheland'' (initially ''Reichsgau Posen'', also: ''Warthegau'') was a Nazi German ''Reichsgau'' formed from parts of Polish territory annexed in 1939 during World War II. It comprised the region of Greater Poland and adjacent ...
in Western Poland, previously incorporated into the German state, (about 120,000), or elsewhere in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
or when they were forcibly repatriated from occupied Germany to the Soviet Union.
Colonies in the Black Sea region
Schwedengebiet
This enclave of German settlement, established by the Russian imperial government, lies on the west bank of theDnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and ...
river in the Beryslav Raion
Beryslav Raion ( uk, Бериславський район, ) is one of the five administrative raions (a ''district'') of Kherson Oblast in southern Ukraine. Its administrative center is located in the city of Beryslav. Its population was 55,97 ...
district of Kherson Oblast, Ukraine, some 12 kilometers (or 7 Versts under the old Tsarist system of measurement) east-north-east (16.6 km by car, and 16.4 km by approved footpaths ) of the town of Beryslav
Beryslav (, ) is a city in Kherson Oblast of southern Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center for Beryslav Raion (district), housing the district's local administration buildings. Beryslav hosts the administration of Beryslav urban hrom ...
on the same side of the river.
Originally settled in 1782 by manumitted ethnic Swedish serfs from the Baltic island of Hiiumaa
Hiiumaa (, ) is the second largest island in Estonia and is part of the West Estonian archipelago, in the Baltic Sea. It has an area of 989 km2 and is 22 km from the Estonian mainland. Its largest town is Kärdla. It is located within ...
(Dagö) in present-day Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
who were freed by Catherine the Great and invited to settle here, the district took its German name — ''Schwedengebiet'' translates as "Swedes' district" — from these earlier settlers, despite the fact that once the Germans began to arrive as official settlers during the Napoleonic period, they soon outnumbered their Swedish precursors.
Due to attrition, Swedish numbers had fallen within a few years of their leaving their Baltic homeland. To make up for this shortfall, new settlers, mostly ethnic Germans originating in the lands of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
, such as Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Württ ...
, and the Austrian Habsburg hereditary lands, as well as Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and Alsace-Lorraine, were invited to settle in the area from the turn of the 19th century. Both the arrival of the Swedes and the later advent of the Germans formed two stages of the same official Russian imperial policy designed to secure what was then a relatively new part of the Russian Empire which had only been in Russia's sway since they had defeated of the Ottoman Empire in 1774 and won these vast southern territories, known first as New Russia
Novorossiya, literally "New Russia", is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later become the southern mainland of Ukraine: the region immediately north of the Black Sea and Crimea. ...
, and later as Southern Russia
Southern Russia or the South of Russia (russian: Юг России, ''Yug Rossii'') is a colloquial term for the southernmost geographic portion of European Russia generally covering the Southern Federal District and the North Caucasian Feder ...
.
The oldest village, first established in 1782, was the Swedish Lutheran village of Gammalsvenskby
Gammalsvenskby ( sv, Gammölsvänskbi, label=Gammalsvenska, lit=Old Swedish Village; uk, Старошведське, translit=Staroshvedske; german: Alt-Schwedendorf) is a former village that is now a neighbourhood of Zmiivka ( uk, Зміїв ...
. In the period 1802–1806, after a generation alone, during which their numbers had been supplemented on occasion by Swedes captured in war and other, mostly temporary, sojourners from Danzig, the local Baltic Swedish community was faced with the arrival of German speakers. This not only meant that they no longer had this area to themselves, but the Swedes had to share their original wooden church with some permanent incomers, ethnic German Lutherans. As it happened, the Germanophones also included Roman Catholics, which was another source of community tension. The Germans of either denomination called the village "Alt-Schwedendorf" (literally, ''old Swedes' village'') after the existing Swedes settlers. Basing themselves in Alt-Schwedendorf for a time, the Germans established several entirely German villages (''Kolonien''). In addition, some Germans also remained in Alt-Schwedendorf. In all, there were the following four initial settlements. They were initially established along confessional lines first in 1782, with the latter ones created in the period 1802 to 1806, viz.:
* ( sv, Gammalsvenskby
Gammalsvenskby ( sv, Gammölsvänskbi, label=Gammalsvenska, lit=Old Swedish Village; uk, Старошведське, translit=Staroshvedske; german: Alt-Schwedendorf) is a former village that is now a neighbourhood of Zmiivka ( uk, Зміїв ...
