Bioprospecting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bioprospecting (also known as biodiversity prospecting) is the exploration of natural sources for
 Bioprospecting-derived resources and products used in agriculture include
Bioprospecting-derived resources and products used in agriculture include
 Bioprospecting-derived
Bioprospecting-derived
 Although some potentially very useful microorganisms are known to exist in nature (eg.
Although some potentially very useful microorganisms are known to exist in nature (eg.
 Prior to collecting
Prior to collecting
 In 1994, the
In 1994, the
Neem tree patent revoked
In 2000 the patent was successfully opposed by several groups from the EU and India including the EU Green Party,
India wins landmark patent battle
 ''
''
 The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) came into force in 1993. It secured rights to control access to genetic resources for the countries in which those resources are located. One objective of the CBD is to enable lesser-developed countries to better benefit from their resources and traditional knowledge. Under the rules of the CBD, bioprospectors are required to obtain
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) came into force in 1993. It secured rights to control access to genetic resources for the countries in which those resources are located. One objective of the CBD is to enable lesser-developed countries to better benefit from their resources and traditional knowledge. Under the rules of the CBD, bioprospectors are required to obtain
small molecule
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs ...
s, macromolecule
A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biophysical processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. The ...
s and biochemical and genetic information that could be developed into commercially
Commerce is the large-scale organized system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions directly and indirectly related to the exchange (buying and selling) of goods and services among two or more parties within local, regional, nation ...
valuable products for the agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
, aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lot ...
, bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluent ...
, cosmetics
Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protec ...
, nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal ...
, or pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
industries. In the pharmaceutical industry, for example, almost one third of all small-molecule drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) between 1981 and 2014 were either natural product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical sy ...
s or compounds derived from natural products.
Terrestrial plants
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude ...
, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
and actinobacteria have been the focus of many past bioprospecting programs, but interest is growing in less explored ecosystems (e.g. seas and oceans) and organisms (e.g. myxobacteria
The myxobacteria ("slime bacteria") are a group of bacteria that predominantly live in the soil and feed on insoluble organic substances. The myxobacteria have very large genomes relative to other bacteria, e.g. 9–10 million nucleotides except ...
, archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaeba ...
) as a means of identifying new compounds with novel biological activities. Species may be randomly screened for bioactivity or rationally selected and screened based on ecological
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ...
, ethnobiological, ethnomedical
Ethnomedicine is a study or comparison of the traditional medicine based on bioactive compounds in plants and animals and practiced by various ethnic groups, especially those with little access to western medicines, e.g., indigenous peoples. The ...
, historical
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
or genomic
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
information.
When a region's biological resources or indigenous knowledge
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK) and local knowledge generally refer to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities. According to the World Intellectual Property Orga ...
are unethically appropriated or commercially exploited without providing fair compensation, this is known as biopiracy. Various international treaties have been negotiated to provide countries legal recourse in the event of biopiracy and to offer commercial actors legal certainty for investment. These include the UN Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
and the Nagoya Protocol
The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization to the Convention on Biological Diversity, also known as the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) is a ...
.
Other risks associated with bioprospecting are the overharvesting of individual species and environmental damage, but legislation has been developed to combat these also. Examples include national laws such as the US Marine Mammal Protection Act
The Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA) was the first act of the United States Congress to call specifically for an ecosystem approach to wildlife management.
Authority
MMPA was signed into law on October 21, 1972, by President Richard Nixon ...
and US Endangered Species Act
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA or "The Act"; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of ec ...
, and international treaties such as the UN Convention on Biological Diversity, the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 167 ...
, and the Antarctic Treaty
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico
, name = Antarctic Treaty System
, image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder
, image_width = 180px
, caption ...
.
Bioprospecting-derived resources and products
Agriculture
biofertilizer
A biofertilizer is a substance which contains living micro-organisms which, when applied to seeds, plant surfaces, or soil, colonize the rhizosphere or the interior of the plant and promotes growth by increasing the supply or availability of prim ...
s, biopesticide
A Biopesticide is a biological substance or organism that damages, kills, or repels organisms seens as pests. Biological pest management intervention involves predatory, parasitic, or chemical relationships.
They are obtained from organisms inclu ...
s and veterinary antibiotics. ''Rhizobium
''Rhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria that fix nitrogen. ''Rhizobium'' species form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of (primarily) legumes and other flowering plants.
The bacteria colonize plant cells ...
'' is a genus of soil bacteria used as biofertilizers, ''Bacillus thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterf ...
'' (also called Bt) and the annonins (obtained from seeds of the plant '' Annona squamosa'') are examples of biopesticides, and valnemulin
Valnemulin (trade name Econor or Biotilina) is a pleuromutilin antibiotic used to treat swine dysentery, ileitis, colitis
Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine ( colon). Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. ...
and tiamulin
Tiamulin (previously thiamutilin) is a pleuromutilin antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibi ...
(discovered and developed from the basidiomycete
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Bas ...
fungi ''Omphalina mutila'' and '' Clitopilus passeckerianus'') are examples of veterinary antibiotics.
Bioremediation
Examples of bioprospecting products used in bioremediation include '' Coriolopsis gallica''- and '' Phanerochaete chrysosporium''-derivedlaccase
Laccases () are multicopper oxidases found in plants, fungi, and bacteria. Laccases oxidize a variety of phenolic substrates, performing one-electron oxidations, leading to crosslinking. For example, laccases play a role in the formation of l ...
enzymes, used for treating beer factory wastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial ...
and for dechlorinating and decolorizing paper mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt ...
effluent
Effluent is wastewater from sewers or industrial outfalls that flows directly into surface waters either untreated or after being treated at a facility. The term has slightly different meanings in certain contexts, and may contain various pollu ...
.
