 Biting is a common zoological behavior involving the active, rapid closing of the jaw around an object. This behavior is found in
Biting is a common zoological behavior involving the active, rapid closing of the jaw around an object. This behavior is found in tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, t ...
ed animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s such as mammals, reptiles, amphibians and fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
, but can also exist in arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s. Myocytic contraction of the muscles of mastication is responsible for generating the force that initiates the preparatory jaw abduction (opening), then rapidly adducts (closes) the jaw and moves the top and bottom teeth towards each other, resulting in the forceful action of a bite.
Biting is one of the main functions in most macro-organisms' life, providing them the ability to forage
Forage is a plant material (mainly plant leaves and stems) eaten by grazing livestock. Historically, the term ''forage'' has meant only plants eaten by the animals directly as pasture, crop residue, or immature cereal crops, but it is also us ...
, hunt, eat
Eating (also known as consuming) is the ingestion of food, typically to provide a heterotrophic organism with energy and to allow for growth. Animals and other heterotrophs must eat in order to survive — carnivores eat other animals, herbi ...
, build, play, fight and protect, and much more. Biting may be a form of physical aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
due to predatory
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill t ...
or territorial
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an ...
intentions, but can also be a normal activity of an animal as it eats, carries objects, softens and prepares food for its young, removes ectoparasites or irritating foreign objects (e.g. burred plant
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
s) from body surface, scratches itself, and grooms other animals.
Animal bites often result in serious punctures, avulsions, fractures, hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vag ...
s, infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
s, envenomation and death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
. In modern human societies, dog bites are the most common types, with children the most common victims and faces the most common targets. Other species that can exhibit such behavior towards human are typically aggressive urban animal
Urban wildlife is wildlife that can live or thrive in urban/suburban environments or around densely populated human settlements such as townships.
Some urban wildlife, such as house mice, are synanthropic, ecologically associated with and even ...
s such as feral cat
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact: it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens ...
s, spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
s and snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s, micropredator
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s such as vampire bats and hematophagic arachnid
Arachnida () is a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals ( arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and ...
s (e.g. mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning "gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "lit ...
es, flea
Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about long, a ...
s, lice
Louse ( : lice) is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been recognized as an order, infraorder, or a parvorder, as a resul ...
, bedbug
Bed bugs are insects from the genus ''Cimex'' that feed on blood, usually at night. Their bites can result in a number of health impacts including skin rashes, psychological effects, and allergy, allergic symptoms. Bed bug bites may lead to ski ...
s and tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s, whose " bites" are actually a form of sting-like puncture rather than true biting), or dangerous wild carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other ...
s such as wolves, big cats, bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the N ...
s, crocodilians and predatory fishes (e.g. shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
s, barracudas and piranha
A piranha or piraña (, , or ; or , ) is one of a number of freshwater fish in the family Serrasalmidae, or the subfamily Serrasalminae within the tetra family, Characidae in order Characiformes. These fish inhabit South American rivers, ...
s).
Types of teeth
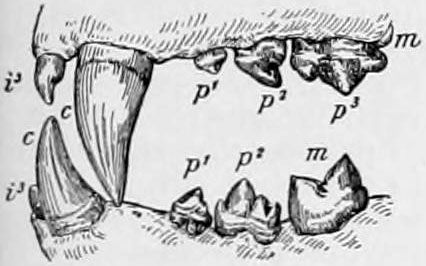 The types of teeth that organisms use to bite varies throughout the animal kingdom. Different types of teeth are seen in
The types of teeth that organisms use to bite varies throughout the animal kingdom. Different types of teeth are seen in herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthp ...
s, carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other ...
s, and omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nut ...
s as they are adapted over many years to better fit their diets. Carnivores possess canine, carnassial, and molar teeth, while herbivores are equipped with incisor teeth and wide-back molars.Animal Teeth , Types of Teeth , DK Find Out. (2018). Retrieved October 28, 2018, from https://www.dkfindout.com/us/animals-and-nature/food-chains/types-teeth/ In general, tooth shape has traditionally been used to predict dieting habits. Carnivores have long, extremely sharp teeth for both gripping prey
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
and cutting meat into chunks. They lack flat chewing
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, ...
teeth because they swallow food in chunks. An example of this is shown by the broad, serrated teeth of great white sharks which prey on large marine animals. On the other hand, herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthp ...
s have rows of wide, flat teeth to bite and chew grass and other plants. Cows spend up to eleven hours a day biting off grass and grinding it with their molars. Omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nut ...
s consume both meat and plants, so they possess a mixture of flat teeth and sharp teeth.