, label=Standard Swedish
Standard Swedish () denotes Swedish as a spoken and written standard language. While Swedish as a written language is uniform and standardized, the spoken standard may vary considerably from region to region. Several prestige dialects have devel ...
, lit=Old Swedish Village, sv, Gammölsvänskbi, label= local Swedish dialect, uk, Старошведське, translit=Staroshvedske, russian: Старошве́дское, translit=Starosvedkaya; also known as (Verbivka); Старошведське and Вербівка are rendered in German as ''Staroschwedske'' and ''Werbiwka'' respectively): originally, and overwhelmingly, Lutheran, it was founded by Swedes in 1782, and later supplemented by German settlers, mostly Lutherans, in the period 1802 to 1806. As the oldest and, then, sole village already established, it served as the short-term mustering place from which three other (German) colonies were settled according to religion and ethnicity. As such, for a time, its inhabitants included some German Roman Catholics who settled to the north in the new village of Klosterdorf, or left the area entirely, for destinations such as the Taurien district of Crimea, further to the south. The majority of the influx, however, consisted of German Lutherans who were settled to the south of Alt-Schwedendorf in what were, at least, at the outset, the exclusively German Lutheran villages of Mühlhausendorf and Schlangendorf, for which, see below. After years of tension between the Lutheran Swedes and Lutheran Germans, the Swedes built their own parish church dedicated to St John the Baptist (consecrated 1886; it was later closed during Soviet times and used for various purposes, but is now refurbished and used as an Orthodox Christian church) in the village of Gammalsvenskby/Alt-Schwedendorf, while the German Lutherans of the two southern neighbouring villages built their own house of worship (''Betthaus'', literally German for ''prayer house'') between the two German Lutheran villages of Mühlhausendorf and Schlangendorf, and dedicated it to St Peter and St Paul (consecrated 1888). As for Alt-Schwedendorf, in 1915, it, along with the three other original villages, was subsumed into modern Zmiivka (see German ''Schlangendorf'', below). As Gammalsvenskby, it is, however, accorded historic status in the region for its association with one of the few settlements of Swedish-speaking colonists in what was once known as South Russia or New Russia
Novorossiya, literally "New Russia", is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later become the southern mainland of Ukraine: the region immediately north of the Black Sea and Crimea. ...
, and now forms part of Ukraine (see article on Gammalsvenskby
Gammalsvenskby ( sv, Gammölsvänskbi, label=Gammalsvenska, lit=Old Swedish Village; uk, Старошведське, translit=Staroshvedske; german: Alt-Schwedendorf) is a former village that is now a neighbourhood of Zmiivka ( uk, Зміїв ...
for more details of this aspect of the village's history and current role as an historic site). The church records of the local Lutheran population, whether German or Swedish, survive for part of the nineteenth century (1833-1885), in the archives of the St Petersburg Evangelical Lutheran Consistory, and have been microfilmed by the Genealogical Society of Utah, and partially indexed. For many years, the records for Alt-Schwedendorf were recorded in tandem with those of Josefstal (older German spelling, ''Josephsthal''; its Ukrainian name is '' Samarivka/Самарівка''), an upriver village in the former Ekaterinoslav
Dnipro, previously called Dnipropetrovsk from 1926 until May 2016, is Ukraine's fourth-largest city, with about one million inhabitants. It is located in the eastern part of Ukraine, southeast of the Ukrainian capital Kyiv on the Dnieper Rive ...
colonies (which see below) over 250 km to the north whose Lutheran pastors visited Alt-Schwedendorf occasionally to perform marriages, leaving the baptisms and burials to be performed by laymen such as the church sexton or village schoolmaster. During that period, Alt-Schwedendorf was effectively a filial chapelry of Josefstal, meaning that many of the records relevant to its inhabitants have been indexed and appear under the mother parish's name rather than the daughter community to which these folk belonged. Confusing as this may be, successful research into this area can mean one encounters records and studies written not only in German, but in also Swedish, Russian, and English. To complicate matters further, when a large number of the ethnic Swedes of the area were allowed to leave the Soviet Union for Sweden, they were provided with a copy of their original parish registers (in German ''Kirchenbücher'', literally ''church books'', or ''Matrikeln'', for ''registers'') dating back to the foundation of the Swedish colony in 1782. These registers include records covering the ethnic German Lutheran population particularly in cases of intermarriage, and cover the whole period of Swedish habitation up to the partial departure in 1929.