Cosmetics and personal care
Cosmetics and personal care products obtained from bioprospecting include '' Porphyridium cruentum''-derivedoligosaccharide
An oligosaccharide (/ˌɑlɪgoʊˈsækəˌɹaɪd/; from the Greek ὀλίγος ''olígos'', "a few", and σάκχαρ ''sácchar'', "sugar") is a saccharide polymer containing a small number (typically two to ten) of monosaccharides (simple sug ...
and oligoelement blends used to treat erythema
Erythema (from the Greek , meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not asso ...
(rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarg ...
, flushing
Flushing may refer to:
Places
* Flushing, Cornwall, a village in the United Kingdom
* Flushing, Queens, New York City
** Flushing Bay, a bay off the north shore of Queens
** Flushing Chinatown (法拉盛華埠), a community in Queens
** Flushin ...
and dark circles
Periorbital dark circles are dark blemishes around the eyes. There are many causes of this symptom, including heredity and bruising.
Causes
Anatomical factors
Bony structure and prominence of the orbicularis oculi muscle can contribute to infra ...
), '' Xanthobacter autotrophicus''-derived zeaxanthin
Zeaxanthin is one of the most common carotenoids in nature, and is used in the xanthophyll cycle. Synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms, it is the pigment that gives paprika (made from bell peppers), corn, saffron, goji (wolfberries) ...
used for skin hydration and UV protection, '' Clostridium histolyticum''-derived collagenase
Collagenases are enzymes that break the peptide bonds in collagen. They assist in destroying extracellular structures in the pathogenesis of bacteria such as ''Clostridium''. They are considered a virulence factor, facilitating the spread of ...
s used for skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
regeneration, and ''Microsporum
''Microsporum'' is a genus of fungi that causes tinea capitis, tinea corporis, ringworm, and other dermatophytoses (fungal infections of the skin). ''Microsporum'' forms both macroconidia (large asexual reproductive structures) and microconi ...
''-derived keratinases used for hair removal
Hair removal, also known as epilation or depilation, is the deliberate removal of body hair or head hair.
Hair typically grows all over the human body and can vary in thickness and length across human populations. Hair can become more visible d ...
.
Nanotechnology and biosensors
Becausemicrobial
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
laccase
Laccases () are multicopper oxidases found in plants, fungi, and bacteria. Laccases oxidize a variety of phenolic substrates, performing one-electron oxidations, leading to crosslinking. For example, laccases play a role in the formation of l ...
s have a broad substrate range, they can be used in biosensor
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector.
The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell rece ...
technology to detect a wide range of organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ...
s. For example, laccase-containing electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials ...
s are used to detect polyphenolic compounds in wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
, and lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity a ...
s and phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are ...
in wastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial ...
.
Pharmaceuticals
Many of the antibacterial drugs in current clinical use were discovered through bioprospecting including theaminoglycoside
Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar). The term can also refer ...
s, tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis.
Common side effects in ...
s, amphenicol
Amphenicols are a class of antibiotics with a phenylpropanoid structure. They function by blocking the enzyme peptidyl transferase on the 50S ribosome subunit of bacteria.
Examples of amphenicols include chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol
Thiamphe ...
s, polymyxin
Polymyxins are antibiotics. Polymyxins B and E (also known as colistin) are used in the treatment of Gram-negative bacterial infections. They work mostly by breaking up the bacterial cell membrane. They are part of a broader class of molecules ...
s, cephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics ...
s and other β-lactam antibiotic
β-lactam antibiotics (beta-lactam antibiotics) are antibiotics that contain a beta-lactam ring in their chemical
structure. This includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins and cephamycins (cephems), monobactams, carbapenems and ...
s, macrolide
The Macrolides are a class of natural products that consist of a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Ma ...
s, pleuromutilin
Pleuromutilin and its derivatives are antibacterial drugs that inhibit protein synthesis in bacteria by binding to the peptidyl transferase component of the 50S subunit of ribosomes.
This class of antibiotics includes the licensed drugs lefamul ...
s, glycopeptides, rifamycin
The rifamycins are a group of antibiotics that are synthesized either naturally by the bacterium '' Amycolatopsis rifamycinica'' or artificially. They are a subclass of the larger family of ansamycins. Rifamycins are particularly effective aga ...
s, lincosamide
Lincosamides are a class of antibiotics, which include lincomycin, clindamycin, and pirlimycin.
Structure
Lincosamides consist of a pyrrolidine ring linked to a pyranose moiety (methylthio-lincosamide) via an amide bond. Hydrolysis of lincosam ...
s, streptogramin Streptogramins are a class of antibiotics.
Streptogramins are effective in the treatment of vancomycin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (VRSA) and vancomycin-resistant ''Enterococcus'' (VRE), two of the most rapidly growing strains of multidru ...
s, and phosphonic acid antibiotics. The aminoglycoside antibiotic streptomycin
Streptomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, ''Burkholderia'' infection, plague, tularemia, and rat bite fever. F ...
, for example, was discovered from the soil bacterium ''Streptomyces griseus
''Streptomyces griseus'' is a species of bacteria in the genus ''Streptomyces'' commonly found in soil. A few strains have been also reported from deep-sea sediments. It is a Gram-positive bacterium with high GC content. Along with most other ...
'', the fusidane antibiotic fusidic acid was discovered from the soil fungus '' Acremonium fusidioides'', and the pleuromutilin antibiotics (eg. lefamulin) were discovered and developed from the basidiomycete fungi ''Omphalina mutila'' and ''Clitopilus passeckerianus''.
Other examples of bioprospecting-derived anti-infective drugs include the antifungal
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as ...
drug griseofulvin
Griseofulvin is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of types of dermatophytoses (ringworm). This includes fungal infections of the nails and scalp, as well as the skin when antifungal creams have not worked. It is taken by mouth.
C ...
(discovered from the soil fungus '' Penicillium griseofulvum''), the antifungal and antileishmanial drug amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis ...