Carrying mechanism
Biting can serve as a carrying mechanism for species such asbeaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
s and ants, the raw power of their species-specific teeth allowing them to carry large objects. In beavers specifically, they have a large tooth adapted for gnawing wood. Their jaw muscles are tuned to power through big trees and carry them back to their dam. In ant behavior, ants use their powerful jaws to lift material back to the colony. They can carry several thousand times their weight due to their bite and adapted to use this to forage for their colonies. Fire ants use their strong bite to get a grip on prey, then inject a toxin via their abdomen and carry the prey back to their territory.
Dangers
Some organisms have dangerous bites that injectvenom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a ...
. Many snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s and lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia al ...
s carry a venomous saliva containing at least one of the major groups of toxins, which include cytotoxins, hemotoxins, myotoxins, and neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and matur ...
s. Spider venom polypeptides target specific ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ...
s, which excites components of the peripheral
A peripheral or peripheral device is an auxiliary device used to put information into and get information out of a computer. The term ''peripheral device'' refers to all hardware components that are attached to a computer and are controlled by th ...
, central and autonomic nervous systems, causing hyperactive neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neur ...
release and subsequently refractory paralysis. Spider bites, or arachnidism
A spider bite, also known as arachnidism, is an injury resulting from the bite of a spider. The effects of most bites are not serious. Most bites result in mild symptoms around the area of the bite. Rarely they may produce a necrotic skin wound ...
, are mainly a form of predation, but also means of self-defense — when trapped or accidentally tampered with by humans, spiders retaliate by biting. The recluse spider
The recluse spiders (''Loxosceles'' (), also known as brown spiders, fiddle-backs, violin spiders, and reapers, is a genus of spiders that was first described by R. T. Lowe in 1832. They are venomous spiders known for their bite, which sometimes ...
and widow species have neurotoxins and necrotizing agents that paralyze and digest prey.
There are several creatures with non-lethal bites that may cause discomfort or diseases. Mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning "gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "lit ...
bites may cause allergic wheals that are itchy and may last a few days; in some areas, they can spread blood-borne diseases (e.g. malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or deat ...
and West Nile fever) via transmission of protozoic
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histor ...
or viral
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
Viral may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marke ...
pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...
s. Similarly, tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
bites spread diseases endemic to their location, most famously Lyme disease, but ticks also serve as disease vectors for Colorado tick fever, African tick bite fever
African tick bite fever (ATBF) is a bacterial infection spread by the bite of a tick. Symptoms may include fever, headache, muscle pain, and a rash. At the site of the bite there is typically a red skin sore with a dark center. The onset of sympto ...
, Tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infectious disease involving the central nervous system. The disease most often manifests as meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Myelitis and spinal paralysis also occurs. In about one thi ...
, etc.
In humans
Biting is also an age appropriatebehavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour ( British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as w ...
and reaction for human children 30 months and younger. Conversely, children above this age are expected to have verbal skills to explain their needs and dislikes, as biting is not seen as age appropriate. Biting may be prevented by methods including redirection, change in the environment and responding to biting by talking about appropriate ways to express anger and frustration. School-age children, those older than 30 months, who habitually bite may require professional intervention. Some discussion of human biting appears in '' The Kinsey Report on Sexual Behavior in the Human Female''.
Criminally, Forensic Dentistry is involved in bite-mark analysis. Because bite-marks change significantly over time, investigators must call for an expert as soon as possible. Bites are then analyzed to determine whether the biter was human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
, self-inflicted or not, and whether DNA was left behind from the biter. All measurements must be extremely precise, as small errors in measurement can lead to large errors in legal judgment.Shanna Freeman"How Forensic Dentistry Works"
''How Stuff Works'', accessed June 28, 2019
See also
*Chewing
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, ...
* Bite force quotient
* Animal bite
References
External links
* {{Animal bites and stings Ethology