* Klosterdorf (literally "Monastery (or, abbey) village", in German, and named for the ruins of a former Orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pa ...
monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer whi ...
in the vicinity; in Russian, ): Roman Catholic, founded in 1804. For many years, Klosterdorf did not have its own priest. Instead it was a filial chapelry served by priests from the city parish of St Pius and St Nicholas in Kherson, part of the Odessa deanery of the Tiraspol Roman Catholic diocese. By 1864, however, the local German Catholic community had raised enough funds to pay for a village chapel dedicated to St Vincent, which eventually became an independent parish church. The last priest, the Reverend Father Johann Lorenzovitch Thauberger, was martyred during the Soviet era repression of worship The whereabouts of any surviving original parish registers of this community are unknown. Under Russian law, however, annual returns copied from the parish registers of birth/baptism, marriage, and death/burial for this community were sent to archives designated by the civil authorities to act as civilian record repositories to document the populace for the purpose of control, taxation, and military service. From 1853 until the shortly after the end of the Russian imperial era, the surviving returns for the area are held in the Tiraspol Roman Catholic Consistory fonds at the Saratov State Archives in Saratov, Russia. Earlier church records are to be found in the fonds covering the Mohilev Roman Catholic Consistory, for the period from 1801 to 1853, with some overlap in the Kherson Roman Catholic Consistory (from 1850 to 1853), until, with the establishment of the diocese of Tiraspol, coverage, backdated by almost a half a decade, became effective from 1853 to 1918.
* Mühlhausendorf (literally German for ''village of the mill houses''; in Russian, ''Mykhailovka'', in Ukrainian, ''Mykhailivka'', both meaning ''Michael's village''): Lutheran when founded in 1803–1805, with a later admixture of Roman Catholic Germans.
* Schlangendorf (literally German for ''Snake village'' because snakes abounded in the area; known in Russian as ''Zmi'ivka''; in modern-day Ukraine, its Ukrainian name is '' Zmiivka'' (Cyrillic alphabet: ''Зміївка''; German rendering ''Smijiwka''): Lutheran when founded in 1803–1805, with a later admixture of Roman Catholic Germans. It now incorporates the area covered by the three other original villages listed above.
By 1886, around the time when large-scale emigration to North America began, the population of the four villages was as follows:
* Alt-Schwedendorf: 515 inhabitants with 65 houses and one Lutheran church
* Klosterdorf: 773 inhabitants with 52 houses and one Roman Catholic chapel
* Mühlhausendorf: 489 inhabitants with 48 houses and one Lutheran prayer house
* Schlangendorf: 474 inhabitants with 46 houses and one Lutheran prayer house
Later, as the original villages' population continued to burgeon, despite overseas emigration, there were '' Tochterkolonien'', i.e. daughter colonies, formed, such as, the following, viz.:
* Friedenheim, founded in 1928
* Hagendorf
* Hoffenthal
* Neu-Klosterdorf, a daughter colony of Klosterdorf (listed above), which was then called in apposition to her offspring, Alt-Klosterdorf. Today this is the village of Kostyrka, not to be confused with the mother village of the same name now subsumed into Zmiivka.
* Neu-Schwedendorf, a daughter colony of Alt-Schwedendorf
During the Second World War, after the German invasion of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
on 22 June 1941, the district was occupied by the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
, and, in 1942, the inhabitants, both Swedes and Germans whom the Nazis considered together as ''ethnic Germans'' (''Volksdeutsche'', in German) and others (such as Ukrainians), were assessed and inventoried by officers of the Reichssippenamt operating under the direction of Kommando Karl Stumpp
Karl Stumpp (12 May 1896 – 20 January 1982) was a German ethnographer of Black Sea German origin who devoted himself to the study of Germans in Eastern Europe and Southeastern Europe, especially those from the lands of the former Russian E ...