(discovered from the soil bacterium ''Streptomyces nodosus
''Streptomyces nodosus'' is a bacterial species in the genus ''Streptomyces''.
Uses
''Streptomyces nodosus'' is used to produce amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmanias ...
''), the antimalarial
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young ...
drug artemisinin
Artemisinin () and its semisynthetic derivatives are a group of drugs used in the treatment of malaria due to '' Plasmodium falciparum''. It was discovered in 1972 by Tu Youyou, who shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for h ...
(discovered from the plant ''Artemisia annua
''Artemisia annua'', also known as sweet wormwood, sweet annie, sweet sagewort, annual mugwort or annual wormwood (), is a common type of wormwood native to temperate Asia, but naturalized in many countries including scattered parts of North Am ...
''), and the antihelminthic
Anthelmintics or antihelminthics are a group of antiparasitic drugs that expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them and without causing significant damage to the host. They may ...
drug ivermectin
Ivermectin (, '' EYE-vər-MEK-tin'') is an antiparasitic drug. After its discovery in 1975, its first uses were in veterinary medicine to prevent and treat heartworm and acariasis. Approved for human use in 1987, today it is used to treat i ...
(developed from the soil bacterium '' Streptomyces avermitilis'').
Bioprospecting-derived pharmaceuticals have been developed for the treatment of non-communicable disease
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, most heart diseases, most cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, ...
s and conditions too. These include the anticancer drug
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
bleomycin
-13- (1''H''-imidazol-5-yl)methyl9-hydroxy-5- 1''R'')-1-hydroxyethyl8,10-dimethyl-4,7,12,15-tetraoxo-3,6,11,14-tetraazapentadec-1-yl}-2,4'-bi-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)carbonyl]amino}propyl)(dimethyl)sulfonium
, chemical_formula =
, C=55 , H=84 , N=1 ...
(obtained from the soil bacterium ''Streptomyces verticillus
''Streptomyces verticillus'' is a species of Gram-positive bacteria in the genus ''Streptomyces''. Whilst screening fermentation broths of this species for bioactivity in the early 1960s, Hamao Umezawa and colleagues at the Institute of Microbi ...
''), the immunosuppressant
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified in ...
drug ciclosporin
Ciclosporin, also spelled cyclosporine and cyclosporin, is a calcineurin inhibitor, used as an immunosuppressant medication. It is a natural product. It is taken orally or intravenously for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease ...
used to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are inv ...
and psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to comple ...
(obtained from the soil fungus ''Tolypocladium inflatum
''Tolypocladium inflatum'' is an ascomycete fungus originally isolated from a Norwegian soil sample that, under certain conditions, produces the immunosuppressant drug ciclosporin. In its sexual stage ( teleomorph) it is a parasite on scarab b ...
''), the anti-inflammatory drug colchicine
Colchicine is a medication used to treat gout and Behçet's disease. In gout, it is less preferred to NSAIDs or steroids. Other uses for colchicine include the management of pericarditis and familial Mediterranean fever. Colchicine is taken b ...
used to treat and prevent gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intens ...
flares (obtained from the plant ''Colchicum autumnale
''Colchicum autumnale'', commonly known as autumn crocus, meadow saffron, or naked ladies, is a toxic autumn-blooming flowering plant that resembles the true crocuses, but is a member of the plant family Colchicaceae, unlike the true crocuses, whi ...
''), the analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
drug ziconotide
Ziconotide (SNX–111; Prialt), also called intrathecal ziconotide (ITZ) because of its administration route, is an atypical analgesic agent for the amelioration of severe and chronic pain. Derived from ''Conus magus'', a cone snail, it is the ...
(developed from the cone snail
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines con ...
''Conus magus
''Conus magus'', common name the magical cone, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Conidae, the cone snails and their allies.
Like all species within the genus ''Conus'', these snails are predatory and venomous. ...
''), and the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and ...
galantamine
Galantamine is used for the treatment of cognitive decline in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease and various other memory impairments. It is an alkaloid that has been isolated from the bulbs and flowers of '' Galanthus nivalis'' (Common snowd ...
used to treat Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As ...
(obtained from plants in the ''Galanthus
''Galanthus'' (from Ancient Greek , (, "milk") + (, "flower")), or snowdrop, is a small genus of approximately 20 species of bulbous perennial herbaceous plants in the family Amaryllidaceae. The plants have two linear leaves and a singl ...
'' genus).
Bioprospecting as a discovery strategy
Bioprospecting has both strengths and weaknesses as a strategy for discovering new genes, molecules, and organisms suitable for development and commercialization.Strengths
small molecule
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs ...
s (also known as natural product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical sy ...
s) are more structurally complex than synthetic chemicals, and therefore show greater specificity towards biological target
A biological target is anything within a living organism to which some other entity (like an endogenous ligand or a drug) is directed and/or binds, resulting in a change in its behavior or function. Examples of common classes of biological targets ...
s. This is a big advantage in drug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.
Historically, drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or b ...
and development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
, especially pharmacological
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemica ...
aspects of drug discovery and development, where off-target effects can cause adverse drug reaction
An adverse drug reaction (ADR) is a harmful, unintended result caused by taking medication. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or result from the combination of two or more drugs. The meaning of this term ...
s.
Natural products are also more amenable to membrane transport
In cellular biology, membrane transport refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such as ions and small molecules through biological membranes, which are lipid bilayers that contain proteins embedded in them. The ...
than synthetic compounds. This is advantageous when developing antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
drugs, which may need to traverse both an outer membrane and plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
to reach their target.
For some biotechnological innovations to work, it is important to have enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s that function at unusually high or low temperatures. An example of this is the polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
(PCR), which is dependent on a DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to crea ...
that can operate at 60°C and above. In other situations, for example dephosphorylation
In biochemistry, dephosphorylation is the removal of a phosphate (PO43−) group from an organic compound by hydrolysis. It is a reversible post-translational modification. Dephosphorylation and its counterpart, phosphorylation, activate and de ...