, the former historian of the area. As a result of the impending German attack, the Soviet authorities had already exiled many of the adult males among the ethnic German population of the district to areas of refuge and captivity east of the Ural mountains. During the German occupation, the area was officially under the Nazi civil administration of the Reichskommissariat Ukraine
During World War II, (abbreviated as RKU) was the civilian occupation regime () of much of Nazi German-occupied Ukraine (which included adjacent areas of modern-day Belarus and pre-war Second Polish Republic). It was governed by the Reich Min ...
until the Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
's successful counteroffensive drove the occupation forces, both military and civil, from the region in 1944.
Dr Karl Stumpp
Karl Stumpp (12 May 1896 – 20 January 1982) was a German ethnographer of Black Sea German origin who devoted himself to the study of Germans in Eastern Europe and Southeastern Europe, especially those from the lands of the former Russian E ...
and Dr Adam Giesinger both published materials on the settlement and history of the Swedish District and its villages. The historical part of this overview is drawn primarily from Stumpp's '' The Emigration from Germany to Russia in the Years 1763 to 1862'' (English translation from the original German, American Historical Society of Germans from Russia, 1973), and Giesinger's '' From Catherine to Khrushchev : The Story of Russia's Germans'' (1974).
Glückstal
* Glückstal (today Hlinaia, Russian Glinoe/Глиное – Moldova/Transnistria) * Neudorf (today Carmanova, Russian Karmanowa/Карманова – Moldova/Transnistria) * Bergdorf (today Kolosova, Russian Kolossowa/Колосова – Kolosova, Ternopil Oblast, Ukraine) * Kassel (today Velykokomariwka ( Komarivka)/Великокомарівка – Ukraine)and their daughter colonies: :* Hoffnungstal (today
Tsebrykove
Tsebrykove ( uk, Цебрикове; russian: Це́бриково, german: Hoffnungstal) is an urban-type settlement with some 2,900 inhabitants in the Rozdilna Raion, Odesa Oblast in Ukraine. It is located about east of Tiraspol and about nort ...
/Цебрикове – Ukraine)
:* Hoffnungsfeld (today Lenine/Леніне – Ukraine)
:* Klein Neudorf (today Nowoseliwka/Новоселівка – Ukraine)
:* Neu-Beresina (today Malosymenowe/Малозименове – Ukraine)
:* Neu-Glückstal (today Zybuliwka/Цибулівка – Ukraine)
:* Neu-Berlin (today Worobjowe/Воробйове – Ukraine)
:* Neu-Kassel (today Sofijiwka/Софіївка – Ukraine)
:* Rosenfeld (today Konopljane/Конопляне – Ukraine)
:* Gnadenfeld (today Nejkowe/Нейкове – Ukraine)
:* Kleinbergdorf (today Crasnoe, Russian Krasnoje/Красное – Moldova/Transnistria)
:* Friedenstal (today Tryhrady/Тригради – Ukraine)
:* Krontal (destroyed – east of Grigoriopol
Grigoriopol (, Moldovan Cyrillic: Григориопол, russian: Григорио́поль, Grigoriopol, uk, Григоріо́поль, Hryhoriopol) is a town in the Administrative-Territorial Units of the Left Bank of the Dniester, Moldova ...
located in – Moldova/Transnistria)
:* Neu-Glückstal (today Wowtsche/Вовче as part of Rymariwka/Римарівка – Ukraine)
:* Koscharka (today Koscharka/Кошарка – Ukraine)
:* Saratow (destroyed, northeast of Koscharka)
Kutschurgan
 * Strassburg (today part of Kuchurhan/Кучурган)
* Selz (today part of Lymanske/Лиманське)
* Kandel (today part of Lymanske/Лиманське)
*
* Strassburg (today part of Kuchurhan/Кучурган)
* Selz (today part of Lymanske/Лиманське)
* Kandel (today part of Lymanske/Лиманське)
* Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
(today part of Kuchurhan/Кучурган)
* Mannheim (today Kam'yanka/Кам'янка)
* Elsass (today Shcherbanka/Щербанка) and their daughter colonies:
:*Ambrose Khutor
:*Balmas, Bessarabia
:*Bezilajweka
:*Bischofsfeld (today Yeremiivka/Єреміївка)
:*Bogunskoje
:*Brilowa
:*Brinnowka
:*Dikowa
:*Diminski
:*Fischer Khutor
:*Fischer-Franz Khutor
:*Georgental (today Sekretarivka/Секретарівка)
:*Jeremejewka
:*Johannestal
:*Kamenka
:*Kaschary
:*Kellersheim (destroyed)
:*Kosenka
:*Koslowka
:*Kutschurgan Khutor
:*Langenberg
:*Larga, Bessarabia
:*Linejewka
:*Mandrowo
:*Marjanowka
:*Matischowka
:*Miller Khutor
:*Milliardowka
:*Miroljubowka
:*Neu-Baden
:*Neu-Elsass
:*Neu-Kandel (today Bohunove/Богунове)
:*Neu-Mannheim (today Novostepanivka/Новостепанівка)
:*Neu-Schlossel Khutor
:*Neu-Selz
:*Neu-Strassburg
:*Nowo-Andreaschewka
:*Ponjatowka
:*Rosaljewka
:*Sachalski
:*Schatzen Khutor
:*Schemiott
:*Schwowe Khutor
:*Severinovka
:*Stepanowka
:*Sturpelz
:*Susanowka
:*Tschebanka
:*Wasiljewka
:*Welter Khutor
:*Wolkowo
Liebental
* Liebental (today Welykodolynske/Великодолинське) : (1803 founded by Lutherans from Württemberg) * Kleinliebental (today Malodolynske/Малодолинське) : (1803 founded by Catholics from Alsace) * Josefstal (today Yosypivka/Йосипівка) : (1803 founded by Catholics from Alsace) * Mariental (today Marjaniwka/Мар'янівка) : (1803 founded by Catholics from Alsace) * Lustdorf (today Burlacha Balka/Бурлача Балка, district of Odessa) : (1805 founded by Württemberger) * Alexanderhilf (today Dobroolexandriwka/Доброолександрівка) : (1805/06 founded by Württemberger) * Neuburg (today Nowohradkiwka/Новоградківка) : (1806 founded by Württemberger) * Peterstal (today Petrodolyns'ke/Петродолинське) * Franzfeld (todayNadlymanske
Nadlymanske ( uk, Надлиманське) is a village in Odesa Raion of Odesa Oblast in Ukraine. It belongs to Maiaky rural hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Nadlymanske is located along the northeast edge of the Dniester Estuary nort ...
/Надлиманське)
* Annental (today Biljary/Білярі)
* Güldendorf (today Krasnosilka/Красносілка)
* Freudental (today Myrne/Мирне)as well as the daughter colonies: :* Friedensfeld (today Syliwka/Силівка) :* Neu-Freudental (today Marynowe/Маринове)
Beresan
Beresan Colony settlements * Blumenfeld (today Krasnopillya/Краснопілля) ** Catholic ** Founded in 1862 by families from the Liebental and Kuchurgan districts (Elsaß, Franzfeld, Kandel, Sulz, Straßburg). ** Conflicting information as to which colony group it belongs, Liebental or Beresan. * Landau (todayShyrokolanivka
Shyrokolanivka ( uk, Широколанівка, russian: Широколановка) is a village in the Mykolaiv Raion of the Mykolaiv Oblast in southern Ukraine. It is located along the east bank of the Berezan River.
Name
The name ''Landau ...
/Широколанівка)
* Speyer (today Pischtschanyj Brid/Піщаний Брід)
* Rohrbach (today Nowoswitliwka/Новосвітлівка)
* Worms (today Wynohradne/Виноградне)
* Sulz (destroyed)
* Karlsruhe (today Stepove, Mykolaiv Raion
Stepove ( uk, Степове) is a village in Mykolaiv Raion, Mykolaiv Oblast in Southern Ukraine. Its population was 1869 in the 2001 Ukrainian Census. Along with another village of Zelenyi Hai, it forms a rural community: ''Stepivska Silska ...
/Степове)
* Rastadt (today Poritschtschja/Поріччя)
* München (today Poritschtschja/Поріччя)
* Katharinental (today Kateryniwka/Катеринівка)
* Johannestal (today Iwaniwka/Іванівка)
* Waterloo (today Stawky/Ставки) as well as the daughter colonies: :* Alexanderfeld (today Berezivka/Березівка) :* Felsenburg (today Welidariwka/Велідарівка) :* Gnadenfeld (today Nejkowe/Нейкове) :* Halbstadt (today Nowoseliwka/Новоселівка) :* Neu Karlsruhe (today Tscherwona Sirka/Червона Зірка) :* Neu Rastadt (today part of Poritschtschja) :* Friedrichstal (destroyed) :* Stuttgart (destroyed)
Molotschna
Molotschna Colony or Molochna Colony was a Russian Mennonite settlement in what is now Zaporizhzhia Oblast in Ukraine. Today, the central village, known as Molochansk, has a population less than 10,000. The settlement is named after the Molochna ...