, it can be desirable to run the reaction at low temperature. Extremophile
An extremophile (from Latin ' meaning "extreme" and Greek ' () meaning "love") is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e. environments that make survival challenging such as due to extreme tem ...
bioprospecting is an important source of such enzymes, yielding thermostable enzymes such as ''Taq'' polymerase (from ''Thermus aquaticus
''Thermus aquaticus'' is a species of bacteria that can tolerate high temperatures, one of several thermophilic bacteria that belong to the ''Deinococcota'' phylum. It is the source of the heat-resistant enzyme ''Taq'' DNA polymerase, one of th ...
''), and cold-adapted enzymes such as shrimp alkaline phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1, alkaline phosphomonoesterase; phosphomonoesterase; glycerophosphatase; alkaline phosphohydrolase; alkaline phenyl phosphatase; orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (alkaline optimum), systematic ...
(from '' Pandalus borealis'').
With the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) now ratified by most countries, bioprospecting has the potential to bring biodiversity-rich and technologically advanced nations together, and benefit them both educationally and economically (eg. information sharing, technology transfer
Technology transfer (TT), also called transfer of technology (TOT), is the process of transferring (disseminating) technology from the person or organization that owns or holds it to another person or organization, in an attempt to transform invent ...
, new product development
In business and engineering, new product development (NPD) covers the complete process of bringing a new product to market, renewing an existing product or introducing a product in a new market. A central aspect of NPD is product design, along ...
, royalty payment
A royalty payment is a payment made by one party to another that owns a particular asset, for the right to ongoing use of that asset. Royalties are typically agreed upon as a percentage of gross or net revenues derived from the use of an asset o ...
).
For useful molecules identified through microbial
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
bioprospecting, scale up of production is feasible at reasonable cost because the producing microorganism can be cultured in a bioreactor
A bioreactor refers to any manufactured device or system that supports a biologically active environment. In one case, a bioreactor is a vessel in which a chemical process is carried out which involves organisms or biochemically active substance ...
.
Weaknesses
 Although some potentially very useful microorganisms are known to exist in nature (eg.
Although some potentially very useful microorganisms are known to exist in nature (eg. lignocellulose
Lignocellulose refers to plant dry matter (biomass), so called lignocellulosic biomass. It is the most abundantly available raw material on the Earth for the production of biofuels. It is composed of two kinds of carbohydrate polymers, cellulose a ...
-metabolizing microbes), difficulties have been encountered cultivating these in a laboratory setting. This problem may be resolvable by genetically manipulating easier-to-culture organisms such as ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'' or ''Streptomyces coelicolor
''Streptomyces albidoflavus'' is a bacterium species from the genus of ''Streptomyces'' which has been isolated from soil from Poland. ''Streptomyces albidoflavus'' produces dibutyl phthalate and streptothricins.
Small noncoding RNA
Bacter ...
'' to express the gene cluster
A gene family is a set of homologous genes within one organism. A gene cluster is a group of two or more genes found within an organism's DNA that encode similar polypeptides, or proteins, which collectively share a generalized function and are ...
responsible for the desired activity.
Isolating and identifying the compound(s) responsible for a biological extract's activity can be difficult. Also, subsequent elucidation of the mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention of the specific molecular targ ...
of the isolated compound can be time-consuming. Technological advancements in liquid chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a ...
, mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is u ...
and other techniques are helping to overcome these challenges.
Implementing and enforcing bioprospecting-related treaties and legislation is not always easy. Drug development is an inherently expensive and time-consuming process with low success rates, and this makes it difficult to quantify the value of potential products when drafting bioprospecting agreements. Intellectual property rights
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, cop ...
may be difficult to award too. For example, legal rights to a medicinal plant
Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesize hundreds of chemical compounds for various functions, including defense and protection ag ...
may be disputable if it has been discovered by different people in different parts of the world at different times.
Whilst the structural complexity of natural products is generally advantageous in drug discovery, it can make the subsequent manufacture of drug candidates difficult. This problem is sometimes resolvable by identifying the part of the natural product structure responsible for activity and developing a simplified synthetic analogue. This was necessary with the natural product halichondrin B, its simplified analogue eribulin now approved and marketed as an anticancer drug
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
.
Bioprospecting pitfalls
Errors and oversights can occur at different steps in the bioprospecting process including collection of source material, screening source material forbioactivity
In pharmacology, biological activity or pharmacological activity describes the beneficial or adverse effects of a drug on living matter. When a drug is a complex chemical mixture, this activity is exerted by the substance's active ingredient or ...
, testing isolated compounds for toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subs ...
, and identification of mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention of the specific molecular targ ...
.
Collection of source material
 Prior to collecting
Prior to collecting biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
material or traditional knowledge
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK) and local knowledge generally refer to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities. According to the World Intellectual Property Or ...
, the correct permissions must be obtained from the source country, land owner etc. Failure to do so can result in criminal proceedings
Criminal procedure is the adjudication process of the criminal law. While criminal procedure differs dramatically by jurisdiction, the process generally begins with a formal criminal charge with the person on trial either being free on bail or i ...
and rejection of any subsequent patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
applications. It is also important to collect biological material in adequate quantities, to have biological material formally identified
''Identified'' is the second studio album by Vanessa Hudgens, released on July 1, 2008 in the U.S. June 24, 2008 in Japan, February 13, 2009 in most European countries and February 16, 2009 in the United Kingdom. The album re ...
, and to deposit a voucher specimen with a repository for long-term preservation and storage. This helps ensure any important discoveries are reproducible.
Bioactivity and toxicity testing
When testing extracts and isolated compounds for bioactivity and toxicity, the use ofstandard Standard may refer to:
Symbols
* Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs
* Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification
Norms, conventions or requirements
* Standard (metrology), an object th ...
protocols (eg. CLSI, ISO, NIH
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
, EURL ECVAM, OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
) is desirable because this improves test result accuracy and reproducibility. Also, if the source material is likely to contain known (previously discovered) active compounds (eg. streptomycin in the case of actinomycetes), then dereplication is necessary to exclude these extracts and compounds from the discovery pipeline as early as possible. In addition, it is important to consider solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
effects on the cells or cell lines
An immortalised cell line is a population of cells from a multicellular organism which would normally not proliferate indefinitely but, due to mutation, have evaded normal cellular senescence and instead can keep undergoing division. The cells ...
being tested, to include reference compounds (ie. pure chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
s for which accurate bioactivity and toxicity data are available), to set limits on cell line passage number (eg. 10–20 passages), to include all the necessary positive and negative controls, and to be aware of assay limitations. These steps help ensure assay results are accurate, reproducible and interpreted correctly.
Identification of mechanism of action
When attempting to elucidate the mechanism of action of an extract or isolated compound, it is important to use multiple orthogonal assays. Using just a single assay, especially a single ''in vitro'' assay, gives a very incomplete picture of an extract or compound's effect on the human body. In the case of ''Valeriana officinalis
Valerian (''Valeriana officinalis'', Caprifoliaceae) is a perennial flowering plant native to Europe and Asia. In the summer when the mature plant may have a height of , it bears sweetly scented pink or white flowers that attract many fly specie ...
'' root extract, for example, the sleep-inducing effects of this extract are due to multiple compounds and mechanisms including interaction with GABA receptor
The GABA receptors are a class of receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the chief inhibitory compound in the mature vertebrate central nervous system. There are two classes of GABA receptors: GABAA and ...
s and relaxation of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit ...
. The mechanism of action of an isolated compound can also be misidentified if a single assay is used because some compounds interfere with assays. For example, the sulfhydryl-scavenging assay used to detect histone acetyltransferase
Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to form ε-''N''-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an ...
inhibition can give a false positive result if the test compound reacts covalently with cysteines.
Biopiracy
The term biopiracy was coined by Pat Mooney, to describe a practice in which indigenous knowledge of nature, originating withindigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
, is used by others for profit, without authorization or compensation to the indigenous people themselves. For example, when bioprospectors draw on indigenous knowledge of medicinal plants which is later patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
ed by medical companies without recognizing the fact that the knowledge is not new or invented by the patenter, this deprives the indigenous community of their potential rights to the commercial product derived from the technology that they themselves had developed. Critics of this practice, such as Greenpeace
Greenpeace is an independent global campaigning network, founded in Canada in 1971 by Irving Stowe and Dorothy Stowe, immigrant environmental activists from the United States. Greenpeace states its goal is to "ensure the ability of the Earth t ...
, claim these practices contribute to inequality between developing countries rich in biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
, and developed countries hosting biotech
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
firms.
In the 1990s many large pharmaceutical and drug discovery companies responded to charges of biopiracy by ceasing work on natural products, turning to combinatorial chemistry Combinatorial chemistry comprises chemical synthetic methods that make it possible to prepare a large number (tens to thousands or even millions) of compounds in a single process. These compound libraries can be made as mixtures, sets of individua ...
to develop novel compounds.
Famous cases of biopiracy

The rosy periwinkle
Therosy periwinkle
''Catharanthus roseus'', commonly known as bright eyes, Cape periwinkle, graveyard plant, Madagascar periwinkle, old maid, pink periwinkle, rose periwinkle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native and endemic to M ...
case dates from the 1950s. The rosy periwinkle, while native to Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
, had been widely introduced into other tropical countries around the world well before the discovery of vincristine
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and marketed under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin's ...
. Different countries are reported as having acquired different beliefs about the medical properties of the plant. This meant that researchers could obtain local knowledge from one country and plant samples from another. The use of the plant for diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
was the original stimulus for research. Effectiveness in the treatment of both Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The conditio ...
and leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
were discovered instead. The Hodgkin lymphoma chemotherapeutic drug vinblastine
Vinblastine (VBL), sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, bladder ca ...
is derivable from the rosy periwinkle.
The Maya ICBG controversy
The Maya ICBG bioprospecting controversy took place in 1999–2000, when the International Cooperative Biodiversity Group led by ethnobiologistBrent Berlin
Overton Brent Berlin (born 1936) is an American anthropologist, most noted for his work with linguist Paul Kay on color, and his ethnobiological research among the Maya of Chiapas, Mexico.
He received his Ph.D. from Stanford University in 196 ...
was accused of being engaged in unethical forms of bioprospecting by several NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in h ...
s and indigenous organizations. The ICBG aimed to document the biodiversity of Chiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil and Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 124 municipalities ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
, and the ethnobotanical
Ethnobotany is the study of a region's plants and their practical uses through the traditional knowledge of a local culture and people. An ethnobotanist thus strives to document the local customs involving the practical uses of local flora for m ...
knowledge of the indigenous Maya people
The Maya peoples () are an ethnolinguistic group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people ...
– in order to ascertain whether there were possibilities of developing medical products based on any of the plants used by the indigenous groups.
The Maya ICBG case was among the first to draw attention to the problems of distinguishing between benign forms of bioprospecting and unethical biopiracy, and to the difficulties of securing community participation and prior informed consent for would-be bioprospectors.