 * Alt-Montal (today Samoschne/Заможне)
* Alt-Nassau (today Wynohradne/Виноградне)
* Blumental (today Riwne/Рівне)
* Durlach (destroyed, south of Tschapajewka/Чапаєвка)
* Friedrichsfeld (today Rosdol/Роздол)
* Grüntal (destroyed, at Tschornosemne/Чорноземне)
* Heidelberg (today Nowohoriwka/Новогорівка)
* Hochheim (today Komsomolske/Комсомольське)
* Hochstädt (today Wyssoke/Високе)
* Hoffental (today in the northern part of Wynohradne)
* Karlsruhe (today Sraskowe/Зразкове)
* Kostheim (today Pokasne/Показне)
* Kronsfeld (today Marjaniwka/Мар'янівка)
* Leiterhausen (today Traktorne/Тракторне)
* Neu-Montal (today Peremoschne/Переможне)
* Neu-Nassau (today Suwore/Суворе)
* Prischib (largely destroyed in the northern part of Wynohradne)
* Reichenfeld (today Plodorodne/Плодородне)
* Rosental (today
* Alt-Montal (today Samoschne/Заможне)
* Alt-Nassau (today Wynohradne/Виноградне)
* Blumental (today Riwne/Рівне)
* Durlach (destroyed, south of Tschapajewka/Чапаєвка)
* Friedrichsfeld (today Rosdol/Роздол)
* Grüntal (destroyed, at Tschornosemne/Чорноземне)
* Heidelberg (today Nowohoriwka/Новогорівка)
* Hochheim (today Komsomolske/Комсомольське)
* Hochstädt (today Wyssoke/Високе)
* Hoffental (today in the northern part of Wynohradne)
* Karlsruhe (today Sraskowe/Зразкове)
* Kostheim (today Pokasne/Показне)
* Kronsfeld (today Marjaniwka/Мар'янівка)
* Leiterhausen (today Traktorne/Тракторне)
* Neu-Montal (today Peremoschne/Переможне)
* Neu-Nassau (today Suwore/Суворе)
* Prischib (largely destroyed in the northern part of Wynohradne)
* Reichenfeld (today Plodorodne/Плодородне)
* Rosental (today Nowe Pole
Nowe (german: Neuenburg in Westpreußen, 1942-1945: ''Neuenburg (Weichsel)'') is a town in Świecie County, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland, with 6,270 inhabitants (2004).
Geographical location
Nowe is located approximately 75 kilom ...
/Нове Поле)
* Tiefenbrunn (today Tschystopillja/Чистопілля)
: (1822 founded by Lutherans from Baden)
* Waldorf (today Schowtnewe/Жовтневе)
* Wasserau (today Wodne/Водне)
* Weinau (today Tschapajewka/Чапаєвка)
* Neudorf (zerstört, south of Wyschnewe/Вишневе)
: (already in 1833 disbanded)
:* Darmstadt (today Romaschky/Ромашки)
:* Kaisertal (today Solota Dolyna/Золота Долина)
Colonies in
Ekaterinoslav
Dnipro, previously called Dnipropetrovsk from 1926 until May 2016, is Ukraine's fourth-largest city, with about one million inhabitants. It is located in the eastern part of Ukraine, southeast of the Ukrainian capital Kyiv on the Dnieper Rive ...
* Billersfeld (today Olexandrivka/Олександрівка)
* Fischersdorf (today Stadtteil Rybalske/Рибальське as part of the Stadtrajons Samara by Dnipro)
* Jamburg (today Dniprove/Дніпрове)
* Josefstal (today Samarivka/Самарівка, largely destroyed) – (Lutherans from Thorn
Thorn(s) or The Thorn(s) may refer to:
Botany
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, sharp structures on plants
* ''Crataegus monogyna'', or common hawthorn, a plant species
Comics and literature
* Rose and Thorn, the two personalities of two DC Com ...