The neem tree
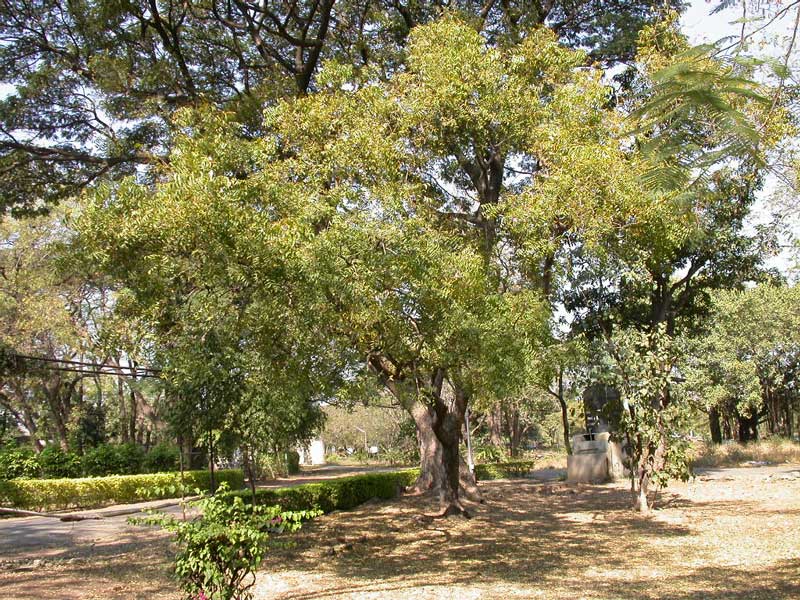
 In 1994, the
In 1994, the U.S. Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of comme ...
and W. R. Grace and Company received a European patent on methods of controlling fungal infections in plants using a composition that included extracts from the neem
''Azadirachta indica'', commonly known as neem, nimtree or Indian lilac, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of two species in the genus '' Azadirachta'', and is native to the Indian subcontinent and most of the countries in Afr ...
tree (''Azadirachta indica''), which grows throughout India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
.Karen Hoggan for the BBC. May 11, 200Neem tree patent revoked
In 2000 the patent was successfully opposed by several groups from the EU and India including the EU Green Party,
Vandana Shiva
Vandana Shiva (born 5 November 1952) is an Indian scholar, environmental activist, food sovereignty advocate, ecofeminist and anti-globalisation author. Based in Delhi, Shiva has written more than 20 books. She is often referred to as "Gand ...
, and the International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements
The International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements (IFOAM - Organics International) is the worldwide umbrella organization for the organic agriculture movement, which represents close to 800 affiliates in 117 countries.
It declares i ...
(IFOAM) on the basis that the fungicidal activity of neem extract had long been known in Indian traditional medicine. WR Grace appealed and lost in 2005.BBC News, March 9, 200India wins landmark patent battle
Basmati rice
In 1997, the US corporationRiceTec
RiceTec Inc. is a private American company based and headquartered in Alvin, Texas, that develops and produces hybrid rice seed for the American and various international markets. RiceTec previously owned the consumer brand name RiceSelect which ...
(a subsidiary of RiceTec AG of Liechtenstein) attempted to patent certain hybrids of basmati
Basmati, , is a variety of long, slender-grained aromatic rice which is traditionally grown in India, Pakistan, and Nepal.
rice and semidwarf long-grain rice. The Indian government challenged this patent and, in 2002, fifteen of the patent's twenty claims were invalidated.
The Enola bean
The Enola bean is a variety of Mexican yellow bean, so called after the wife of the man who patented it in 1999. The allegedly distinguishing feature of the variety is seeds of a specific shade of yellow. The patent-holder subsequently sued a large number of importers of Mexican yellow beans with the following result: "...export sales immediately dropped over 90% among importers that had been selling these beans for years, causing economic damage to more than 22,000 farmers in northern Mexico who depended on sales of this bean." A lawsuit was filed on behalf of the farmers and, in 2005, the US-PTO ruled in favor of the farmers. In 2008, the patent was revoked.''Hoodia gordonii''
Hoodia gordonii
''Hoodia gordonii'', also known as Bushman’s hat, is a leafless spiny succulent plant supposed to have therapeutic properties in folk medicine. It grows naturally in Botswana, South Africa and Namibia. The species became internationally know ...
'', a succulent plant
In botany, succulent plants, also known as succulents, are plants with parts that are thickened, fleshy, and engorged, usually to retain water in arid climates or soil conditions. The word ''succulent'' comes from the Latin word ''sucus'', me ...
, originates from the Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal d ...
of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
. For generations it has been known to the traditionally living San people
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are members of various Khoe, Tuu, or Kxʼa-speaking indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures that are the first cultures of Southern Africa, and whose territories span Botswana, Namibia, Angola, Zam ...
as an appetite suppressant
An anorectic or anorexic is a drug which reduces appetite, resulting in lower food consumption, leading to weight loss. By contrast, an appetite stimulant is referred to as orexigenic.
The term is (from the Greek ''ἀν-'' (an-) = "without" ...
. In 1996 South Africa's Council for Scientific and Industrial Research
The Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) is South Africa's central and premier scientific research and development organisation. It was established by an act of parliament in 1945 and is situated on its own campus in the c ...
began working with companies, including Unilever
Unilever plc is a British multinational consumer goods company with headquarters in London, England. Unilever products include food, condiments, bottled water, baby food, soft drink, ice cream, instant coffee, cleaning agents, energy dri ...
, to develop dietary supplements based on ''Hoodia''. Originally the San people were not scheduled to receive any benefits from the commercialization of their traditional knowledge, but in 2003 the South African San Council made an agreement with CSIR in which they would receive from 6 to 8% of the revenue from the sale of ''Hoodia'' products.
In 2008 after having invested €20 million in R&D on ''Hoodia'' as a potential ingredient in dietary supplements
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order ...
for weight loss, Unilever terminated the project because their clinical studies did not show that ''Hoodia'' was safe and effective enough to bring to market.
Further cases
The following is a selection of further recent cases of biopiracy. Most of them do not relate to traditional medicines. * Thirty-six cases of biopiracy in Africa. * The case of the Maya people's ''pozol
Pozol (from the Nahuatl ) is the name of both fermented corn dough and the cocoa drink made from it, which has its origins in Pre-Columbian Mexico. The drink is consumed in the south of Mexico in the states of Chiapas and Tabasco. It is a t ...
'' drink.