(1780) and Danzig (1789))
* Kronsgarten (southern part of Pidhorodne
Pidhorodne ( ) is a town in Dnipro Raion of Dnipropetrovsk Oblast (province) of Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Pidhorodne urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: In 2001, the population was 17,763.
The populated pla ...
/Підгородне) – (Frisian Mennonites from Marienburg (1789))
* Mariental/Marienfeld (today Majorka/Майорка)
Planer colonies in
Mariupol
Mariupol (, ; uk, Маріу́поль ; russian: Мариу́поль) is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast ( Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius River. Prior to the 2022 Russia ...
* Kirschwald (today Wyschnjuwate/Вишнювате)
* Tiegenhof (today Asow/Азов)
* Rosengart (Rajhorod – today northern part of Lystwjanka/Листвянка)
* Schönbaum (today Lystwjanka/Листвянка)
* Kronsdorf (Kasjanoselsk – today northern part of Rosiwka/Розівка)
* Grunau (Alexandronewsk – today in the northeastern part of Rosiwka/Розівка)
* Rosenberg (today Rosiwka/Розівка)
* Wickerau (today Kusneziwka/Кузнецівка)
* Reichenberg (today Bahatiwka/Багатівка)
* Kampenau (Kamenske – today southern part of Marjaniwka/Мар'янівка)
* Mirau (today Myrske/Мирське)
* Kaiserdorf (today Probudschennja/Пробудження)
* Göttland (today Marjaniwka/Мар'янівка)
* Neuhof (today Nowodworiwka/Новодворівка)
* Eichwald (today Uryzke/Урицьке)
* Tiegenort (today Antoniwka/Антонівка)
* Tiergart (destroyed – northeast of Antoniwka)
* Ludwigstal (today Karla Libknechta Karla may refer to:
People
* Karla (name), a feminine given name
* Petras Karla (1937–1969), Soviet Olympic rower
Places
* Karla, Kose Parish, a village in Harju County, Estonia
* Karla, Rae Parish, a village in Harju County, Estonia
* K� ...
/Карла Лібкнехта)
Swabia colonies in
Berdyansk
Berdiansk or Berdyansk ( uk, Бердя́нськ, translit=Berdiansk, ; russian: Бердя́нск, translit=Berdyansk ) is a port city in the Zaporizhzhia Oblast (province) in south-eastern Ukraine. It is on the northern coast of the Sea o ...
* Neu-Hoffnung (today the western part of Ossypenko/Осипенко)
* Neu-Hoffnungstal (today Dolynske/Долинське)
* Neu-Stuttgart (today Jelysawetiwka/Єлизаветівка)
* Rosenfeld (today Oleniwka/Оленівка)
Miscellaneous colonies
* Alt Danzig (today Krupske) * Colonists districtCrimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
* Mennonite colony Molotschna
Molotschna Colony or Molochna Colony was a Russian Mennonite settlement in what is now Zaporizhzhia Oblast in Ukraine. Today, the central village, known as Molochansk, has a population less than 10,000. The settlement is named after the Molochna ...
* Mennonite colony Chortiza
* Daughter colony Kronau
Colonies in Maximovich, South of Donetsk:
* Ostheim
Ostheim vor der Rhön is a town in Northern Bavaria in the district of Rhön-Grabfeld in Franconia. Though politically part of Bavaria since 1947, it was historically a part of Thuringia, and remains religiously, architecturally, and to some exten ...
(today Telmanowe), daughter settlement of Neu-Hoffnung
* Rosenfeld
Rosenfeld is a German name meaning "rose field" or "field of roses"
It may refer to:
Places
* Rosenfeld, Germany, a town in Baden-Württemberg
* Rosenfeld, Manitoba, a Canadian village in the Rural Municipality of Rhineland
* Rosenfeld (Melk), a ...
(today Swobodne)
Notable people
*Jeanna Friske
Jeanna Vladimirovna Friske (russian: link=no, Жанна Владимировна Фриске; born Jeanna Vladimirovna Kopylova; 8 July 1974 – 15 June 2015), better known by the stage name Zhanna Friske, was a Russian actress, singer and mo ...