* The case of the Maya and other people's use of ''Mimosa tenuiflora
''Mimosa tenuiflora'', syn. ''Mimosa hostilis'', also known as jurema preta, calumbi (Brazil), tepezcohuite (México), carbonal, cabrera, jurema, black jurema, and binho de jurema, is a perennial tree or shrub native to the northeastern region of ...
'' and many other cases.
* The case of the Andean ''maca MACA or maca can mean:
* Maca (plant)
Places
Geography
* Maca District, Peru
* Cerro Macá, stratovolcano in the Aisén Region of Chile
* Maca River, Romania
Outer space
* 5228 Máca, a minor planet
People
* Alain Maca (born 1950), Belgian ...
'' radish.
* The cases of ''turmeric
Turmeric () is a flowering plant, ''Curcuma longa'' (), of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae, the rhizomes of which are used in cooking. The plant is a perennial, rhizomatous, herbaceous plant native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast ...
'' (India), '' karela'' (India), ''quinoa
Quinoa (''Chenopodium quinoa''; , from Quechua ' or ') is a flowering plant in the amaranth family. It is a herbaceous annual plant grown as a crop primarily for its edible seeds; the seeds are rich in protein, dietary fiber, B vitamins, ...
'' (Bolivia), ''oubli
''Pentadiplandra brazzeana'' is an evergreen shrub or liana that is the only species assigned to the genus ''Pentadiplandra'', and has been placed in a family of its own called Pentadiplandraceae. It produces large red berries, sometimes mottled ...
'' berries (Gabon), and others.
* The case of captopril
Captopril, sold under the brand name Capoten among others, is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and some types of congestive heart failure. Captopril was the first oral ACE inhibitor found ...
(developed from a Brazilian tribe's arrowhead poison).
Legal and political aspects
Patent law
One common misunderstanding is that pharmaceutical companiespatent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
the plants they collect. While obtaining a patent on a naturally occurring organism as previously known or used is not possible, patents may be taken out on specific chemicals isolated or developed from plants. Often these patents are obtained with a stated and researched use of those chemicals. Generally the existence, structure and synthesis of those compounds is not a part of the indigenous medical knowledge that led researchers to analyze the plant in the first place. As a result, even if the indigenous medical knowledge is taken as prior art, that knowledge does not by itself make the active chemical compound "obvious," which is the standard applied under patent law.
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, patent law
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A p ...
can be used to protect "isolated and purified" compounds – even, in one instance, a new chemical element (see USP 3,156,523). In 1873, Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur (, ; 27 December 1822 – 28 September 1895) was a French chemist and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation and pasteurization, the latter of which was named afte ...
patented a "yeast" which was "free from disease" (patent #141072). Patents covering biological inventions have been treated similarly. In the 1980 case of ''Diamond v. Chakrabarty
''Diamond v. Chakrabarty'', 447 U.S. 303 (1980), was a United States Supreme Court case dealing with whether living organisms can be patented. Writing for a five-justice majority, Chief Justice Warren E. Burger held that human-made bacteria could ...
'', the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
upheld a patent on a bacterium that had been genetically modified to consume petroleum, reasoning that U.S. law permits patents on "anything under the sun that is made by man." The United States Patent and Trademark Office
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Commerce that serves as the national patent office and trademark registration authority for the United States. The USPTO's headquarters are in Alex ...
(USPTO) has observed that "a patent on a gene covers the isolated and purified gene but does not cover the gene as it occurs in nature".
Also possible under US law is patenting a cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture ...
, a new variety of an existing organism. The patent on the Enola bean (now revoked) was an example of this sort of patent. The intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
laws of the US also recognize plant breeders' rights
Plant breeders' rights (PBR), also known as plant variety rights (PVR), are rights granted to the breeder of a new variety of plant that give the breeder exclusive control over the propagating material (including seed, cuttings, divisions, tissue ...
under the Plant Variety Protection Act, 7 U.S.C. §§ 2321–2582.
Convention on Biological Diversity
informed consent
Informed consent is a principle in medical ethics and medical law, that a patient must have sufficient information and understanding before making decisions about their medical care. Pertinent information may include risks and benefits of treat ...
to access such resources, and must share any benefits with the biodiversity-rich country. However, some critics believe that the CBD has failed to establish appropriate regulations to prevent biopiracy. Others claim that the main problem is the failure of national governments to pass appropriate laws implementing the provisions of the CBD. The Nagoya Protocol
The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization to the Convention on Biological Diversity, also known as the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) is a ...
to the CBD, which came into force in 2014, provides further regulations. The CBD has been ratified, acceded or accepted by 196 countries and jurisdictions globally, with exceptions including the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
and United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
.
Bioprospecting contracts
The requirements for bioprospecting as set by CBD has created a new branch of internationalpatent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
and trade law, bioprospecting contracts. Bioprospecting contracts lay down the rules of benefit sharing between researchers and countries, and can bring royalties to lesser-developed countries. However, although these contracts are based on prior informed consent and compensation (unlike biopiracy), every owner or carrier of an indigenous knowledge and resources are not always consulted or compensated, as it would be difficult to ensure every individual is included. Because of this, some have proposed that the indigenous or other communities form a type of representative micro-government that would negotiate with researchers to form contracts in such a way that the community benefits from the arrangements. Unethical bioprospecting contracts (as distinct from ethical ones) can be viewed as a new form of biopiracy.
An example of a bioprospecting contract is the agreement between Merck and INBio of Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
.
Traditional knowledge database
Due to previous cases of biopiracy and to prevent further cases, the Government of India has converted traditional Indian medicinal information from ancient manuscripts and other resources into an electronic resource; this resulted in theTraditional Knowledge Digital Library
The Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL) is an Indian digital knowledge repository of the traditional knowledge, especially about medicinal plants and formulations used in Indian systems of medicine.