, singer
* Johnny Gottselig
Johannes “Johnny” Gottselig (russian: Иван Гоцелиг) (June 24, 1905 – May 15, 1986) was a professional ice hockey left winger who played 16 seasons for the Chicago Black Hawks of the National Hockey League (NHL) between 1928 and 19 ...
, National Hockey League player and coach, The Chicago Black Hawks
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
* Chris Isaak
Christopher Joseph Isaak (born June 26, 1956) is an American singer, songwriter, guitarist and occasional actor. He is widely known for his breakthrough hit and signature song " Wicked Game", as well as other songs such as "Blue Hotel", " Baby ...
, American singer and actor
* Georg Leibbrandt
Georg Leibbrandt (6 September 1899 – 16 June 1982) was a Nazi German bureaucrat and diplomat. He occupied leading foreign policy positions in the Nazi Party Foreign Policy Office (APA) and the Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territo ...
, Nazi functionary
* Vyacheslav Polozov
Vyacheslav Michailovich Polozov (russian: Вячеслав Михайлович Полозов; January 1, 1950) nicknamed "Slava", is a Soviet-born opera singer, professor of voice, entrepreneur. He sang at many opera houses around the world, ap ...
, opera singer
* Pyotr Schmidt
Pyotr Petrovich Schmidt (russian: Пётр Петрович Шмидт; – ) was one of the leaders of the Sevastopol Uprising during the Russian Revolution of 1905.
Early years
Pyotr Petrovich Schmidt was born in 1867 in Odessa, Russian E ...
, Russian naval officer and 1905 revolutionary
* Athanasius Schneider
Athanasius Schneider, ORC (born Anton Schneider on 7 April 1961) is a Catholic prelate, serving as the Auxiliary Bishop of Astana in Kazakhstan. He is a member of the Canons Regular of the Holy Cross of Coimbra. He is known for championing th ...
, Auxiliary Roman Catholic Bishop of Nur-Sultan
Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan.
The city lies on the banks of the Ishim River in the north-central part of Kazakhstan, within the Akmola Region, tho ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, theologian and author
* Karl Stumpp
Karl Stumpp (12 May 1896 – 20 January 1982) was a German ethnographer of Black Sea German origin who devoted himself to the study of Germans in Eastern Europe and Southeastern Europe, especially those from the lands of the former Russian E ...
, ethnologist and Nazi functionary in German-occupied Ukraine
* Hayley Wickenheiser
Hayley Wickenheiser (born August 12, 1978) is a Canadian former ice hockey player, resident physician and assistant general manager for the Toronto Maple Leafs. She was the first woman to play full-time professional men’s hockey in a positio ...
, Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice h ...
player from Shaunavon, Saskatchewan
Shaunavon (, ) is a town in southwest Saskatchewan. At the junction of Highways 37 and 13, it is 110 kilometres from Swift Current, 163 kilometres from the Alberta border, and 74 kilometres from the Montana border. Shaunavon was established ...
. Wickenheiser’s family immigrated to Western Canada from Odessa in the early part of the 20th century.
* Immanuel Winkler, Pastor in Hoffnungstal, vicar in Kassel and representative of the Black Sea Germans
See also
*History of Germans in Russia and the Soviet Union
The German minority population in Russia, Ukraine, and the Soviet Union stemmed from several sources and arrived in several waves. Since the second half of the 19th century, as a consequence of the Russification policies and compulsory militar ...
* Askania-Nova (settlement)
Askania-Nova (Ukrainian: Асканія-Нова), or New-Askania is an urban-type settlement in Kakhovka Raion, Kherson Oblast, southern Ukraine, near the Askania-Nova biosphere reserve. It hosts the administration of the Askania-Nova settlement ...
* Baltic Germans
Baltic Germans (german: Deutsch-Balten or , later ) were ethnic German inhabitants of the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea, in what today are Estonia and Latvia. Since their coerced resettlement in 1939, Baltic Germans have markedly declin ...
* Ukrainians in Germany
As of 2020 the number of Ukrainians in Germany was approximately 145,500. This number more than doubled in 2022. Germany's Ukrainians have created a number of institutions and organizations, such as the Central Association of Ukrainians in Germany ...
References
External links
Black Sea German Research
American Historical Society of Germans from Russia
Germans from Russia Settlement Locations Google Map
{{National minorities of Ukraine German diaspora in Europe Ethnic groups in Ukraine German diaspora in Ukraine