History
Set up in 2001, as a colla ...
in 2001. The texts are being recorded from Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
** Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, na ...
, Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
, Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' Persian and
information centre
which as of April 2006 lists some 3000 "monographs, reports and serials". * Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (United Nations Environment Programme)
Bibliography of Journal Articles on the Convention on Biological Diversity
(March 2006). Contains references to almost 200 articles. Some of these are available in full text from th
CBD information centre
* *
Out of Africa: Mysteries of Access and Benefit-Sharing
– a 2006 report on biopiracy in Africa b
The Edmonds Institute
Cape Town Declaration
– Biowatch South Africa
Genetic Resources Action International (GRAIN)
Indian scientist denies accusation of biopiracy
–
African 'biopiracy' debate heats up
–
Bioprospecting: legitimate research or 'biopiracy'?
–
Topics include: Monsanto's species-wide patent on all genetically modified soybeans (EP0301749); Synthetic Biology Patents (artificial, unique life forms); Terminator Seed Technology; etc...
Who Owns Biodiversity, and How Should the Owners Be Compensated?
''Plant Physiology'', April 2004, Vol. 134, pp. 1295–1307 * {{Property navbox Bioethics Botany Plant genetics Plant breeding Biodiversity Food security Plant conservation Seeds Sustainable agriculture Commercialization of traditional medicines
'' Persian and
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
; made available to patent offices in English, German, French, Japanese and Spanish. The aim is to protect India's heritage from being exploited by foreign companies. Hundreds of yoga poses are also kept in the collection. The library has also signed agreements with leading international patent offices such as European Patent Office
The European Patent Office (EPO) is one of the two organs of the European Patent Organisation (EPOrg), the other being the Administrative Council. The EPO acts as executive body for the organisation
(EPO), United Kingdom Trademark & Patent Office (UKTPO) and the United States Patent and Trademark Office
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Commerce that serves as the national patent office and trademark registration authority for the United States. The USPTO's headquarters are in Alex ...
to protect traditional knowledge
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK) and local knowledge generally refer to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities. According to the World Intellectual Property Or ...
from biopiracy as it allows patent examiner A patent examiner (or, historically, a patent clerk) is an employee, usually a civil servant with a scientific or engineering background, working at a patent office. Major employers of patent examiners are the European Patent Office (EPO), the U ...
s at International Patent Offices to access TKDL databases for patent search and examination purposes.
See also
*Intellectual capital Intellectual capital is the result of mental processes that form a set of intangible objects that can be used in economic activity and bring income to its owner (organization), covering the competencies of its people ( human capital), the value rela ...
/Intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
* Natural capital
Natural capital is the world's stock of natural resources, which includes geology, soils, air, water and all living organisms. Some natural capital assets provide people with free goods and services, often called ecosystem services. All of t ...
* Biological patent
A biological patent is a patent on an invention in the field of biology that by law allows the patent holder to exclude others from making, using, selling, or importing the protected invention for a limited period of time. The scope and reach of ...
* Traditional knowledge
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK) and local knowledge generally refer to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities. According to the World Intellectual Property Or ...
/Indigenous knowledge
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK) and local knowledge generally refer to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities. According to the World Intellectual Property Orga ...
* Pharmacognosy
Pharmacognosy is the study of medicinal plants and other natural substances as sources of drugs. The American Society of Pharmacognosy defines pharmacognosy as "the study of the physical, chemical, biochemical, and biological properties of dru ...
* Plant breeders' rights
Plant breeders' rights (PBR), also known as plant variety rights (PVR), are rights granted to the breeder of a new variety of plant that give the breeder exclusive control over the propagating material (including seed, cuttings, divisions, tissue ...
* Bioethics
Bioethics is both a field of study and professional practice, interested in ethical issues related to health (primarily focused on the human, but also increasingly includes animal ethics), including those emerging from advances in biology, me ...
* Maya ICBG bioprospecting controversy
* International Cooperative Biodiversity Group
* Biological Diversity Act, 2002
* Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) (1994)
* International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture
The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (also known as ITPGRFA, International Seed Treaty or Plant Treaty), is a comprehensive international agreement in harmony with the Convention on Biological Diversity, ...
(2001)
References
Bibliography and resources
* The Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (United Nations Environment Programme) maintains ainformation centre
which as of April 2006 lists some 3000 "monographs, reports and serials". * Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (United Nations Environment Programme)
Bibliography of Journal Articles on the Convention on Biological Diversity
(March 2006). Contains references to almost 200 articles. Some of these are available in full text from th
CBD information centre
* *
External links
Out of Africa: Mysteries of Access and Benefit-Sharing
– a 2006 report on biopiracy in Africa b
The Edmonds Institute
Cape Town Declaration
– Biowatch South Africa
Genetic Resources Action International (GRAIN)
Indian scientist denies accusation of biopiracy
–
SciDev.Net
SciDev.Net is a not-for-profit organisation that produces news, views and analysis about science and technology in the context of global development. It primarily engages with development professionals, policymakers, researchers, the media and the ...
African 'biopiracy' debate heats up
–
SciDev.Net
SciDev.Net is a not-for-profit organisation that produces news, views and analysis about science and technology in the context of global development. It primarily engages with development professionals, policymakers, researchers, the media and the ...
Bioprospecting: legitimate research or 'biopiracy'?
–
SciDev.Net
SciDev.Net is a not-for-profit organisation that produces news, views and analysis about science and technology in the context of global development. It primarily engages with development professionals, policymakers, researchers, the media and the ...
* ETC Group papers on Biopiracy Topics include: Monsanto's species-wide patent on all genetically modified soybeans (EP0301749); Synthetic Biology Patents (artificial, unique life forms); Terminator Seed Technology; etc...
Who Owns Biodiversity, and How Should the Owners Be Compensated?
''Plant Physiology'', April 2004, Vol. 134, pp. 1295–1307 * {{Property navbox Bioethics Botany Plant genetics Plant breeding Biodiversity Food security Plant conservation Seeds Sustainable agriculture Commercialization of traditional medicines